Capturing the Turning Hook of Stress-Dilatancy Curve of Crushable Calcareous Sand
Abstract
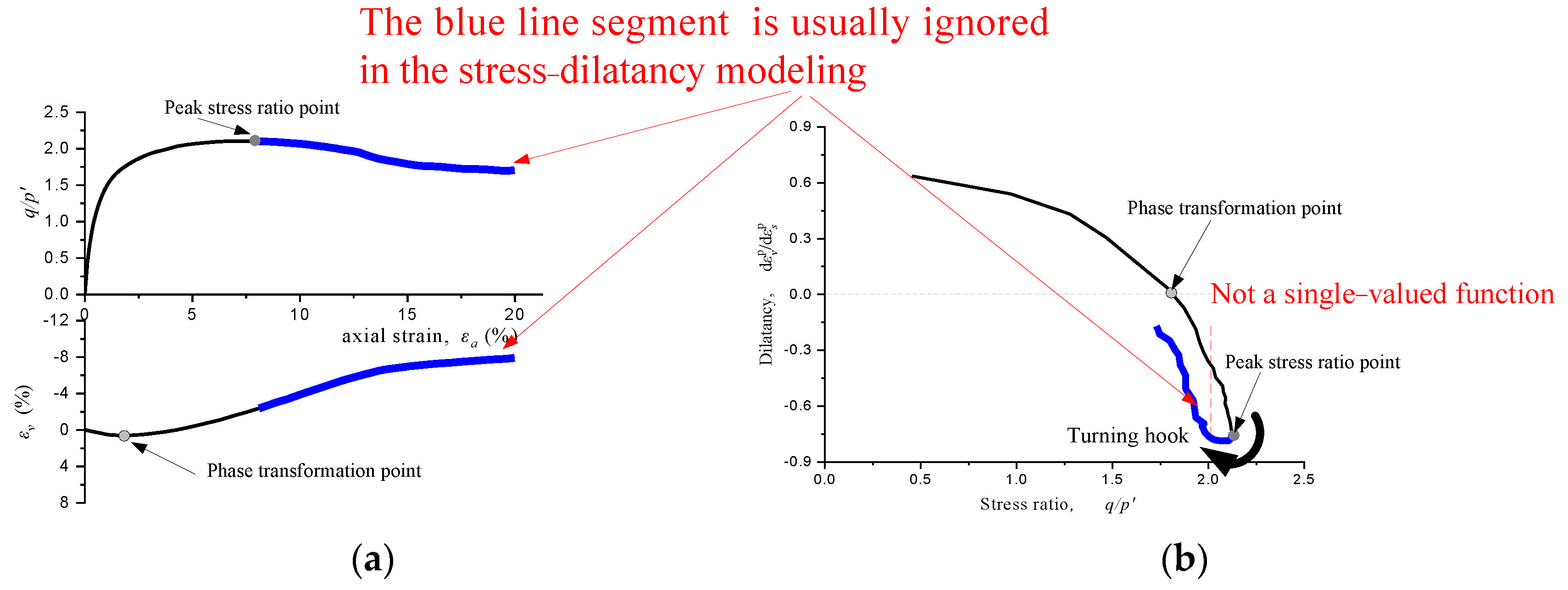
:1. Introduction
2. Stress-DilatancyModel
2.1. Model Establishment
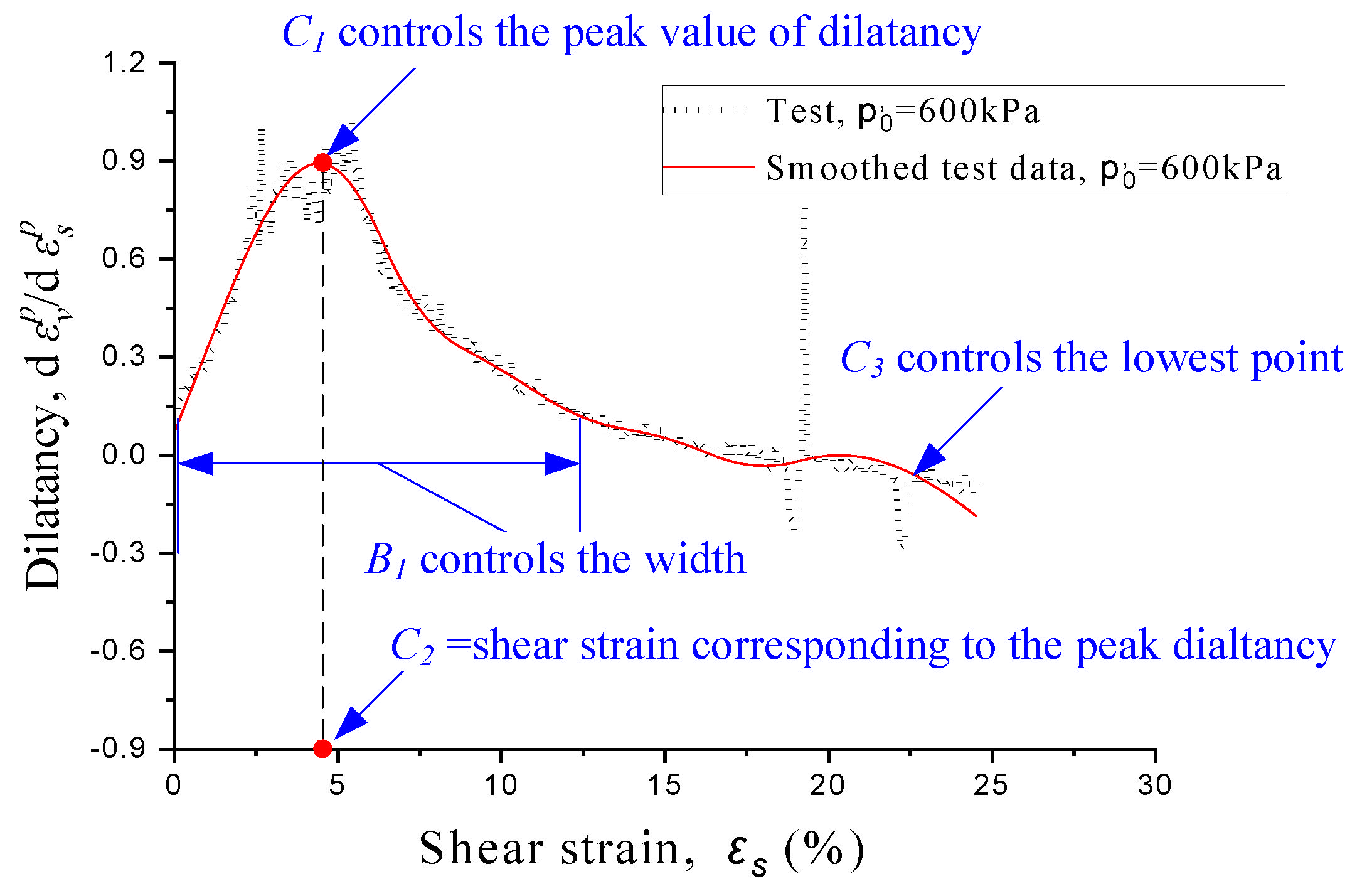
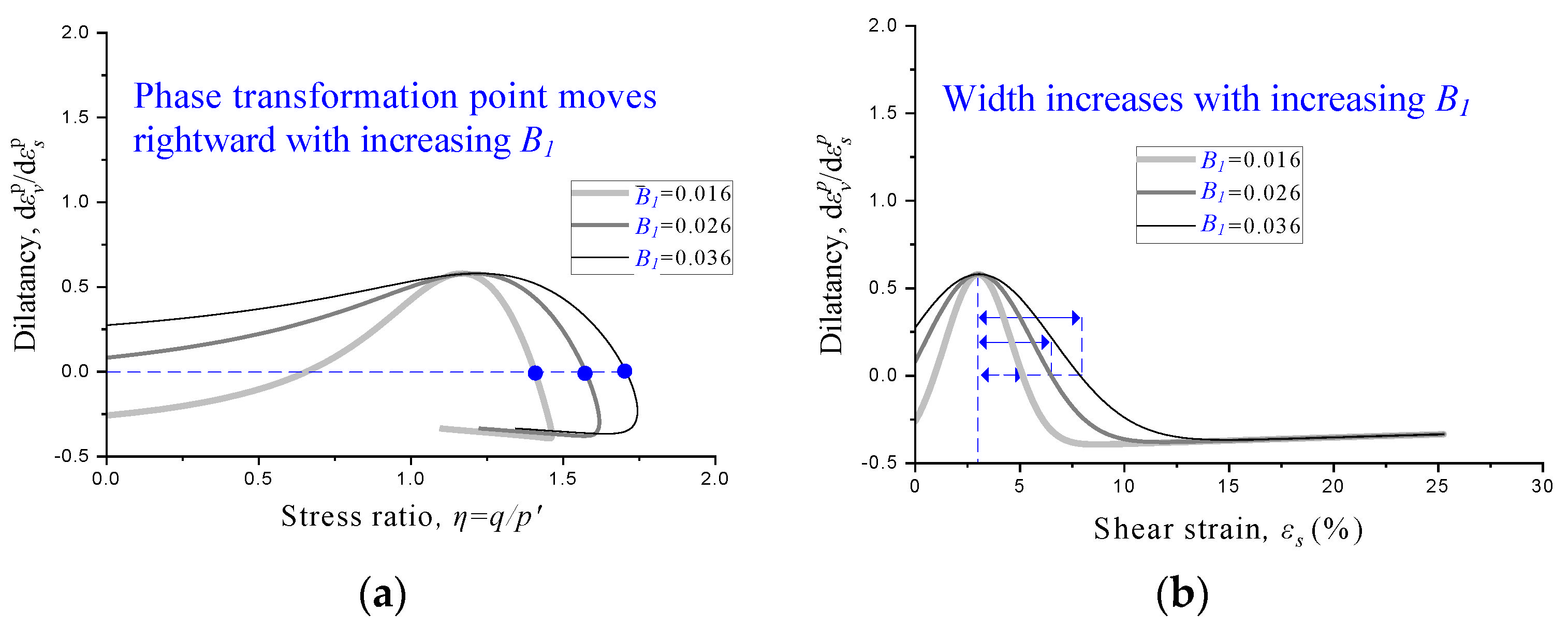
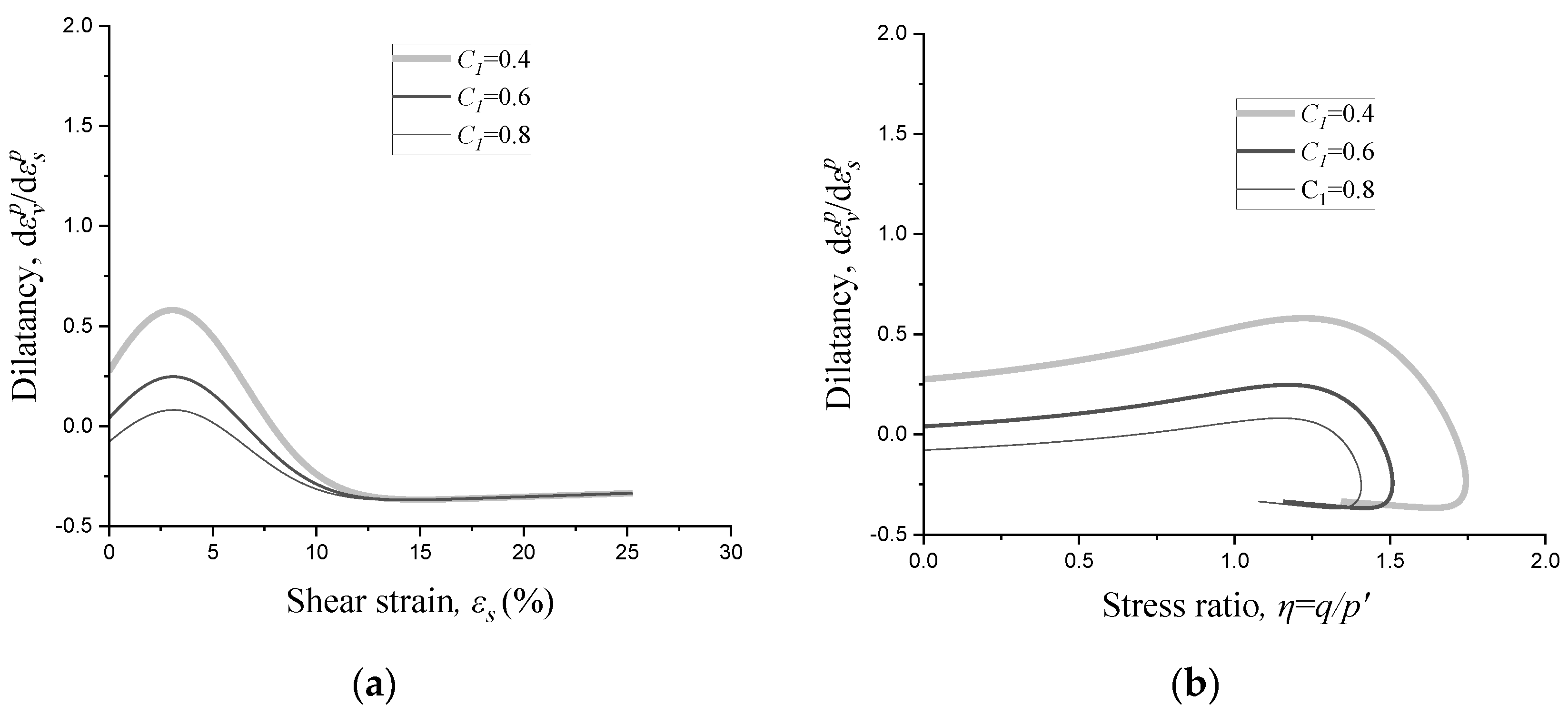
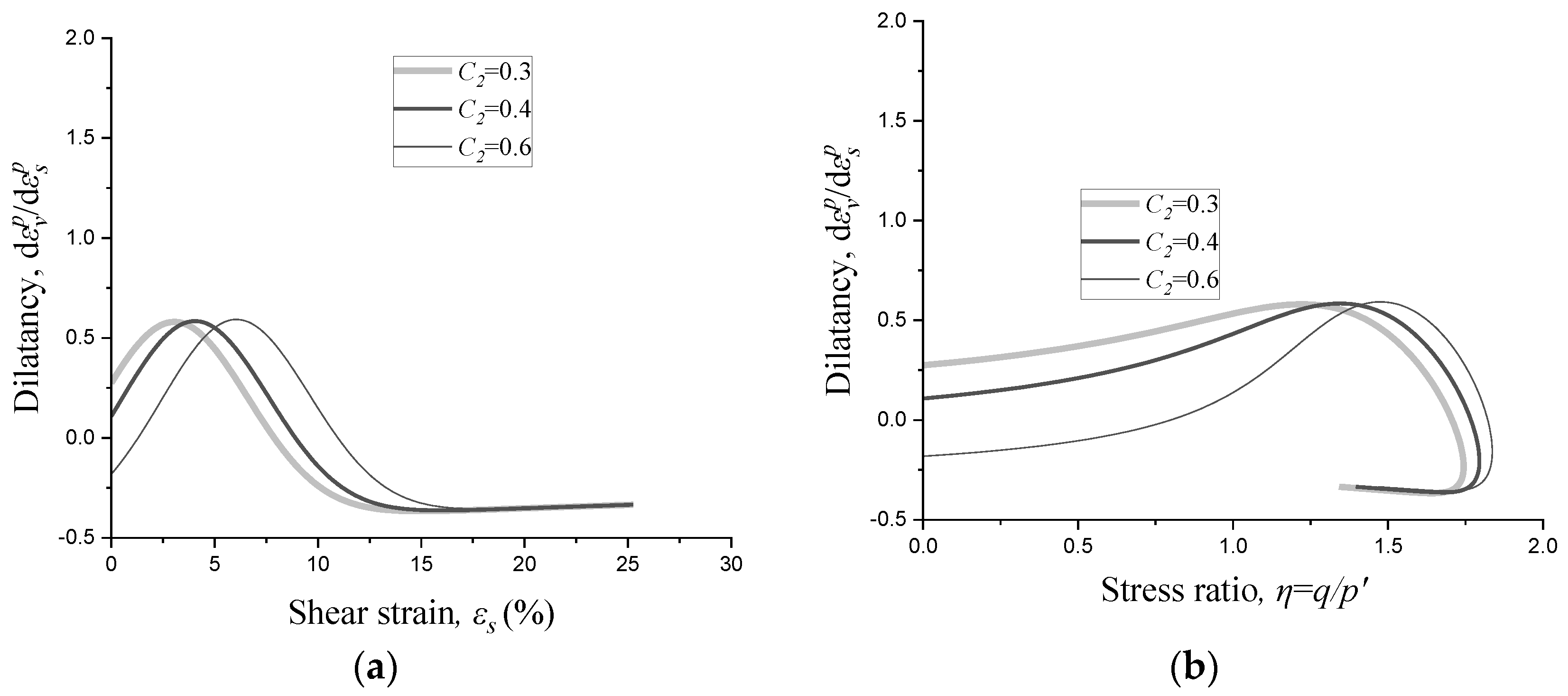
2.2. Effects of Parameters on Dilatancy
3. Model Verification by Colloidal-Silica-Stabilized Calcareous Sand
3.1. Experimental Materials
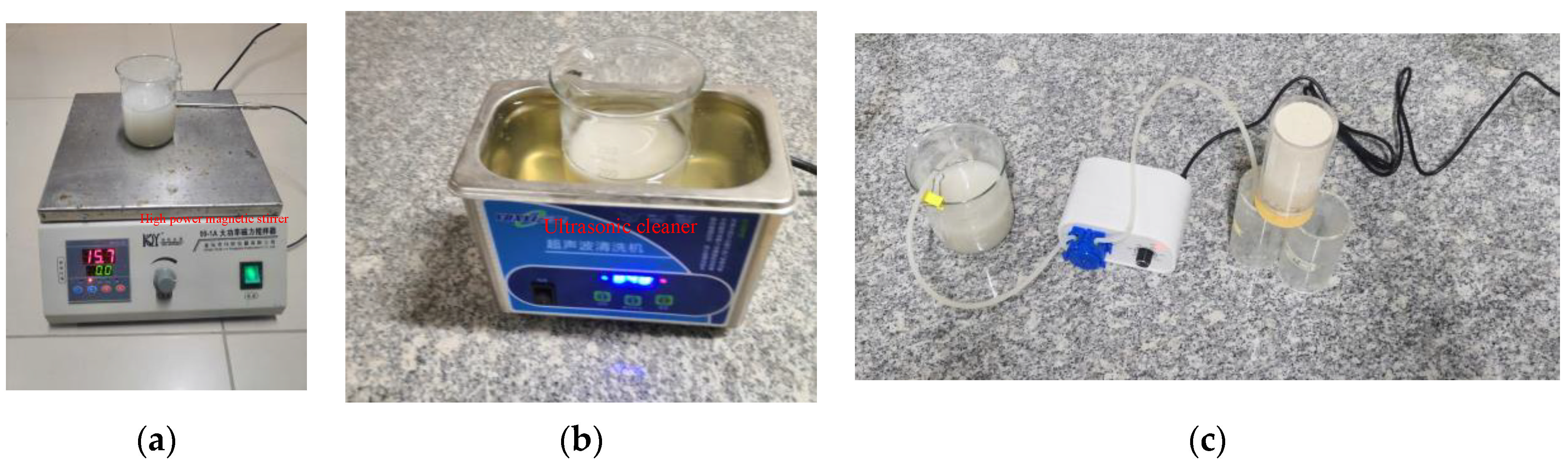
3.2. Specimen Preparation and Testing Apparatus
3.3. Experimental Plan
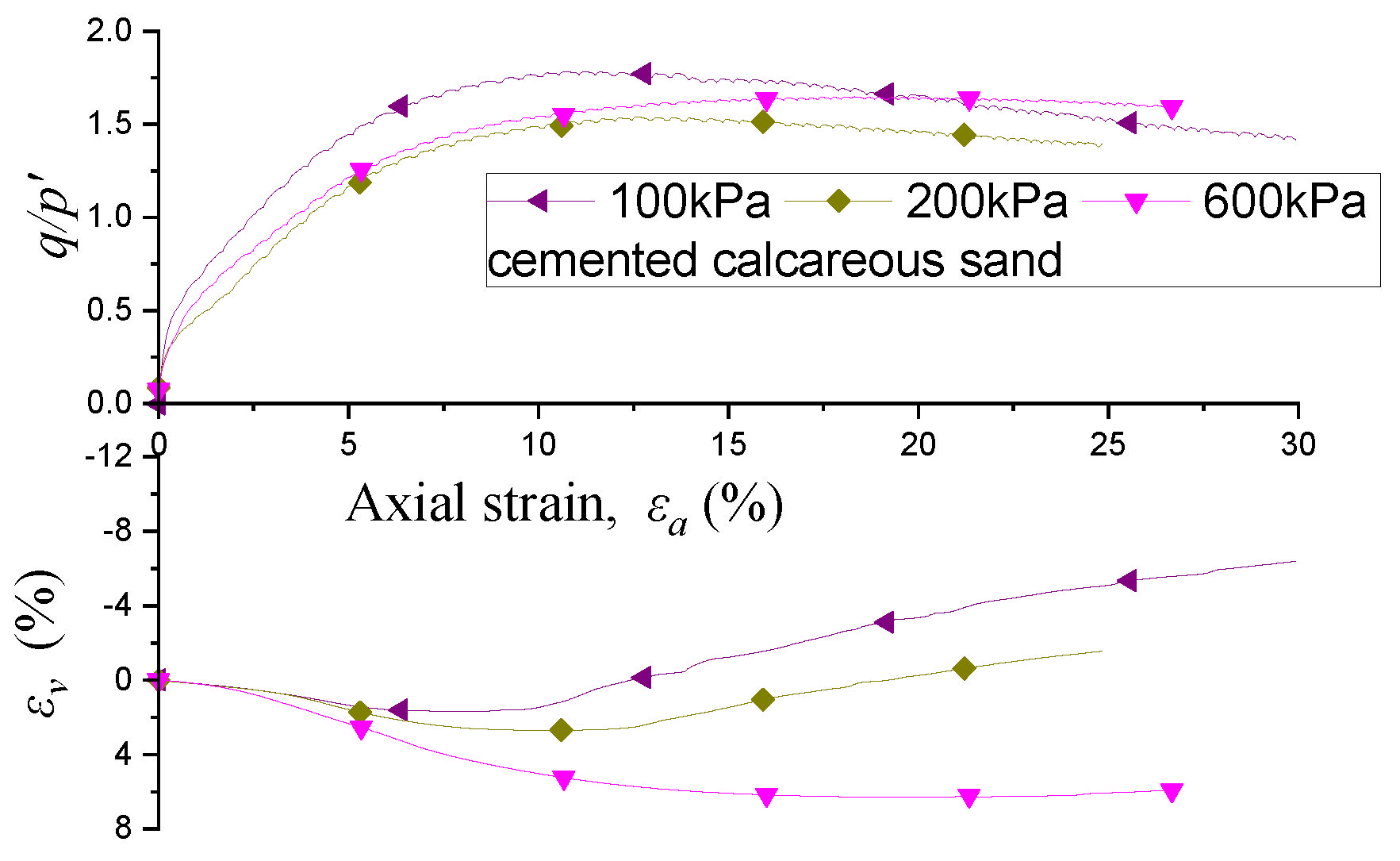
3.4. Testing Results
3.5. Parameter Determination
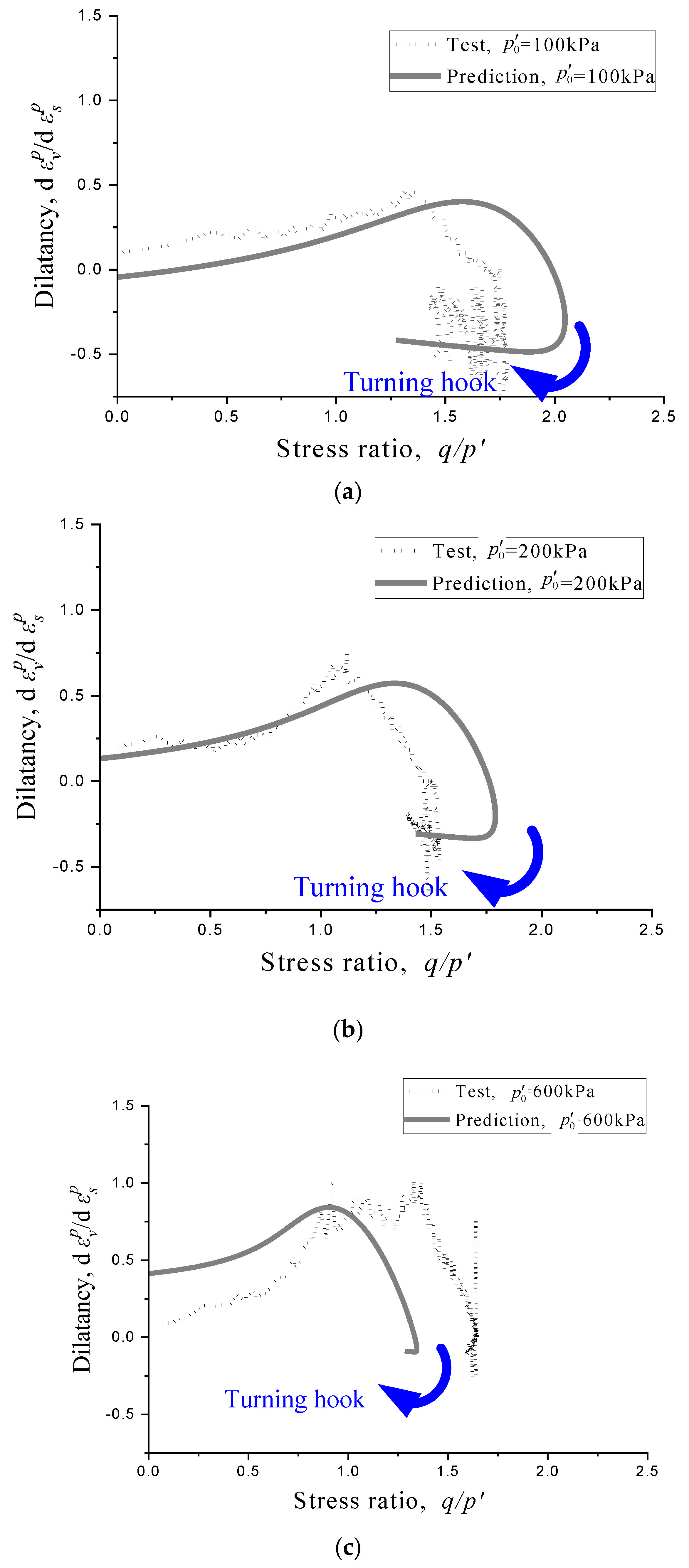
3.6. Simulation of Stress-Dilatancy Relationship
4. Comparison with Four Existing Models
4.1. Introduction of the Four Existing Stress-Dilatancy Models
4.2. Parameter Determination for the Four Existing Stress-Dilatancy Models
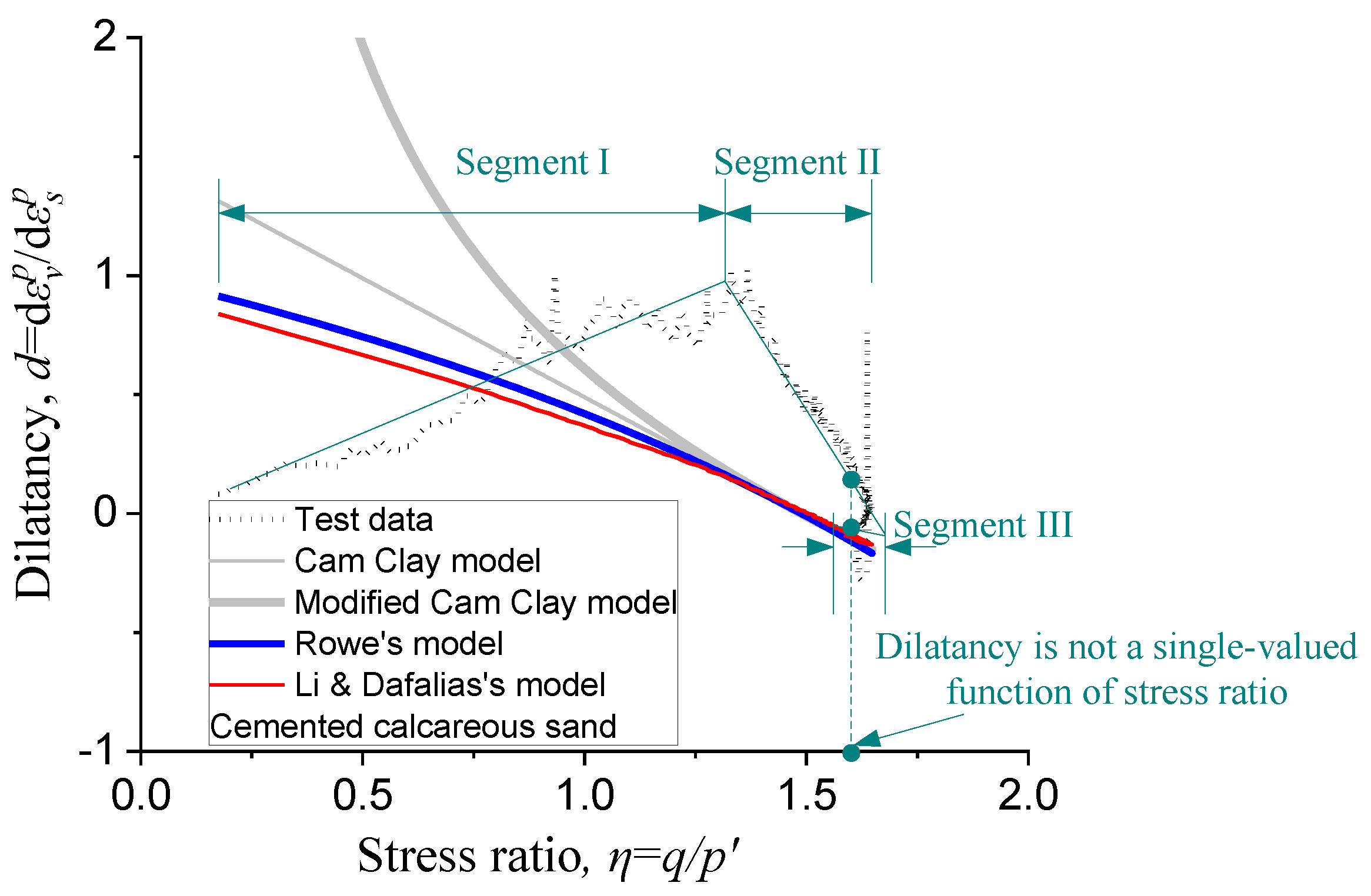
4.3. Comparison of Predictions of Stress-Dilatancy Relationship
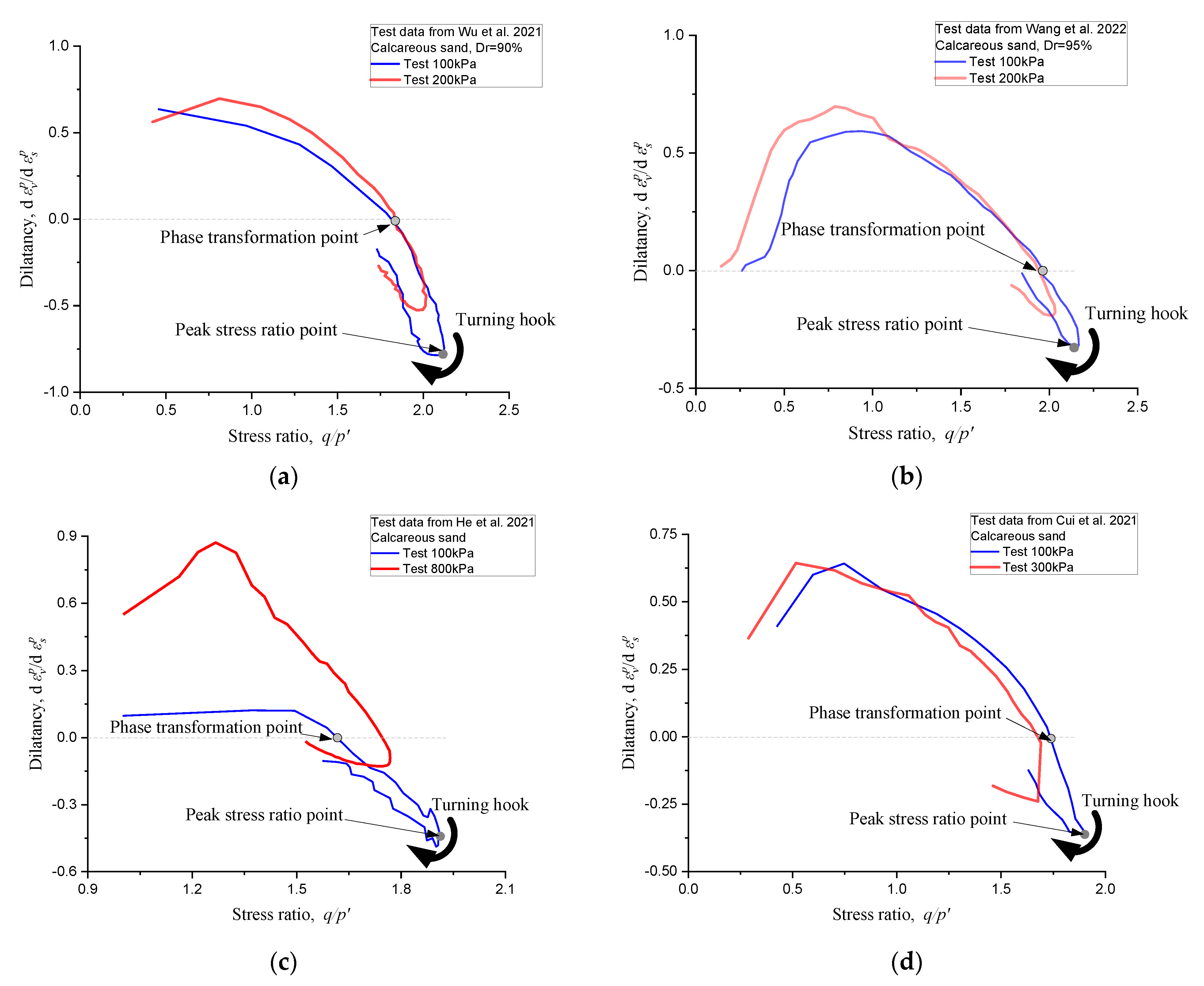
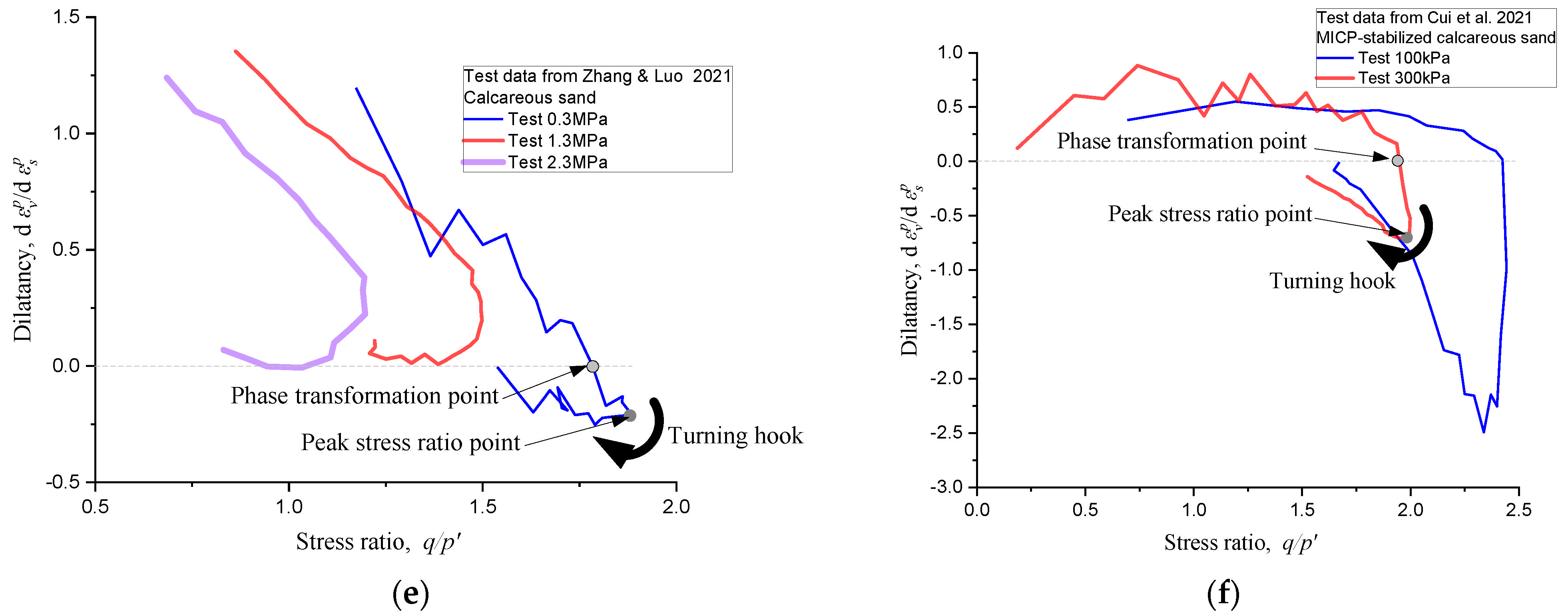
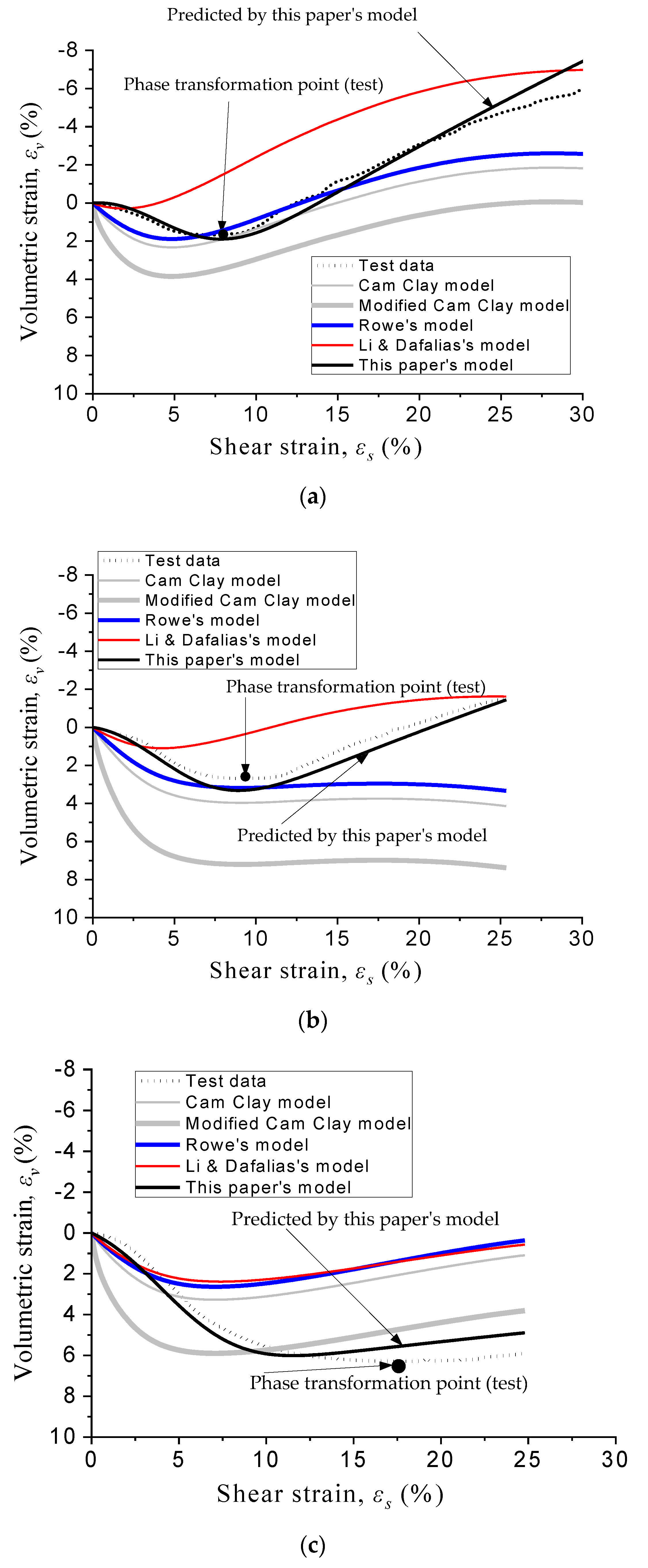
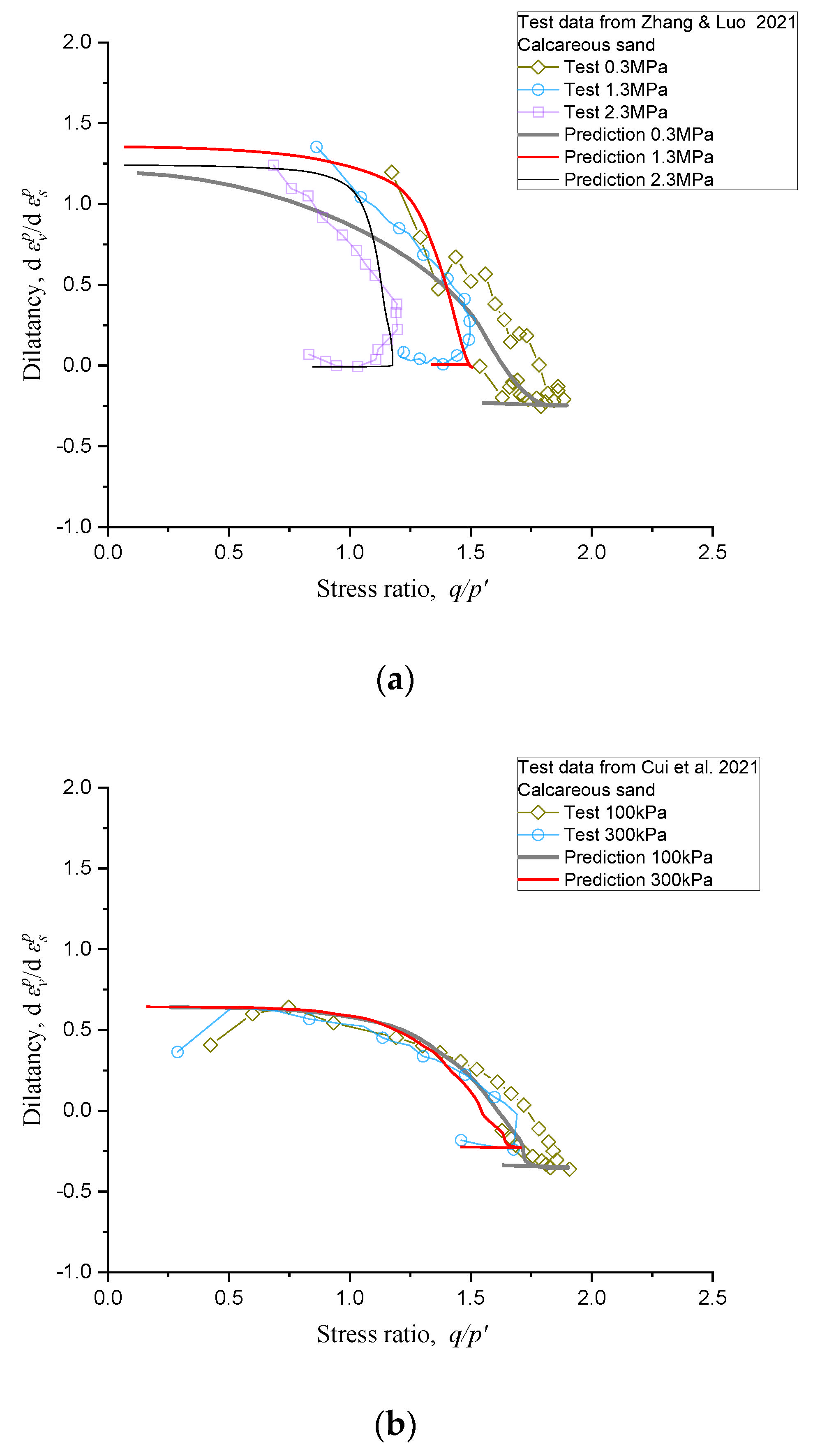
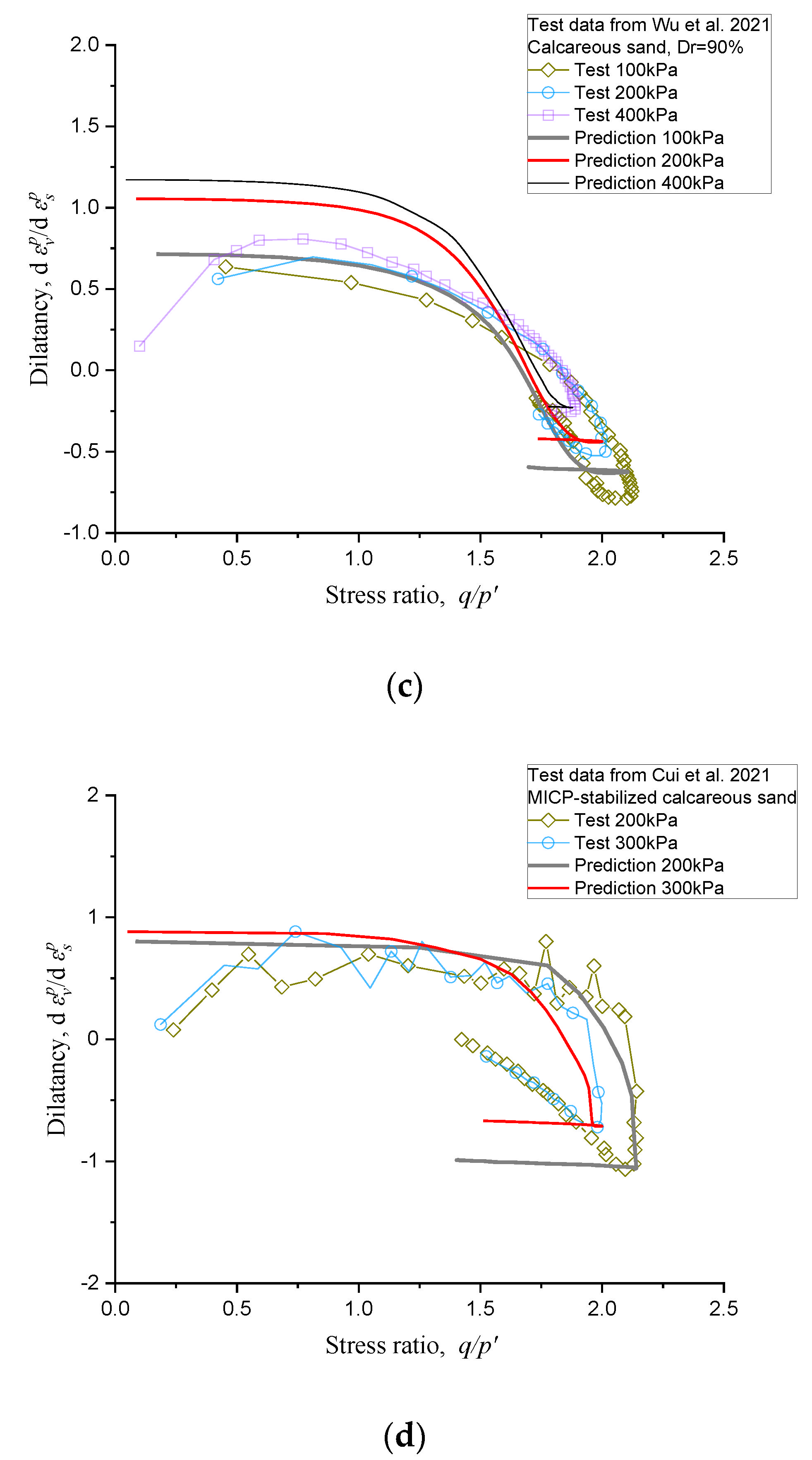
