Covert Underwater Acoustic Communication Using Marine Ambient Noise Without Detectable Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. System of Studied CUAC Schemes
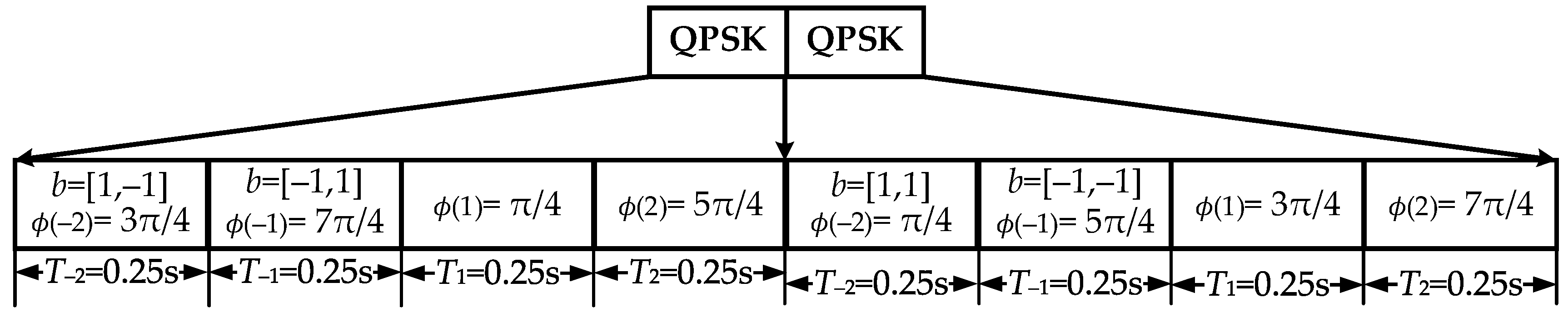
2.1. Modulation Method
2.2. Demodulation Method
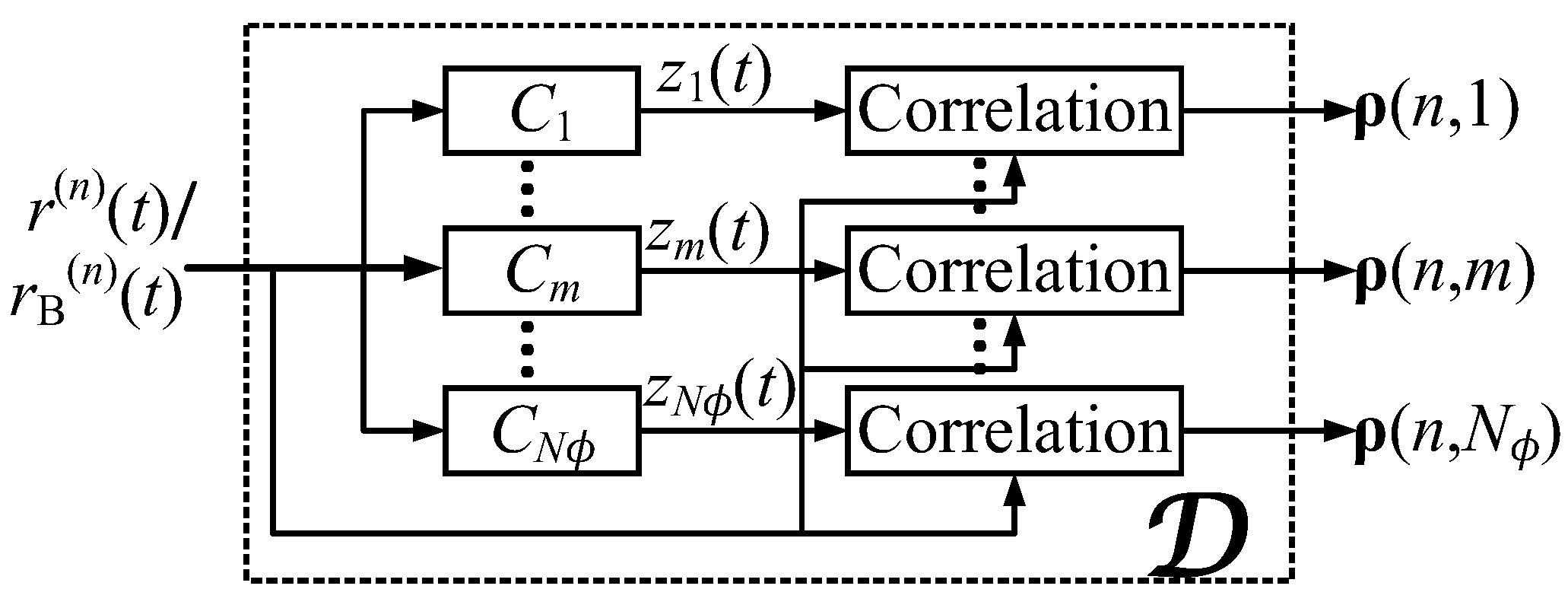
2.3. System Diagram
- Step (1)
- Filter the initial signal with raised-cosine function and down sample to obtain baseband signal ;
- Step (2)
- Divide into N small segments equally as Equation (1);
- Step (3)
- Select rotation phase combination related to transmitted symbols according to OMPS as Equation (10);
- Step (4)
- Multiply the rotation phases with N small segments as Equation (2) and modulate by raised-cosine function to obtain the information-bearing signal ;
- Step (5)
- Generate the transmitted baseband signal as Equation (3);
- Step (6)
- Modulate using raised-cosine function to obtain transmitted signal ;
- Step (7)
- Transmit or convolve with the channel, and obtain the received signal ;
- Step (8)
- Resample with Doppler coefficient , and obtain ;
- Step (9)
- Filter with raised-cosine function to obtain baseband signal ;
- Step (10
- Use the steganography algorithms to obtain intermediate signals as Equation (2);
- Step (11)
- Obtain the demodulation values related to by cross-correlation as Equation (4);
- Step (12)
- Repeat Step 7–10 for each Doppler coefficient in and obtain the demodulation values ;
- Step (13)
- Make decision according to the index of maximal values of , and the is -th symbol sequence .
