Conceptualizing Aeolian Sediment Transport in a Cellular Automata Model to Simulate the Bio-Geomorphological Evolution of Beach–Dune Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. DuBeVeg Model
2.1.1. Aeolian Module
2.1.2. Hydrodynamic Module
2.1.3. Vegetation Module
2.2. DuBeVeg Adaptation to Represent Saltation
2.3. Model Settings and Test Scenarios
2.3.1. Test Scenarios
2.3.2. Model Parameters
DuBeVeg Default Representation
DuBeVeg Adaptation to Saltation
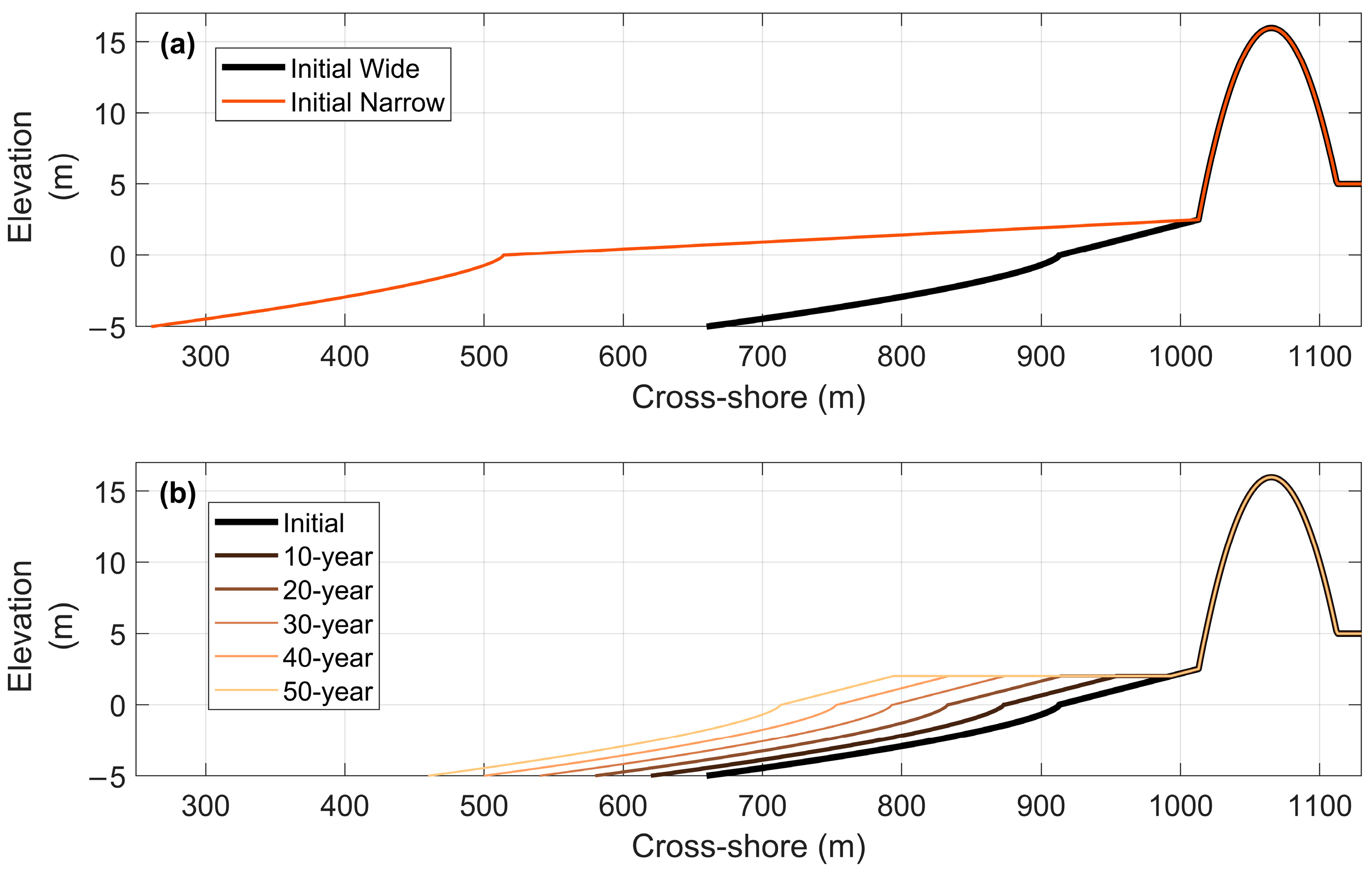
2.3.3. Boundary and Initial Conditions
3. Results
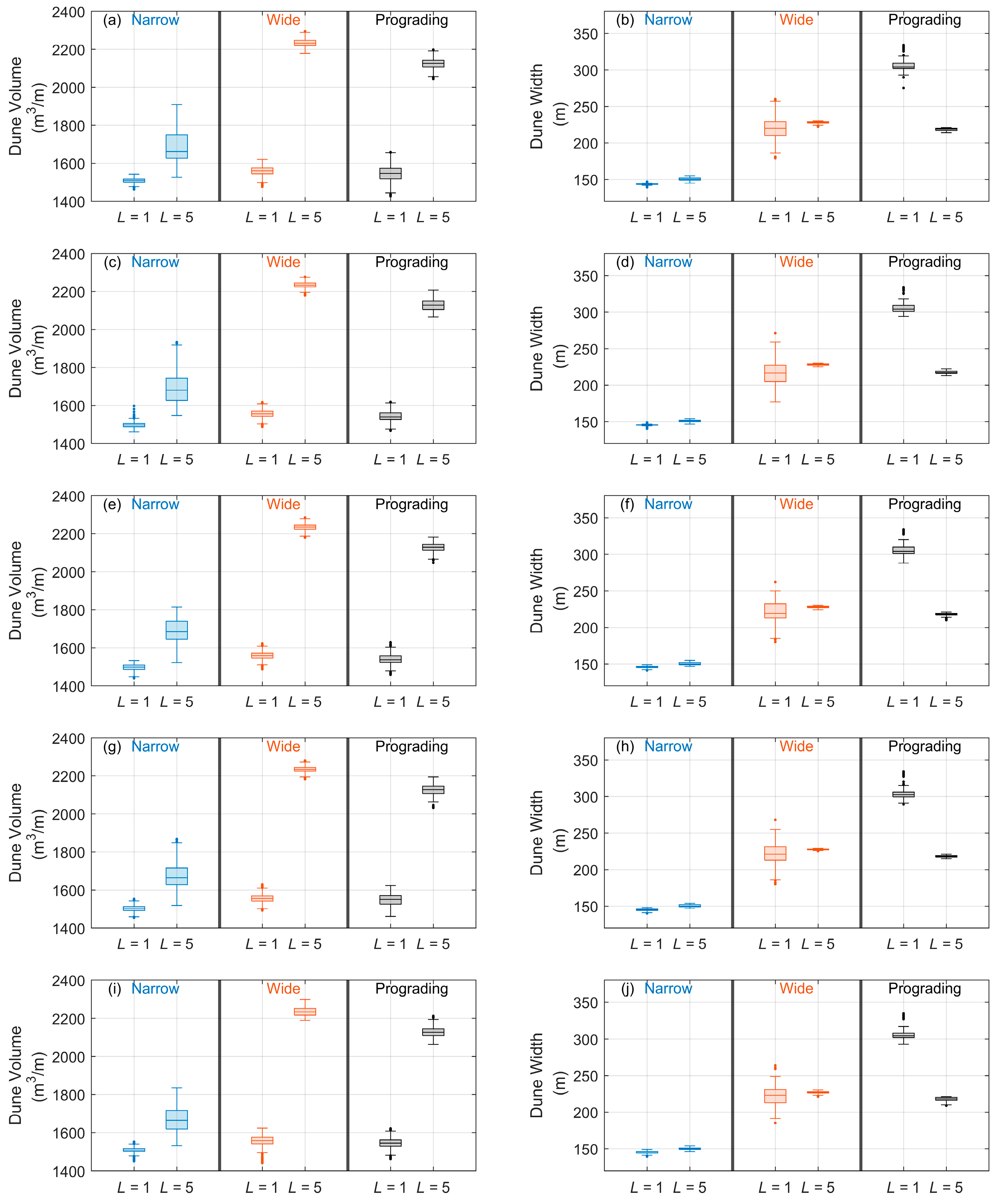
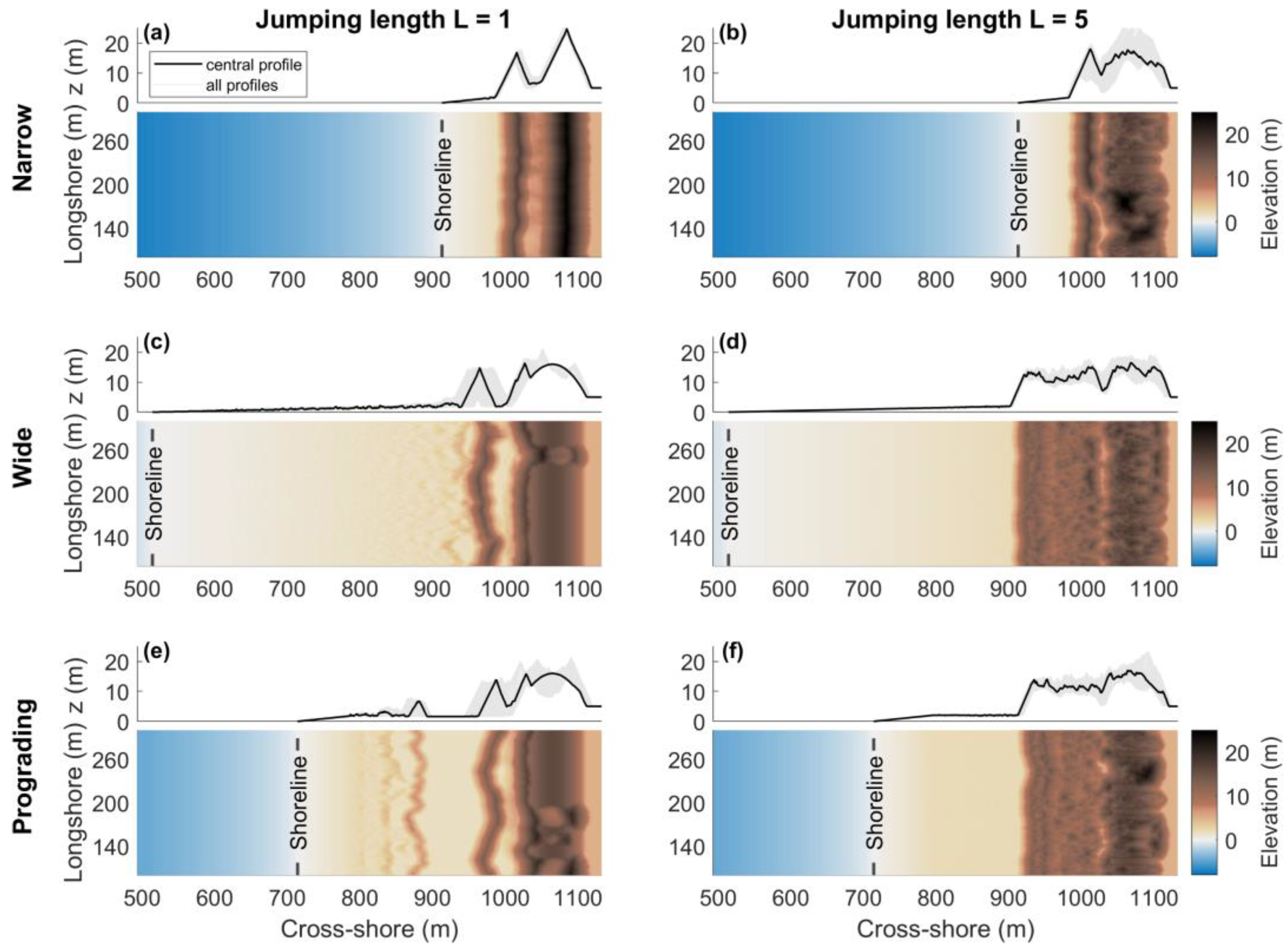
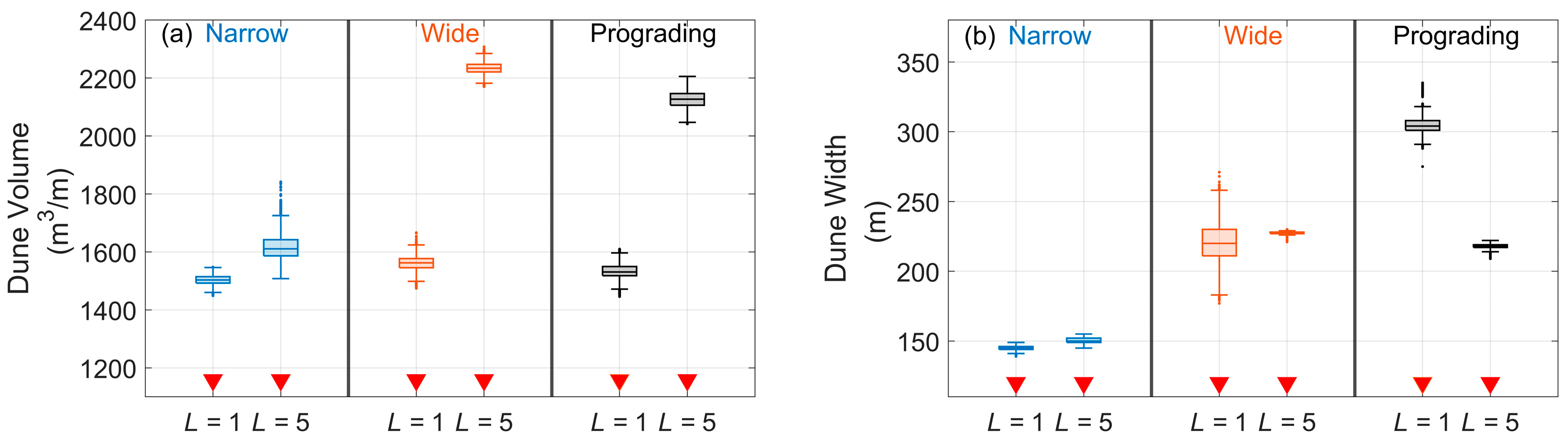
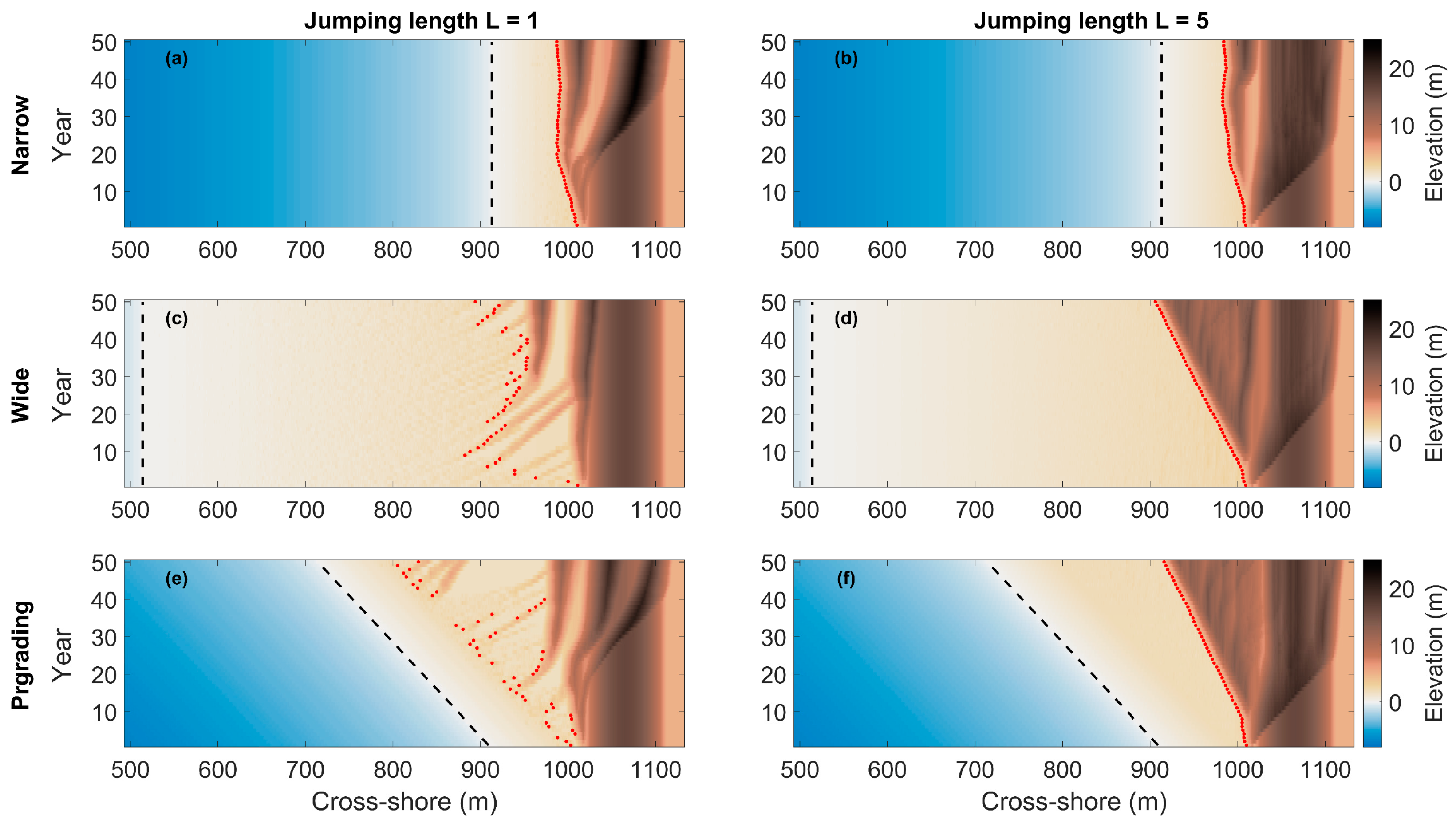
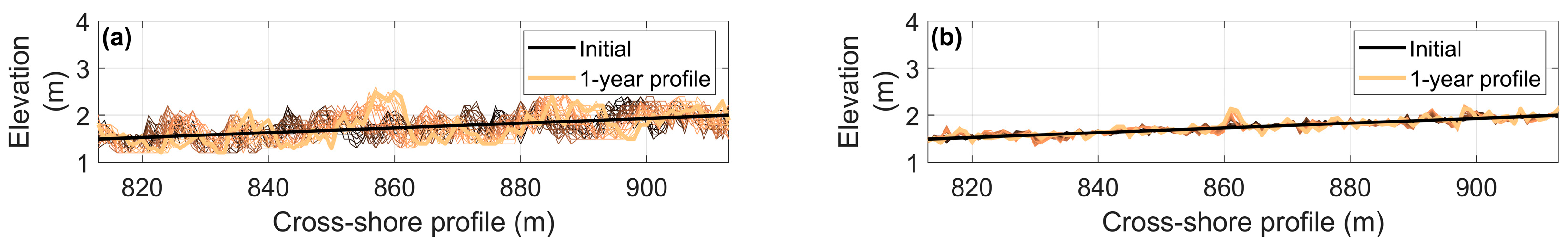
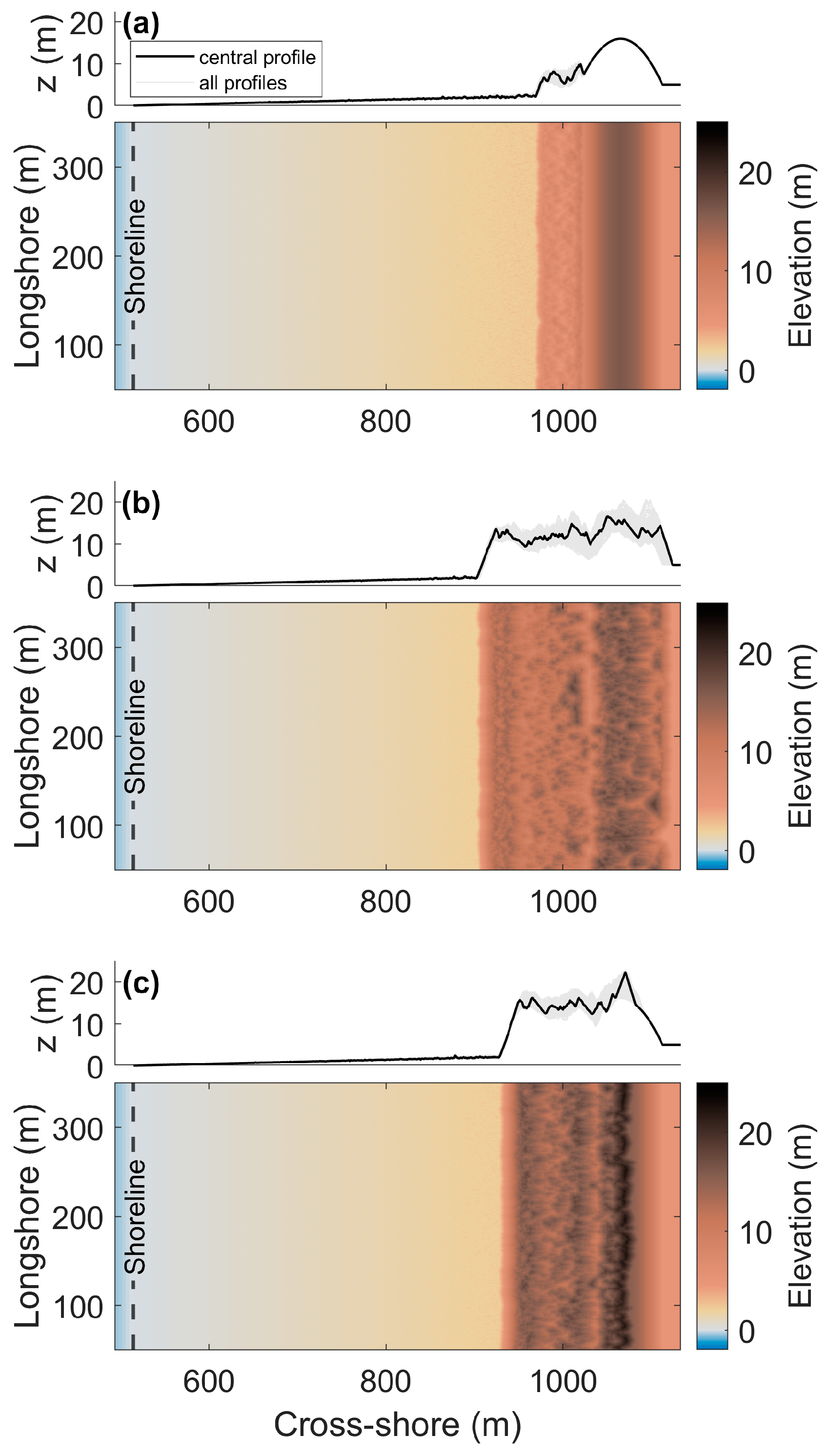
3.1. Foredune Morphology after 50 Years
3.2. Beach–Dune Evolution
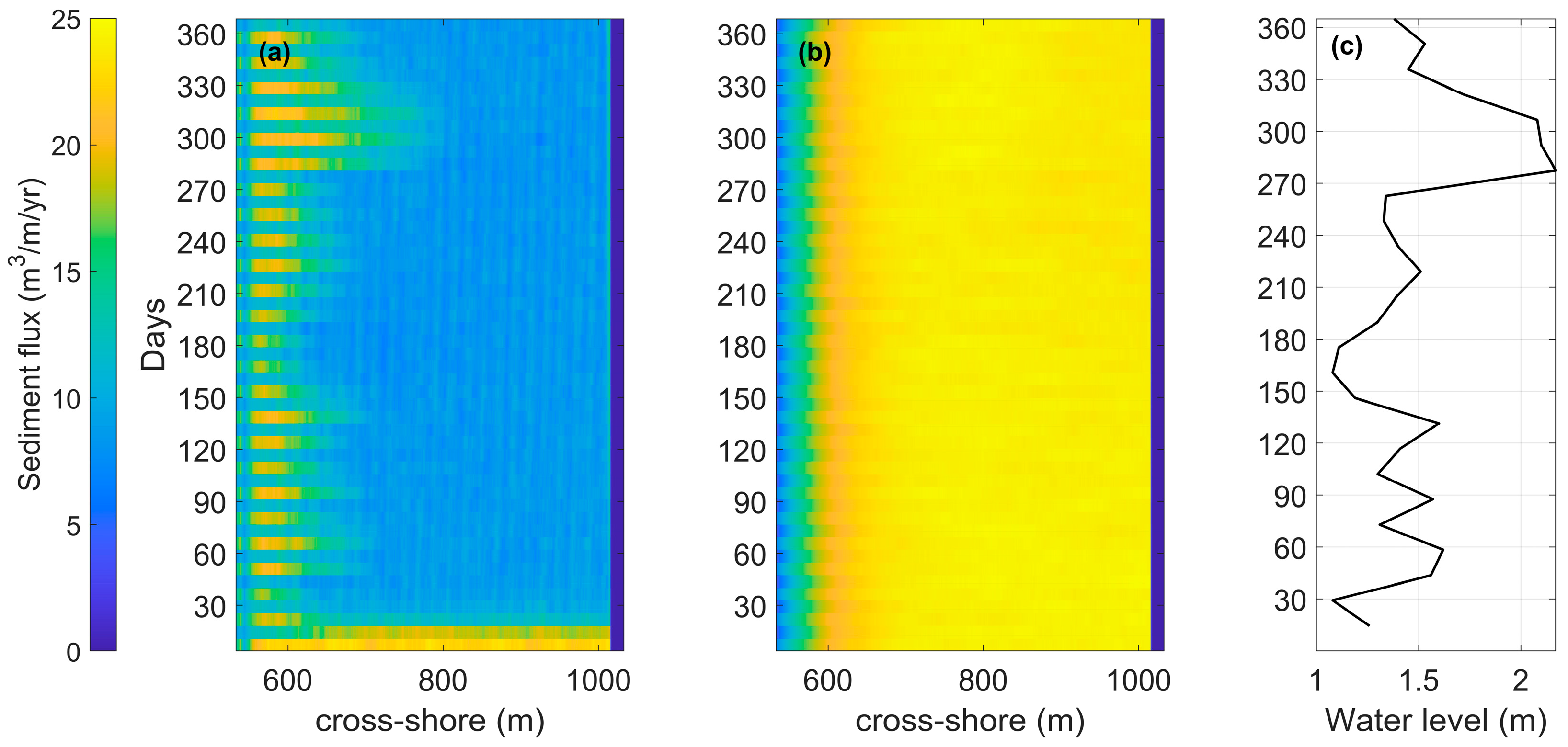
3.2.1. Sediment Flux Evolution
3.2.2. Beach–Dune Dynamics
4. Discussion
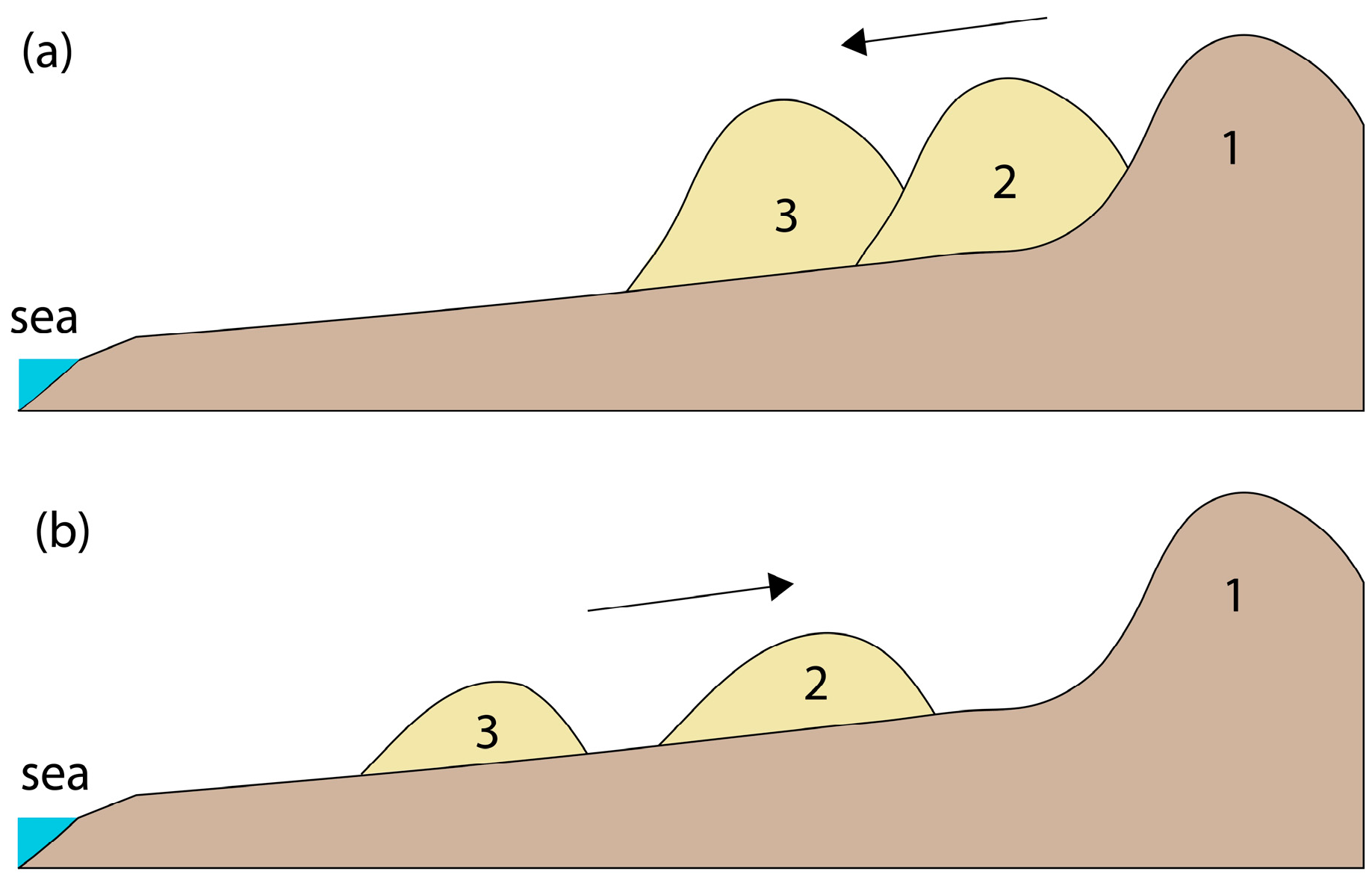
4.1. Beach–Dune Dynamics and Sediment Transport Modes
4.2. Foredune Morphology and Vegetation Effectiveness Limit
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Defeo, O.; McLachlan, A.; Schoeman, D.S.; Schlacher, T.A.; Dugan, J.; Jones, A.; Lastra, M.; Scapini, F. Threats to Sandy Beach Ecosystems: A Review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 81, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Smith, M.D.; Slott, J.M.; Murray, A.B. The Value of Disappearing Beaches: A Hedonic Pricing Model with Endogenous Beach Width. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2011, 61, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, M.E.; Hoggart, S.P.G.; Simmonds, D.J.; Bichot, A.; Colangelo, M.A.; Bozzeda, F.; Heurtefeux, H.; Ondiviela, B.; Ostrowski, R.; Recio, M.; et al. Shifting Sands? Coastal Protection by Sand Banks, Beaches and Dunes. Coast. Eng. 2014, 87, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucrezi, S.; Saayman, M.; Van der Merwe, P. An Assessment Tool for Sandy Beaches: A Case Study for Integrating Beach Description, Human Dimension, and Economic Factors to Identify Priority Management Issues. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 121, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, Y.L.; Osleeb, J.P.; Viola, M.R. Tourism-Generated Earnings in the Coastal Zone: A Regional Analysis. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 20, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.; Hagenaars, G.; Ranasinghe, R.; Baart, F.; Donchyts, G.; Aarninkhof, S. The State of the World’s Beaches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Ranasinghe, R.; Mentaschi, L.; Plomaritis, T.A.; Athanasiou, P.; Luijendijk, A.; Feyen, L. Sandy Coastlines under Threat of Erosion. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2020, 10, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegatte, S.; Green, C.; Nicholls, R.J.; Corfee-Morlot, J. Future Flood Losses in Major Coastal Cities. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkel, J.; Lincke, D.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Perrette, M.; Nicholls, R.J.; Tol, R.S.J.; Marzeion, B.; Fettweis, X.; Ionescu, C.; Levermann, A. Coastal Flood Damage and Adaptation Costs under 21st Century Sea-Level Rise. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3292–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasnoot, M.; Kwadijk, J.; Van Alphen, J.; Le Bars, D.; Van Den Hurk, B.; Diermanse, F.; Van Der Spek, A.; Oude Essink, G.; Delsman, J.; Mens, M. Adaptation to Uncertain Sea-Level Rise; How Uncertainty in Antarctic Mass-Loss Impacts the Coastal Adaptation Strategy of the Netherlands. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 034007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, P.; Fröhle, P. Bridging the Gap between Coastal Engineering and Nature Conservation?: A Review of Coastal Ecosystems as Nature-Based Solutions for Coastal Protection. J. Coast. Conserv. 2022, 26, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, J. Nature-Based Solutions for Coastal Resilience in South Africa. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2023, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manes, S.; Gama-Maia, D.; Vaz, S.; Pires, A.P.F.; Tardin, R.H.; Maricato, G.; Bezerra, D.D.S.; Vale, M.M. Nature as a Solution for Shoreline Protection against Coastal Risks Associated with Ongoing Sea-Level Rise. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 235, 106487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, S.; Meire, P.; Bouma, T.J.; Herman, P.M.J.; Ysebaert, T.; De Vriend, H.J. Ecosystem-Based Coastal Defence in the Face of Global Change. Nature 2013, 504, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keijsers, J.G.S.; Giardino, A.; Poortinga, A.; Mulder, J.P.M.; Riksen, M.J.P.M.; Santinelli, G. Adaptation Strategies to Maintain Dunes as Flexible Coastal Flood Defense in The Netherlands. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2015, 20, 913–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meulen, F.; Ijff, S.; Van Zetten, R. Nature-Based Solutions for Coastal Adaptation Management, Concepts and Scope, an Overview. Nord. J. Bot. 2023, 2023, e03290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiforni-Silva, F.; Wijnberg, K.M.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. On the Relation between Beach-Dune Dynamics and Shoal Attachment Processes: A Case Study in Terschelling (NL). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, F.; Tomasicchio, G.R.; Frega, F.; Leone, E.; Francone, A.; Pantusa, D.; Barbaro, G.; Foti, G. Beach–Dune System Morphodynamics. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psuty, N.P. The Coastal Foredune: A Morphological Basis. Ecol. Stud. 2004, 171, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, A.D.; Hesp, P.A. Wave, Beach and Dune Interactions in Southeastern Australia. Mar. Geol. 1982, 48, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.L.; Nordstrom, K.F. Trends in Research on Beaches and Dunes on Sandy Shores, 1969–2019. Geomorphology 2020, 366, 106737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, I.J.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Bauer, B.O.; Hesp, P.A.; Delgado-Fernandez, I.; Ollerhead, J.; Smyth, T.A.G. Scale-Dependent Perspectives on the Geomorphology and Evolution of Beach-Dune Systems. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 220–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, A.C.W. Grains in Motion. In Aeolian Geomorphology: A New Introduction; Livingstone, I., Warren, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 27–60. [Google Scholar]
- Coco, G.; Murray, A.B. Patterns in the Sand: From Forcing Templates to Self-Organization. Geomorphology 2007, 91, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.; Ashton, A.D.; Coco, G. From Cusps to Capes: Self-Organised Shoreline Shapes. In Sandy Beach Morphodynamics; Jackson, D.W.T., Short, A.D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 277–295. ISBN 9780081029275. [Google Scholar]
