Trapezia Crabs That Dwell in Distinctive Day/Night Canopy Compartments of a Marine Animal Forest, Forage on Demersal Plankton
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
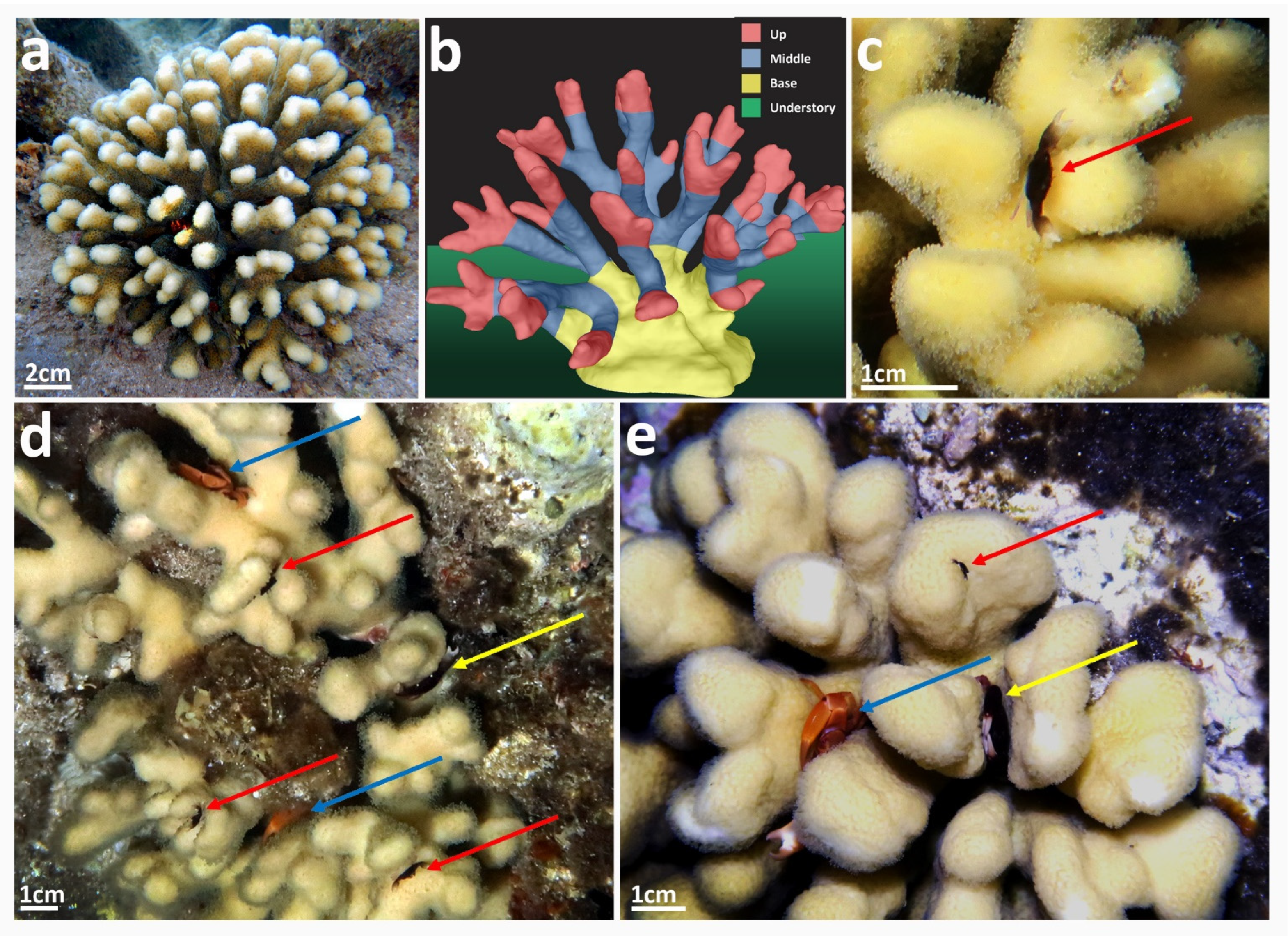
2.1. Canopy Compartment Usage by Trapezia Crabs-Day and Night Field Surveys
2.2. Canopy Compartment Usage by Crabs-Laboratory Experiments
2.3. Feeding on Planktonic Organisms-Laboratory Experiments
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Day and Night Surveys
3.2. Canopy’s Compartment Usage by Crabs-Laboratory Experiments
3.3. Plankton Foraging-Laboratory Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rossi, S.; Bramanti, L.; Gori, A.; Orejas, C. Animal forests of the world: An overview. In Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 1–28. ISBN 9783319210117. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, N.A.J.; Nash, K.L. The importance of structural complexity in coral reef ecosystems. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horoszowski-Fridman, Y.B.; Rinkevich, B. Restoring the animal forests: Harnessing silviculture biodiversity concepts for coral transplantation. In Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 1313–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Cheng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fan, X. Functional tradeoffs and feature recognition of rural production—Living—Ecological spaces. Land 2022, 11, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuel, Y.; Ziv, Y.; Rinkevich, B. Strahler ordering analyses on branching coral canopies: Stylophora pistillata as a case study. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, J.S.; Pratchett, M.S.; Hutchings, P.A.; Geoffrey, J.P. Coral-associated invertebrates: Diversity, ecological importance and vulnerability to disturbance. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. An Annu. Review. 2011, 49, 43–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belmaker, J. Species richness of resident and transient coral-dwelling fish responds differentially to regional diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaka-Kudla, L.M. The global biodiversity of coral reefs: A comparison with rain forests. In Biodiversity II: Understanding and protecting our biological resources; Reaka-Kudla, L.M., Wilson, D.E., Wilson, E.O., Eds.; Joseph Henry Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 83–108. ISBN 0309052270. [Google Scholar]
- Pisapia, C.; Stella, J.; Silbiger, N.J.; Carpenter, R. Epifaunal invertebrate assemblages associated with branching Pocilloporids in Moorea, French Polynesia. PeerJ. 2020, 8, e9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, H.T.; Ishii, S.I.; Hiura, T. Exploring the relationships among canopy structure, stand productivity, and biodiversity of temperate forest ecosystems. For. Sci. 2004, 50, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhinny, C.; Gibbons, P.; Brack, C.; Bauhus, J. Fauna-habitat relationships: A basis for identifying key stand structural attributes in temperate Australian eucalypt forests and woodlands. Pac. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 12, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M.; Jones, C.G.; Lawton, J.H.; Shachak, M. Organisms as Ecosystem Engineers. Oikos 1994, 69, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horoszowski-Fridman, Y.B.; Brêthes, J.C.; Rahmani, N.; Rinkevich, B. Marine silviculture: Incorporating ecosystem engineering properties into reef restoration acts. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H. Diversity in tropical rain forests and coral reefs. Science 1978, 199, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinkevich, B. The branching coral Stylophora pistillata: Contribution of genetics in shaping colony landscape. Isr. J. Zool. 2002, 48, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.L. The distribution of feeding habits among animals in a tropical rain forest. J. Anim. Ecol. 1962, 31, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, D.L. Vertical stratification of birds in a tropical dry forest. Condor 1971, 73, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colquhoun, M.K.; Morley, A. Vertical zonation in woodland bird communities. J. Anim. Ecol. 1943, 12, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimbacher, P.S.; Stork, N.E. Vertical stratification of feeding guilds and body size in beetle assemblages from an Australian tropical rainforest. Austral Ecol. 2007, 32, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Amorim, D.; Brown, B.V.; Boscolo, D.; Ale-Rocha, R.; Alvarez-Garcia, D.M.; Balbi, M.I.P.A.; de Marco Barbosa, A.; Capellari, R.S.; de Carvalho, C.J.B.; Couri, M.S.; et al. Vertical stratification of insect abundance and species richness in an Amazonian tropical forest. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, M. Observations on the distribution of diurnal mosquitoes in a tropical forest. Ecology 1944, 25, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, M.; Taira, A. Population structure of six sympatric species of Trapezia associated with the hermatypic coral Pociliopora damicornis with a hypothesis of mechanisms promoting their coexistence. J. Jpn. Coral Reef Soc. 1999, 1, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulyshen, M.D. Arthropod vertical stratification in temperate deciduous forests: Implications for conservation-oriented management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 261, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Kitching, R.L.; Cao, M.; Creedy, T.J.; Fayle, T.M.; Freiberg, M.; Hewitt, C.N.; Itioka, T.; Koh, L.P.; Ma, K.; et al. Forests and their canopies: Achievements and horizons in canopy science. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaish, L.; Abelson, A.; Rinkevich, B. Branch to colony trajectory in a modular organism: Pattern formation in the indo-pacific coral Stylophora pistillata. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaish, L.; Rinkevich, B. Critical evaluation of branch polarity and apical dominance as dictators of colony astogeny in a branching coral. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shefy, D.; Rinkevich, B. Stylophora pistillata—A model colonial species in basic and applied studies. In Handbook of Marine Model Organisms in Experimental Biology; Boutet, A., Schierwater, B., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galil, B. The adaptive functional structure of mucus-gathering setae in trapezid crabs symbiotic with corals. Symbiosis 1987, 4, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, W.K. Community structure among the animals inhabiting the coral Pocillopora damicornis at Heron Island, Australia. In Symbiosis in the Sea; Vernberg, W.B., Ed.; University of South Carolina Press: Columbia, SC, USA, 1974; pp. 219–243. [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen, J.W. Trapezia and Tetralia (Decapoda, Brachyura, Xanthidae) as obligate ectoparasites of pocilloporid and acroporid corals. Pac. Sci. 1967, 21, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, P. Brachyuran crabs symbiotic with scleractinian corals: A review of their biology. Micronesica 1976, 12, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, W.K. Animals associated with living corals. In Biology and Geology of Coral Reefs; Jones, O.A., Endean, R., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; Volume 3, pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Glynn, P.W. Increased survivorship on corals harboring crustacean symbionts. Mar. Biol. Lett. 1983, 4, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, H.L.; Holbrook, S.J.; Schmitt, R.J.; Brooks, A.J. Symbiotic crabs maintain coral health by clearing sediments. Coral Reefs 2006, 25, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratchett, M.S. Influence of coral symbionts on feeding preferences of crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster planci in the western pacific. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 214, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stier, A.C.; Mckeon, C.S.; Osenberg, C.W.; Shima, J.S. Guard crabs alleviate deleterious effects of vermetid snails on a branching coral. Coral Reefs 2010, 29, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, E.M. Niche Overlap and Competition among Five Sympatric Congeneric Species of Xanthid Crabs. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Stimson, J. Stimulation of fat-body production in the polyps of the coral Pocillopora damicornis by the presence of mutualistic crabs of the genus Trapezia. Mar. Biol. 1990, 106, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkevich, B.; Wolodarsky, Z.; Loya, Y. Coral-crab association: A compact domain of a multilevel trophic system. Hydrobiologia 1991, 216–217, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinkevich, B.; Loya, Y. Senescence and dying signals in a reef building coral. Experientia 1986, 42, 320–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P. Movements between coral colonies in Trapezia ferruginea (Crustacea: Brachyura), an obligate symbiont of scleractinian corals. Mar. Biol. 1978, 46, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, M.; Yonaha, C. Community organization of associates of the scleractinian coral Pocillopora damicornis: Effects of colony size and interactions among the obligate symbionts. Galaxea 1992, 11, 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, C.K. Ecological Study of the Decapod Crustaceans Commensal with the Branching Coral Pocillopora meandrina var. Nobilis verrill. Master’s Thesis, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Counsell, C.W.W.; Donahue, M.J.; Edwards, K.F.; Franklin, E.C.; Hixon, M.A. Variation in coral-associated cryptofaunal communities across spatial scales and environmental gradients. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, J.S.; Munday, P.L.; Jones, G.P. Effects of coral bleaching on the obligate coral-dwelling crab Trapezia cymodoce. Coral Reefs 2011, 30, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuel, Y.; Ziv, Y.; Rinkevich, B. Coral-inhabiting Trapezia crabs forage on demersal plankton. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 964725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, A.N. Quantitative analysis of watershed geomorphology. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1957, 38, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oksanen, J. Vegan: Ecological diversity. R Package Version 2.4-4; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Goslee, S.C.; Urban, D.L. The ecodist package for dissimilarity-based analysis of ecological data. J. Stat. Softw. 2007, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, B.; Torchiano, M. lmPerm: Permutation tests for linear models. R Package Version 2.1.0. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lmPerm/lmPerm.pdf (accessed on 2 August 2016).
- Hervé, M. “RVAideMemoire” Testing and plotting procedures for biostatistics, Version 0.9-81.2. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/RVAideMemoire/RVAideMemoire.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2021).