3. Simulation Results
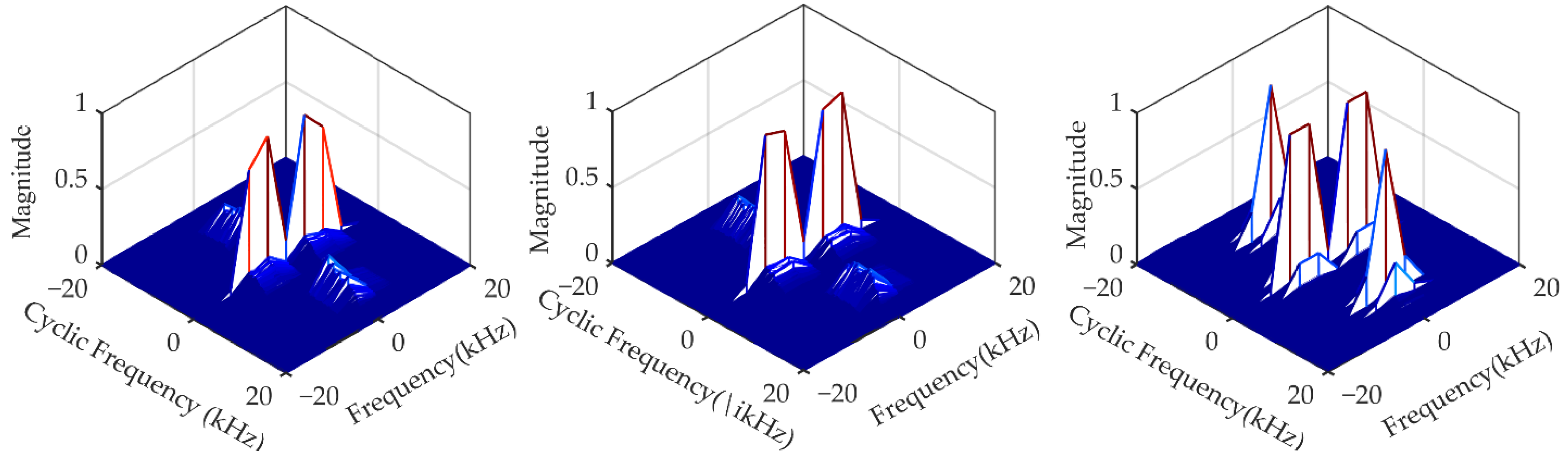
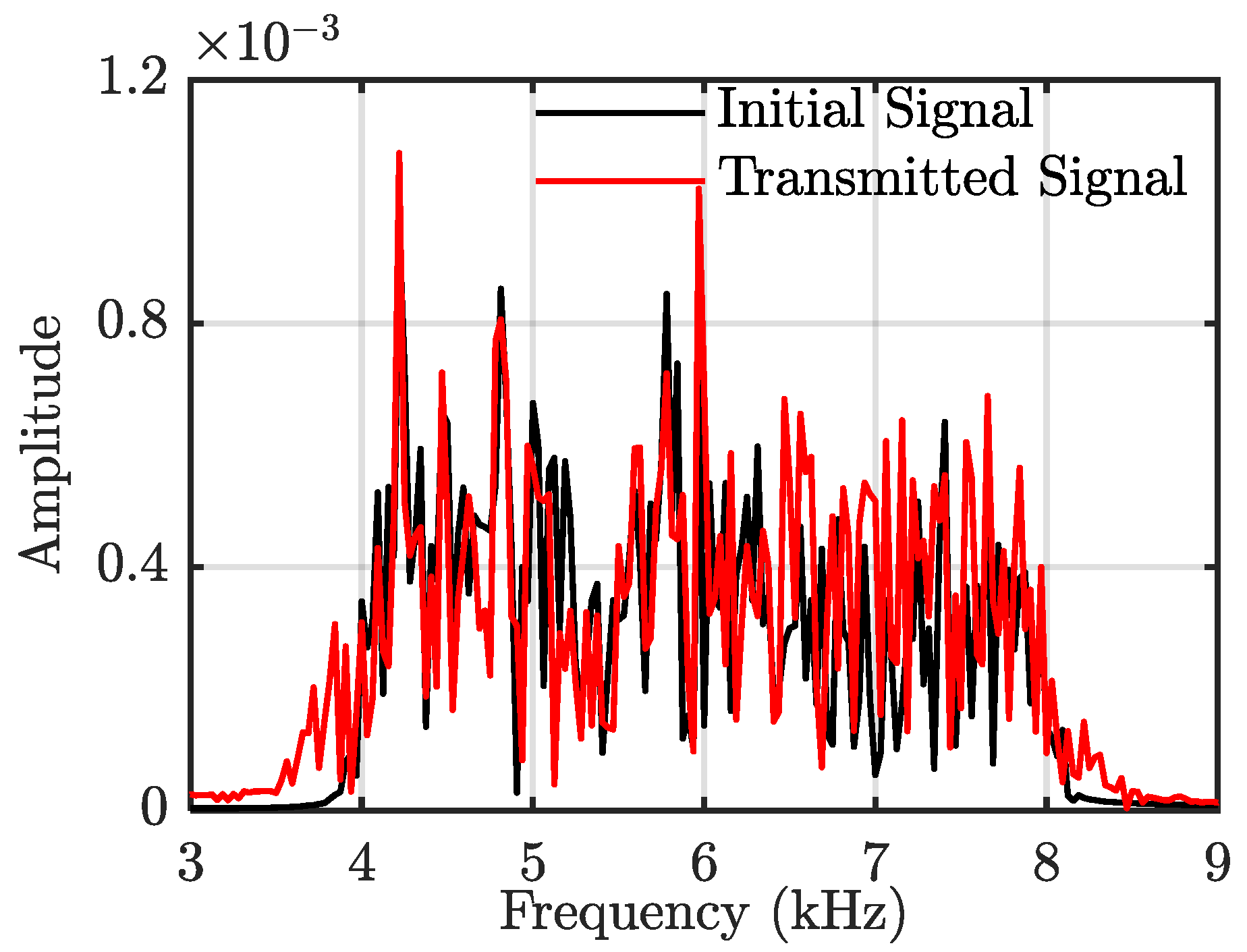
3.1. Signal Feature of the Studied CUAC
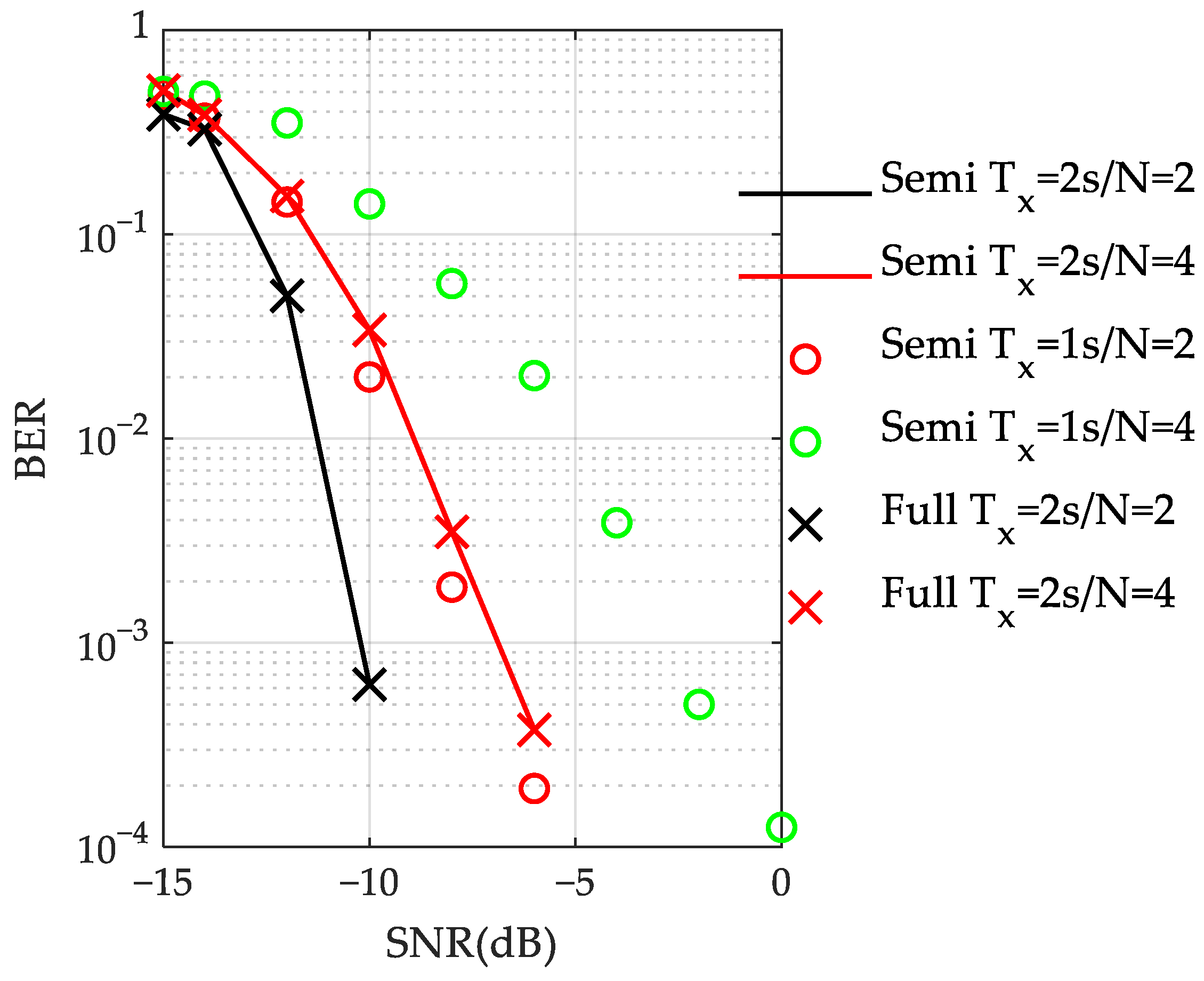
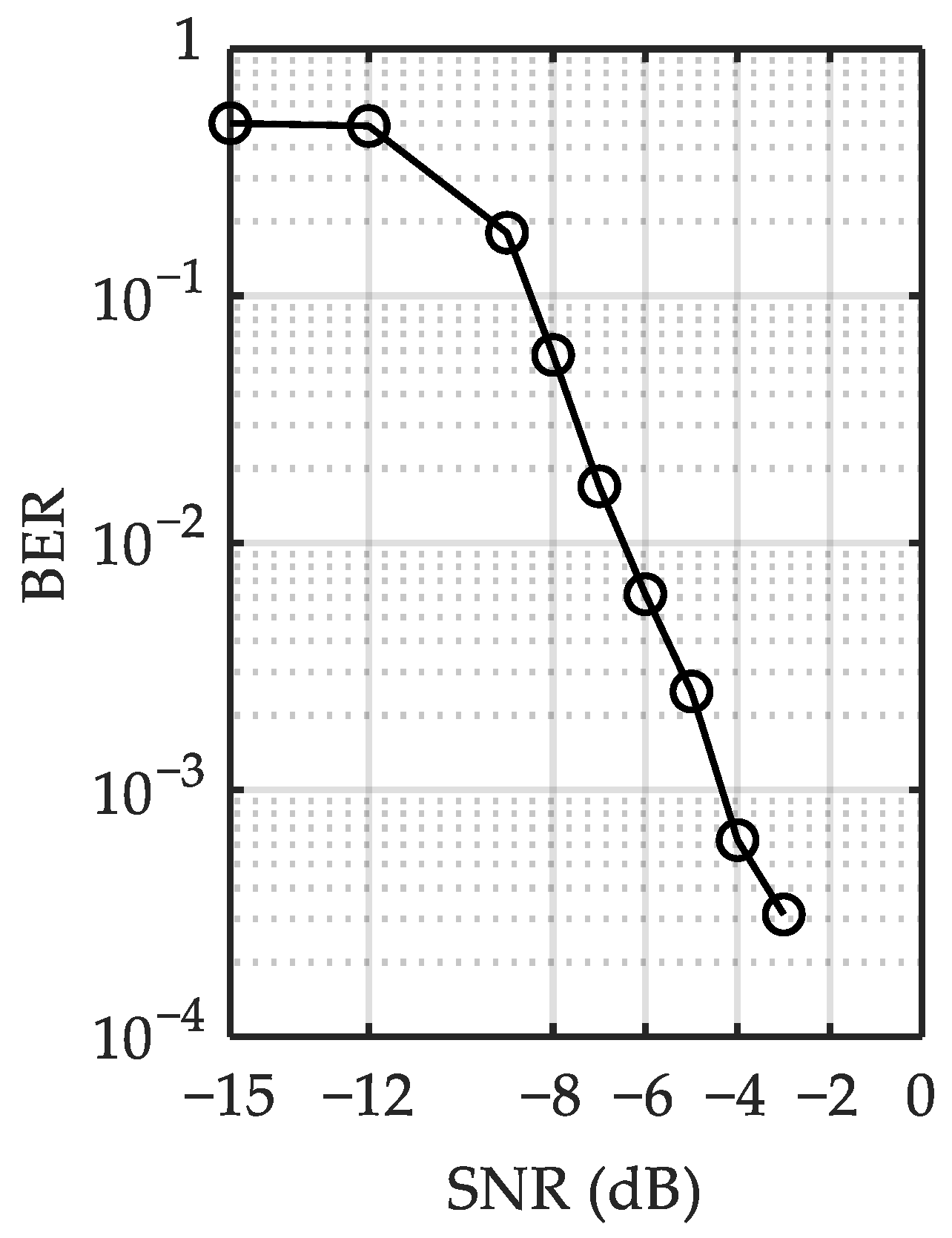
3.2. Simulation of the Studied CUAC
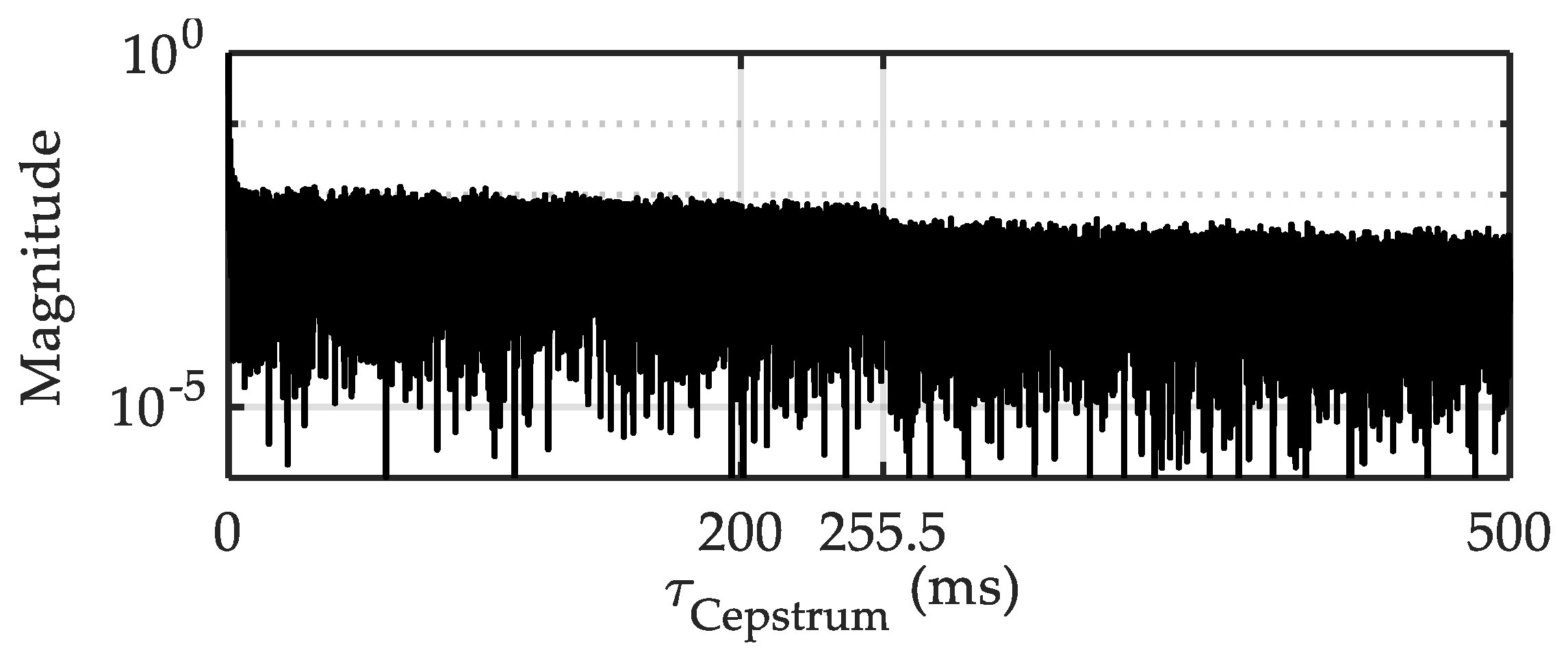
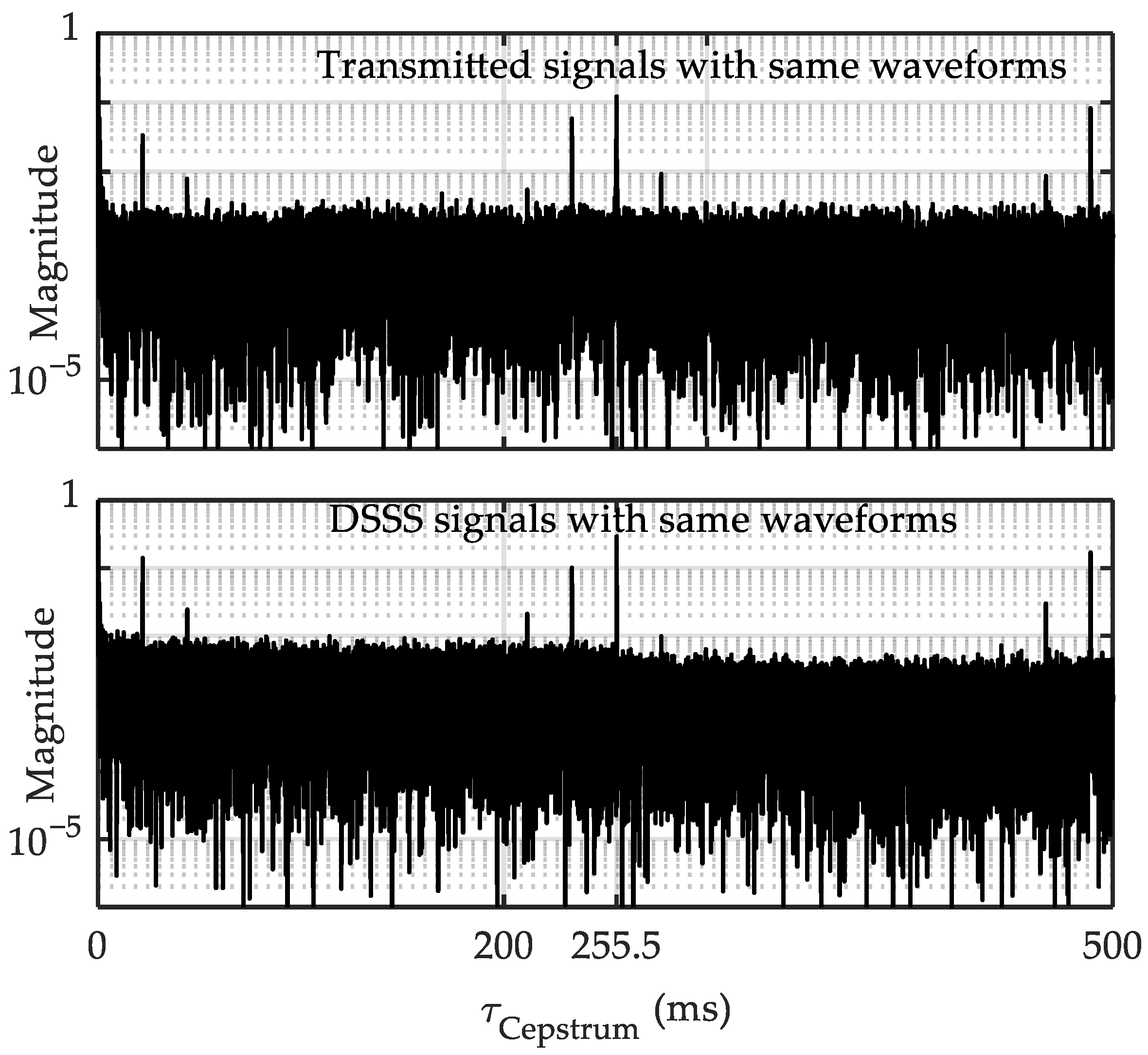
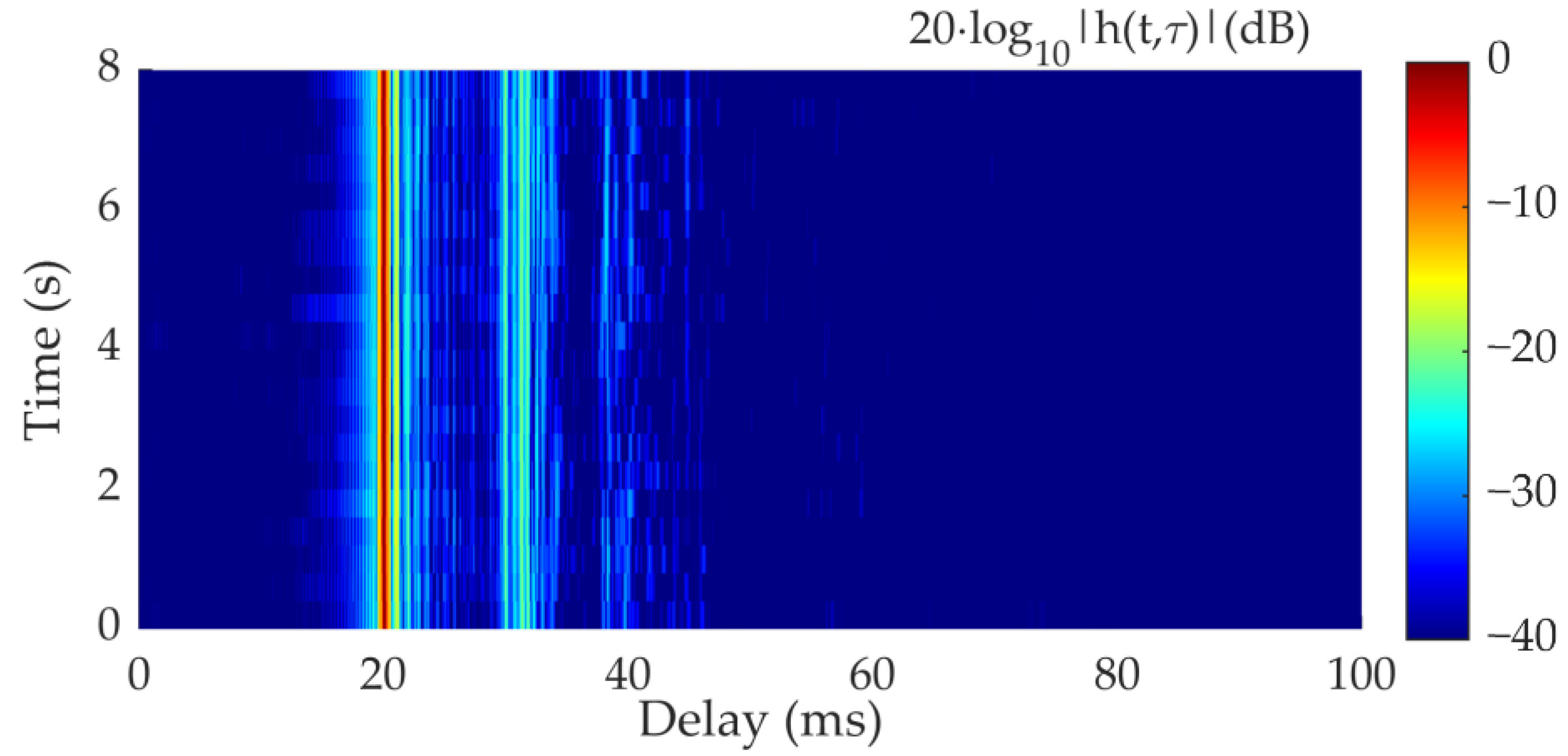
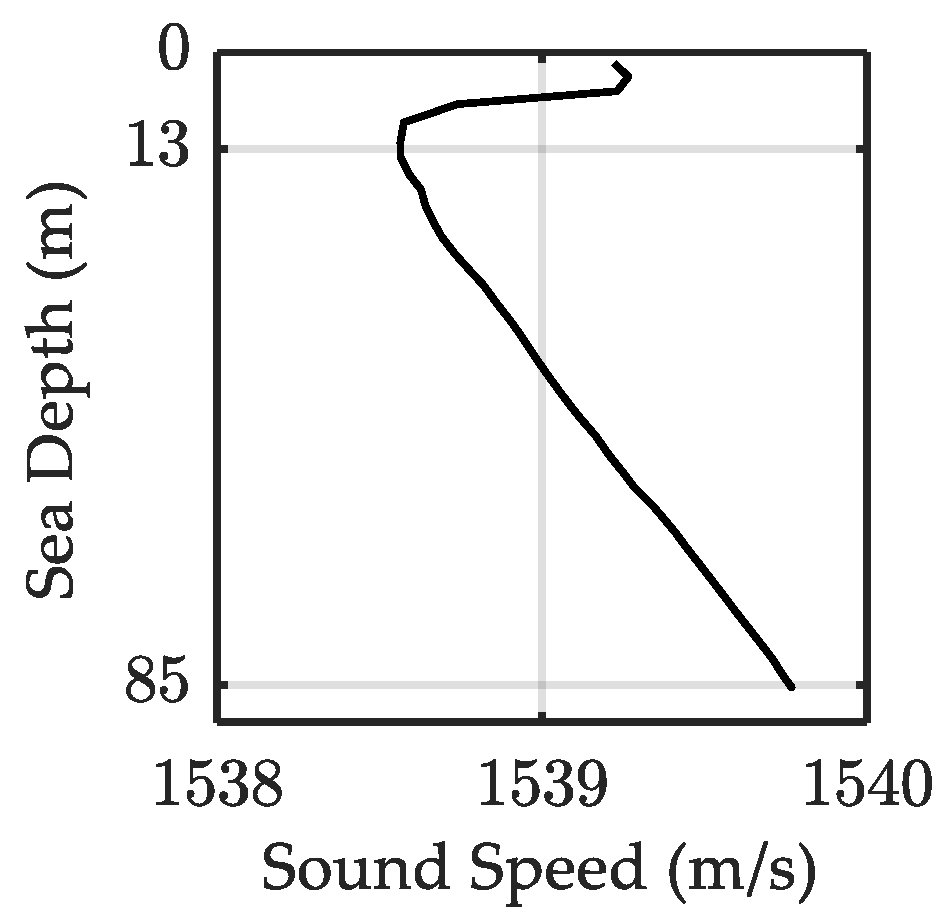
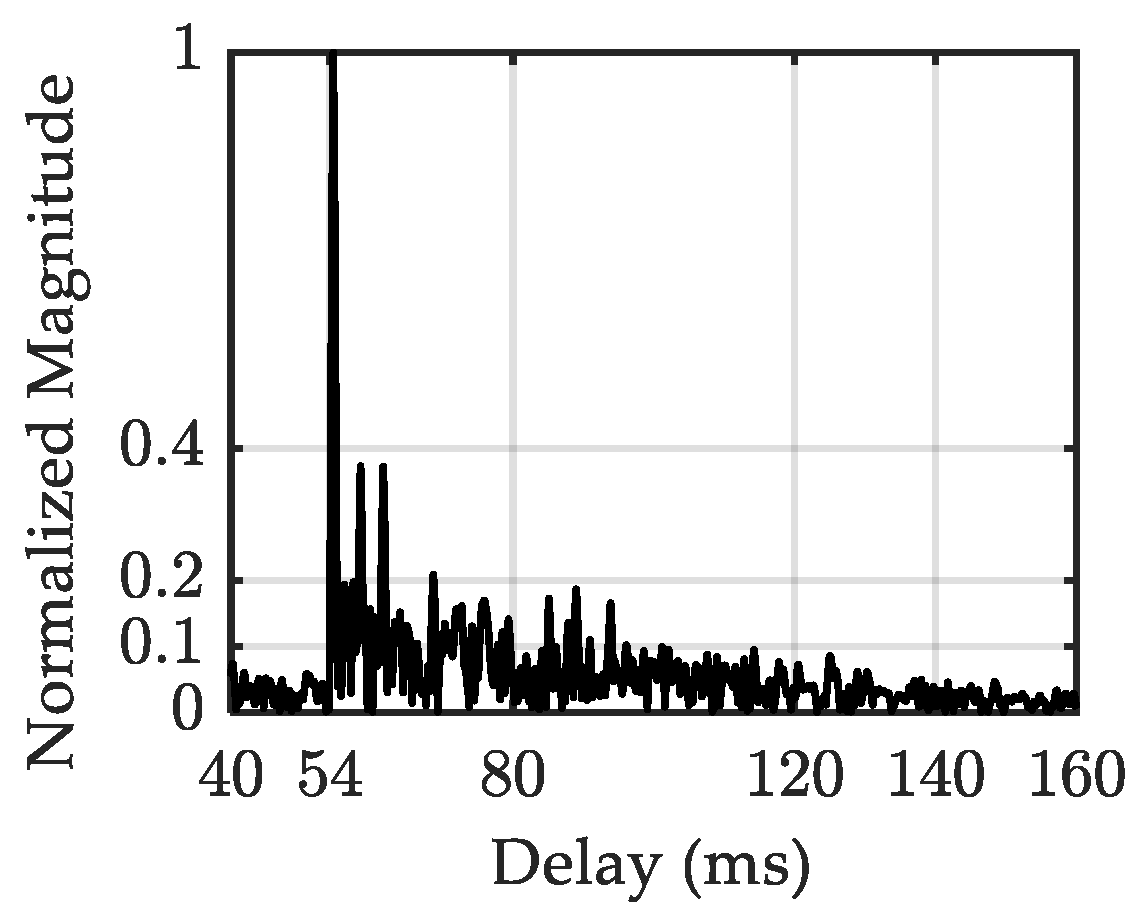
4. Sea Trial Results
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lynch, R.S.; Willett, P.K.; Reinert, J.M. Some analysis of the LPI concept for active sonar. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2012, 37, 446–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.J.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, S.; Chen, D.J.; Sha, X.J.; Shen, X.M. On physical layer security: Weighted fractional Fourier transform based user cooperation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 5498–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, J.; He, H.; Li, J.; Roberts, W. Covert underwater acoustic communications. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 2898–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, R.; Goeckel, D.; Towsley, D.; Bash, B.A.; Guha, S. Covert wireless communication with artificial noise generation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 7252–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I. Wireless secure communications using UWB noise waveforms with code spectrum modulation. