Minimum Hydrogen Consumption Energy Management for Hybrid Fuel Cell Ships Using Improved Weighted Antlion Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- An energy management strategy based on IW-ALO is proposed to minimize equivalent hydrogen consumption, enhance ship operation economy, and reduce battery degradation.
- (2)
- The IW-ALO algorithm dynamically determines the optimal equivalence factor according to real-time operating conditions, enabling IW-ECMS to achieve globally optimal power distribution.
- (3)
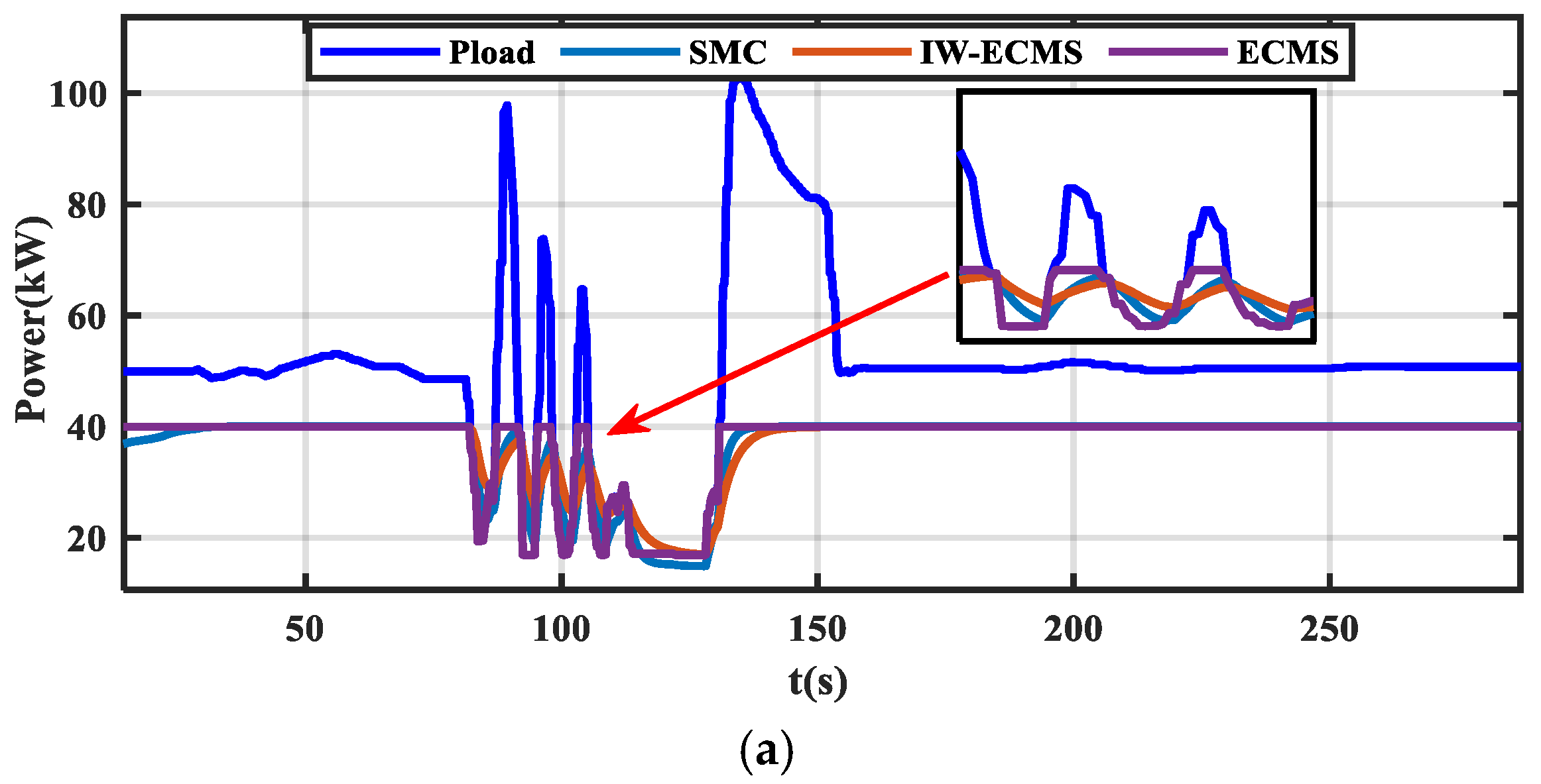
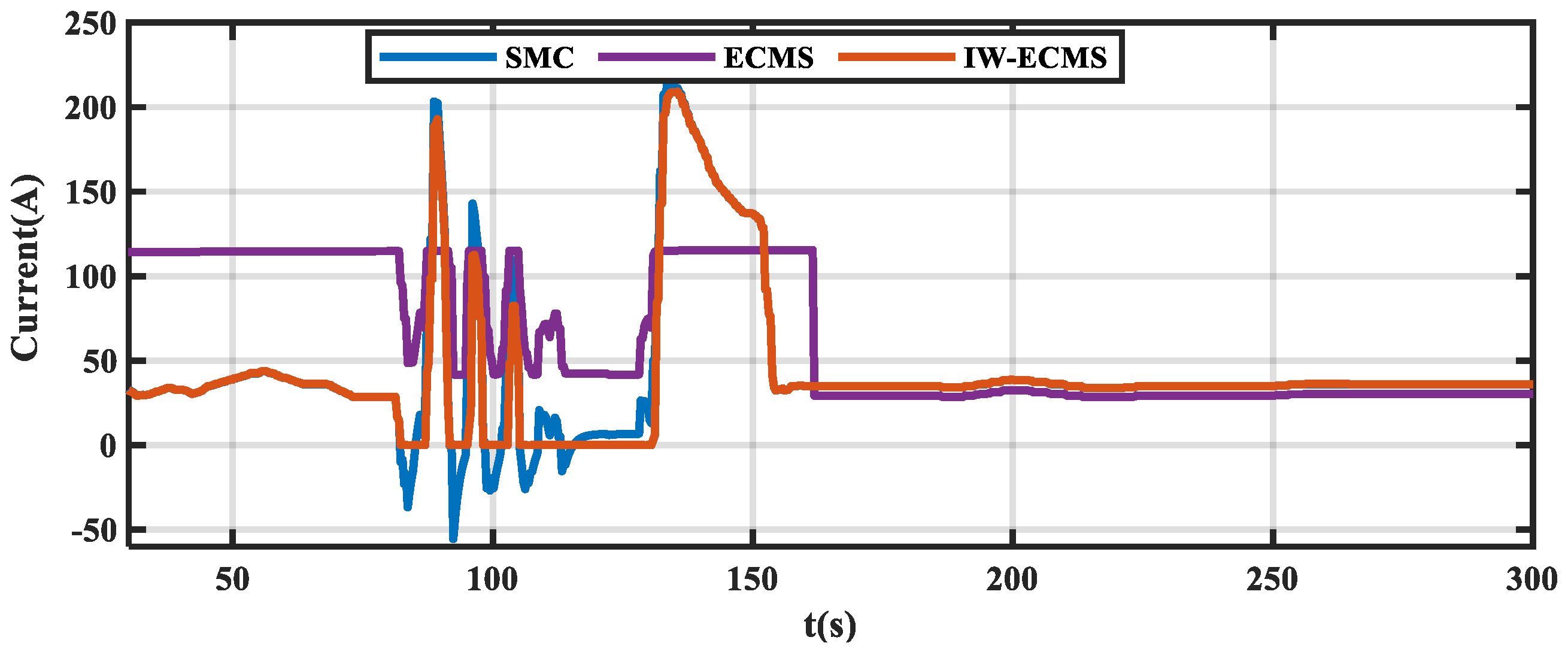
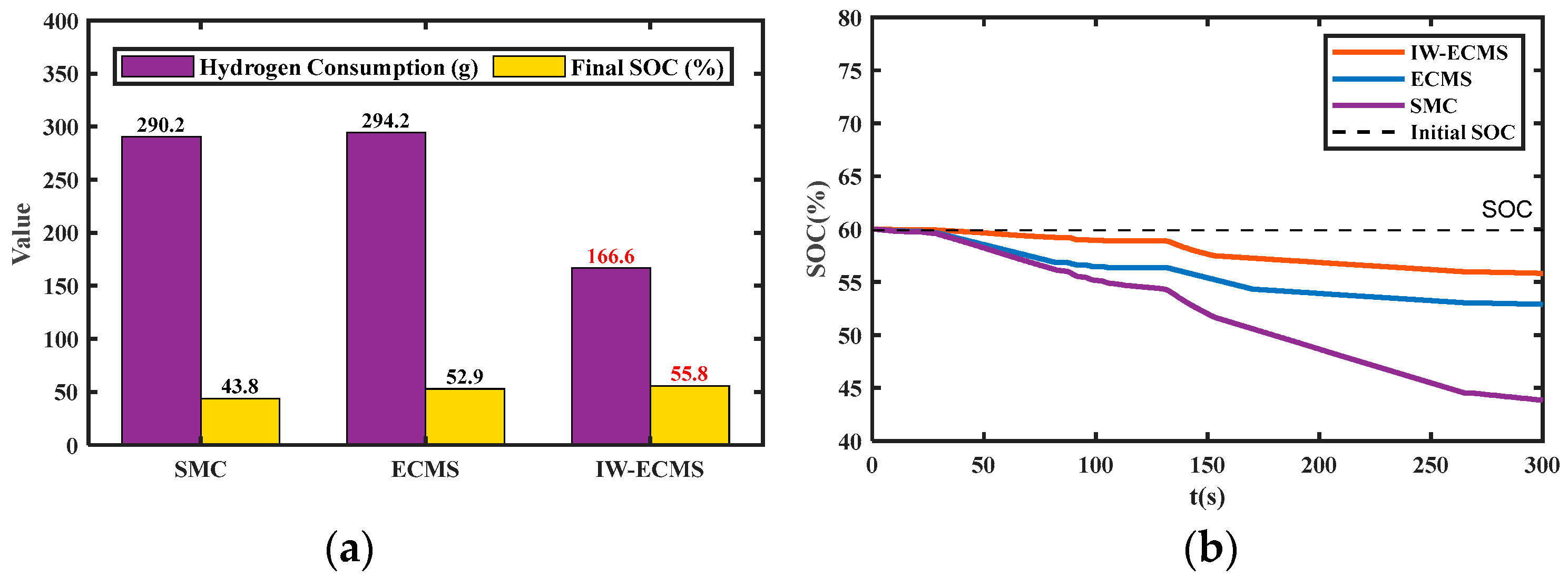
- Compared with rule-based SMC and conventional ECMS strategies, IW-ECMS effectively smooths battery power fluctuations and reduces hydrogen consumption by 42.6% and 43.4%, respectively.
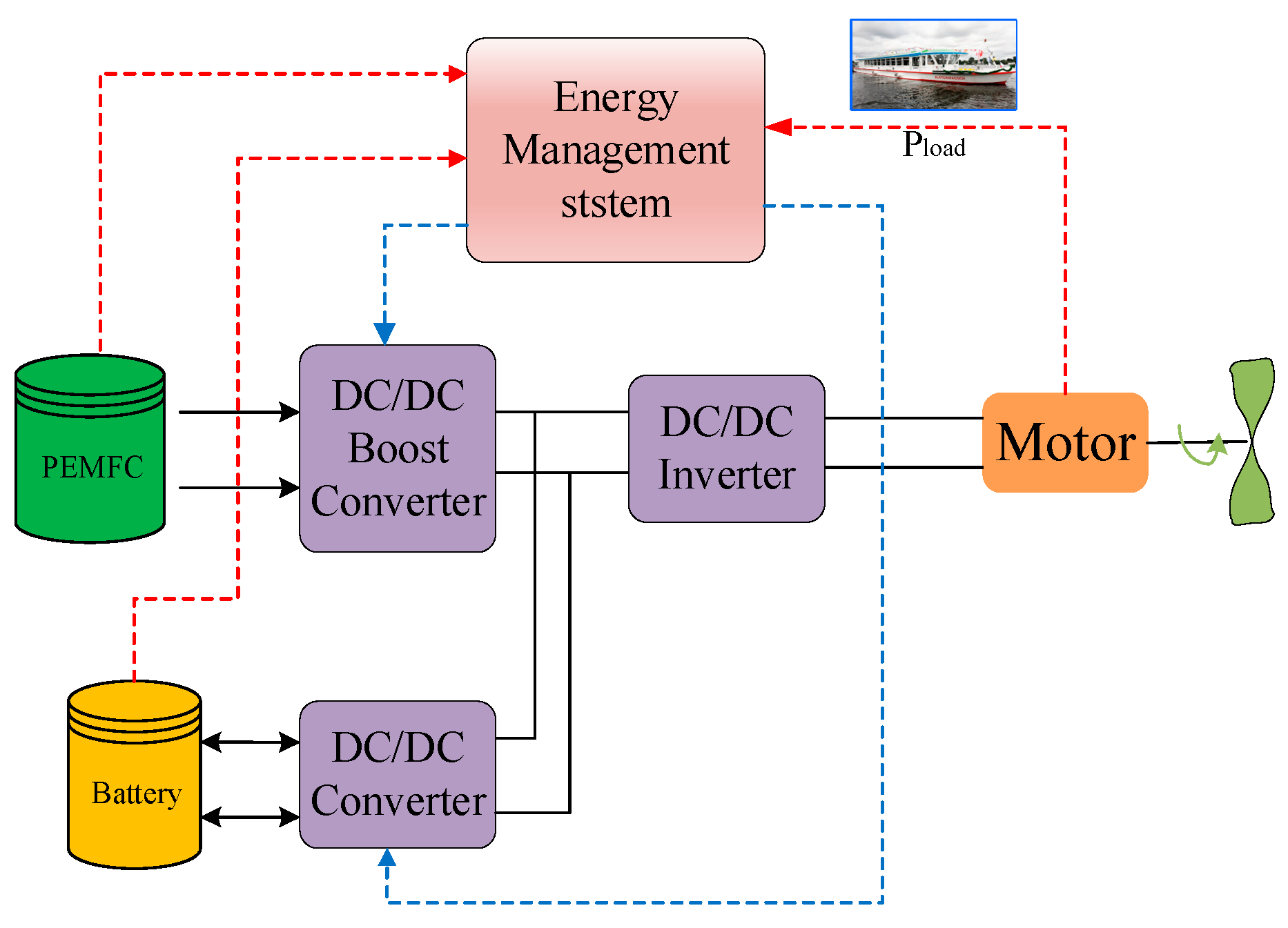
2. Hybrid Energy Storage System Modeling
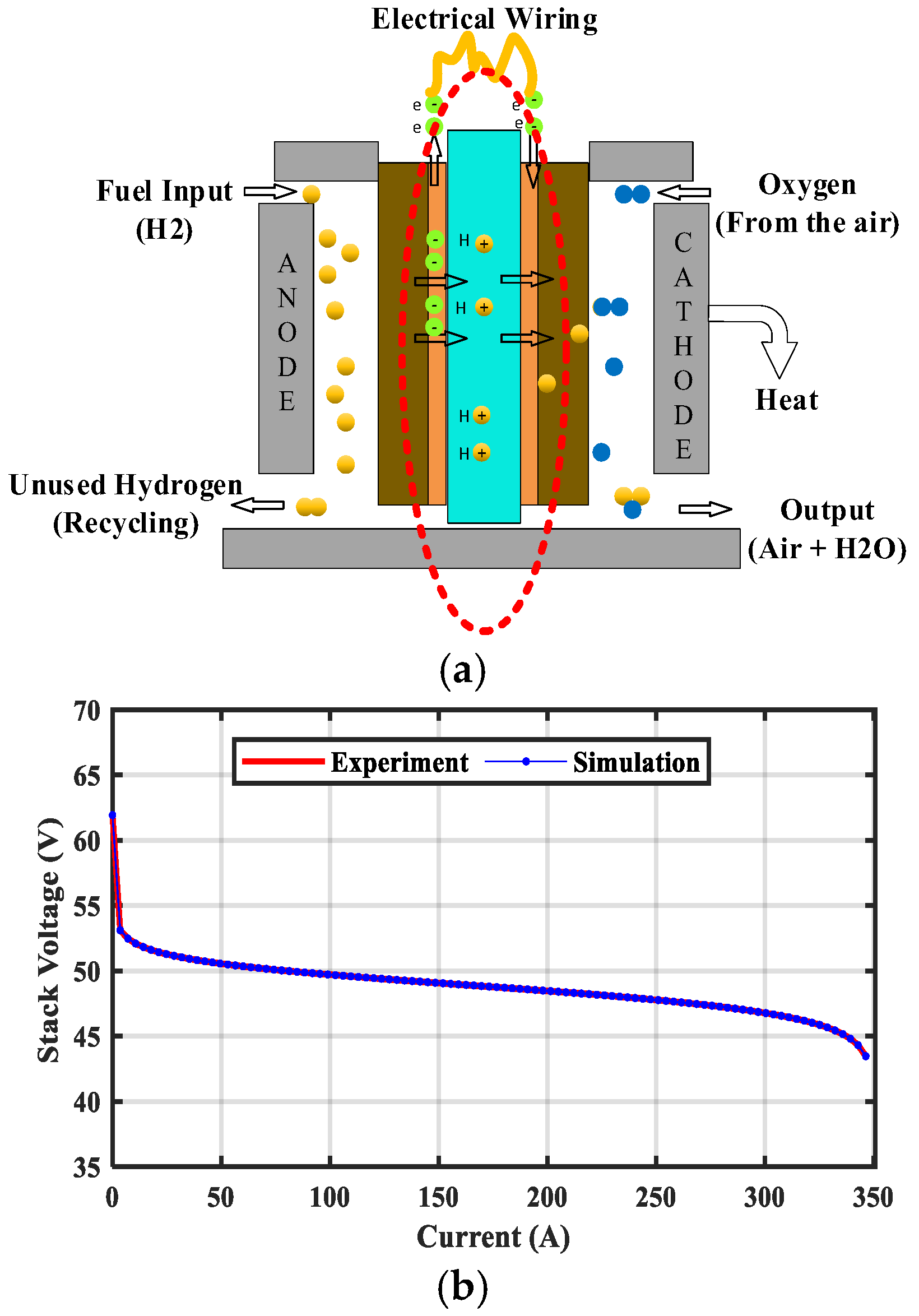
2.1. Fuel Cell Model
2.2. Battery Model
2.3. DC/DC Converter Model
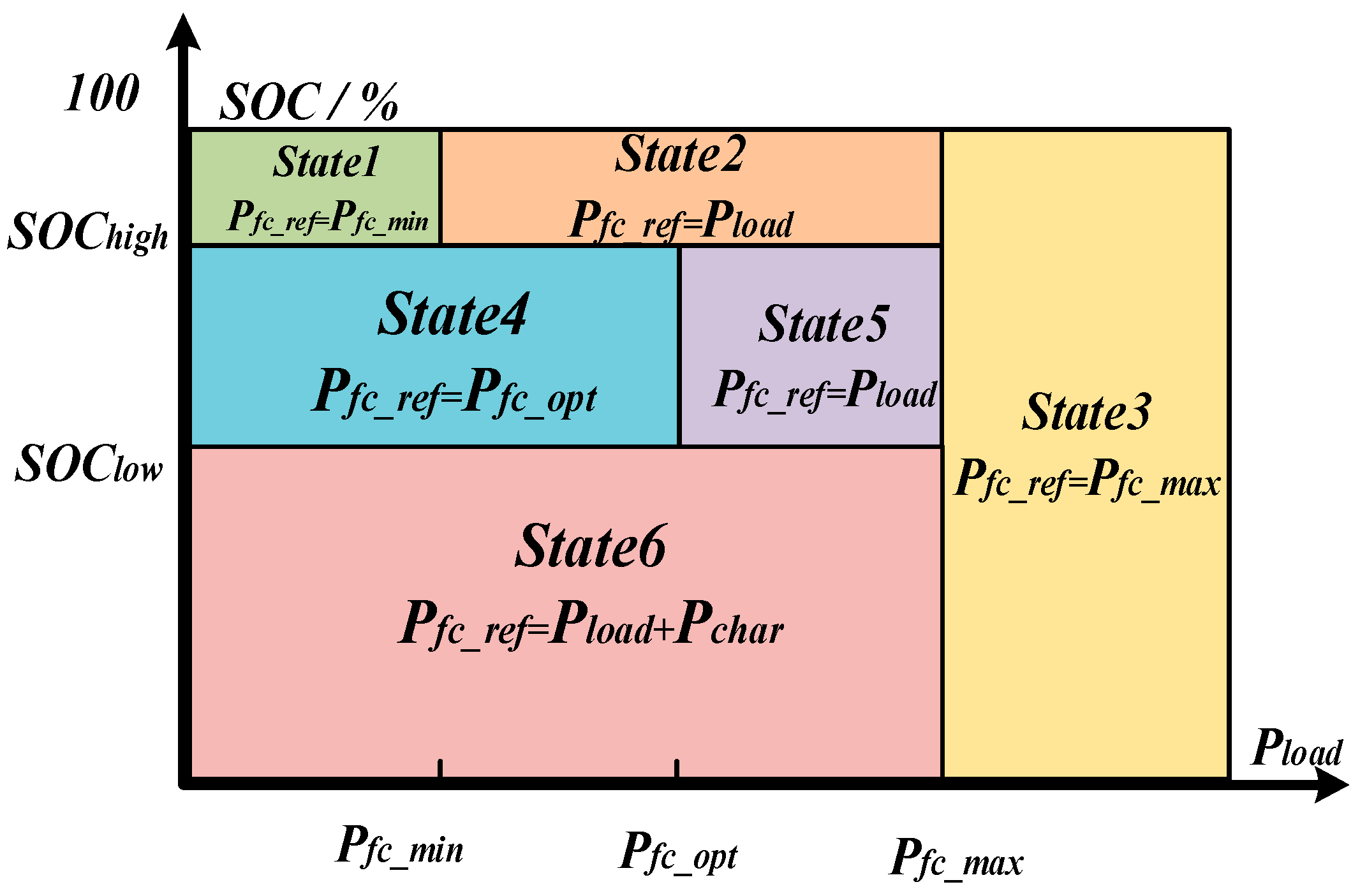
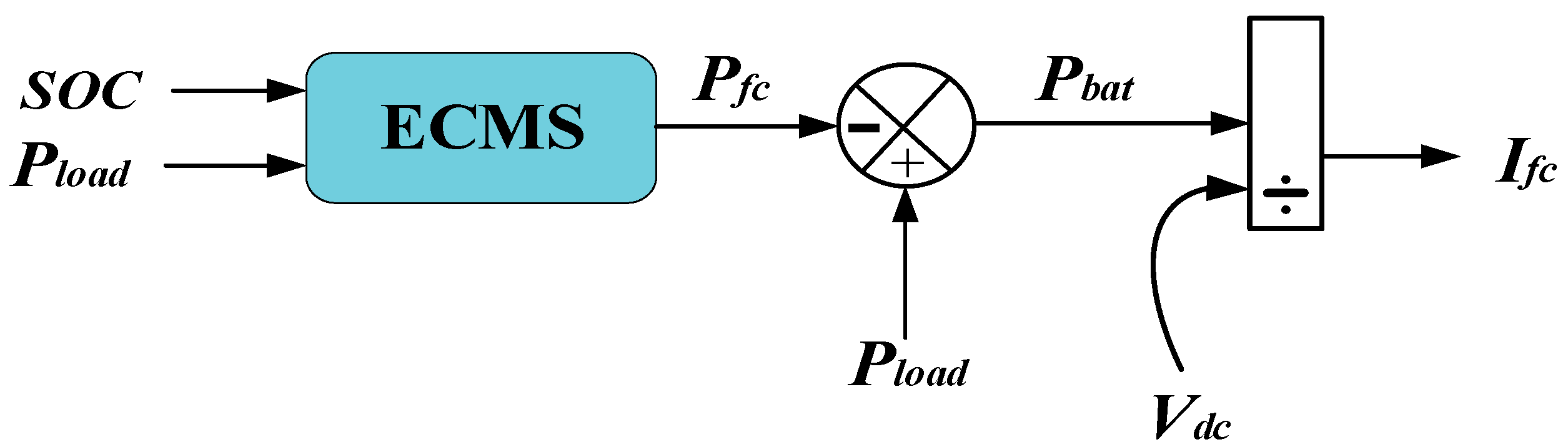
3. Energy Management Strategy
3.1. Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy
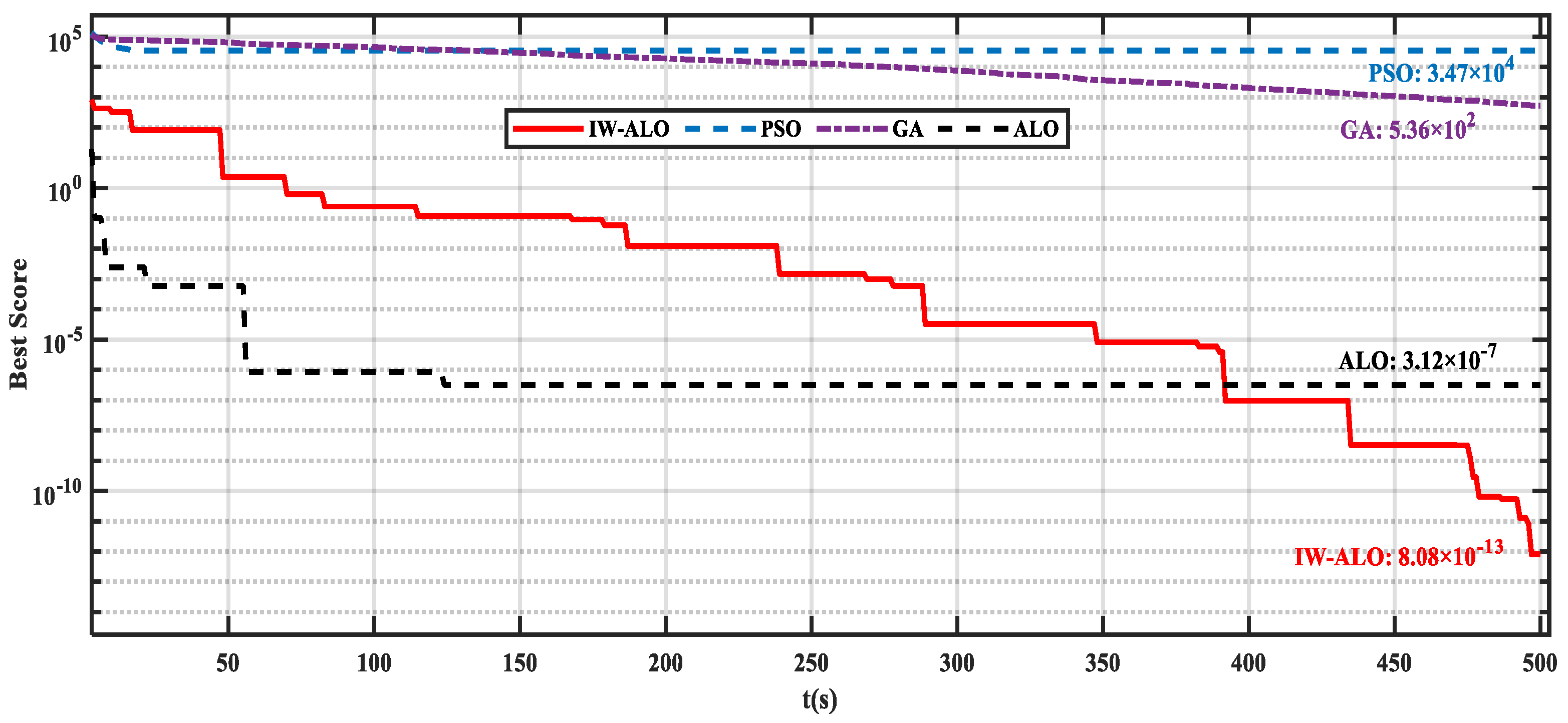
3.2. Improved Weighted Antlion Optimization Algorithm
- (1)
- Population Initialization
- (2)
- Population Iterative Update
- (3)
