Identification Modeling of Ship Maneuvering Motion Based on AE-MSVR
Abstract
1. Introduction
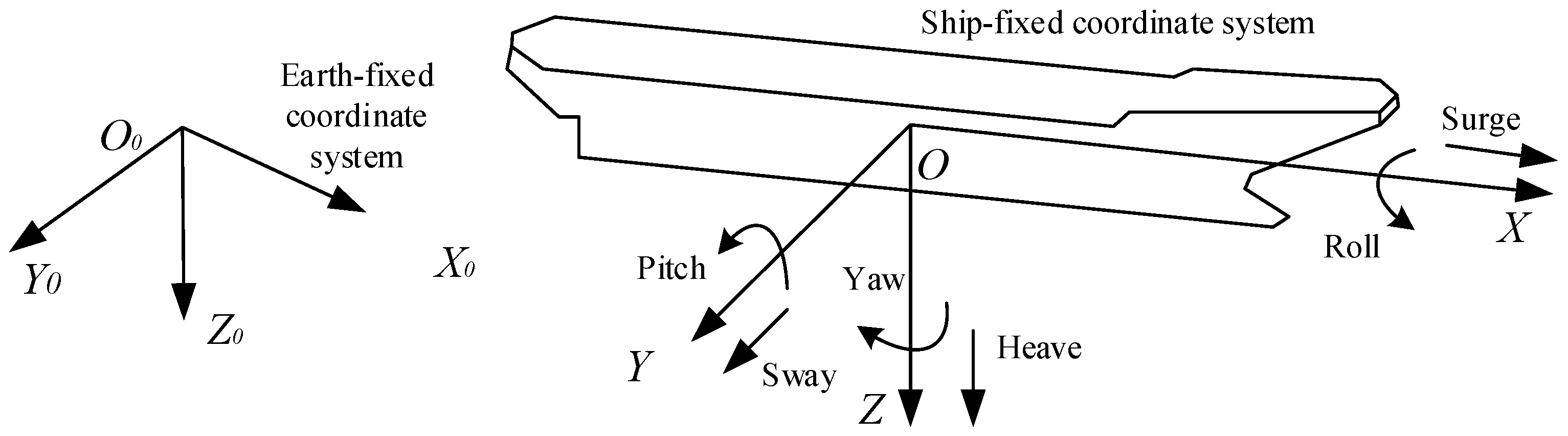
2. Ship Maneuvering Model
2.1. The 3-DOF Mathematical Model
2.2. Reconstructed Identification Model
3. AE-MSVR
3.1. MSVR
3.2. AE
- t: iteration index.
- P: base vector determining evolutionary starting position.
- : attenuation factor balancing algorithmic exploration/exploitation.
- : the i-th random step size.
- : control parameter for differential vector (self-adaptive step size).
- , : sampled solutions from , satisfying .
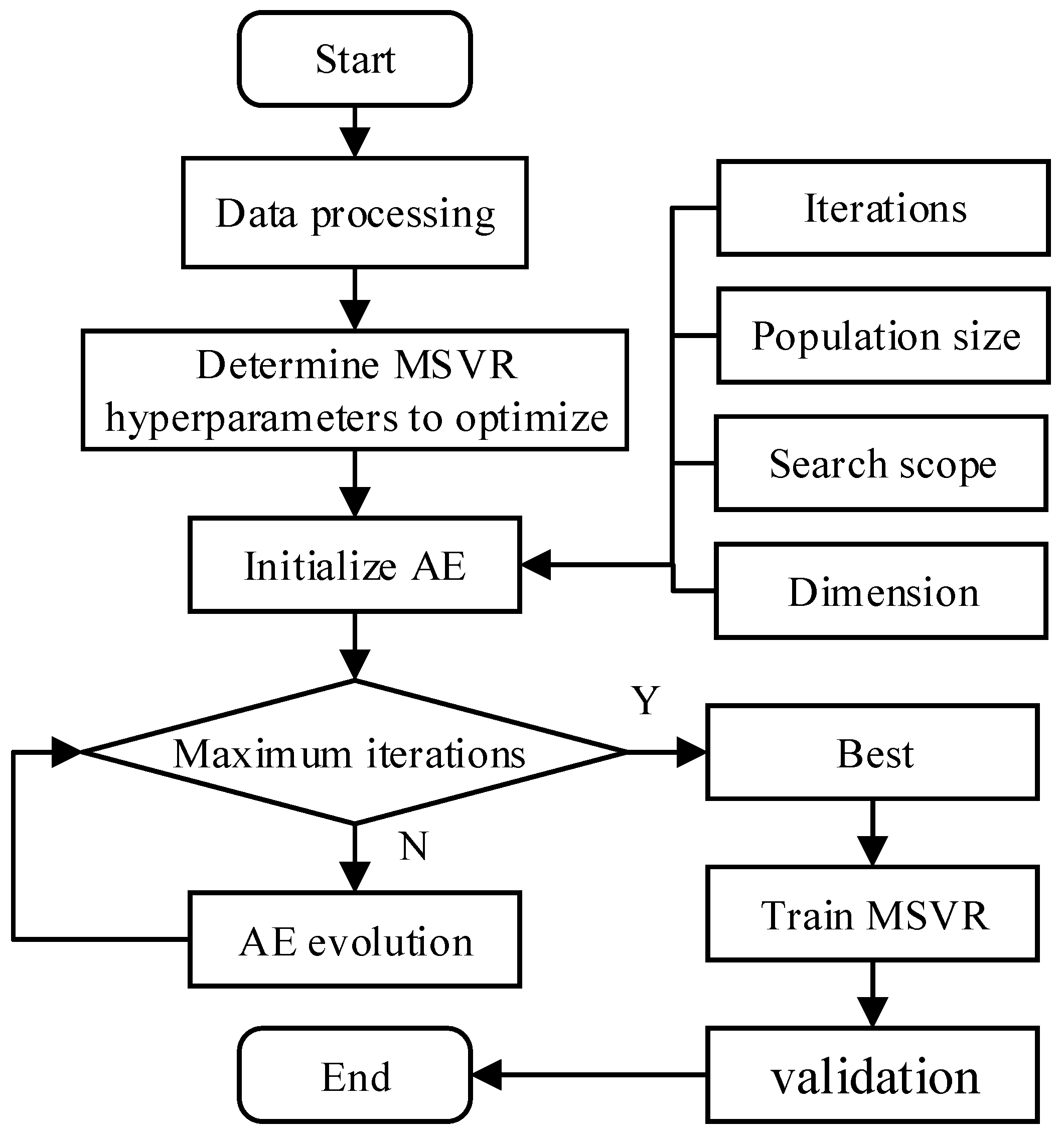
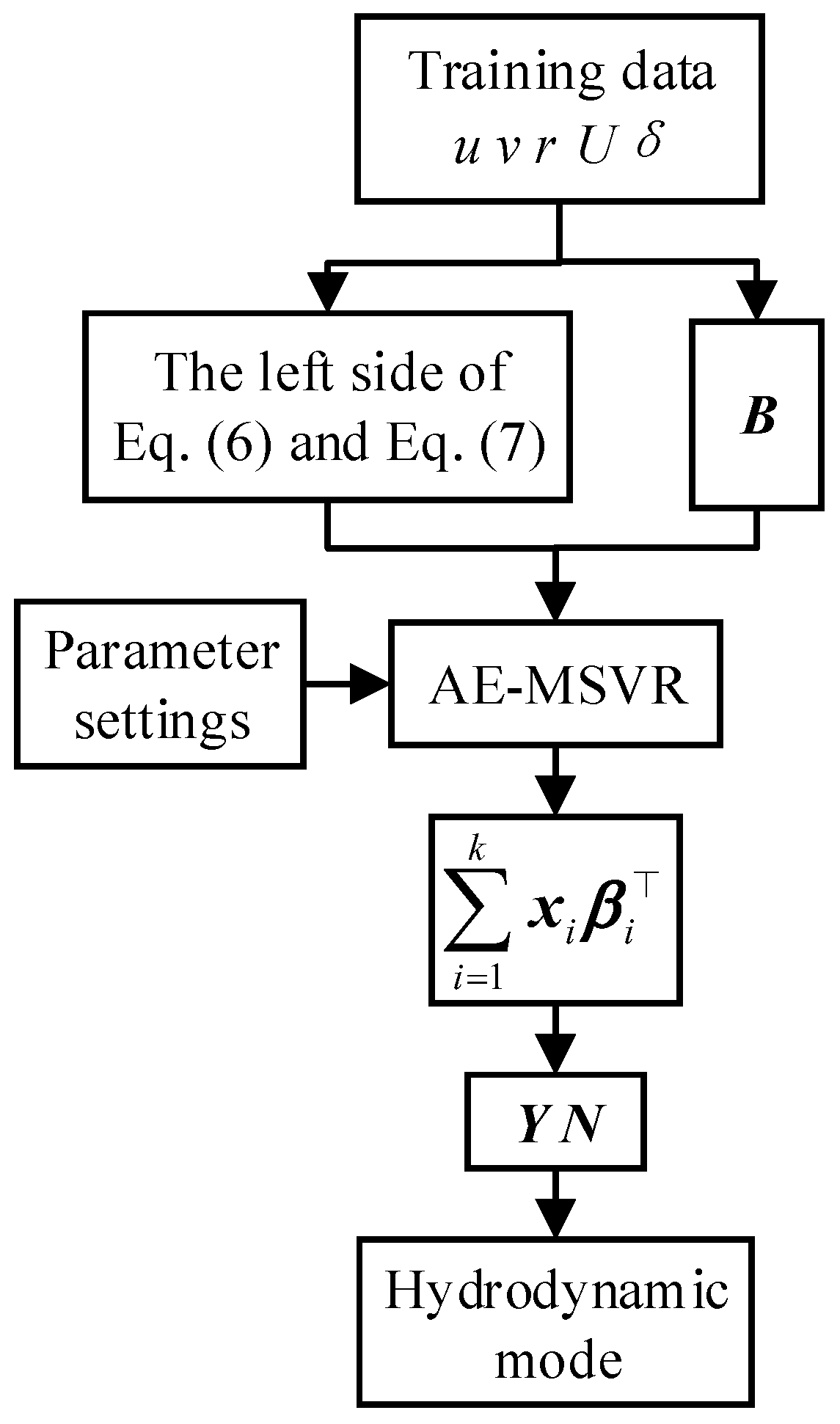
3.3. AE-MSVR
4. Model Validation
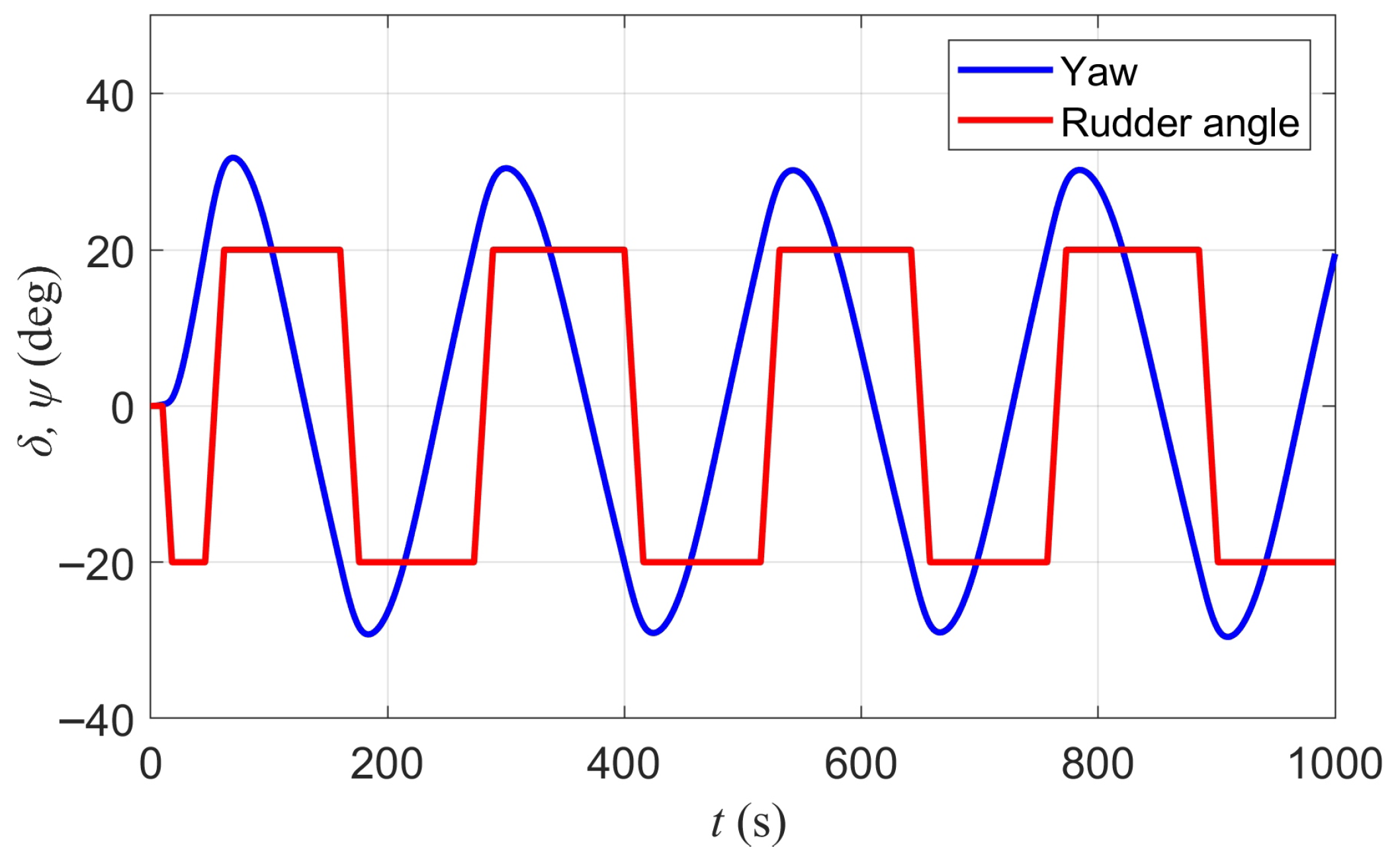
4.1. Training Data
4.2. Identification Process
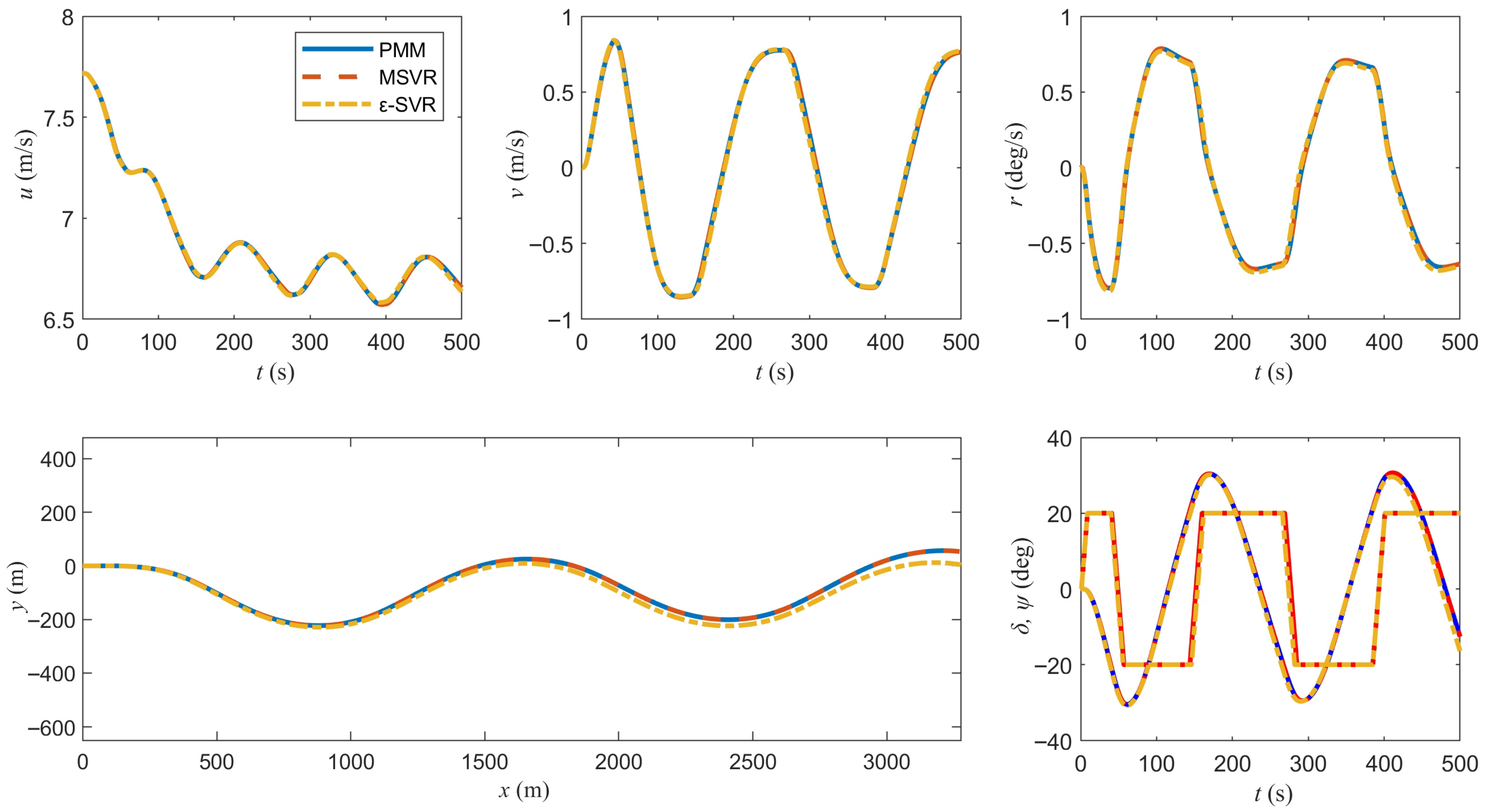
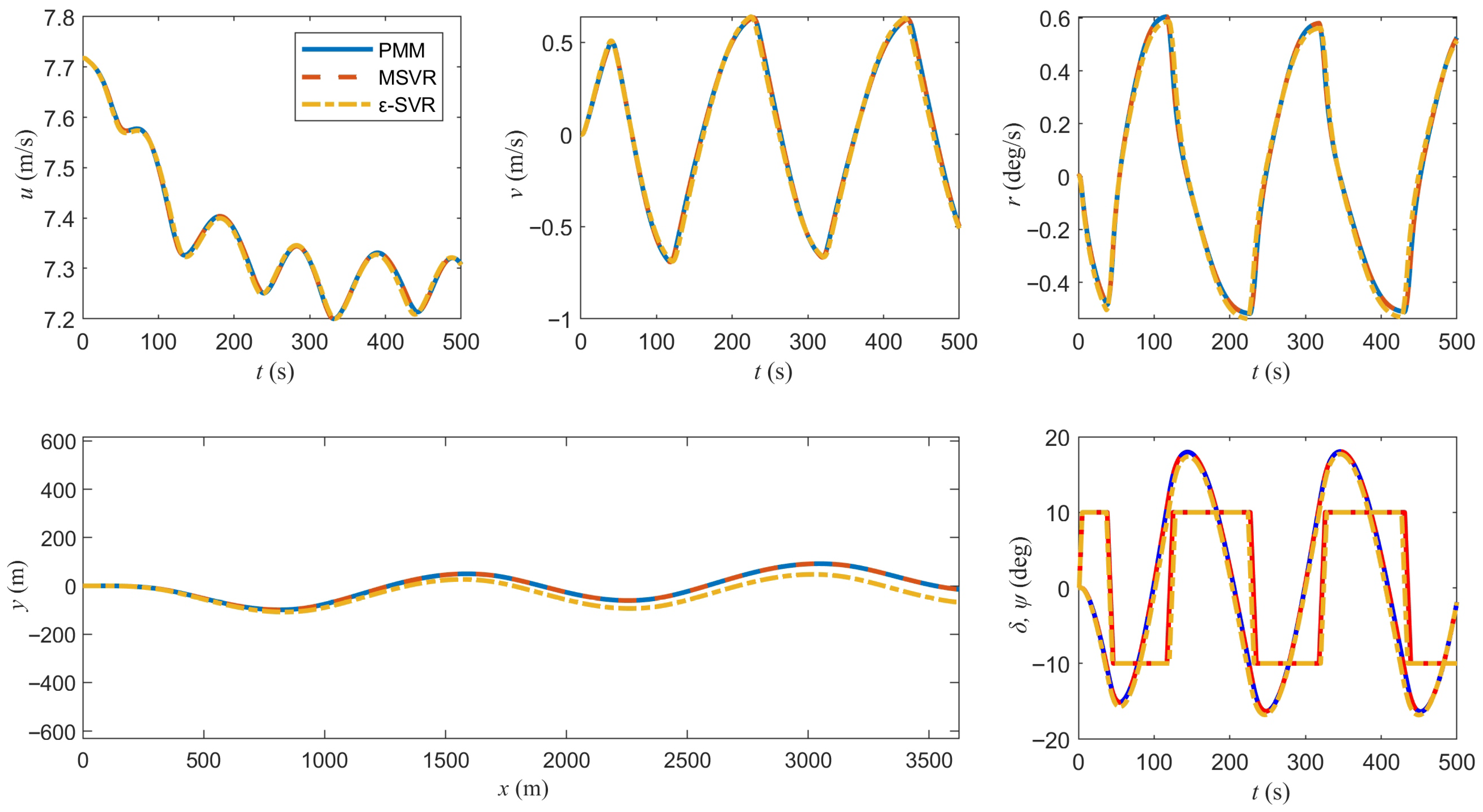
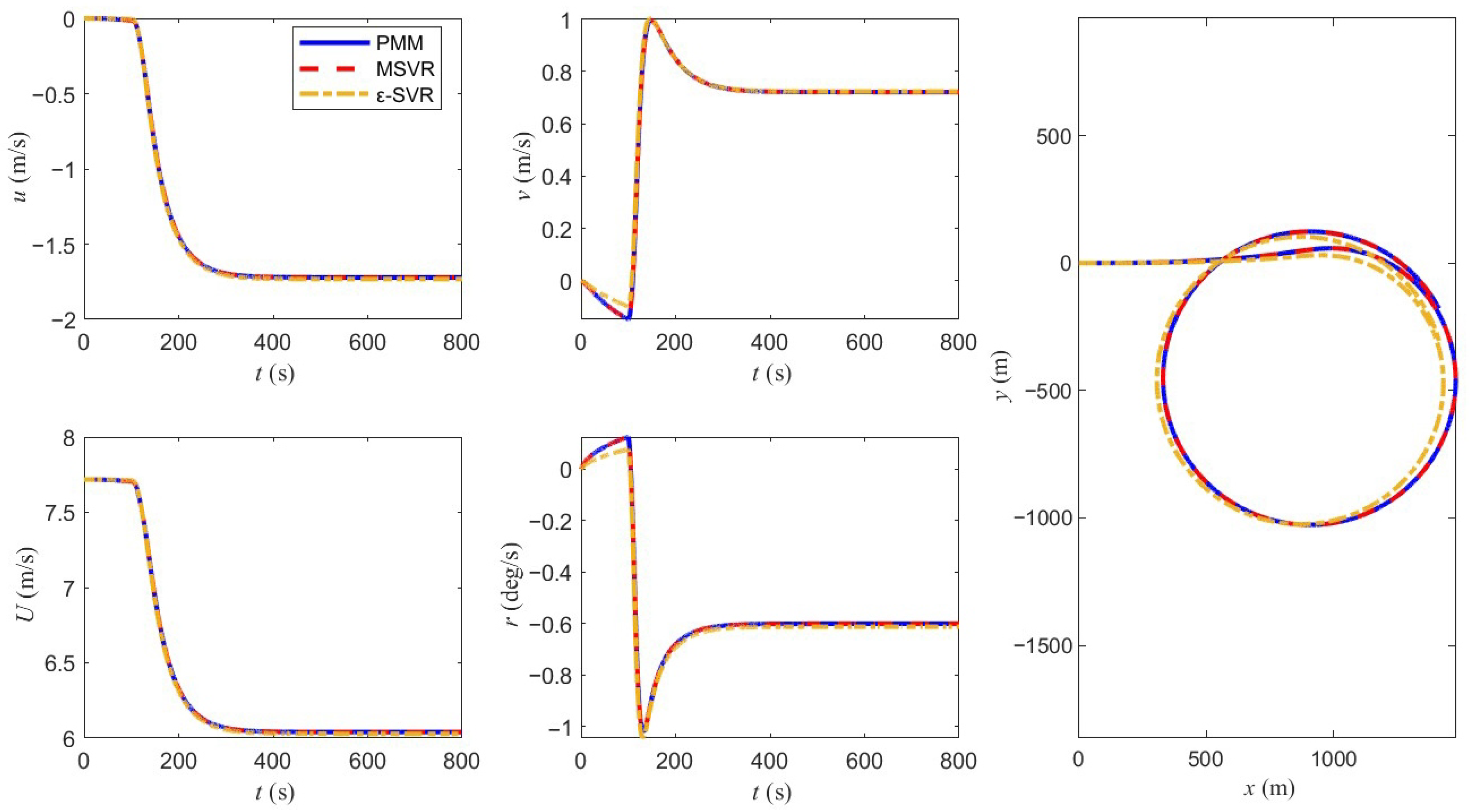
4.3. Identification Results
4.4. Identified Model Validation
5. Model Identification Under Disturbance
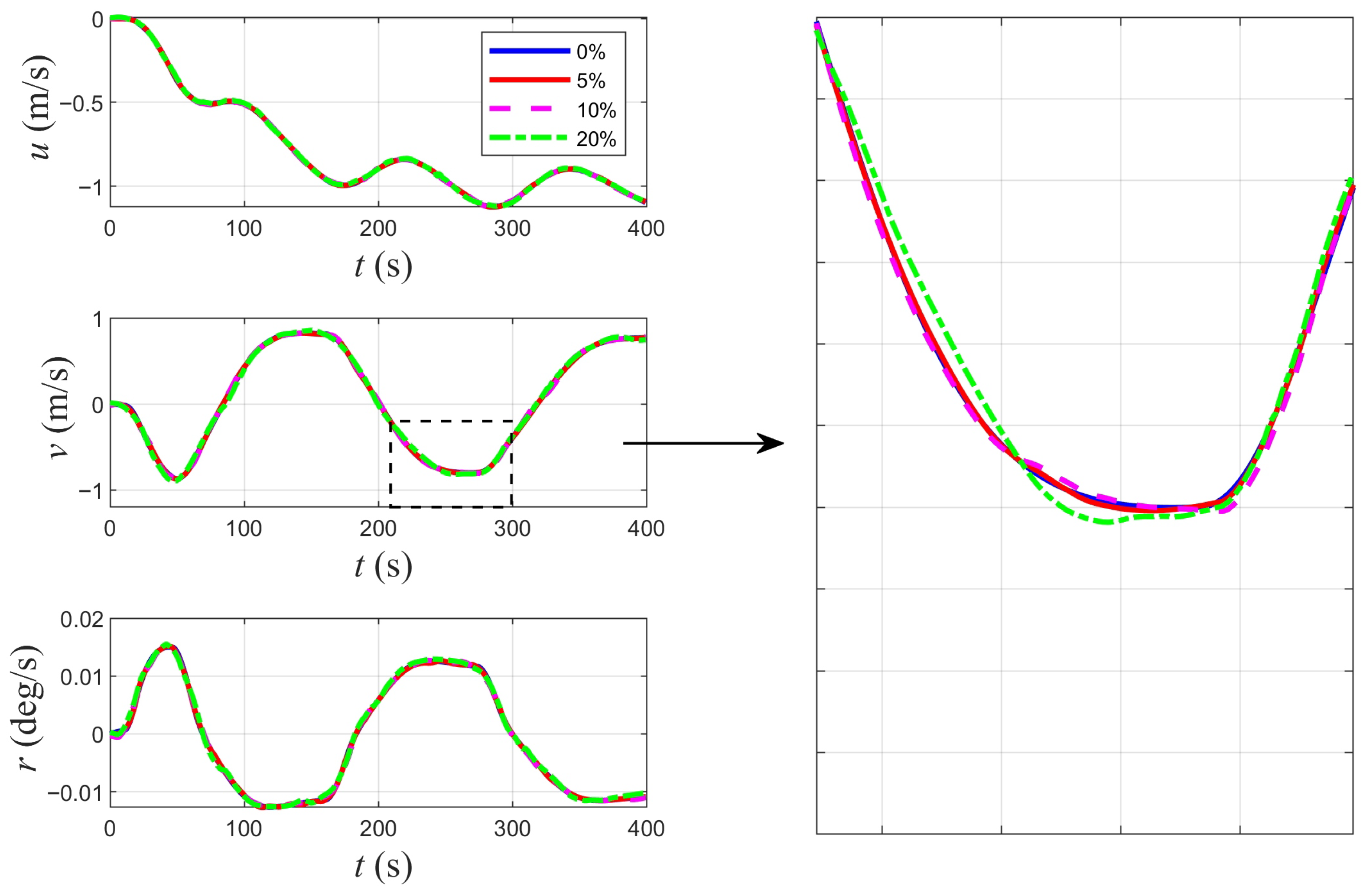
5.1. Disturbance Model
5.2. Identification Under Disturbance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IMO. Interim Guidelines on the Second Generation Intact Stability Criteria; Technical Report MSC.1/Circ.1627; IMO: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Skulstad, R.; Li, G.; Fossen, T.I.; Vik, B.; Zhang, H. A hybrid approach to motion prediction for ship docking-integration of a neural network model into the ship dynamic model. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 2501311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abkowitz, M.A. Lectures on Ship Hydrodynamics–Steering and Manoeuvrability; Report No. Hy-5; Hydro- and Aerodynamics Laboratory: Lyngby, Denmark, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, H.; Ji, Y.; Xu, L.