Assessment of Inflation Schemes on Parameter Estimation and Their Application in ENSO Prediction in an OSSE Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Zebiak–Cane Model
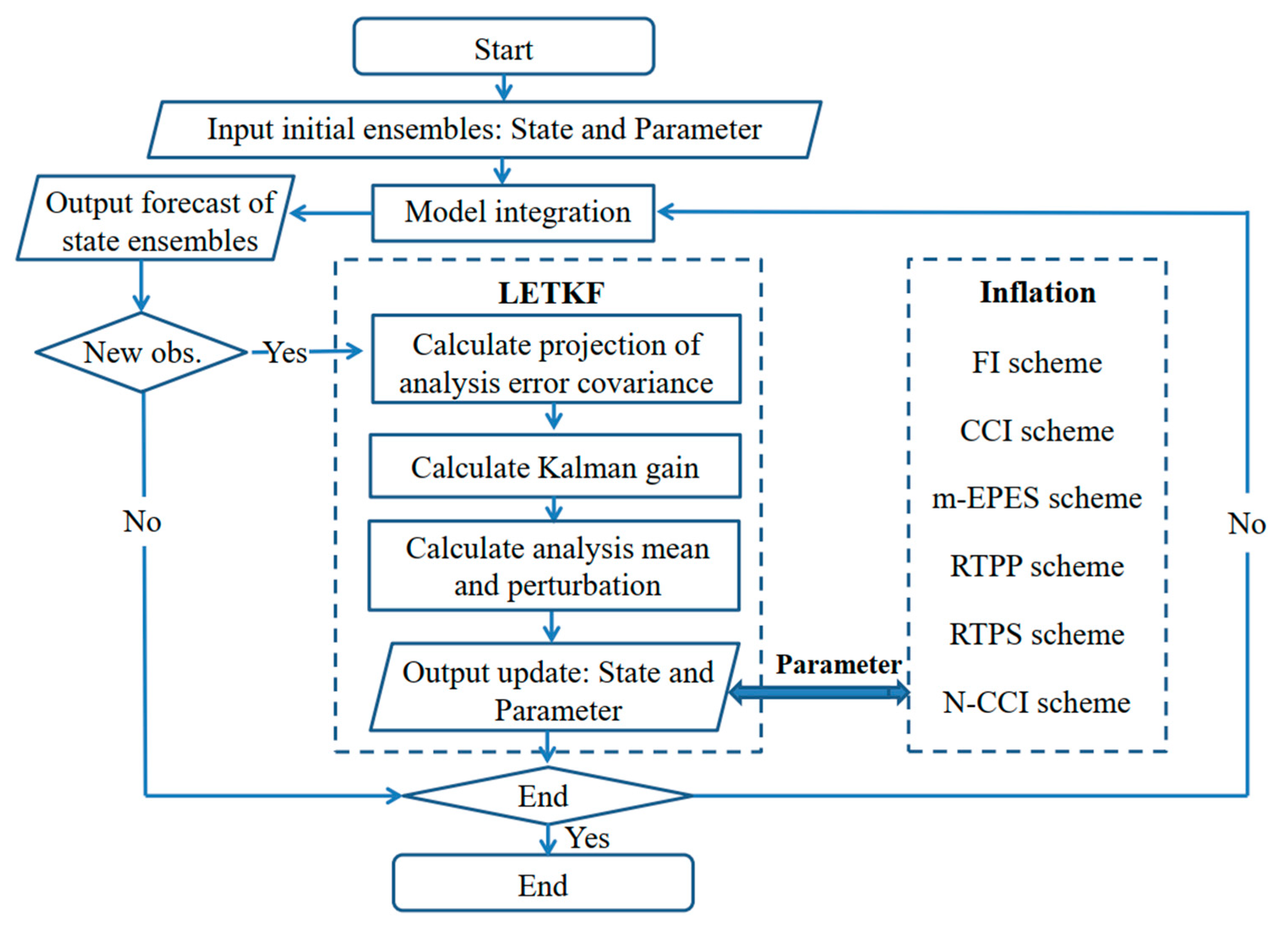
2.2. LETKF-Based Parameter Estimation
2.3. The Observing System
2.4. Inflation Schemes
3. The Sensitivity Study
3.1. Factors in Inflation Schemes
3.2. Initial Guess of Parameter
3.3. State Inflations
4. Results
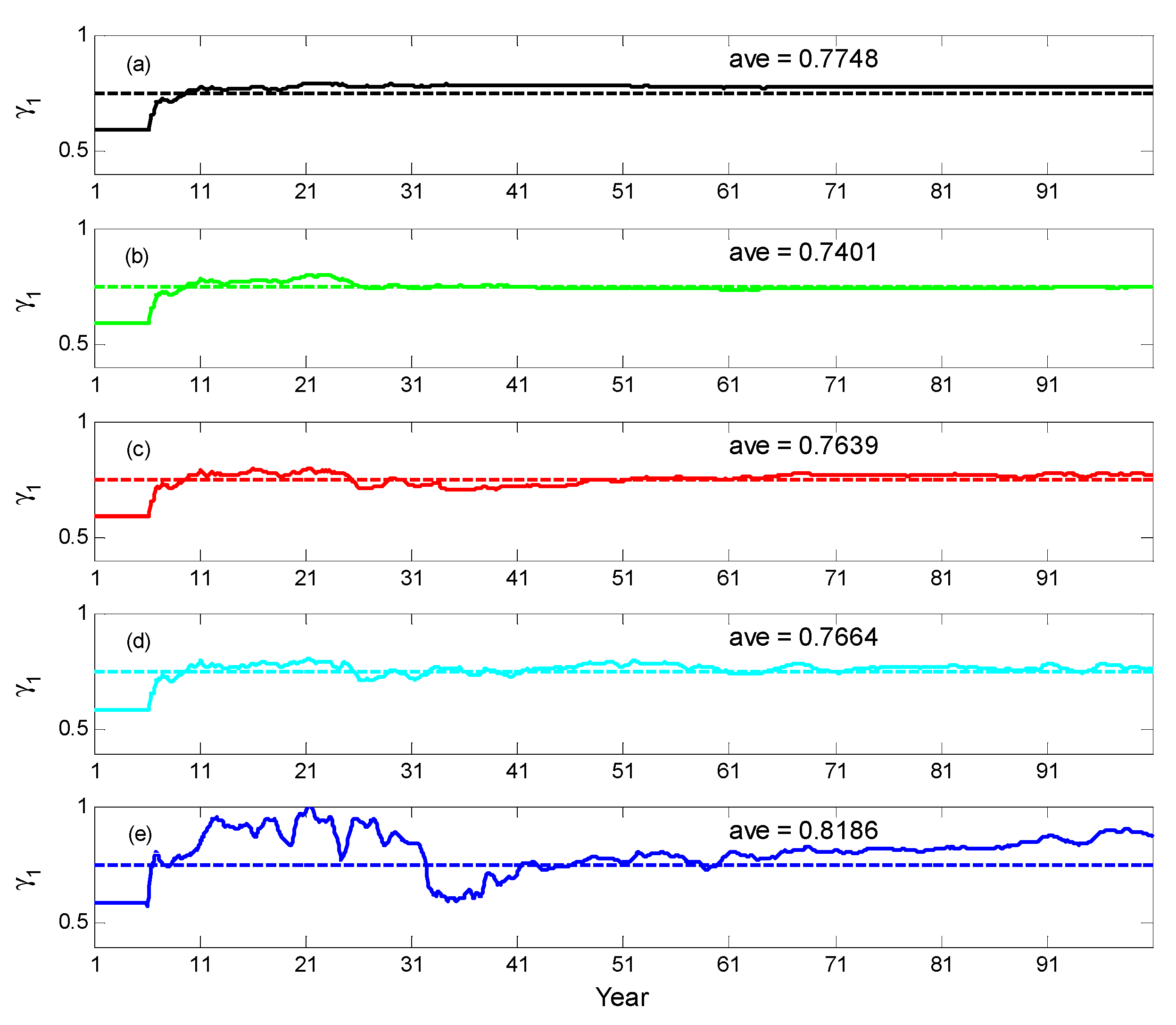
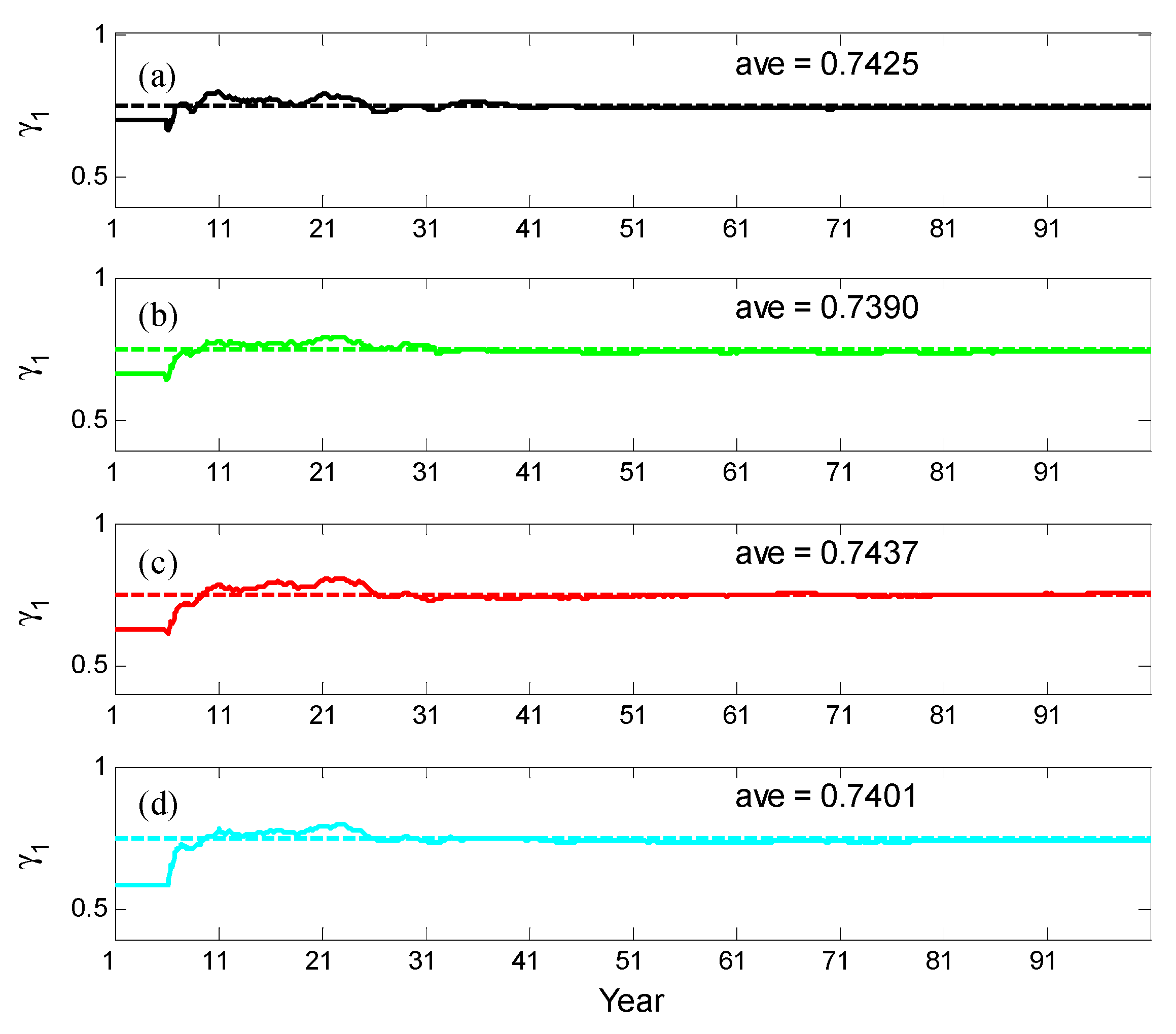
4.1. Single-Parameter Estimation
4.1.1. Estimated Single Parameter
4.1.2. Model States and ENSO Prediction
4.2. Multiple-Parameter Estimation
4.2.1. Estimated Multiple Parameters
4.2.2. Model State and ENSO Prediction
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, R.-H.; Moum, J.N.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Li, D. Physics-informed deep-learning parameterization of ocean vertical mixing improves climate simulations. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwac044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Cane, M.A.; Kaplan, A.; Zebiak, S.E.; Huang, D. Predictability of El Niño over the past 148 years. Nature 2004, 428, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, R.-H. Impact of altimetry data on ENSO ensemble initializations and predictions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L13611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’kane, T.J.; Sandery, P.A.; Monselesan, D.P.; Sakov, P.; Chamberlain, M.A.; Matear, R.J.; Collier, M.A.; Squire, D.T.; Stevens, L. Coupled Data Assimilation and Ensemble Initialization with Application to Multiyear ENSO Prediction. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 997–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, T.; Song, X.; Shen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Chen, D. An extension of LDEO5 model for ENSO ensemble predictions. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 2979–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stainforth, D.A.; Aina, T.; Christensen, C.; Collins, M.; Faull, N.; Frame, D.J.; Kettleborough, J.A.; Knight, S.; Martin, A.; Murphy, J.M.; et al. Uncertainty in predictions of the climate response to rising levels of greenhouse gases. Nature 2005, 433, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J. ENSO ensemble prediction: Initial error perturbations vs. model error perturbations. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2516–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.-J.; Gao, C.; Zhang, R.