Estimating Spatiotemporal Fishing Effort of Trawlers with Vessel-Monitoring System Data: A Case Study of the Sea Area of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Pre-Processing and Labeling
2.3. Feature Extraction
2.4. Fishing Behavior Recognition Based on the Slime Mould Algorithm-Optimized Light Gradient-Boosting Machine Algorithm
2.4.1. An Overview of the Fishing Behavior Recognition Model
2.4.2. Principle of SMA-LightGBM
- LightGBM Algorithm
- 2.
- Slime Mould Algorithm
- 3.
- The Slime Mould Algorithm-Optimized LightGBM
| Algorithm 1 Pseudo-code of SMA-LightGBM |
| Inputs: The population size and maximum number of iterations The upper and lower boundaries of the nine parameters of LightGBM Outputs: The best solution Initialize the positions of slime mould () while iteration do Calculate the cross-validation score of LightGBM as fitness Update , Calculate the by Equation (5) for each search portion do Update , , Update positions by Equation (6) Return and |
2.4.3. Training and Testing Phases of the Fishing Behavior Classifier
2.4.4. Performance Evaluation of the Fishing Behavior Classifier
2.5. Calculation Method of the Fishing Effort
3. Results
3.1. Experiment and Evaluation of Fishing Behavior Recognition
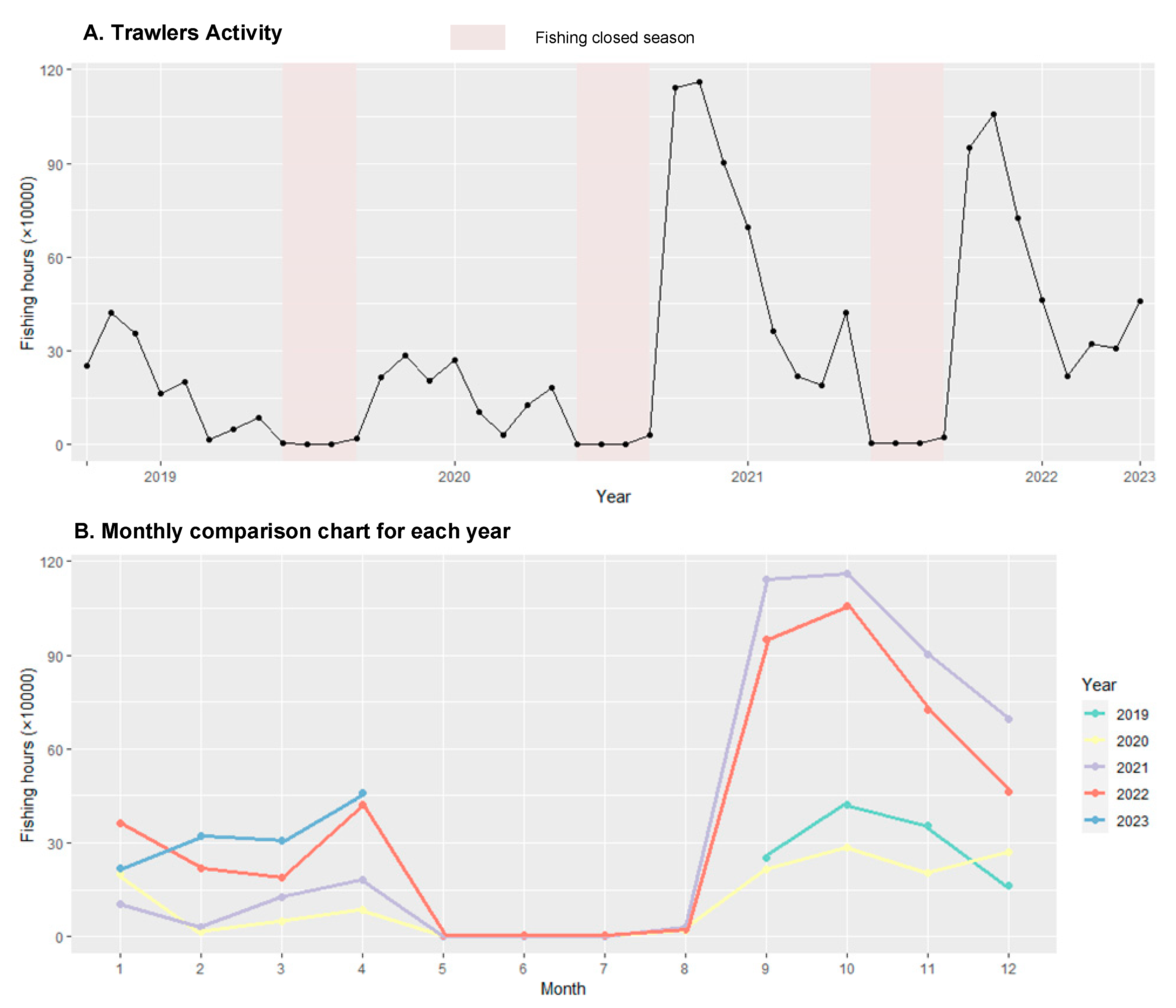
3.2. Estimating Spatiotemporal Fishing Effort of Trawlers
4. Discussion
4.1. Model and Fishing Effort Estimation
4.2. Model Performance for Fisheries’ Management and Policy Implementation
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The presented method showed a remarkable generalization ability and high accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and Matthews correlation coefficient in the test, with scores of 98.23%, 98.75%, 97.75%, and 0.9646, respectively. The MAE of the fishing effort of the trawlers was 0.3031 kW·h, and the R2 score was 0.9772.
- (2)
- The spatial distribution of fishing effort was primarily concentrated in three key areas: 121° E~124° E, 35.5° N~39° N; 119.7° E~122.7° E, 33.8° N~35.5° N; and 123° E~124° E, 33.5° N~35° N.
- (3)
- The temporal distribution exhibited periodic variations, which were closely associated with human activities such as the celebration of the Lunar New Year and the periods closed to fishing. The slope of the change in fishing effort concerning latitude distribution was approximately 2, whereas for longitude distribution, it was approximately −1.25.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture, Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jason, S.L.; Reg, A.W. Global ecosystem overfishing: Clear delineation within real limits to production. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav0474. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.; Tang, Y.; Chang, B.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Y. Evolution of marine fisheries management in China from 1949 to 2019: How did China get here and where does China go next. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Vincent, A.C.J. China’s policies on bottom trawl fisheries over seven decades (1949–2018). Mar. Pol. 2020, 122, 104256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, X.D.; Wan, R.J.; Jin, X.S.; Shan, X.J.; Guan, L.S. Ichthyoplankton Succession and Assemblage Structure in the Bohai Sea During the Past 30 Years Since the 1980s. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2018, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Chen, T. Impact of fuel subsidies on bottom trawl fishery operation in China. Mar. Pol. 2022, 138, 104977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, N.L.; Béné, C.; Hall, S.J.; Allison, E.H.; Heck, S.; Ratner, B.D. Diagnosis and management of small-scale fisheries in developing countries. Fish Fish. 2007, 8, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; He, Y. Management of China’s capture fisheries: Review and prospect. Aquac. Fish. 2019, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y. A qualitative appraisal of China’s efforts in fishing capacity management. J. Ocean Univ. China 2007, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National People’s Congress. Fisheries Law of the People’s Republic of China; The National People’s Congress: Beijing, China, 1986.
- Zhao, L.; Sun, H.W.; Zheng, S.N.; Geng, R. Construction path of new fishery management system. Agric. Outlook 2016, 12, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Finance; Ministry of Agriculture. Regulations on the Management of Special Funds Using for Marine Fishermen to Change Their Jobs; Ministry of Finance: Beijing, China; Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2003.
- Ministry of Agriculture. Animal Husbandry and Fisheries, The State Council Opinions on Control Index of Offshore Fishing Vessels; The State Council: Beijing, China, 1987.
- Ministry of Finance; Ministry of Agriculture State Price Bureau. Measures for Collection and Use of Fishery Resources Proliferation and Protection Fees; Ministry of Finance: Beijing, China; Ministry of Agriculture State Price Bureau: Beijing, China, 1988.
- Ministry of Agriculture. Notice on Revising the Provisions on the Arrangement and Management of Fishing Season Production in the Main Fishing Grounds of East China Sea, Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea; Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 1995.