5. Further Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, X.Z.; Cui, J.; Chen, Y.L.; Wu, Y.H.; Yamamoto, H. Experimental investigation on mechanical behavior and particle crushing of calcareous sand retrieved from South China Sea. Eng. Geol. 2021, 280, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shan, Y.; Cui, J.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, J.H.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhu, C.Q. Dilatancy of the foundation filling material of island-reefs in the South China Sea. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.H.; Shan, H.F.; Xia, T.D.; Liu, Z.-J. The effect of temperature on the drained shear behavior of calcareous sand. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 613–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.J.; Zheng, J.J.; Chu, J.; Wu, C.-C.; Lai, H.-J. Bio-mediated calcium carbonate precipitation and its effect on the shear behaviour of calcareous sand. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 1377–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, M. Dilatancy and critical state of calcareous sand incorporating particle breakage. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04020030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, A.; Wroth, C.P. Critical State Soil Mechanics; McGraw-Hill: London, UK, 1968; pp. 100–101. [Google Scholar]
- Roscoe, K.H.; Burland, J.B. On the Generalized Stress–Strain Behaviour of ‘Wet’ Clay. In Engineering Plasticity; Heyman, J., Leckie, F.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1968; pp. 535–609. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, P.W. The Stress–Dilatancy Relation for Static Equilibrium of an Assembly of Particles in Contact. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Physicl Sci. 1962, 269, 500–527. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, W.X.; Ye, G.L.; Zhang, F.M. A unified constitutive model for cemented/non-cemented soils under monotonic and cyclic loading. Acta Geotech. 2021; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajo, A.; Cecinato, F.; Hueckel, T. Chemo-mechanical modeling of artificially and naturally bonded soils. Geomech. Energ. Envir. 2019, 18, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.M.; Li, X.S. A model for natural soil with bonds. Géotechnique 2011, 61, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.S.; Tan, S.M.; Schnaid, F. A critical state framework for modelling bonded geomaterials. Geomech. Geoeng. 2007, 2, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, I.F.; Hilder, T. A theoretical framework for constructing elastic/plastic constitutive models of triaxial tests. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Meth. Geomech. 2002, 26, 1313–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, I.F.; Muhunthan, B. On the relationship between stress–dilatancy, anisotropy, and plastic dissipation for granular materials. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, I.F.; Muhunthan, B.; Qu, B. Thermomechanical state parameter models for sands. Géotechnique 2010, 60, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Xu, Z. A thermodynamics-based hyperelasticplastic coupled model unified for unbonded and bonded soils. Int. J. Plast. 2021, 137, 102902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Stuedlein, A.W.; Evans, T.M. Liquefaction Modeling for Biocemented Calcareous Sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, R.G.; Guo, P.J. A pressure and density dependent dilatancy model for granular materials. Soils Found. 1999, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Dafalias, Y.F. Dilatancy for cohesionlesssoils. Géotechnique 2000, 50, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, K.J.; Huang, X.; O’Sullivan, C. Energy dissipation in soilsamplesduringdrained triaxial shearing. Géotechnique, 2018; 68, 421–433. [Google Scholar]
- Agapoulaki, G.I.; Papadimitriou, A.G. Rheological Properties of Colloidal Silica Grout for Passive Stabilization Against Liquefaction. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.M.; Lin, Y. Colloidal silica transport through liquefiable porous media. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 1702–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Kobayashi, M. Transport of colloidal silica in unsaturated sand: Effect of charging properties of sand and silica particles. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.M.; Conlee, C.T.; Rollins, K.M. Full-scale field testing of colloidal silica grouting for mitigation of liquefaction risk. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2007, 133, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallagher, P.M.; Pamuk, A.; Abdoun, T. Stabilization of liquefiable soils using colloidal silica grout. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2007, 19, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlee, C.T.; Gallagher, P.M.; Boulanger, R.W.; Kamai, R. Centrifuge Modeling for Liquefaction Mitigation Using Colloidal Silica Stabilizer. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2012, 138, 1334–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Rodríguez, J.A.; Antonio-Izarraras, V.M.; Bandini, P.; López-Molina, J.A. Cyclic strength of a natural liquefiable sand stabilized with colloidal silica grout. Can. Geotech. J. 2008, 45, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, P.M.; Mitchell, J.K. Influence of colloidal silica grout on liquefaction potential and cyclic undrained behavior of loose sand. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 22, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllos, P.K.; Georgiannou, V.N.; Pavlopoulou, E.; Dafalias, Y.F. Strength and dilatancy of sand before and after stabilisation with colloidal-silica