Implications of Flume Simulation for the Architectural Analysis of Shallow-Water Deltas: A Case Study from the S Oilfield, Offshore China
Abstract
1. Introduction
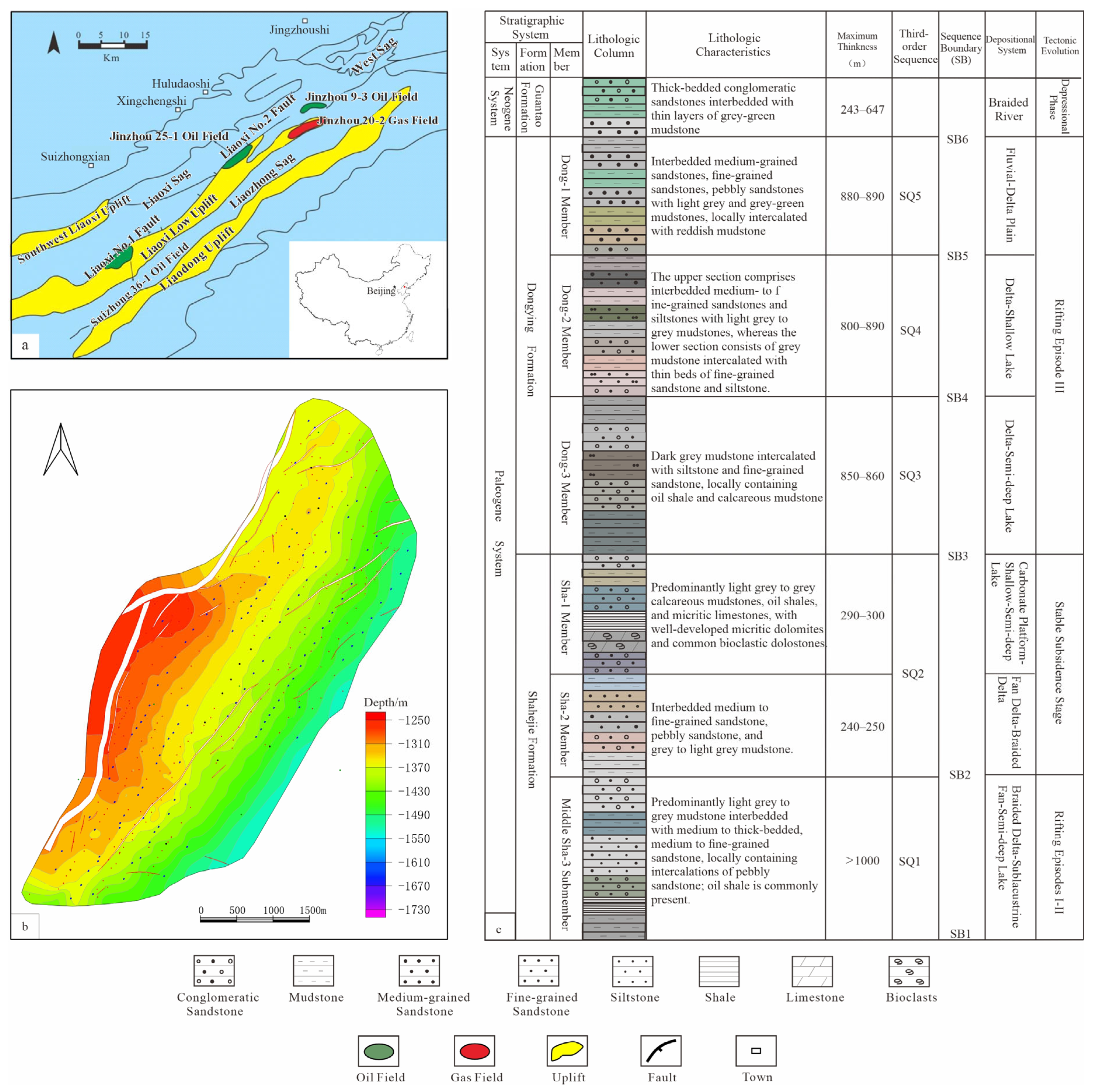
2. Regional Geological Setting
3. Data Analysis
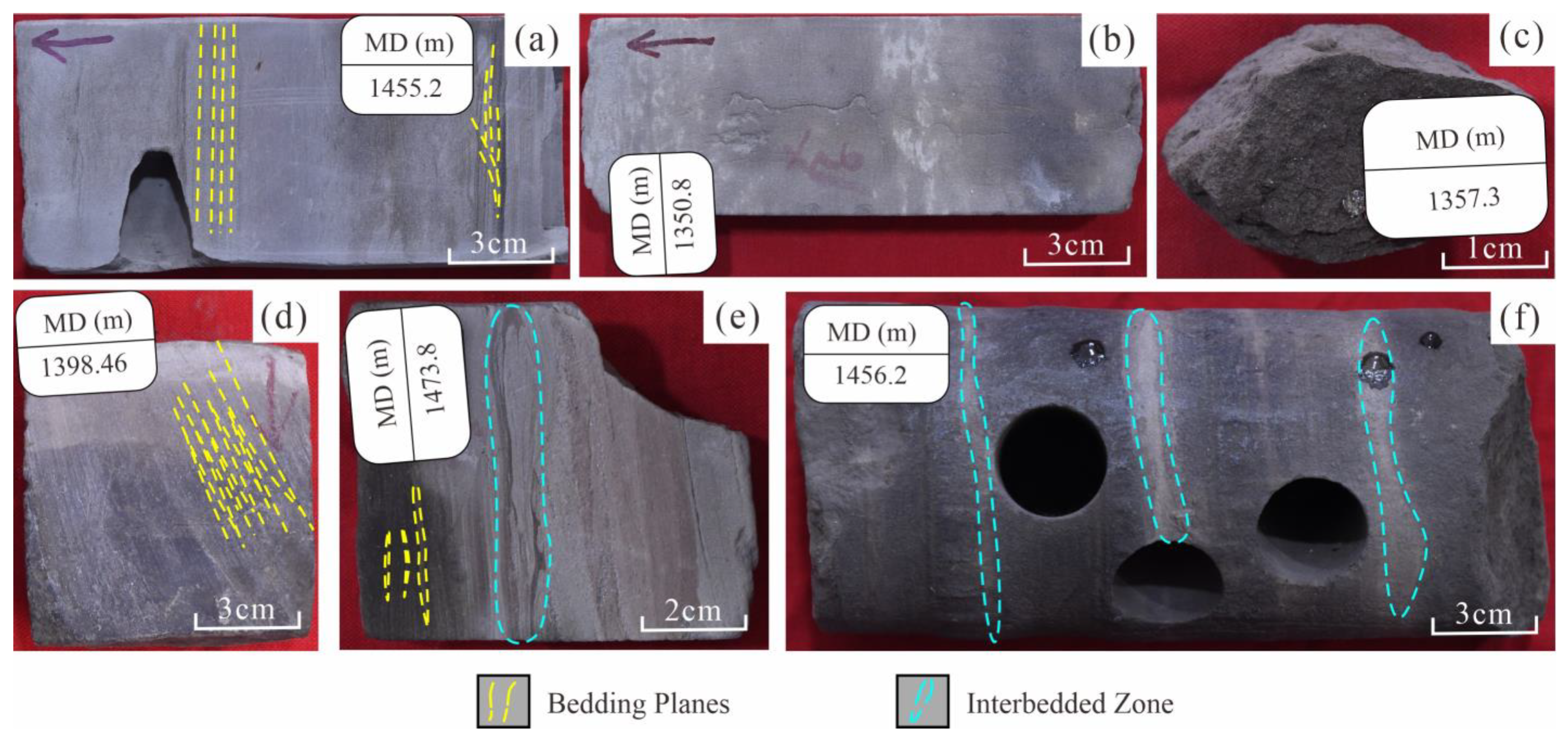
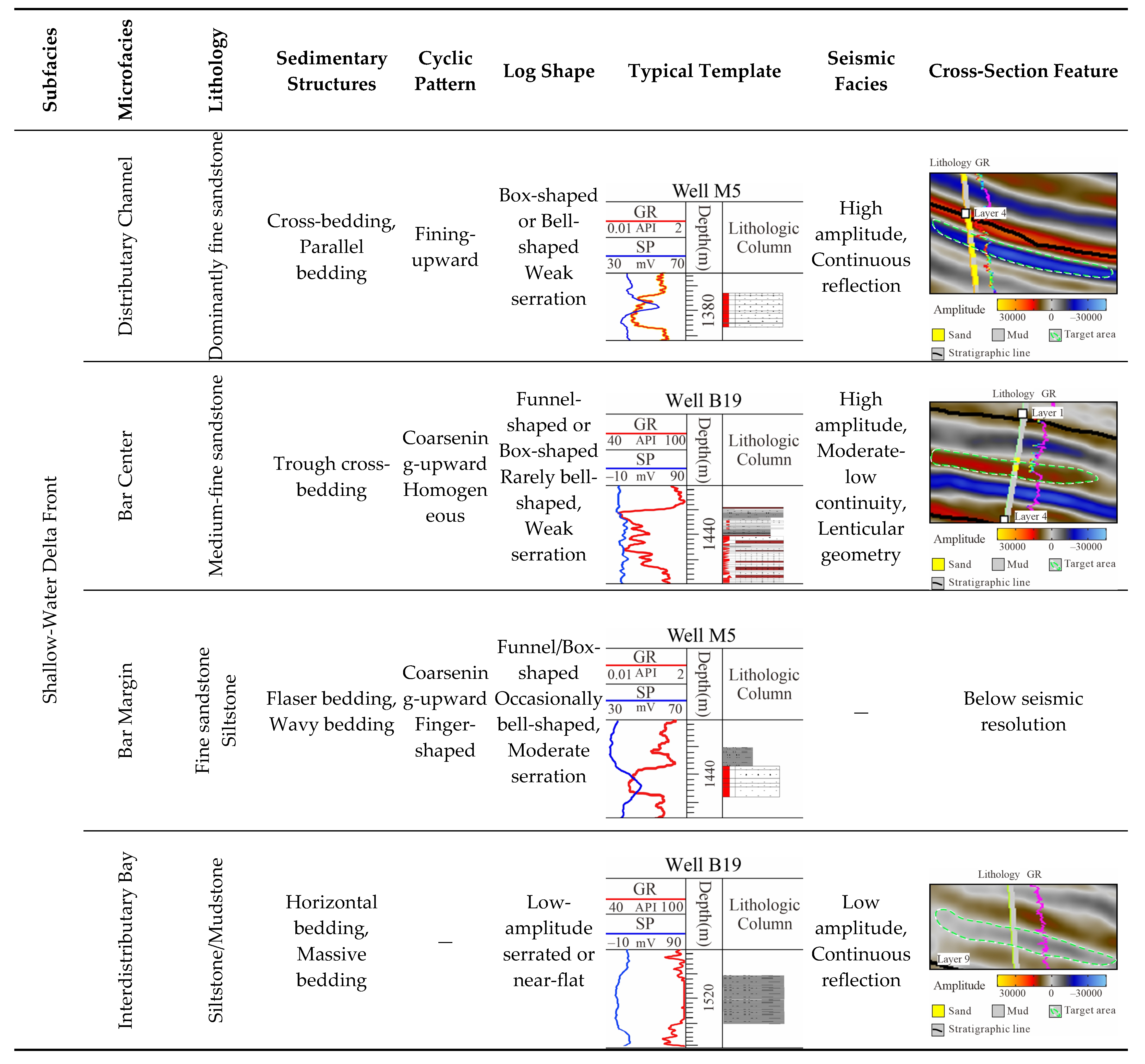
3.1. Facies Identification
3.2. Microfacies Characteristics
3.2.1. Distributary Channels
