Different Types of Near-Inertial Internal Waves Observed by Lander in the Intermediate-Deep Layers of the South China Sea and Their Generation Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Lander Observation
2.2. Sea Level Anomalies
2.3. Cross-Calibrated Multiplatform Wind Vector Analysis
2.4. Accurate Algorithm for Frequency and Phase
2.5. Bicoherence
3. Results
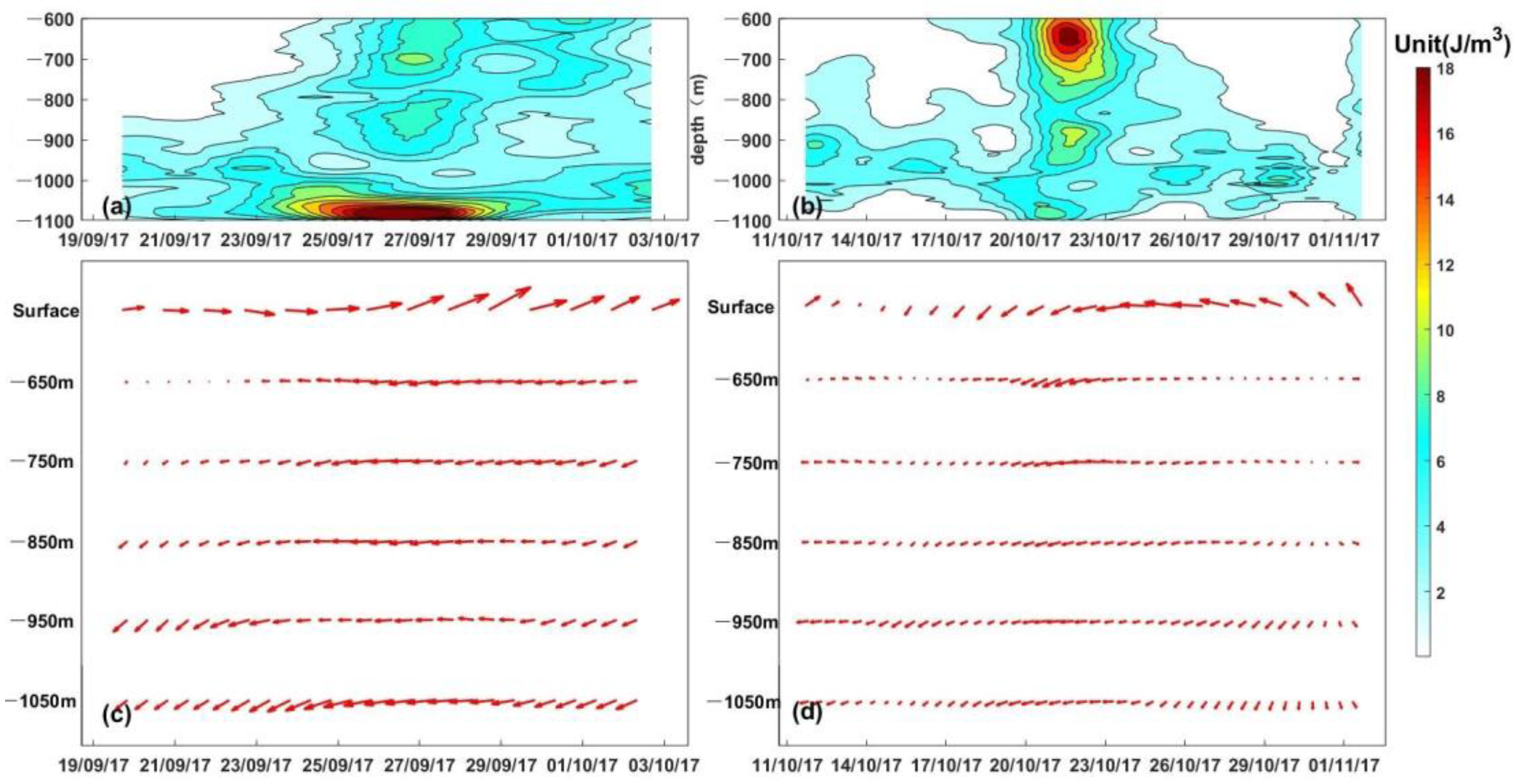
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Near-Inertial Kinetic Energy
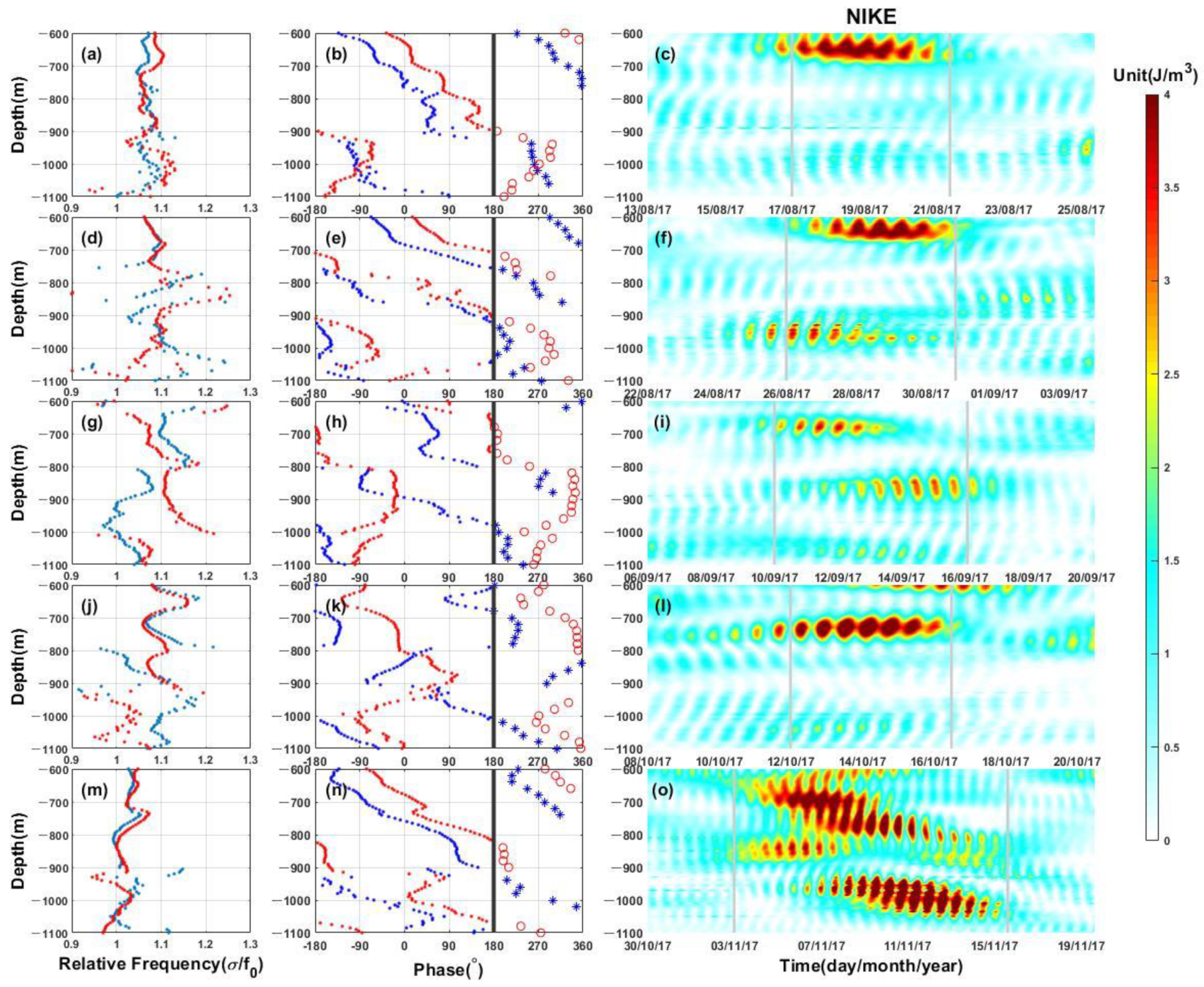
3.2. Frequency and Phase of Five NIWs
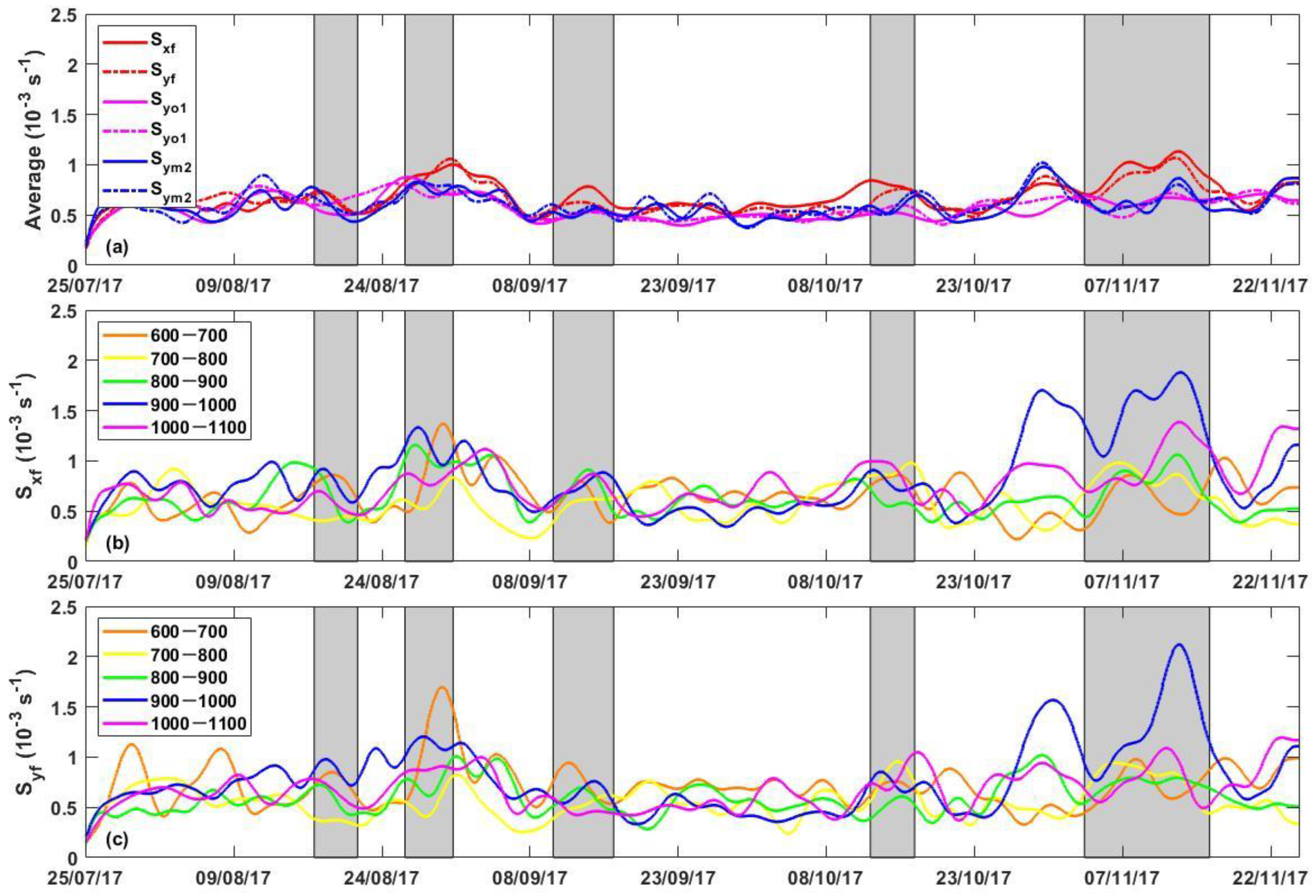
3.3. Shearing of Near-Inertial Waves
4. NIWs Generation Mechanism
4.1. Typhoons
4.2. Role of the Parametric Subharmonic Instability Mechanism
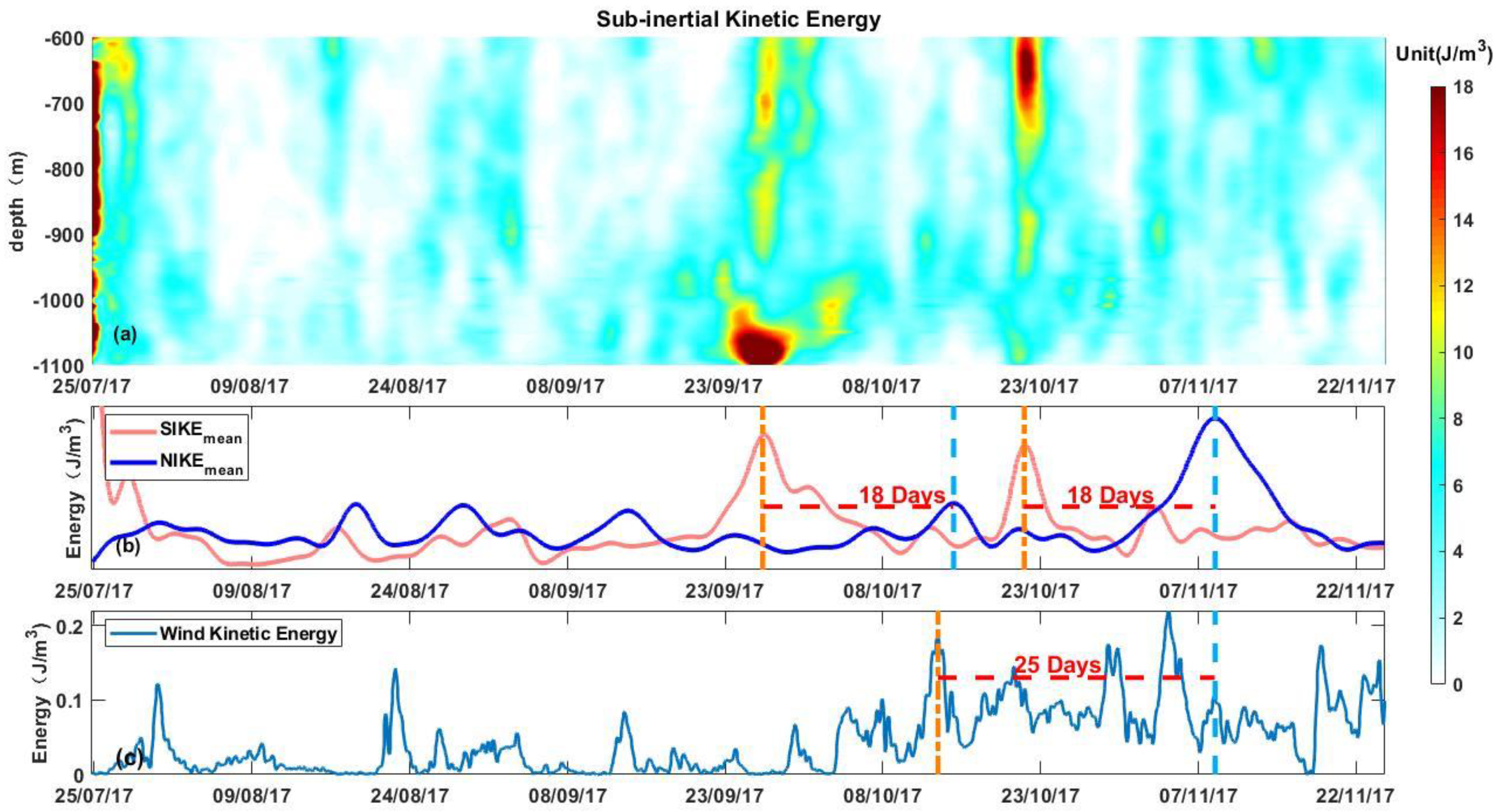
4.3. Subinertial Currents
4.4. Seabed Reflection
4.5. Monsoons
4.6. Lee Wave
5. Discussion
6. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, L.L. Observations and models of inertial waves in the deep ocean. Rev. Geophys. 1981, 19, 141–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alford, M.H.; MacKinnon, J.A.; Simmons, H.L.; Nash, J.D. Near-inertial internal gravity waves in the ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Boyer, A.; Alford, M.H.; Pinkel, R.; Hennon, T.D.; Yang, Y.J.; Ko, D.; Nash, J. Frequency shift of near-inertial waves in the South China Sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2020, 50, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacKinnon, J.A.; Gregg, M.C. Near-inertial waves on the New England shelf: The role of evolving stratification, turbulent dissipation, and bottom drag. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2005, 35, 2408–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Lee, E.M.; Umlauf, L. Internal wave mixing in the Baltic Sea: Near-inertial waves in the absence of tides. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.J.; Pitcher, G.C.; Probyn, T.A.; Kudela, R.M. The influence of diurnal winds on phytoplankton dynamics in a coastal upwelling system off southwestern Africa. Deep. Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 101, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Zhao, W.; Huthnance, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, J. Observed upper ocean response to typhoon Megi (2010) in the Northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2014, 119, 3134–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, H.; Yu, F.; Nan, F.; Yang, B.; Guan, S.; Zhang, Y. Observation of near-inertial oscillations induced by energy transformation during typhoons. Energies 2019, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Li, D.; Wei, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T. Observed Near Inertial Waves in the Wake of Typhoon Linfa (2015) in the Northern South China Sea. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2019, 18, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, J.A.; Winters, K.B. Subtropical catastrophe: Significant loss of low-mode tidal energy at 28.9°. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.H.; Shang, X.D.; van Haren, H.; Chen, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z. Observations of parametric subharmonic instability-induced near-inertial waves equatorward of the critical diurnal latitude. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikurashin, M.; Ferrari, R. Radiation and dissipation of internal waves generated by geostrophic motions impinging on small-scale topography: Theory. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 1055–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tian, J. Cascade of internal wave energy catalyzed by eddy-Topography interactions in the deep South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2019GL086510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, R. Gravity wave radiation from vortex trains in rotating shallow water. J. Fluid Mech. 1994, 281, 81–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes, B.; Shay, L.K. Near-inertial wave wake of Hurricanes Katrina and Rita over mesoscale oceanic eddies. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 1320–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xue, H.; Wang, D.; Xie, Q. Observed near-inertial kinetic energy in the northwestern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 4965–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Li, J.; Ning, D. Horizontal variations of typhoon-forced near-inertial oscillations in the south China sea simulated by a numerical model. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 180, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Pan, J.; Wang, D.; Chen, G.; Sun, L.; Yao, J. Generation of near-inertial oscillations by summer monsoon onset over the South China Sea in 1998 and 1999. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2016, 118, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qi, Y.; Jing, Z. Upper ocean near-inertial response to the passage of two sequential typhoons in the northwestern South China Sea. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2019, 62, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossby, C.G. On the mutual adjustment of pressure and velocity distributions in certain simple current systems, II. J. mar. Res. 1938, 1, 239–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, B.J.; Bretherton, F.P. Atmospheric frontogenesis models: Mathematical formulation and solution. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, C.; Skamarock, W.C.; Rotunno, R. Frontal dynamics near and following frontal collapse. J. Atmos. Sci. 1993, 50, 3194–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plougonven, R.; Snyder, C. Inertia–gravity waves spontaneously generated by jets and fronts. Part I: Different baroclinic life cycles. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 2502–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danioux, N. Bilan des Campagnes Océanographiques Françaises 2012, French Oceanographic Cruises Report. IFREMER. 2013. Available online: https://archimer.ifremer.fr/doc/00149/26002/ (accessed on 1 March 2022).