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. Maximum likelihood-based gradient estimation for multivariable nonlinear systems using the multiinnovation identification theory. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control. 2020, 30, 5446–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, C.; Xue, G. Hydrodynamic parameter identification for ship manoeuvring mathematical models using a Bayesian approach. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 195, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, R.; Pei, T.; Lian, L. Adaptive anti-noise least-squares algorithm for parameter identification of unmanned marine vehicles: Theory, simulation, and experiment. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 25, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakita, K.; Maki, A.; Umeda, N.; Miyauchi, Y.; Shimoji, T.; Rachman, D.M.; Akimoto, Y. On neural network identification for low-speed ship maneuvering model. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, T.; Fossen, T.I. Practical aspects of frequency-domain identification of dynamic models of marine structures from hydrodynamic data. Ocean. Eng. 2011, 38, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, D.; Duan, Y. Online ship motion identification modeling and its application to course-keeping control. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 294, 116853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V. An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, Z.; Yu, L.; Cai, W. System identification modeling of ship manoeuvring motion in 4 degrees of freedom based on support vector machines. China Ocean. Eng. 2015, 29, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.L.; Zou, Z.J. Parametric Identification of Ship Maneuvering Models by Using Support Vector Machines. J. Ship Res. 2009, 53, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, G.; Wu, B.; Æsøy, V.; Zhang, H. Parameter identification of ship manoeuvring model under disturbance using support vector machine method. Ships Offshore Struct. 2021, 16, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hassani, V.; Guedes Soares, C. Comparing generic and vectorial nonlinear manoeuvring models and parameter estimation using optimal truncated least square support vector machine. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2020, 97, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guedes Soares, C. Hydrodynamic coefficient estimation for ship manoeuvring in shallow water using an optimal truncated LS-SVM. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 191, 106488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Cao, Q.; Shen, Y.; Chen, M.; Ding, Y.; Ding, Y. Predicting the motion of a USV using support vector regression with mixed kernel function. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, P.; Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, G.; Hao, G. Grey-box identification modeling of ship maneuvering motion based on LS-SVM. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 266, 112957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Song, L.; Liu, Z.; Yao, J. Identification of ship hydrodynamic derivatives based on LS-SVM with wavelet threshold denoising. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuia, D.; Verrelst, J.; Alonso, L.; Perez-Cruz, F.; Camps-Valls, G. Multioutput support vector regression for remote sensing biophysical parameter estimation. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Fernandez, M.; de Prado-Cumplido, M.; Arenas-Garcia, J.; Perez-Cruz, F. SVM multiregression for nonlinear channel estimation in multiple-input multiple-output systems. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2004, 52, 2298–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Shang, X.; Jin, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W. Black-box modeling of ship maneuvering motion using multi-output least-squares support vector regression based on optimal mixed kernel function. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 293, 116663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Zou, Z.J. Black-box modeling of ship maneuvering motion based on multi-output nu-support vector regression with random excitation signal. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 257, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, X.; Ren, H.; Li, C.; Feng, X. Non-parametric identification modeling and prediction of intelligent ship maneuvering motion based on real ship test at sea. Ocean. Eng. 2025, 330, 121267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Hu, Z.; Lu, S.; Liu, Y. Maneuverability parameter identification of a water-jet USV based on truncated weighted LSSVM integrated with adaptive mutation PSO algorithm. Ocean. Eng. 2025, 321, 120474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J. Modified grey wolf optimizer-based support vector regression for ship maneuvering identification with full-scale trial. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2022, 27, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Identification modeling of ship manoeuvring motion based on ISSA-SVR. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 313, 119364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, Q. Alpha evolution: An efficient evolutionary algorithm with evolution path adaptation and matrix generation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 137, 109202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Li, X. Measures to diminish the parameter drift in the modeling of ship manoeuvring using system identification. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2017, 67, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, Z.; Hou, X.; Xu, F. System identification modelling of ship manoeuvring motion based on ɛ-support vector regression. J. Hydrodyn. 2015, 27, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cruz, F.; Vázquez, A.N.; Alarcón-Diana, P.L.; Artés-Rodríguez, A. An IRWLS procedure for SVR. In Proceedings of the 2000 10th European Signal Processing Conference, Tampere, Finland, 4–8 September 2000; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chislett, M.; Strom-Tejsen, J. Planar motion mechanism tests and full-scale steering and manoeuvring predictions for a Mariner class vessel. Int. Shipbuild. Prog. 1965, 12, 201–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutulo, S.; Guedes Soares, C. An algorithm for offline identification of ship manoeuvring mathematical models from free-running tests. Ocean. Eng. 2014, 79, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Length overall () | 171.8 m |
| Length between perpendiculars () | 160.93 m |
| Maximum beam (B) | 23.17 m |
| Design draft (T) | 8.23 m |
| Design displacement (∇) | 18,541 m3 |
| Design speed () | 15 kn (7.7175 m/s) |