- Su, M.; Wang, L.; Xiang, J.; Ma, Y. Adjustment trend of China’s marine fishery policy since 2011. Mar. Pol. 2021, 124, 104322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, S.; Cao, J.; Ge, S. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the implementation of the “dual control system” for fishing vessels in China and policy recommendations. China Fish. 2018, 4, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Chang, Y.-C.; Zhang, L. Azn ocean community with a shared future: Conference report. Mar. Pol. 2020, 116, 103888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Zulfiqar, K. A comparative analysis of the environmental policies in China and Pakistan: Developing a legal regime for sustainable ChinaPakistan economic corridor (CPEC) under the Belt and road initiative (BRI). IPRI J. 2021, 21, 83–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Fisheries cooperation in the SouthSouth China sea: Evaluating the options. Mar. Pol. 2018, 89, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Huang, S. China’s policies and practice on combatting IUU in distant water fisheries. Aquac. Fish. 2021, 6, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhang, C.L.; Xu, B.D.; Liu, Y.W.; Ren, Y.P.; Chen, Y. Evaluating the efficacy of fisheries management strategies in China for achieving multiple objectives under climate change. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 245, 106870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Peng, D.M.; Liu, H.H.; Mu, Y.T.; Kim, D.H. Is China’s Fishing Capacity Management Sufficient? Quantitative Assessment of China’s Efforts toward Fishing Capacity Management and Proposals for Improvement. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture. Notice on Further Strengthening the Control of Domestic Fishing Vessels and Implementing the Total Management of Marine Fishery Resources; Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Su, X.; Chen, X. Comparative study for input control output control in fishery management. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2021, 3, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Agriculture. Notice on Adjusting Domestic Fishery Fishing and Aquaculture Oil Price Subsidy Policies to Promote the Sustainable and Healthy Development of Fisheries; Ministry of Agriculture: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Ou, C.H.; Tseng, H.S. The fishery agreements and management systems in the East China Sea. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2010, 5, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, D. Managing the resources of the China Seas: China’s bilateral fisheries agreements with Japan, South Korea, and Vietnam. Asia-Pac. J. 2005, 3, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Q.; Shan, X.J.; Jin, X.S.; Gorfin, E.H.; Guan, L.S.; Yang, T. Evolution of China’s Total Allowable Catch (TAC) system: Review and way forward. Mar. Policy 2023, 147, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Sun, M.; Ren, Y.P.; Chen, Y. Fisher behavior matters: Harnessing spatio-temporal fishing effort information to support China’s fisheries management. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2021, 210, 105665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.K.; Aitor, F.; Jose, L.S.L. Daily variation of fishing effort and ex-vessel prices in a western Mediterranean multi-species fishery: Implications for sustainable management. Mar. Policy 2015, 61, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Vanessa, S.; Francese, M.; Guillaume, B.; Gwenael, C.; Matthew, C.; Romain, C.H.; Geraldine, C.; Mark, D.; Oscar, E.; Ruth, H.; et al. Spatial assessment of fishing effort around European marine reserves: Implications for successful fisheries management. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Hugo, P.; Christopher, K.P.; Miguel, M.; Marco, S.; Karen, A.B.; Frederic, V. The Portuguese industrial pelagic longline fishery in the Northeast Atlantic: Catch composition, spatio-temporal dynamics of fishing effort, and target species catch rates. Fish. Res. 2023, 264, 106730. [Google Scholar]
- Ashley, T.; Colin, J.D.; Carolyn, M.I.; Stuart, E.J.; Greg, G.S.; Christopher, T.S.; Brett, T.P.; Olaf, P.J. Estimating fishing effort across the landscape: A spatially extensive approach using models to integrate multiple data sources. Fish. Res. 2021, 233, 105768. [Google Scholar]
