Impacts of Hurricanes on Nutrient Export and Ecosystem Metabolism in a Blackwater River Estuary Complex
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
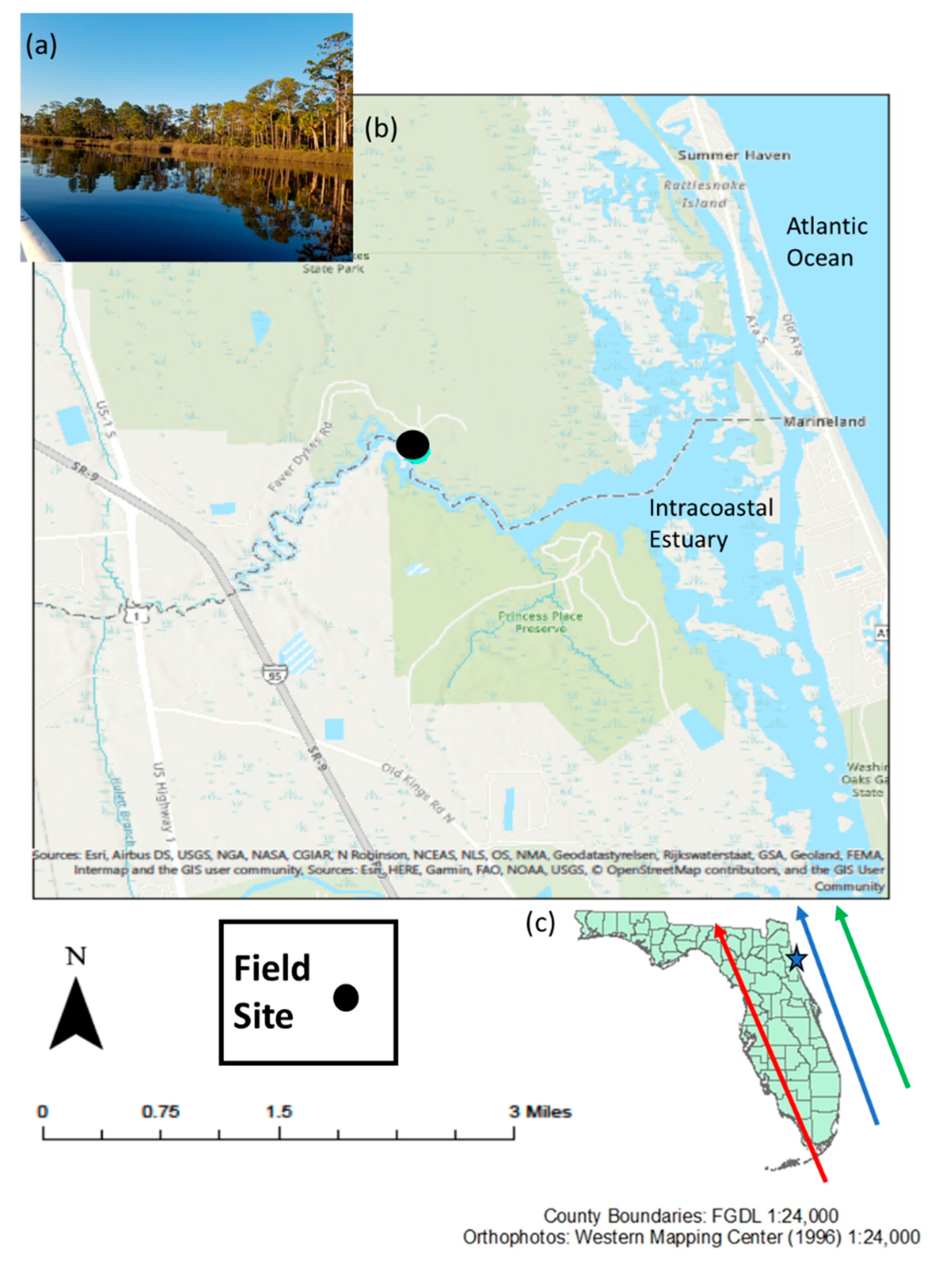
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Meteorological Events
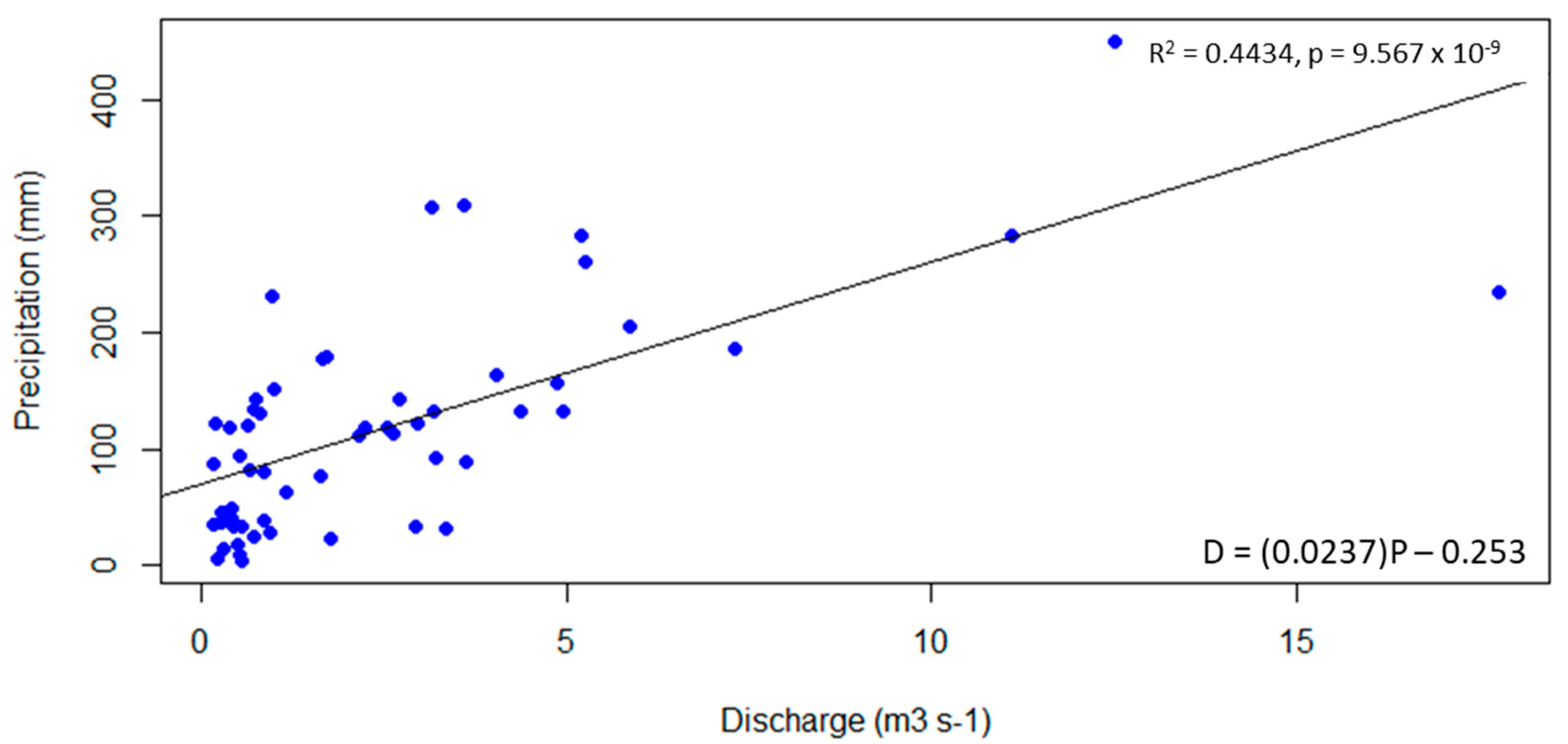
2.3. Export Calculations and Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ecosystem Metabolism
3. Results
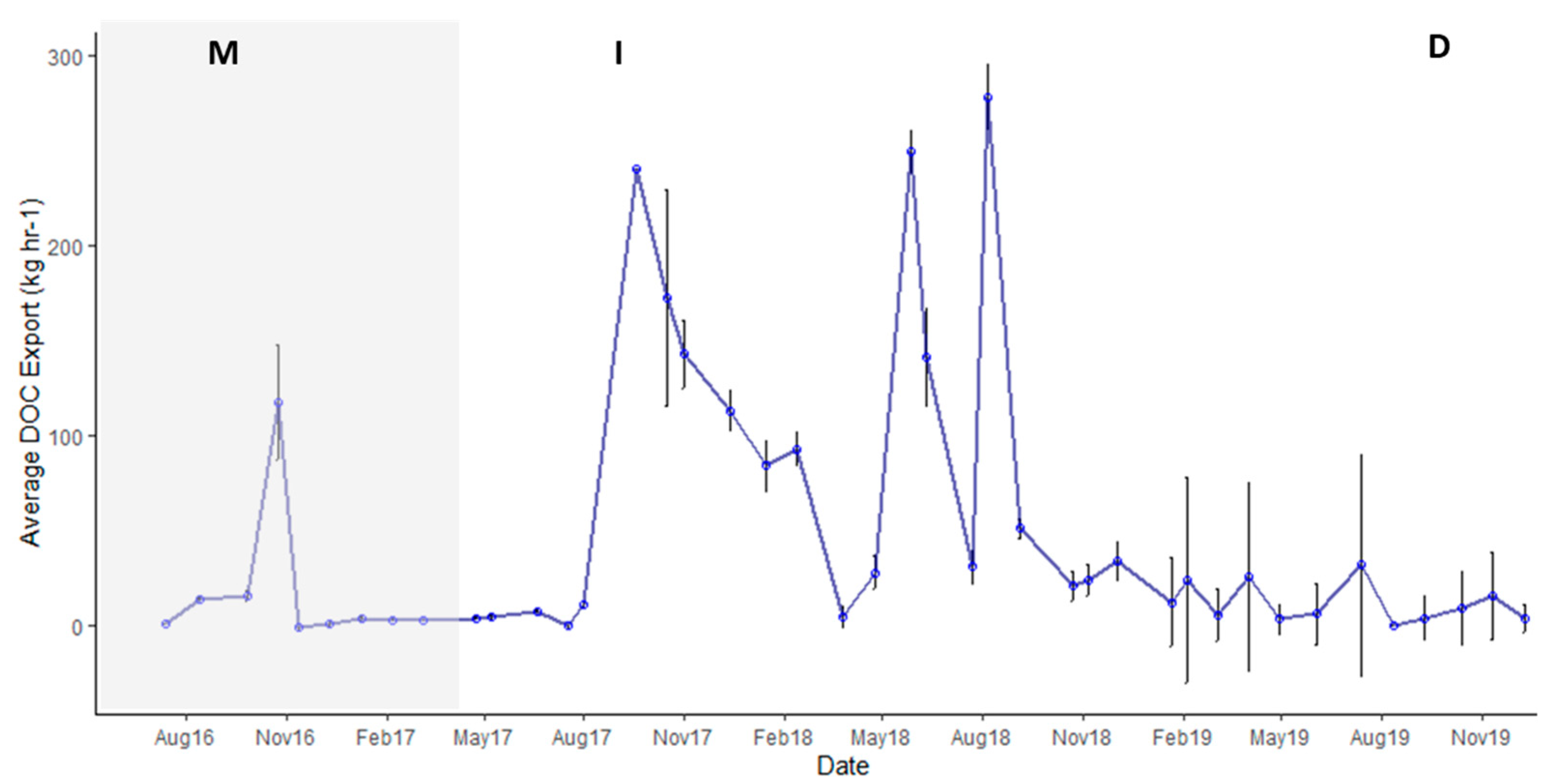
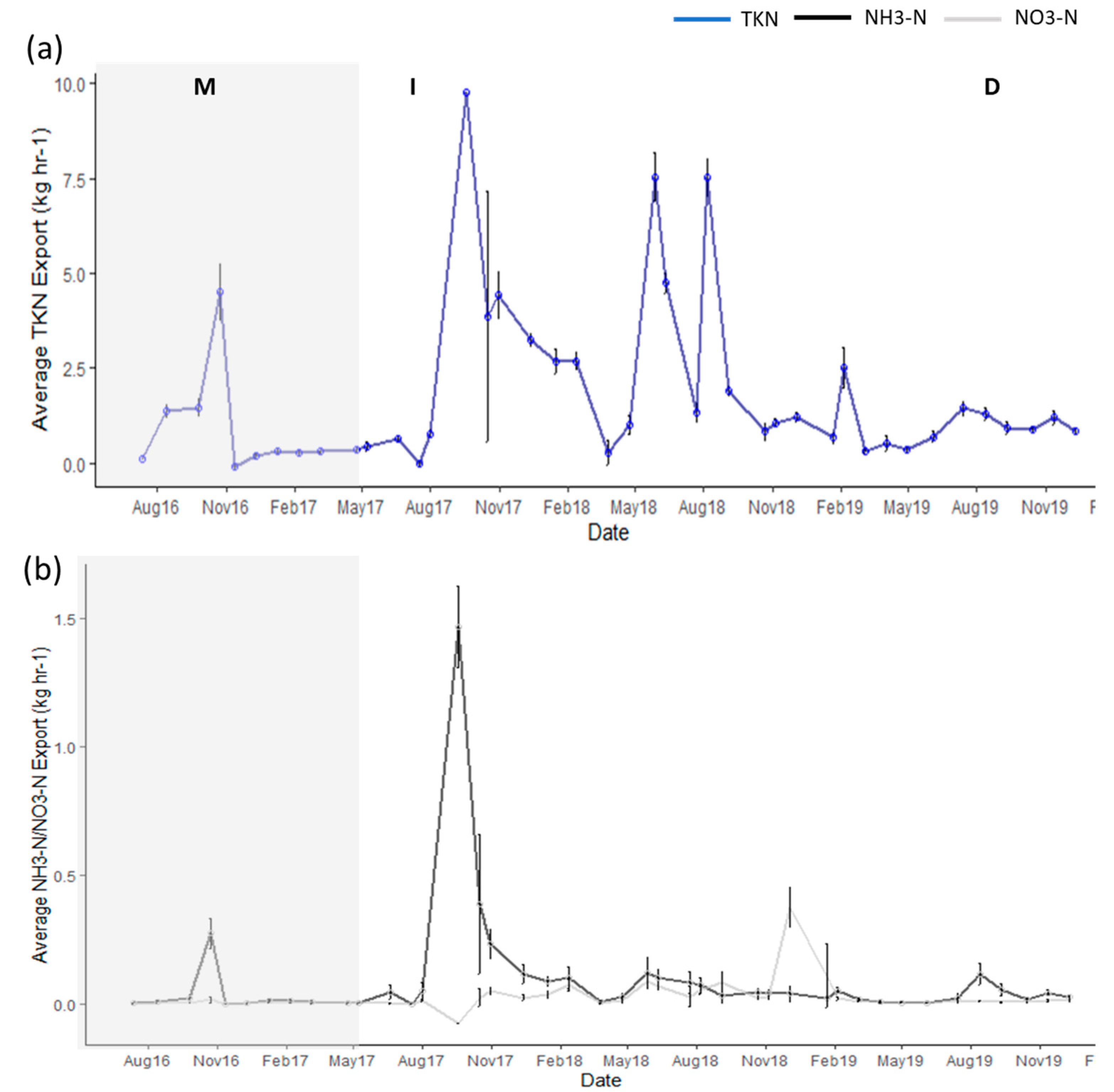
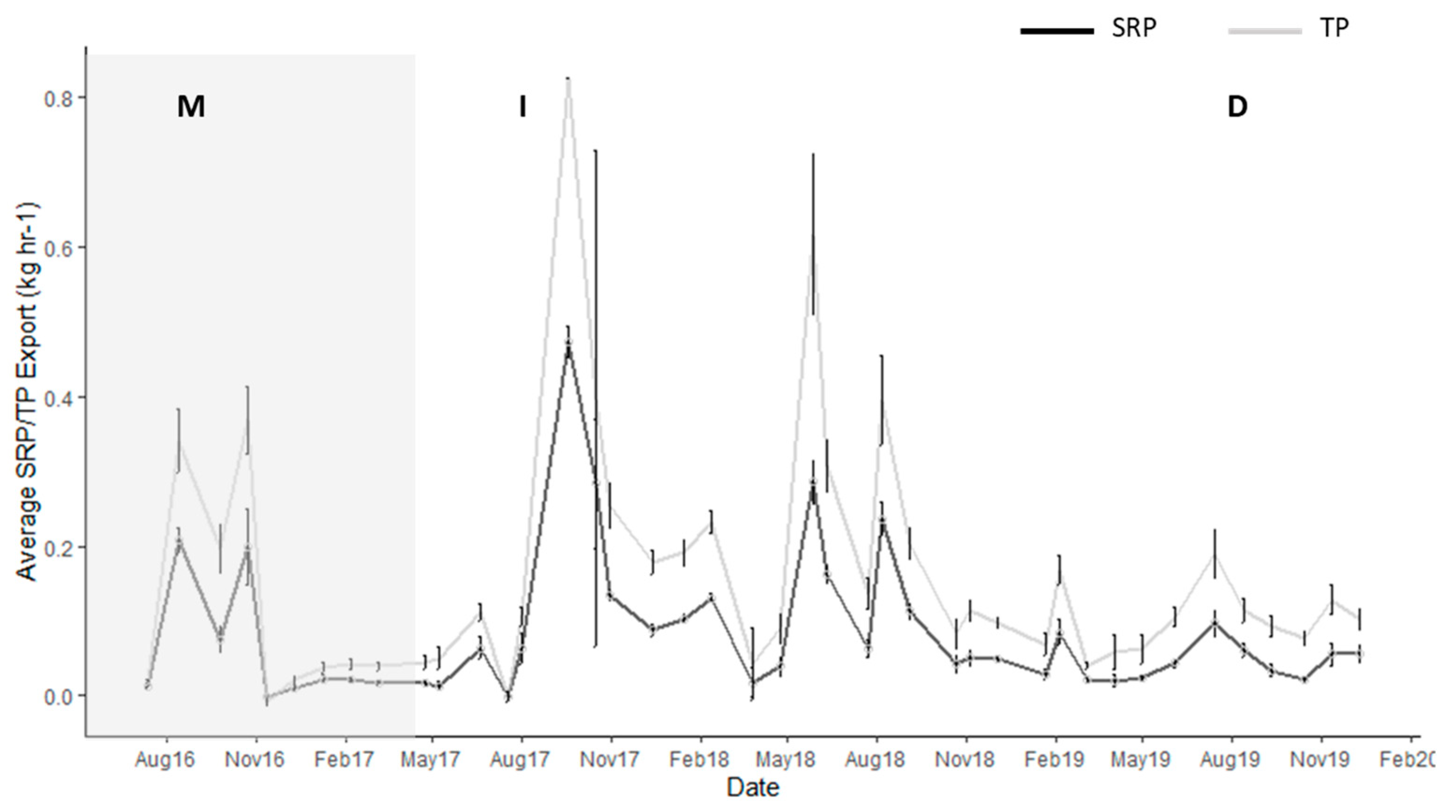
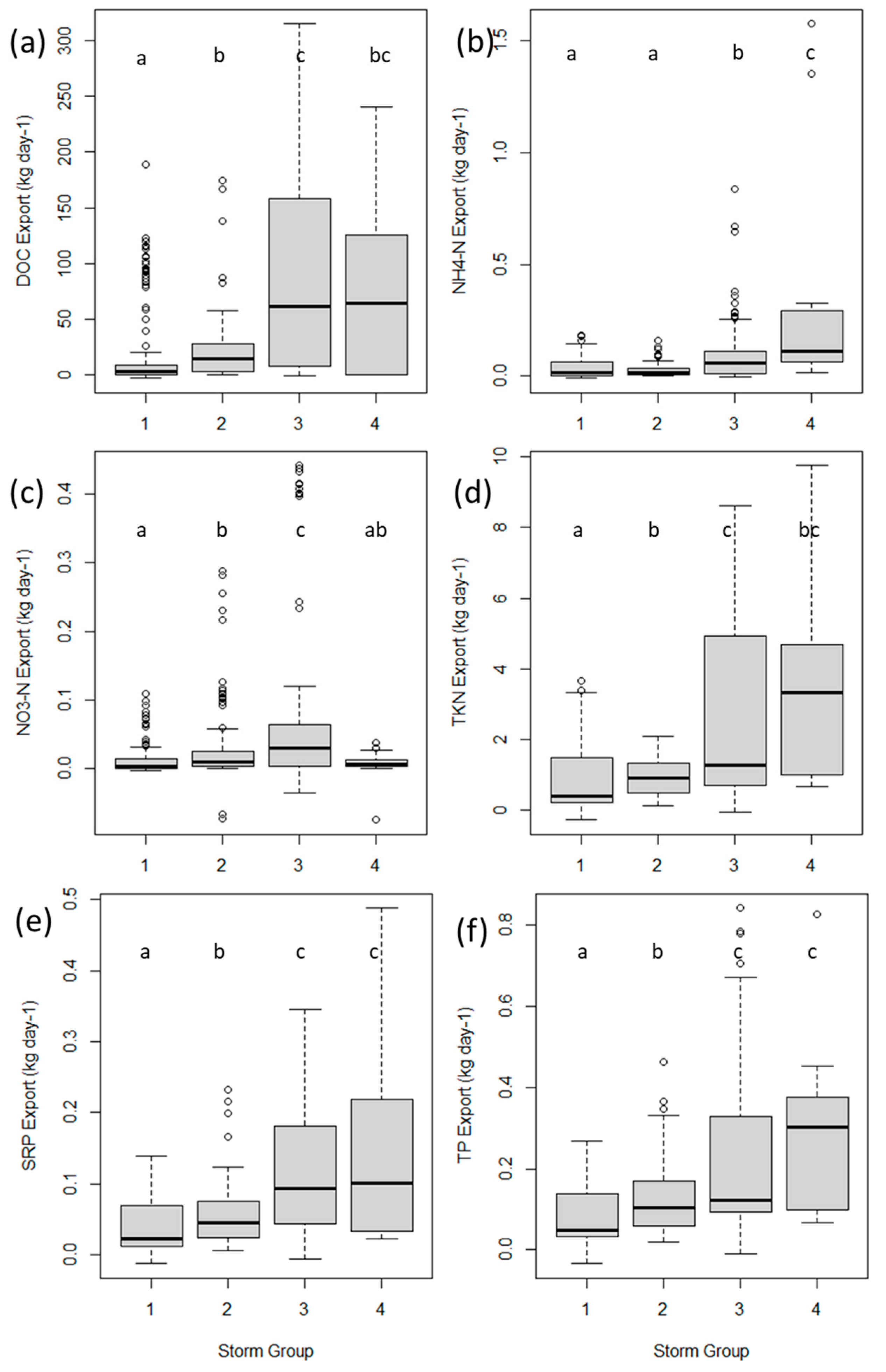
3.1. Export of DOC and Nutrients
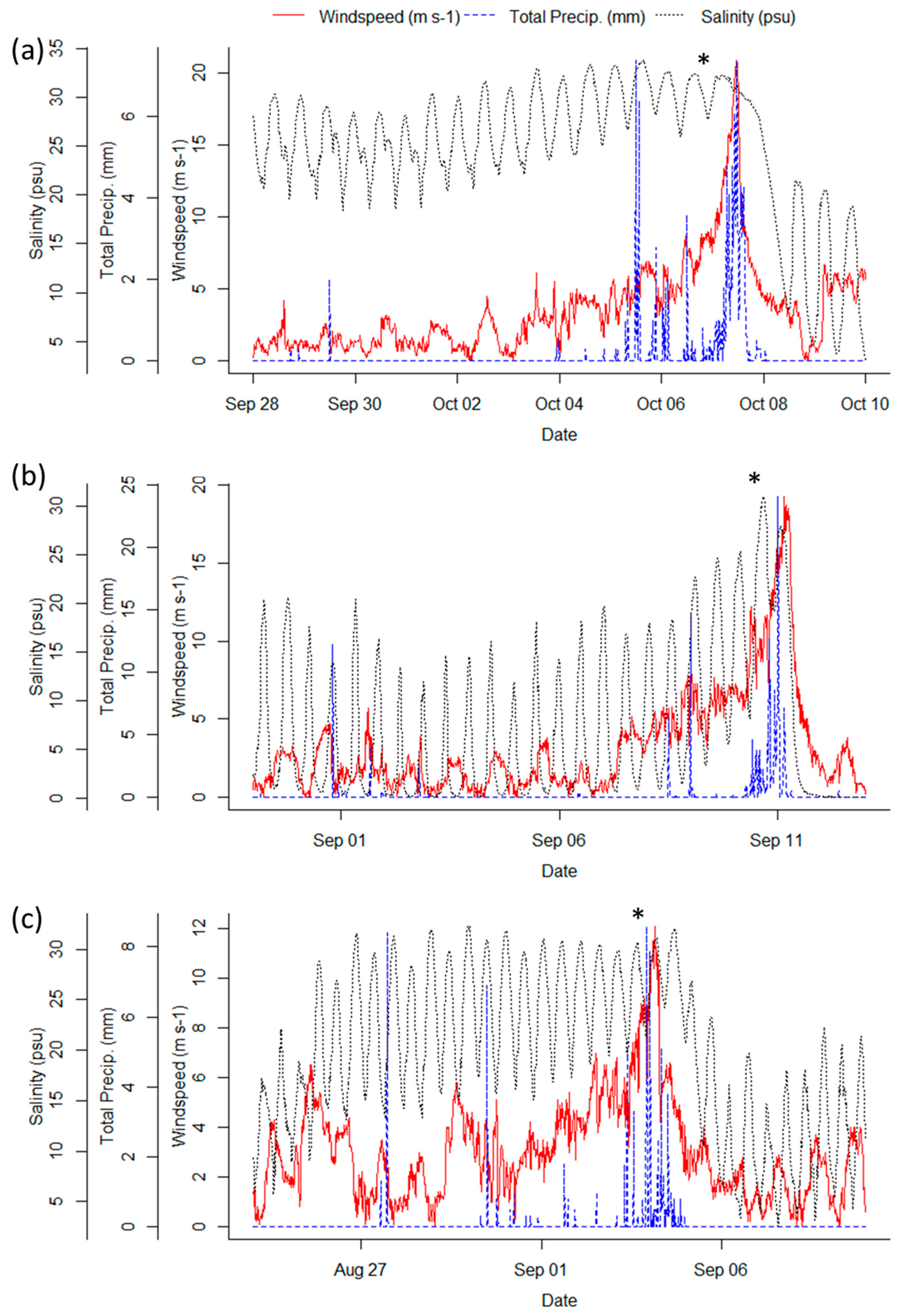
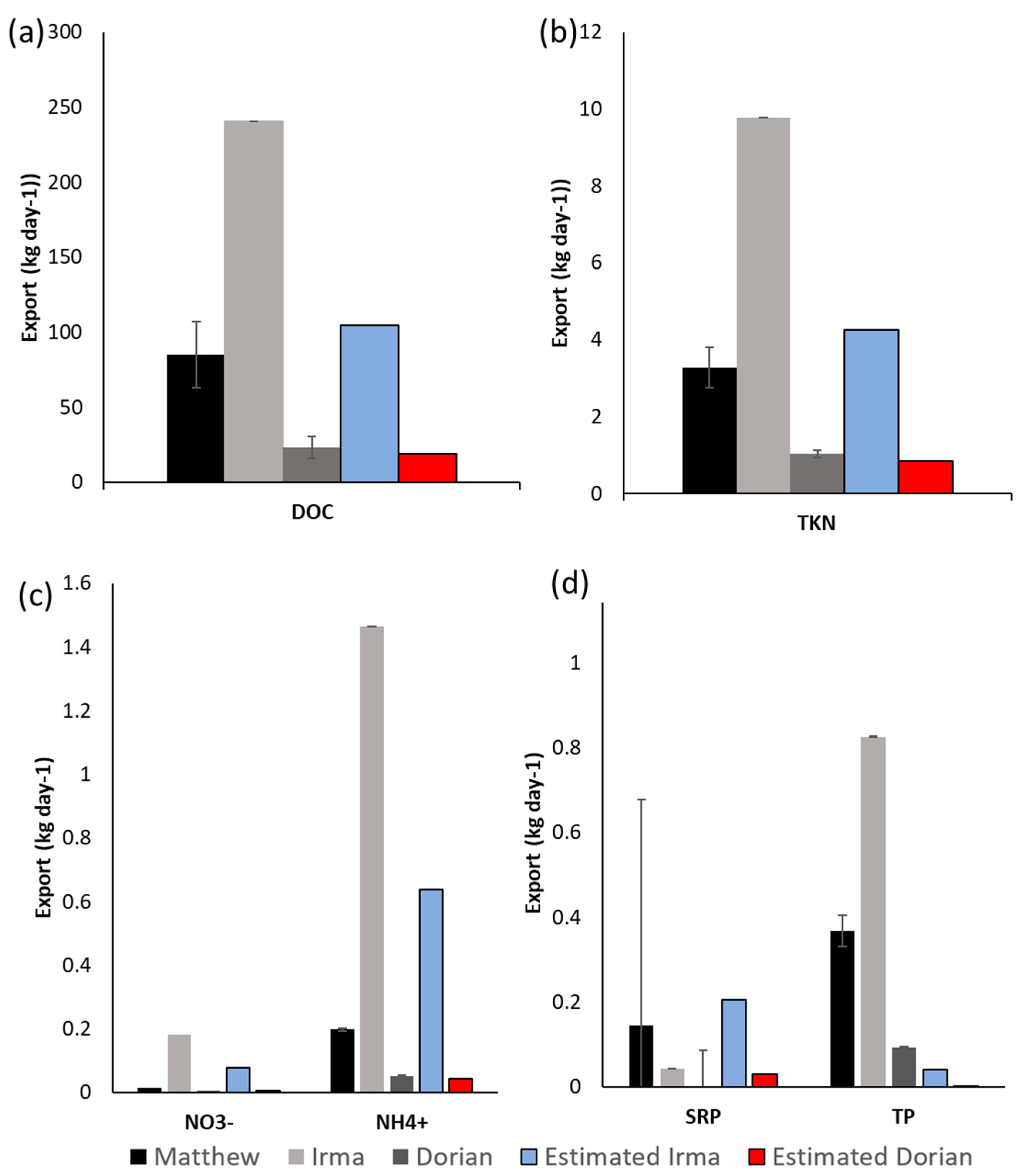
3.2. Hurricane Export
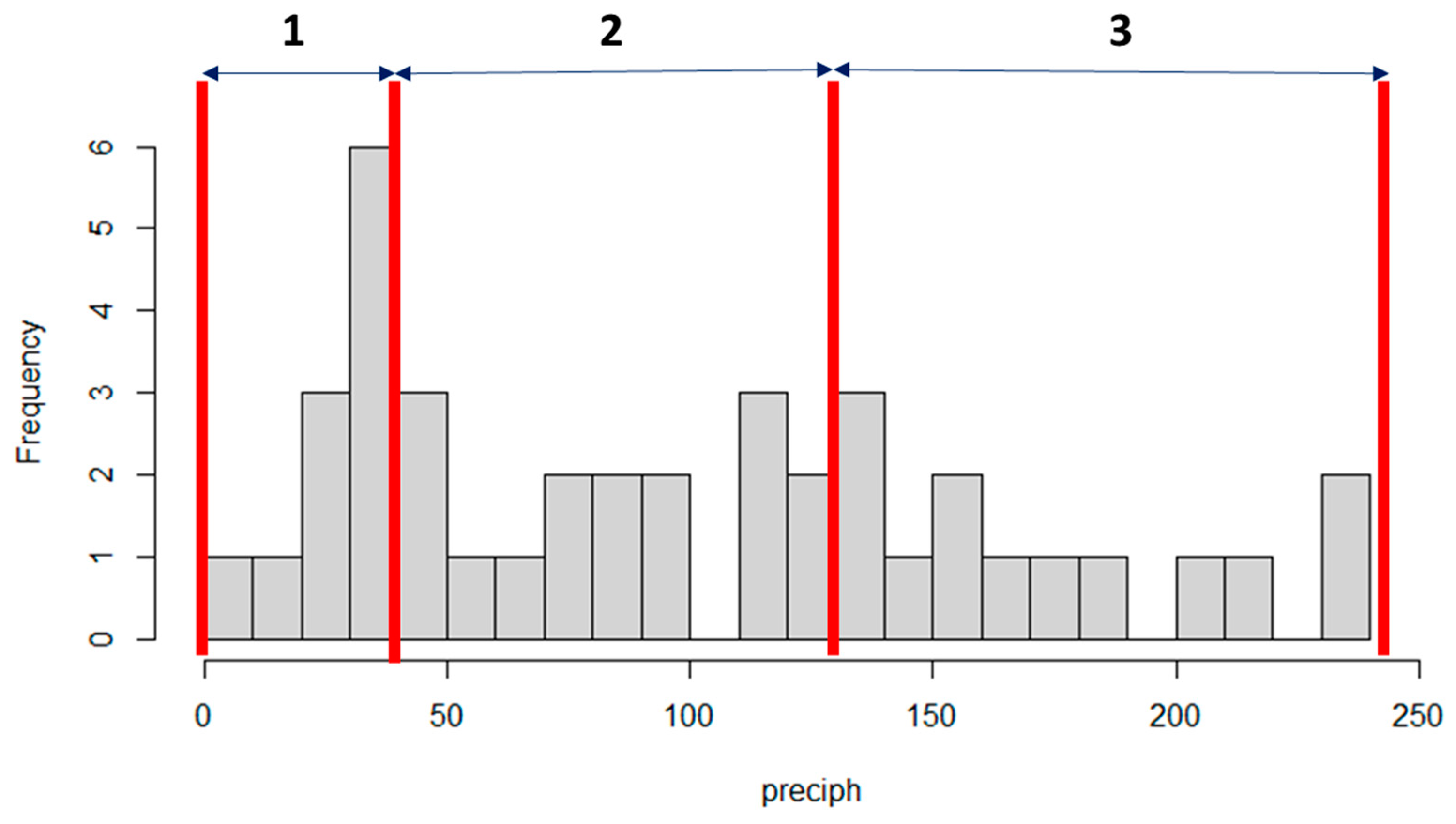
3.3. Storm Group Comparison
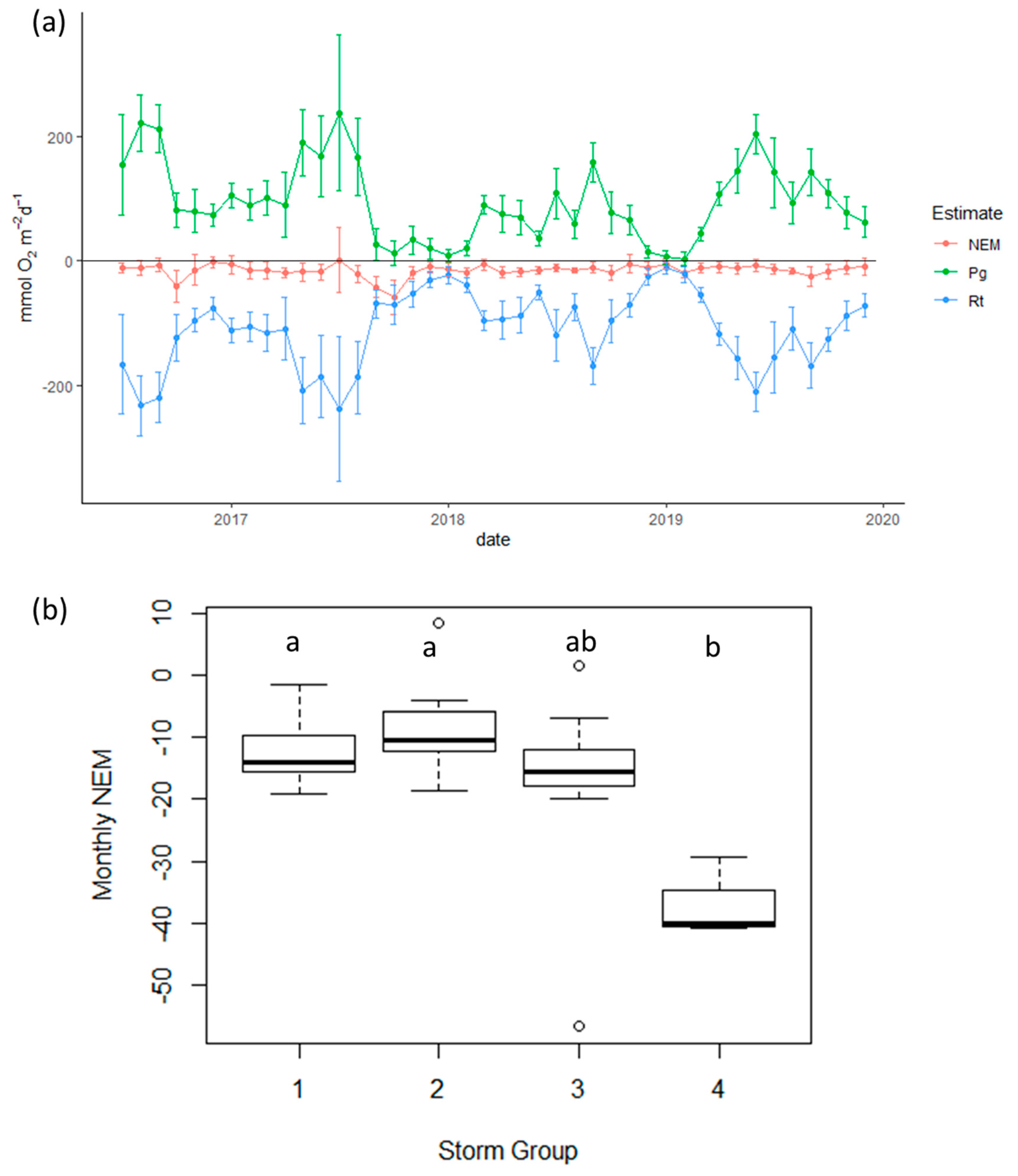
3.4. Ecosystem Metabolism
4. Discussion
4.1. Organic Matter Export
4.2. Evaluation of Ecosystem Metabolism
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edmiston, H.L.; Fahrny, S.A.; Lamb, M.S.; Levi, L.K.; Wanat, J.M.; Avant, J.S.; Wren, K.; Selly, N.C. Tropical Storm and Hurricane Impacts on a Gulf Coast Estuary: Apalachicola Bay, Florida. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 2008, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.O.; Wollheim, W.M.; Mulukutla, G.K.; Mineau, M.M. Characterizing Storm-Event Nitrate Fluxes in a Fifth Order Suburbanizing Watershed Using In Situ Sensors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7756–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, R.A.; Barras, J.A. Hurricane Impacts on Coastal Wetlands: A Half-Century Record of Storm-Generated Features from Southern Louisiana. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 275, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Peet, R.K.; Lee, M.T.; Urban, D.L. Hurricane Disturbances, Tree Diversity, and Succession in North Carolina Piedmont Forests, USA. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.; Skea, J.; Shukla, P.R.; Pirani, A.; Moufouma-Okia, W.; Péan, C.; Pidcock, R.; et al. Global Warming of 1.5 °C: An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/ar6-syr/ (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Emanuel, K. Increasing Destructiveness of Tropical Cyclones over the Past 30 Years. Nature 2005, 436, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Inamdar, S. Storm Event Patterns of Particulate Organic Carbon (POC) for Large Storms and Differences with Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC). Biogeochemistry 2014, 118, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Inamdar, S. Extreme Storms and Changes in Particulate and Dissolved Organic Carbon in Runoff: Entering Uncharted Waters? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Kelble, C.R.; Fischer, C.J.; Moore, L. Hurricane Katrina Induced Nutrient Runoff from an Agricultural Area to Coastal Waters in Biscayne Bay, Florida. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Wan, Y.; Stoffella, P.J. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Nitrogen Concentration and Speciation in Runoff and Storm Water in the Indian River Watershed, South Florida. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 19561–19569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidzadeh, H.; Uzun, H.; Ruecker, A.; Miller, D.; Vernon, J.; Zhang, H.; Bao, S.; Tsui, M.T.K.; Karanfil, T.; Chow, A.T. Extreme Flooding Mobilized Dissolved Organic Matter from Coastal Forested Wetlands. Biogeochemistry 2017, 136, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, J.D.; Elliott, E.M.; Avery, G.B.; Kieber, R.J.; Mead, R.N.; Willey, J.D.; Mullaugh, K.M. Isotopic Composition of Nitrate in Sequential Hurricane Irene Precipitation Samples: Implications for Changing NOxsources. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavorivska, L.; Boyer, E.W.; Grimm, J.W.; Miller, M.P.; DeWalle, D.R.; Davis, K.J.; Kaye, M.W. Variability of Dissolved Organic Carbon in Precipitation during Storms at the Shale Hills Critical Zone Observatory. Hydrol. Processes 2017, 31, 2935–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannote, R.L.; Minshall, G.W.; Cummins, K.W.; Sedell, J.R.; Cushing, C.E. The River Continuum Concept. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Saiers, J.E. Event Controlled DOC Export from Forested Watersheds. Biogeochemistry 2010, 100, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lu, Y.; Dash, P.; Das, P.; Li, J.; Capps, K.; Majidzadeh, H.; Elliott, M. Hurricane Pulses: Small Watershed Exports of Dissolved Nutrients and Organic Matter during Large Storms in the Southeastern USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, J.A.; Mitsch, W.J.; Song, K.; Miao, S.L. Contribution of Different Wetland Plant Species to the DOC Exported from a Mesocosm Experiment in the Florida Everglades. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Crosswell, J.R.; Van Dam, B.; Hall, N.S.; Rossignol, K.L.; Osburn, C.L.; Hounshell, A.G.; Sloup, R.S.; Harding, L.W., Jr. Two Decades of Tropical Cyclone Impacts on North Carolina’s Estuarine Carbon, Nutrient and Phytoplankton Dynamics: Implications for Biogeochemical Cycling and Water Quality in a Stormier World. Biogeochemistry 2018, 141, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, H.T. Primary Production in Flowing Waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1956, 1, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, E.P. Trends Expected in Stressed Ecosystems. BioScience 1985, 35, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoellein, T.J.; Bruesewitz, D.A.; Richardson, D.C. Revisiting Odum (1956): A Synthesis of Aquatic Ecosystem Metabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2013, 58, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffrey, J.M. Production, Respiration and Net Ecosystem Metabolism U.S. Estuaries. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2003, 81, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avery, G.B.; Kieber, R.J.; Willey, J.D.; Shank, G.C.; Whitehead, R.F. Impact of Hurricanes on the Flux of Rainwater and Cape Fear River Water Dissolved Organic Carbon to Long Bay, Southeastern United States. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, GB3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinckney, J.L.; Paerl, H.W.; Tester, P.; Richardson, T.L. The Role of Nutrient Loading and Eutrophication in Estuarine Ecology. Environ. Health Perscpectives 2001, 109, 699–706. [Google Scholar]
- Bacopoulos, P. Tide-Surge Historical Assessment of Extreme Water Levels for the St. Johns River: 1928–2017. J. Hydrol. 2017, 553, 624–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, P.A.; Saiers, J.E.; Sobczak, W.V. Hydrological and Biogeochemical Controls on Watershed DOM Transport: Pulse-Shunt Concept. Ecology 2016, 97, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.R. Hurricane Matthew; National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cangialosi, J.P.; Latto, A.S.; Berg, R. National Hurricane Center Tropical Cyclone Report; National Hurricane Center: Miami, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- NERR National Estuarine Research Reserve System- Centralized Data Management Office. Available online: https://cdmo.baruch.sc.edu (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- USGS National Water Information System: Web Interface. Available online: https://waterdata.usgs.gov/nwis/inventory/?site_no=02247222 (accessed on 15 October 2019).
- Kassambara, A. “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots [R Package Ggpubr Version 0.4.0]. Available online: https://rdocumentation.org/packages/ggplot2/versions/3.3.3 (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Wickham, H.; Francois, R.; Henry, L.; Muller, K. A Grammar of Data Manipulation [R Package Dplyr Version 1.0.6]. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Beck, M.W. SWMPr: An R Package for Retrieving, Organizing, and Analyzing Environmental Data for Estuaries. R J. 2016, 8, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thébault, J.; Schraga, T.S.; Cloern, J.E.; Dunlavey, E.G. Primary Production and Carrying Capacity of Former Salt Ponds after Reconnection to San Francisco Bay. Wetlands 2008, 28, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogle, D.; Wheeler, P.; Dinno, A. FSA: Fisheries Stock Analysis. Available online: https://fishr-core-team.github.io/FSA/ (accessed on 19 May 2021).