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Conference on Ultrawideband and Ultrashort Impulse Signals, Sevastopol, Ukraine, 6–10 September 2010; pp. 165–167. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, D.; Couto, D.J.; Beaudeau, J.P. Low probability of exploitation waveform design using Barankin bound formulation 2018. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 29–31 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.C.; Yang, W.B. Low probability of detection underwater acoustic communications using direct-sequence spread spectrum. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 124, 3632–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.C.; Yang, W.B. Performance analysis of direct-sequence spread-spectrum underwater acoustic communications with low signal-to-noise-ratio input signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.B.; Yang, X.X. Chaotic direct sequence spread spectrum for secure underwater acoustic communication. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 104, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leus, G.; van Walree, P.A. Multiband OFDM for covert acoustic communications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2008, 26, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leus, G.; van Walree, P.A.; Boschma, J.; Fanciullacci, C.; Gerritsen, H.; Tusoni, P. Covert underwater communications with multiband OFDM. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2008, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 15–18 September 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- van Walree, P.A.; Sangfelt, E.; Leus, G. Multicarrier spread spectrum for covert acoustic communications. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2008, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 15–18 September 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- van Walree, P.A.; Leus, G. Robust underwater telemetry with adaptive turbo multiband equalization. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2009, 34, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Z.; Qiao, G.; Ismail, A. Covert underwater acoustic communication using dolphin sounds. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, EL300–EL306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Z.; Ma, T.L.; Qiao, G.; Ma, L.; Yin, Y.L. Biologically inspired covert underwater acoustic communication by mimicking dolphin whistles. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 120, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Duan, F.J.; Fu, X.; Yan, H.; Hua, B. Bio-inspired steganography for secure underwater acoustic communications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.J.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Sun, Z.B.; Fu, X.; Duan, F.J. Covert underwater communication based on combined encoding of diverse time-frequency features of sperm whale clicks. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 171, 107600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Jiang, J.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Sun, Z.B.; Li, Z.C.; Fu, X.; Duan, F.J. Bionic covert underwater communication focusing on the overlapping of whistles and clicks generated by different cetacean individuals. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 183, 108279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Jia, N.; Guo, S.M.; Xiao, D.; Huang, J.C.; Chen, G. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing cyclic shift keying spread spectrum camouflaging underwater acoustic communication with dolphin whistles as information carrier. ACTA Acoust. 2018, 43, 753–761. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.P.; Qu, Y.; Wu, Z.Q.; Nowak, M.J.; Ellinger, J.; Wicks, M.C. RF steganography via LFM chirp radar signals. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picinbono, B.; Devaut, P. Optimal linear-quadratic systems for detection and estimation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1988, 34, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.A. Cyclostationarity in Communications and Signal Processing; Statistical Signal Processing Inc.: Yountville, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, W.W.; Lee, W.J. Detecting wireless steganography with wavelet analysis. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.A. Signal interception: A unifying theoretical framework for feature detection. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1988, 36, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punchihewa, A.; Zhang, Q.; Dobre, O.A.; Spooner, C.; Rajan, S.; Inkol, R. On the cyclostationarity of OFDM and single carrier linearly digitally modulated signals in time dispersive channels: Theoretical developments and application. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2010, 9, 2588–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Yang, T.C. Blind cyclostationary carrier frequency and symbol rate estimation for underwater acoustic communication. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 10–15 June 2012; pp. 3482–3486. [Google Scholar]
- Fehske, A.; Gaeddert, J.; Reed, J.H. A new approach to signal classification using spectral correlation and neural networks. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Symposium on New Frontiers in Dynamic Spectrum Access Networks, Baltimore, MD, USA, 8–11 November 2005; pp. 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Like, E.; Chakravarthy, V.D.; Ratazzi, P.; Wu, Z.Q. Signal classification in fading channels using cyclic spectral analysis. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2009, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.J.; Gong, Y.; Wang, K.; Lu, W.D.; Hua, J.Y. Covert digital communication systems based on joint normal distribution. IET Commun. 2017, 11, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cek, M.E. Covert communication using skewed α-Stable distributions. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.J.; Jin, W.B.; Zhou, K.; Hua, J.Y. A covert digital communication system using skewed α-stable distributions for internet of things. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 113131–113141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cek, M.E. M-ary alpha-stable noise modulation in spread-spectrum communication. Fluct. Noise Lett. 2015, 14, 1550022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.J.; Wang, K.; Gong, Y.; Lu, W.D.; Hua, J.Y. Structure and performance analysis of an SαS-based digital modulation system. IET Commun. 