- Conclude the iterations and return the optimal solution
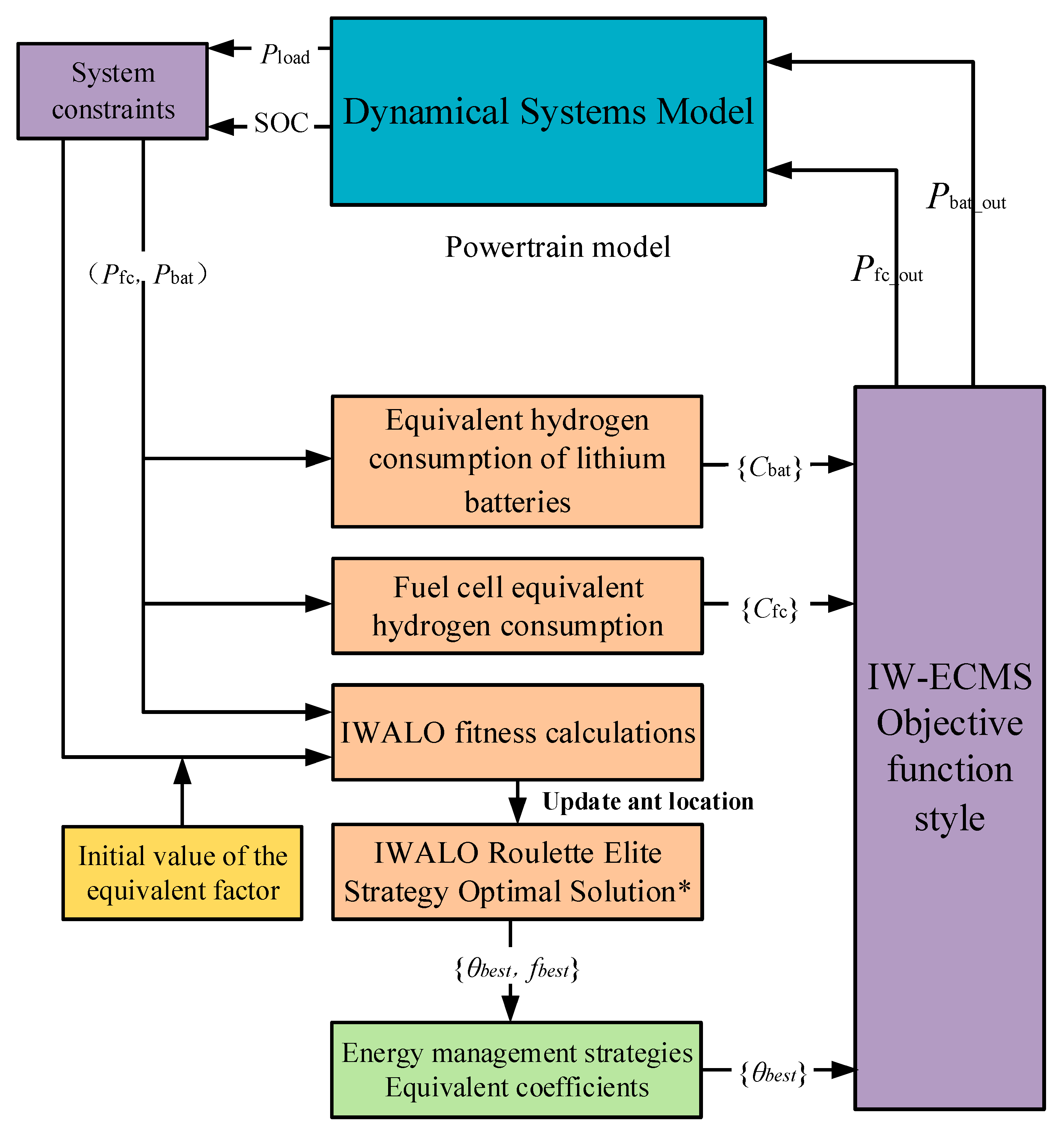
3.3. The Proposed Energy Management Strategy Based on IW-ECMS
4. Simulation and Results Analysis
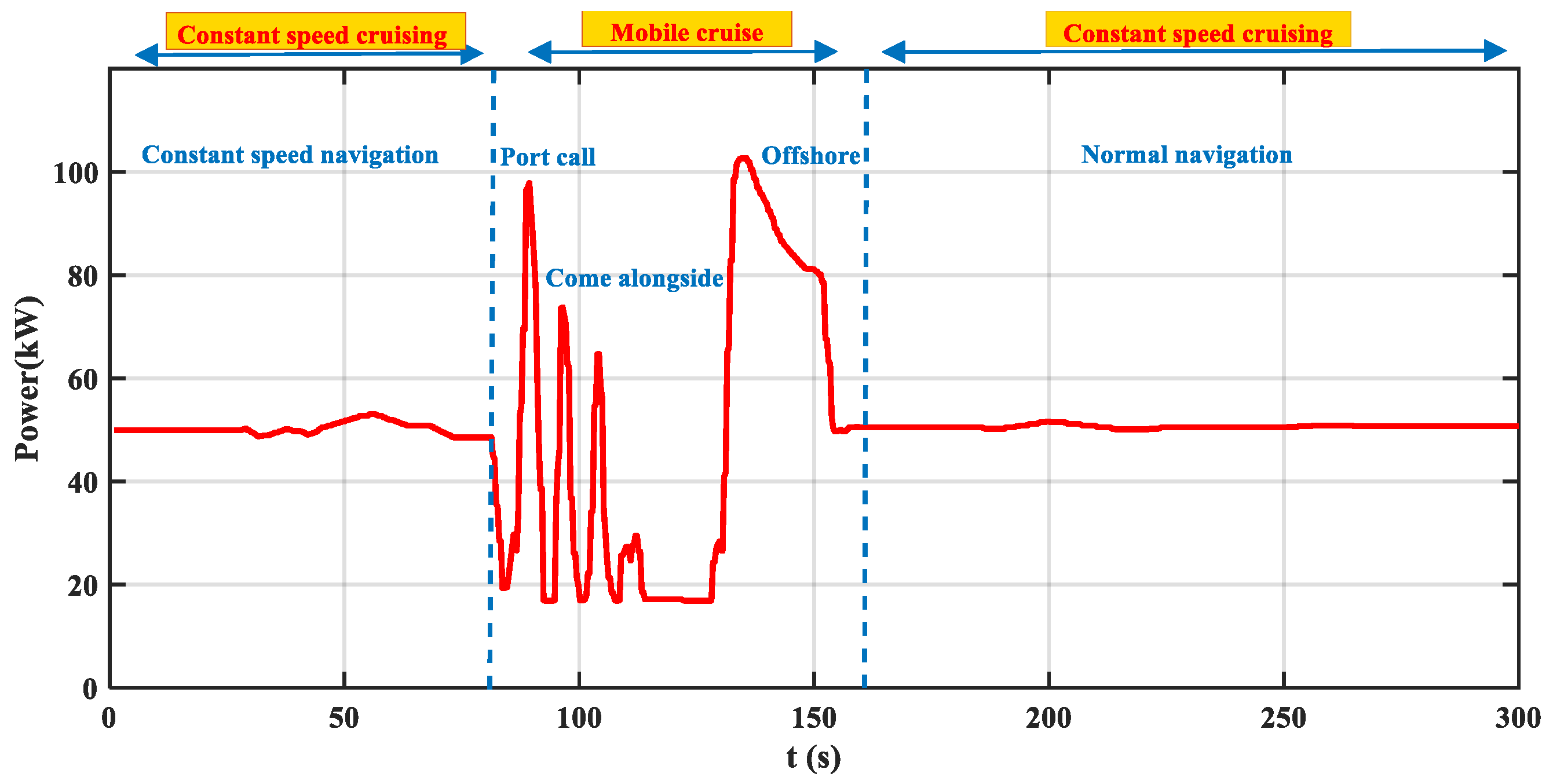
4.1. Simulation Setup
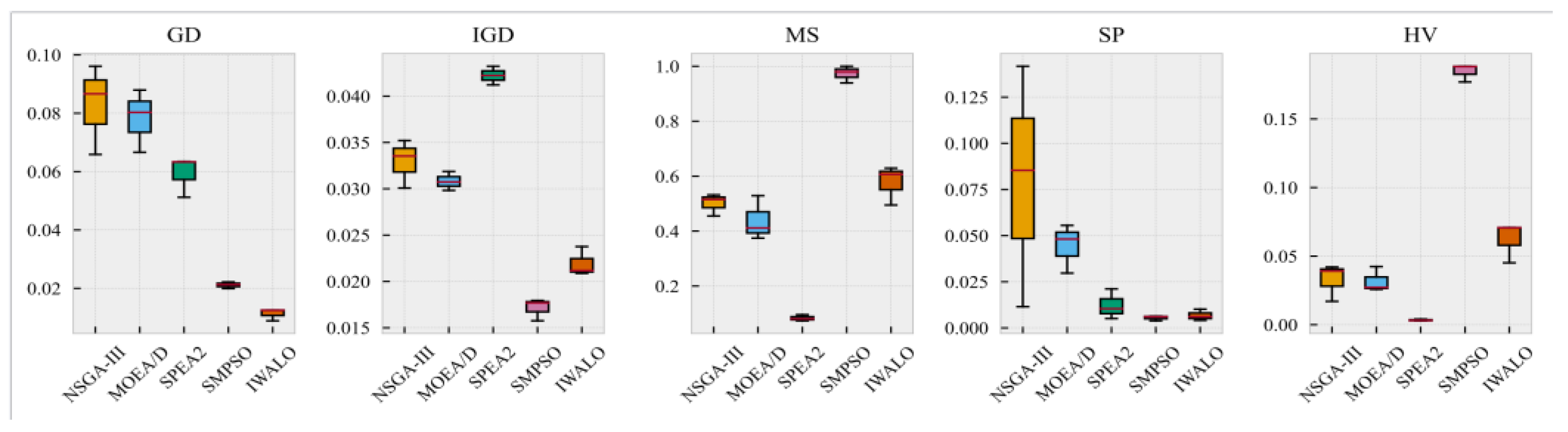
4.2. Comparative Simulation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, H.; Xue, W.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y. Bibliometric analysis for ocean renewable energy: An comprehensive review for hotspots, frontiers, and emerging trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Lang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Tong, L.; Shen, B.; Long, T.; Mao, W. Energy management system for hybrid ship: Status and perspectives. Ocean Eng. 2024, 310, 118638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edrington, C.S.; Ozkan, G.; Papari, B.; Gonsoulin, D.E.; Perkins, D.; Vu, T.V.; Vahedi, H. Distributed energy management for ship power systems with distributed energy storage. J. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2020, 19 (Suppl. S1), 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bassam, A.M.; Phillips, A.B.; Turnock, S.R.; Wilson, P.A. Development of a multi-scheme energy management strategy for a hybrid fuel cell driven passenger ship. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Chen, H.; Han, J.; Chen, Y.; Kuang, J.; Charpentier, J.