- Castelle, B.; Coco, G. The Morphodynamics of Rip Channels on Embayed Beaches. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 43, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.J.; Floc’h, F.; Almeida, L.P.M.; Almar, R.; Jaud, M. Morphodynamic Modelling of Beach Cusp Formation: The Role of Wave Forcing and Sediment Composition. Geomorphology 2021, 389, 107798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocurek, G.; Ewing, R.C. Aeolian Dune Field Self-Organization—Implications for the Formation of Simple versus Complex Dune-Field Patterns. Geomorphology 2005, 72, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Su, Y.; He, N.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Experimental Study on the Stable Morphology and Self-Attraction Effect of Subaqueous Barchan Dunes. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agredano, R.; Cienfuegos, R.; Catalán, P.; Mignot, E.; Bonneton, P.; Bonneton, N.; Martínez, C. Morphological Changes in a Cuspate Sandy Beach under Persistent High-Energy Swells: Reñaca Beach (Chile). Mar. Geol. 2019, 417, 105988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrineau, P.; Tchakerian, V.P. Geomorphology and Dynamics of a Coastal Transgressive Dune System, Central California. Phys. Geogr. 2022, 43, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuber, A.; Álvarez, M.C.; Mendoza, E.; Díaz-Flores, M.Á.; Galicia-Pérez, M.; Torres-Orozco, E. Monitoring Beach Shape Development and Sediment Dynamics on a Sandy Beach with Low Anthropogenic Influence. Land 2022, 11, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, B.T. Eolian Dunes: Computer Simulations and Attractor Interpretation. Geology 1995, 23, 1107–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawardena, Y.; Ilic, S.; Southgate, H.N.; Pinkerton, H. Analysis of the Spatio-Temporal Behaviour of Beach Morphology at Duck Using Fractal Methods. Mar. Geol. 2008, 252, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonstad, M.A. Cellular Automata in Geomorphology. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Shroder, J.F., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego CA, USA, 2013; pp. 117–134. ISBN 9780080885223. [Google Scholar]
- Barrio-Parra, F.; Rodríguez-Santalla, I. Cellular Automata to Understand the Behaviour of Beach-Dune Systems: Application to El Fangar Spit Active Dune System (Ebro Delta, Spain). Comput. Geosci. 