| A | 1 s | 0.5 s | 0.1 s | 0.01 s | B | 1 s | 0.5 s | 0.1 s | 0.01 s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 127.1 | 127.9 | 129.0 | 129.4 | 1118.1 | 1254.7 | 1354.2 | 1371.3 | ||
| 873.5 | 875.2 | 880.1 | 882.2 | 1506.4 | 1691.3 | 1838.1 | 1870.6 | ||
| 384.5 | 383.8 | 385.3 | 386.1 | 934.8 | 962.1 | 970.1 | 970.7 | ||
| 214.9 | 229.3 | 234.0 | 233.4 | 2182.4 | 2258.3 | 2270.7 | 2267.3 | ||
| 220.2 | 233.8 | 240.7 | 241.9 | 1812.5 | 1925.1 | 1975.1 | 1991.8 | ||
| 8.8 | 9.3 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 2894.5 | 3092.6 | 3170.9 | 3197.6 | ||
| 9.8 | 10.2 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 551.7 | 598.9 | 630 | 637.7 | ||
| 777.0 | 828.7 | 844.7 | 843.2 | 114.3 | 115.6 | 112.8 | 112.4 | ||
| 61.9 | 62.9 | 63.3 | 63.7 | 2349.2 | 2487.9 | 2566.6 | 2597.8 | ||
| 29.1 | 29.0 | 29.1 | 29.3 | 589.3 | 616.7 | 637.9 | 645.9 | ||
| 47.8 | 50.6 | 50.3 | 49.5 | ||||||
| 620.1 | 651.6 | 668.9 | 672.5 | ||||||
| 325 | 326.5 | 331.7 | 332 | ||||||
| 288.6 | 293.5 | 301.1 | 301.5 | ||||||
| 23.1 | 23.4 | 23.8 | 23.9 |
| X | PMM | AE-MSVR | SVR | Y | PMM | AE-MSVR | SVR | N | PMM | AE-MSVR | SVR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −184 | −183.9 | −185.2 | −1160 | −1160.0 | −1158.2 | −264 | −264 | −262.4 | |||
| −110 | −109.4 | −116.6 | −499 | −499.0 | −498.1 | −166 | −166 | −165.4 | |||
| −215 | −212.9 | −220.0 | −8078 | −8080.0 | −8150.4 | 1636 | 1638.7 | 1667.5 | |||
| −899 | −898.8 | −923.0 | 15,356 | 15,354.2 | 15,312.0 | −5483 | −5481 | −5484.0 | |||
| 18 | 18 | 13.8 | −1160 | −1160.2 | −1156.2 | −264 | −263.8 | −250.6 | |||
| −95 | −95 | −94.6 | −499 | −499.1 | −497.3 | −166 | −165.9 | −162.2 | |||
| −190 | −190 | −190.2 | 278 | 278.0 | 277.6 | −139 | −139 | −139.0 | |||