- Shakespeare, C.J.; Taylor, J.R. The spontaneous generation of inertia–gravity waves during frontogenesis forced by large strain: Theory. J. Fluid Mech. 2014, 757, 817–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Tandon, A.; Kunze, E.; Mahadevan, A. Spontaneous generation of near-inertial waves by the Kuroshio Front. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 2381–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yin, B.; Hou, Y.; Xu, Y. Variability of internal tides and near-inertial waves on the continental slope of the northwestern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2013, 118, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Gan, J. Comparison of typhoon-induced near-inertial oscillations in shear flow in the northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Guo, Z.; Song, J.; Lv, X.; He, H.; Fan, W. Near-inertial waves and their underlying mechanisms based on the South China Sea internal wave experiment (2010–2011). J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2018, 123, 5026–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, D.; Hu, J.; Tai, C.K.; Sun, Z. A case study of near-inertial oscillation in the South China Sea using mooring observations and satellite altimeter data. J. Oceanogr. 2011, 67, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Hou, Y.; Hu, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Shallow ocean response to tropical cyclones observed on the continental shelf of the northwestern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 3817–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Powers, E.J. Digital bispectral analysis and its applications to nonlinear wave interactions. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 1979, 7, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alford, M.H.; Whitmont, M. Seasonal and spatial variability of near-inertial kinetic energy from historical moored velocity records. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2007, 37, 2022–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Hu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, C. Strong near-inertial oscillations in geostrophic shear in the northern South China Sea. J. Oceanogr. 2011, 67, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComas, C.H.; Briscoe, M.G. Bispectra of internal waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1980, 97, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.S.; Gregg, M.C. Persistent near-diurnal internal waves observed above a site of M2 barotropic-to-baroclinic conversion. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2006, 36, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Laurent, L.; Naveira Garabato, A.C.; Ledwell, J.R.; Thurnherr, A.M.; Toole, J.M.; Watson, A.J. Turbulence and diapycnal mixing in Drake Passage. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, A.R. Continental shelf waves and the response of sea level to weather systems. J. Geophys. Res. 1964, 69, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysak, L.A.; Hamon, B.V. Low-frequency sea level behavior and continental shelf waves off North Carolina. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 74, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.K.; Buchwald, V.T. The generation of continental shelf waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1969, 35, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlond, P.H.; Mysak, L.A. Waves in the Ocean; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Thiebaut, S.; Vennell, R. Observation of a fast continental shelf wave generated by a storm impacting Newfoundland using wavelet and cross-wavelet analyses. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, E.H.; Brink, K.H. Coastal-trapped waves off the coast of South Africa: Generation, propagation and current structures. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1990, 20, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, M.; Dai, D.; Qiao, F. Three dimensional simulation of internal wave attractors in the Luzon Strait. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2015, 34, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


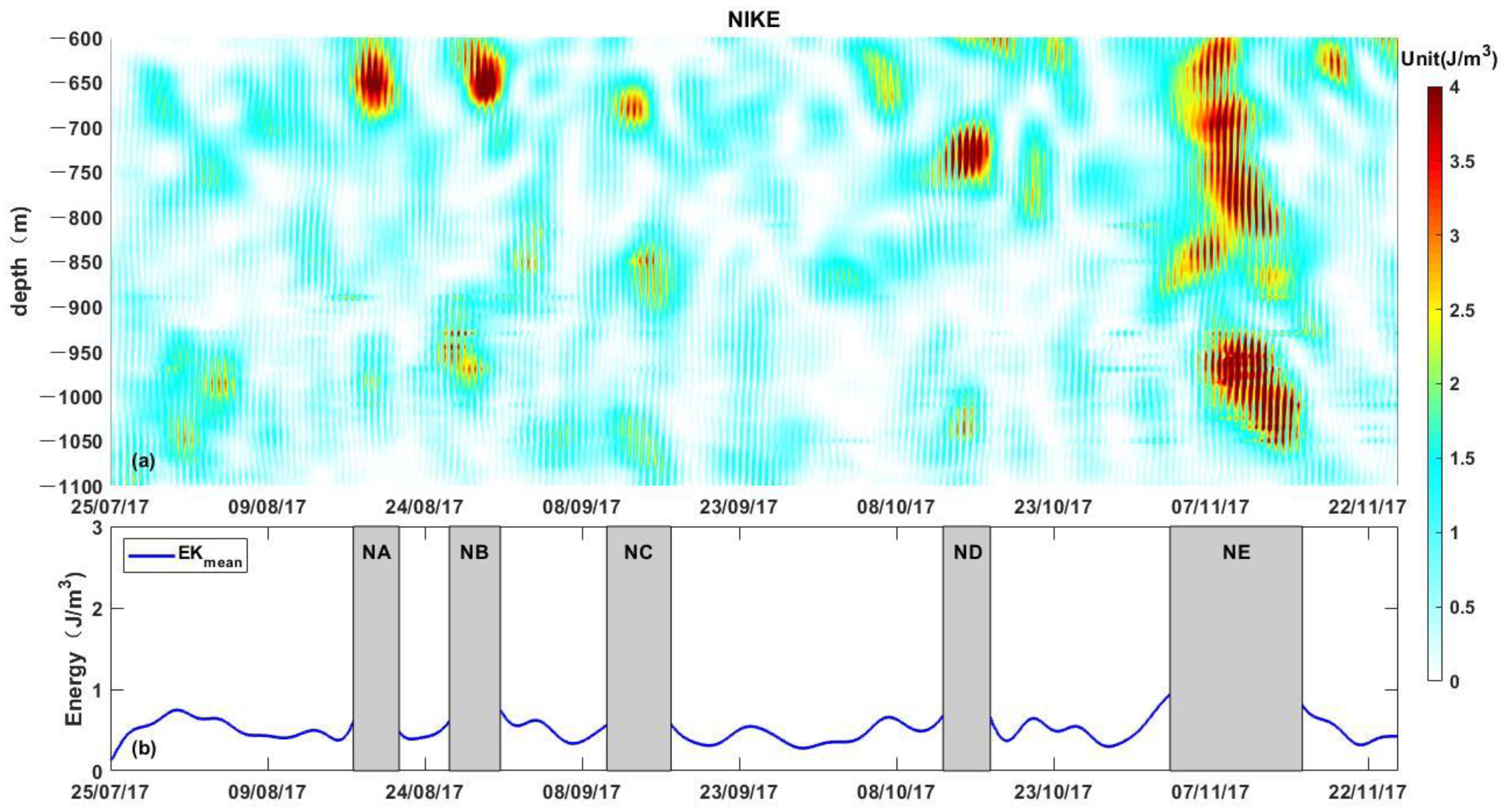



| Typhoon | Closest Distance (km) | Moving Speed (m/s) | Central Pressure (hPa) | Closest Time | NIW | Energy Maximum Time | Time Difference (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roke | 104.27 | 6.46 | 1004 | 22 July | NA | 19 August | 28 |
| Haitang | 107.15 | 8.46 | 985 | 30 July | NB | 29 August | 30 |
| Hato | 184.82 | 5.48 | 975 | 22 August | NC | 13 September | 22 |
| Mawar | 198.09 | 2.41 | 996 | 1 September | Weak NIWs after NC | 24 September | 23 |
| Guchol | 2.63 | 4.20 | 1006 | 7 September | 17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, H.; Xu, T.; Li, B.; Yang, B.; Wei, Z.; Yu, F. Different Types of Near-Inertial Internal Waves Observed by Lander in the Intermediate-Deep Layers of the South China Sea and Their Generation Mechanisms. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10050594
Hou H, Xu T, Li B, Yang B, Wei Z, Yu F. Different Types of Near-Inertial Internal Waves Observed by Lander in the Intermediate-Deep Layers of the South China Sea and Their Generation Mechanisms. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(5):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10050594
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Huaqian, Tengfei Xu, Bin Li, Bing Yang, Zexun Wei, and Fei Yu. 2022. "Different Types of Near-Inertial Internal Waves Observed by Lander in the Intermediate-Deep Layers of the South China Sea and Their Generation Mechanisms" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 5: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10050594
APA StyleHou, H., Xu, T., Li, B., Yang, B., Wei, Z., & Yu, F. (2022). Different Types of Near-Inertial Internal Waves Observed by Lander in the Intermediate-Deep Layers of the South China Sea and Their Generation Mechanisms. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(5), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10050594






