Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Salinity Stratification during the Wet Season in the Pearl River Estuary, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methodology
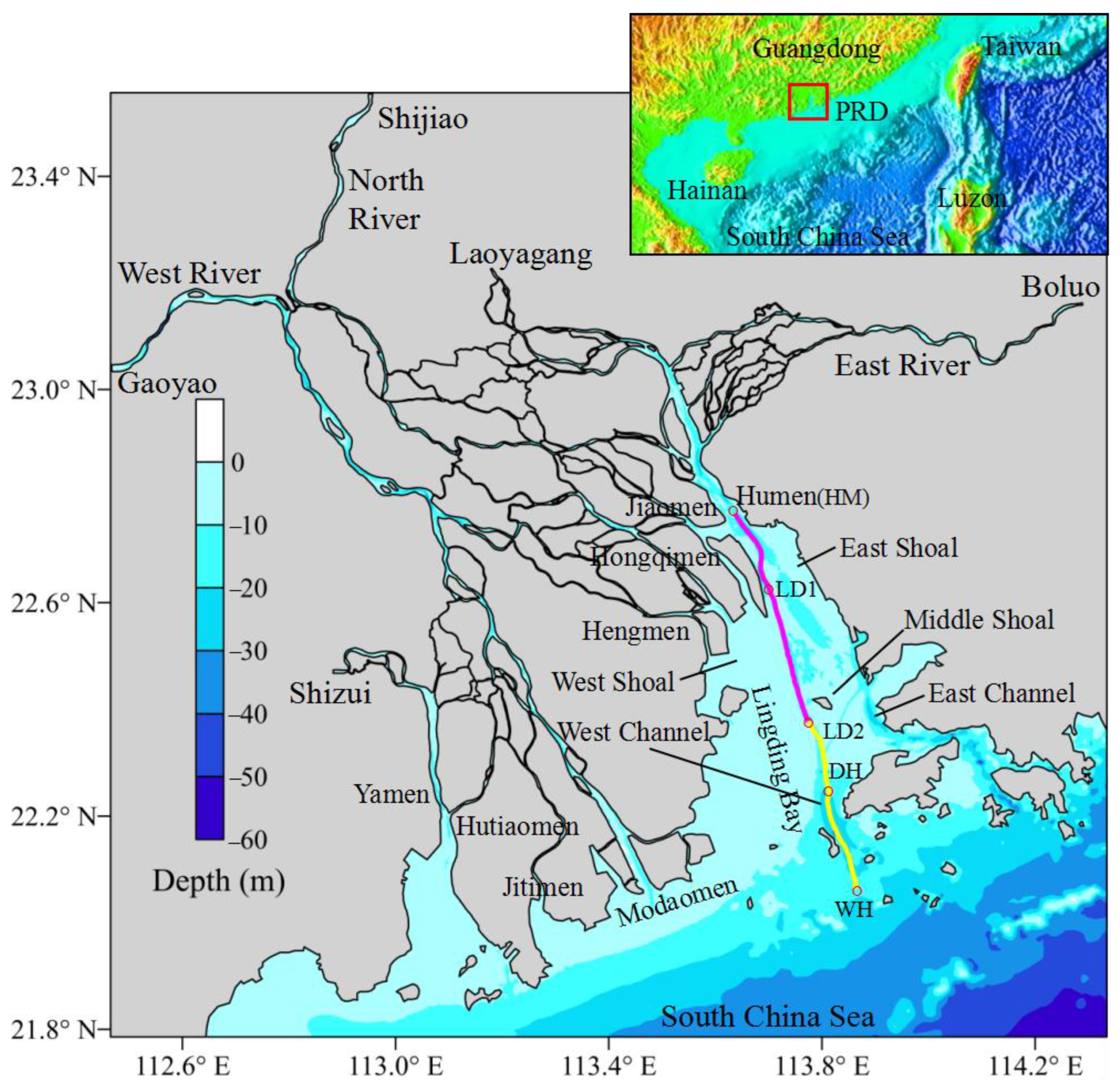
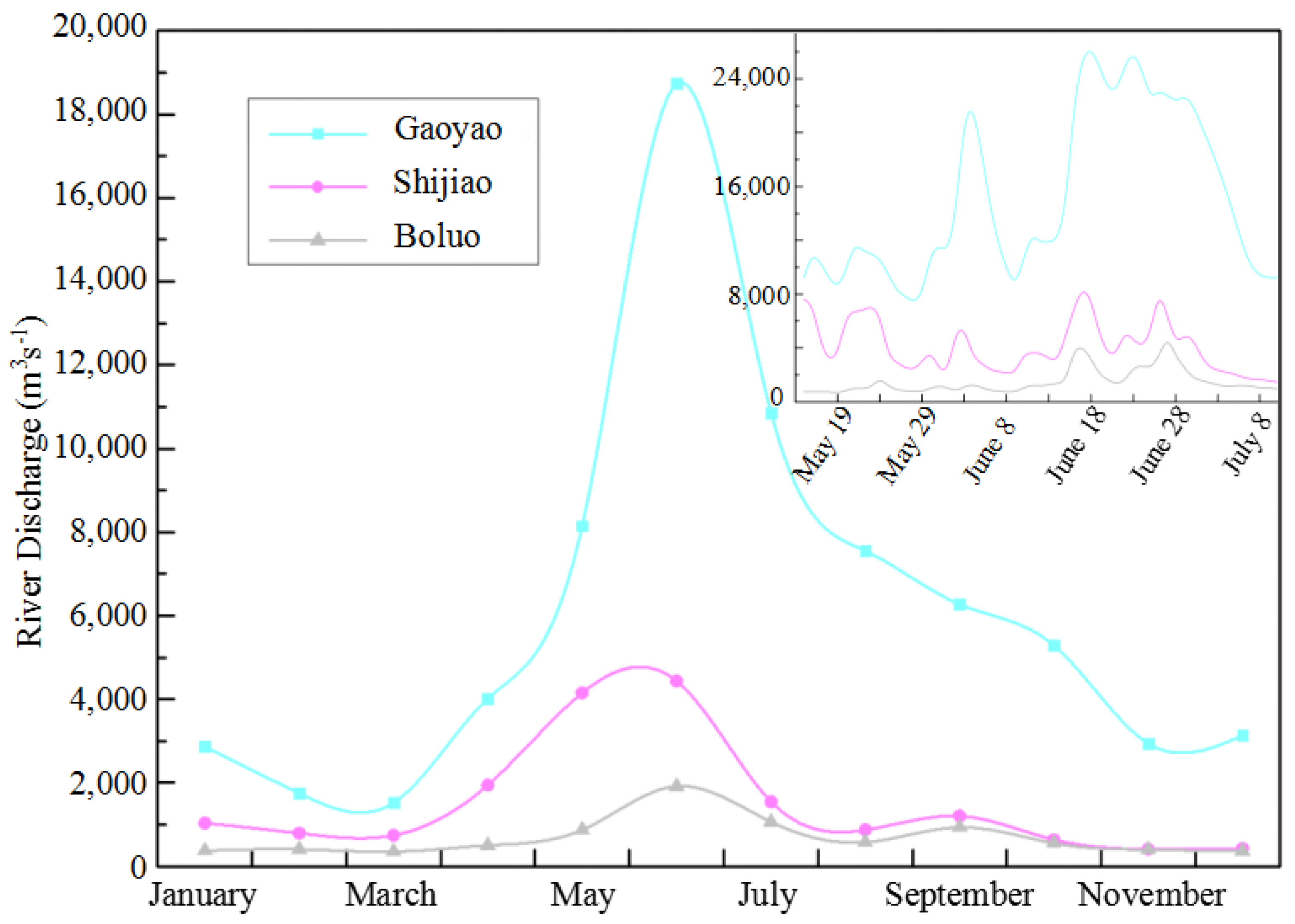
2.1. Study Area
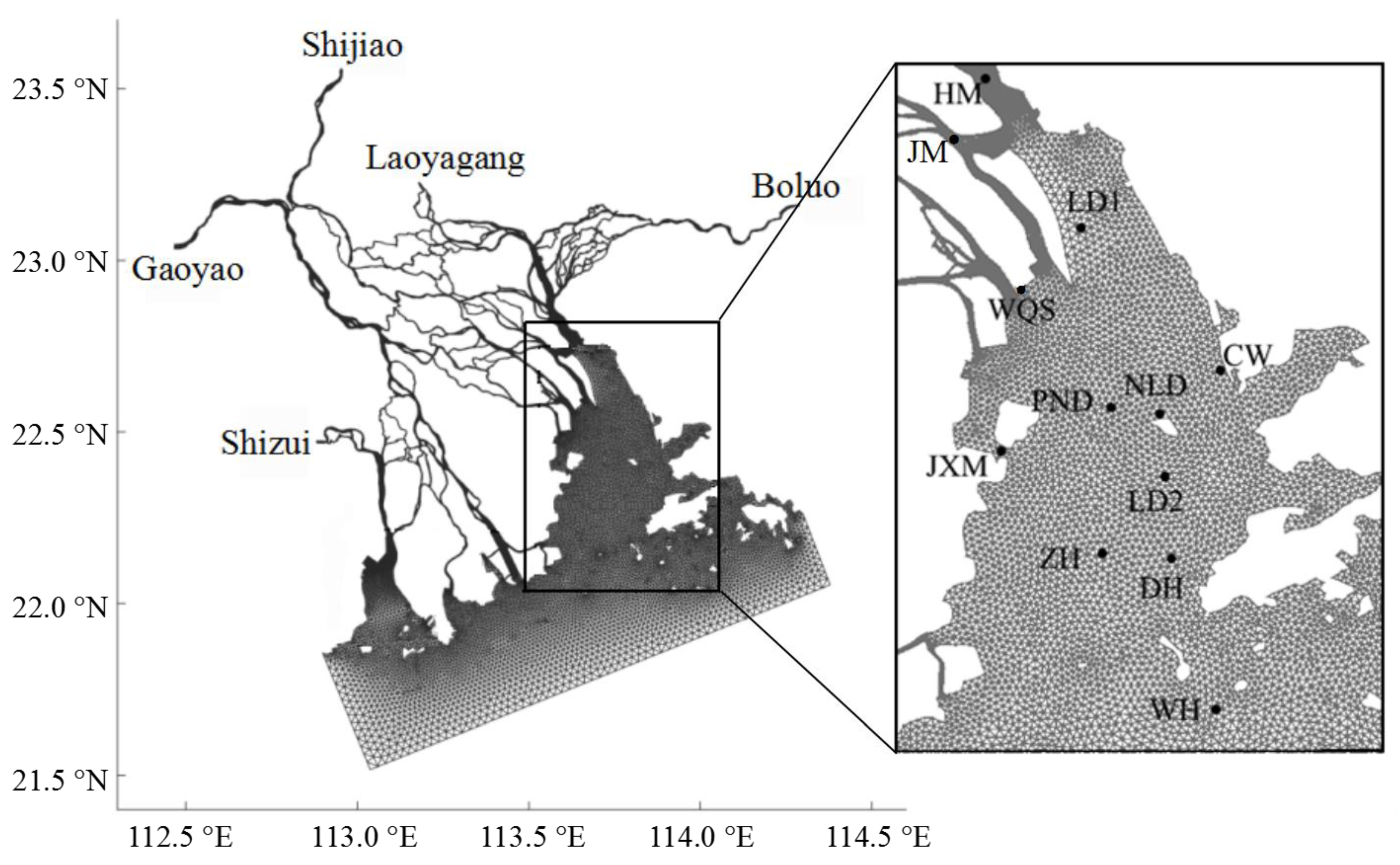
2.2. Numerical Modelling
2.3. Evaluations of Stratification
2.3.1. The Gradient Richardson Number
2.3.2. The Potential Energy Anomaly
3. Results
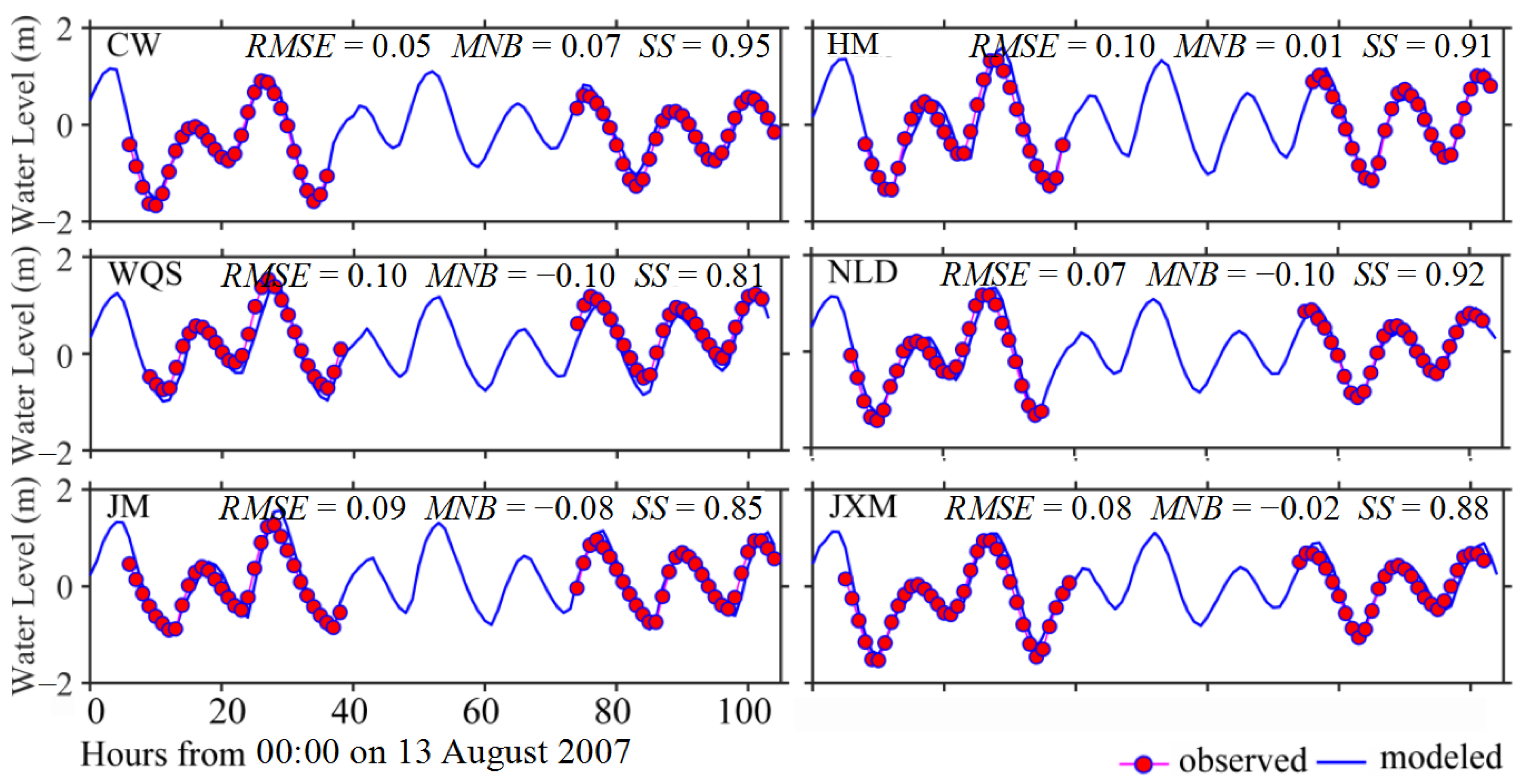
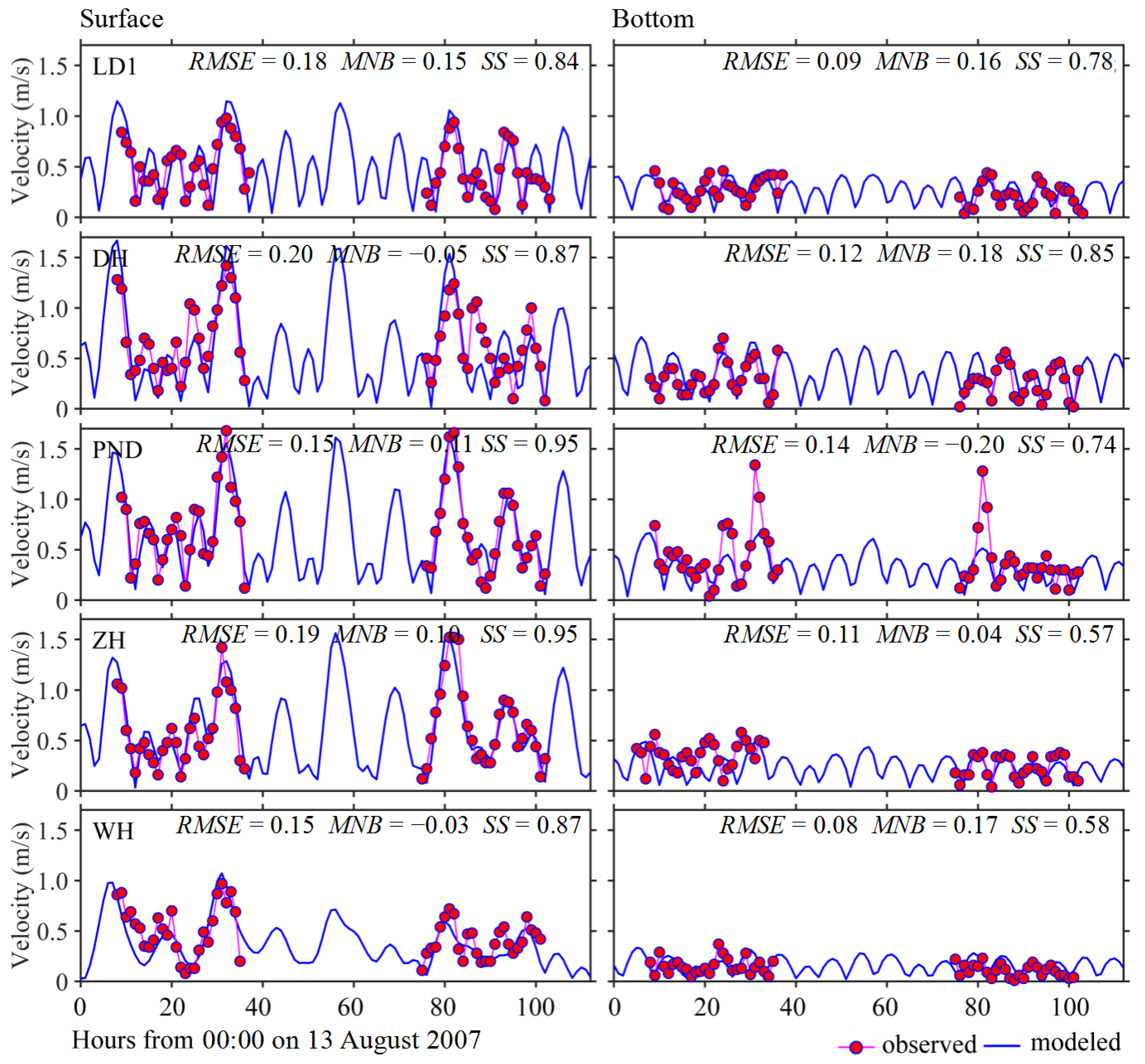
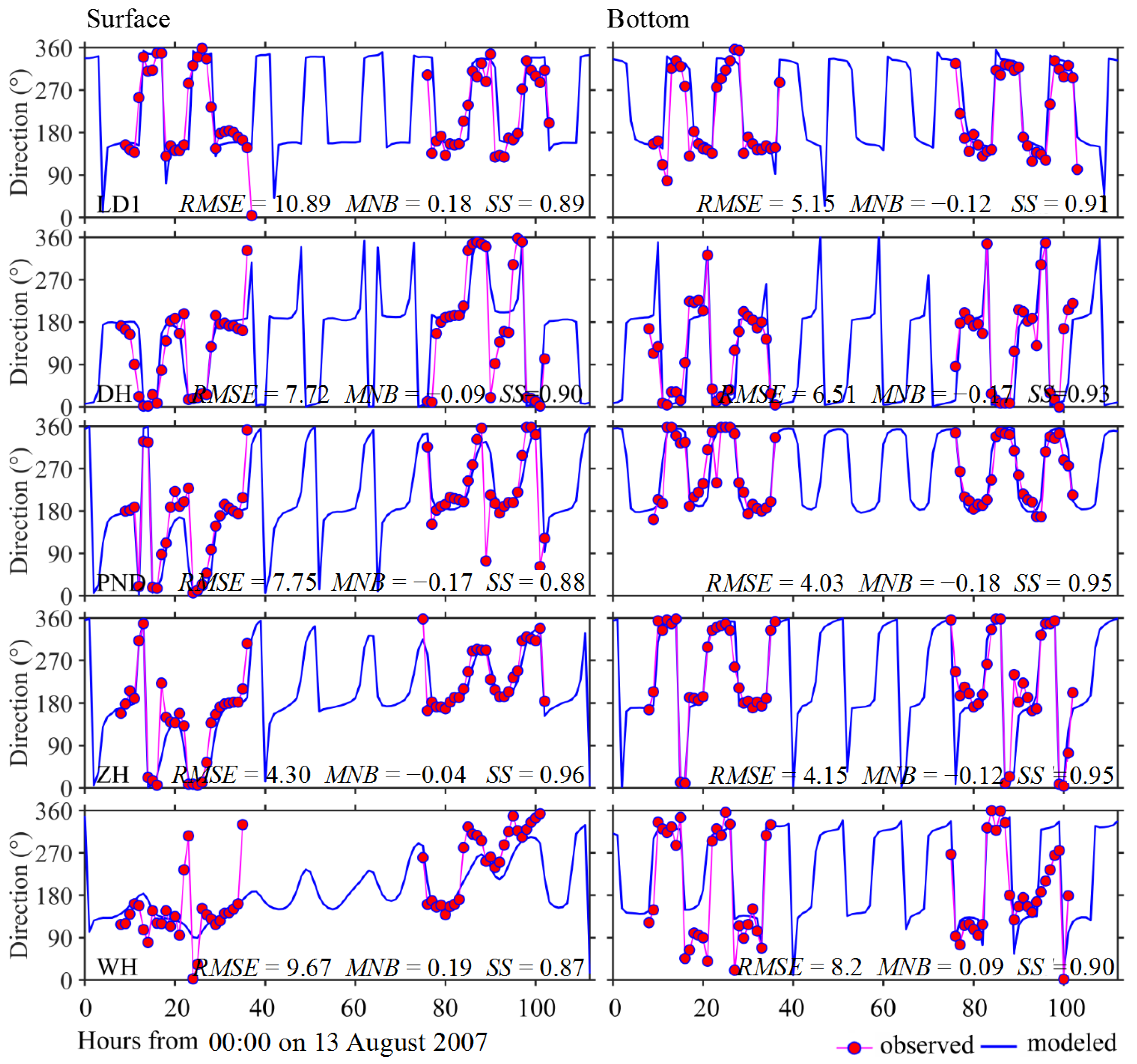
3.1. Model Validations
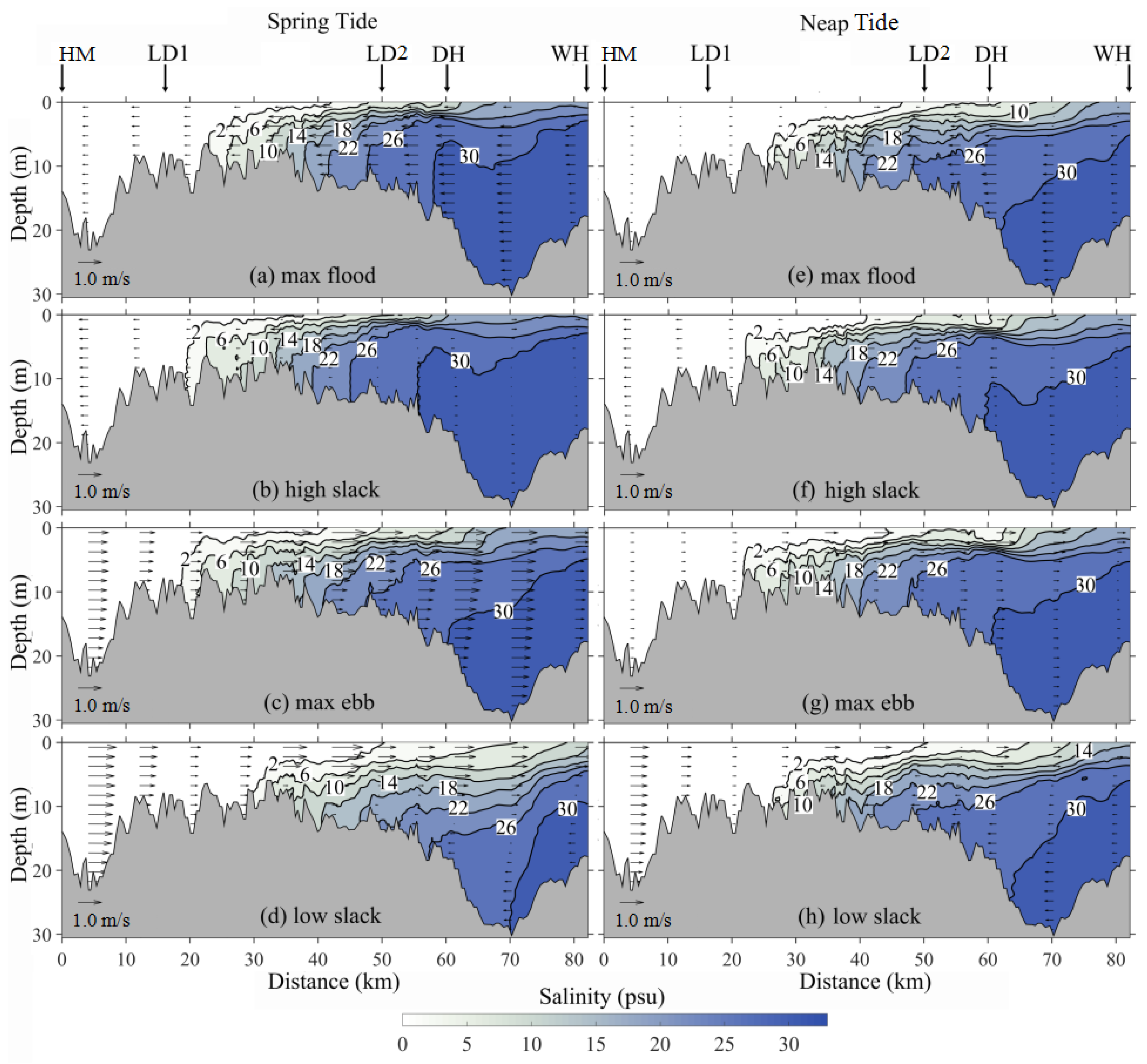
3.2. Along-Channel Velocity and Salinity Structure
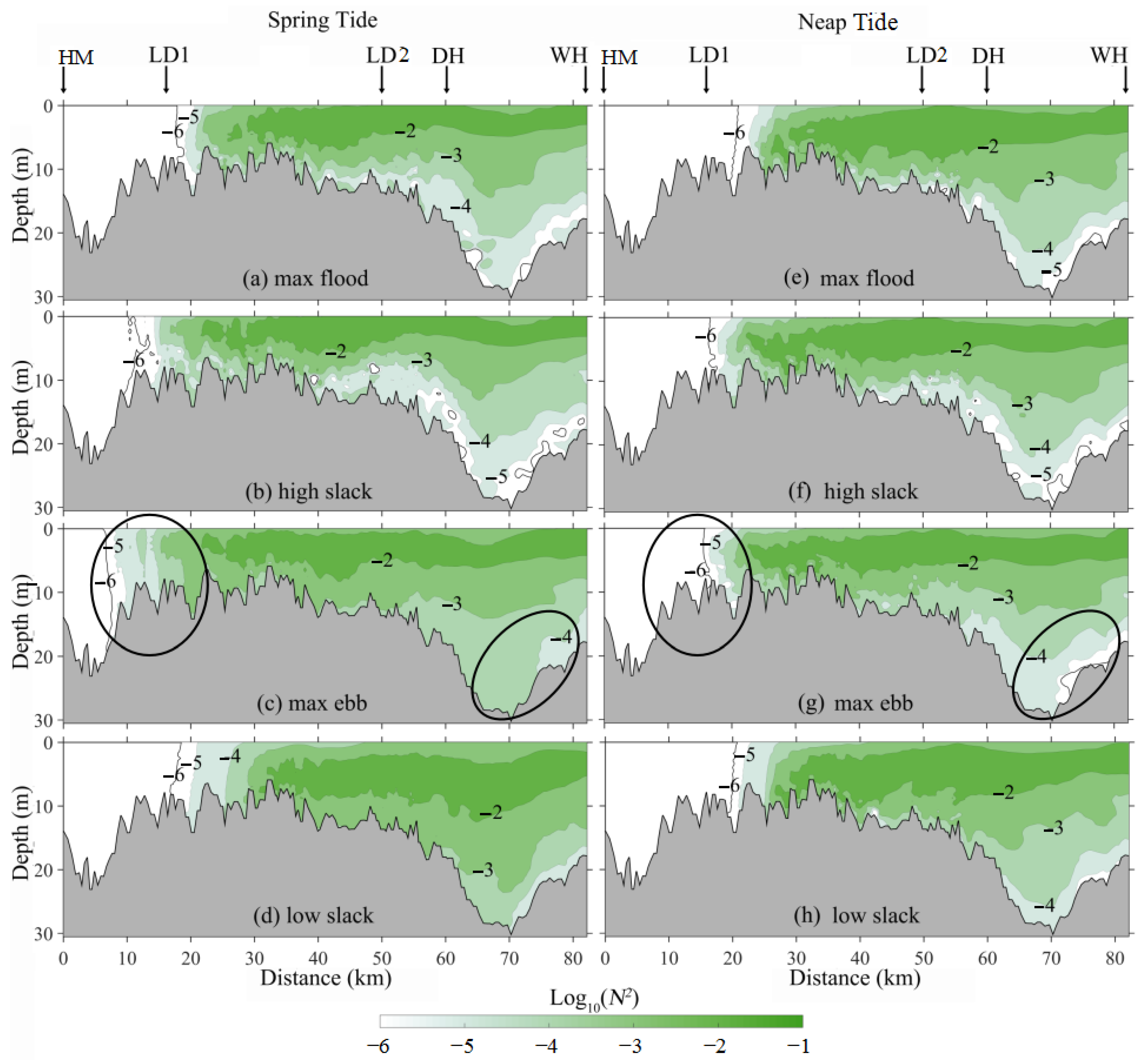
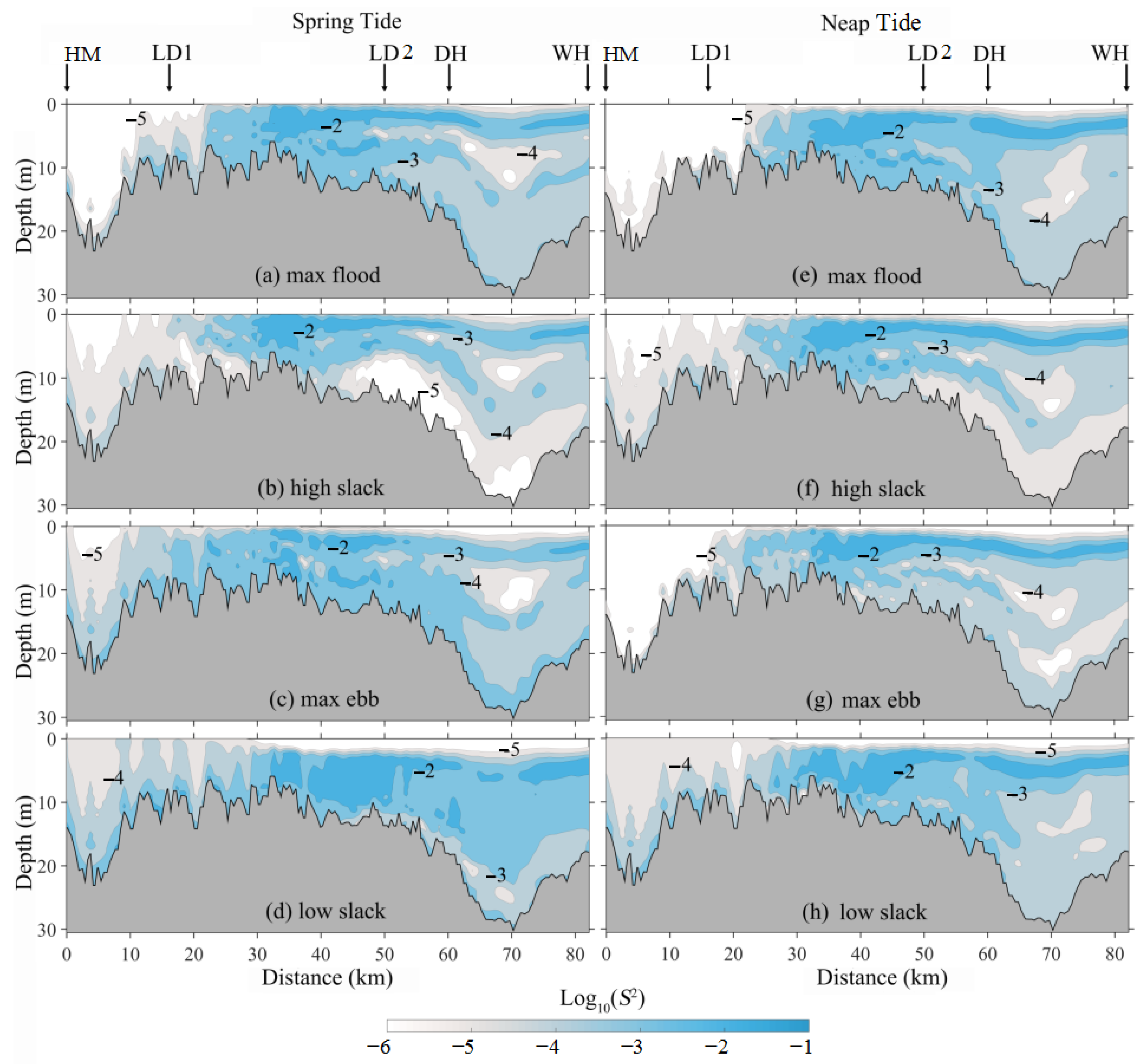
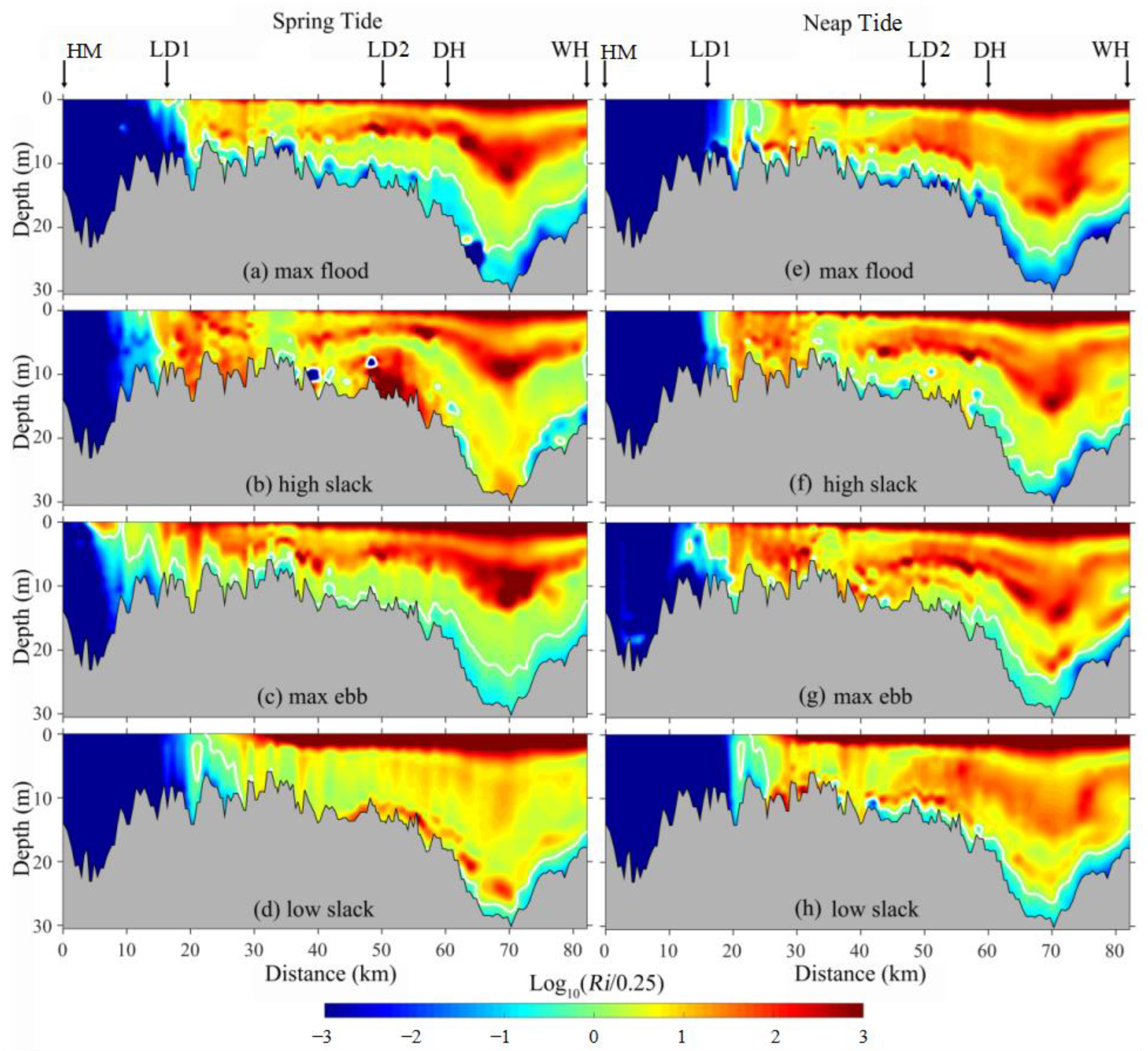
3.3. Stratification Indicated by Richardson Number
4. Discussion
4.1. The Change Rate of Potential Energy Anomaly
4.2. Physical Mechanisms Contributing to Spring–Neap and Intratidal Variabilities of Salinity Stratification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansen, D.V.; Rattray, M. Gravitational circulation in straits and estuaries. J. Mar. Res. 1965, 23, 104–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.B.; Wang, Y.G.; Ruan, X.H.; Xu, Q. Modeling residual circulation and stratification in Oujiang River Estuary. China Ocean Eng. 2012, 26, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R. The importance of suppression of turbulence by stratification on the estuarine turbidity maximum. Estuaries 1993, 16, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, R.P.; Rijnsburger, S.; Horner-Devine, A.R.; Souza, A.J.; Pietrzak, J.D. The impact of storms and stratification on sediment transport in the Rhine region of freshwater influence. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 4456–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, A.Y.; Neilson, B.J. Hypoxia and salinity in Virginia estuaries. Estuaries 1987, 10, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Z.; Lin, J.; Wang, D.X. Numerical study on salinity stratification in the Pamlico River Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 80, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hetland, R.D.; Ruiz, V.; DiMarco, S.F.; Wu, H. Stratification duration and the formation of bottom hypoxia over the Texas-Louisiana shelf. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 238, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharples, J.; Simpson, J.H.; Brubaker, J.M. Observations and modelling of periodic stratification in the Upper York River Estuary, Virginia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1994, 38, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, P.; Blain, C.A.; Di Iorio, D.; Hansell, H. Mixing and Turbulence in a Flooding Coastal River. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2013, 139, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fischer, H.B. Mass transport mechanisms in partially stratified estuaries. J. Fluid Mech. 1972, 53, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, K.R. Estuaries: A Physical Introduction, 2nd ed.; John Wiley Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, J.; Bowers, D. Models of stratification and frontal movement in shelf seas. Deep. Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1981, 28, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.H.; Brown, J.; Matthews, J.; Allen, G. Tidal Straining, Density Currents, and Stirring in the Control of Estuarine Stratification. Estuaries 1990, 13, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, H.; Hofmeister, R. A dynamic equation for the potential energy anomaly for analysing mixing and stratification in estuaries and coastal seas. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2008, 77, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, W.C.; Fernandes, E.H.; Rocha, L.A. Straining and advection contributions to the mixing process in the Patos Lagoon estuary, Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, C03016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Geyer, W.R.; Traykovski, P.A.; Nidzieko, N.J. Effects of estuarine and fluvial processes on sediment transport over deltaic tidal flats. Cont. Shelf Res. 2013, 60, S40–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, J.J.; Ridderinkhof, H.; Maas, L.R.M.; van Aken, H.M. Intra- and intertidal variability of the vertical current structure in the Marsdiep basin. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 93, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Shi, J.Z.; Hu, G.-D.; Xiong, L.-B. Circulation and mixing along the North Passage in the Changjiang River estuary, China. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 148, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, Q.; Shen, J.; Du, J. The alteration of lateral circulation under the influence of human activities in a multiple channel system, Changjiang Estuary. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 242, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chant, R.J.; Stoner, A.W. Particle trapping in a stratified flooddominated estuary. J. Mar. Res. 2001, 59, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, D.A.; Smith, J.D. Circulation, density distribution and neap-spring transitions in the Columbia River Estuary. Prog. Oceanogr. 1990, 25, 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R.; Trowbridge, J.H.; Bowen, M.M. The Dynamics of a Partially Mixed Estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2000, 30, 2035–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, D. The period of simple vertical oscillations in the atmosphere. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1927, 53, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Scully, M.E.; Geyer, W.R. The role of advection, straining, and mixing on the tidal variability of estuarine stratification. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2012, 42, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, J.R.; Stacey, M.T.; Burau, J.R.; Monismith, S.G. Interaction of lateral baroclinic forcing and turbulence in an estuary. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becherer, J.; Stacey, M.T.; Umlauf, L.; Burchard, H. Lateral circulation generates flood tide stratification and estuarine exchange flow in a curved tidal inlet. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2015, 45, 638–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, O.; Stacey, M.; Senn, D.; Holleman, R.; MacVean, L. Longitudinal versus lateral estuarine dynamics and their role in tidal stratification patterns in lower south San Francisco Bay. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 5888–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.L. Longitudinal Transportation Mechanism of Sallinity in west channel of Lingding Bay in dry season, China. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2012, 347–353, 1898–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Li, S.; Wang, D. Hypoxia in the Pearl River Estuary, the South China Sea, in July 1999. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2009, 12, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.; Sun, L.; Shi, R.; Zhou, W.; Dang, A. Saltwater intrusion induced by a complete neap tide and its effect on nutrients variation in the estuary of Pearl River, China. J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ruan, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, H. Long-term change in tidal dynamics and its cause in the Pearl River Delta, China. Geomorphology 2010, 120, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Shi, P.; Yin, K.; Gan, J.; Qi, Y. Tides and tidal currents in the Pearl River Estuary. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.M.; Zhang, W. Tidal impacts on downstream hydraulic geometry of a tide-influenced delta. Ocean Dyn. 2020, 70, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Friedrichs, M.A.M.; Wang, H.V.; Irby, I.D.