-F.; Aϊt-Ahmed, N.; Benbouzid, M. Optimal SOC Control and Rule-Based Energy Management Strategy for Fuel-Cell-Based Hybrid Vessel including Batteries and Supercapacitors. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, K.; Liang, J. A reinforcement learning-based energy management strategy for fuel cell hybrid vehicle considering real-time velocity prediction. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 274, 116453. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Meng, X.; Gao, F.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W. Approximate Cost-Optimal Energy Management of Hydrogen Electric Multiple Unit Trains Using Double Q-Learning Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 9099–9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, G.; Delprat, S.; Guerra, T.M.; Rimaux, J.; Santin, J.J. Equivalent consumption minimization strategy for parallel hybrid powertrains. In Proceedings of the IEEE 55th Vehicular Technology Conference, Birmingham, AL, USA, 6–9 May 2002; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, L. Bi-level optimal sizing and energy management of hybrid electric propulsion systems. Appl. Energy 2020, 260, 114134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, K.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y. Research on Energy Management for Ship Hybrid Power System Based on Adaptive Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Yang, X. An ECMS for Multi-Objective Energy Management Strategy of Parallel Diesel Electric Hybrid Ship Based on Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm. Energies 2021, 14, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, P.; Torreglosa, J.; Fernández, L.; Jurado, F. Viability study of a FC-battery-SC tramway controlled by equivalent consumption minimization strategy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 9368–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Tan, S.; Guerrero, J.M.; Vasquez, J.C. MPC-informed ECMS based real-time power management strategy for hybrid electric ship. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, J. Optimal Energy Control of Battery Hybrid System for Marine Vessels by Applying Neural Network Based on Equivalent Consumption Minimization Strategy. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, D.; Zhao, K.; Wang, L.; Wang, K. State of health estimation of lithium-ion battery based on improved ant lion optimization and support vector regression. J. Energy Storage 2022, 50, 104215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, R. Application of improved ant-lion algorithm for power systems. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0311563. [Google Scholar]
