Abstract
During scientific expeditions in Indonesia and Vietnam, several sponge specimens belonging to the genus Cladocroce were collected. The integration of morphological and molecular analyses, incorporating species delimitation models (ABGD, ASAP, and bPTP) and phylogenetic approaches using three molecular markers (COI, 28S, and 18S–ITS1–5.8S–ITS2–28S), allowed us to discriminate three congeneric species. Two of these species (C. burapha and C. pansinii sp. nov.) were supported by morphological and molecular data, whereas a third species (C. lamellata sp. nov.) was delimited by morphological data only. We formally describe two new species, C. pansinii sp. nov. and C. lamellata sp. nov. C. aculeata is a newly recorded species for Indonesia and the first documented finding after the original description. The re-examination of the type material of C. burapha, and indirectly the molecular approach, allowed us to confirm that C. burapha lives in sympatry with C. pansinii sp. nov. in Vietnam and with C. lamellata in Indonesia. Thanks to these findings, we relocated the paratype of C. burapha to the new species described here, i.e., C. pansinii sp. nov.
1. Introduction
Genus Cladocroce Topsent, 1892, belongs to the family Chalinidae Gray, 1867 (ord. Haplosclerida Topsent, 1928), and its distinctive characteristic is the presence of multispicular ascending tracts within a subisotropic reticulation of oxeas [1]. The genus comprises species mostly typical of deep water [2]. At present, out of the 19 recognized species [3], 8 eight are found in tropical areas all around the world, and only five of these have been recorded in shallow waters [4]. Among these tropical shallow representatives, C. burapha Putchakarn, de Weerdt, Sonchaeng & van Soest, 2004, may be found in brackish environments with fluctuant periods of lower salinity such as coastal lagoons and mangroves [5], while the others are related to coral reefs and rocky substrates (e.g., [4,6,7]).
Surveys conducted in Ha Long Bay (Vietnam) (see [8,9]) and North Sulawesi (Indonesia) (see [5]) allowed us to collect several samples of Cladocroce, some of them ascribed to two new species, which are described here. Moreover, C. aculeata Pulitzer-Finali, 1982, is a new record for Indonesia and the first documented finding after the original description.
Integrative taxonomy approaches [10], based on DNA barcoding combined with morphological characterizations, were applied to shed light on the relationship between putative Cladocroce species, very closely aligned with C. burapha, living in sympatry in Vietnamese marine lake systems and Indonesian coastal reef and mangrove environments. Investigations based on morphological and molecular evidence, conducted on C. burapha (holotype and paratype) reference material, together with recent specimens from Hawai’i (USA) [7,11,12] and newly collected samples unveiled conspecificity discrepancies between C. burapha’s holotype and paratype with consequent proposed taxonomical changes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sponge Sample Collection
The specimens studied here were sampled from the Indonesian Archipelago and in Vietnam (Figure 1). The Indonesian samples were collected in the frame of a cooperation agreement between Sam Ratulangi University (Indonesia) and the Polytechnic University of Marche (Italy) at Bunaken National Park (North Sulawesi) (see [13] for site descriptions) in the period 2005–2008 and on Bangka Island (North Sulawesi) in 2011 (see [5]).
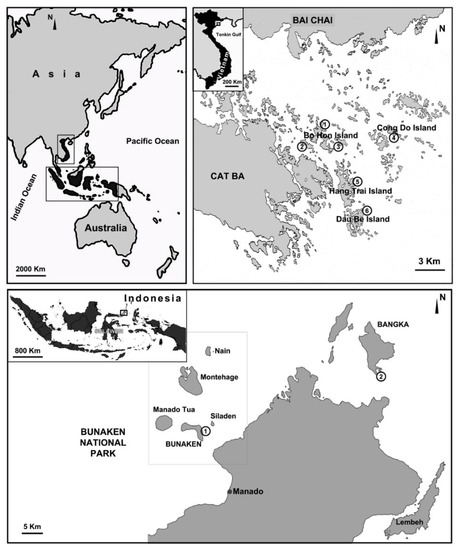
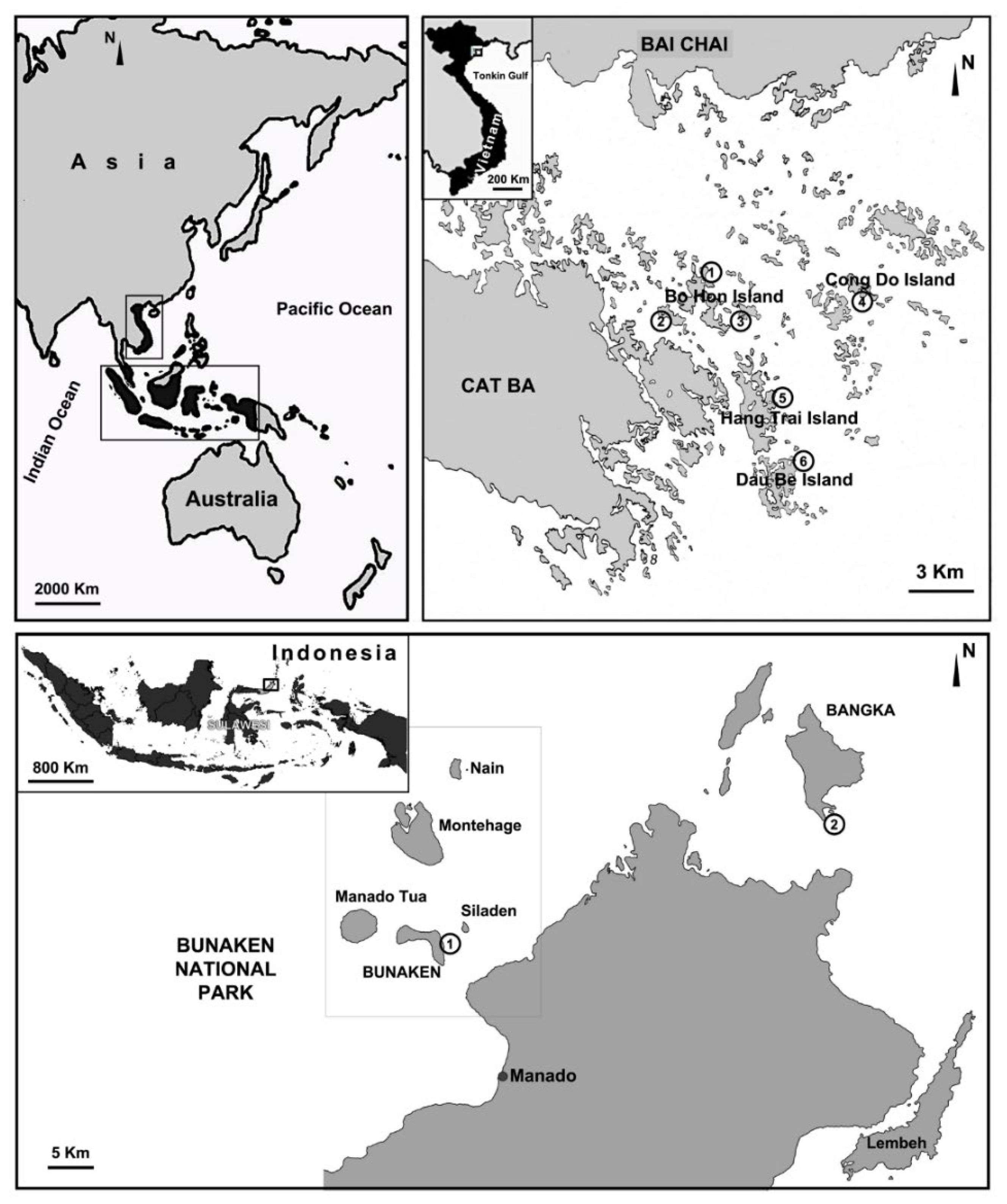
Figure 1.
Map of the sampled stations in North Sulawesi (Indonesia) and Ha Long Bay (Vietnam). Ha Long Bay (Vietnam), four island groups (Bo Hon, Hang Trai, Dau Be, Cong Do) with six sampling stations: (1) Hang Luong Lake; (2) Me Cung Lake; (3) Bui Xam Lake; (4) Hang Toi Dark Cave; (5) Hang Du I Lake; (6) Coastal Site II. North Sulawesi (Indonesia), two sampling stations: (1) Timur (Bunaken Island); (2) Thangiung Husi (Bangka).
The Vietnamese samples were collected in Ha Long Bay (North Vietnam) along the coastal areas and in marine karst lakes during field campaigns performed in April 2003, September 2003, April 2004, and August 2018, as a cooperative affiliation between the Polytechnic University of Marche, the University of Genova, and the Institute of Marine Environment and Resources (IMER) for the study of biodiversity and conservation in coastal areas of Vietnam (see [8,9] for site descriptions). All samples were collected by scuba diving from a 0–40 m depth and were fixed in 70% or 100% ethanol.
2.2. Morphological Characterization
The spicule complement and skeletal architecture were examined under light and scanning electron microscope (SEM); spicule preparations and hand-cut sections of sponge portions were performed following the methodologies in Núñez-Pons et al. [14]. For each spicule type, measurements were obtained from 30 spicules and are reported as the range of the smallest length–(mean ± standard deviation)–largest length × smallest width–(mean ± standard deviation)–largest width. For SEM analyses, dissociated spicules were transferred onto stubs and sputter coated with gold. SEM preparations were observed under a Philips XL 20 (Polytechnic University of Marche, Ancona, Italy).
The type material was deposited at the Museo Civico di Storia Naturale “G. Doria” of Genova (MSNG).
