Using Machine Learning Methodology to Model Nutrient Discharges from Ports: A Case Study of a Fertilizer Terminal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
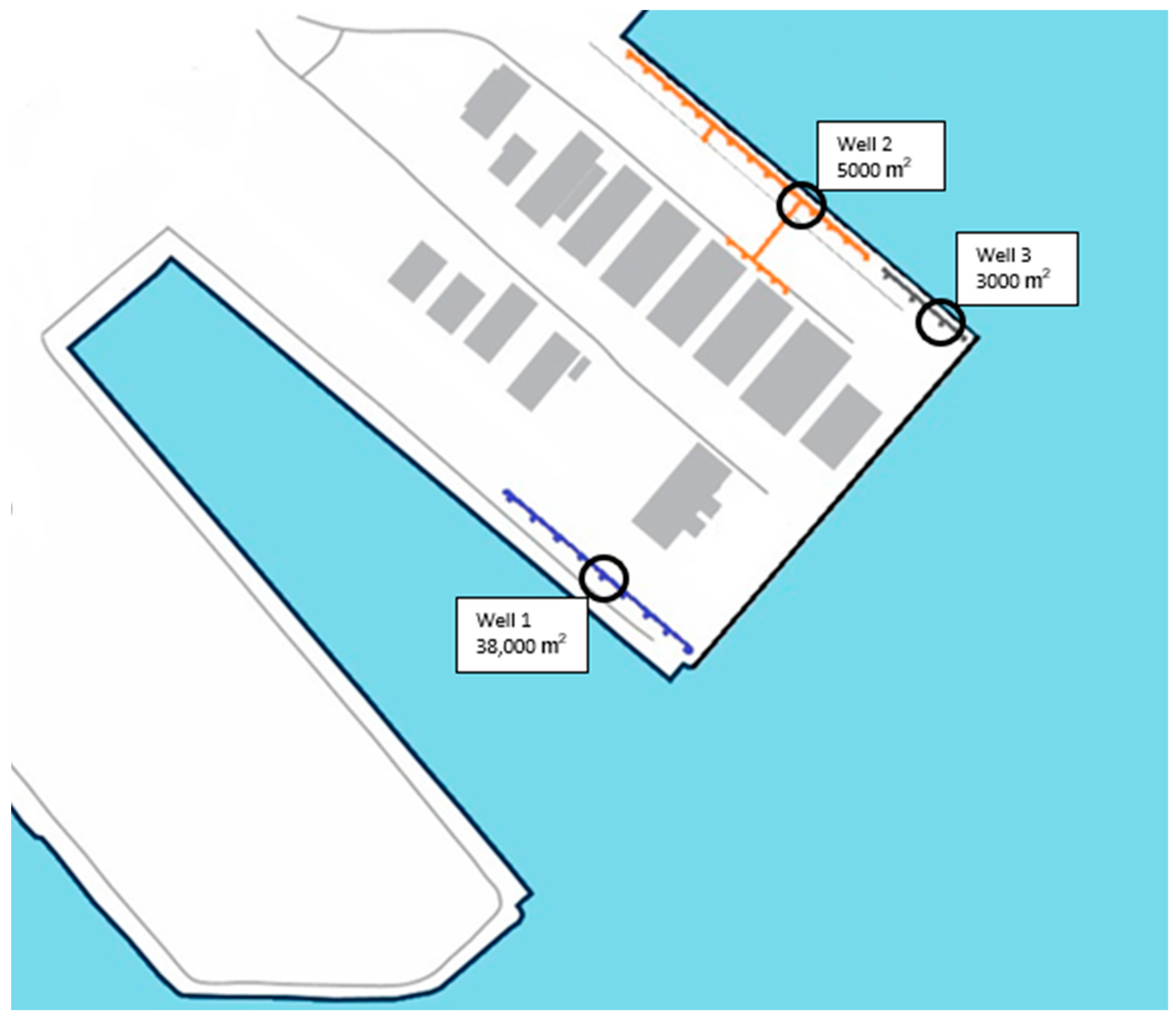
2.1. Field Measurement
2.2. Modeling Nutrient Discharges
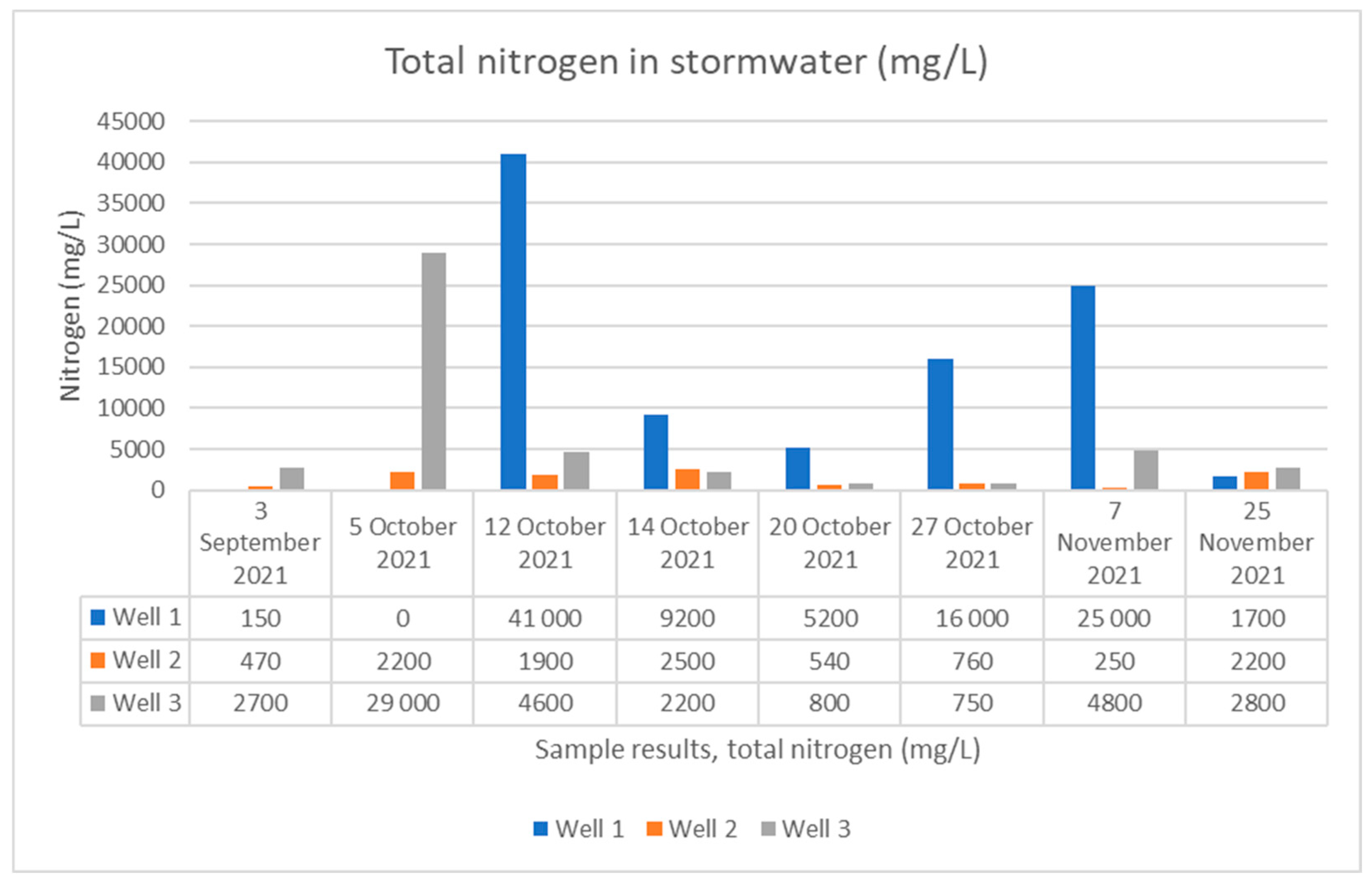
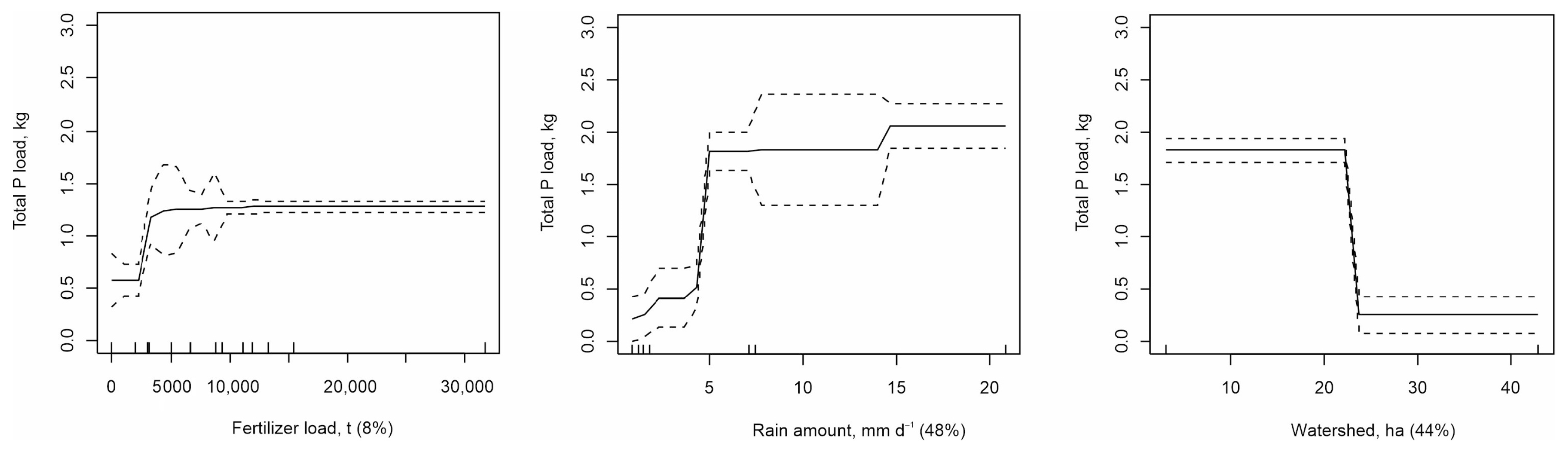
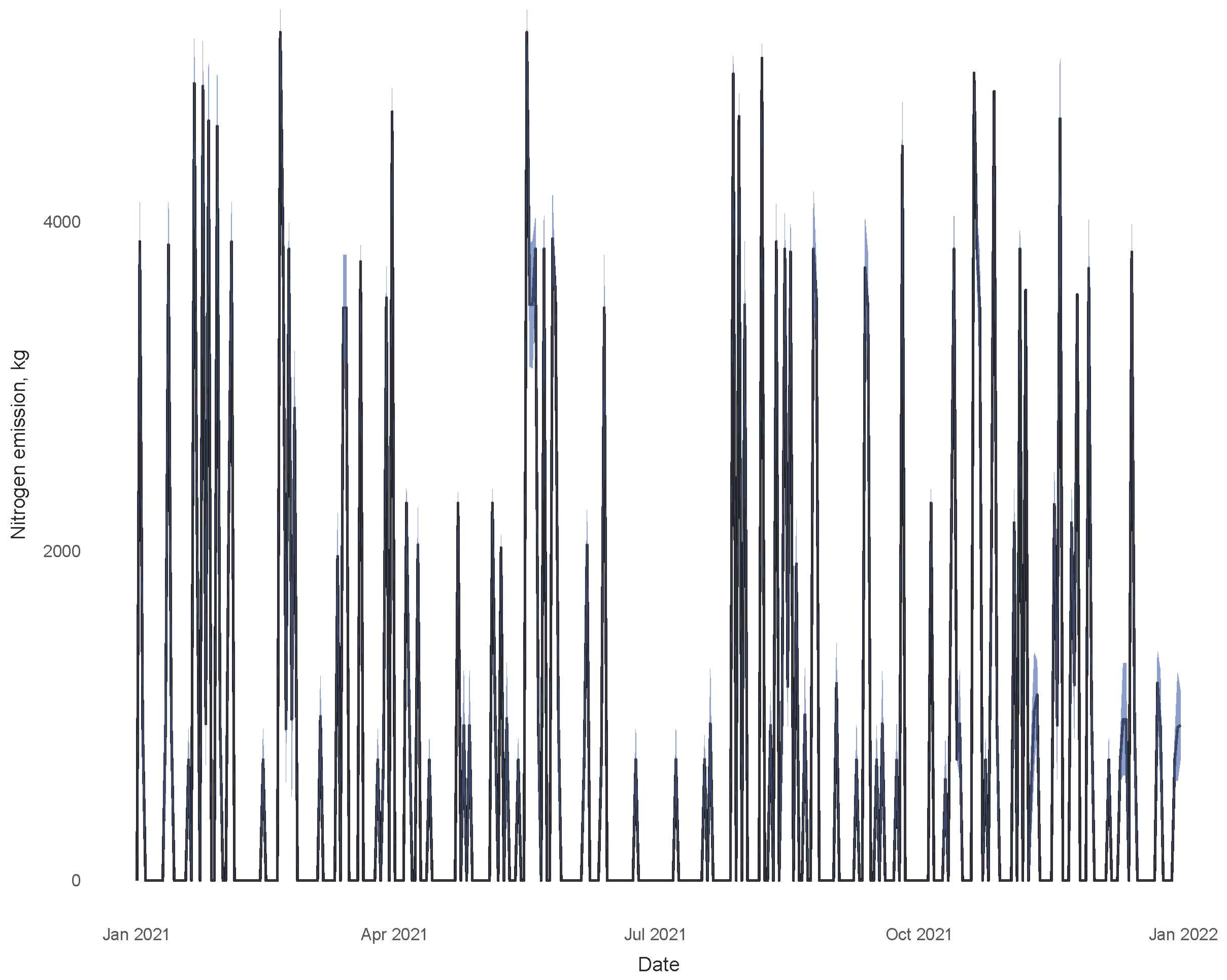
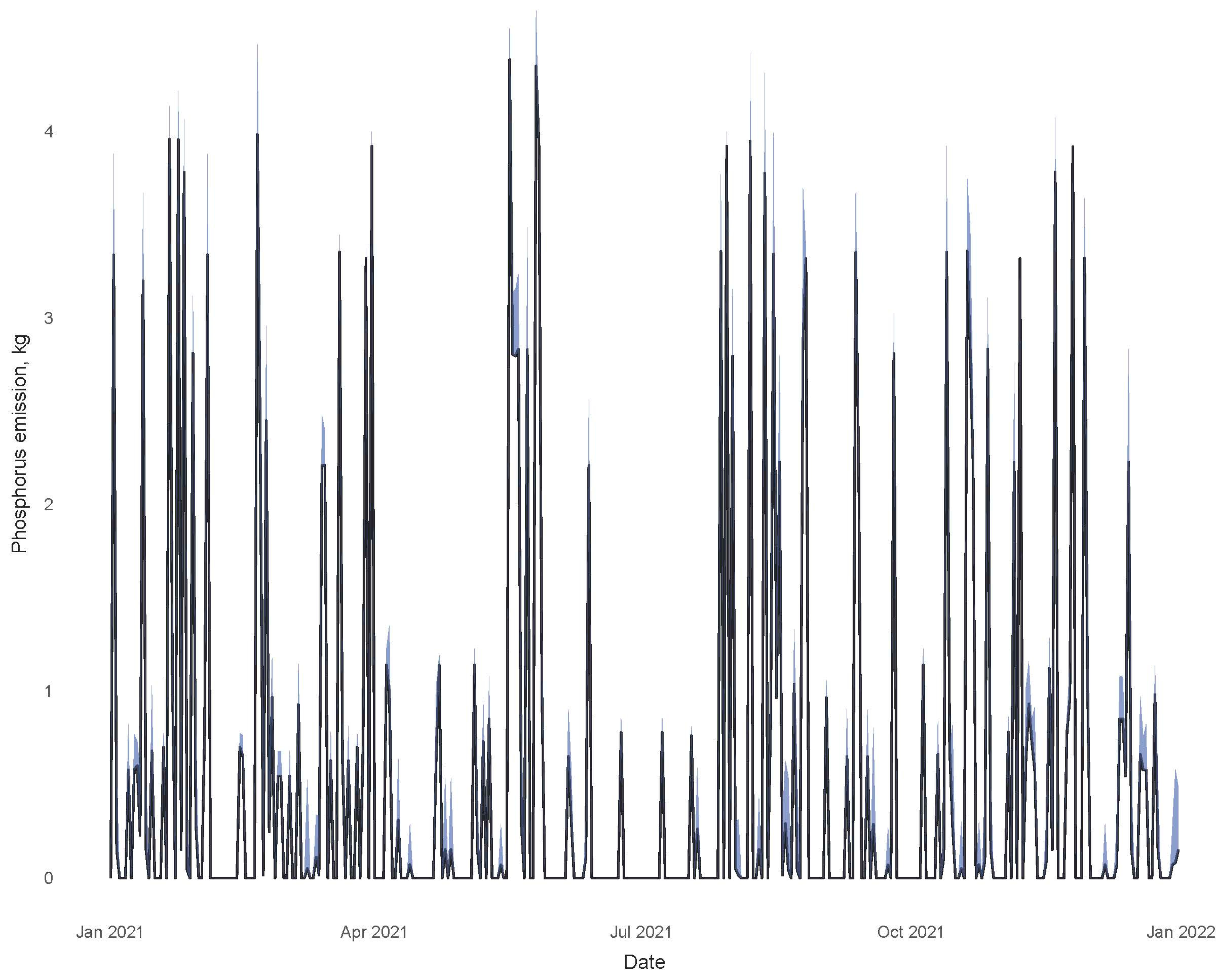
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.; Müller-Karulis, B.; Carstensen, J.; Conley, D.J.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Andersen, J.H. Past, Present and Future Eutrophication Status of the Baltic Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HELCOM. Baltic Sea Action Plan 2021 Update. 2021. Available online: https://helcom.fi/baltic-sea-action-plan/ (accessed on 16 April 2023).