- Seyedali, M. The ant lion optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2015, 83, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motapon, S.N.; Tremblay, O.; Dessaint, L.A. Development of a generic fuel cell model: Application to a fuel cell vehicle simulation. Int. J. Power Electron. 2012, 4, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Xing, L.; Liang, C.; Tu, Z. Modeling and dynamic characteristic simulation of air-cooled proton exchange membrane fuel cell stack for unmanned aerial vehicle. Renew. Energy 2022, 188, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, O.; Dessaint, L.-A. Experimental Validation of a Battery Dynamic Model for EV Applications. World Electr. Veh. J. 2009, 3, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motapon, S.N.; Dessaint, L.A.; Al-Haddad, K. A comparative study of energy management schemes for a fuel-cell hybrid emergency power system of more-electric aircraft. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 1320–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, C.; Hao, D.; Zhu, Z.; Ran, H.; Cao, D. Optimization-oriented adaptive equivalent consumption minimization strategy based on short-term demand power prediction for fuel cell hybrid vehicle. Energy 2021, 227, 120305. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ravey, A.; Péra, M.-C. Real-time cost-minimization power-allocating strategy via model predictive control for fuel cell hybrid electric vehicles. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 229, 113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yen, G.G.; Sahoo, A.; Chang, L.; Gu, T. On the estimation of pareto front and dimensional similarity in many-objective evolutionary algorithm. Inf. Sci. 2021, 563, 375–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Movahedi, H.; Siegel, J.B.; Stefanopoulou, A.G. Empirical Modeling of degradation in lithium-ion batteries and validation in complex scenarios. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2023, 56, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Wood, E.; Santhanagopalan, S.; Kim, G.H.; Neubauer, J.; Pesaran, A. Models for Battery Reliability and Lifetime; No. NREL/CP-5400-57746; National Renewable Energy Lab. (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheraghi, R.; Jahangir, M.H. Multi-objective optimization of a hybrid renewable energy system supplying a residential building using NSGA-II and MOPSO algorithms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 294, 117515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommuri, N.K.; McGordon, A.; Allen, A.; Truong, D.Q. Evaluation of a Modified Equivalent Fuel-Consumption Minimization Strategy Considering Engine Start Frequency and Battery Parameters for a Plugin Hybrid Two-Wheeler. Energies 2020, 13, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Chen, D.; Wu, Z.; Ren, P. Nonlinear methods for evaluating and online predicting the lifetime of fuel cells. Appl. Energy. 