-H. Model parameter-related optimal perturbations and their contributions to El Niño prediction errors. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 52, 1425–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhu, J. Balanced multivariate model errors of an intermediate coupled model for ensemble Kalman filter data assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Duan, W.; Zheng, F.; Tang, Y. On the “spring predictability barrier” for strong El Niño events as derived from an intermediate coupled model ensemble prediction system. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1614–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Rosati, A.; Delworth, T. A study of enhancive parameter correction with coupled data assimilation for climate estimation and prediction using a simple coupled model. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2012, 64, 10963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Dubey, A.K. Sensitivity of convective parameterization schemes in regional climate model: Precipitation extremes over India. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2021, 146, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y. Impact of convection scheme on ENSO prediction of SINTEX-F2. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2023, 103, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Bretherton, C.S. The University of Washington Shallow Convection and Moist Turbulence Schemes and Their Impact on Climate Simulations with the Community Atmosphere Model. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3449–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Q.; Cao, X.Q.; Zhang, W.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Estimating parameters for coupled air-sea model with variational method. Acta Phys. Sin. 2012, 61, 110401. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z. A study of the impact of parameter optimization on ENSO predictability with an intermediate coupled model. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 46, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, F.; Jin, Y. Parameter Optimization for Real-World ENSO Forecast in an Intermediate Coupled Model. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2019, 147, 1429–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.-J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhang, S.; Wu, X.-R.; Liu, Z. Mitigation of coupled model biases induced by dynamical core misfitting through parameter optimization: Simulation with a simple pycnocline prediction model. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2014, 21, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jacob, R.; Lu, F.; Rong, X.; Wu, S. Ensemble-Based Parameter Estimation in a Coupled General Circulation Model. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 7151–7162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Rong, X.; Jacob, R.; Wu, S.; Lu, F. Ensemble-Based Parameter Estimation in a Coupled GCM Using the Adaptive Spatial Average Method. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 4002–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Lu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhao, M.; Vecchi, G.A.; Zhang, R.; et al. Estimating Convection Parameters in the GFDL CM2.1 Model Using Ensemble Data Assimilation. J. Adv. Model. Earth Syst. 2018, 10, 989–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annan, J.D. Parameter estimation using chaotic time series. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2005, 57, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, X.-M.; Zhang, F.; Nielsen-Gammon, J.W. Ensemble-based simultaneous state and parameter estimation for treatment of mesoscale model error: A real-data study. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L08802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Ishikawa, Y.; Awaji, T. Specifying Air-Sea Exchange Coefficients in the High-Wind Regime of a Mature Tropical Cyclone by an Adjoint Data Assimilation Method. SOLA 2010, 6, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, Y.; Xie, L. Adjusting the Wind Stress Drag Coefficient in Storm Surge Forecasting Using an Adjoint Technique. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cao, A.; Chen, H.; Lv, X. Estimation of Bottom Friction Coefficients Based on an Isopycnic-Coordinate Internal Tidal Model with Adjoint Method. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Navon, I.M.; Li, W. A Study of Coupling Parameter Estimation Implemented by 4D-Var and EnKF with a Simple Coupled System. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.-S.; Kalnay, E.; Miyoshi, T.; Liu, J.; Fung, I. Estimation of surface carbon fluxes with an advanced data assimilation methodology. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D24101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Rosati, A.; Delworth, T.L.; Liu, Y. Impact of Geographic-Dependent Parameter Optimization on Climate Estimation and Prediction: Simulation with an Intermediate Coupled Model. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2012, 140, 3956–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Rosati, A.; Delworth, T.L. A study of impact of the geographic dependence of observing system on parameter estimation with an intermediate coupled model. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 40, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, G.; Higuchi, T.; Kagimoto, T.; Hirose, N. Prediction of ocean state by data assimilation with the ensemble Kalman filter. In SCIS & ISIS SCIS & ISIS; Japan Society for Fuzzy Theory and Intelligent Informatics: Fukuoka, Japan, 2006; pp. 1884–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.; Srivastava, A.; Mishra, A.K. Upper Ocean Four-Dimensional Variational Data Assimilation in the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal. Mar. Geodesy 2017, 41, 230–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X.; Han, G. Correction of biased climate simulated by biased physics through parameter estimation in an intermediate coupled model. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 47, 1899–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L.; Anderson, S.L. A Monte Carlo implementation of the nonlinear filtering problem to produce ensemble assimilations and forecasts. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1999, 127, 2741–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, A.; Zhang, F.; Nielsen-Gammon, J.W. Ensemble-Based Simultaneous State and Parameter Estimation in a Two-Dimensional Sea-Breeze Model. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2006, 134, 2951–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutt, A. Divergence of the Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter (LETKF) by Nonlocal Observations. Front. Appl. Math. Stat. 2020, 6, hal-02861799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Coupled data assimilation and parameter estimation in coupled ocean–atmosphere models: A review. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 54, 5127–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Song, X.; Shen, Z. Parameter Estimation Based on a Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter Applied to El Niño–Southern Oscillation Ensemble Prediction. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.J.; Pulido, M.; Miyoshi, T. Estimating Model Parameters with Ensemble-Based Data Assimilation: Parameter Covariance Treatment. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2013, 91, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, F. Atmospheric simulations using a GCM with simplified physical parametrizations. I: Model climatology and variability in multi-decadal experiments. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 20, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Snyder, C.; Sun, J. Impacts of Initial Estimate and Observation Availability on Convective-Scale Data Assimilation with an Ensemble Kalman Filter. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1238–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, J.S.; Hamill, T.M. Evaluating Methods to Account for System Errors in Ensemble Data Assimilation. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2012, 140, 3078–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebiak, S.E.; Cane, M.A. A model El Niño-Southern oscillation. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1987, 115, 2262–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, B.R.; Kostelich, E.J.; Szunyogh, I. Efficient data assimilation for spatiotemporal chaos: A local ensemble transform Kalman filter. Phys. D Nonlinear Phenom. 2007, 230, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S. Carbon Cycle Data Assimilation Using a Coupled Atmosphere Vegetation Model and the Local Ensemble Transform Kalman filter. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Maryland, Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.-S.; Kalnay, E.; Liu, J.; Fung, I.; Miyoshi, T.; Ide, K. “Variable localization” in an ensemble Kalman filter: Application to the carbon cycle data assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D09110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, J.J.; Pulido, M.; Miyoshi, T. Estimating Model Parameters with Ensemble-Based Data Assimilation: A Review. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. II 2013, 91, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, L.; Saito, K.; Hotta, D. Analysis and design of covariance inflation methods using inflation functions. Part 1: Theoretical framework. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 3638–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.L. An ensemble adjustment Kalman filter for data assimilation. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2001, 129, 2884–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Hoteit, I. Ensemble Kalman Filtering with a Divided State-Space Strategy for Coupled Data Assimilation Problems. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2014, 142, 4542–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Xue, M. Simultaneous Estimation of Microphysical Parameters and Atmospheric State with Simulated Radar Data and Ensemble Square Root Kalman Filter. Part I: Sensitivity Analysis and Parameter Identifiability. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2008, 136, 1630–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Xue, M. Simultaneous Estimation of Microphysical Parameters and Atmospheric State with Simulated Radar Data and Ensemble Square Root Kalman Filter. Part II: Parameter Estimation Experiments. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2008, 136, 1649–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, A.; Zhang, F.; Nielsen-Gammon, J.W. Ensemble-based simultaneous state and parameter estimation with MM5. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L12801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z. Convection-Permitting Forecasts Initialized with Continuously Cycling Limited-Area 3DVAR, Ensemble Kalman Filter, and “Hybrid” Variational–Ensemble Data Assimilation Systems. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2014, 142, 716–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Zavala-Garay, J.; Arango, H.G.; Edwards, C.A.; Anderson, J.; Hoar, T. Regional and basin scale applications of ensemble adjustment Kalman filter and 4D-Var ocean data assimilation systems. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 189, 102450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, G.; Cohn, S.E. Construction of correlation functions in two and three dimensions. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 125, 723–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J. Predictability in the Midst of Chaos: A Scientific Basis for Climate Forecasting. Science 1998, 282, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Kumar, A.; Wang, W. An analysis of seasonal predictability in coupled model forecasts. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 36, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almar, R.; Boucharel, J.; Graffin, M.; Abessolo, G.O.; Thoumyre, G.; Papa, F.; Ranasinghe, R.; Montano, J.; Bergsma, E.W.J.; Baba, M.W.; et al. Influence of El Niño on the variability of global shoreline position. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gharamti, M. Enhanced Adaptive Inflation Algorithm for Ensemble Filters. Mon. Weather. Rev. 2018, 146, 623–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, Y. On the Localization in Strongly Coupled Ensemble Data Assimilation Using a Two-Scale Lorenz Model. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T. The Gaussian Approach to Adaptive Covariance Inflation and Its Implementation with the Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 1519–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Duan, W.; Vannitsem, S. Improving forecasts of El Niño diversity: A nonlinear forcing singular vector approach. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Duan, W.; Jiang, L. Model errors of an intermediate model and their effects on realistic predictions of El Niño diversity. Int. J. Clim. 2022, 42, 7443–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, T. Reducing Model Error Effects in El Niño–Southern Oscillation Prediction Using Ensemble Coupled Data Assimilation. Remote. Sens. 2023, 15, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lian, T.; Fu, C.; Cane, M.A.; Tang, Y.; Murtugudde, R.; Song, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, L. Strong influence of westerly wind bursts on El Niño diversity. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jacob, R. Understanding the control of extratropical atmospheric variability on ENSO using a coupled data assimilation approach. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 48, 3139–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, R.-H. A Hybrid Neural Network Model for ENSO Prediction in Combination with Principal Oscillation Pattern Analyses. Adv. Atmospheric Sci. 2022, 39, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Heureux, M.L.; Levine, A.F.Z.; Newman, M.; Ganter, C.; Luo, J.; Tippett, M.K.; Stockdale, T.N. ENSO Prediction. AGU 2020, 10, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N.; Prabhat, F. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.-G.; Kim, J.-H.; Luo, J.-J. Deep learning for multi-year ENSO forecasts. Nature 2019, 573, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

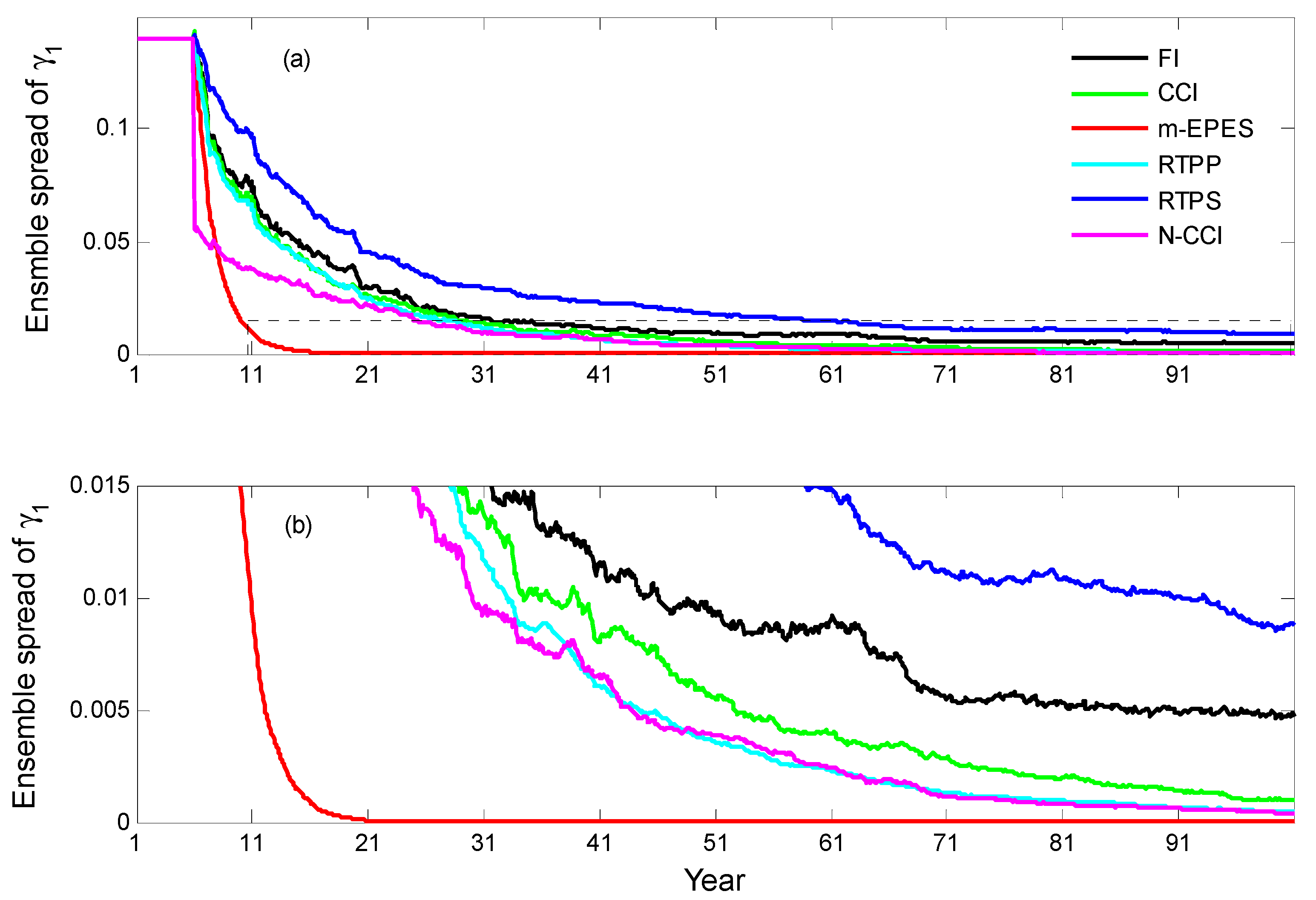
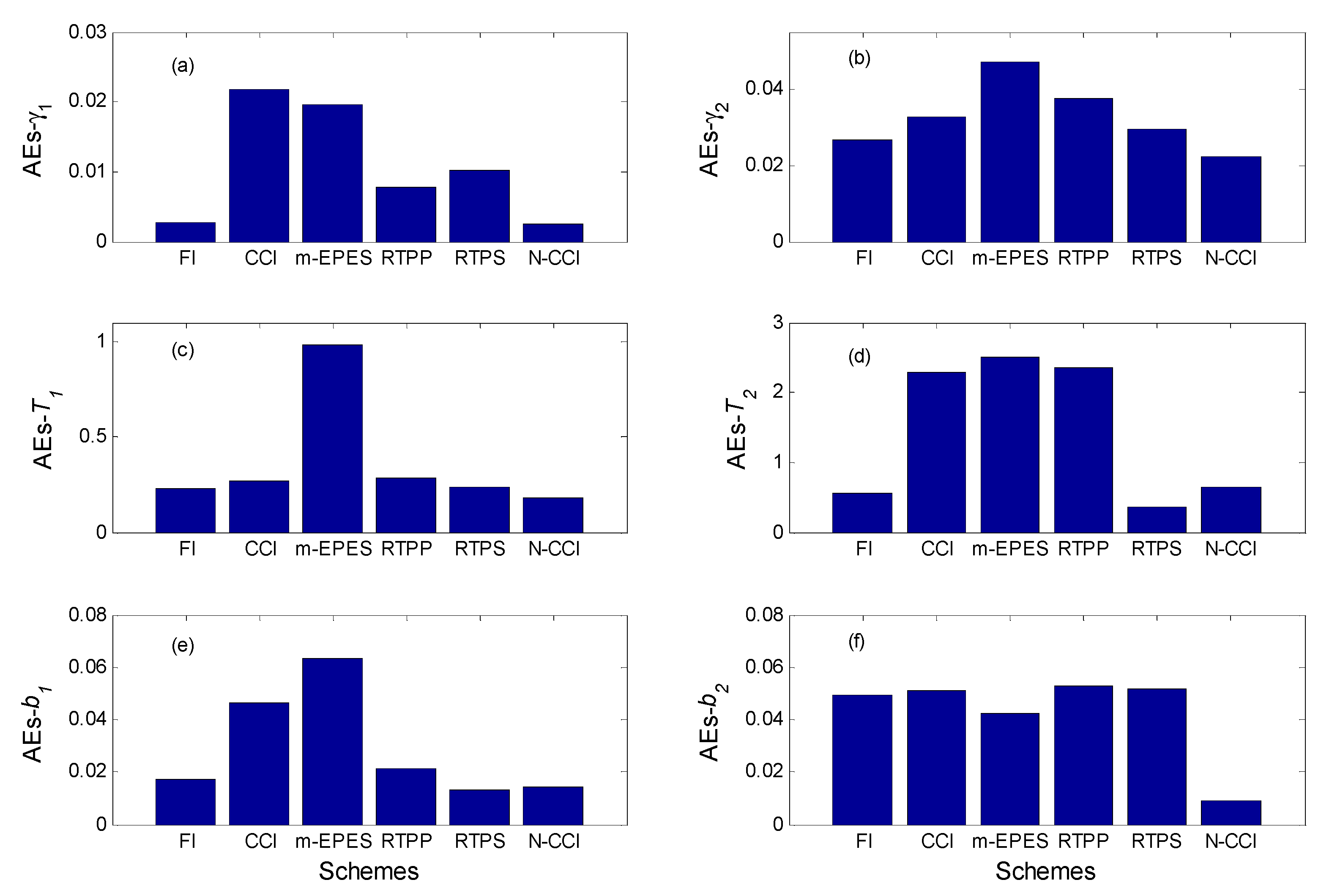
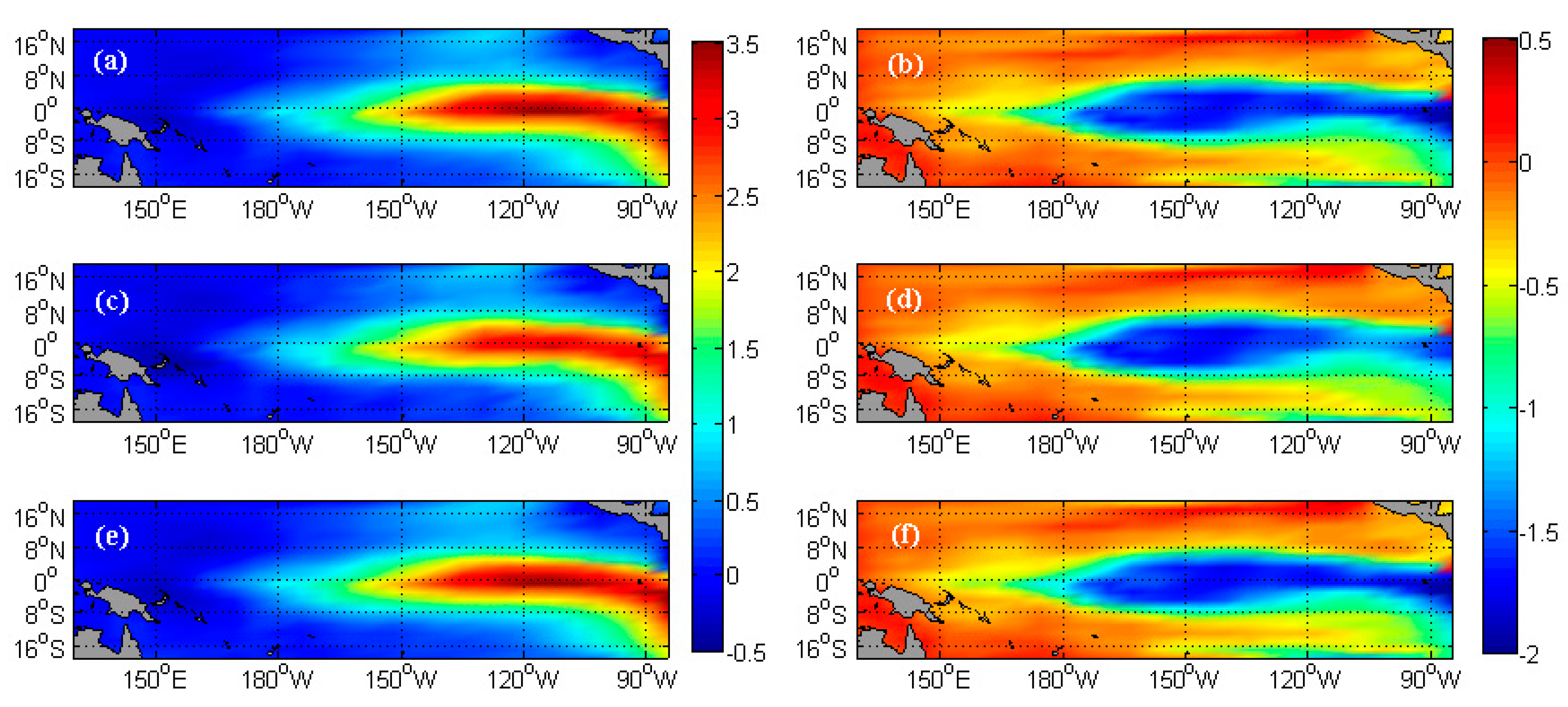
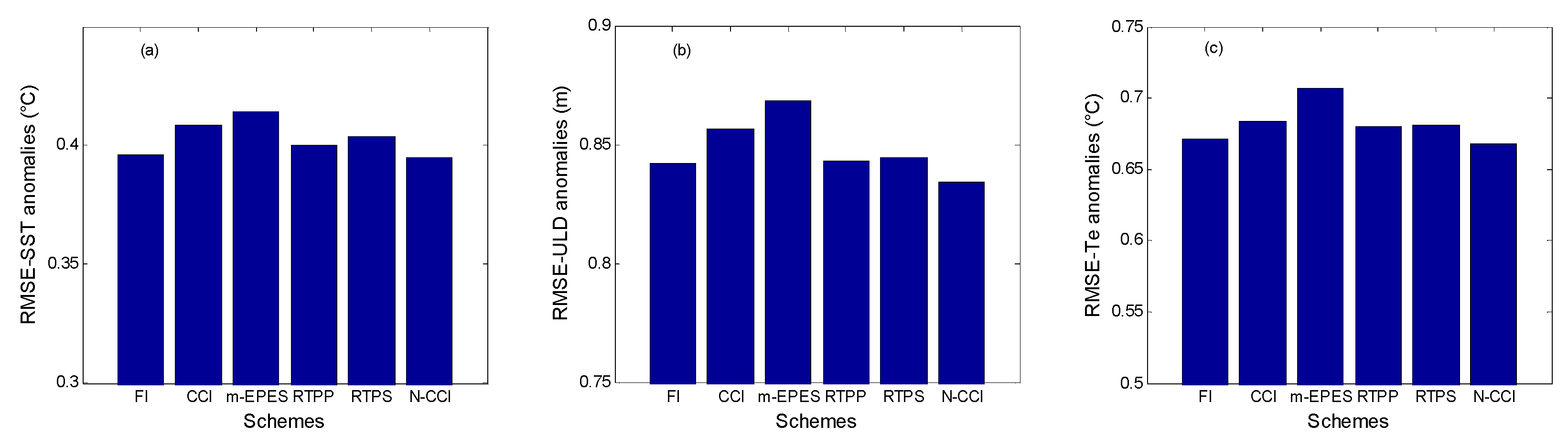
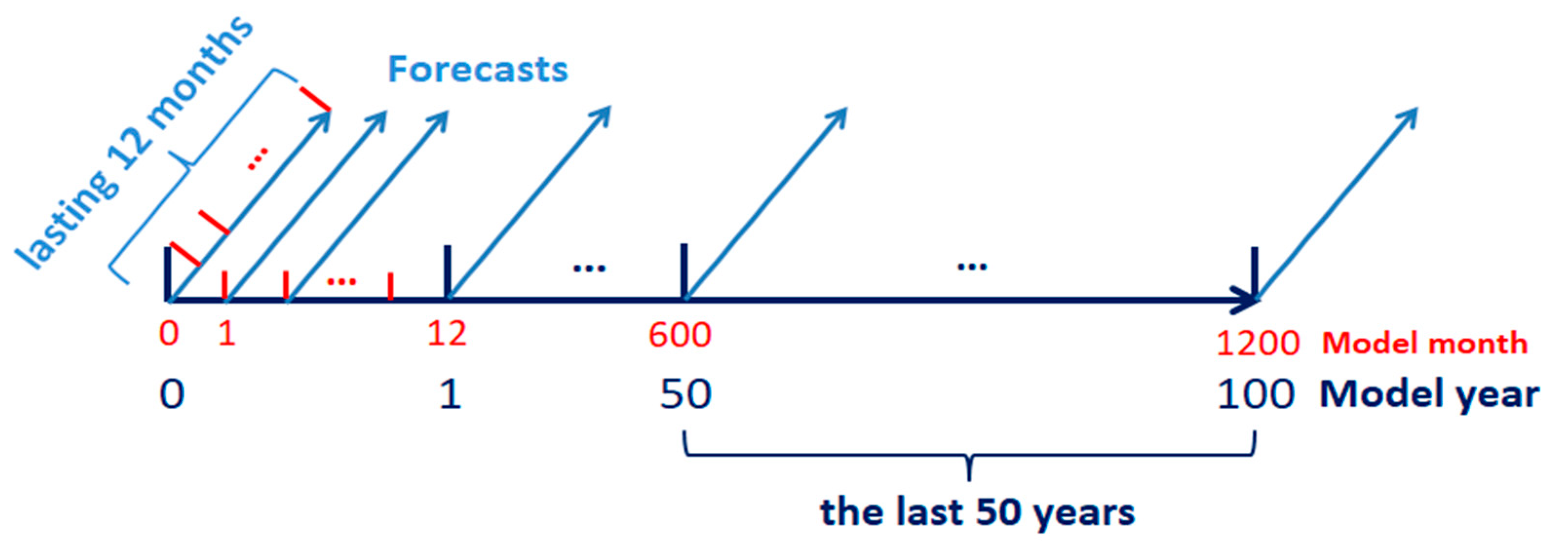

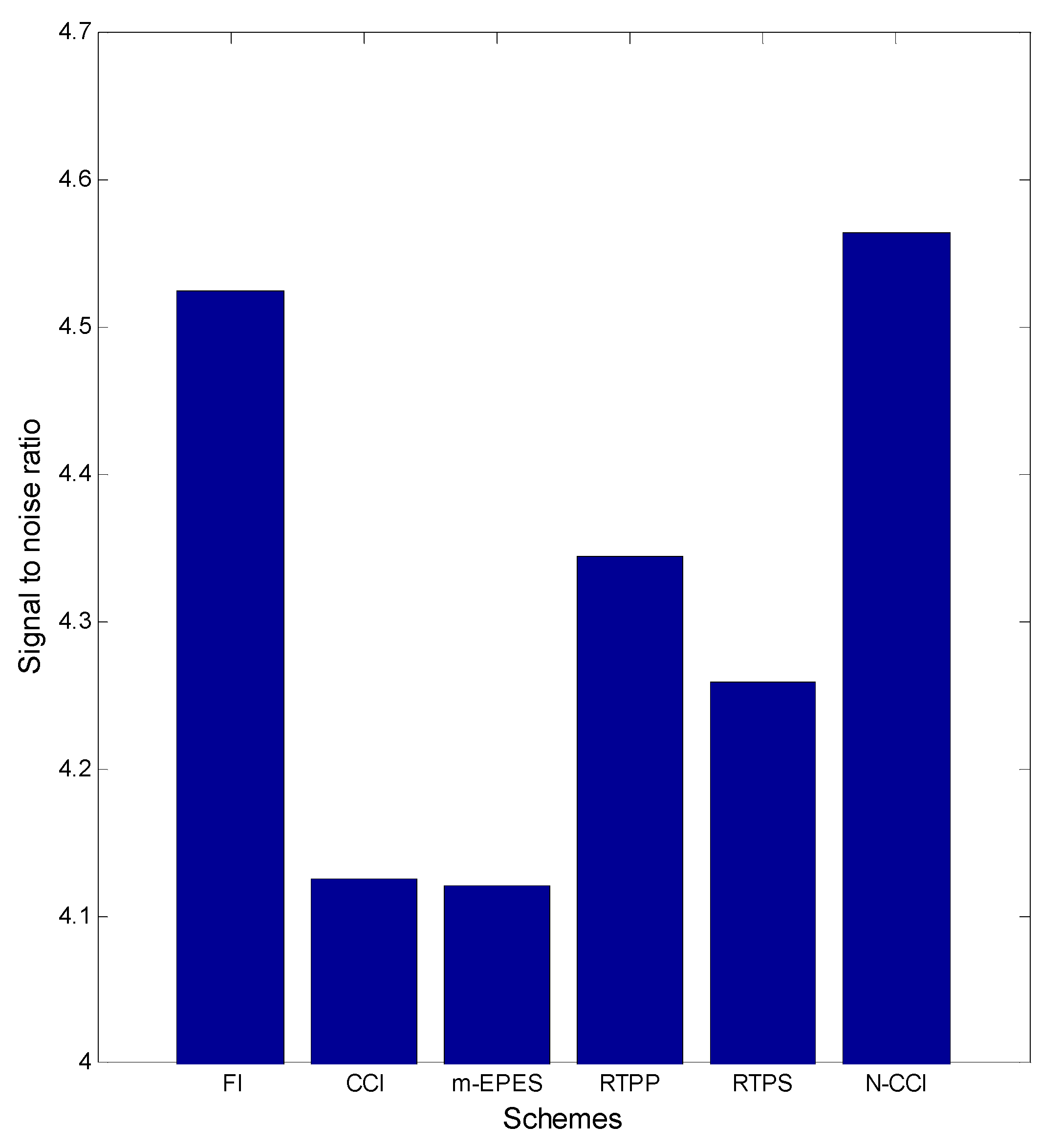

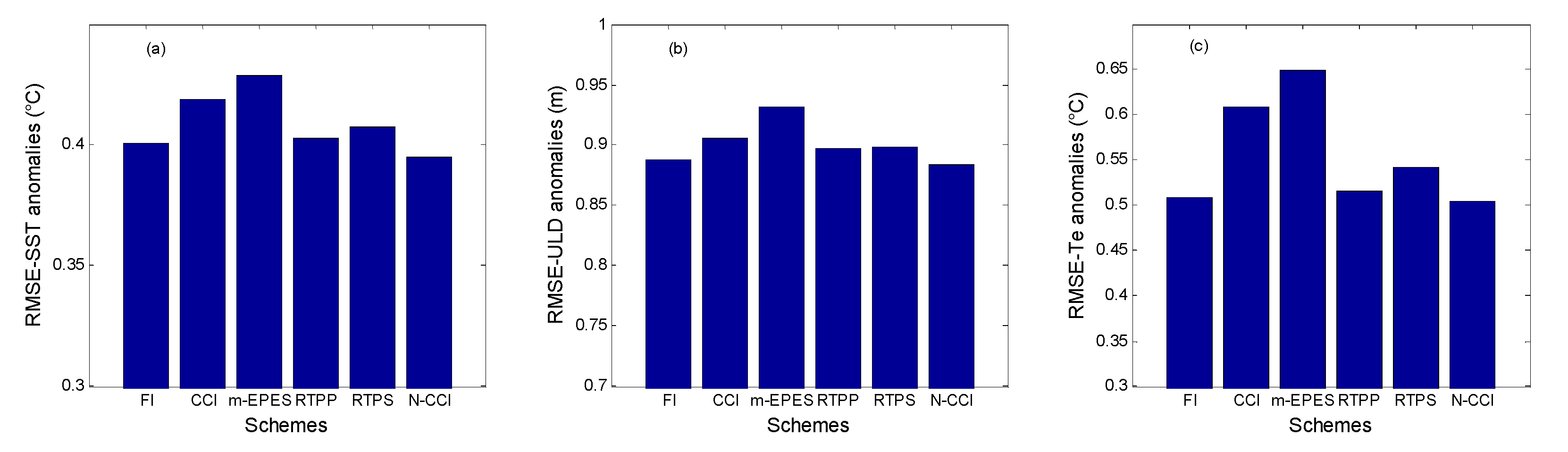
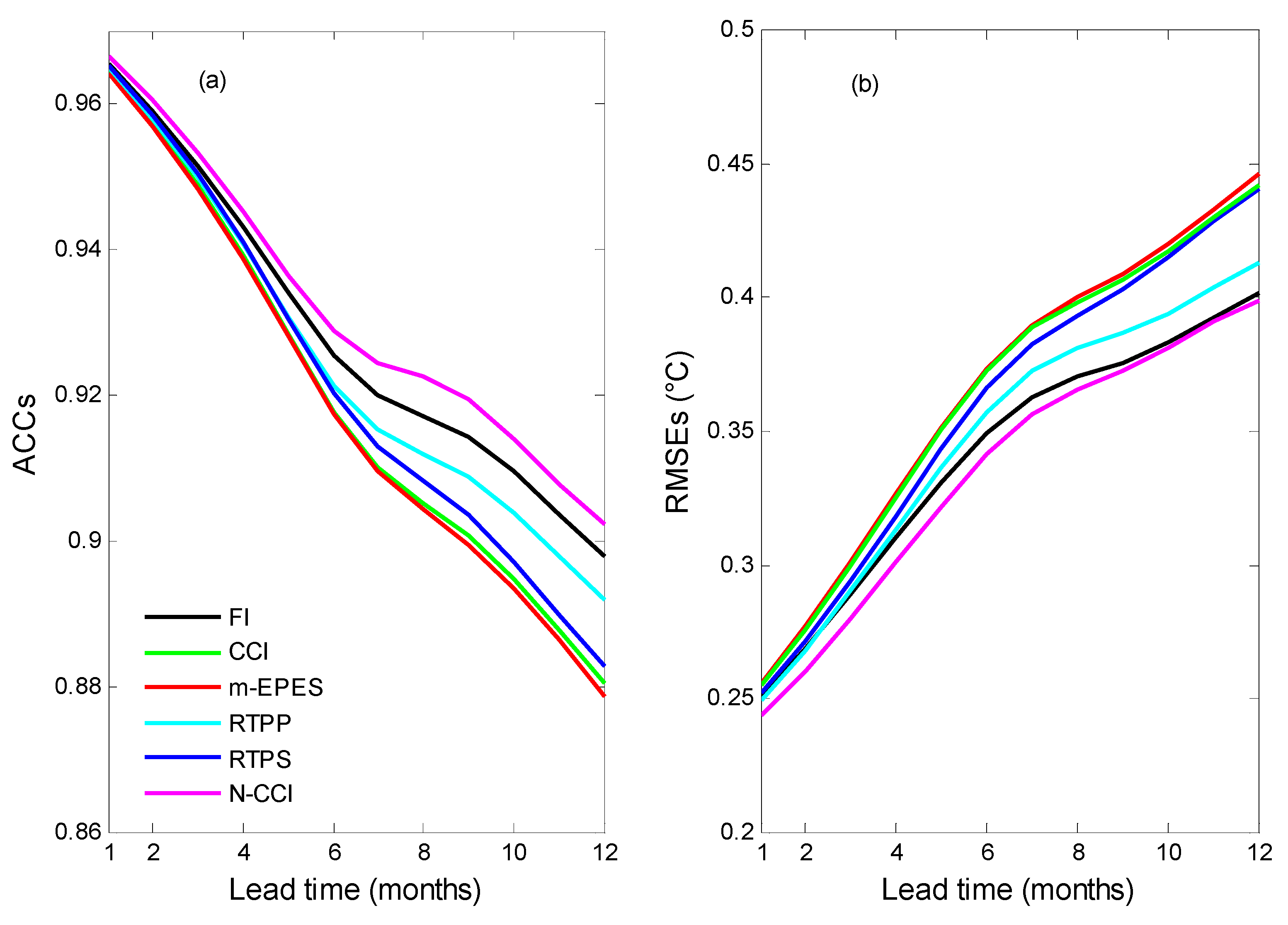
| Pars. | Physical Meanings | Truths | Biased Guess |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength of mean upwelling advection term | 0.75 | 0.6 | |
| Strength of anomalous upwelling advection term | 0.75 | 0.6 | |
| Amplitude of subsurface temperature anomaly + perturbations | 28 | 22.4 | |
| Amplitude of subsurface temperature anomaly for − perturbations | −40 | −48 | |