The reference material used for comparison was obtained from the following institutions: BIMS-I Institute of Marine Science, Burapha University, Thailand; ZMA Zoological Museum Amsterdam, University of Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
2.3. Molecular Investigation
2.3.1. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
The genomic DNA of the sponge samples was purified using the Quick-gDNA Miniprep Kit (ZYMO RESEARCH, Irvine, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s protocols and was stored at −20 °C. Three gene marker regions were targeted. The mitochondrial Cytochrome C Oxidase subunit 1 (COI) was amplified for the standard COI partition (~640 bp) with the universal Folmer [15] dgHCO2198 (5′-GGTCAACAAATCATAAAGAYATYGG-3′) and dgLCO1490 (5′-TAAACTTCAGGGTGACCAAARAAYCA-3′) primers and for the Erpenbeck’s ‘I3-M11’ extension (~560 bp), overlapping ~60 bp with Folmer’s 3′ partition, using the sponge-specific primers PorCOI2fwd (5′-AATATGNGGGCNCCNGGNATNAC-3′) and PorCOI2rev (5′-ACTGCCCCCATNGATAAAACAT-3′) [16]. The nuclear fragment covering 18S-ITS1-5.8S-ITS2-28S—hereinafter, referred to as ITSs (~850 bp)—was amplified with RA2 (5′-ACTGCCCCCATNGATAAAACAT-3′) priming on the 3′ terminus of the 18S small ribosomal subunit and the ITS2.2 primer (5′-CCTGGTTAGTTTCTTTTCCTCCGC-3′) targeting the 5′ terminus of the 28S large ribosomal subunit [17]. The 28S C region was amplified with the primers 28S-C2-fwd (5′-GAAAAGAACTTTGRARAGAGAGT-3′) and (28S-D2-revc 5′-TCCGTGTTT CAAGACGGG-3′), yielding a ~340 bp fragment [18]. PCR amplifications were performed in 25 μL reactions containing 2.5 μL (2 mM) of buffer, 1 μL dNTPs (2 mM), 0.8 μL (20 μg/μL) of BSA, 0.3 μL (5 U/μL) of Roche Taq DNA Polymerase, 0.8 μL (10 mM) of each primer, and 1 μL of template DNA, following a thermocycling profile of 5 min at 95 °C; followed by 35 cycles of 30 s at 94 °C, 45 s at 50–57 °C and 90 s at 72 °C; and a final extension for 10 min at 72 °C. The amplified PCR products were checked in 1% agarose gels under UV light and quantified on NanoDrop® at Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn, Naples, Italy.
Sanger sequencing was performed bi-directionally at Servizio di Biologia Molecolare (RIMAR Dept, Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn, Naples, Italy.) on a Thermo Fisher Scientific 48 capillary ABI 3730xl DNA Analyzer, using 4.5 micromolar of each of the corresponding PCR primer pairs and 15 femtomoles/uL of the DNA template. Chromatograms were visualized, assembled, and corrected on Geneious Prime® 2022.2.2 (http://www.geneious.com) [19], and poriferan origin was checked by BLAST against NCBI GenBank (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/ accessed on 23 October 2022) [20]. Sequences and specimen descriptions were deposited in GenBank (accession numbers: COI entries: OP950351–OP950360; 28S entries: OP955945–OP955951; and ITSs entries: OP955954–OP955959) and Sponge Barcoding Project databases for public access.
2.3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
The resulting sequences from the Folmer and Erpenbeck partitions were concatenated to obtain a final COI fragment of ~1100 bp, which seems to afford better taxonomic resolution in Porifera and other diploblasts [21]. Reference sequences for the three markers, COI, 28S, and ITSs, from sponges in the Genus Cladocroce, along with the outgroup Haliclona (Gellius) cymaeformis (Esper, 1806) in the family Chalinidae were downloaded from GenBank (Table S1) and aligned against our sequences correspondingly for each marker with MAFFT [22] under default settings in Geneious Prime® 2022.2.2 [19]. The alignments were manually trimmed, with COI sequences yielding 1047 base pairs (bp) long, 28S spanning 531 bp, and ITSs 815 bp. COI sequences were checked for stop codons using the translate function (DNA to protein) in Geneious Prime® 2022.2.2 [19]. Alignments of the non-coding genes (28S and ITSs) were curated from blocks of gap positions’ variability on Gblocks 0.91b (http://phylogeny.lirmm.fr/phylo_cgi/one_task.cgi?task_type=gblocks accessed on 23 November 2022), to clean poorly aligned positions and eliminate divergent regions, applying stringent settings [23]. For the 28S, Gblocks did not result in an improvement of the data; hence, the original alignment (531 bp) was used for the phylogeny and species delimitation approaches below. Instead, for ITSs, the best output after Gblocks yielded an alignment of 505 bp, which was used for downstream analyses. All three definitive sequence sets were concatenated, resulting in a 2128 bp-length alignment (28S = 531 bp and COI = 1047 bp, ITSs = 505 bp).
