Underwater Target Search Path Planning Based on Sound Speed Profile Clustering and Improved Ant Colony Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Path planning is conducted with consideration of the influences of the underwater acoustic environment. Compared with traditional geometric path planning, this method fully accounts for the impacts of acoustic and topographic factors on the sonar detection range, and exhibits a higher level of refinement;
- Introduction of SSP clustering. Based on the spatial correlation of SSPs, the SSPs in adjacent sea areas with similar characteristics are clustered. This significantly reduces the high time consumption caused by the large spatial scale of the mission area;
- Improvement of the ACO algorithm. Aiming at the specific problem of path planning, the pheromone evaporation rate is dynamically set and the heuristic information is improved, resulting in its performance being superior to that of other benchmark algorithms.
2. Related Work
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. SSP Clustering
3.2.1. Calculation of SSP
3.2.2. EOF Decomposition
3.2.3. Data Point Construction
3.2.4. K-Means Clustering
- Initialization: Randomly select K points as initial cluster centers;
- Assignment: Allocate each data point to the cluster with the nearest center;
- Update: Recalculate each cluster’s center as the mean of all points within the cluster;
- Iteration: Repeat steps 2 and 3 until cluster centers stabilize or the maximum number of iterations Nmax is reached.
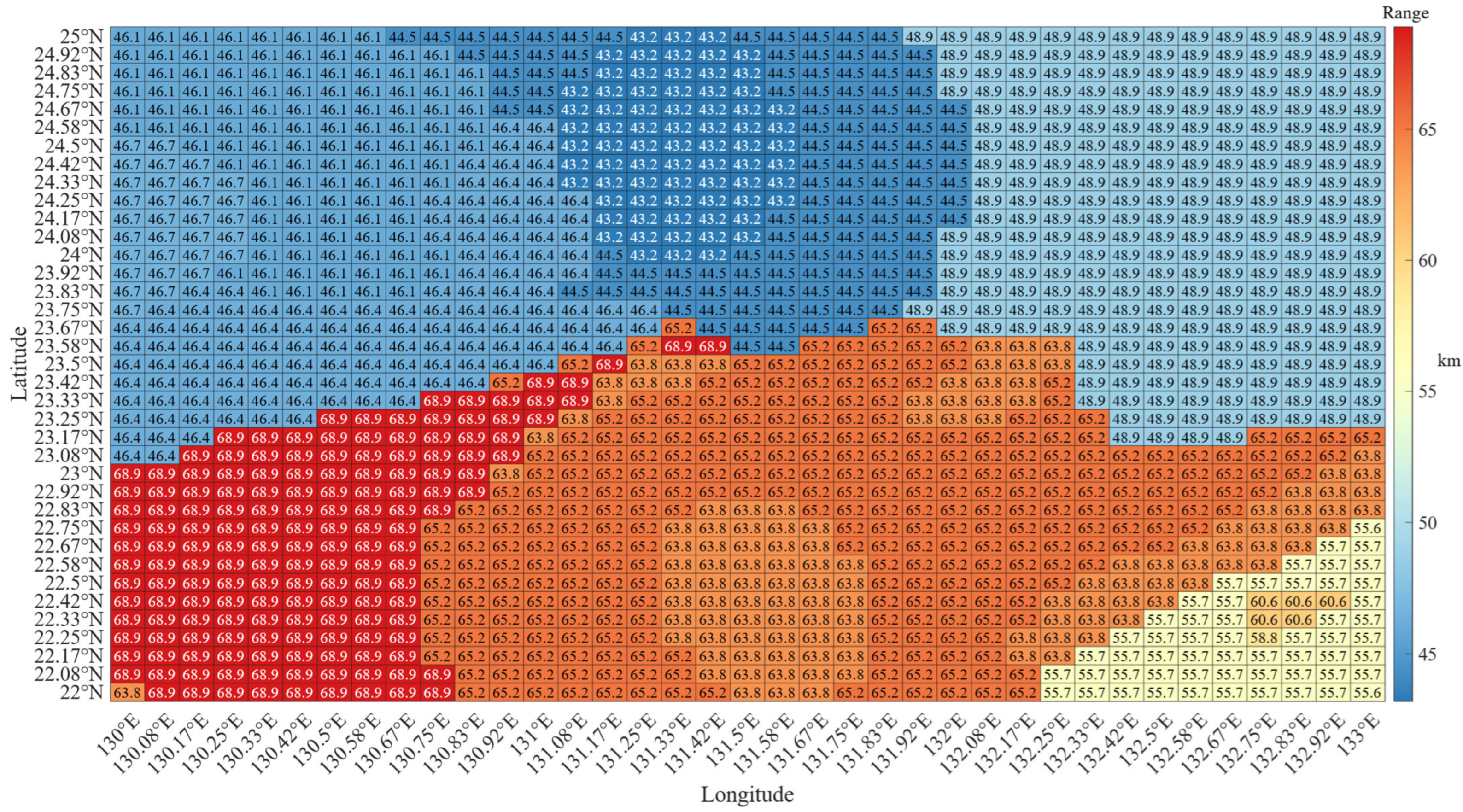
3.3. Sonar Search Distance Estimation
3.3.1. Transmission Loss
3.3.2. Noise Level
3.3.3. Other Sonar Parameters
3.4. Path Planning and Optimization
3.4.1. Improved Ant Colony Optimization
| Algorithm 1 Improved Ant Colony Optimization |
| Input: Initial population L0, population size M, individual dimension N, number of iterations I |