3.2.2. Mouth Bars
3.2.3. Interdistributary Bay
4. Methods
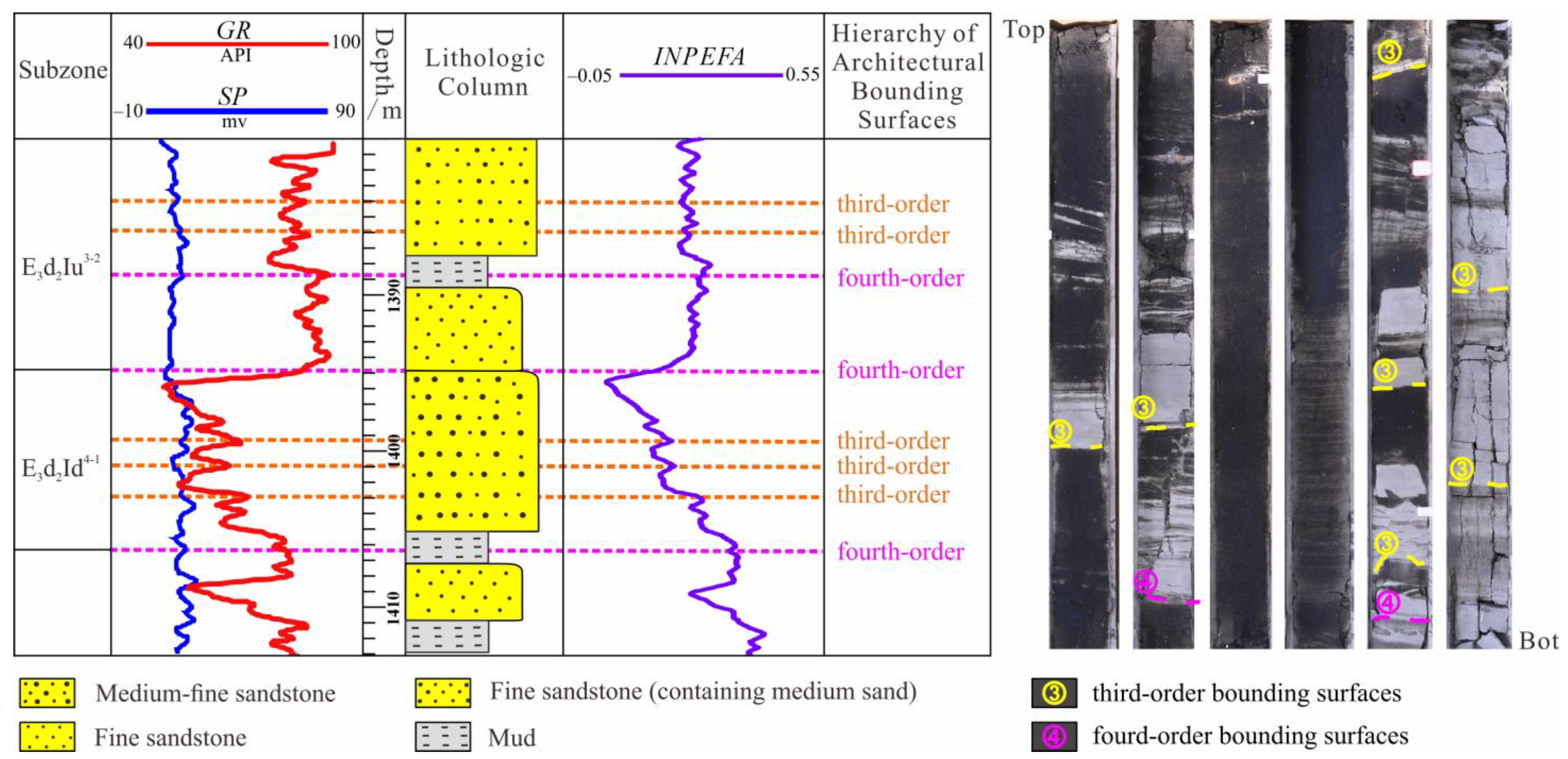
4.1. Reservoir Genesis and Architectural Hierarchy Classification
4.2. Architectural Delineation
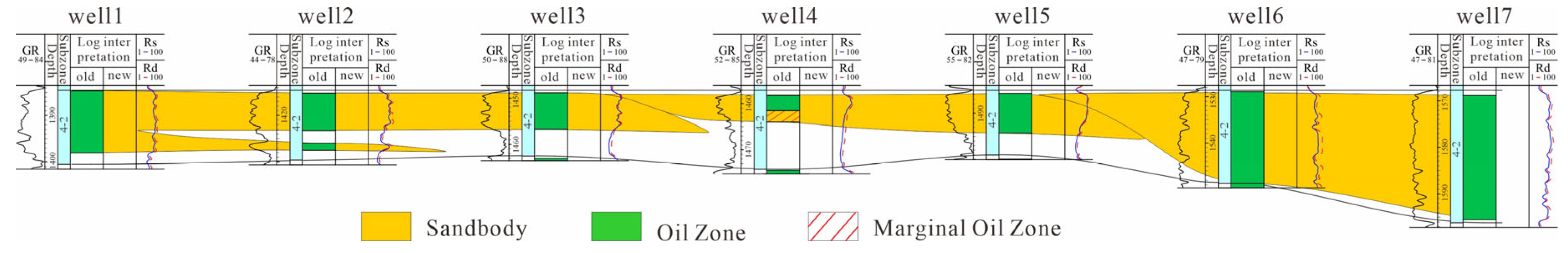
4.2.1. Vertical Architectural Unit Division
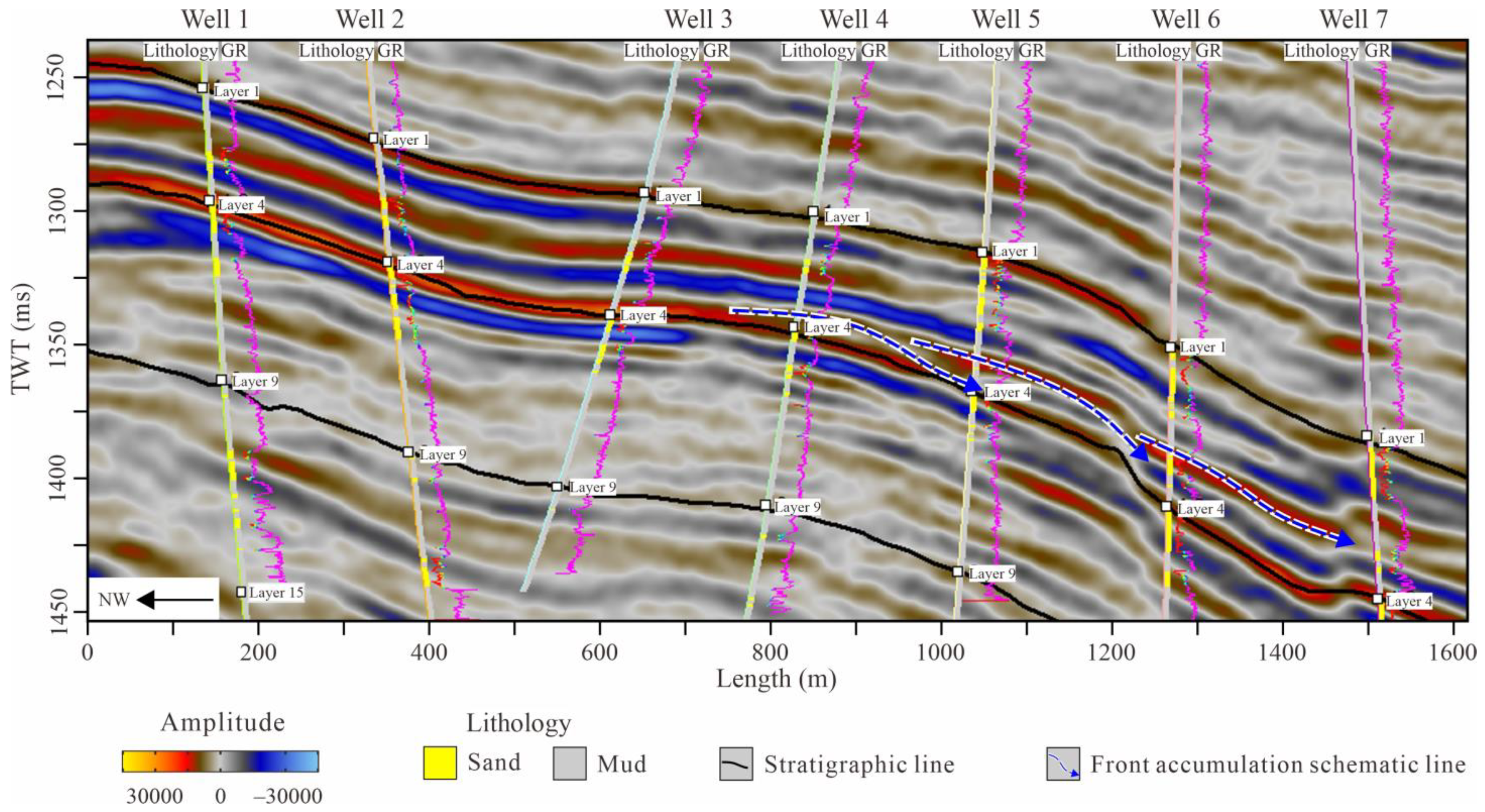
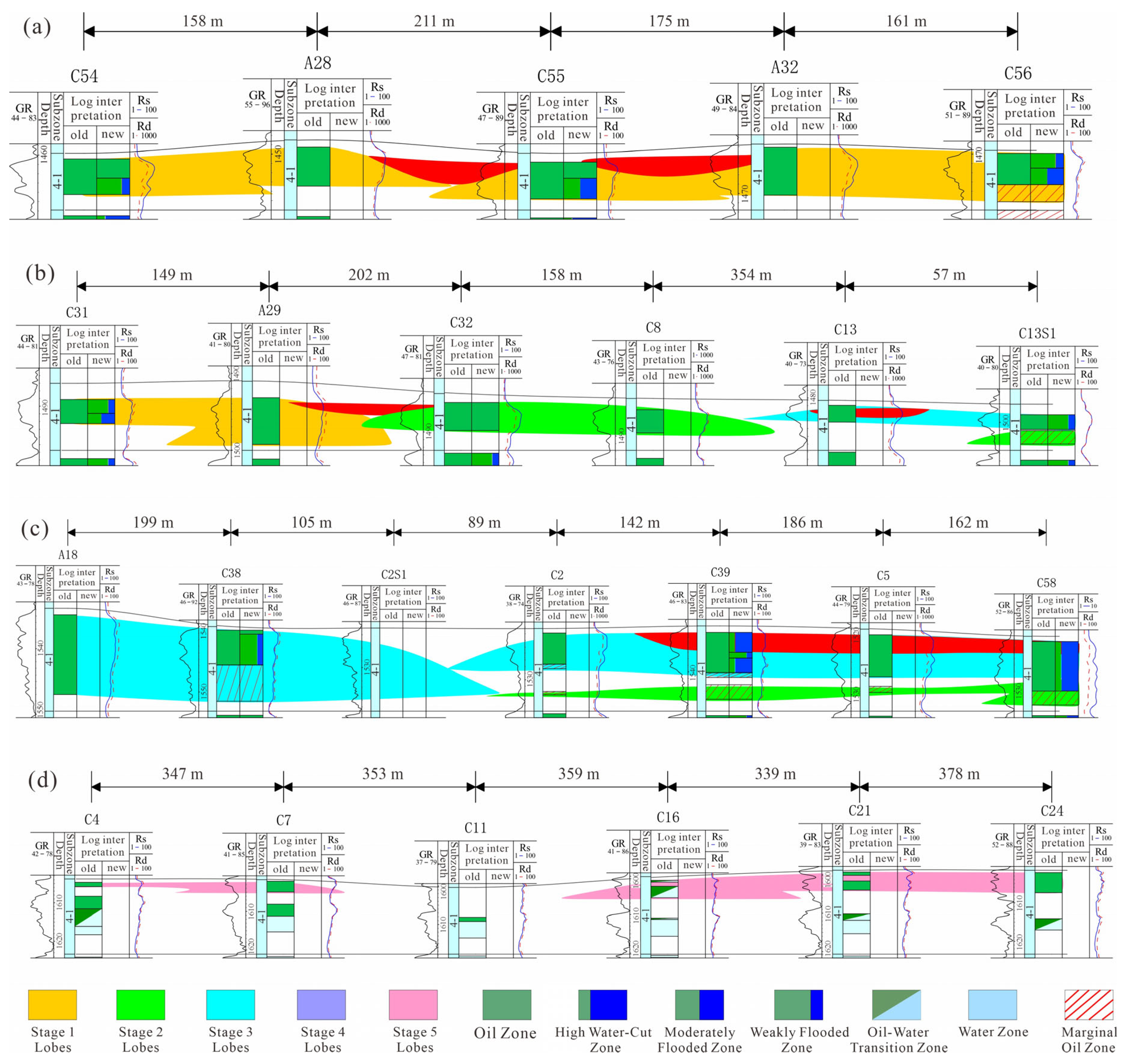
4.2.2. Planar Single-Lobe Boundary Identification
- (1)
- Lateral Facies Change: Lobe boundaries are marked by bar-edge sands or mudstones between bar sands, exhibiting a “thick–thin–thick” spatial pattern. For example, mudstone between wells C7 and C16 indicates a boundary near C11 (Figure 9d).
- (2)
- Sand body Base Elevation Difference: Consistent base elevation characterizes a single lobe. Significant elevation differences, as between wells A29 and C32 in subzone 4-1 (Figure 9b), indicate separate lobes.
- (3)
- Sand body Scale Difference: Pronounced thickness variations between adjacent sand bodies, such as between C2S1 and C2 (Figure 9c), suggest lobe boundaries.
- (4)
- Well Log Curve Morphology Difference: Contemporaneous lobes show similar log shapes. Abrupt changes, e.g., from funnel-shaped (A28) to bell-shaped (C55) logs (Figure 9a), indicate separate lobes.