2016, 93, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchyn, T.E.; Hugenholtz, C.H. A New Tool for Modeling Dune Field Evolution Based on an Accessible, GUI Version of the Werner Dune Model. Geomorphology 2012, 138, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sherman, D.J.; Li, B. Aeolian Creep Transport: A Review. Aeolian Res. 2021, 51, 100711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Schneider, R.; Kolb, J.; Teichmann, T.; Dudzinska-Nowak, J.; Harff, J.; Hanebuth, T.J.J. Land-Sea Interaction and Morphogenesis of Coastal Foredunes—A Modeling Case Study from the Southern Baltic Sea Coast. Coast. Eng. 2015, 99, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozier, O.; Narteau, C. A Real-Space Cellular Automaton Laboratory. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2014, 39, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, A.; Kikuchi, M.; Nishimori, H.; Endo, N.; Taniguchi, K. Cellular Model for Sand Dunes with Saltation, Avalanche and Strong Erosion: Collisional Simulation of Barchans. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2011, 36, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.; Burrough, S.; Wiggs, G.; Hills, T.; Thomas, D.; Moseki, M. Uneven Surface Moisture as a Driver of Dune Formation on Ephemeral Lake Beds under Conditions Similar to the Present Day: A Model-Based Assessment from the Makgadikgadi Basin, Northern Botswana. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2021, 46, 3078–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadal, C.; Narteau, C.; du Pont, S.C.; Rozier, O.; Claudin, P. Periodicity in Fields of Elongating Dunes. Geology 2020, 48, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayaud, J.R.; Bailey, R.M.; Wiggs, G.F.S. A Coupled Vegetation/Sediment Transport Model for Dryland Environments. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 875–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nield, J.M.; Baas, A.C.W. Investigating Parabolic and Nebkha Dune Formation Using a Cellular Automaton Modelling Approach. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2007, 33, 724–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keijsers, J.G.S.; De Groot, A.V.; Riksen, M.J.P.M. Modeling the Biogeomorphic Evolution of Coastal Dunes in Response to Climate Change. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2016, 121, 1161–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiforni-Silva, F.; Wijnberg, K.M.; de Groot, A.V.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. The Effects of Beach Width Variability on Coastal Dune Development at Decadal Scales. Geomorphology 2019, 329, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiforni-Silva, F.; Wijnberg, K.M.; de Groot, A.V.