Maximum likelihood (ML) trees were built for each marker separately and for the concatenated alignment (see below) with IQTree with 1500 ultrafast bootstrap replicates [24], under the most-accurate genetic models: TN + F for 28S, HKY + F for COI, and K2P + G4 for ITSs (Gblocks curated spanning 505 nt), according to ModelFinder [25]. Bayesian inference (BI) trees were constructed with MrBayes [26] with the GTR GAMMA model and Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) set for 1,100,000 generations, 4 chains, a 200 generations’ sampling frequency, and 500 burn-in values (Supplementary File S2, Table S3). Phylogenetic analytic tools were run on CIPRES (http://www.phylo.org/ accessed on 25 November 2022) [27], and ML and BI trees were visualized and edited with Figtree (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ accessed on 25 November 2022). Since the representation of all markers was uneven across samples, the trees built with the concatenated data were not used for phylogenetic studies or species delimitation.
2.3.3. Species Delimitation
Species delimitation was calculated on COI, 28S, and curated ITSs data using three methods via web servers: Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery (ABGD), Assemble Species by Automatic Partitioning (ASAP), and Bayesian implementation of the Poisson-Tree-Processes model (bPTP).
ABGD was performed with the Kimura-2 parameter (K2P) and relative gap width (X = 1.5) (www.abi.snv.jussieu.fr/public/abgd/ accessed on 23 November 2022). ABGD calculates the barcode gap by setting a series of prior intraspecific divergences, which are iteratively refined [28].
ASAP was run with Kimura (K80) ts/tv set to 2 (https://bioinfo.mnhn.fr/abi/public/asap/asapweb.html accessed on 23 November 2022). ASAP computes species partitions based on pairwise genetic distances, together with the probability of panmixia (P-val), relative gap width (W), and ranked results by the ASAP score: the lower the score, the better the partitioning is [29]. The outcomes of the number of species predicted by the ASAP 1st and ASAP 2nd scores were selected.
bPTP was fed with ML trees constructed in IQTree and processed for 50 million generations, with a 100 generations’ sampling frequency and 25% burn-in (https://species.h-its.org/ptp/ accessed on 23 November 2022). Speciation events were inferred in PTP using MCMC based on a shift in the number of substitutions between internal nodes [30].
3. Results
Systematics:
- Class Demospongiae Sollas, 1885;
- Order Haplosclerida Topsent, 1928;
- Family Chalinidae Gray, 1867;
- Genus Cladocroce Topsent, 1892;
- Type species: Cladocroce fibrosa Topsent, 1892: 72;
- Cladocroce aculeata Pulitzer-Finali, 1982
(Figure 2).
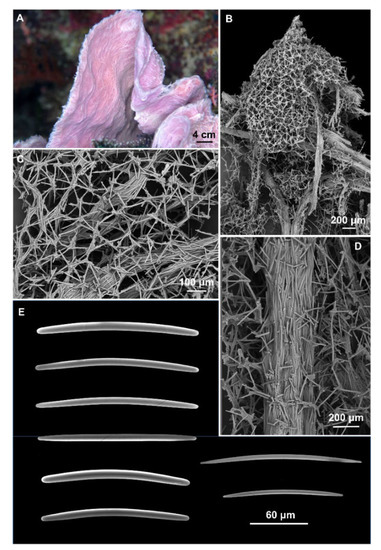
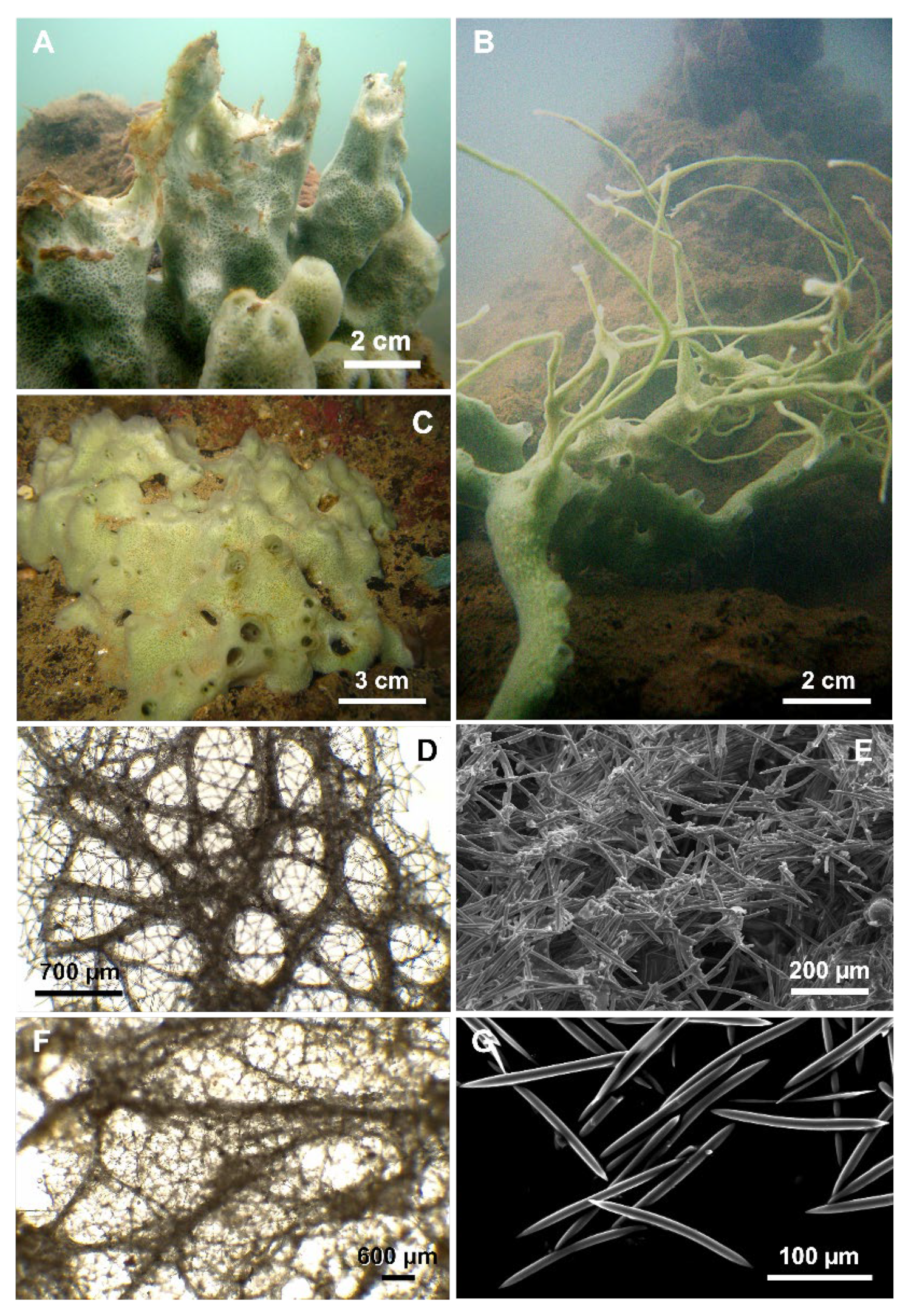
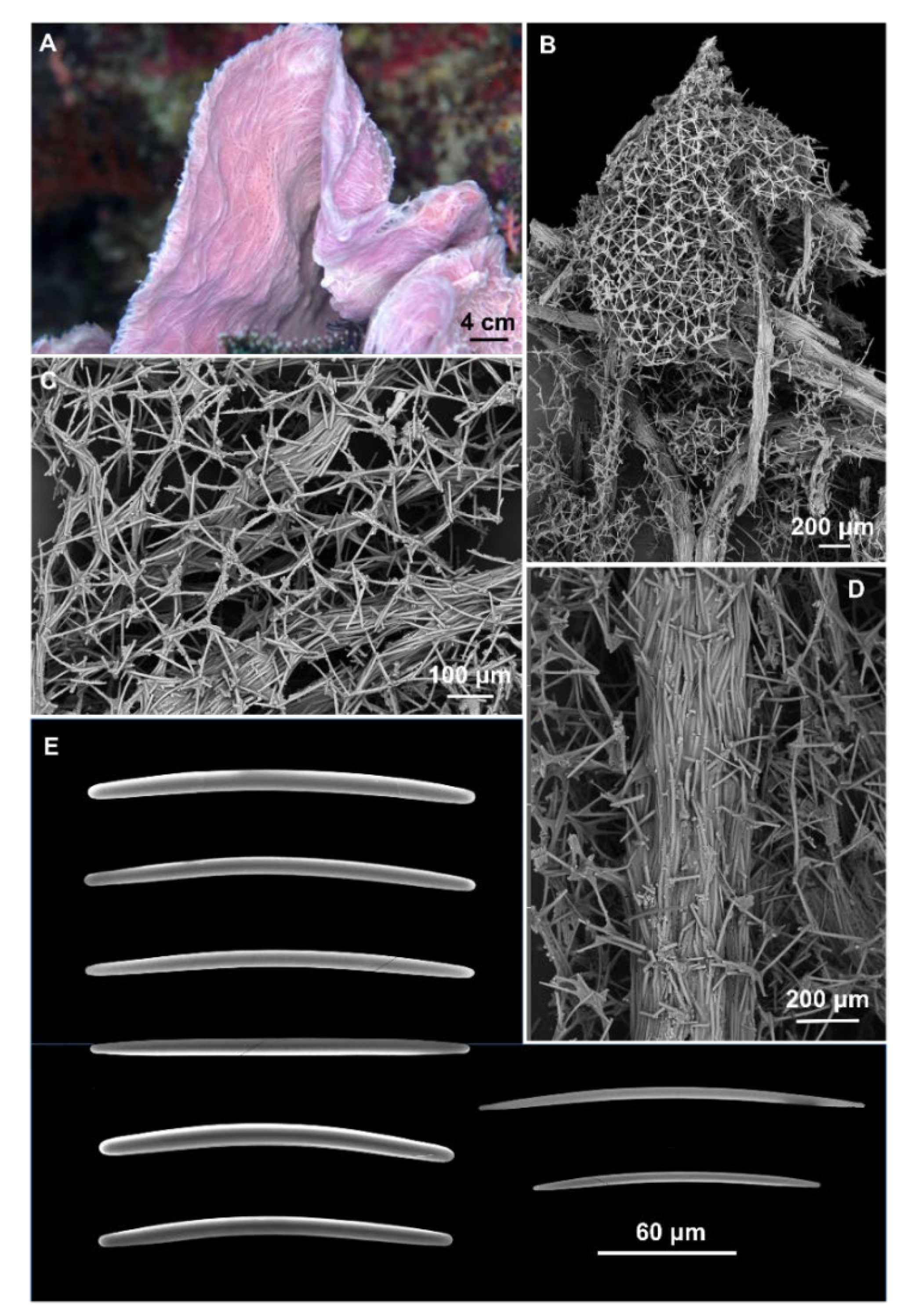
Figure 2.
Cladocroce aculeata Pulitzer-Finali, 1982. (A) sample BUNA 440; (B) ectosomal isodictyal skeleton with ascending fibers creating a conule; (C) ectosomal skeleton; (D) multispicular fiber of the choanosomal skeleton; (E) oxeas.
Material examined: BUNA440, Bunaken, North Sulawesi, Indonesia, 05/2007, depth not stated.
Description: Small fragment of about 2 × 2 cm and 2–3 mm thick obtained from a convoluted, lamellate sponge (Figure 2A). Surface hispid with conules scattered on one side and numerous oscules on the opposite side. Consistency is firm, but elastic. The color is violet in life (Figure 2A) and white in alcohol.
Skeleton: The ectosomal skeleton is a regular, isotropic, tangential network, formed by unispicular meshes (Figure 2B,C). The choanosomal skeleton is formed by multispicular, anastomosing fibers (45–175 μm thick), and ascending, parallel fibers (Figure 2B,D), whose extremities create the conules (Figure 2B). Among the ascending fibers is the regular isotropic network (Figure 2B,D).
Spicules: Oxeas slightly curved or straight, with acerate, blunt, and stepped tips (Figure 2E). They measure 125–(154.3 ± 12.9)–180 × 2.5–(6.6 ± 2.5)–10 μm.
Distribution and ecology: The species was described as from the Great Barrier Reef (Lizard Island, Australia) and later collected from Papua New Guinea by Smith et al. [31]. In Indonesia, the species was associated with coral reefs.
Remarks: Morphological characterization: The study of the holotype (MSNG 46940) of C. aculeata, described by Pulitzer-Finali [32], confirmed the identification in terms of shape and size of the spicules (120–160 × 4–6.8 μm); also, the sizes of the fibers were comparable (50–170 μm in thickness). The sponge’s external morphology fits with the holotype as well; Pulitzer-Finali [32] described his small fragment as “a curved lamella […] apparently belonging to a tubular sponge”. Smith et al. [30] reported in this species the presence of molecules inhibiting human kinesin, but did not describe or illustrate the sponge. This is a newly recorded species for Indonesia and the first documented finding after the original description.
Cladocroce burapha Putchakarn, de Weerdt, Sonchaeng & van Soest, 2004
(Figure 3).
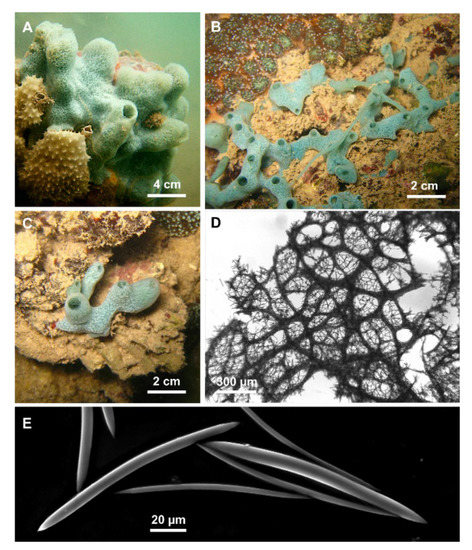
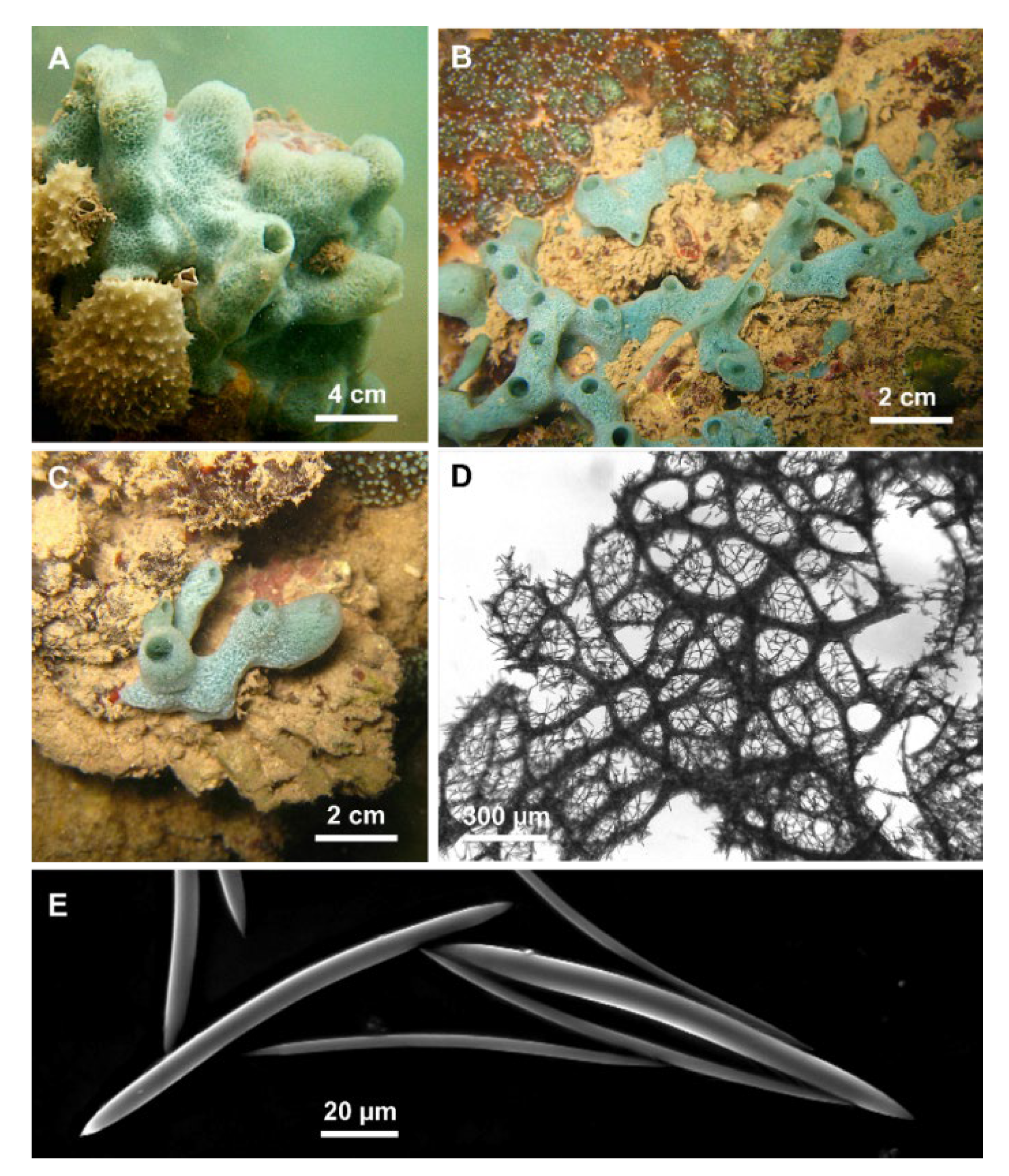
Figure 3.