| Output: Optimal search path xbest |
return xbest; |
3.4.2. Population and Coding
3.4.3. Dynamic Pheromone Update
3.4.4. Improvement of Heuristic Information
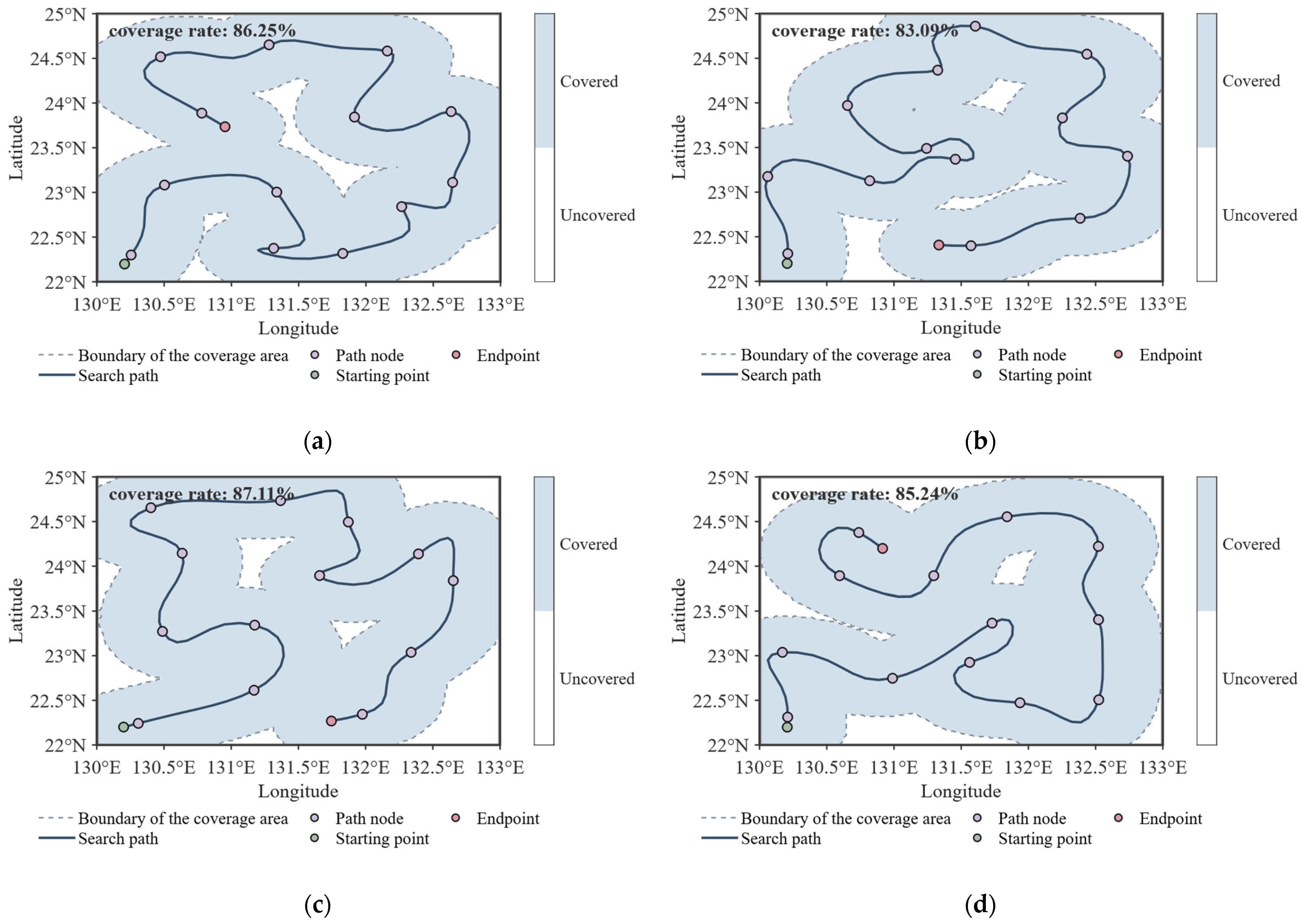
4. Experiment Result and Analysis
4.1. Results of SSP Clustering
4.2. Sound Field Modeling Results
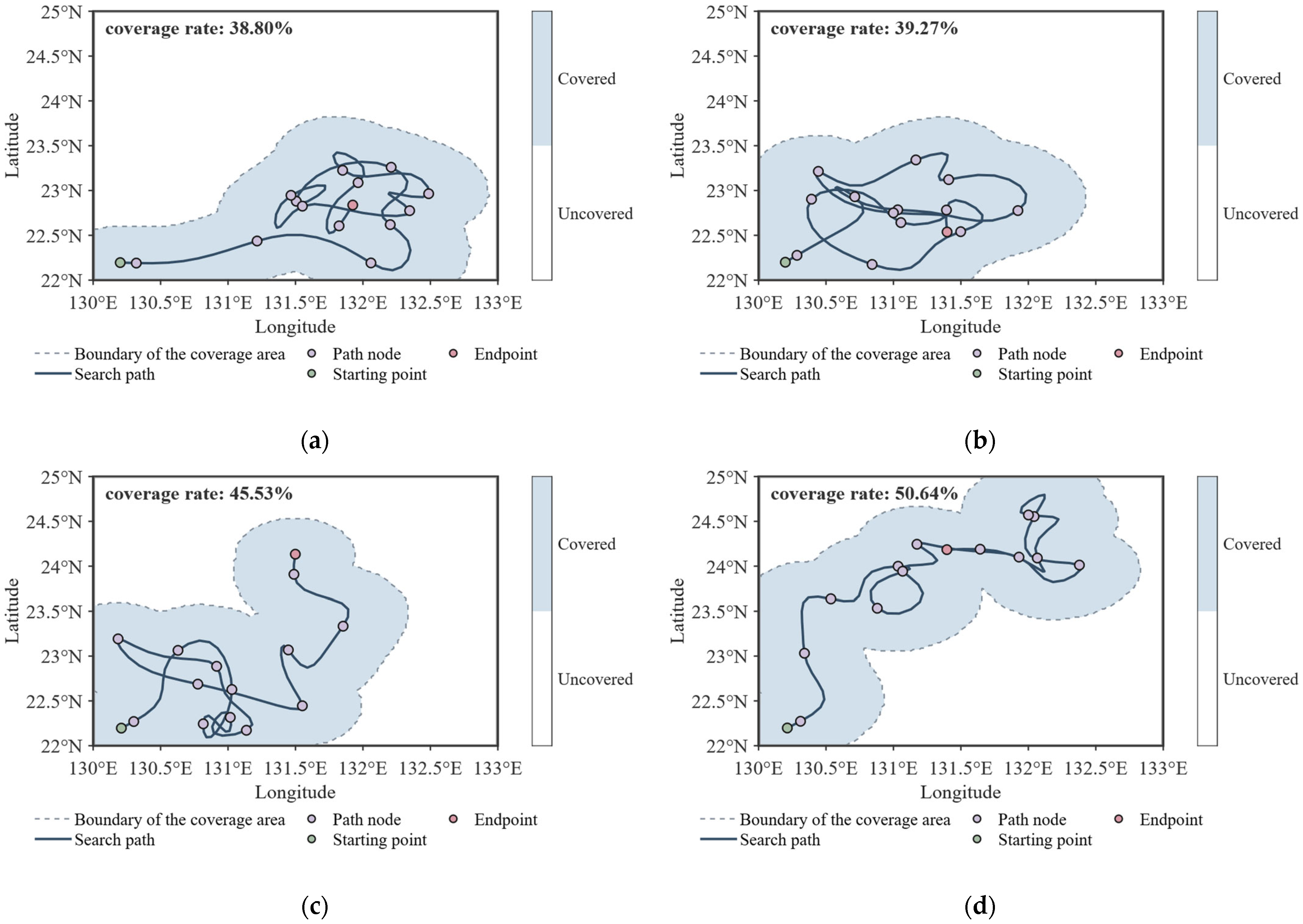
4.3. Path Optimization Results
4.4. Analysis of Optimization Algorithms
4.4.1. Parameter Setting
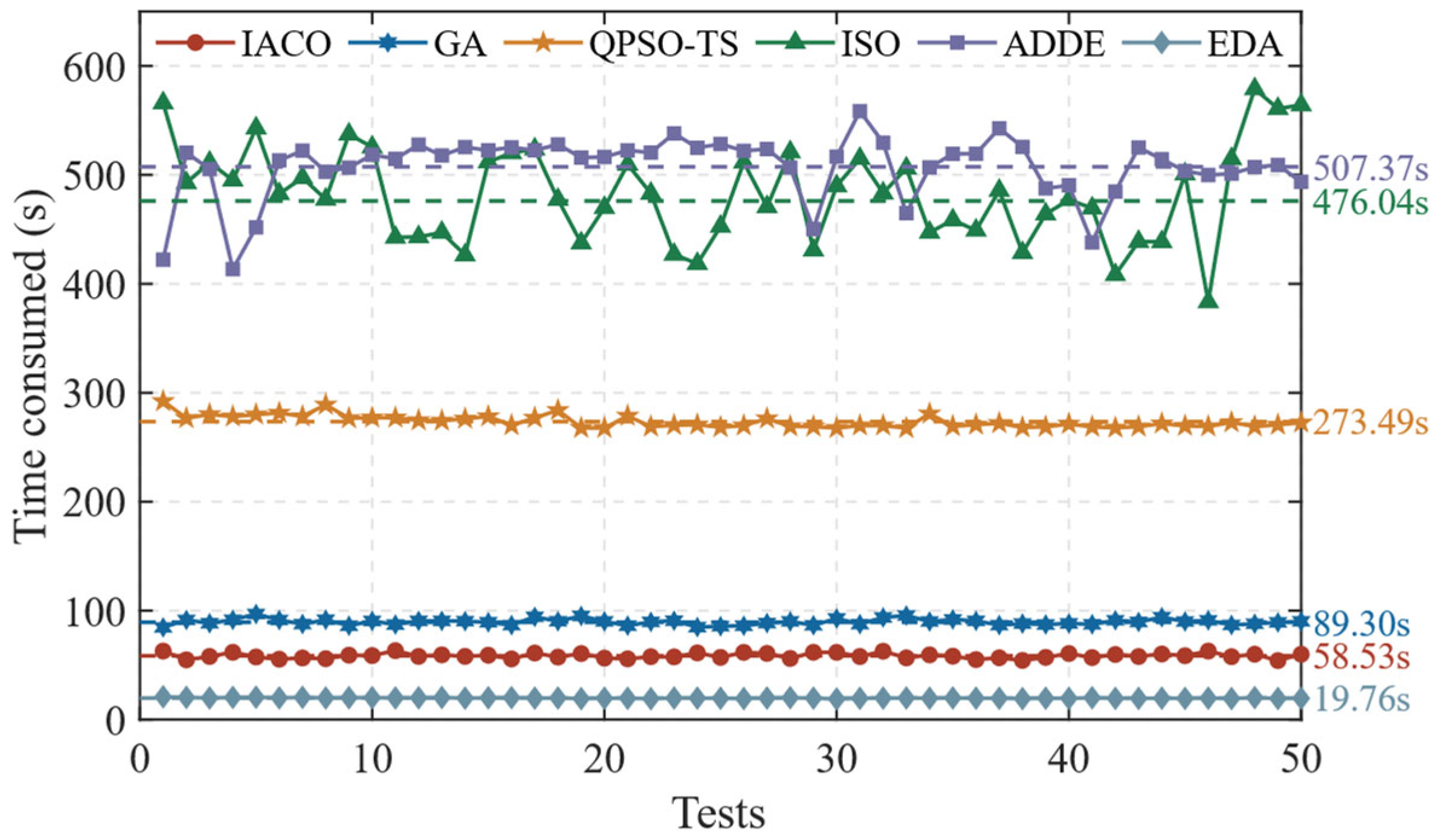
4.4.2. Performance Analysis
4.4.3. Statistical Significance Test
4.4.4. Computational Complexity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qian, L.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Hong, M.; Han, J. Underwater target search and placement strategies based on an improved hidden Markov model. Sci. Sin. Technol. 2025, 55, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urick, R.J. Principles of Underwater Sound, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 1–425. ISBN 9780070660878. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Su, X.; Cui, J.; Yang, G. Coordinated path planning of USV&AUV for an underwater target. Control. Decis. 2021, 36, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.L. Geoacoustic modeling of the sea floor. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 68, 1313–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Johnson-Roberson, M. Multi-altitude multi-sensor fusion framework for AUV exploration and survey. In Proceedings of the 2014 Oceans-St. John’s, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 14–19 September 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medwin, H.; Clay, C.S. Fundamentals of Acoustical Oceanography; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–712. ISBN 978-0-12-487570-8. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, T.C.A.; Lin, Y.T.; Porter, M.B. Underwater Sound Propagation Modeling in a Complex Shallow Water Environment. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 751327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Shang, H.; Zhu, Q. An efficient RRT-based motion planning algorithm for autonomous underwater vehicles under cylindrical sampling constraints. Auton. Robot. 2023, 47, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, L. An Adaptive Evolutionary Multi-Objective Estimation of Distribution Algorithm and Its Application to Multi-UAV Path Planning. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 50038–50051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, B.; Jia, M.; Xu, H.; Xu, J.; Wen, Z.; Li, B.; Zhang, D. Coverage path planning for maritime search and rescue using reinforcement learning. Ocean Eng. 2021, 241, 110098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Y. Optimization of route planning based on active towed array sonar for underwater search and rescue. Ocean Eng. 2025, 330, 121249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiao, W.; Liu, Y. Research on Path Optimization for Underwater Target Search Under the Constraint of Sea Surface Wind Field. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, Z. A Computational Method for Acoustic Interaction with Large Complicated Underwater Structures Based on the Physical Mechanism of Structural Acoustics. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 3631241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, G. A Time-Domain Wavenumber Integration Model for Underwater Acoustics Based on the High-Order Finite Difference Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, F.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Porter, M.B.; Schmidt, H. Computational Ocean Acoustics, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 377–452. ISBN 978-1-4419-8677-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mackenzie, K.V. Nine-term equation for sound speed in the oceans. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 70, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A Computer Movie Simulating Urban Growth in the Detroit Region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qu, K.; Li, Z. An Enhanced Approach for Sound Speed Profiles Inversion Using Remote Sensing Data: Sample Clustering and Physical Regression. Electronics 2025, 14, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, J.; Luo, Y.; Peng, D. Reconstruction Performance Analysis for Basis Function of the Sound Speed Profile. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 45, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, P.; Lu, J.; Lu, J.; Xiu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, T. Underwater SSP Measurement and Estimation: A Survey. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhai, J. A Novel Sound Speed Profile Prediction Method Based on the Convolutional Long-Short Term Memory Network. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Meng, Z. Reconstruction of Ocean Front Model Based on Sound Speed Clustering and Its Effectiveness in Ocean Acoustic Forecasting. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, M.S. Clustering Analysis of a Yearlong Record of Ambient Sound on the Chukchi Shelf in the 40 Hz to 4 kHz Frequency Range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2021, 150, 1597–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Han, X.; Wei, L.; Cao, R.; Wei, Z. Depth discrimination of passive sources in the Beaufort Sea of the Arctic. Acta Acust. 