- Raudsepp, U.; Maljutenko, I.; Kõuts, M.; Granhag, L.; Wilewska-Bien, M.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Eriksson, K.M.; Johansson, L.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Karl, M.; et al. Shipborne nutrient dynamics and impact on the eutrophication in the Baltic Sea. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 671, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Environment Agency; European Maritime Safety Agency. European Maritime Transport Environmental Report 2021. Publications Office. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2800/3525 (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Majamäki, E. Discharges to the Sea from Baltic Sea Shipping in 2006–2020; Maritime Working Group Meeting document MARITIME 21-2021 of Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission; Baltic Marine Environment Protection Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2021; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Jalkanen, J.-P.; Johansson, L.; Wilewska-Bien, M.; Granhag, L.; Ytreberg, E.; Eriksson, K.M.; Yngsell, D.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Magnusson, K.; Raudsepp, U.; et al. Modeling of discharges from Baltic Sea shipping. Ocean Sci. 2021, 17, 699–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägerbrand, A.K.; Brutemark, A.; Svedén, J.B.; Gren, I.-M. A review on the environmental impacts of shipping on aquatic and nearshore ecosystems. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 695, 133637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nellesen, T. A Technical Guidance for the Handling of Wastewater in Ports of the Baltic Sea Special Area under MARPOL Annex IV. Helsinki Commission—HELCOM. 2019. Available online: https://helcom.fi/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Technical-guidance-for-the-handling-of-wastewater-in-ports.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Moldanová, J.; Hassellöv, I.-M.; Matthias, V.; Fridell, E.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Ytreberg, E.; Quante, M.; Tröltzsch, J.; Maljutenko, I.; Raudsepp, U.; et al. Framework for the environmental impact assessment of operational shipping. AMBIO 2021, 51, 754–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HELCOM. CCB Draft Report on Potential Sources of Nutrient Inputs: Baltic Sea Ports Handling Fertilizers; Maritime Working Group: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Grote, M.; Mazurek, N.; Gräbsch, C.; Zeilinger, J.; Le Floch, S.; Wahrendorf, D.-S.; Höfer, T. Dry bulk cargo shipping—An overlooked threat to the marine environment? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John Nurminen Foundation. Fertilizer Shipping Project. 2021. Available online: https://johnnurmisensaatio.fi/en/projects/fertilizer-shipping-project/ (accessed on 5 May 2023).
