Mineralogical and Mechanical Characterization of Concrete Blocks for Artificial Reefs: A Comparative Study with Natural Coral Skeletons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
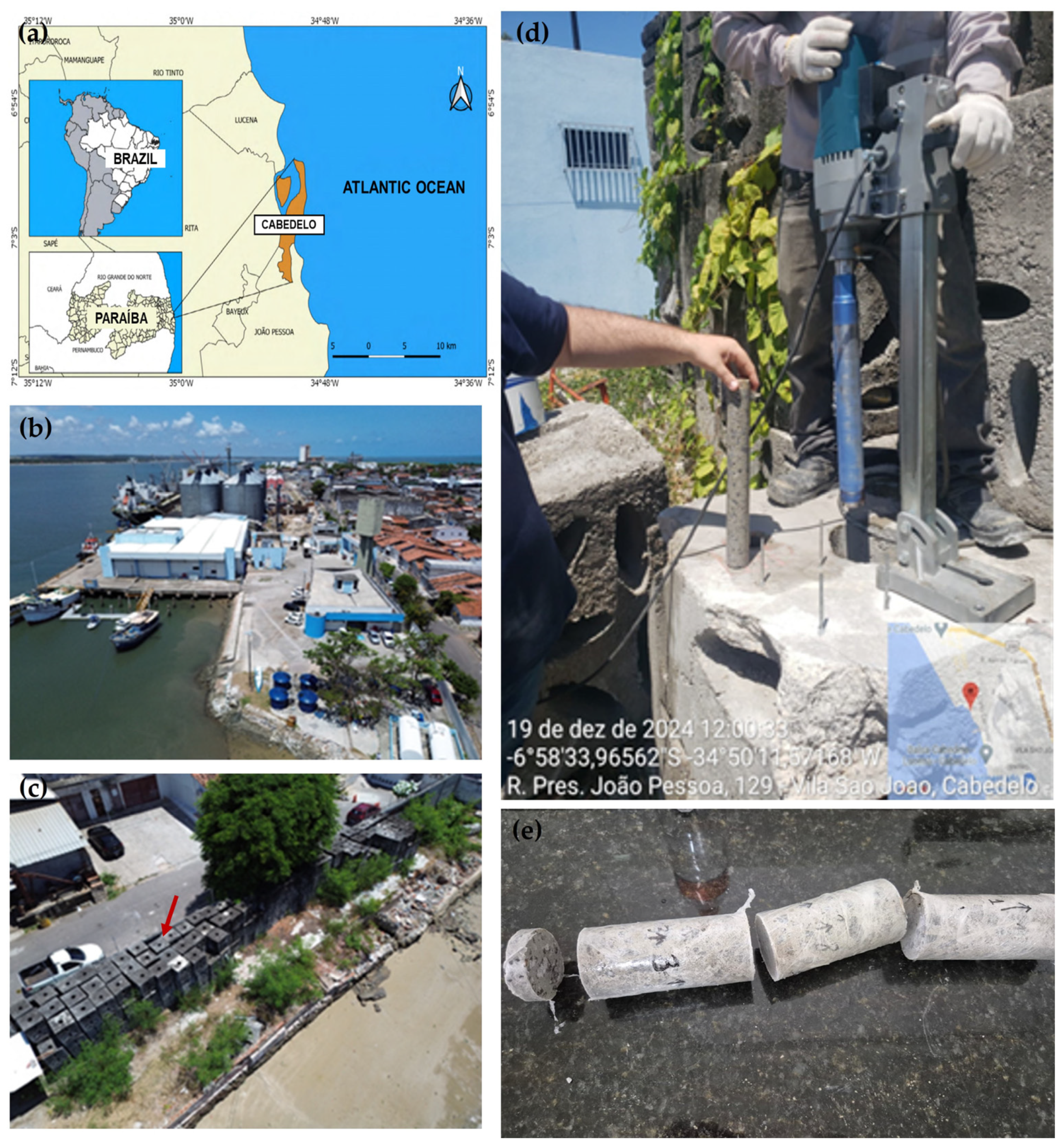

2.2. Microstructural Characterization
2.3. Physical and Mechanical Characterization
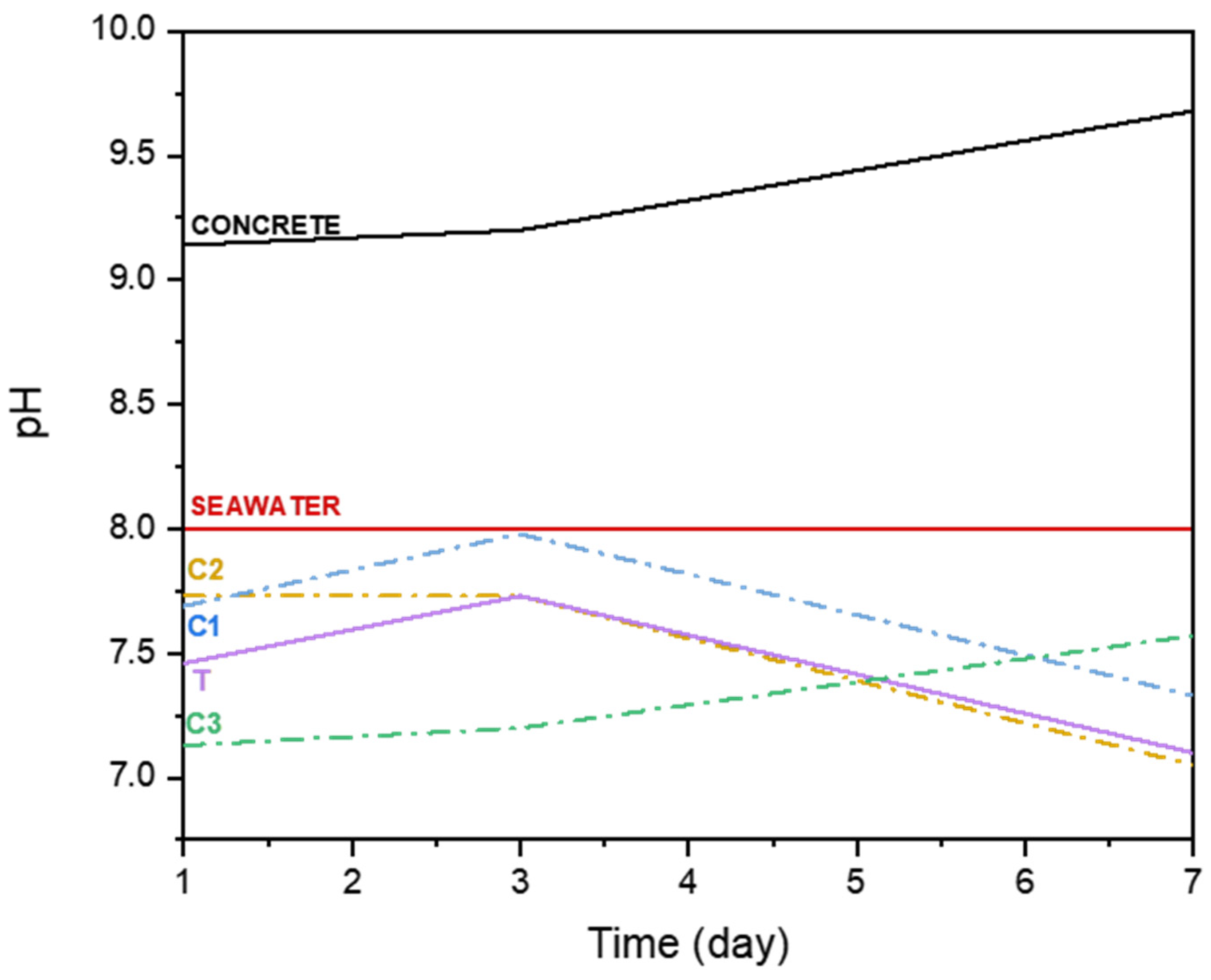
2.4. pH Test
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TG)
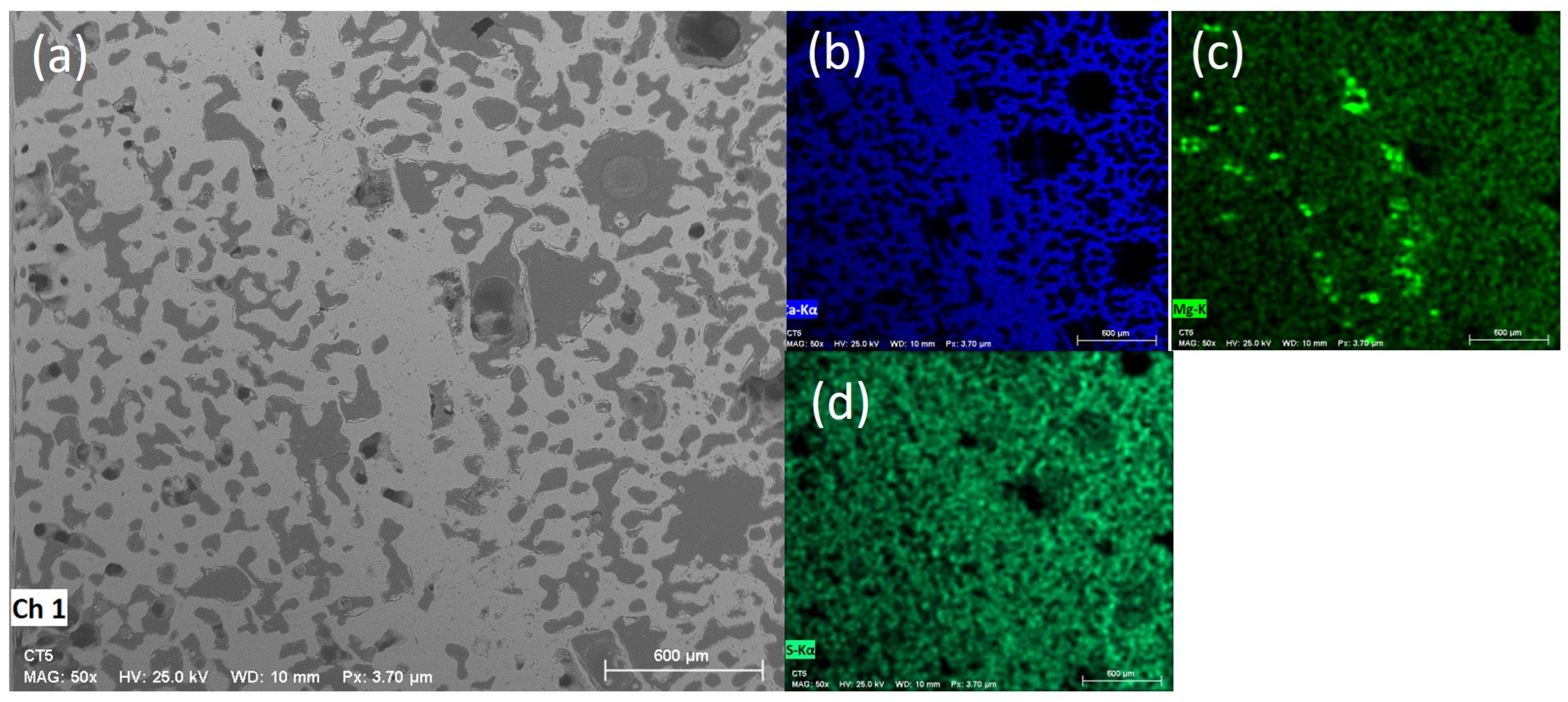
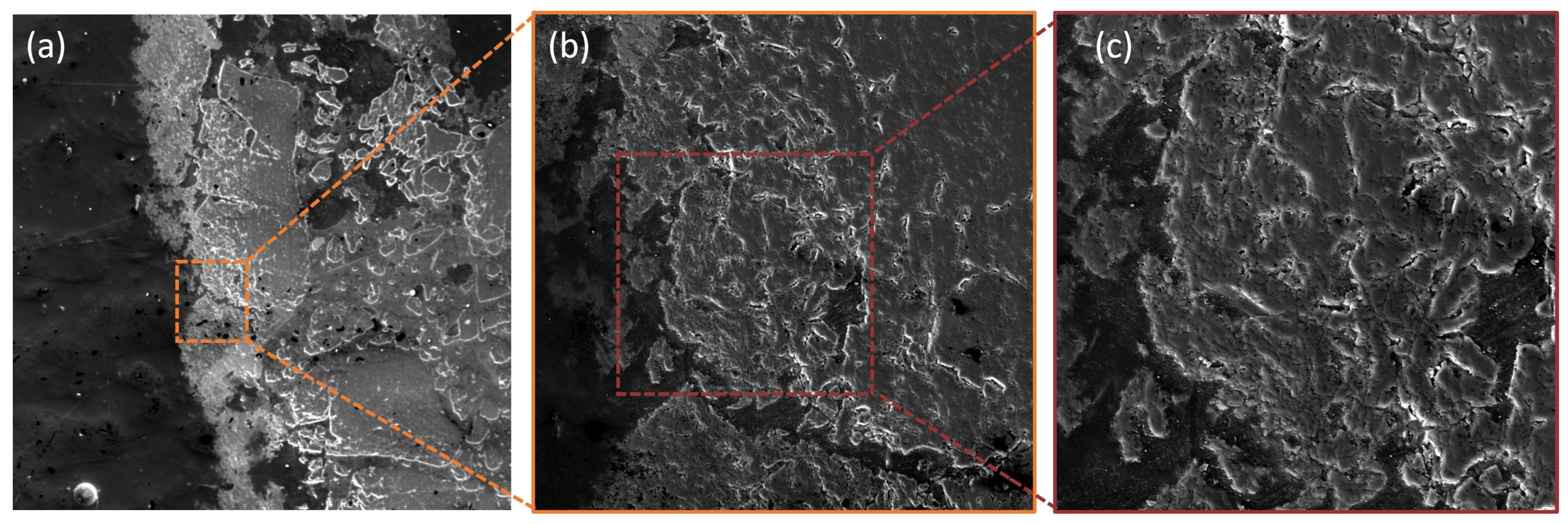
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS)
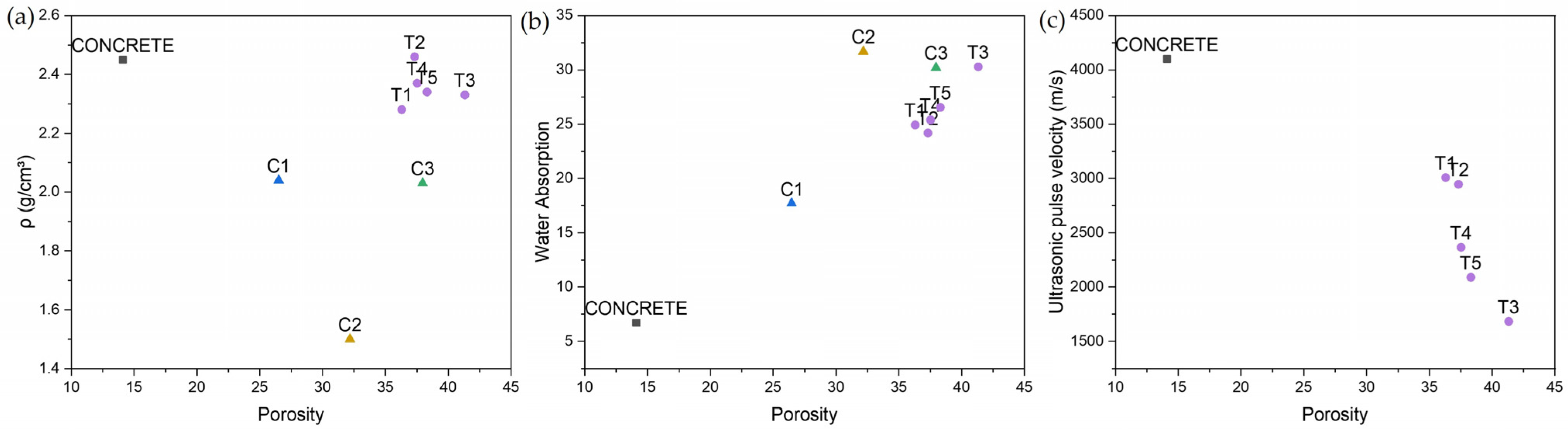
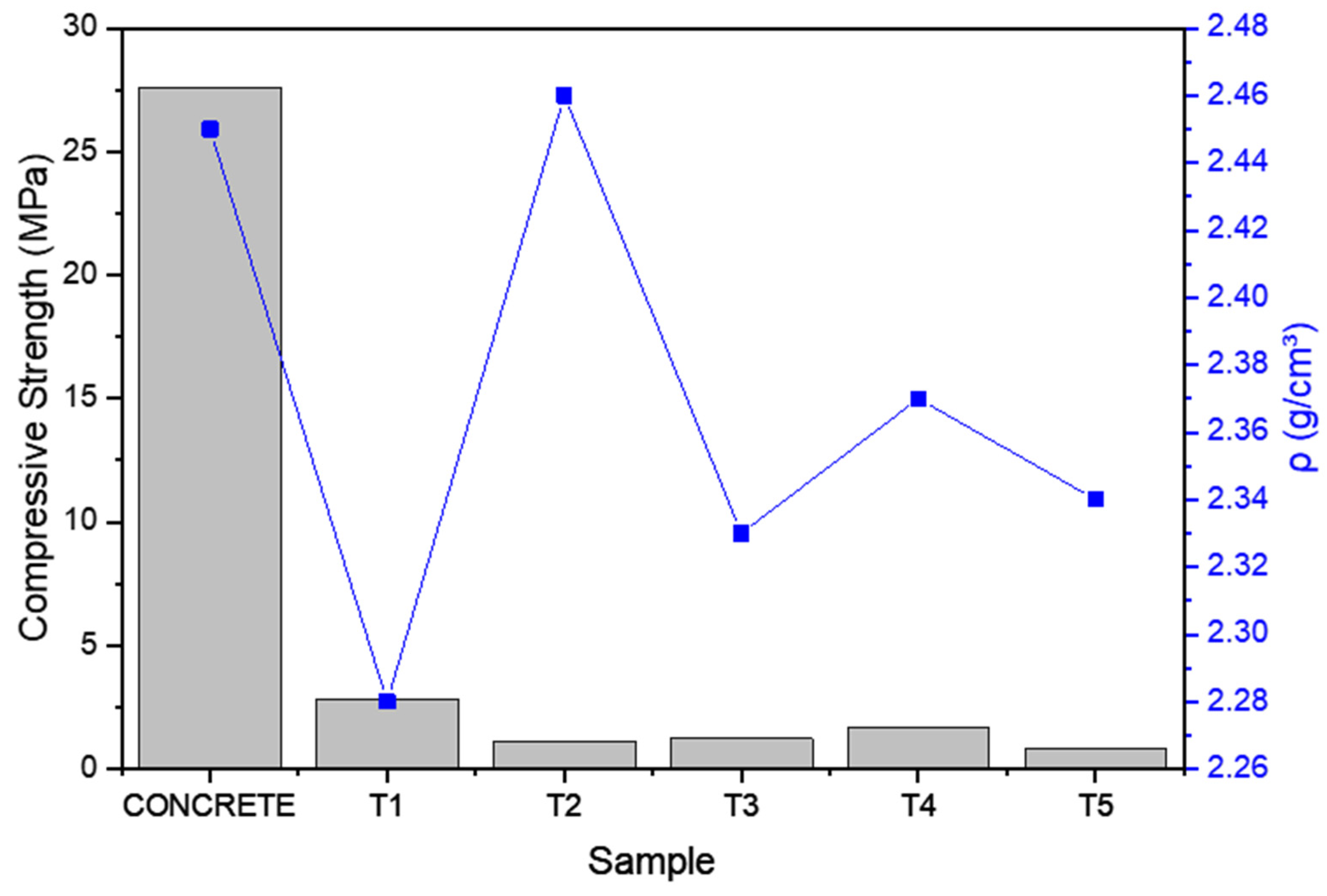
3.5. Physical and Mechanical Characterization
3.6. pH Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hughes, T.P.; Barnes, M.L.; Bellwood, D.R.; Cinner, J.E.; Cumming, G.S.; Jackson, J.B.C.; Kleypas, J.; van de Leemput, I.A.; Lough, J.M.; Morrison, T.H.; et al. Coral Reefs in the Anthropocene. Nature 2017, 546, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, M.A.; Amini, S.; Goodkin, N.F.; Tanzil, J.T.I.; Chua, J.Q.I.; Fabbro, G.N.; Fan, T.Y.; Schmidt, D.N.; Miserez, A. Environmental Impact on the Mechanical Properties of Porites Spp. Corals. Coral Reefs 2021, 40, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgoe, J.; Davy, S.K.; Weis, V.M.; Rodriguez-Lanetty, M. Triggers, Cascades, and Endpoints: Connecting the Dots of Coral Bleaching Mechanisms. Biol. Rev. 2024, 99, 715–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, T.L.P.; Gondim, A.I. Bleaching in Scleractinians, Hydrocorals, and Octocorals during Thermal Stress in a Northeastern Brazilian Reef. Mar. Biodivers. 2016, 46, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, V.M. Cell Biology of Coral Symbiosis: Foundational Study Can Inform Solutions to the Coral Reef Crisis. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2019, 59, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. A Research Review of Interventions to Increase the Persistence and Resilience of Coral Reefs; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-309-48535-7. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, O.; Weizman, M.; Oren, A.; Neri, R.; Parnas, H.; Shashar, N.; Tarazi, E. Design and Application of a Novel 3D Printing Method for Bio-Inspired Artificial Reefs. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 188, 106892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström-Einarsson, L.; Babcock, R.C.; Bayraktarov, E.; Ceccarelli, D.; Cook, N.; Ferse, S.C.A.; Hancock, B.; Harrison, P.; Hein, M.; Shaver, E.; et al. Coral Restoration—A Systematic Review of Current Methods, Successes, Failures and Future Directions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, L.; Camp, E.F.; Edmondson, J.; Edmondson, J.; Agius, T.; Hosp, R.; Coulthard, P.; Edmondson, S.; Suggett, D.J. Adoption of Coral Propagation and Out-Planting via the Tourism Industry to Advance Site Stewardship on the Northern Great Barrier Reef. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 225, 106199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoester, E.G.; Groenendijk, M.H.; Murk, A.J.; Osinga, R. Some like It Dirty: Less Frequent Nursery Cleaning Can Reduce Reef Restoration Costs with Limited Negative Effects on Coral Performance. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 201, 107209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, U. Coral Reef Rehabilitation through Transplantation of Staghorn Corals: Effects of Artificial Stabilization and Mechanical Damages. Coral Reefs 2003, 22, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbiger, N.J.; Nelson, C.E.; Remple, K.; Sevilla, J.K.; Quinlan, Z.A.; Putnam, H.M.; Fox, M.D.; Donahue, M.J. Nutrient Pollution Disrupts Key Ecosystem Functions on Coral Reefs. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxton, A.B.; Shertzer, K.W.; Bacheler, N.M.; Kellison, G.T.; Riley, K.L.; Taylor, J.C. Meta-Analysis Reveals Artificial Reefs Can Be Effective Tools for Fish Community Enhancement but Are Not One-Size-Fits-All. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 534479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matus, I.V.; Alves, J.L.; Góis, J.; Vaz-Pires, P.; Barata da Rocha, A. Artificial Reefs through Additive Manufacturing: A Review of Their Design, Purposes and Fabrication Process for Marine Restoration and Management. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2024, 30, 87–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.C.; Collins, K.J.; Lockwood, A.P.M.; Mallinson, J.J.; Turnpenny, W.H. Colonization and Fishery Potential of a Coal-Ash Artificial Reef, Poole Bay, United Kingdom. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 1263–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Vivier, B.; Dauvin, J.C.; Navon, M.; Rusig, A.M.; Mussio, I.; Orvain, F.; Boutouil, M.; Claquin, P. Marine Artificial Reefs, a Meta-Analysis of Their Design, Objectives and Effectiveness. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, H.D.; Evans, A.J.; Banner, A.J.; Moore, P.J. Reefcrete: Reducing the Environmental Footprint of Concretes for Eco-Engineering Marine Structures. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilha, R.D.A.; Henkes, J.A. A Utilização de Recifes Artificiais Marinhos Como Ferramenta de Recuperação Da Fauna Marinha. Rev. Gestão Sustentabilidade Ambient. 2012, 1, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, J.C.; Lucena, L.F.L.; Henriques, G.F.; Ferreira, R.L.S.; dos Anjos, M.A.S. Use of Banana Leaf Ash as Partial Replacement of Portland Cement in Eco-Friendly Concretes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 346, 128467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayek, M.; Salgues, M.; Souche, J.-C.; Cunge, E.; Giraudel, C.; Paireau, O. Influence of the Intrinsic Characteristics of Cementitious Materials on Biofouling in the Marine Environment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wai, O.W.H.; Xie, J.; Li, X. Biomineralization To Prevent Microbially Induced Corrosion on Concrete for Sustainable Marine Infrastructure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ji, T.; Yang, Z.; Ye, Y. Preliminary Investigation of Artificial Reef Concrete with Sulphoaluminate Cement, Marine Sand and Sea Water. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupasinghe, M.; Nicolas, R.S.; Lanham, B.S.; Morris, R.L. Sustainable Oyster Shell Incorporated Artificial Reef Concrete for Living Shorelines. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 410, 134217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhang, P. Effects of Carbonation Curing Regimes on Alkalinity of Self-Compacting Concretes for Marine Artificial Reef. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesemann, C.A.; Antoun, M.; Teune, I.; Schollbach, K.; Rippen, J.; Hylkema, A.; Oosterhoff, B.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Effect of Carbonation on Eco-Friendly Binders for Marine Infrastructures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 477, 141293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, S.; Peng, L.; Wang, N.; Meng, T.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, F. Preliminary Investigation and Life Cycle Assessment of Artificial Reefs with Recycled Brick-Concrete Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 432, 136618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ou, Z.; Peng, W.; Guo, T.; Deng, W.; Chen, Y. Literature Review of Coral Concrete. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 43, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lyu, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; Sun, D. The Development of Coral Concretes and Their Upgrading Technologies: A Critical Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 1004–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, D.; Vasconcelos, E.; Riul, P.; Freitas, N.; Miranda, G. Dataset