- Mangiafico, S. Package ‘rcompanion’ Functions to support extension education program evaluation. R Package Version 2020, 2.3.26. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rcompanion/rcompanion.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Britayev, T.A.; Spiridonov, V.A.; Deart, Y.V.; El-Sherbiny, M. Biodiversity of the community associated with Pocillopora verrucosa (Scleractinia: Pocilloporidae) in the Red Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2017, 47, 1093–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vytopil, E.; Willis, B.L. Epifaunal community structure in Acropora spp. (Scleractinia) on the Great Barrier Reef: Implications of coral morphology and habitat complexity. Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, S.; Cúrdia, J.; Pereira, F.; Guerra-García, J.M.; Santos, M.N.; Cunha, M.R. Biodiversity patterns of epifaunal assemblages associated with the gorgonians Eunicella gazella and Leptogorgia lusitanica in response to host, space and time. J. Sea Res. 2014, 85, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, J.S.; Barrier, G.; Marine, R.; Authority, P.; Jones, G.P. Variation in the structure of epifaunal invertebrate assemblages among coral hosts. Coral Reefs 2018, 37, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmel, K.; Riegert, J.; Paul, L.; Novotný, V. Vertical stratification of an avian community in New Guinean tropical rainforest. Popul. Ecol. 2016, 58, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, R.H.; MacArthur, J.W. On bird species diversity. Ecology 1961, 42, 59–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, A.W.; Bray, R.N. Day versus night activity of reef fishes in a kelp forest off Santa Barbara, California. Fish. Bull. 1976, 74, 703–717. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Cooper, P.; Fulton, C.J.; Fox, R.J. Quantifying epifaunal secondary production within tropical macroalgal meadows: Seasonality and sensitivity to canopy structure. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 4267–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmaker, J.; Polak, O.; Shashar, N.; Ziv, Y. Geographic divergence in the relationship between Paragobiodon echinocephalus and its obligate coral host. J. Fish Biol. 2007, 71, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, N. The effects of habitat complexity on the macroinvertebrates colonising wood substrates in a lowland stream. Oecologia 1991, 85, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, L.H.L.; Todd, P.A. Structural complexity and component type increase intertidal biodiversity independently of area. Ecology 2016, 97, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, D.M.; Wang, L.H.; Fan, T.Y.; Chen, C.S.; Lee, R.W.; Sogin, E.; Gates, R.D. Diversity in skeletal architecture influences biological heterogeneity and Symbiodinium habitat in corals. Zoology 2013, 116, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seben, K.P.; Deriemer, K. Diel cycles of expansion and contraction in coral reef anthozoans. Mar. Biol. 1977, 256, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidelberg, K.B.; Sebens, K.P.; Purcell, J.E. Composition and sources of near reef zooplankton on a Jamaican forereef along with implications for coral feeding. Coral Reefs 2004, 23, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahel, R.; Yahel, G.; Genin, A. Near- bottom depletion of zooplankton over coral reefs: I: Diurnal dynamics and size distribution. Coral Reefs 2005, 24, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ory, N.C.; Dudgeon, D.; Duprey, N.; Thiel, M. Effects of predation on diel activity and habitat use of the coral-reef shrimp Cinetorhynchus hendersoni (Rhynchocinetidae). Coral Reefs 2014, 33, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, I.A.; Zapata-Hernández, G.; Fowles, A.E.; Gaymer, C.F.; Stuart-Smith, R.D. The awakening of invertebrates: The daily dynamics of fishes and mobile invertebrates at Rapa Nui’s multiple use marine protected area. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2020, 31, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzurro, E.; Pais, A.; Consoli, P.; Andaloro, F. Evaluating day-night changes in shallow Mediterranean rocky reef fish assemblages by visual census. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 2245–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, W.K. Distribution and ecology of animals associated with branching corals (Acropora spp.) from the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1994, 55, 193–211. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, M.J.; Nel, J.A.J. Dominance and population structure of freshwater crabs (Potamonautes perlatus Milne Edwards). South Afr. J. Zool. 1998, 33, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neil, S.J. Size assessment and cues: Studies of hermit crab contests. Behaviour 1985, 92, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.H.; Herberholz, J. Crustacean models of aggression. In Biology of Aggression; Nelson, R.J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 38–64. ISBN 9780199865444. [Google Scholar]