gel. Géotechnique 2021, 72, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.F.; Tao, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z. The effect of carbon nanotubes on the strength of sand seeped by colloidal silica in triaxial testing. Materials 2021, 14, 6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.F.; Chen, R.Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Z.H. Effect of Wood Fiber on the Strength of Calcareous Sand Rapidly Seeped by Colloidal Silica. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Advances in Civil Engineering and Materials and 1st World Symposium on Sustainable Bio-Composite Materials and Structrues, Nanjing, China, 9–11 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinou, c.; Biscontin, G.; Jiang, N.J.; Soga, K. Application of microbially induced carbonate precipitation to form bio-cemented artificial sandstone. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. 2021, 13, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.J.; Zheng, J.J.; Dahal, B.K.; Lai, H.J.; Huang, Z.F.; Wu, C.C. Effect of waste rubber particles on the shear behaviour of bio-cemented calcareous sand. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Yin, L.Y.; Tang, C.S.; Zhu, C.; Cheng, Q.; Li, H.; Lv, C. Tensile behavior of bio-cemented, fiber-reinforced calcareous sand from coastal zone. Eng. Geol. 2021, 294, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Stuedlein, A.W.; Pan, Z.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Evans, T.M.; He, X.; Lin, H.; Chu, J.; Passen, L.A.V. Toe-bearing capacity of precast concrete piles through biogrouting improvement. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2020, 146, 06020026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Dong, B.W.; Yu, J.; Cai, Y.Y.; Peng, X.Q.; Zhou, X.Q. Effect of different mineralization modes on strengthening calcareous sand under simulated seawater conditions. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.Z.; Ye, Z.; Shen, C.F.; Zhou, W.J. Interface shear behavior between MICP-treated calcareous sand and steel. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04020455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.Z.; Li, Y.L.; Liu, Z.Y. Shear resistance of MICP cementing material at the interface between calcareous sand and steel. Mater. Lett. 2020, 274, 128009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Liu, H.L.; Xiao, Y.; Stuedleinc, A.W.; Evans, T.M. Liquefaction resistance of bio-cemented calcareous sand. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 107, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Specific Gravity, Gs | Max. Dry Density (kg/m3) | Min. Dry Density (kg/m3) | Relative Density | Coefficient of Uniformity, Cu | Coefficient of Curvature, Cc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.79 | 1370 | 1190 | 0.516 | 1.9 | 1.09 |
| SiO2 (%) | pH | Density (g/cm3) | Viscosity (Pa.s) | Average Particle Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 8.5~10.0 | 1.12~1.14 | 5.0 × 10−3 | 10~20 |
| Diameter (nm) | Length (μm) | Density (g/cm3) | Purity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100–600 | 50–100 | 3.21 | 98 |
| 1.49 | 120 | 2.9 | 2.68 | 0.16 | 0.036 | 0.42 | 0.039 | −3.52 | 0.26 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, W.; Tao, Y.; Chen, R. Capturing the Turning Hook of Stress-Dilatancy Curve of Crushable Calcareous Sand. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091269
Jin W, Tao Y, Chen R. Capturing the Turning Hook of Stress-Dilatancy Curve of Crushable Calcareous Sand. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(9):1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091269
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Weifeng, Ying Tao, and Rongzhong Chen. 2022. "Capturing the Turning Hook of Stress-Dilatancy Curve of Crushable Calcareous Sand" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 9: 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091269
APA StyleJin, W., Tao, Y., & Chen, R. (2022). Capturing the Turning Hook of Stress-Dilatancy Curve of Crushable Calcareous Sand. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(9), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10091269