Cladocroce burapha Putchakarn, de Weerdt, Sonchaeng & van Soest, 2004. (A,C) massive, tubular growth forms (HL139, HL139/18); (B) specimen with repent habit (HL116/18); (D) choanosomal skeleton at light microscopy; (E) oxeas.
Material examined: MA6, Bangka Is., North Sulawesi, September 2011, 0–1 m depth. MA19 (a, e), Bangka Is., North Sulawesi, September 2011, 0–1 m depth. HL 116/18, Hang Trai Island—out Hang Du I Lake, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 22 August 2018. HL 119/18, Hang Trai Island—out Hang Dui I Lake, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 22 August 2018, 1 m depth. HL 121/18, Hang Trai Island—out Hang Dui I Lake, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 22 August 2018, 1 m depth. HL 139, Bo Hon Island—Bui Xam Lake, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 24 April 2004, 1 m depth. HL 139/18, out Bui Xam—Bo Hon Island, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 23 August 2018, 1 m depth.
Additional material: Holotype BIMS-I 1382.
Description: Cladocroce with massive, tubular (Figure 3A,C), or repent habit (Figure 3B). Oscules are round (3–8 mm in diameter) and raised. The sponge surface can be smooth or with shallow ridges and grooves (e.g., HL 139 in Figure 3A). In situ, the external color was light green to aquamarine. The inner color is generally light tan also in the preserved (both in ethanol and dried) specimens. Consistency is rather soft.
Skeleton: The ectosome is an isodictyal, tangential reticulation with scarce spongin. A very similar reticulation is present also in the choanosome, reinforced by a second, rather irregular reticulation of thick plurispicular tracts forming roundish or elongated meshes (Figure 3D). The plurispicular fibers range from 16.1 to 80 µm in thickness (Table 1).

Table 1.
Cladocroce burapha Putchakarn et al. 2004: morphological features of the studied specimens.
Spicules: Oxeas straight or slightly curved (Figure 3E) (80–160 × 2.5–9.5 µm). Points are generally sharp, but, in some specimens, blunt extremities are common, determining the presence of stylote and strongylote forms. All sample measurements of oxeas are in Table 1.
Distribution and ecology: The species seems to prefer shallow (maximum depth 15 m) and calm (bays, marine lakes, mangroves) waters, with variable salinity. Specimens from Indonesia were collected in mangrove forests, while those from Vietnam in salt-water lakes and shallow reefs [5,9]. C. burapha was described from the eastern coast of the Gulf of Thailand and recorded also in Vietnam and Indonesia. In 2017, Núñez-Pons et al. reported this species in Hawai’i, but this last identification is rejected here based on new data (see below) [7].
Remarks: Morphological characterization: The examination of the holotype material (BIMS-I1382) allowed us to confirm the specific determination. Specimens from Vietnam and Indonesia reported here fit with the holotype of C. burapha in the general shape and color and in the skeletal elements: the shape and size of the oxeas are similar and also the skeletal organization with quite thin fibers and quite small mesh diameter (Table 1). The taxonomic status of the other specimen (BIMS-I1383) described in Putchakarn et al. [6] should be maintained as C. burapha.
On the contrary, on the basis of the present findings, we do not agree with considering the paratype of C. burapha (ZMA Por. 17921) conspecific with the holotype; the details are clarified below, in the C. pansinii sp. nov. remarks.
Cladocroce lamellata Bertolino & Calcinai sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:C51F2F4E-C125-4633-9B60-F26AB4849545
(Figure 4).
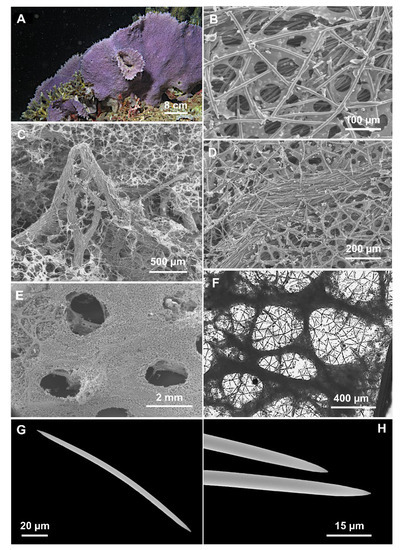
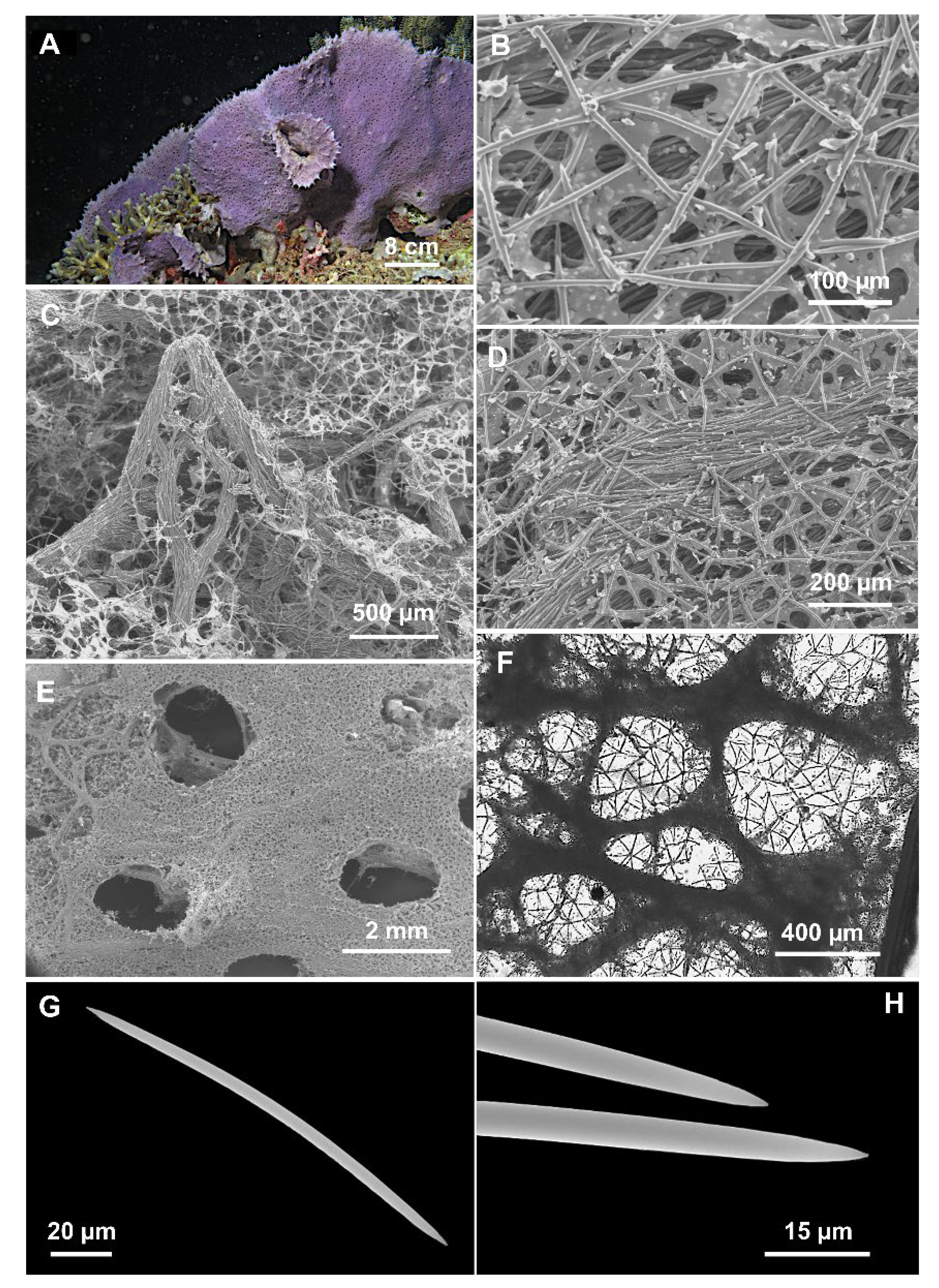
Figure 4.