2019, 254, 113730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, E.; Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Zou, B.; Li, H.; Wan, Y.; Wang, K.; Jiang, K. Dynamic ultrasonic response modeling and accurate state of charge estimation for lithium ion batteries under various load profiles and temperatures. Appl. Energy 2023, 355, 122210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Qiu, Y.; Xie, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Breaz, E.; Ravey, A.; Gao, F. Energy management strategy based on optimal system operation loss for a fuel cell hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 71, 2650–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
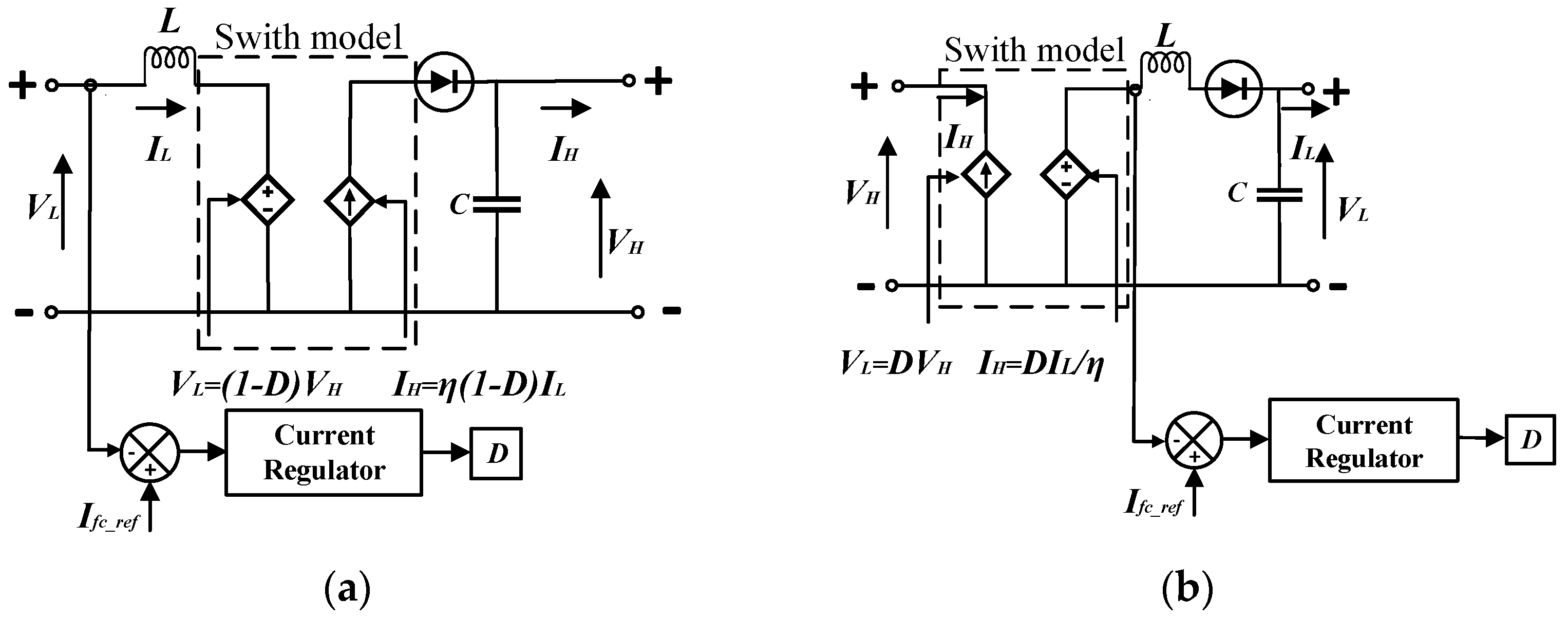




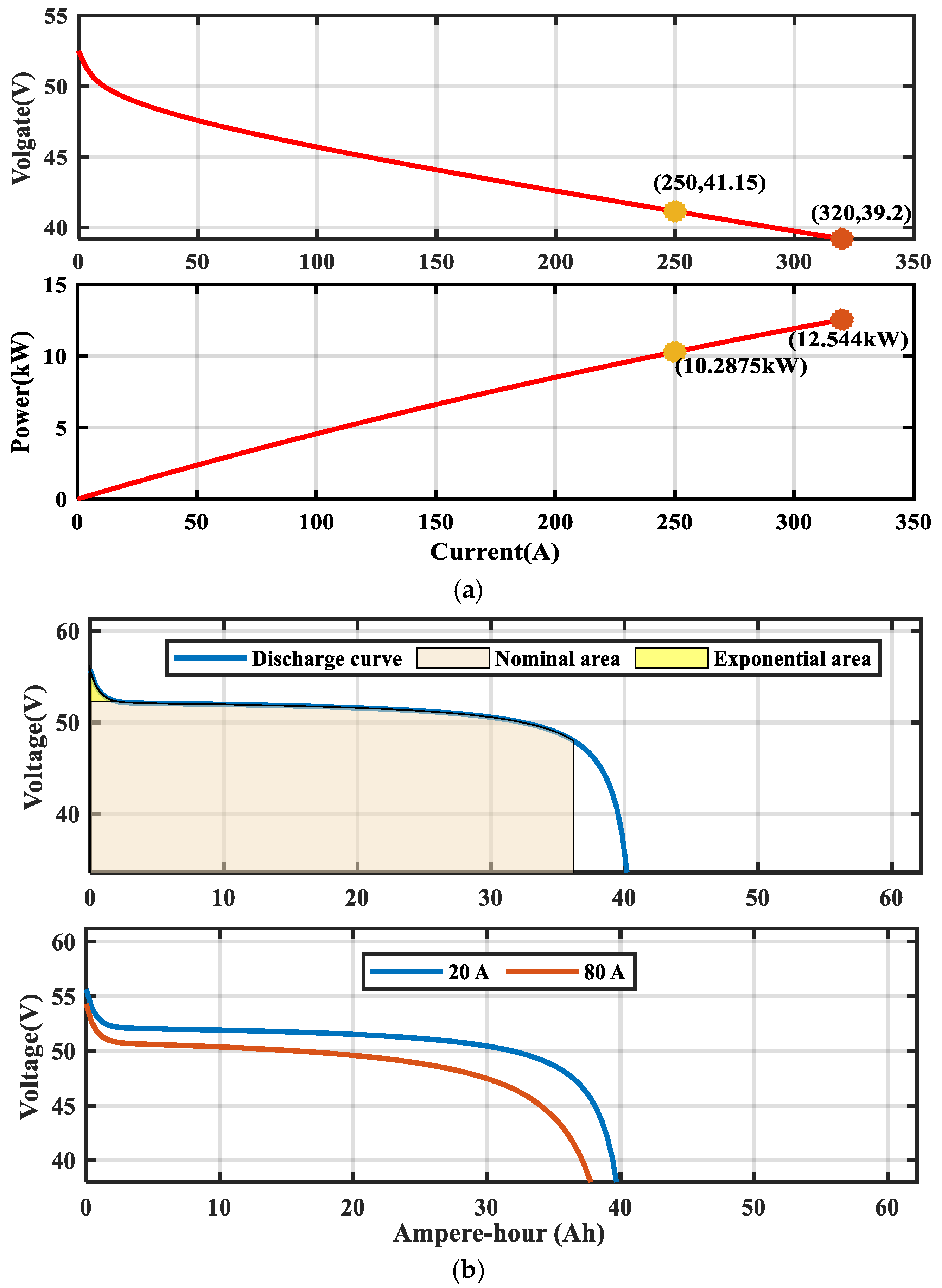

| Parameter | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel cell parameter | Output Voltage Range | 52.5–52.46 V |
| Rated Operating Point | (41.15 V, 250 A) | |
| Maximum Operating Point | (39.2 V, 320 A) | |
| Rated Fuel Cell Power | 50% | |
| Operating Temperature | 45 °C | |
| Battery parameter | Output Voltage | 48 V |
| Rated Capacity | 40 Ah | |
| Full Charge Voltage | 55.88 V | |