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. The Influence of Groundwater Depth on Coastal Dune Development at Sand Flats Close to Inlets. Ocean Dyn. 2018, 68, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppema, D.W.; Baas, A.C.W.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H.; Wijnberg, K.M. Cellular Automaton Modelling of the Effects of Buildings on Aeolian Bedform Dynamics. Aeolian Res. 2022, 59, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockdon, H.F.; Holman, R.A.; Howd, P.A.; Sallenger, A.H. Empirical Parameterization of Setup, Swash, and Runup. Coast. Eng. 2006, 53, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.G.; Dalrymple, R.A. Coastal Processes with Engineering Applications, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vesterby, H.; Mangor, K.; Refsgaard, A. Modelling Groundwater Flow in Beach Profiles for Optimising Stabilising Measures. In Proceedings of the International Coastal Symposium, Rotorua, New Zealand, 24–28 April 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nield, J.M.; Baas, A.C.W. The Influence of Different Environmental and Climatic Conditions on Vegetated Aeolian Dune Landscape Development and Response. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 64, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baas, A.C.W. Chaos, Fractals and Self-Organization in Coastal Geomorphology: Simulating Dune Landscapes in Vegetated Environments. Geomorphology 2002, 48, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, H. Genesis-A Generalized Shoreline Change Numerical. J. Coast. Res. 1989, 5, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Arens, S.M.; Wiersma, J. The Dutch Foredunes: Inventory and Classification. J. Coast. Res. 1994, 10, 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- Hesp, P.A. Foredunes and Blowouts: Initiation, Geomorphology and Dynamics. Geomorphology 2002, 48, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, P.A.; Arens, S.M. Crescentic Dunes at Schiermonnikoog, The Netherlands. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1997, 22, 785–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, P.; Nield, J.M.; Wiggs, G.F.S.; Baddock, M.C.; Bristow, N.R.; Best, J.L.; Christensen, K.T.; Claudin, P. Field Evidence for the Initiation of Isolated Aeolian Sand Patches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2022GL101553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddock, M.C.; Nield, J.M.; Wiggs, G.F.S. Early-Stage Aeolian Protodunes: Bedform Development and Sand Transport Dynamics. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montreuil, A.L.; Moelans, R.; Houthuys, R.; Bogaert, P.; Chen, M. Characterization of Intertidal Bar Morphodynamics Using a Bi-Annual Lidar Dataset. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D.; Yang, Y.; Ollerhead, J.; Hesp, P.A.; Walker, I.J. The Effects of Surface Moisture on Aeolian Sediment Transport Threshold and Mass Flux on a Beach. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2008, 33, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southgate, H.N. Data-Based Yearly Forecasting of Beach Volumes along the Dutch North Sea Coast. Coast. Eng. 2011, 58, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, A.; Diamantidou, E.; Pearson, S.; Santinelli, G.; den Heijer, K. A Regional Application of Bayesian Modeling for Coastal Erosion and Sand Nourishment Management. Water 2019, 11, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rader, A.M.; Pickart, A.J.; Walker, I.J.; Hesp, P.A.; Bauer, B.O. Foredune Morphodynamics and Sediment Budgets at Seasonal to Decadal Scales: Humboldt Bay National Wildlife Refuge, California, USA. Geomorphology 2018, 318, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.B.; Short, A.D.; Ruggiero, P.; Woodroffe, C.D. Interdecadal Foredune Changes along the Southeast Australian Coastline: 1942–2014. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, P.A. A 34 Year Record of Foredune Evolution, Dark Point, NSW, Australia. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 65, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.L.; Nordstrom, K.F. Aeolian Sediment Transport and Landforms in Managed Coastal Systems: A Review. Aeolian Res. 2011, 3, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshianlamouki, E.; Augstijn, E.; Brugnach, M.; Voinov, A.; Wijnberg, K.M. A Particpiatory Modelling Approach to Cognitive Mapping of the Socio-Environmanental System of Sandy Anthropogenic Shores in the Netherlands. Soc. Sci. Res. Netw. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickling, W.G.; Davidson-Arnott, R.G.D. Aeolian Sediment Transport on Beaches and Coastal Sand Dunes. In Proceedings of the Canadian Symposium on Coastal Sand Dunes, Guelph, ON, Canada; 1990; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Arens, S.M.; Mulder, J.P.M.; Slings, Q.L.; Geelen, L.H.W.T.; Damsma, P. Dynamic Dune Management, Integrating Objectives of Nature Development and Coastal Safety: Examples from the Netherlands. Geomorphology 2013, 199, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arens, S.M.; Baas, A.C.W.; Van Boxel, J.H.; Kalkman, C. Influence of Reed Stem Density on Foredune Development. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2001, 26, 1161–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, Y.; Mochizuki, N.; Nakashima, T. Influence of Vegetation on Aeolian Sand Transport Rate from a Backshore to a Foredune at Hasaki, Japan. Sedimentology 2005, 52, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Unit | Default Representation | Adaptation to Saltation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell width and length | m | 1 | 1 |
| Cell height (h) | m | 0.1 | 0.02 |
| Jumping length (L) | m | 1 | 5 |
| - | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| - | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| Shadow angle | Degrees | 15 | 15 |
| Angle of repose, bare cells | Degrees | 30 | 30 |
| Angle of repose, vegetated cells | Degrees | 35 | 35 |
| - | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| - | 0.012 | 0.012 | |
| - | 0 | 0 | |
| - | 1 | 1 | |
| - | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
| - | - | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teixeira, M.; Horstman, E.M.; Wijnberg, K.M. Conceptualizing Aeolian Sediment Transport in a Cellular Automata Model to Simulate the Bio-Geomorphological Evolution of Beach–Dune Systems. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071278
Teixeira M, Horstman EM, Wijnberg KM. Conceptualizing Aeolian Sediment Transport in a Cellular Automata Model to Simulate the Bio-Geomorphological Evolution of Beach–Dune Systems. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(7):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071278
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeixeira, Manuel, Erik M. Horstman, and Kathelijne M. Wijnberg. 2023. "Conceptualizing Aeolian Sediment Transport in a Cellular Automata Model to Simulate the Bio-Geomorphological Evolution of Beach–Dune Systems" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 7: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071278
APA StyleTeixeira, M., Horstman, E. M., & Wijnberg, K. M. (2023). Conceptualizing Aeolian Sediment Transport in a Cellular Automata Model to Simulate the Bio-Geomorphological Evolution of Beach–Dune Systems. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(7), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11071278