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. A 3D, cross-scale, baroclinic model with implicit vertical transport for the Upper Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries. Ocean Model. 2016, 107, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Ye, F.; Stanev, E.V.; Grashorn, S. Seamless cross-scale modeling with SCHISM. Ocean Model. 2016, 102, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, G.; Erofeeva, S. Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol. 2002, 19, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacey, M.T.; Rippeth, T.P.; Nash, J.D. Turbulence and stratification in estuaries and coastal seas. In Treatise on Estuarine and Coastal Science; Wolanski, E., McLusky, D.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 9–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, K.F. Circulation and diffusion. In Estuaries; Lauff, G.H., Ed.; AAAS Publication: New York, NY, USA, 1967; pp. 15–36. [Google Scholar]
- MacCready, P.; Geyer, W.R. Advances in estuarine physics. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2010, 2, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, W.R.; MacCready, P. The estuarine circulation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 175–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, M. Effects of wind straining on estuarine stratification: A combined observational and modeling study. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 2363–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, W.R.; Smith, J.D. Shear instability in a highly stratified estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1987, 17, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, H. Observations of stratified turbulent mixing in an estuary: Neap-to-spring variations during high river flow. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 45, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.J.; Feng, J.J.; Gao, X.Y.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, M.R.; Kong, J. Estuarine circulation and mechanism of mixing and stratification in the Modaomen Estuary. Adv. Water Sci. 2017, 28, 908–921, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Purkiani, K.; Becherer, J.; Flöser, G.; Gräwe, U.; Mohrholz, V.; Schuttelaars, H.M.; Burchard, H. Numerical analysis of stratification and destratification processes in a tidally energetic inlet with an ebb tidal delta. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.I.; Somerfield, P.J.; Gilbert, F.J. Quantifying uncertainty in high-resolution coupled hydrodynamic-ecosystem models. J. Mar. Syst. 2007, 64, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, D. A soil-based approach to rainfall-runoff modelling in ungauged catchments for England and Wales. Ph.D. Thesis, Cranfield University, Cranfield, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Stacey, M.T.; Monismith, S.G.; Burau, J.R. Observations of turbulence in a partially stratified estuary. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1999, 29, 1950–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, D.K.; Geyer, W.R.; Lerczak, J.A. Structure, variability, and salt flux in a strongly forced salt wedge estuary. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monismith, S.G.; Kimmerer, W.; Burau, J.R.; Stacey, M.T. Structure and flow-induced variability of the subtidal salinity field in Northern San Francisco Bay. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2002, 32, 3003–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, F.; Ji, X.; Zhang, W.; Zou, H.; Jiang, W.; Xu, Y. Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Salinity Stratification during the Wet Season in the Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121927
Yang F, Ji X, Zhang W, Zou H, Jiang W, Xu Y. Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Salinity Stratification during the Wet Season in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(12):1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121927
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Fang, Xiaomei Ji, Wei Zhang, Huazhi Zou, Wenzhi Jiang, and Yanwen Xu. 2022. "Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Salinity Stratification during the Wet Season in the Pearl River Estuary, China" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 12: 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121927
APA StyleYang, F., Ji, X., Zhang, W., Zou, H., Jiang, W., & Xu, Y. (2022). Characteristics and Driving Mechanisms of Salinity Stratification during the Wet Season in the Pearl River Estuary, China. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(12), 1927. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10121927