| Affect the nonlinearity of subsurface temperature anomaly for + perturbations | 1.25 | 1.0 | |
| Affect the nonlinearity of subsurface temperature anomaly for − perturbations | 3.0 | 2.4 |
| Algorithms | Schemes | Factors/Thresholds in SPE | Convergence Times in SPE | Factors/Thresholds in MPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FI | (1.0005~1.2]) | 284 | 1.0005 (1.0005~1.2]) |
| 2 | CCI | (0.001~0.1]) | 355 | 0.012, 0.016, 0.45, 1.95, 0.02, 0.07 (omitted) |
| 3 | m-EPES | 0.95 (0.8~1.2]) | 70 | 0.98 (0.8~1.2]) |
| 4 | RTPP | (0.1~1.2]) | 288 | 0.45 (0.1~1.2]) |
| 5 | RTPS | 0.6 (0.1~1.2]) | 434 | 0.2 (0.1~1.2]) |
| 6 | N-CCI | (0.08~0.4]) | 168 | ], ],],],],] (omitted) |
| Experiments | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0005 | 1.002 | 1.005 | 1.10 | 1.20 | |
| Convergence time | 349 | 284 | 573 | 1162 | / |
| Experiments | Assimilated Data | To Be Estimated |
|---|---|---|
| SPE | SST anomalies | SST anomalies and , , , , , or |
| MPE | SST anomalies | SST anomalies, , , , , , and |
| SE | SST anomalies | SST anomalies |
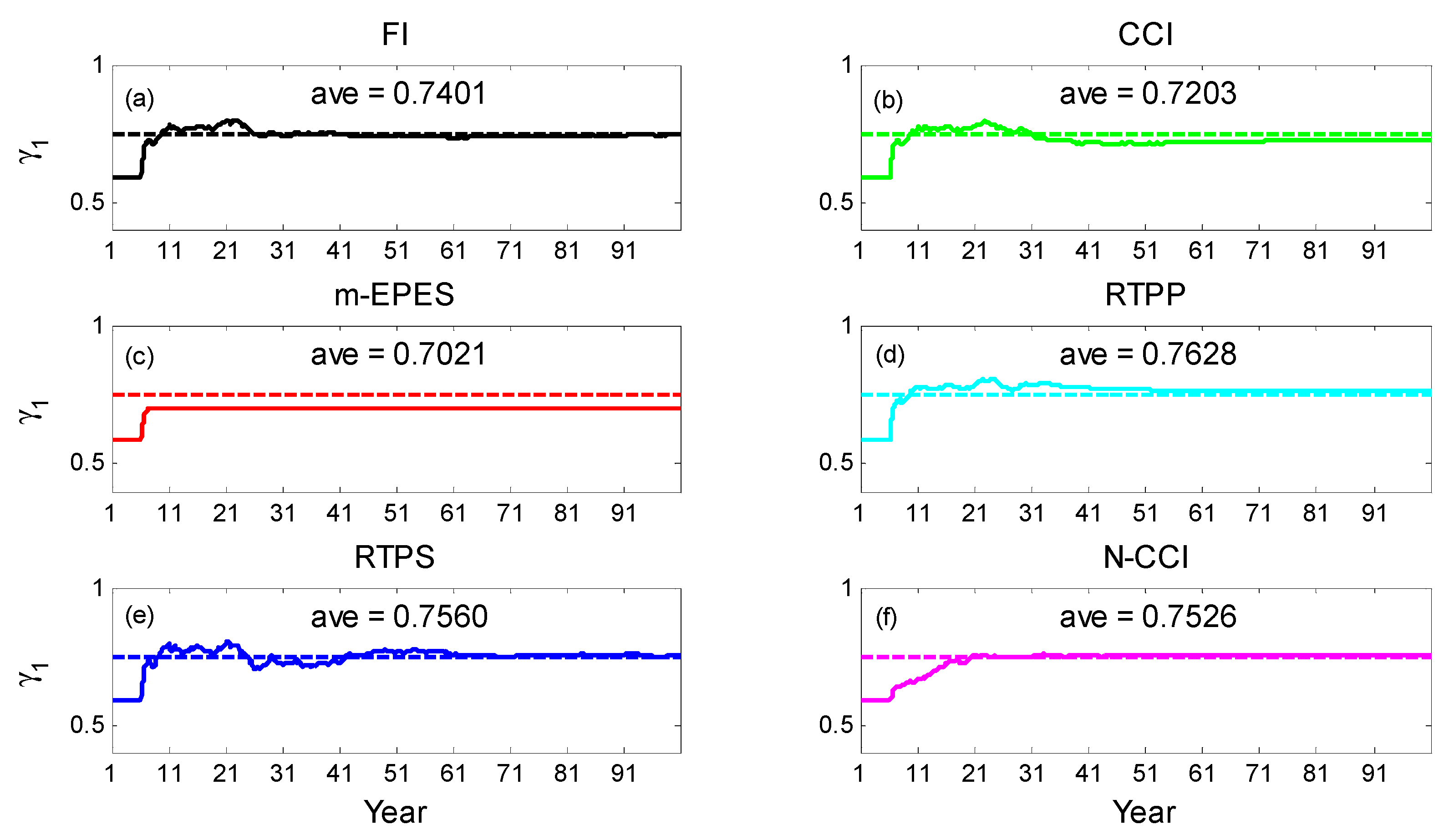
| Experiments | FI | CCI | m-EPES | RTPP | RTPS | N-CCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ1 | 0.7401 | 0.7203 | 0.7021 | 0.7628 | 0.7560 | 0.7526 |
| FI | CCI | m-EPES | RTPP | RTPS | N-CCI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| After | 0.8427 | 2.7813 | 2.8775 | 1.1755 | 1.5584 | 0.6913 |
| Decay (%) | 85.96 | 53.64 | 52.04 | 80.41 | 74.03 | 88.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y. Assessment of Inflation Schemes on Parameter Estimation and Their Application in ENSO Prediction in an OSSE Framework. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11102003
Gao Y. Assessment of Inflation Schemes on Parameter Estimation and Their Application in ENSO Prediction in an OSSE Framework. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2023; 11(10):2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11102003
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yanqiu. 2023. "Assessment of Inflation Schemes on Parameter Estimation and Their Application in ENSO Prediction in an OSSE Framework" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 11, no. 10: 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11102003
APA StyleGao, Y. (2023). Assessment of Inflation Schemes on Parameter Estimation and Their Application in ENSO Prediction in an OSSE Framework. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 11(10), 2003. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse11102003