of Macrobenthic Species in Urban Coastal Reef Environments in Brazilian Northeast. Data Brief 2020, 31, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massei, K.; Souza, M.C.S.; da Silva, R.M.; Neumann, V.H.d.M.L.; Manso, V.D.A.V.; Vianna, P.C.G.; Junior, A.V.F.; da Silva Moura, C.M.; de Lavôr, L.F.; de Carvalho Araújo, R.; et al. Multi-Proxy Assessment of Coral Reef Formation and Biotic-Abiotic Diversity in an Urban Coastal Reef Ecosystem in Northeastern Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massei, K.; Souza, M.C.S.; da Silva, R.M.; Costa, D.d.A.; Vianna, P.C.G.; Crispim, M.C.; de Miranda, G.E.C.; Eggertsen, L.; Eloy, C.C.; Santos, C.A.G. Analysis of Marine Diversity and Anthropogenic Pressures on Seixas Coral Reef Ecosystem (Northeastern Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, D.S.L.; de Vasconcelos, E.R.T.P.P.; Riul, P.; de Freitas, N.D.A.; de Miranda, G.E.C. Evaluation of the Conservation Status and Monitoring Proposal for the Coastal Reefs of Paraíba, Brazil: Bioindication as an Environmental Management Tool. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 194, 105208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.H.C.; Passavante, J.Z.d.O. Recifes Artificiais Marinhos: Modelos e Utilizações No Brasil e No Mundo. Bol. Tec. Cient. CEPENE 2007, 15, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Filho, O.d.R.M.; Callou, A.B.F.; Santos, M.S.T. Políticas Públicas e Extensão Pesqueira Em Cabedelo, Paraíba. Interações Campo Gd. 2010, 11, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ABNT NBR 16697; Portland Cement—Requirements. ABNT: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2018; 12p.
- ASTM C595; Specification for Blended Hydraulic Cements. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008; 7p.
- de Lima, W.P.; Pessoa-Gutierres, H.E. Impactos Ambientais No Parque Natural Municipal de Cabedelo—Estado Do Paraíba (PB), Brasil. Rev. Geográfica América Cent. 2021, 1, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, G.F.; Tavares, J.C.; Neto, A.D.d.L.T. Carbonatação Natural e Modelos de Previsão Para Concretos de Cimento Portland: Uma Revisão. Rev. Principia—Divulg. Científica e Tecnológica do IFPB 2023, 60, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Snellings, R.; Lothenbach, B. A Practical Guide to Microstructural Analysis of Cementitious Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781498738651. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C642; Test Method for Density, Absorption, and Voids in Hardened Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021; 3p.