| 798 | 798.1 | 779.3 | −90 | −90.0 | −89.6 | 45 | 45 | 42.3 | |||
| 93 | 93 | 92.3 | 556 | 555.9 | 554.3 | −278 | −277.9 | −270.0 | |||
| 93 | 93 | 86.1 | 278 | 277.8 | 271.7 | −139 | −138.8 | −87.8 | |||
| −4 | −3.9 | −3.6 | 13 | 13 | 17.5 | ||||||
| 1190 | 1189.0 | 1213.1 | −489 | −488.2 | −476.2 | ||||||
| −4 | −4.0 | −3.6 | 3 | 3 | 1.6 | ||||||
| −8 | −8.0 | −8.6 | 6 | 6 | 8.0 | ||||||
| −4 | −4.0 | −2.7 | 3 | 3 | −0.4 |
| X | PMM | AE-MSVR | Y | PMM | AE-MSVR | N | PMM | AE-MSVR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −184 | −183.96 | −1160 | −1159.95 | −264 | −264.04 | |||
| −110 | −108.55 | −499 | −498.97 | −166 | −166.02 | |||
| −215 | −202.21 | −8078 | −8080.85 | 1636 | 1644.69 | |||
| −899 | −898.95 | 15,356 | 15,352.17 | −5483 | −5477.4 | |||
| 18 | 18 | −1160 | −1160.59 | −264 | −263.31 | |||
| −95 | −94.99 | −499 | −499.48 | −166 | −165.58 | |||
| −190 | −189.86 | 278 | 278.01 | −139 | −139.01 | |||
| 798 | 798.02 | −90 | −90 | 45 | 45.04 | |||
| 93 | 93 | 556 | 555.46 | −278 | −277.66 | |||
| 93 | 93.11 | 278 | 273.64 | −139 | −136.86 | |||
| −4 | −3.93 | 13 | 12.88 | |||||
| 1190 | 1186.86 | −489 | −486.02 | |||||
| −4 | −4 | 3 | 3 | |||||
| −8 | −7.97 | 6 | 5.98 | |||||
| −4 | −3.59 | 3 | 2.72 |
| MSE | CC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AE-MSVR | SVR | AE-MSVR | SVR | ||
| 20°Z | u | 4.56 × 10−11 | 6.12 × 10−5 | 0.9999 | 0.9996 |
| v | 1.05 × 10−14 | 2.13 × 10−7 | 0.9999 | 0.9990 | |
| r | 1.89 × 10−11 | 5.02 × 10−4 | 0.9999 | 0.9993 | |
| 10°Z | u | 4.16 × 10−10 | 3.29 × 10−5 | 0.9999 | 0.9992 |
| v | 6.97 × 10−14 | 2.79 × 10−7 | 0.9999 | 0.9968 | |
| r | 2.32 × 10−10 | 6.75 × 10−4 | 0.9999 | 0.9984 | |
| 35°T | u | 1.44 × 10−7 | 1.27 × 10−4 | 0.9999 | 0.9999 |