Cladocroce lamellata Bertolino & Calcinai sp. nov. (A) sponge in situ (sample PH 9); (B) isodictyal, tangential reticulation of the ectosome; (C) magnification of tracts that reinforce the choanosome skeleton and form the conulose surface; (D) choanosomal skeleton with multispicular tract and the isodictyal reticulation in between; (E) exhalant side with oscula; (F) deeper choanosomal skeleton at light microscopy; (G) oxea; (H) magnification of the oxea tips.
Material examined: Holotype: MSNG 61503, TH A, Thangiung Husi, Bangka Island (North-Sulawesi), 10 October 2011 about 20 m depth.
Paratype: MSNG 61504, TH B, Thangiung Husi, Bangka Island (North-Sulawesi), 10 October 2011 about 20 m depth.
Other material: TH C, Thangiung Husi, Bangka Island (North-Sulawesi), 10 October 2011; TH D, Thangiung Husi, Bangka Island (North-Sulawesi) 9 October 2011 about 20 m depth; BA 7, Bangka Island (North-Sulawesi), 12 September 2011, 20 m depth; PH 9, Timur, Bunaken Island, (North-Sulawesi), 13 January 2005, 20 m depth.
Diagnosis: Cladocroce characterized by lamellate shape and with peculiar arrangement of the openings of the aquiferous system, separated on the two sponge sides. The skeleton is characterized by large primary fibers of the choanosome up to 500 µm.
Description: Lamellate sponge (Figure 4A), anchored directly to the substrate; it is violet in situ and in the dried state. Only one sample is yellowish (TH C). Alcohol-preserved samples are light cream colored. The holotype consists of two portions of about 8 × 4 and 5 × 4 cm. The paratype consists of a fragment of about 8 × 8 cm. The sponge is hard and firm; the general appearance of the sponge is different on the two sides. The inhalant side has a shaggy surface, with numerous scattered conules 2–3 mm high. A thin ectosomal membrane covers the sponge surface; ostia are not clearly visible. Conules are formed by choanosomal tracts that run to the surface, making it hispid (Figure 4C). The exhalant side is less shaggy, with shorter conules (<1 mm), and bears numerous oscula (1.5–2 mm in diameter) (Figure 4E).
Skeleton: The ectosomal skeleton is an isodictyal, tangential reticulation (Figure 4B,C,E) supported by multispicular (about 20 spicules) tracts, 40–130 µm thick, which protruding from the surface and create the conules (Figure 4C); between the multispicular tracts an unispicular, a less regular skeleton is present (Figure 4D,F). The deeper tracts are thicker, up to 500 µm in diameter (Figure 4F), and create polygonal meshes of 400–(977.5 ± 524)–1900 µm.
Spicules: Oxeas slightly curved, with acerate and hastate tips (Figure 4G,H) (125–195 × 2.5–7.5 µm). All sample measurements of oxeas are in Table 2.

Table 2.
Spicules measurements of Cladocroce lamellata sp. nov.
Etymology: The new species is named after its characteristic lamellate shape.
Remarks: There are only five valid species from the Indo-Pacific Ocean [3]: C. aculeata Pulitzer-Finali, 1982, C. tubulosa Pulitzer-Finali, 1993, C. burapha Putchakarn et al., 2004, C. reina Aguillar-Camacho & Carballo, 2010, and C. incurvata Lévi & Lévi, 1983 (Table 3). This last species, described from New Caledonia, is a laminar sponge with a thin stalk, and it was found at a 400 m depth. Furthermore, the oxeas are different in size (180–220 × 8–10 µm), and the multispicular fibers reach 300 µm. Among the other Indo-Pacific species, typical of shallow waters, C. aculeata differs from this new species due to its smaller oxeas (120–160 × 4–6.8 µm, [32]), with rounded strongylote tips (Figure 2E). The analysis of the holotype confirmed the differences between C. aculeata and C. lamellata sp. nov. in the shape of the oxeas (constantly similar to strongyles in C. aculeata) and also in the skeletal organization considering that, in C. aculeata, the multispicular tracts of the main skeleton are thinner (50–170 μm). C. burapha (considered as indicated previously in the remarks of the species) differs from C. lamellata sp. nov. due to the growth form and color (Table 1). The spicular tracts are thinner than those of C. lamellata sp. nov. Furthermore, the sponge surface is different because C. burapha is smooth, without conules. C. tubulosa differs by its tubular shape and due to the smaller spicule size (67–74 × 3.5 µm). C. reina is a cushion-shaped sponge, recorded in the Tropical East Pacific Province; it differs also by its smooth surface, raised round oscula of 3–9 mm in diameter and also for the thinner multispicular tracts (up to 150 µm). The differences between C. lamellata sp. nov. and the other new species of the genus Cladocroce described in this paper are discussed in the remarks below.

Table 3.
Cladocroce genus: morphological features and distribution of hitherto known species.
Cladocroce pansinii Bertolino & Calcinai sp. nov.
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:BF872778-3692-4C8C-874B-06F42D719280
(Figure 5)
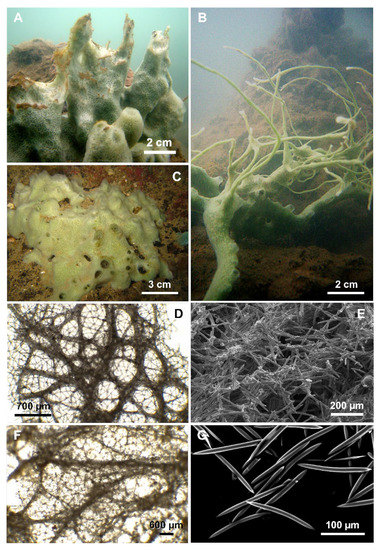
Figure 5.
Cladocroce pansinii Bertolino & Calcinai sp. nov. (A) massive specimen (HL19); (B) a specimen (HL110) with repent habit and thin processes; (C) massive specimen with a large base and short digitations (HL117/18); (D) plurispicular tracts of the superficial choanosomal skeleton forming a network of rounded or polygonal meshes, supporting the isodictyal reticulation of the ectosome at light microscopy; (E) ectosomal skeleton; (F) deeper choanosomal skeleton formed by plurispicular tracts that branch and anastomose without forming a regular reticulum at light microscopy; (G) oxeas.
Holotype: MSNG 52833, HL 19, Dau Be Island—Coastal Site II, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 4 April 2003, 2–4 m depth, reef.
Paratype: MSNG 52834, HL 65, Cong Do Island—Hang Toi Dark Cave, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 14 September 2003, 1–1.5 m depth, semi-dark tunnel, rock.
Examined material: HL 60 and HL 70bis, Cong Do Island—Hang Toi Dark Cave, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 14 September 2003, 1–1.5 m depth. HL 95, Bo Hon Island—Bui Xam Lake, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 15 September 2003, 1.5 m depth, rock and mud. HL 110, Bo Hon Island—Hang Luong Lake (cove), Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 16 September 2003, 2 m depth, rock and algae. HL 117/18, Hang Trai Island—out Hang Dui I Lake, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 22 August 2018, 2–3 m depth, rock and mud. HL 125/18, Bo Hon Island—Bui Xam Lake, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 23 August 2018, 2 m depth, rock and mud. HL 162/18, Me Cung Lake, Ha Long Bay, Vietnam, 24 August 2018, 2 m depth.
Additional material: Paratype of C. burapha ZMA POR 17921.
Diagnosis: Massive, with tubular processes. Tracts of oxeas of the choanosome up to 300 µm in thickness and wide meshes up to 991 µm. Oxeas 125–200 µm long and up to 12 µm in thickness.
Description: The sponge is generally massive, with a thick base from which stout digitations, with apical oscules, arise (Figure 5A,C). The oscules (2 to 8 mm in diameter) are at the digitation extremities, but are also scattered on the sponge body. In the latter case, they are bordered by thin rims up to 5 mm high. The holotype (HL 19) (Figure 5A) is massive with tubular processes, which often coalesce; these processes are up to 10 cm high and 3 cm across, tapering with conical tips (Figure 5A). In more sheltered conditions, as those occurring frequently in the marine lakes of Ha Long Bay, the sponge shows a repent habit (Specimen HL 95), producing also numerous, thin (2–3 mm in diameter), and long (15–20 cm) anastomosing processes (Figure 5B). The color in vivo of the Vietnamese specimens is light green and does not show much variation. Alcohol-preserved and dried specimens become beige to light brown. The consistency is firm and scarcely elastic.
Skeleton: The ectosome is an isodictyal network of triangular and quadrangular meshes with very few sparse spicules (Figure 5D,E). It is easily detachable in the dried specimens. In the choanosome, in proximity to the sponge surface, tracts of spicules organize to form a network of rounded or polygonal meshes, supporting the ectosome (see Table 4 for measurements) (Figure 5D,E). Deeper, the skeleton is formed by plurispicular tracts, which branch and anastomose without forming a regular reticulum (Figure 5F). The unispicular sub-isotropic reticulum is present also in the choanosome, between the plurispicular tracts (Figure 5F).

Table 4.
Cladocroce pansinii sp. nov.: morphological features of the studied specimens.
Spicules: Straight or slightly curved oxeas, generally with pointed ends (Figure 5G) (125–200 × 3.7–15 µm). One or both of the extremities may be blunted, and malformations are seldom observed. All sample measurements of oxeas are in Table 4.
Ecology: The species is rather common in Ha Long Bay. It was collected at a 2–4 m depth in very impoverished reef environments.
Etymology: Named after Prof. Maurizio Pansini in consideration of his fundamental contribution to sponge taxonomy.
Remarks: Morphological characterization: The other Indo-Pacific species of Cladocroce hitherto described [3] are: C. aculeata Pulitzer-Finali, 1982, C. incurvata Lévi & Lévi, 1983, C. tubulosa Pulitzer-Finali, 1993, C. burapha (Putchakarn et al., 2004), and C. reina Aguilar-Camacho & Carballo, 2010 (see previous remarks and Table 3).