2025, 50, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ge, Y.; Guan, Z.; Ye, G.; Feng, H. Path planning of underwater vehicle based on improved particle swarm algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2024 36th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Xi’an, China, 25–27 May 2024; pp. 5584–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, A. AUV Path Planning Based on Improved Ant Colony Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, and Communication, Fuzhou, China, 25–27 November 2023; Volume 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Rosas, U.; Montiel, O.; Sepúlveda, R. Mobile robot path planning using membrane evolutionary artificial potential field. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 77, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Rosas, U.; Picos, K.; Pantrigo, J.J.; Montemayor, A.S.; Cuesta-Infante, A. Mobile Robot Path Planning Using a QAPF Learning Algorithm for Known and Unknown Environments. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 84648–84663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Geng, L.; Zhang, S. Knowledge hierarchy-based dynamic multi-objective optimization method for AUV path planning in cooperative search missions. Ocean Eng. 2024, 312, 119267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Dou, J. Path planning of autonomous underwater vehicle in unknown environment based on improved deep reinforcement learning. Ocean Eng. 2024, 301, 117547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millero, F.J.; Li, X. On equations for the speed of sound in seawater-comment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1994, 95, 2757–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, C.C.; Parthiot, F. Depth-pressure relationships in the oceans and seas. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 103, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Leng, L. Inversion Prediction Method for Sound Speed Profile. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2019, 37, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk, W.; Snodgrass, F.; Caiiier, G. Edge Waves on the Continental Shelf. Science 1956, 123, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woezel, J.L.; Ewing, M.; Pekeris, C.L. Propagation of Sound in the Ocean. In Geological Society of America Memoirs; Geological Society of America: Boulder, CO, USA, 1948; Volume 27, pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappert, F.D. The parabolic approximation method. In Wave Propagation and Underwater Acoustics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1977; Volume 70, pp. 224–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Q.; Fu, Z.; Xu, W.; Xue, M.; Rashed, Y.F.; Zheng, J. FEM-PIKFNN for underwater acoustic propagation induced by structural vibrations in different ocean environments. Comput. Math. Appl. 2024, 176, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Y. Dynamic hybrid parallel computing of the Ray Model for solving underwater acoustic fields in vast sea. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenz, G.M. Acoustic ambient noise in the ocean: Speactra and source. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1962, 34, 1936–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kularia, Y.; Bhattacharya, P. Analysis of Acoustic Channel Characteristics for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. Control. Eng. 2016, 3, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.H. Noise directionality for surface sources in range-dependent environments. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 102, 2655–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Cao, M.; Song, B. A new approach to smooth path planning of mobile robot based on quartic Bezier transition curve and improved PSO algorithm. Neurocomputing 2022, 473, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Peng, X. Underwater glider 3D path planning with adaptive segments and optimal motion parameters based on improved JADE algorithm. Ocean Eng. 2024, 299, 117377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Tang, K.; Lozano, J.A. Estimation of Distribution Algorithms based Unmanned Aerial Vehicle path planner using a new coordinate system. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Beijing, China, 6–11 July 2014; pp. 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Yang, D.; Zhong, C.; Yan, S.; Zhang, L. An Improved Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm for Multi-Agent Path Planning. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Networking Systems of AI, Shanghai, China, 19–20 November 2021; pp. 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

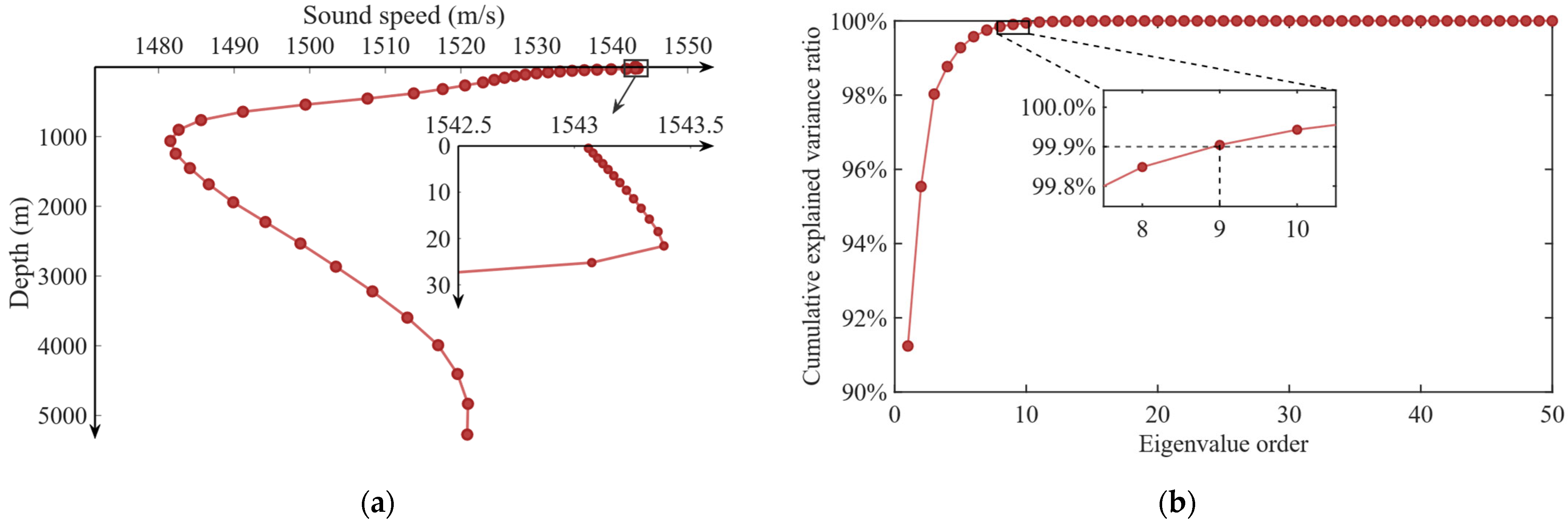
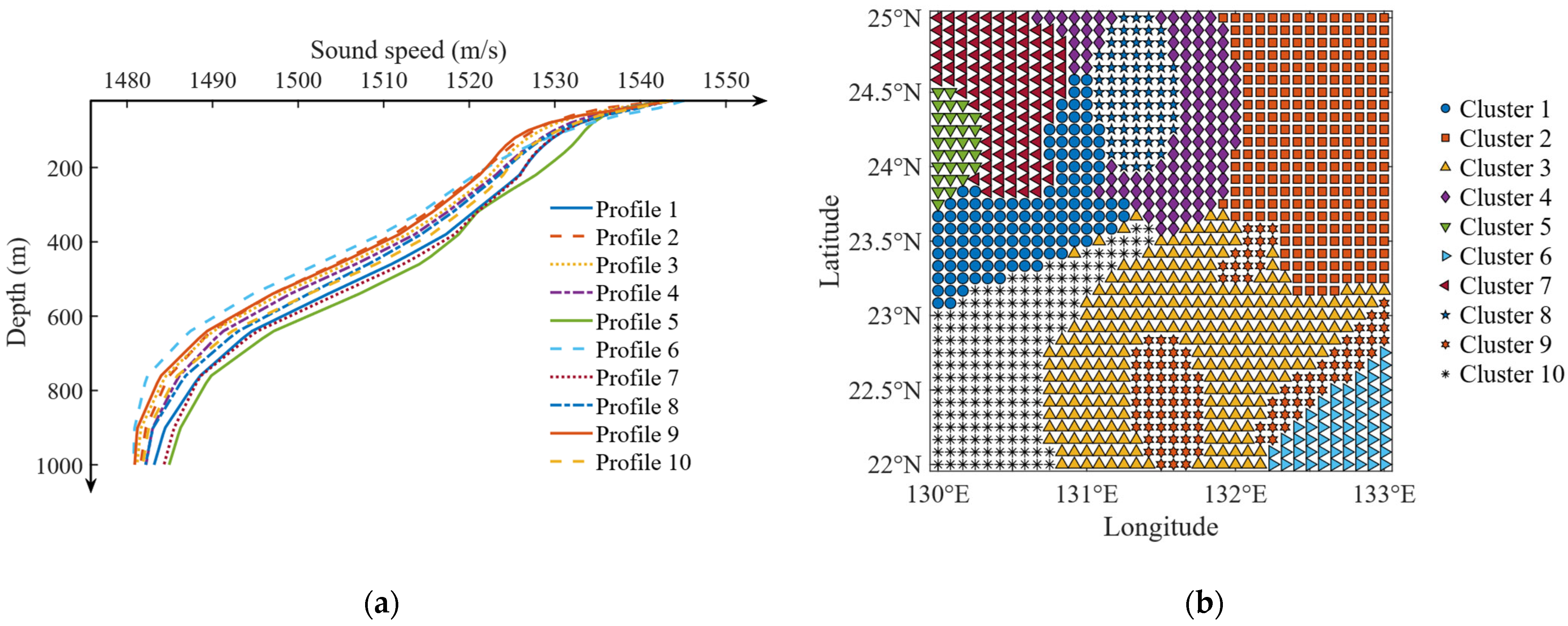



| K Value | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silhouette coefficient s | 0.2982 | 0.3141 | 0.3158 | 0.3432 | 0.3319 | 0.3331 | 0.3630 | 0.3396 | 0.3785 |
| Cluster | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latitude (° N) | 23.71 | 24.16 | 22.79 | 24.35 | 24.15 | 22.25 | 24.50 | 24.50 | 22.63 | 22.71 |
| Longitude (° E) | 130.61 | 132.54 | 131.68 | 131.58 | 130.10 | 132.72 | 130.45 | 131.33 | 131.99 | 130.49 |
| Clustering Applied | Time Consumption |
|---|---|
| Yes | 10.84 min |
| No | 24.74 h |
| Algorithm | Parameter Values |
|---|---|
| IACO | Initial pheromone concentration: 1; Pheromone importance factor: 1; Heuristic information importance factor: 4; Basic evaporation rate: 0.2; Pheromone increment constant: 100; Elite proportion: 0.1 |
| GA | Crossover probability: 0.5; Mutation probability: 1/N; Tournament selection size: 3; Elite retention ratio: 0.15 |
| QPSO-TS | Contraction-expansion coefficient: 0.75; Tabu list length: 10; Tabu tenure: 5 |