2016, 10, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.D.; Doherty, J.F. A steganographic approach to sonar tracking. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 44, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitcolas F.A., P.; Anderson, R.J.; Kuhn, M.G. Information hiding-a survey. Proc. IEEE 1999, 87, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passerieux, J.M. Stealth underwater acoustic communications based upon steganography techniques, 2014. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference and Exhibition on Underwater Acoustics, Rhodes, Greece, 22–27 June 2014; pp. 1199–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Kemerait, R.; Childers, D. Signal detection and extraction by cepstrum techniques. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1972, 18, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Walree, P.A.; Jenserud, T. A discrete-time channel simulator driven by measured scattering functions. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2008, 26, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


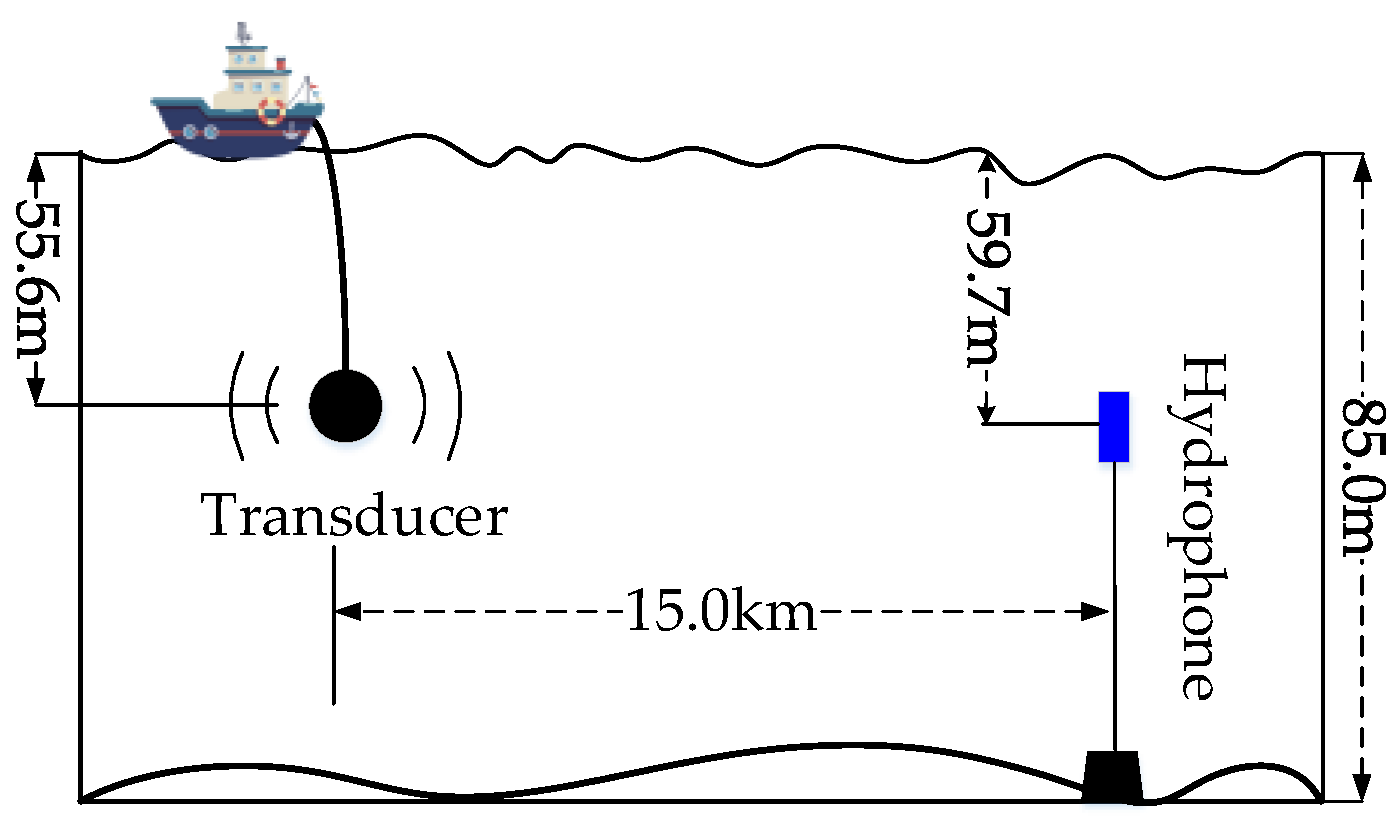




| Sea Depth | Range | Tx Depth | Rx Depth | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 163.0 m | 5.0 km | 63.0 m | 80.0 m | 4–8 kHz |
| (s) | (s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-search | 1 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Semi-search | 1 | 4 | 0.25 |