Cladocroce aculeata, from the Great Barrier Reef, differs from the present species especially in the external morphology, due to the spiny processes reminded by the specific name, and in the spicules, which are much smaller (125–180 × 2.5–10 μm) and almost always with blunt extremities. C. incurvata differs from the present species as it is a lamellate sponge, ochre in color; it was described in New Caledonia from deep waters (170–190 m). C. tubulosa, from east Africa, has smaller spicule tracts (8–12 µm) and shorter spicules (not exceeding 75 µm in Pulitzer-Finali’s preparations) with respect to the new species. The other two species, C. burapha and C. reina, are close to C. pansinii sp. nov.
Cladocroce reina has been described from the Pacific coast of Mexico. It is a cushion-shaped or encrusting sponge, green or blue. Its oxeas are smaller in size (130–175 × 5–7.5 μm), and the choanosomal tracts are thinner (30–150 µm).
The main differences between the new species and C. burapha (as previously pointed out) are in the size of the oxeas (in C. burapha, the largest size of the oxeas does not reach the minimum value of the oxeas of C. pansinii sp. nov.) and in the diameter of the spicule tracts and of the meshes, which are always bigger in C. pansinii sp. nov. (see Table 1 and Table 4 for comparison).
The study of the type material of C. burapha supported us in defining the new taxonomic status of the specimen indicated as a paratype of C. burapha (ZMA Por. 17921) by Putchakarn et al. [6], assigning it to the species C. pansinii sp. nov. described here. Already, Putchakarn et al. [6] underlined the great variability between the holotype and paratype of C. burapha, especially in the size of the oxeas and in the coloration. Nevertheless, they found that their specimens were similar “with respect to form, consistency, skeletal architecture and shape of the oxeas” adding that “additional specimens may give more insight in the variability in different populations of C. burapha n. sp.” The re-examination of the type material confirmed the differences in the spicule size, but also in the size of the fibers and of the meshes (Table 1 and Table 4) (not discussed by Putchakarn et al. [6]), thus supporting the attribution of the paratype (ZMA Por. 17921) to C. pansinii sp. nov.
Núñez-Pons et al. [7] reported two specimens identified as C. burapha in Hawai’i; these sponges are described as light blue and grey, with oxeas, fibers, and meshes comparable in size to C. pansinii sp. nov. (Table 4). Based on the statements above, also these specimens should be identified as C. pansinii sp. nov.
C. pansinii sp. nov. differs from C. lamellata sp. nov. in the general shape, respectively massive and fan-shaped, and in the surface, which is smooth in C. pansinii sp. nov. and conulose in C. lamellata sp. nov. The spicules tracts and meshes are larger and particularly ticker in C. lamellata sp. nov. (see Table 3 and species descriptions).
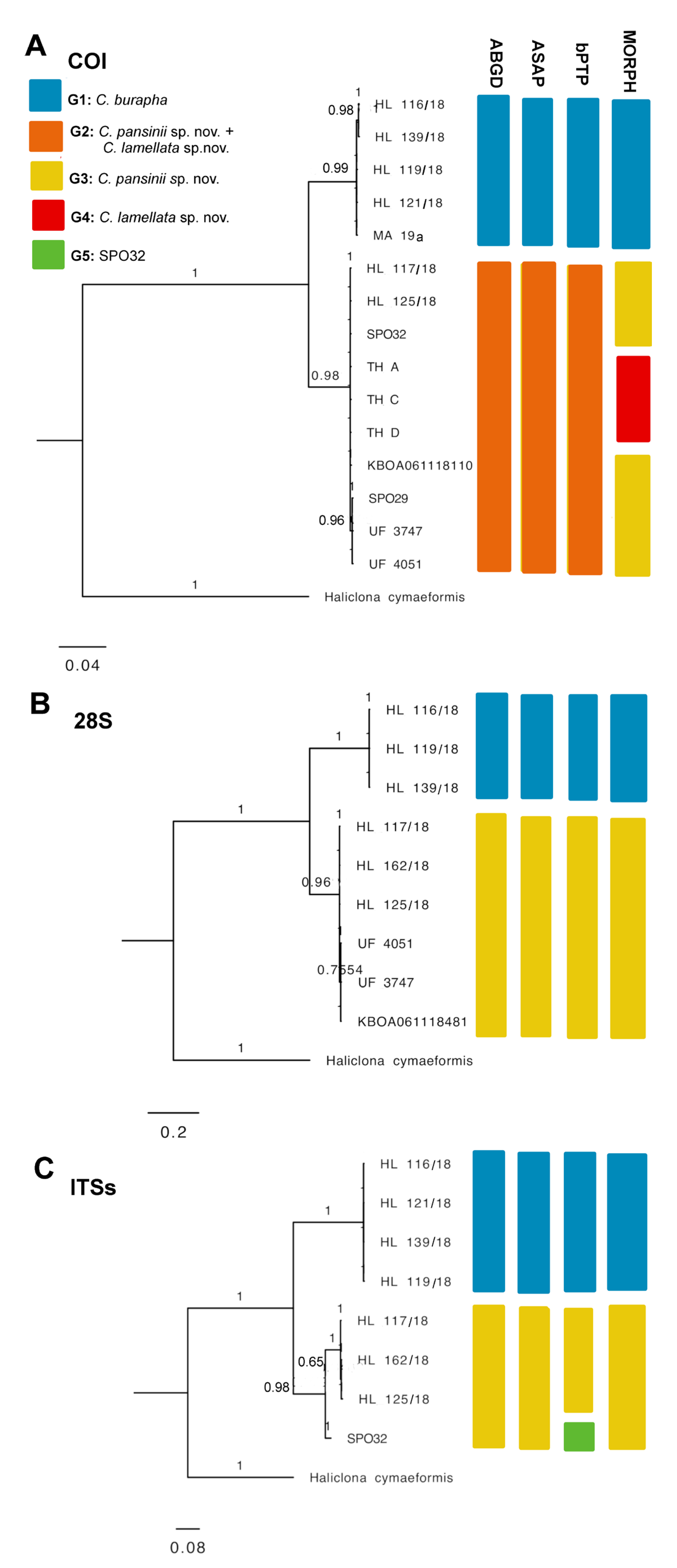
Molecular Species Delimitation
We were able to gather molecular data from three of the four Cladocroce species reported here. Ten COI sequences (covering the Folmer and Erpenbeck partitions) in total were obtained from C. burapha (HL 116/18, MA 19a, HL 119/18, HL 121/18, and HL 139/18), C. lamellata sp. nov. (TH A, TH C, and TH D), and C. pansinii sp. nov. (HL 117/18 and HL 125/18), whereas, for the nuclear markers, six 28S barcodes were retrieved from the species C. burapha (116 HL/18, HL 119/18, and HL 139/18) and C. pansinii sp. nov. (117 HL/18, HL 125/18, and HL 162/18), while the ITSs yielded seven sequences, four from C. burapha (116/18, HL 119/18, HL 121/18, and HL 139/18) and three C. pansinii sp. nov. (HL 117/18, HL 125/18, and HL 162/18). The nuclear gene markers in C. lamellata were unsuccessful in yielding barcodes, and Sample TH B failed at any genetic amplification.
The COI fragments including the Folmer and Erpenbeck partitions 100% matched each other among the Vietnamese (HL 116/18, HL 119/18, HL 121/18, and HL 139/18) and Indonesian (MA 19a) C. burapha samples, saving a nucleotide disparity in position 876 differing 116 HL/18 and HL 139/18 from HL 119/18, HL 121/18, and MA 19a. These sequences revealed 93.696% similarity, displaying 66 variable sites with respect to the specimen SPO32 from Hawai’i (named C. burapha in [7]), C. lamellata sp. nov. (TH A, TH C, TH D) from Indonesia, and C. pansinii sp. nov. (HL 117/18 and HL 125/18) from Vietnam and 67 nucleotide divergencies with the specimen SPO29 (named C. burapha in [7]) and Cladocroce sp. UF_3747, UF_4051 and KBOA061118110 from Hawai’i [11,12]. C. pansinii sp. nov. Samples HL 117/18 and HL 125/18 yielded identical (100% similarity) sequences and 100% matched SPO 32 from Hawai’i (named C. burapha in [7]) and C. lamellata sp. nov. (TH A, TH C, TH D) from Indonesia, and they were different in one nucleotide (at position 885), hence 99.969% matching with SPO 29 (named C. burapha in [7]) and UF_3747, UF_4051, and KBOA061118110 from Hawai’i (named Cladocroce sp. in [11,12]) (Table S3). Cladocroce burapha Samples 116 HL/18, HL 119/18, and HL 139/18 had identical 28S sequences (531 bp). They differed in 127 nucleotide calls (75.049% similarity) with C. pansinii sp. nov. HL 117/18, HL 125/18, and Hl 162/18 from Vietnam and in 130 variable sites (74.656% similarity) from Cladocroce sp. UF_3747, UF_4051, and KBOA061118481 from Hawai’i [11,12]. 28S sequences in 117 HL/18, HL 125/18, and HL 162/18 (C. pansinii sp. nov.) 100% matched and revealed a difference of three nucleotide sites (99.399% similarity) from Cladocroce sp. UF_3747, UF_4051, and KBOA061118481 from Hawai’i [11,12] (Table S3). The ITSs fragments of Vietnamese C. burapha HL 116/18, HL 119/18, HL 121/18, and HL 139/18 were 100% identical. In the curated alignment (after Gblocks), the similarity of these ITSs sequences with respect to those of C. pansinii sp. nov. HL 117/18, HL 125/18, and HL 162/18 was between 75.273 and 75.636% (with 134, 135, and 136 variable sites, respectively) and differed in 127 nucleotide calls (76.909% similarity) with that of SPO32 from Hawai’i (named C. burapha in [7]). They differed by 36–37 variable sites (93.455–93.273% similarity) from SPO 32 from Hawai’i (named C. burapha in [7]) and were dissimilar in 134–136 nucleotide calls (75.636–75.273% similarity) from the ITSs sequences of C. burapha HL 116/18, HL 119/18, HL 121/18, and HL 139/18. Among the C. pansinii samples, HL 117/18’s ITS sequence had one nucleotide difference with HL 162/18 and three variable sites with HL 125/18, and these two last samples were different by two nucleotide calls, all three being 99.866–99.455% identical (Table S3).