- Askew, A.J. Derivation of Formulae for Variable Lag Time. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenson, E.M. A Catchment Storage Model for Runoff Routing. J. Hydrol. 1964, 2, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.J.; Prairie, Y.T.; Caraco, N.F.; McDowell, W.H.; Tranvik, L.J.; Striegl, R.G.; Duarte, C.M.; Kortelainen, P.; Downing, J.A.; Middelburg, J.J.; et al. Plumbing the Global Carbon Cycle: Integrating Inland Waters into the Terrestrial Carbon Budget. Ecosystems 2007, 10, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arellano, A.R.; Bianchi, T.S.; Osburn, C.L.; D’Sa, E.J.; Ward, N.D.; Oviedo-Vargas, D.; Joshi, I.D.; Ko, D.S.; Shields, M.R.; Kurian, G.; et al. Mechanisms of Organic Matter Export in Estuaries with Contrasting Carbon Sources. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 3168–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallin, M.A.; Mciver, M.R.; Ensign, S.H.; Cahoon, L.B. Photosynthetic and Heterotrophic Impacts of Nutrient Loading to Blackwater Streams. Ecol. Appl. 2004, 14, 823–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, J.L. A Blackwater Perspective on Riverine Ecosystems. BioScience 1990, 40, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.; Raymond, P.A. Dissolved Organic Matter Export from a Forested Watershed during Hurricane Irene. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Lohrenz, S.E.; Mojzis, A.K. Effects of Tropical Cyclones on River Chemistry: A Case Study of the Lower Pearl River during Hurricanes Gustav and Ike. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chan, C.; Diao, J. Hurricanes Substantially Reduce the Nutrients in Tropical Forested Watersheds in Puerto Rico. Forests 2022, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.; Cho, H.; An, S.U.; Choi, A.; Kim, B.; Yoon, C.; Thamdrup, B.; Hyun, J.H. Impacts of Typhoon-Induced Heavy Rainfalls and Resultant Freshwater Runoff on the Partitioning of Organic Carbon Oxidation and Nutrient Dynamics in the Intertidal Sediments of the Han River Estuary, Yellow Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, M.J. Do Not Only Connect: A Model of Infiltration-Excess Overland Flow Based on Simulation. Earth Surf. Processes Landf. 2014, 39, 952–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herbert, E.R.; Boon, P.; Burgin, A.J.; Neubauer, S.C.; Franklin, R.B.; Ardón, M.; Hopfensperger, K.N.; Lamers, L.P.M.; Gell, P. A Global Perspective on Wetland Salinization: Ecological Consequences of a Growing Threat to Freshwater Wetlands. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, T.; Ward, N.; Julian, P.; Reddy, K.R.; Osborne, T.Z. Impacts of Hurricane Disturbance on Water Quality across the Aquatic Continuum of a Blackwater River to Estuary Complex. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996; ISBN 0471511854. [Google Scholar]
- Weston, N.B.; Dixon, R.E.; Joye, S.B. Ramifications of Increased Salinity in Tidal Freshwater Sediments: Geochemistry and Microbial Pathways of Organic Matter Mineralization. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111, G01009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ardón, M.; Morse, J.L.; Colman, B.P.; Bernhardt, E.S. Drought-Induced Saltwater Incursion Leads to Increased Wetland Nitrogen Export. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 2976–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallin, M.A.; Corbett, C.A. How Hurricane Attributes Determine the Extent of Environmental Effects: Multiple Hurricanes and Different Coastal Systems. Estuaries Coasts 2006, 29, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellman, J.B.; Hood, E.; Edwards, R.T.; D’Amore, D.V. Changes in the Concentration, Biodegradability, and Fluorescent Properties of Dissolved Organic Matter during Stormflows in Coastal Temperate Watersheds. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, G01021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.R. Spiraling down the River Continuum: Stream Ecology and the U-Shaped Curve. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2007, 26, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.L.; Edwards, R.T. Ecosystem Metabolism and Turnover of Organic Carbon along a Blackwater River. Ecology 1990, 71, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dix, N.G.; Phlips, E.J.; Gleeson, R.A. Water Quality Changes in the Guana Tolomato Matanzas National Estuarine Research Reserve, Florida, Associated with Four Tropical Storms. J. Coast. Res. 2008, 55, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Hurricane | Approx. Cumulative Precip. (cm) | Max Wind Speed (m s−1) | Sustained Wind Speed (m s−1) | Storm Surge (m) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matthew | 34.5 | 38.6 | 29.3 | 1.6 | [27] |
| Irma | 25.96 | 37.4 | 30.4 | 1.3 | [28] |
| Dorian | 5.6 | 26.4 | 20.6 | 0.93 | [29] |
| Concentration (mg L−1) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hurricanes | P (mm) | DOC | SD | NH3-N | SD | TKN | SD | NO3-N | SD | SRP | SD | TP | SD |
| Matthew | 142 | 31 | 8.4 | 0.032 | 0.031 | 0.53 | 0.16 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.053 | 0.013 | 0.37 | 0.05 |
| Irma | 284 | 32 | 0 | 0.195 | 0.021 | 1.30 | 0.00 | 0.024 | 0.000 | 0.063 | 0.003 | 0.83 | 0.00 |
| Dorian | 112 | 21 | 4.8 | 0.059 | 0.026 | 0.95 | 0.08 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.034 | 0.006 | 0.093 | 0.01 |
| High Precipitation | |||||||||||||
| June 2017 | 231 | 11 | 0.6 | 0.060 | 0.037 | 0.91 | 0.06 | 0.004 | 0.000 | 0.091 | 0.020 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| August 2017 | 179 | 11 | 2.0 | 0.051 | 0.039 | 0.80 | 0.13 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 0.066 | 0.021 | 0.11 | 0.01 |
| October 2017 | 236 | 37 | 6.2 | 0.070 | 0.035 | 1.24 | 0.23 | 0.010 | 0.005 | 0.050 | 0.010 | 0.40 | 0.33 |
| May 2018 | 164 | 41 | 1.2 | 0.019 | 0.009 | 1.23 | 0.08 | 0.017 | 0.003 | 0.047 | 0.003 | 0.62 | 0.11 |
| June 2018 | 185 | 37 | 6.6 | 0.027 | 0.008 | 1.25 | 0.08 | 0.020 | 0.004 | 0.043 | 0.003 | 0.31 | 0.04 |
| August 2018 | 157 | 4 | 0.6 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 1.15 | 0.07 | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.036 | 0.004 | 0.40 | 0.06 |
| Storm/Month | DOC | NH3-N | SRP | TKN | NO3-N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| October 2016 (Matthew) | 14.3 | 25.2 | 17.0 | 16.7 | 2.6 |
| September 2017 (Irma) | 39.0 | 180.8 | 54.0 | 48.2 | 32.8 |
| September 2019 (Dorian) | 3.3 | 6.8 | 3.8 | 4.6 | 1.0 |
| June 2017 | 1.2 | 5.2 | 7.1 | 3.1 | 0.5 |
| August 2017 | 1.8 | 6.2 | 7.5 | 3.9 | 2.1 |
| October 2017 | 27.5 | 41.0 | 25.6 | 22.0 | 9.3 |
| May 2018 | 41.8 | 15.3 | 33.7 | 38.5 | 19.1 |
| June 2018 | 22.9 | 12.8 | 18.4 | 23.4 | 14.0 |
| August 2018 | 46.7 | 9.2 | 27.8 | 38.4 | 13.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schafer, T.; Dix, N.; Dunnigan, S.; Reddy, K.R.; Osborne, T.Z. Impacts of Hurricanes on Nutrient Export and Ecosystem Metabolism in a Blackwater River Estuary Complex. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10050661
Schafer T, Dix N, Dunnigan S, Reddy KR, Osborne TZ. Impacts of Hurricanes on Nutrient Export and Ecosystem Metabolism in a Blackwater River Estuary Complex. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(5):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10050661
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchafer, Tracey, Nicole Dix, Shannon Dunnigan, K. Ramesh Reddy, and Todd Z. Osborne. 2022. "Impacts of Hurricanes on Nutrient Export and Ecosystem Metabolism in a Blackwater River Estuary Complex" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 5: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10050661
APA StyleSchafer, T., Dix, N., Dunnigan, S., Reddy, K. R., & Osborne, T. Z. (2022). Impacts of Hurricanes on Nutrient Export and Ecosystem Metabolism in a Blackwater River Estuary Complex. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(5), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10050661