- (5)
- Hydrocarbon Saturation Difference: Major differences in saturation or flooding characteristics between adjacent wells, like between C31 and C13S1 (Figure 9b), suggest different lobes.
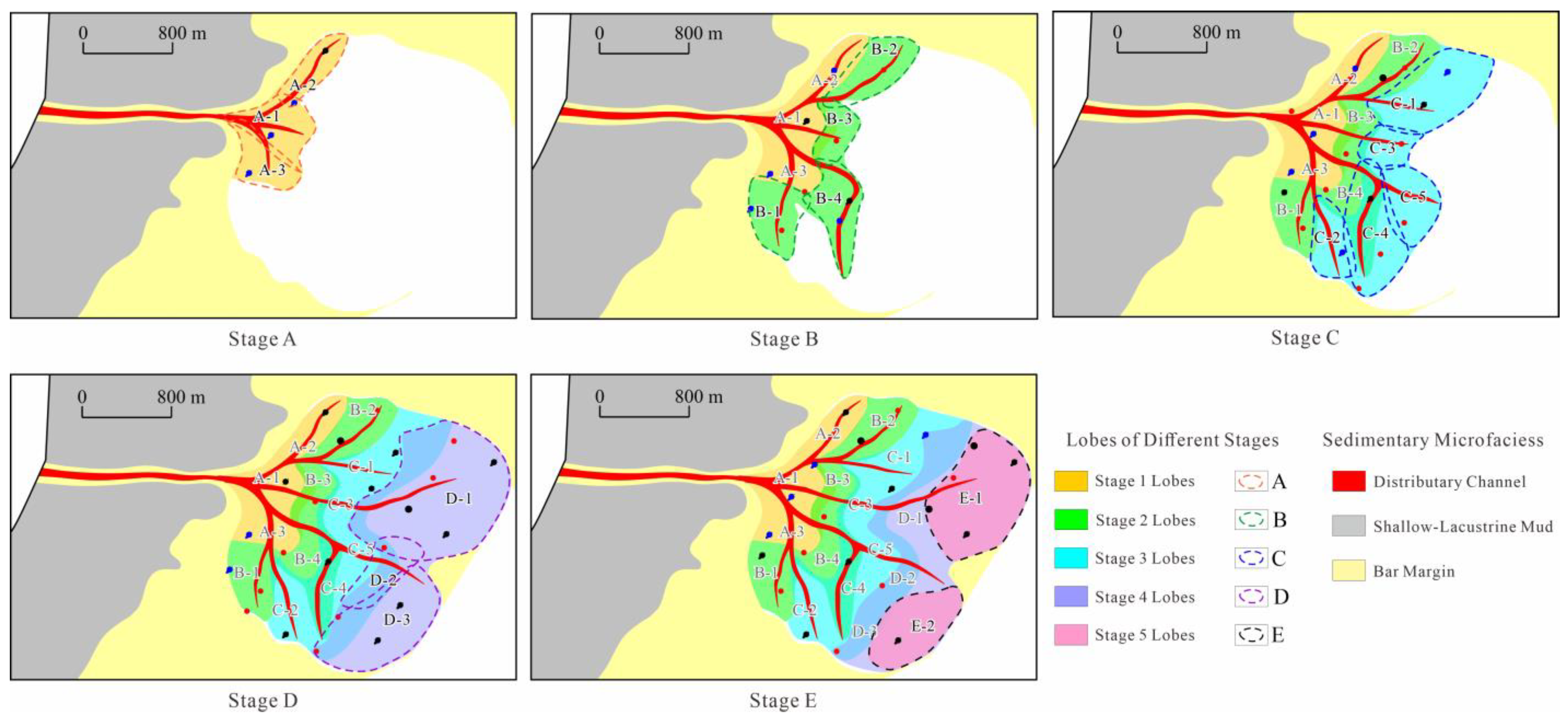
4.2.3. Depositional Evolution Analysis
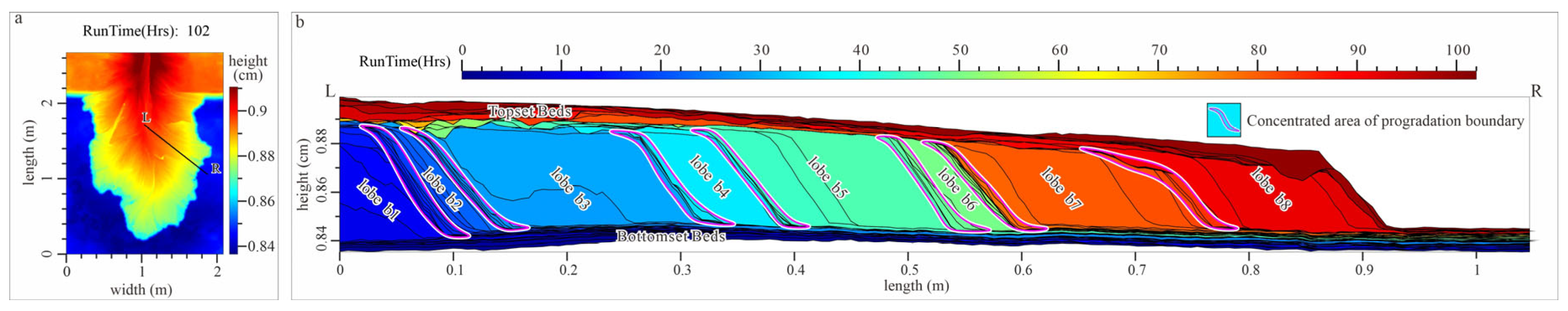
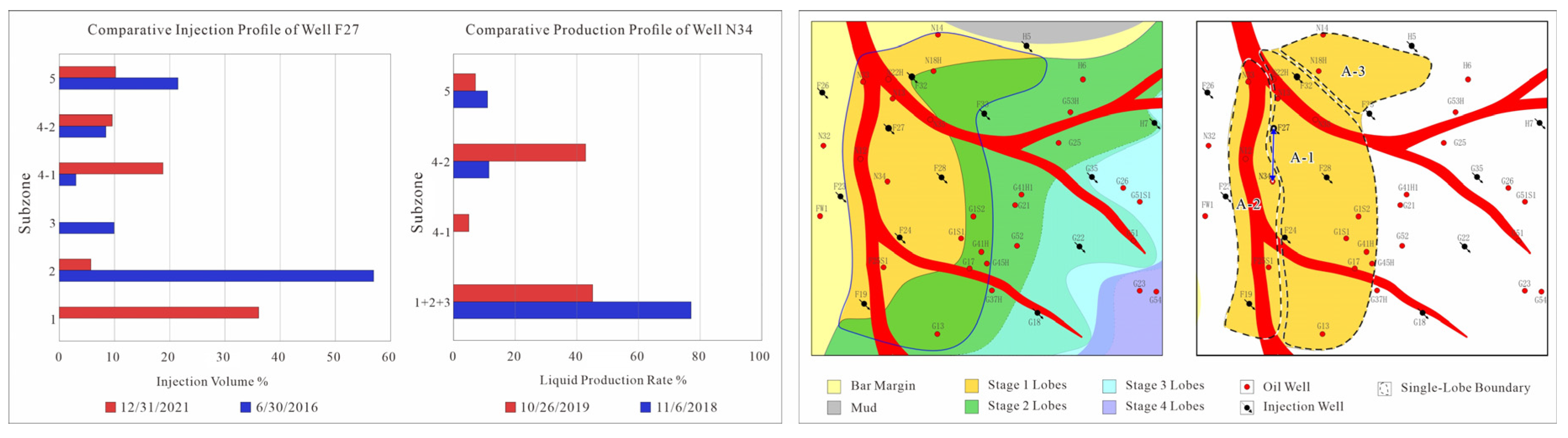
4.3. Dynamic Validation
5. Results and Discussion
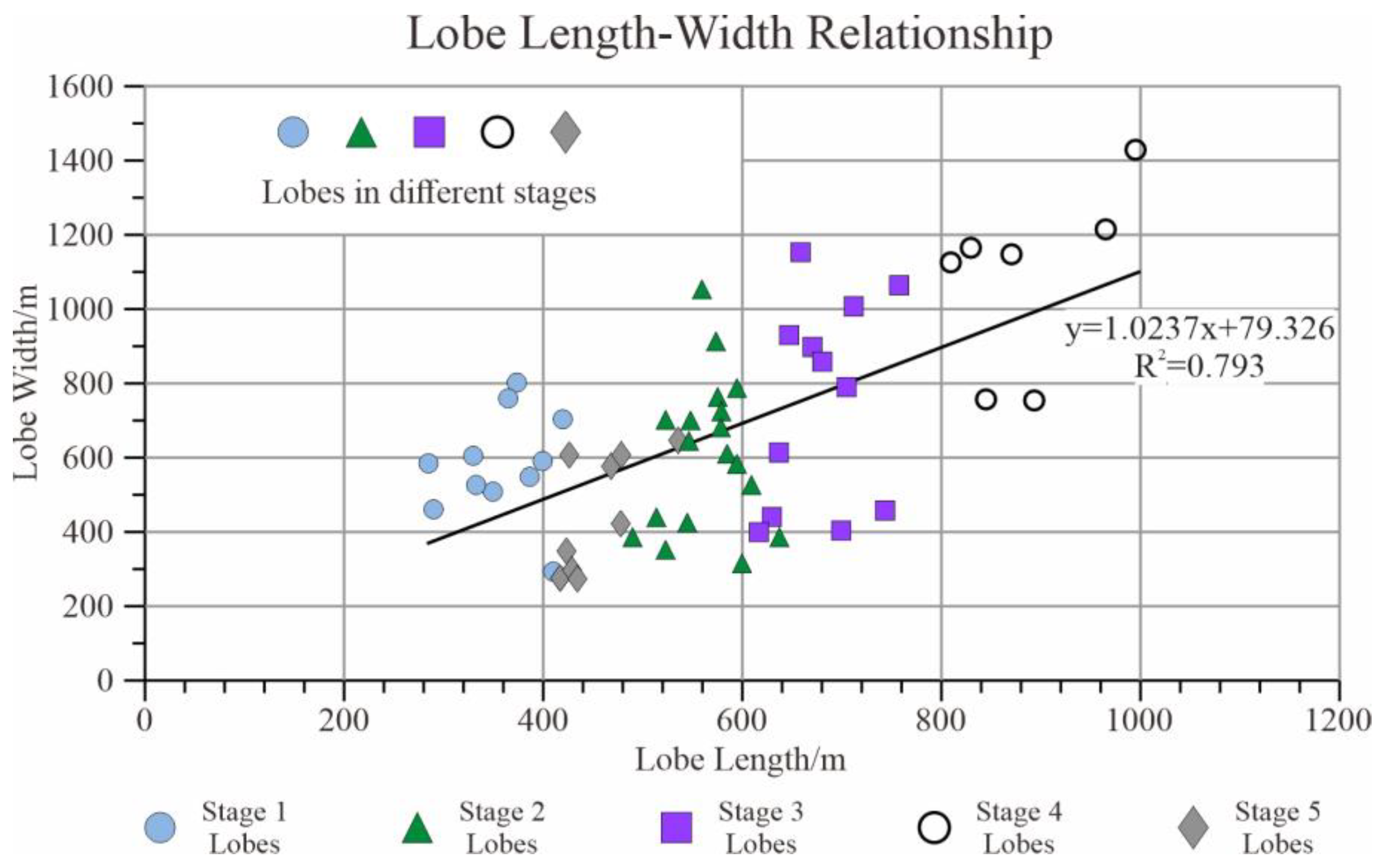
5.1. Lobe Dimension
5.2. Architectural Pattern
5.3. Comparison of Typical Shallow-Water Deltas
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- This study establishes a depositional model for thick, sand-rich shallow-water deltas through integrated analysis of well-log, seismic, and sedimentological data, confirming mouth-bar sands as the primary reservoir units arranged in extensive lobate complexes.
- (2)
- Flume simulations reveal a unique delta growth mechanism where trunk distributary channels generate accretionary lobes, with subsequent channel bifurcation initiating new depositional cycles that produce vertically stacked “channel-over-bar” configurations.