The ABGD and ASAP models yielded similar outcomes of species delimitation. The 15 query COI sequences were divided into two groups, with HL 116/18, HL 139/18, HL 119/18, HL 121/18, and MA 19 clustered into Group 1; specimens HL 117/18, HL 125/18, SPO 32, KBOA061118110, TH A, TH C, TH D, SPO 29, UF 3747, and UF 4051 clustered into Group 2 (ABGD: P = 3.59 × 10−2, barcode gap distance = 0.021; ASAP: P-val (rank) = 1.00 × 10−5; threshold dist = 0.021). In the 28S data, two partitions are proposed, Group 1 formed by HL 116/18, HL 119/18, and HL 139/18 and Group 2 comprising HL 117/18, HL 162/18, HL 125/18, KBOA061118481, UF 3747, and UF 4051 (ABGD: P = 1.00 × 10−1, barcode gap distance = 0.128; ASAP: P-val (rank) = 1.02 × 10−2; threshold dist = 0.126). Similarly, the ITS set yielded two partitions, Group 1 with HL 116/18, HL 121/18, HL 139/18, and HL 119/18 and Group 2 with SPO 32, HL 117/18, HL 162/18, and HL 125/18 (ABGD: P = 1.00 × 10−1, barcode gap distance = 0.106; ASAP: P-val (rank) = 2.38 × 10−2; threshold dist = 0.105). In the three markers, Group 1 represents C. burapha specimens, while Group 2 includes C. pansinii sp. nov. from Vietnam and specimens of Cladocroce from Hawai’i (incorporating C. lamellata sp. nov. in the COI set) cluster (Figure 4 and Table S1; Supplementary File S1); bTPT also supported these two major groups for COI, 28S, and ITS data, yet in the ITSs, bTPT suggested a third tentative species within Group 2, separating SPO 32 from HL 117/18, HL 162/18, and HL 125/18. We believe this sub-partition is not taxonomically significant (see below; Figure 6, Supplementary File S2).
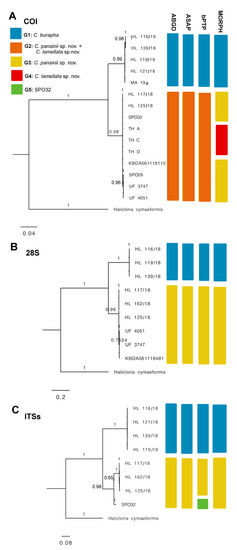
Figure 6.
Bayesian inference phylogeny of genus Cladrocroce based on three genetic markers: (A) COI including Former and Erpenbeck partitions, 1047 bp; (B) 28S C region, 531 bp; (C) ITSs spanning partial 18S–ITS1–5.8S–ITS2–28S partial, after Gblocks curation, 505 bp. Bars represent results of species delimitation analyses: ABGD, ASAP, bPTP, and morphological delimitation (MORPH). Different colors represent different groups.
The phylogenetic trees used in the analyses were constructed for the three separate sets, COI, 28S, and ITSs. Concatenated trees were not used, as the coverage of sequence data was uneven across all markers in some samples (e.g., TH A, TH C, and TH D lacked two marker genes). This generated some background cluttered branching between certain close nodes –especially in the ML phylogenies, more likely related to different levels of sequence data availability, rather than to real phylogenetic dissimilarities (Supplementary File S2). In lieu, the corresponding ML and BI trees had practically identical topologies in the three separate datasets. All trees supported a clear separation of C. burapha representatives from the C. pansinii sp. nov. cluster, with the latter including those previously classified as C. burapha and Cladocroce sp. from Hawai’i (now redefined as C. pansinii sp. nov.) and the newly described Vietnamese samples. In the COI phylogeny, C. lamellata sp. nov. was englobed within the C. pansinii sp. nov. cluster, whereas the ITS tree showed an internal branching within C. pansinii sp. Nov. separating SPO 32 from Hawai’i from the Vietnamese samples. This branching is unlikely to represent a separate species, but probably indicates local intraspecific variability (Figure 6, Supplementary File S2).
Based on nucleotide dissimilarities, genetic distances, ML and BI phylogenies, and ABGD, ASAP, and bPTP species delimitation models, the three marker genes clearly discriminated the C. pansinii sp. nov. cluster formed by Vietnamese Samples HL 117/18, HL 125/18, and HL 162/18 and Hawai’ian entries SPO 29, SPO 32, UF 3747, UF 4051, KBOA061118481, and KBOA061118110 from C. burapha Samples HL 116/18, HL 119/18, HL 121/18, and HL 139/18 from Vietnam and MA 19a from Indonesia. All the analyses also implied that C. burapha from Hawai’i (as in [7]; i.e., SPO 29 and SPO 32) should be redefined as C. pansinii sp. nov. Moreover, this is likely to be extended to several Cladocroce sp. Hawai’ian entries present in GenBank, i.e., UF 3747, UF 4051, KBOA061118481, and KBOA06111811 (as in [11,12]; discussed below).
According to the only genetic data available for C. lamellata sp. nov., the COI, there was no evident separation of C. lamellata sp. nov. (Specimens TH A, TH C, and TH D from Indonesia) from the cluster formed by C. pansinii sp. nov. composed of specimens from Vietnam (HL 117/18, HL 125/18), from Hawai’i (SPO 29 and SPO 32 named C. burapha in [7], and UF 3747, UF 4051, and KBOA061118110, named by [11,12] as Cladocroce sp.). This outcome, even if incongruent with the morphological data (see above), might represent only an inconclusive result, taking into consideration the often poor resolution of the COI marker in Porifera [36]. Indeed, we still support C. lamellata sp. nov. as a novel separate species, based on its divergent morphotype and diagnostic traits. Further considerations are addressed in the following sections.
4. Discussion
The coastal areas of Ha Long Bay (Vietnam) and North Sulawesi (Indonesia) comprise a wide assortment of environments, including shallow salty to brackish lakes, lagoons and mangroves, and deeper coral reefs, rocky bottoms, sandy beds, and plant or algal meadows [37,38]. Such heterogeneous habitat availability can be a driver of new species radiation, forcing organisms to acclimatize and diversify across a variety of ecological niches [39]. In this sense, the phylum Porifera has been demonstrated to be particularly rich and diverse in these areas and able to colonize most of the mentioned habitats, revealing a growing number of new species described in recent years [9,40]. Adding to these records, here, we provide the description of two new species in the genus Cladocroce, recognized through integrated taxonomy with morphological and molecular approaches.
C. pansinii sp. nov. was recognized as a new species, clearly differentiated from its closest sympatric congeneric, C. burapha, via morphological discriminant characteristics (larger size of the oxeas and larger spicule tracts and meshes) and through phylogenetic analyses and species delimitation.
The re-examination of the type material of C. burapha evidenced strong inconsistencies in the morphological diagnostic traits between the holotype and the paratype; instead, a close affinity of the paratype (ZMA Por. 17921) with C. pansinii sp. nov. (e.g., oxeas, fibers, and meshes comparable in size) is evident. The holotype (BIMS-I1382), in lieu, keeps strong closeness with specimens from Vietnam and Indonesia, which we identified as C. burapha. This fact suggests the assignment of the paratype of C. burapha to this new species, C. pansinii sp. nov. This conclusion is indirectly supported by the phylogenetic trees that clearly separate our specimens of C. burapha and C. pansinii into two distinct clusters.
Furthermore, specimens previously classified as C. burapha from Hawai’i (i.e., SPO 29, SPO 32; [7]) also should be redefined as C. pansinii sp. nov., as they display closer morphological affinity with C. pansinii sp. nov. and cluster together in the same phylogenetic branching and species delimitations. Molecular analyses also implied that Cladocroce sp. reported from Hawai’i as vouchers UF 3747, UF 4051, KBOA061118481, and KBOA06111811 from [11,12] take part of the same cluster above and should, hence, be defined as C. pansinii sp. nov. These samples again revealed larger oxeas, fibers, and mesh sizes than those found in C. pansinii sp. nov. ([7]; J. Vicente, personal communication).
This would make us aware of the possible incongruences between holotypes and paratypes. Because these inconsistencies, which often derive from vague descriptions on damaged material and/or assumed morphological variation/plasticity, can lead to an underestimation of biodiversity [41].
The other new species described here, C. lamellata sp. nov., was clearly separate from C. pansinii sp. nov. by morphological diagnosis (e.g., different shape, surface ornamentation, and size of the spicule tracts and meshes). Molecular data, based only on the COI marker, was not able to discriminate between these two species. The low molecular resolution of COI in Porifera, due to slow evolution rates in basal Metazoa [36], may not be sufficient to disclose delimitation between C. lamellata sp. nov. and C. pansinii sp. nov., which may be more closely related to each other than C. burapha. Nonetheless, other markers with faster mutation times, such as 28S and ITS, may have better resolution [42], but unfortunately, we were unable to amplify these fragments. Discordance between morphological and molecular species boundaries within the same genus has been already reported in sponges [43]. The ITS markers, for instance, have higher evolutionary rates, but may yield too much intraspecific intragenomic variability [44]. This could be the reason why certain methods based on phylogeny in our study (e.g., ML, BI, and bPTP) separated SPO 32 from the rest of C. pansinii sp. nov. This is unlikely to be a real species delimitation, but likely a local intraspecific polymorphism.
C. lamellata sp. nov. and C. pansinii sp. nov. have not been found at the moment living in sympatry with each other, but both instead do coexist with C. burapha. Considering their different ranges of distribution known at the present time, we may speculate C. lamellata sp. nov. could have evolved from the widely present C. pansinii sp. nov. in Indonesia. C. burapha, instead, seems to prefer shallow (maximum depth 15 m) and calm (bays, marine lakes, mangroves) waters and reveals smaller spicule sizes, with respect to C. pansinii sp. nov. and C. lamellata sp. nov., which can be found in deeper marine habitats and display larger spicules. Larger spicules in length and thickness have been correlated with populations living in deeper habitats with lower temperatures and higher silica concentration [45,46]; however, the depth difference in our sample set might not be as relevant to follow this tendency. Intraspecific variability has been generally usually considered as the main explanation in these cases of high phenotypic plasticity, but our results, coming from molecular analyses, highlight that speciation processes can be another way to interpret and disentangle these issues.
