Coupling Effects of a Top-Hinged Buoyancy Can on the Vortex-Induced Vibration of a Riser Model in Currents and Waves
Abstract
1. Introduction
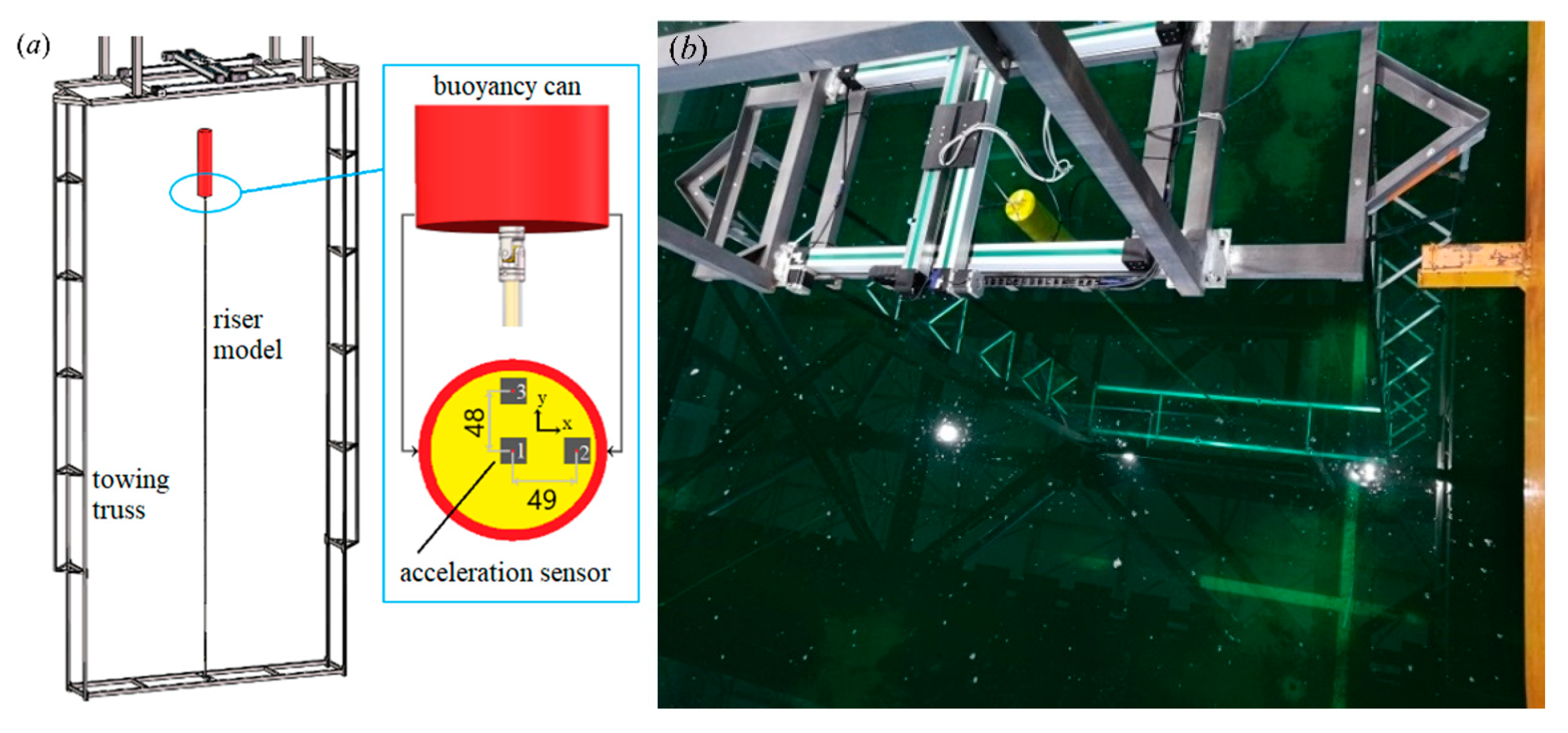
2. Experimental Set-Up
2.1. Test Devices
2.2. Test Model
2.3. Testing Conditions
3. Data Processing
4. Coupling effects of VIM on VIV under Uniform Flow
4.1. VIM Characteristics of the Buoyancy Can
4.2. VIV Responses Coupled with VIM
5. Coupling Effects of Wave Load
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.; Li, H.; Qiu, Z.; Leng, D.; Li, Z.; Li, W. A mini review of recent progress on vortex-induced vibrations of marine risers. Ocean Eng. 2020, 195, 106704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Wang, C.; He, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, K.; Ren, M. The Experimental Study of Dynamic Response of Marine Riser under Coupling Effect of Multiparameter. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Li, Z.; Chan, R.W.; Luo, H.; Duan, G.; Huang, B.; Wu, H. Study on the Vibration Characteristics of Marine Riser Based on Flume Experiment and Numerical Simulation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, J.R.; Bearman, P.W.; Huarte, F.H.; Pattenden, R.J. Laboratory measurements of vortex-induced vibrations of a vertical tension riser in a stepped current. J. Fluids Struct. 2005, 21, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trim, A.D.; Braaten, H.; Lie, H.; Tognarelli, M.A. Experimental investigation of vortex-induced vibration of long marine risers. J. Fluids Struct. 2005, 21, 335–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.S.; Shah, U.H. Vortex-induced vibrations and control of marine risers: A review. Ocean Eng. 2018, 152, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.M.; Niedzwecki, J.M.; Fu, S.; Li, R.; Yang, J. VIV response of a flexible cylinder with varied coverage by buoyancy elements and helical strakes. Mar. Struct. 2014, 39, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lie, H.; Larsen, C.M.; Liapis, S.; Baarholm, R. Vortex-induced vibration of a flexible cylinder: Interaction of the in-line and cross-flow responses. J. Fluids Struct. 2016, 63, 238–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, M.S.; Sarkar, S. Effect of stochastic parametric noise on vortex induced vibrations. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 153, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Xie, B.; Zang, Z.; Chen, E.; Hou, J. Vortex-Induced Vibration and Fatigue Damage Assessment for a Submarine Pipeline on a Sand Wave Seabed. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Duan, M.; Chen, R.; Wang, S.; Li, H. Test Study on Vortex-Induced Vibration of Deep-Sea Riser under Bidirectional Shear Flow. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, Z.; Dai, H.; Wang, L.; He, F. Nonplanar multi-modal vibrations of fluid-conveying risers under shear cross flows. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 88, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kang, Z.; Ni, W.; Xie, Z. Coupling effects of top-end dynamic boundary with a planar trajectory of “8” on three-dimensional VIV characteristics. Mar. Struct. 2022, 86, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.H.; Park, H.I.; Koterayama, W. A numerical and experimental study on dynamics of a towed low-tension cable. In Proceedings of the ISOPE International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Kitakyushu, Japan, 26–31 May 2002; ISOPE: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2002; p. ISOPE-I. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, R.G.; Litton, R.W.; Mamidipudi, P. Highly compliant rigid (HCR) riser model tests and analysis. In Proceedings of the Offshore Technology Conference, Houston, TX, USA, 3–6 May 1999; OTC: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; p. OTC-10973. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Fu, S.; Baarholm, R.; Wu, J.; Larsen, C.M. Fatigue damage induced by vortex-induced vibrations in oscillatory flow. Mar. Struct. 2015, 40, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, S.; Larsen, C.M.; Baarholm, R.; Wu, J.; Lie, H. Dominant parameters for vortex-induced vibration of a steel catenary riser under vessel motion. Ocean Eng. 2017, 136, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, E.; Zhao, M.; Wu, H. Numerical investigation of the vibration of a circular cylinder in oscillatory flow in oblique directions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, J.; Cao, P.; Xu, Y.; Fu, S.; Liu, C. Experimental investigation on vortex-induced vibration of a flexible pipe under higher mode in an oscillatory flow. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neshamar, O.E.; O’Donoghue, T. Flow-induced vibration of a cantilevered cylinder in oscillatory flow at high KC. J. Fluids Struct. 2022, 109, 103476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.; Zhao, W.; Wan, D. Numerical study of vortex-induced vibration of a flexible cylinder with large aspect ratios in oscillatory flows. Ocean Eng. 2021, 238, 109730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, M.; Zheng, Z.; Guo, S.; Gan, K. Impacts of top-end vessel sway on vortex-induced vibration of the submarine riser for a floating platform in deep water. Ocean Eng. 2015, 99, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Dai, H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, L. Nonlinear dynamics of a fluid-conveying pipe under the combined action of cross-flow and top-end excitations. Appl. Ocean Res. 2017, 62, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xue, H.; Tang, W. Nonlinear dynamic response analysis of marine risers under non-uniform combined unsteady flows. Ocean Eng. 2020, 213, 107687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, Y.; Duan, Z.; Xue, H.; Tang, W. Numerical investigation on vortex-induced vibration of catenary riser conveying fluid under top-end heave excitation. Ships Offshore Struct. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Kang, Z.; Stoesser, T.; Xie, Z.; Massie, L. Experimental investigation on the VIV of a slender body under the combination of uniform flow and top-end surge. Ocean Eng. 2020, 216, 108094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chai, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Y. Three-dimensional nonlinear vortex-induced vibrations of top-tension risers considering platform motion. Ocean Eng. 2022, 263, 112393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Fu, S.; Xu, Y.; Huang, J. Application of a modified wake oscillator model to vortex-induced vibration of a free-hanging riser subjected to vessel motion. Ocean Eng. 2022, 253, 111165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jaiman, R.K.; Adaikalaraj, P.F.B.; Shen, L.; Tan, S.B.; Wang, W. Vortex-induced vibration of a free-hanging riser under irregular vessel motion. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Offshore Mechanics and Arctic Engineering, Busan, Korea, 18–24 June 2016; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 49934, p. V002T08A040. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; You, Y. Vortex-induced vibration of a flexible fluid-conveying riser due to vessel motion. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 223, 107288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, L.P.; Sha, Y.; Cao, J. Overall design and analysis of free-standing vertical risers. Ship Ocean Eng. 2011, 40, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.F.; Xu, S.P.; Guo, H.Y. Parametric study of global response behavior of deepwater free standing hybrid risers. J. Ship Mech. 2011, 15, 996–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; Ni, W.; Ma, G.; Xu, X. A model test investigation on vortex-induced motions of a buoyancy can. Mar. Struct. 2017, 53, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Ni, W.; Zhang, L.; Ma, G. An experimental study on vortex induced motion of a tethered cylinder in uniform flow. Ocean Eng. 2017, 142, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.H.K.; Govardhan, R. A brief review of recent results in vortex-induced vibrations. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2008, 96, 713–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ai, S.; Sun, L.; Soares, C.G. Vortex-induced vibrations of catenary risers in varied flow angles. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2024, 269, 109086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauvtis, N.A.; Williamson, C.H.K. The effect of two degrees of freedom on vortex-induced vibration at low mass and damping. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 509, 23–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fan, N.; Zheng, D.; Fu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Nian, T. Predicting impact forces on pipelines from deep-sea fluidized slides: A comprehensive review of key factors. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, T. A mass transfer-based LES modelling methodology for analyzing the movement of submarine sediment flows with extensive shear behavior. Coast. Eng. 2024, 191, 104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Aspect Ratio | Length (m) | Outer Diameter (m) | Inner Diameter (m) | Mass Ratio | EI (N·m2) | EA (N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 5 | 0.02 | 0.008 | 2.33 | 42.62 | 1.470 × 106 |
| Order Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency (Hz) | 0.993 | 2.344 | 4.639 | 7.666 |
| Aspect Ratio | Length (m) | Diameter (m) | Displacement (kg) | Mass Iratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.37 | 0.805 | 0.15 | 14.23 | 0.34 |
| Item | Wave Height (m) | Period (s) | Flow Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CM-01-01~CM-01-18 | 0 | 0 | 0.1~0.44 |
| WM-01-01~WM-01-05 | 0.2 | 1.5~2.5 | 0 |
| WM-02-01~WM-02-04 | 0.1~0.3 | 2 | 0 |
| WM-03-01~WM-03-18 | 0.2 | 2 | 0.1~0.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C. Coupling Effects of a Top-Hinged Buoyancy Can on the Vortex-Induced Vibration of a Riser Model in Currents and Waves. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050751
Yu C, Zhang S, Zhang C. Coupling Effects of a Top-Hinged Buoyancy Can on the Vortex-Induced Vibration of a Riser Model in Currents and Waves. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(5):751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050751
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Chi, Sheng Zhang, and Cheng Zhang. 2024. "Coupling Effects of a Top-Hinged Buoyancy Can on the Vortex-Induced Vibration of a Riser Model in Currents and Waves" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 5: 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050751
APA StyleYu, C., Zhang, S., & Zhang, C. (2024). Coupling Effects of a Top-Hinged Buoyancy Can on the Vortex-Induced Vibration of a Riser Model in Currents and Waves. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(5), 751. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12050751