- (3)
- The resulting three-dimensional reservoir architecture features individual lobes controlled by discrete distributary channels, while laterally amalgamated lobes from multiple channels form composite sand bodies—providing critical constraints for reservoir modeling of analogous systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hoy, R.G.; Ridgway, K.D. Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy of fan-delta and river-delta deposystems, Pennsylvanian Minturn Formation, Colorado. AAPG Bull. 2003, 87, 1169–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bao, Z.D.; Lin, Y.B.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Dou, L.; Kong, B. Genetic types and sedimentary model of sandbodies in a shallow-water delta: A case study of the first member of Cretaceous Yaojia Formation in Qian’an area, south of Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2017, 44, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Liu, K.Y.; Yan, J.-H.; Wang, Q.; Pu, X.-G.; Yang, H.-Y. Sedimentary characteristics and evolution of shallow water delta systems of the Lower Permian Shanxi Formation in the Bohai Bay Basin region. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausen, T.G.; Røe, S.L.; Olaussen, S. Clinoform development and topset evolution in a mud-rich delta–the Middle Triassic Kobbe Formation, Norwegian Barents Sea. Sedimentology 2018, 65, 1132–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Fan, Z.; Xue, H.; Sun, Z.; Yu, T. Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy of the Paleogene lower second member of the Shahejie Formation, W79 Block, Wenliu Oilfield, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Russ. Geol. Geophys. 2016, 57, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, S.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Xu, Z. Diagenetic controls on the reservoir quality of tight reservoirs in digitate shallow-water lacustrine delta deposits: An example from the Triassic Yanchang Formation, southwestern Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2022, 146, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.S.; Hu, M.Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Kane, O.I.; Deng, Q.J.; Hu, Z.G.; Li, H.; Ngia, N.R. Sedimentary characteristics and implications for hydrocarbon exploration in a retrograding shallow-water delta: An example from the fourth member of the Cretaceous Quantou Formation in the Sanzhao depression, Songliao Basin, NE China. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 929–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.B.; Bao, Z.D.; Dou, L.X.; Zang, D.S.; Mao, S.W.; Song, J.; Zhao, J.H.; Wang, Z.C. Sedimentary characteristics and pattern of distributary channels in shallow water deltaic red bed succession: A case from the Late Cretaceous Yaojia formation, southern Songliao Basin, NE China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2018, 171, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, S.Q.; Liu, J.; Du, X.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, X.Q.; Wang, J. A case study on statistical wireline log parameters in identifying shallow-water delta microfacies of Late Dongying Formation, northern Liaozhong Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhu, X.M.; Zhu, S.F.; McElroy, B. Impact of deep-time palaeoclimate on the sedimentary records and morphology of lacustrine shoal-water deltas, upper Eocene Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay basin, China. Sedimentology 2021, 68, 3253–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.B.; Luo, S.S.; He, Y.B.; Yin, T.J.; Shang, F.; Lv, Q.Q.; Luo, J.X. Study on sedimentation simulation experiment of gentle-slope shallow braided river delta. J. Water Resour. Archit. Eng. 2011, 9, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.R.; Lin, C.S.; Zhang, Z.T.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.Y. Sedimentary evolution and controlling factors of Early-Mid Miocene deltaic systems in the northern Pearl River mouth Basin, South China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.M.; Ye, L.; Xie, S.H.; Yang, K.; Qin, Y. Sedimentary model sand case study of sand-rich shallow-water delta in continental lacustrine basins with low accommodation. J. Palaeogeogr. Chin. Ed. 2023, 25, 959–975. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Tan, H.H. Ultra-thick reservoir description technology based on spectral inversion and its application in "sand-rich" extremely shallow-water delta reservoirs in Bohai Sea area. China Offshore Oil Gas 2015, 27, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, M.C.; Qin, T.; Jiang, T. Prediction of “sand-rich” fluvial reservoirs and hydrocarbon accumulation patterns in the Minghuazhen Formation, western Bohai Sea. In Proceedings of the 2017 Geophysical Technology Seminar of the Chinese Petroleum Society, Qingdao, China, 17–20 April 2017; Bohai Oil Research Institute: Tianjin, China, 2017; pp. 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.G.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, B.; Jia, H.L. Fine characterization of sandbodies in “sand-rich” fluvial sedimentary reservoirs. Geophys. Prospect. Pet. 2021, 60, 461–470. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, V.M.; Ronald, J.S. The role of tidal, wave and river currents in the evolution of mixed-energy deltas: Example from the Lajas Formation (Argentina). Sedimentology 2016, 63, 824–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, A.A.; Storms, J.E.; Walstra, D.J.R. The impact of clastic syn-sedimentary compaction on fluvial-dominated delta morphodynamics. Depos. Rec. 2023, 9, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, Z.B.; Liu, C.; Tian, B.; Zhang, R. Reservoir architecture of delta front in S Oilfield, Liaodong Bay Depression and its control on remaining oil distribution. J. Northeast Pet. Univ. 2016, 40, 1–8+141. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H.; Wu, S.H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Deng, M.; Feng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C. Internal architectural patterns of bar fingers within digitate shallow-water delta: Insights from the shallow core, GPR and Delft3D simulation data of the Ganjiang Delta, China. Lithosphere 2023, 2022, 9120724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Wang, P.F.; Shang, B.B.; Huo, C.L.; Xu, J. Distribution of remaining oil in delta front based on reservoir architecture: A case study of Oil Group I in the Lower Member 2 of Dongying Formation in S Oilfield, Bohai Bay Basin. Fault-Block Oil Gas Field 2019, 26, 580–586. [Google Scholar]
- Du, X.F.; Pang, X.J.; Huang, X.B.; Wang, B.H. Characteristics of the source-to-sink system for the Paleogene Sha 2 Member of northern Liaoxi Sag, offshore Bohai Bay Basin and its control on beach bar sands. Oil Gas Geol. 2023, 44, 662–674. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.F. Two tectonic systems in the Cenozoic Bohai Bay Basin and their genetic interpretation. Geol. China 2004, 31, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, N.S.; Xu, W.; Zuo, Y.H.; Chang, J.; Liu, C.N. Meso-Cenozoic lithospheric thermal structure and thermo-rheological evolution of the Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Sci. Front. 2017, 24, 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.G.; Jiang, S.; Huan, L.; Sun, Z.Q. Sequence stratigraphy of the lacustrine rift basin in the Paleogene system of the Bohai Sea area: Architecture mode, deposition filling pattern, and response to tectonic rifting processes. Interpretation 2020, 8, SF57–SF79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhou, X.H.; Lai, W.C.; Li, J.P.; Shi, W.L. Sedimentary model and new exploration discoveries of the second member of Paleogene Dongying Formation in the middle section of Liaoxi Low Uplift. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2011, 38, 619–624. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Z.B.; Jia, X.F.; Wang, G.C.; Tian, B. Characterization of reservoir plane heterogeneity based on reservoir architecture research. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2018, 40, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H.; Wu, S.H.; Yang, Q.; Yu, B. A fine characterization method for delta front reservoirs based on architectural interfaces: A case study of Paleogene Lower Dongying Formation in Suizhong Oilfield. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2016, 16, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Z.B.; Liao, X.W.; Wang, G.C.; Tian, B. Research on remaining oil distribution in delta front sandbodies during high water-cut stage. J. Southwest Pet. Univ. Sci. Technol. Ed. 2022, 44, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Patruno, S.; Hampson, G.J.; Jackson, C.A.L.; Dreyer, T. Clinoform geometry, geomorphology, facies character and stratigraphic architecture of a sand-rich subaqueous delta: Jurassic Sognefjord Formation, offshore Norway. Sedimentology 2015, 62, 350–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltan, R.; Mountney, N.P. Interpreting complex fluvial channel and barform architecture: Carboniferous Central Pennine Province, northern England. Sedimentology 2016, 63, 207–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilertsen, R.S.; Corner, G.D.; Aasheim, O.D.D.; Hansen, L. Facies characteristics and architecture related to palaeodepth of Holocene fjord–delta sediments. Sedimentology 2011, 58, 1784–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo-Díaz, Y.Z.E.; Jenchen, U.; Guerrero-Suastegui, M. Facies and depositional systems of the Galeana Sandstone Member (Taraises Formation, Lower Cretaceous, northeastern Mexico). Rev. Mex. Cienc. Geol. 2008, 25, 438–464. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbe, O.B. Reservoir sandstone grain-size distributions: Implications for sequence stratigraphic and reservoir depositional modelling in Otovwe field, onshore Niger Delta Basin, Nigeria. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.S.; Wang, T.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, T.Y. The sedimentary and tectonic features of the Niger Delta. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2019, 35, 1238–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Miall, A.D. Architectural-element analysis: A new method of facies analysis applied to fluvial deposites. Earth Sci. Rev. 1985, 22, 261–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Liu, C.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; Wang, Y. The important turning points during evolution of Cenozoic basin offshore the Bohai Sea: Evidence and regional dynamics analysis. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2012, 55, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J.W.; Yang, B.L.; Jiang, J.G. The influence of water level changes on sand bodies at river-dominated delta fronts: The Gubei Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Pet. Sci. 2022, 19, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Wu, J.; Lyu, Q.; Fang, D. Sedimentary characteristics and seismic geomorphology of the upper third member of Eocene Dongying Formation in double slope systems of Laoyemiao transverse anticline, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 109, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olariu, C.; Bhattacharya, J.P. Terminal distributary channels and delta front architecture of river-dominated delta systems. J. Sediment. Res. 2006, 76, 212–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bao, Z.; Dou, L.; Xu, Q. Diagenetic alterations related to sedimentary architecture of deltaic distributary channels in red beds of the Cretaceous Yaojia Formation, Songliao Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 203, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, A.A.; Storms, J.E.A.; Jagers, H.R.A.; van Der Vegt, H. The influence of syn-depositional compaction on clastic sediment distribution in river-dominated deltas: A modelling study. Depos. Rec. 2025, 11, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhu, X.M.; Xie, H.S.; Yang, K.; Zhang, M.Z.; Qin, W. Restoration methods of sedimentary palaeogeomorphology and applications: A case study of the First Member of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Raoyang sag. J. Palaeogeogr. Chin. Ed. 2023, 25, 1139–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Miall, A.D. Facies architecture in elastic sedimentary basins. In New Perspectives in Basin Analysis; Kleinspehn, K.L., Paola, C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988; pp. 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Miall, A.D. The Geology of Fluvial Deposits: Sedimentary Facies, Basin Analysis, and Petroleum Geology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; p. 582. [Google Scholar]
- Fisk, H.N.; Kolb, C.R.; McFarlan, E.; Wilbert, L.J. Sedimentary framework of the modern Mississippi delta [Louisiana]. J. Sediment. Res. 1954, 24, 76–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Li, Y.H.; Zhai, W.B.; Zhao, W.X.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.H.; Guo, Y.Q. Types and genetic models of sand bodies in shallow water delta front of extremely gentle slope lake basin:A case study of Chang 81 submember of Triassic in Haotan area, Ordos Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 2025, 37, 140–152. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.S.; Huang, S.B.; Huang, Q.Z.; Xie, P.F.; Wang, L.X.; Wu, W. Sedimentary characteristics and genesis model of the Eocene shallow-water delta front in the Koulele Oilfield, Termit Basin, Niger. Lithol. Reserv. 2025, 37, 12–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, D.M.; Kulp, M.; Penland, S.; Flocks, J.; Kindinger, J. Morphologic and stratigraphic evolution of muddy ebb-tidal deltas along a subsiding coast: Barataria Bay, Mississippi River Delta. Sedimentology 2004, 51, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | S Oilfield (Prototype) | Flume Experiment (Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Slope | Gentle slope zone: avg. 0.08° Slope-break zone: 1.37° | Avg. 0.2° |
| Water–Sediment Conditions | High sediment supply (coarse-grained), strong hydrodynamics | Water discharge: 500 mL/s |
| Sediment supply: 2 g/s | ||
| Sediment Composition | Sand-dominated (medium-fine sand >60%) | Medium-fine sand: D50 = 200 μm quartz Silt: D50 = 70 μm quartz Clay: Montmorillonite powder |
| Water Level | Short-term base-level fall during rapid progradation | Step 1–40: 10 cm (stable) Step 41–70: 9 cm (−1 cm) Step 71–100: 8 cm (−1 cm) Step 101–117: 5 cm (−3 cm) |
| Monitoring | - | Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) every 30 min, Time-lapse photography (1-s interval) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Xiong, G.; Yin, Y.; Feng, W.; Li, J.; Xie, P.; Hu, X.; Wang, X. Implications of Flume Simulation for the Architectural Analysis of Shallow-Water Deltas: A Case Study from the S Oilfield, Offshore China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112095
Wang L, Xiong G, Yin Y, Feng W, Li J, Xie P, Hu X, Wang X. Implications of Flume Simulation for the Architectural Analysis of Shallow-Water Deltas: A Case Study from the S Oilfield, Offshore China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112095
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lixin, Ge Xiong, Yanshu Yin, Wenjie Feng, Jie Li, Pengfei Xie, Xun Hu, and Xixin Wang. 2025. "Implications of Flume Simulation for the Architectural Analysis of Shallow-Water Deltas: A Case Study from the S Oilfield, Offshore China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112095
APA StyleWang, L., Xiong, G., Yin, Y., Feng, W., Li, J., Xie, P., Hu, X., & Wang, X. (2025). Implications of Flume Simulation for the Architectural Analysis of Shallow-Water Deltas: A Case Study from the S Oilfield, Offshore China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2095. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112095