- ASTM C597; Test Method for Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Through Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022; 4p.
- ASTM C39; Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021; 8p.
- Wang, W.-C.; Huang, W.-H.; Lee, M.-Y.; Duong, H.T.H.; Chang, Y.-H. Standardized Procedure of Measuring the PH Value of Cement Matrix Material by Ex-Situ Leaching Method (ESL). Crystals 2021, 11, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.-Y.; Shafigh, P.; Katman, H.Y.; Ibrahim, Z. Effect of Filtering Method on the PH Measurement of Cement Mortar in Ex-Situ Leaching. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, I.; Barras, C.; de Nooijer, L.J.; Mouret, A.; Geerken, E.; Oron, S.; Reichart, G.-J. Coupled Calcium and Inorganic Carbon Uptake Suggested by Magnesium and Sulfur Incorporation in Foraminiferal Calcite. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 2115–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, S.M.; Ries, J.B.; Hardie, L.A. Low-Magnesium Calcite Produced by Coralline Algae in Seawater of Late Cretaceous Composition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15323–15326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aufort, J.; Demichelis, R. Magnesium Impurities Decide the Structure of Calcium Carbonate Hemihydrate. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 8028–8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conci, N.; Griesshaber, E.; Rivera-Vicéns, R.E.; Schmahl, W.W.; Vargas, S.; Wörheide, G. Molecular and Mineral Responses of Corals Grown under Artificial Calcite Sea Conditions. Geobiology 2024, 22, e12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.B. Review: Geological and Experimental Evidence for Secular Variation in Seawater Mg/Ca (Calcite-Aragonite Seas) and Its Effects on Marine Biological Calcification. Biogeosciences 2010, 7, 2795–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoester, E.G.; Vos, A.; Saru, C.; Murk, A.J.; Osinga, R. Concrete Evidence: Outplanted Corals for Reef Restoration Do Not Need Extended Curing of Ordinary Portland Cement. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2024, 11, 241064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, L.M.; Willerth, S.M. Evaluating the Biocompatibility of Ceramic Materials for Constructing Artificial Reefs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 10, 1292584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, J.B. Effects of Secular Variation in Seawater Mg/Ca Ratio (Calcite–Aragonite Seas) on CaCO3 Sediment Production by the Calcareous Algae Halimeda, Penicillus and Udotea—Evidence from Recent Experiments and the Geological Record. Terra Nova 2009, 21, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrmeister, U.; Soldati, A.L.; Jacob, D.E.; Häger, T.; Hofmeister, W. Raman Spectroscopy of Synthetic, Geological and Biological Vaterite: A Raman Spectroscopic Study. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Silva, P.; Kaandorp, J.; Huisman, L.; Marie, B.; Zanella-Cléon, I.; Guichard, N.; Miller, D.J.; Marin, F. The Skeletal Proteome of the Coral Acropora Millepora: The Evolution of Calcification by Co-Option and Domain Shuffling. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2099–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farfan, G.A.; Apprill, A.; Cohen, A.; DeCarlo, T.M.; Post, J.E.; Waller, R.G.; Hansel, C.M. Crystallographic and Chemical Signatures in Coral Skeletal Aragonite. Coral Reefs 2022, 41, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, M.; Tamura, K.; Kitanaka, R.; Oka, H.; Akao, K.; Ozaki, Y. Attenuated Total Reflection Infrared and Far-Infrared, and Raman Spectroscopy Studies of Minerals, Rocks, and Biogenic Minerals. Appl. Spectrosc. 2024, 78, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, F.Z.; Mihály, J.; Sajó, I.; Katona, R.; Hajba, L.; Aziz, F.A.; Mink, J. FT-Raman and FTIR Spectroscopic Characterization of Biogenic Carbonates from Philippine Venus Seashell and Porites Sp. Coral. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2008, 39, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naggi, A.; Torri, G.; Iacomini, M.; Colombo Castelli, G.; Reggi, M.; Fermani, S.; Dubinsky, Z.; Goffredo, S.; Falini, G. Structure and Function of Stony Coral Intraskeletal Polysaccharides. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 2895–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Halfar, J. First Evidence of Chitin in Calcified Coralline Algae: New Insights into the Calcification Process of Clathromorphum Compactum. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mass, T.; Putnam, H.M.; Drake, J.L.; Zelzion, E.; Gates, R.D.; Bhattacharya, D.; Falkowski, P.G. Temporal and Spatial Expression Patterns of Biomineralization Proteins during Early Development in the Stony Coral Pocillopora Damicornis. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Halfar, J.; Adey, W.H.; Nash, M.; Paulo, C.; Dittrich, M. The Role of Chitin-Rich Skeletal Organic Matrix on the Crystallization of Calcium Carbonate in the Crustose Coralline Alga Leptophytum Foecundum. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganot, P.; Loentgen, G.; Marin, F.; Plasseraud, L.; Allemand, D.; Tambutté, S. An Alternative and Effective Method for Extracting Skeletal Organic Matrix Adapted to the Red Coral Corallium Rubrum. Biol. Open 2022, 11, bio059536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falini, G.; Fermani, S.; Goffredo, S. Coral Biomineralization: A Focus on Intra-Skeletal Organic Matrix and Calcification. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 46, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.; Delattre, F.; Levacher, D. Experimental Methods to Evaluate the Carbonation Degree in Concrete—State of the Art Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylmén, R.; Jäglid, U. Carbonation of Portland Cement Studied by Diffuse Reflection Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2013, 7, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuif, J.; Dauphin, Y.; Berthet, P.; Jegoudez, J. Associated Water and Organic Compounds in Coral Skeletons: Quantitative Thermogravimetry Coupled to Infrared Absorption Spectrometry. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2004, 5, Q11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, F.; Brizi, L.; Franzellitti, S.; Mengoli, S.; Fermani, S.; Polishchuk, I.; Baraldi, N.; Ricci, F.; Palazzo, Q.; Caroselli, E.; et al. Coral Micro- and Macro-Morphological Skeletal Properties in Response to Life-Long Acclimatization at CO2 Vents in Papua New Guinea. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, P.U.P.A.; Bergmann, K.D.; Boekelheide, N.; Tambutté, S.; Mass, T.; Marin, F.; Adkins, J.F.; Erez, J.; Gilbert, B.; Knutson, V.; et al. Biomineralization: Integrating Mechanism and Evolutionary History. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambutté, S.; Holcomb, M.; Ferrier-Pagès, C.; Reynaud, S.; Tambutté, É.; Zoccola, D.; Allemand, D. Coral Biomineralization: From the Gene to the Environment. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 408, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, J.; Labady, M.; Albornoz, A.; Yunes, S. Porosities and Pore Sizes in Coralline Calcium Carbonate. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1522–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T.; Tanimizu, M.; Inoue, M.; Suzuki, A.; Iwasaki, N.; Kawahata, H. Mg Isotope Fractionation in Biogenic Carbonates of Deep-Sea Coral, Benthic Foraminifera, and Hermatypic Coral. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2755–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Meng, R.; Zhao, H.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, F.; Tucker, M.E.; Deng, J.; Yan, H. The Incorporation of Mg2+ Ions into Aragonite during Biomineralization: Implications for the Dolomitization of Aragonite. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1078430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servetto, N.; de Aranzamendi, M.C.; Bettencourt, R.; Held, C.; Abele, D.; Movilla, J.; González, G.; Bustos, D.M.; Sahade, R. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Responses of the Antarctic Coral Malacobelemnon Daytoni to Ocean Acidification. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 170, 105430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrario, F.; Suskiewicz, T.; Johnson, L.E. A Seascape Approach for Guiding Effective Habitat Enhancement: Spatially explicit modeling of kelp–grazer interactions. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2021, 9, 00013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, J.; Ramsby, B.D.; Flores, F.; Dada, T.; Antunes, E.; Abdul Wahab, M.A.; Severati, A.; Negri, A.P.; Diaz-Pulido, G. Effects of Material Type and Surface Roughness of Settlement Tiles on Macroalgal Colonisation and Early Coral Recruitment Success. Coral Reefs 2024, 43, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhiar, M.T.; Kong, S.Y.; Bai, Y.; Susilawati, S.; Zahidi, I.; Paul, S.C.; Raghunandan, M.E. Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Concrete Incorporating Silica Fume and Waste Rubber Powder. Polymers 2022, 14, 4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Abbas, Y.M.; Fares, G. Enhancing Cementitious Concrete Durability and Mechanical Properties through Silica Fume and Micro-Quartz. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; Shi, L.; Sun, D. Coral Aggregate Concrete: Numerical Description of Physical, Chemical and Morphological Properties of Coral Aggregate. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 100, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of Coral Aggregate Properties on the Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity of Concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 107935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Fang, B.; Wu, J. Effect of Diagenetic Variation on the Static and Dynamic Mechanical Behavior of Coral Reef Limestone. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 893–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A. Assessing the Effects of Supplementary Cementitious Materials on Concrete Properties: A Review. Discov. Civ. Eng. 2024, 1, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, M.; Samimi, K. Effect of Silica Fume on Self-Compacting Earth Concrete: Compressive Strength, Durability and Microstructural Studies. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 472, 140815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, J.A.; Abuel-Naga, H. Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Testing of Accelerated Carbonation Cured-Eco-Bricks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X. Progressive Failure and Fracture Characteristics of Coral Reef Limestone under Triaxial Compression. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025, 318, 110948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.S.; Huynh, T.-P. Long-Term Mechanical Properties and Durability of High-Strength Concrete Containing High-Volume Local Fly Ash as a Partial Cement Substitution. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, J.A. Mechanical Properties of Coral Skeleton: Compressive Strength and Its Adaptive Significance. Paleobiology 1978, 4, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, K.; Cox, E.; Newtson, C. Effects of Mechanical Fracturing and Experimental Trampling on Hawaiian Corals. Environ. Manag. 2003, 31, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.A.R.E.; de Godoy Fernandes, L.V.; de Souza, F.E.S.; Marotta, H.; da Costa Fernandes, F.; Mello, T.M.S.; Monteiro, N.S.C.; Rocha, A.A.; Coutinho, R.; de Almeida Fernandes, L.D.; et al. Carbonate System in the Cabo Frio Upwelling. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos e Silva, C.A.; Monteiro, N.S.C.; Cavalcante, L.M.; Junior, W.T.; Rocha Carneiro, M.E.; Soares de Souza, F.E.; Borges Garcia, C.A.; Damasceno, R.N.; de Araújo Rocha, A. Inventory of Water Masses and Carbonate System from Brazilian’s Northeast Coast: Monitoring Ocean Acidification. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, L.C.; Koch, M.; de Beer, D. Biotic Control of Surface PH and Evidence of Light-Induced H+ Pumping and Ca2+-H+ Exchange in a Tropical Crustose Coralline Alga. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Jiménez, A.F.; Palomo, A. New Cements for the 21st Century: The Pursuit of an Alternative to Portland Cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiung, A.; Tan, W.; Loke, L.; Firth, L.; Heery, E.; Ducker, J.; Clark, V.; Pek, Y.; Birch, W.; Ang, A.; et al. Little Evidence That Lowering the PH of Concrete Supports Greater Biodiversity on Tropical and Temperate Seawalls. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 656, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maboloc, E.A.; Szeto, J.H.-Y.; Yuen, K.C.-H.; Wong, S.C.-C.; Astudillo, J.C.; Cai, L.; Hao, L.; Zhang, S.; Chui, A.P.-Y.; Fang, J.K.-H. Seawater-Conditioned Cement as a Viable Substrate for Coral Larval Settlement. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2025, 88, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartanto, R.S.; Loke, L.H.L.; Heery, E.C.; Hsiung, A.R.; Goh, M.W.X.; Pek, Y.S.; Birch, W.R.; Todd, P.A. Material Type Weakly Affects Algal Colonisation but Not Macrofaunal Community in an Artificial Intertidal Habitat. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 176, 106514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghahari, S.A.; Ramezanianpour, A.M.; Ramezanianpour, A.A.; Esmaeili, M. An Accelerated Test Method of Simultaneous Carbonation and Chloride Ion Ingress: Durability of Silica Fume Concrete in Severe Environments. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1650979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
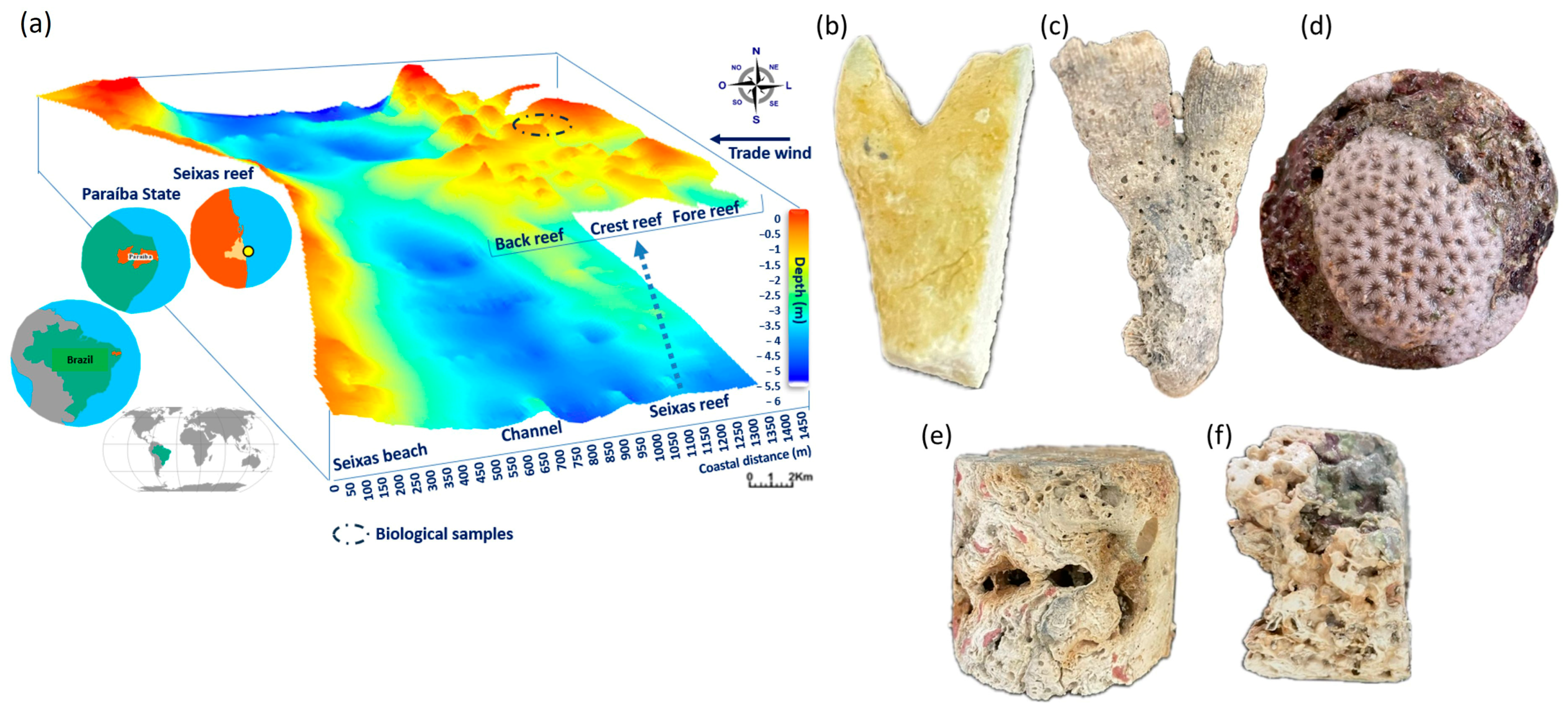
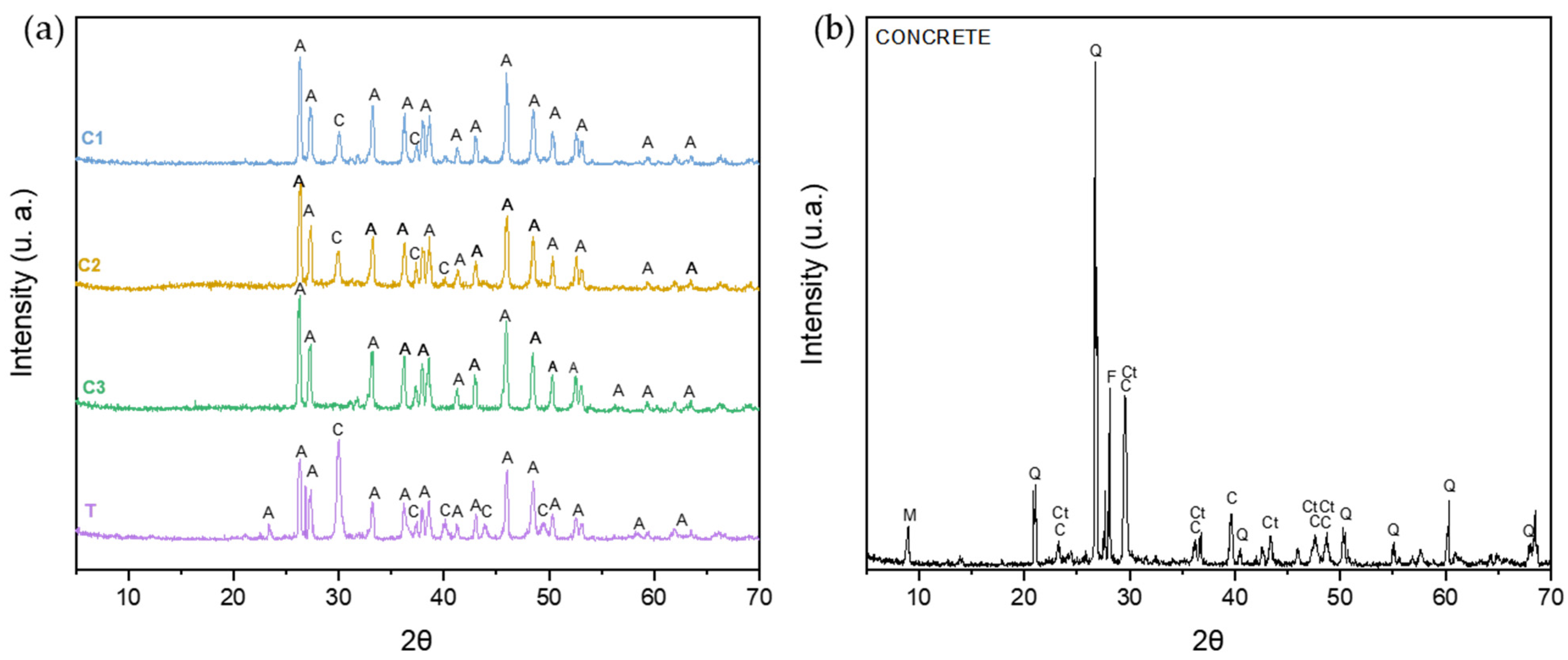
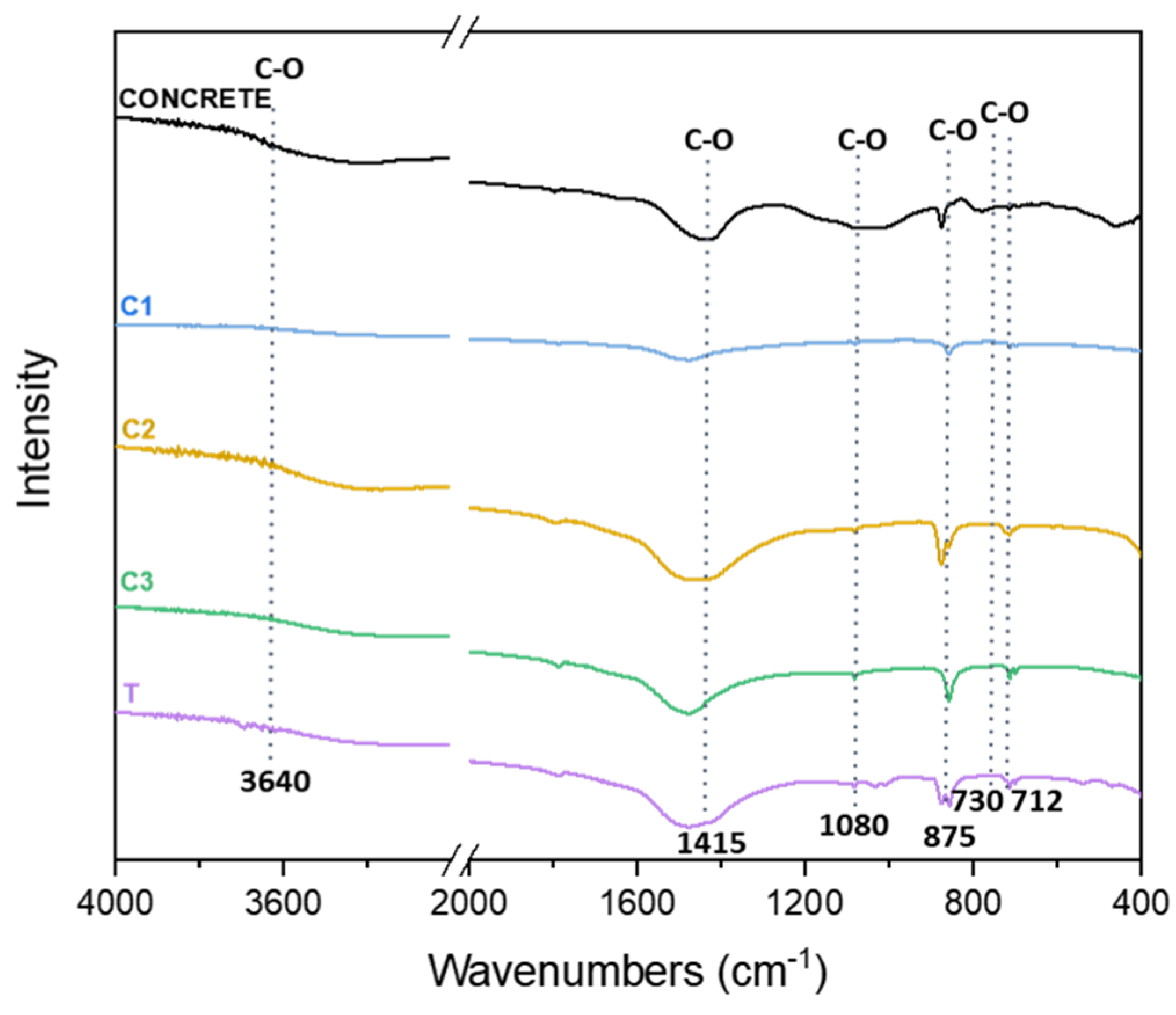
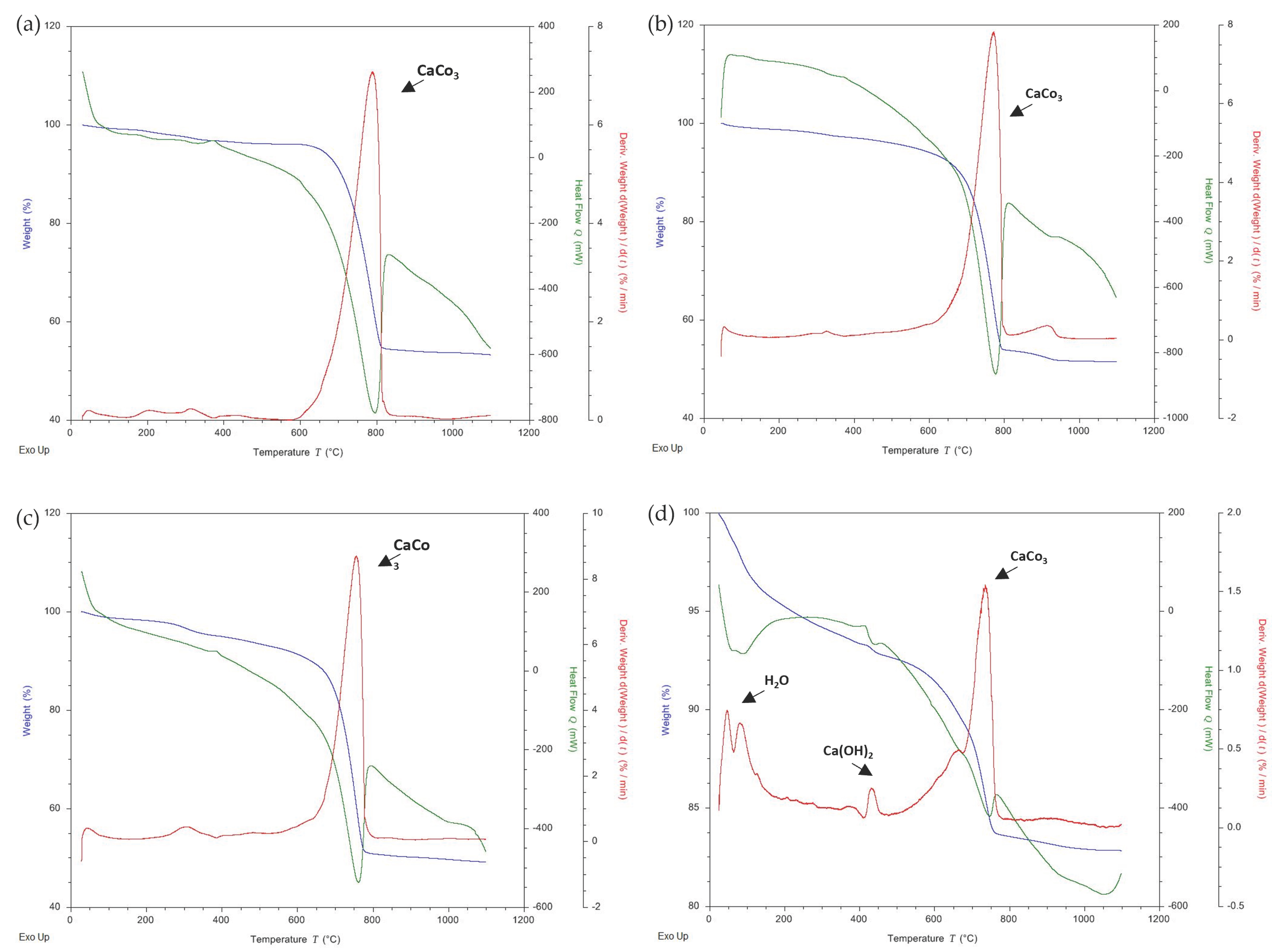


| Sample | Code |
|---|---|
| Millepora alcicornis | C1 |
| Mussismilia harttii | C2 |
| Siderastrea stellata | C3 |
| Core samples of reef fragments | T |
| Sample | Code |
|---|---|
| Portland Cement (CP IV-RS) | 350 kg |
| Coarse Sand | 0.27 m3 |
| Small Aggregate | 0.125 m3 |
| Medium Aggregate | 0.26 m3 |
| Silica Fume (microsilica) | 12% of cement weight |
| Superplasticizer | 2% of cement weight |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sousa, M.F.d.; Natividade, C.D.d.; Lima Filho, M.R.F.; Torres, S.M.; Santos, A.J.V.d.; Rocha, R.A.S.d.; Henriques, G.F.; Massei, K.; Souza, W.M.d. Mineralogical and Mechanical Characterization of Concrete Blocks for Artificial Reefs: A Comparative Study with Natural Coral Skeletons. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101886
Sousa MFd, Natividade CDd, Lima Filho MRF, Torres SM, Santos AJVd, Rocha RASd, Henriques GF, Massei K, Souza WMd. Mineralogical and Mechanical Characterization of Concrete Blocks for Artificial Reefs: A Comparative Study with Natural Coral Skeletons. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(10):1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101886
Chicago/Turabian StyleSousa, Mykel Fernandes de, Cláudio Dybas da Natividade, Marçal Rosas Florentino Lima Filho, Sandro Marden Torres, Alexsandro José Virgínio dos Santos, Rochanna Alves Silva da Rocha, Glauco Fonsêca Henriques, Karina Massei, and Wesley Maciel de Souza. 2025. "Mineralogical and Mechanical Characterization of Concrete Blocks for Artificial Reefs: A Comparative Study with Natural Coral Skeletons" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 10: 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101886
APA StyleSousa, M. F. d., Natividade, C. D. d., Lima Filho, M. R. F., Torres, S. M., Santos, A. J. V. d., Rocha, R. A. S. d., Henriques, G. F., Massei, K., & Souza, W. M. d. (2025). Mineralogical and Mechanical Characterization of Concrete Blocks for Artificial Reefs: A Comparative Study with Natural Coral Skeletons. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(10), 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13101886