| Rated Discharge Current Internal Resistance Battery Voltage Response Time | 17.4 A 0.012 Ω 30 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, P.; Ning, W.; Ming, P.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, Z.; Yang, W.; Jia, B.; Xu, Y. Minimum Hydrogen Consumption Energy Management for Hybrid Fuel Cell Ships Using Improved Weighted Antlion Optimization. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101929
Zhou P, Ning W, Ming P, Liu Z, Wang X, Zhao Z, Yan Z, Yang W, Jia B, Xu Y. Minimum Hydrogen Consumption Energy Management for Hybrid Fuel Cell Ships Using Improved Weighted Antlion Optimization. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101929
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Peng, Wenfei Ning, Peiwu Ming, Zhaoting Liu, Xi Wang, Zhengwei Zhao, Zhaoying Yan, Wenjiao Yang, Baozhu Jia, and Yuanyuan Xu. 2025. "Minimum Hydrogen Consumption Energy Management for Hybrid Fuel Cell Ships Using Improved Weighted Antlion Optimization" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101929
APA StyleZhou, P., Ning, W., Ming, P., Liu, Z., Wang, X., Zhao, Z., Yan, Z., Yang, W., Jia, B., & Xu, Y. (2025). Minimum Hydrogen Consumption Energy Management for Hybrid Fuel Cell Ships Using Improved Weighted Antlion Optimization. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1929. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101929