- Stendera, S.; Adrian, R.; Bonada, N.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hugueny, B.; Januschke, K.; Pletterbauer, F.; Hering, D. Drivers and stressors of freshwater biodiversity patterns across different ecosystems and scales: A review. Hydrobiologia 2012, 696, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floren, A. Sampling arthropods from the canopy by insecticidal knockdown. In Manual on Field Recording Techniques and Protocols for All Taxa Biodiversity Inventories; Eymann, J., Degref, J., Häuser, C., Monje, J.C., Samyn, Y., Vandenspiegel, D., Eds.; ABC Taxa: Brussels, Belgium, 2010; Volume 8, pp. 158–172. [Google Scholar]
- Christian, J.J. Social subordination, population density, and mammalian evolution. Science 1970, 168, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.; Blanchard, J.L.; Newman, S.P.; Dryden, C.S.; Mumby, P.J. High refuge availability on coral reefs increases the vulnerability of reef-associated predators to overexploitation. Ecology 2018, 99, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holbrook, S.J.; Brooks, A.J.; Schmitt, R.J. Variation in structural attributes of patch-forming corals and in patterns of abundance of associated fishes. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2002, 53, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, J. Exposure and time use in willow tit flocks: The cost of subordination. Anim. Behav. 1987, 35, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbicki, M.; Bozec, Y.; Labrosse, P.; Letourneur, Y.; Mou-Tham, G.; Wantiez, L. Diet composition of carnivorous fishes from coral reef lagoons of New Caledonia. Aquat. Living Resour. 2005, 18, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Styring, A.R.; Bin Hussin, M.Z. Foraging ecology of woodpeckers in lowland Malaysian rain forests. J. Trop. Ecol. 2004, 20, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, M.S.; Mohd Sah, S.A. Foraging patterns reveal niche separation in tropical insectivorous birds. Acta Ornithol. 2012, 47, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittelbach, G.G. Foraging efficiency and body size: A study of optimal diet and habitat use by bluegills. Ecology 1981, 62, 1370–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacia, E.; Duarte, C.M. Sediment retention by a Mediterranean Posidonia oceanica meadow: The balance between deposition and resuspension. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2001, 52, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizien, K.; Ghisalberti, M. Living in the canopy of the animal forest: Physical and biogeochemical aspects. In Marine Animal Forests: The Ecology of Benthic Biodiversity Hotspots; Rossi, S., Bramanti, L., Gori, A., Orejas, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 507–528. ISBN 9783319210124. [Google Scholar]



| Treatment Type | Between Treatments | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live | Dead | None | |||||||
| Type of behavior | Failure/Success | Medium | Large | Medium | Large | Medium | Large | ꭓ2 | p |
| Predation | Failure | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 16 | 22 | 90.7 | <0.001 * |
| Success | 14 | 21 | 14 | 21 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Reaction | Failure | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 10 | 63.2 | <0.001 * |
| Success | 16 | 22 | 16 | 21 | 0 | 12 | |||
| Within treatments— between body sizes | ꭓ2 | p | ꭓ2 | p | ꭓ2 | p | |||
| Predation | 0.08 | >0.05 | 0.08 | >0.05 | 0.95 | >0.05 | |||
| Reaction | 0.95 | >0.05 | 0 | 1 | 10.36 | <0.001 * | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shmuel, Y.; Ziv, Y.; Rinkevich, B. Trapezia Crabs That Dwell in Distinctive Day/Night Canopy Compartments of a Marine Animal Forest, Forage on Demersal Plankton. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101522
Shmuel Y, Ziv Y, Rinkevich B. Trapezia Crabs That Dwell in Distinctive Day/Night Canopy Compartments of a Marine Animal Forest, Forage on Demersal Plankton. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2022; 10(10):1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101522
Chicago/Turabian StyleShmuel, Yaniv, Yaron Ziv, and Baruch Rinkevich. 2022. "Trapezia Crabs That Dwell in Distinctive Day/Night Canopy Compartments of a Marine Animal Forest, Forage on Demersal Plankton" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 10, no. 10: 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101522
APA StyleShmuel, Y., Ziv, Y., & Rinkevich, B. (2022). Trapezia Crabs That Dwell in Distinctive Day/Night Canopy Compartments of a Marine Animal Forest, Forage on Demersal Plankton. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 10(10), 1522. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse10101522