| ISO | Chaotic mapping parameter: 0.5; Dynamic weight factor: 1.2; Gaussian disturbance intensity: 0.2 |
| ADDE | Initial mean of scaling factor: 0.5; Initial mean of crossover probability: 0.5; Elite proportion: 0.1 |
| EDA | Minimum variable value: 1; Maximum variable value: 16; Retention proportion: 0.5 |
| Statistical Indicators | GA | QPSO-TS | ISO | ADDE | EDA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank sum statistic | 2905.0 | 3701.5 | 3556.0 | 3687.0 | 3775.0 |
| p-value | 0.0089 | 5.1818 × 10−16 | 1.2113 × 10−12 | 1.1738 × 10−15 | 7.0661 × 10−18 |
| Algorithm | Computational Complexity |
|---|---|
| IACO | O(I·(M·f + 16M·N + M·logM)) |
| GA | O(I·(M·f + 16M·N + M·logM)) |
| QPSO-TS | O(I·(M·f + 16M·N + t·ns·N·f)) |
| ISO | O(I·(M·f + 16M·N + M·logM)) |
| ADDE | O(I·(M·f + 16M·N + M·logM)) |
| EDA | O(I·(M·f + 16M·N)) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, W.; Shang, L. Underwater Target Search Path Planning Based on Sound Speed Profile Clustering and Improved Ant Colony Optimization. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101983
Wang W, Liu Y, Xiao W, Shang L. Underwater Target Search Path Planning Based on Sound Speed Profile Clustering and Improved Ant Colony Optimization. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101983
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenjun, Yuhao Liu, Wenbin Xiao, and Longquan Shang. 2025. "Underwater Target Search Path Planning Based on Sound Speed Profile Clustering and Improved Ant Colony Optimization" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101983
APA StyleWang, W., Liu, Y., Xiao, W., & Shang, L. (2025). Underwater Target Search Path Planning Based on Sound Speed Profile Clustering and Improved Ant Colony Optimization. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101983