Our work expands the knowledge of species distribution along iconic hotspots of the Indo-Pacific Oceans and inspires research on marine biodiversity. Regarding the classification Porifera, our findings strongly supported the assumptions of other authors (e.g., [42]) for the lack of species resolution using one genetic marker and the necessity to combine morphological observations with a multilocus-based approach.
Supplementary Materials
The following Supporting Information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jmse11061240/s1, Table S1: Table S1_List of Seqs.xlsx; File S2: Supplementary_Results_S2_Species_delimitation_Trees.docx; Table S3: Table S3 _Distance_matrixes_ABGD.xlsx. References [7,11,12] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B., B.C., C.C. and L.N.-P.; methodology, M.B., C.C., B.C., L.N.-P., F.R., J.E. and V.M.; software, L.N.-P.; validation, D.C.T., D.M.M., M.B., B.C., C.C., L.N.-P. and G.B.; formal analysis, L.N.-P., B.C. and M.B; investigation, C.C. and M.B.; resources, C.C., G.B., B.C, L.N.-P., D.C.T. and D.M.M.; data curation, B.C., M.B. and L.N.-P.; writing—original draft preparation, B.C., M.B. and L.N.-P.; writing—review and editing, G.B. and V.M.; visualization, B.C, L.N.-P. and M.B.; supervision, G.B., M.B., D.C.T. and D.M.M.; project administration, G.B., C.C., D.C.T. and D.M.M.; funding acquisition, G.B., C.C., L.N.-P., D.C.T. and D.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the research project for international cooperation KC09.11/16-20 “Study on biodiversity of limestone islands and limestone archipelagos in Vietnam’s waters; propose solutions and models for use and protection, survival and sustainable development”, the project cod NVCC 23.02/20-20, and a MIUR contribution for the Italy–Indonesia Scientific and Technological Cooperation—Annex III Project CODE: STA No. 16.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Sequences and specimen descriptions have been deposited in GenBank (accession numbers: COI entries: OP950351–OP950360; 28S entries: OP955945–OP955951; and ITSs entries: OP955954–OP955959) and Sponge Barcoding Project databases for public access.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to P. De Luca, E. Mauriello, and R. Pannone from SBM at SZN for curated work in Sanger sequencing procedures and E. D’Aniello, C. La Vecchia, and M. L. Palomba for laboratory assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aguilar-Camacho, J.M.; Carballo, J.L. First record of Cladocroce (Porifera: Haplosclerida: Chalinidae) from the eastern pacific ocean with the description of Cladocroce reina sp. nov. Zootaxa 2010, 68, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerdt, W.H. Family Chalinidae Gray, 1867. In Systema Porifera; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 852–873. [Google Scholar]
- De Voogd, N.J.; Alvarez, B.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Carballo, J.L.; Cárdenas, P.; Díaz, M.-C.; Dohrmann, M.; Downey, R.; Hajdu, E.; Hooper, J.N.A.; et al. World Porifera Database. 2022. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org/porifera (accessed on 12 October 2022).
- Santos, G.G.; Da Silva, L.P.; Alliz, A.; Pinheiro, U. Cladocroce caelum sp nov from the Brazilian coast; First record of the genus in the South Atlantic. Zootaxa 2014, 3847, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcinai, B.; Bastari, A.; Makapedua, D.M.; Cerrano, C. Mangrove sponges from Bangka Island (North Sulawesi, Indonesia) with the description of a new species. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2017, 97, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putchakarn, S.; De Weerdt, W.H.; Sonchaeng, P.; Van Soest, R.W.M. A New Species of Cladocroce Topsent, 1892 (Porifera, Haplosclerida) from the Gulf of Thailand. Beaufortia 2004, 54, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Pons, L.; Calcinai, B.; Gates, R.D. Who’s there?—First morphological and DNA barcoding catalogue of the shallow Hawai’ian sponge fauna. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Azzini, F.; Bavestrello, G.; Calcinai, B.; Pansini, M.; Sarti, M.; Thung, D. Marine lakes of karst islands in Ha Long Bay (Vietnam). Chem. Ecol. 2006, 22, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrano, C.; Bavestrello, G.; Bertolino, M.; Thung, D.C.; Pansini, M.; Sarti, M.; Núñez Pons, L.; Calcinai, B. The Ha Long Bay marine ecosystem. An unprecedented opportunity for evolutionary studies on marine taxa. In Innovations in Land, Water and Energy for Vietnam’s Sustainable Development; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Camillo, C.G.; Gravili, C.; De Vito, D.; Pica, D.; Piraino, S.; Puce, S.; Cerrano, C. The importance of applying Standardised Integrative Taxonomy when describing marine benthic organisms and collecting ecological data. Invertebr. Syst. 2018, 32, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.; Osberg, A.; Marty, M.J.; Rice, K.; Toonen, R.J. Influence of palatability on the feeding preferences of the endemic Hawaiian tiger cowrie for indigenous and introduced sponges. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2020, 647, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, J.; Webb, M.K.; Paulay, G.; Rakchai, W.; Timmers, M.A.; Jury, C.P.; Bahr, K.; Toonen, R.J. Unveiling hidden sponge biodiversity within the Hawaiian reef cryptofauna. Coral Reefs 2022, 41, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, F.; Ponti, M.; Scinto, A.; Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C. Possible effects of human impacts on epibenthic communities and coral rubble features in the marine Park of Bunaken (Indonesia). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 85, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Pons, L.; Mazzella, V.; Rispo, F.; Efremova, J.; Calcinai, B. DNA Barcoding Procedures for Taxonomical and Phylogenetic Studies in Marine Animals: Porifera as a Case Study. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2498, 195–223. [Google Scholar]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, J.R.; Rachello-Dolmen, P.G.; Parra-Velandia, F.; Schönberg, C.H.L.; Breeuwer, J.A.J.; van Soest, R.W.M. Molecular evidence of cryptic speciation in the “cosmopolitan” excavating sponge Cliona celata (Porifera, Clionaidae). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2010, 56, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wörheide, G.; Nichols, S.A.; Goldberg, J. Intragenomic variation of the rDNA internal transcribed spacers in sponges (Phylum Porifera): Implications for phylogenetic studies. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 33, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chombard, C.; Boury-Esnault, N.; Tillier, S. Reassessment of Homology of Morphological Characters in Tetractinellid Sponges Based on Molecular Data. Syst. Biol. 1998, 47, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erpenbeck, D.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Wörheide, G. CO1 phylogenies in diploblasts and the “Barcoding of Life”—Are we sequencing a suboptimal partition? Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 550–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castresana, J. Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 540–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Mrbayes 3.2: Efficient bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop, GCE 2010; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kapli, P.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A. A general species delimitation method with applications to phylogenetic placements. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.E.; Hong, W.; Zachariah, M.M.; Harper, M.K.; Matainaho, T.K.; Van Wagoner, R.M.; Ireland, C.M.; Vershinin, M. Single-molecule inhibition of human kinesin by adociasulfate-13 and -14 from the sponge Cladocroce aculeata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18880–18885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulitzer-Finali, G. Some new or little-known sponges from the Great Barrier Reef of Australia. Bollettino dei Musei e degli Istituti Biologici dell’Università di Genova 1982, 48–49, 87–141. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, R.W.M. Sponges of the Guyana Shelf. Zootaxa 2017, 4217, 1–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundbeck, W. Porifera. (Part I) Homorrhaphidae and Heterorrhaphidae. In The Danish Ingolf-Expedition; Bianco Luno: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1902; Volume 6, pp. 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lehnert, H.; Stone, R.P. Two new species of sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae) from the Aleutian Islands, Alaska. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 2016, 96, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Meier, R.; Todd, P.A.; Chou, L.M. Slow mitochondrial COI sequence evolution at the base of the metazoan tree and its implications for DNA barcoding. J. Mol. Evol. 2008, 66, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomascik, T.; Mah, A.J.; Anugerah, N.; Moosa, M.K. The Ecology of the Indonesian Sea Part Two; Dalhousie University: Halifax, NS, Canada, 1997; ISBN 978-1-4629-0503-4. [Google Scholar]
- Trang, C.T.T.; Thung, D.C.; Van Nam, L.; Kha, P.T.; Van Bach, N.; Ngoc, D.H. Assessment of Sea Water Quality in some Limestone Island and Archipelagos areas, Viet Nam. VNU J. Sci. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 36, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, P.; Pérez, T.; Boury-Esnault, N. Sponge Systematics Facing New Challenges. In Advances in Marine Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 61, pp. 79–209. ISBN 9780123877871. [Google Scholar]
- Calcinai, B.; Cerrano, C.; Núñez-Pons, L.; Pansini, M.; Thung, D.C.; Bertolino, M. A new species of Spongilla (Porifera, demospongiae) from a karst lake in Ha Long Bay (Vietnam). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrijenhoek, R.C. Cryptic species, phenotypic plasticity, and complex life histories: Assessing deep-sea faunal diversity with molecular markers. Deep. Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2009, 56, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Franco, C.M.M.; Sorokin, S.J.; Zhang, W. Development of a multilocus-based approach for sponge (phylum Porifera) identification: Refinement and limitations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debiasse, M.B.; Hellberg, M.E. Discordance between morphological and molecular species boundaries among Caribbean species of the reef sponge Callyspongia. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itskovich, V. Intragenomic variation of rDNA internal transcribed spacers in the endemic Baikal sponge Lubomirskia baikalensis (Pallas, 1776) (Spongillida, Lubomirskiidae): Implications for Porifera barcoding. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subagio, I.B.; Setiawan, E.; Hariyanto, S.; Irawan, B. Spicule size variation in Xestospongia testudinaria Lamarck, 1815 at Probolinggo-Situbondo coastal. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1854, 020034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavestrello, G.; Bonito, J.; Sarà, M. Influence of depth on the size of sponge spicules. Sci. Mar. 1993, 57, 415–420. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).