- Francois, B.; Rasmus, N.; Clara, U.; Josefine, E.; Henrik, D. Detailed mapping of fishing effort and landings by coupling fishing logbooks with satellite-recorded vessel geo-location. Fish. Res. 2010, 106, 41–53. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, J.E. An interview-based approach to assess marine mammal and sea turtle captures in artisanal fisheries. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Cordova, E.; Del Solar, A.; Alfaro-Shigueto, J.; Mangel, J.C.; Diaz, B.; Carrillo, O.; Sarmiento, D. Captures of manta and devil rays by small-scale gillnet fisheries in northern Peru. Fish. Res. 2017, 195, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candan, U.S.; Tomoharu, E.; Suzanne, K.; Heidi, D. Prediction of fishing effort distributions using boosted regression trees. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin, D.W.; Patrick, D.O.; Natalie, C.B. Improving effort estimates and informing temporal distribution of recreational salmon fishing in British Columbia, Canada using high-frequency optical imagery data. Fish. Res. 2022, 249, 106251. [Google Scholar]
- Malvestuto, S.P. Sampling the recreational fishery. In Fisheries Techniques, 2nd ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bathesda, MD, USA, 1996; pp. 591–623. [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson, E.A.; Berkowitz, J.; Bull, C.J. Sample size requirements for detecting changes in some fisheries statistics from small trout lakes. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1988, 8, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeyoon, P.; Jungsam, L.; Katherine, S.; Timothy, H.; Brian, A.W.; Nathan, A.M.; Kenji, T.; Hiroshi, K.; Yoshioki, O.; David, A.K. Illuminating dark fishing fleets in North Korea. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Ganggang, G.; Wei, F.; Jialun, X.; Shengmao, Z.; Heng, Z.; Fenghua, T.; Tianfei, C. Identification for operating pelagic light-fishing vessels based on NPP/VIIRS low light imaging data. Trans. CSAE 2017, 33, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Brett, T.P.; Scott, B. Estimating fishing effort from remote traffic counters: Opportunities and challenges. Fish. Res. 2018, 204, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Mullowney, D.R.; Dawe, E.G. Development of performance indices for the Newfoundland and Labrador snow crab (Chionoecetes opilio) fishery using data from a vessel monitoring system. Fish. Res. 2009, 100, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.; D’Andrea, L.; Parisi, A.; Martinelli, M.; Belardinelli, A.; Boccoli, F.; Cignini, I.; Tordoni, M.; Cataudella, S. Assessing the fishing footprint using data integrated from different tracking devices: Issues and opportunities. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascal, T.; Joseph, M.; Christian, M.; Kerstin, S.S. AIS and VMS ensemble can address data gaps on fisheries for marine spatial planning. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3769. [Google Scholar]
- Gerritsen, H.D.; Minto, C.; Lordan, C. How much of the seabed is impacted by mobile fishing gear? Absolute estimates from Vessel Monitoring System (VMS) point data. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 523–531. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; He, R.; Ruan, X.; Yang, H. Footprints of fishing vessels in Chinese waters based on automatic identification system data. J. Sea Res. 2022, 187, 102255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, S.-L.; Fan, W.; Shi, H.-M.; Yuan, S.-L. Spatial analysis of the fishing behaviour of tuna purse seiners in the western and central Pacific based on vessel trajectory data. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.M.; Sunny, E.T.; Simon, J.; Paul, D.E.; Carla, A.H. Estimating high resolution trawl fishing effort from satellite-based vessel monitoring system data. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2006, 64, 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Peel, D.; Good, N.M. A hidden markov model approach for determining vessel activity from vessel monitoring system data. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 68, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, S.; Burgos, J.M.; Gerlotto, F. Lévy trajectories of Peruvian purse-seiners as an indicator of the spatial distribution of anchovy (Engraulis ringens). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; South, A.B.; Jennings, S. Developing reliable, repeatable and accessible methods to provide high-resolution estimates of fishing effort distributions from vessel monitoring system (VMS) data. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustinato, B.; Marie, P.E.; Jérôme, G.S. Estimating fishing effort in small-scale fisheries using GPS tracking data and random forests. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107321. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.L.; Zhang, S.M.; Zhou, W.F.; Cui, X.S.; Zhang, B.B.; Fan, W. Calculating the fishing effort of longline fishing vessel in the western and central pacific ocean using AIS. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 198–203. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Y. Research on the Behavior Identification Method of Fishing Vessels Based on Deep Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- David, A.K.; Juan, K.; Timothy, H. Tracking the global footprint of fisheries. Science 2018, 359, 904–908. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Mao, M.; Xia, M. Dynamics of wave generation and dissipation processes during cold were events in the Bohai Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 280, 108161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J. Assessing the need for the designation of the Yellow Sea Particularly Sensitive Sea Area (PSSA). Mar. Policy 2022, 137, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wu, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z. Mapping coastal fishing grounds and assessing the effectiveness of fishery regulation measures with AIS data: A case study of the sea area around the Bohai Strait, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 223, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.L.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.F.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.D.; Ye, Q.W.; Liu, T.Y. LightGBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, S.C.; Cai, P.X.; Lei, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.R. Information entropy-based differential evolution with extremely randomized trees and LightGBM for protein structural class prediction. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 136, 110064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S. Slime mould algorithm: A new method for stochastic optimization. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 111, 300–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhang, K.F.; Li, Z.B. Mounting Behaviour Recognition for Pigs Based on Deep Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.M.; Cui, X.S.; Wu, Y.M.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, X.; Fan, W. Analyzing space-time characteristics of Xiangshan trawling based on Beidou Vessel Monitoring System Data. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 151–156. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Definition of Some Key Terms [EB/OL]. Fisheries and Aquaculture Department. 1997. Available online: https://www.fao.org/docrep/003/w4230e/w4230e09.htm (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Tiralongo, F.; Messina, G.; Lombardo, B.M. Discards of elasmobranchs in a trammel net fishery targeting cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis Linnaeus, 1758, along the coast of Sicily (central Mediterranean Sea). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 20, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiralongo, F.; Mancini, E.; Ventura, D.; De Malerbe, S.; Paladini De Mendoza, F.; Sardone, M.; Arciprete, R.; Massi, D.; Marcelli, M.; Fiorentino, F.; et al. Commercial catches and discards composition in the central Tyrrhenian Sea: A multispecies quantitative and qualitative analysis from shallow and deep bottom trawling. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of iterations | 394 | Learning rate | 0.2393 | Max depth | 97 |
| Minimum leaf node instance weight | 82.0298 | Regularization parameters γ | 0.5233 | Regularization parameters λ | 0.3453 |
| Instance sampling rate | 0.2869 | Feature sampling rate | 0.8381 | Number of leaf nodes | 353 |
| Methods | Test Result | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC | MCC | SN | SP | |
| ELM | 0.9417 | 0.8844 | 0.9187 | 0.9652 |
| RF | 0.9821 | 0.9643 | 0.9925 | 0.9723 |
| XGBoost | 0.9820 | 0.9640 | 0.9892 | 0.9752 |
| LightGBM | 0.9811 | 0.9622 | 0.9860 | 0.9766 |
| GA-LightGBM | 0.9809 | 0.9619 | 0.9859 | 0.9763 |
| HHO-LightGBM | 0.9819 | 0.9638 | 0.9879 | 0.9763 |
| SMA-LightGBM | 0.9823 | 0.9646 | 0.9875 | 0.9775 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Lu, F.; Xu, S.; Liu, H.; Xue, M.; Cui, G.; Ma, Z.; Fang, H.; Wang, Y. Estimating Spatiotemporal Fishing Effort of Trawlers with Vessel-Monitoring System Data: A Case Study of the Sea Area of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010064
Li D, Lu F, Xu S, Liu H, Xue M, Cui G, Ma Z, Fang H, Wang Y. Estimating Spatiotemporal Fishing Effort of Trawlers with Vessel-Monitoring System Data: A Case Study of the Sea Area of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(1):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010064
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dan, Feng Lu, Shuo Xu, Huiyuan Liu, Muhan Xue, Guohui Cui, Zhenhua Ma, Hui Fang, and Yu Wang. 2024. "Estimating Spatiotemporal Fishing Effort of Trawlers with Vessel-Monitoring System Data: A Case Study of the Sea Area of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 1: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010064
APA StyleLi, D., Lu, F., Xu, S., Liu, H., Xue, M., Cui, G., Ma, Z., Fang, H., & Wang, Y. (2024). Estimating Spatiotemporal Fishing Effort of Trawlers with Vessel-Monitoring System Data: A Case Study of the Sea Area of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010064