| v | 9.80 × 10−9 | 2.37 × 10−4 | 0.9999 | 0.9995 | |
| r | 5.69 × 10−9 | 3.51 × 10−4 | 0.9999 | 0.9995 | |
| Maneuvering Characteristics | Reference Value (m) | 5% | 10% | 20% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value (m) | Deviation (%) | Value (m) | Deviation (%) | Value (m) | Deviation (%) | ||
| Steady turning radius | 576 | 587 | 2.0 | 533 | −7.4 | 453 | −21.3 |
| Maximum transfer | 1028 | 1050 | 2.1 | 985 | −4.2 | 770 | −25.0 |
| Maximum advance | 710 | 715 | 0.7 | 750 | 5.6 | 661 | −6.8 |
| Transfer at 90 (deg) heading | 385 | 399 | 3.6 | 373 | −3.1 | 283 | −26.6 |
| Advance at 90 (deg) heading | 705 | 710 | 0.8 | 745 | 5.7 | 659 | −6.5 |
| Tactical diameter at 180 (deg) heading | 1023 | 1045 | 2.2 | 980 | −4.1 | 768 | −24.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wen, X.; Peng, J.; Dong, F.; Zhou, R.; Ye, J. Identification Modeling of Ship Maneuvering Motion Based on AE-MSVR. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101942
Yuan Q, Liu Z, Wen X, Peng J, Dong F, Zhou R, Ye J. Identification Modeling of Ship Maneuvering Motion Based on AE-MSVR. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101942
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Qiang, Zhihong Liu, Xiaofei Wen, Jinzhi Peng, Fei Dong, Ruiping Zhou, and Jun Ye. 2025. "Identification Modeling of Ship Maneuvering Motion Based on AE-MSVR" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101942
APA StyleYuan, Q., Liu, Z., Wen, X., Peng, J., Dong, F., Zhou, R., & Ye, J. (2025). Identification Modeling of Ship Maneuvering Motion Based on AE-MSVR. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1942. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101942