| Full/Semi-search | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Full/Semi-search | 2 | 4 | 0.5 |
| Index | Symbol Sequence | Index | Symbol Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [1,1;1,1] | 9 | [−1,1;1,1] |
| 2 | [1,1;1,−1] | 10 | [−1,1;1,−1] |
| 3 | [1,1;−1,1] | 11 | [−1,1;−1,1] |
| 4 | [1,1;−1,−1] | 12 | [−1,1;−1,−1] |
| 5 | [1,−1;1,1] | 13 | [−1,−1;1,1] |
| 6 | [1,−1;1,−1] | 14 | [−1,−1;1,−1] |
| 7 | [1,−1;−1,1] | 15 | [−1,−1;−1,1] |
| 8 | [1,−1;−1,−1] | 16 | [−1,−1;−1,−1] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Huang, J.; Jia, N.; Wang, B.; Guo, S. Covert Underwater Acoustic Communication Using Marine Ambient Noise Without Detectable Features. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122217
Liu B, Huang J, Jia N, Wang B, Guo S. Covert Underwater Acoustic Communication Using Marine Ambient Noise Without Detectable Features. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(12):2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Biao, Jianchun Huang, Ning Jia, Biao Wang, and Shengming Guo. 2024. "Covert Underwater Acoustic Communication Using Marine Ambient Noise Without Detectable Features" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 12: 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122217
APA StyleLiu, B., Huang, J., Jia, N., Wang, B., & Guo, S. (2024). Covert Underwater Acoustic Communication Using Marine Ambient Noise Without Detectable Features. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(12), 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12122217