- Act on Environmental Protection 2014/527. Ministry of Justice, Finland. Translations of Finnish Acts and Decrees. 2014. Available online: https://finlex.fi/en/laki/kaannokset/2014/en20140527_20190049.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Regional State Administrative Agency. Environmental Permit. ESAVI/288/04.08/2013. 2015. Available online: https://ylupa.avi.fi/api/v1/documents/attachment/1711630 (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Anttila-Huhtinen, M. Water Monitoring in Kotka Port Areas in 2020. Research Report No. 514/2021; Water and Environment Association of the River Kymijoki: Tampere, Finland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Finnish Meteorological Institute. Annual Rainfall and Intensity of Rain, Hourly Observations Table. 2021. Available online: https://fmiodata-convert-api-prod.out.ocp.fmi.fi/preview/f91e92ca-f928-4fec-9281-8a27f2133010/?locale=fi (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J.H. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; 744p. [Google Scholar]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R.; Hastie, T. A working guide to boosted regression trees. J. Anim. Ecol. 2008, 77, 802–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCluskey, W.J.; Daud, D.Z.; Kamarudin, N. Boosted regression trees: An application for the mass appraisal of residential property in Malaysia. J. Financ. Manag. Prop. Constr. 2014, 19, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO. MARPOL Annex IV. Resolution MEPC.200(62). Special Area Provisions and the Designation of the Baltic Sea as a Special Area. 2011. Available online: https://wwwcdn.imo.org/localresources/en/KnowledgeCentre/IndexofIMOResolutions/MEPCDocuments/MEPC.200(62).pdf (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Holmberg, J. Study of Grey Water Samples from Cargo and Passenger Ships and an Assessment of the Impacts of Wastewater on the Marine Environment. Research Report No. 519/2021; Water and Environment Association of the River Kymijoki: Tampere, Finland, 2021; ISSN 2670-2185. [Google Scholar]
- Kotta, J.; Stechele, B.; Barboza, F.R.; Kaasik, A.; Lavaud, R. Towards environmentally friendly finfish farming: A potential for mussel farms to compensate fish farm effluents. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 60, 1314–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Estonia. Text by Paaver, T. Fisheries and Aquaculture Division. 2023. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/en/countrysector/ee/en?lang=en (accessed on 16 May 2023).
- Coalition Clean Baltic. CCB Report-Concept Best Available Technologies & Techniques: Bulk Fertilizer Handling; Coalition Clean Baltic: Uppsala, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Port of Åhus. Project WISA, Report 3.3. In Interreg South Baltic; European Regional Development Fund: Sydsverige, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lappalainen, S.-T.; Kotta, J.; Tombak, M.-L.; Tapaninen, U. Using Machine Learning Methodology to Model Nutrient Discharges from Ports: A Case Study of a Fertilizer Terminal. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010143
Lappalainen S-T, Kotta J, Tombak M-L, Tapaninen U. Using Machine Learning Methodology to Model Nutrient Discharges from Ports: A Case Study of a Fertilizer Terminal. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2024; 12(1):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010143
Chicago/Turabian StyleLappalainen, Suvi-Tuuli, Jonne Kotta, Mari-Liis Tombak, and Ulla Tapaninen. 2024. "Using Machine Learning Methodology to Model Nutrient Discharges from Ports: A Case Study of a Fertilizer Terminal" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 12, no. 1: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010143
APA StyleLappalainen, S.-T., Kotta, J., Tombak, M.-L., & Tapaninen, U. (2024). Using Machine Learning Methodology to Model Nutrient Discharges from Ports: A Case Study of a Fertilizer Terminal. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 12(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse12010143









