Early Detection of Zymoseptoria tritici in Winter Wheat by Infrared Thermography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Wheat Varieties
2.2. Inoculation with Z. tritici
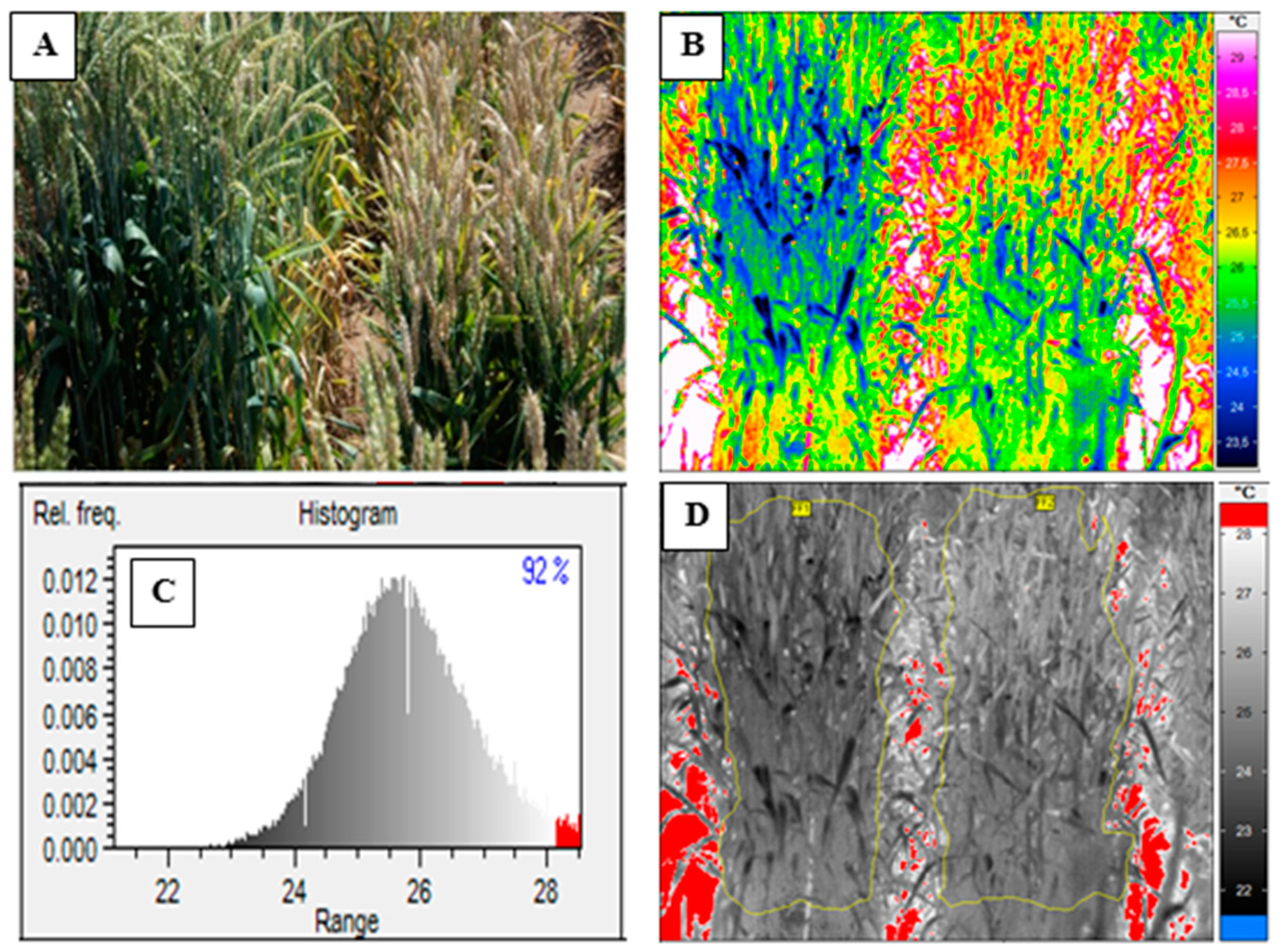
2.3. Acquiring Thermal Images
2.4. Visual Scoring
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
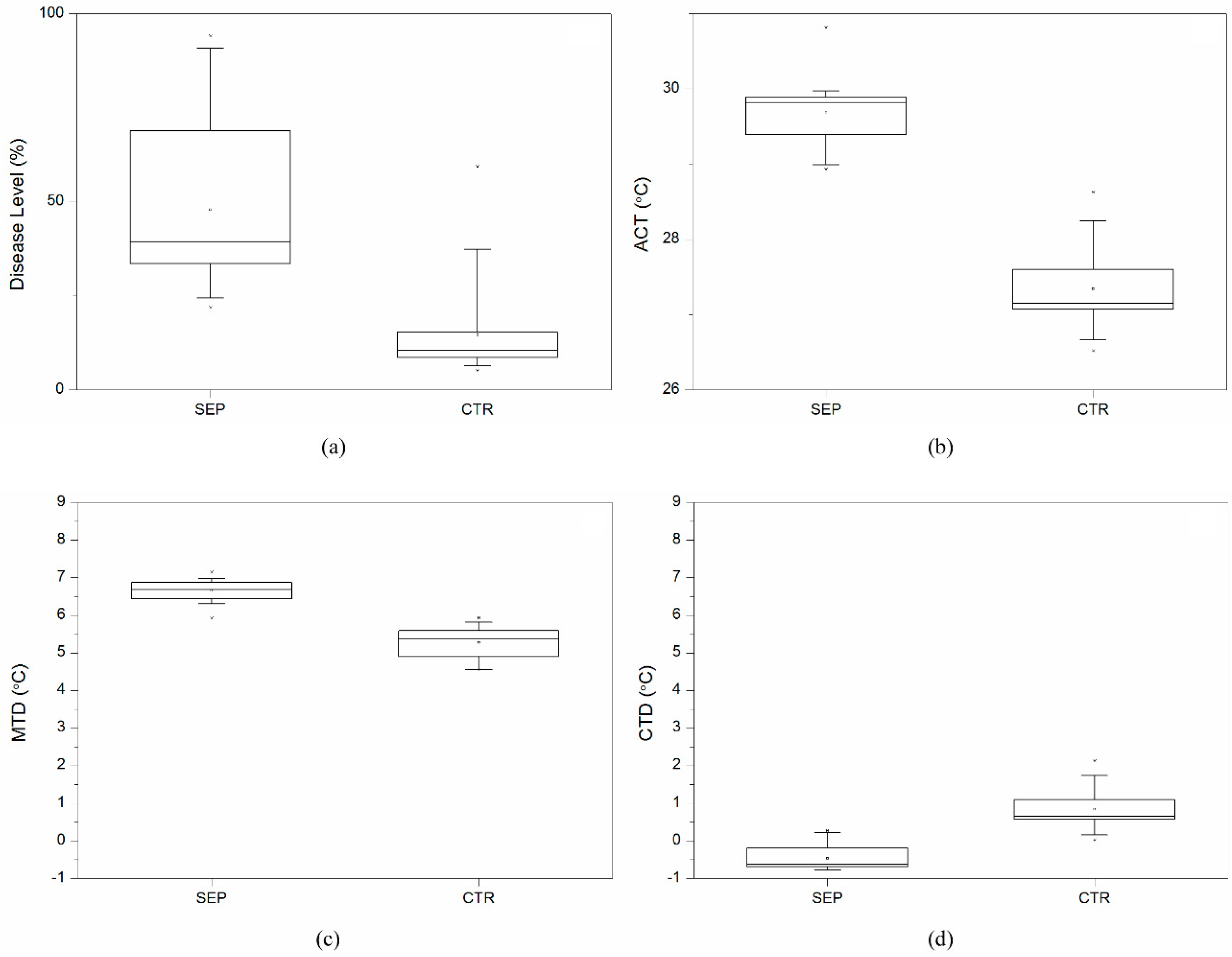
3.1. Disease Level and Temperature Effects across 25 Wheat Varieties
3.2. Temperature Effects Related to Disease Level for 25 Wheat Varieties
3.3. Temperature Effect on Wheat Varieties
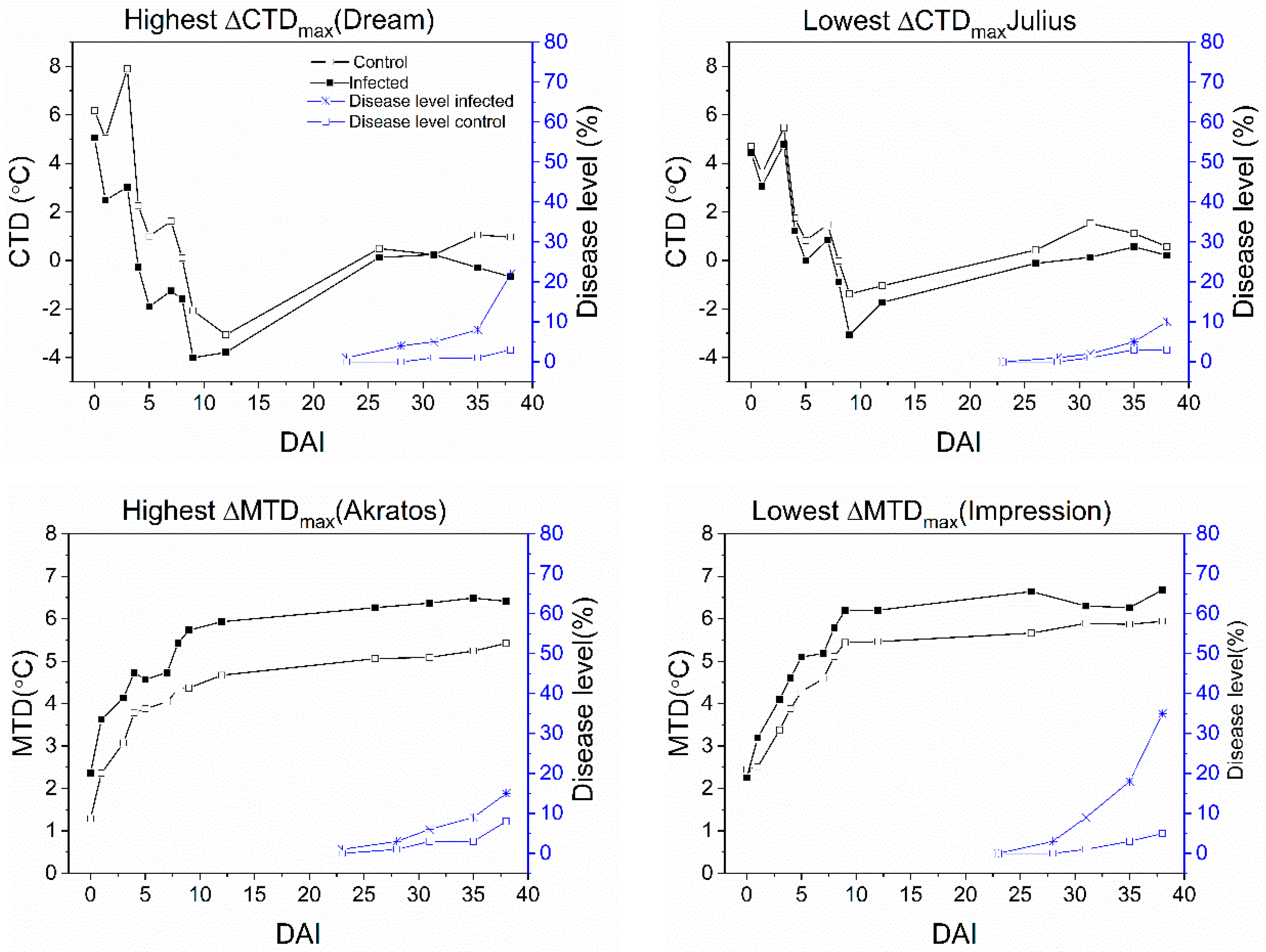
3.4. Temporal Development of Disease Level and Temperature Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siddiqui, K. Green biotechnology at the crossroads of nanobiotechnology, globalization, poverty alleviation and food sovereignty. Indian J. Crop. Sci. 2007, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dhlamini, Z.; Spillane, C.; Moss, J.P.; Ruane, J.; Urquia, N.; Sonnino, A. Status of Research and Application of Crop Biotechnologies in Developing Countries: Preliminary Assessment; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, D.; Mar, I.; Sears, L. (Eds.) Enhancing the Use of Crop Genetic Diversity to Manage Abiotic Stress in Agricultural Production Systems; IPGRI: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Vinocur, B.; Altman, A. Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: Towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 2003, 218, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosina, P.; Reynolds, M.; Dixon, J.; Joshi, A. Stakeholder perception of wheat production constraints, capacity building needs, and research partnerships in developing countries. Euphytica 2007, 157, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Afzal, M.; Noorka, I. Prediction of yield losses in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in relation to epidemiological factors in Faisalabad. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Duveiller, E.; Singh, P.R.; Nicol, J.M. The challenges of maintaining wheat productivity: Pests, diseases, and potential epidemics. Euphytica 2007, 157, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, R.; Ubeda, A.; Paya, M.; Alves, M.; del Olmo, E.; Lopez, J.L.; San Feliciano, A. Synthesis and enzyme inhibitory activities of a series of lipidic diamine and amino alcohol derivatives on cytosolic and secretory phospholipases A2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, S.; Mishra, A.; Ehsani, R.; Davis, C. A review of advanced techniques for detecting plant diseases. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 72, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshou, D.; Bravo, C.; Oberti, R.; West, J.; Ramon, H.; Vougioukas, S.; Bochtis, D. Intelligent multi–sensor system for the detection and treatment of fungal diseases in arable crops. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 184, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lamb, D.W.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J. Identification of yellow rust in wheat using in-situ spectral reflectance measurements and airborne hyperspectral imaging. Precis. Agric. 2007, 8, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, P. Development of hyperspectral imaging technique for the detection of apple surface defects and contaminations. J. Food Eng. 2004, 61, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Angenot, L.; Harnischfeger, G. Analysis of Strychnos nux-vomica, Strychnos icaja and Strychnos ignatii extracts by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry and multivariate analysis techniques. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bauriegel, E.; Giebel, A.; Geyer, M.; Schmidt, U.; Herppich, W.B. Early detection of fusarium infection in wheat using hyper–spectral imaging. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2011, 75, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, J.; Misra, R.K.; Payero, J. Prospects of using infrared thermography for irrigation scheduling of wheat crop. In Proceedings of the Australian Irrigation Conference and Exhibition 2010: One Water Many Futures, Sydney, Australia, 8–10 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zia, S.; Spohrer, K.; Merkt, N.; Wenyong, D.; He, X.; Müller, J. Non-invasive water status detection in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) by thermography. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2009, 2, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, H.G. Use of infrared thermometry for estimation of stomatal conductance as a possible aid to irrigation scheduling. Agric. For. Meterorol. 1999, 95, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.G.; Stoll, M.; Santos, T.; de Sousa, C.; Chaves, M.M.; Grant, O.M. Use of infrared thermography for monitoring stomatal closure in the field: Application to grapevine. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyal, Z.; Sharen, A.L.; Prescott, J.M. The Septoria Diseases of Wheat, Concepts and Methods of Disease Management; CIMMYT: Texcoco, Mexico, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C.; Bancal, M.-O.; Lannou, C.; Ney, B. Quantification of the effects of Septoria tritici blotch on wheat leaf gas exchange with respect to lesion age, leaf number, and leaf nitrogen status. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenthal, M.; Steiner, U.; Dehne, H.W.; Oerke, E.C. Effect of downy mildew development on transpiration of cucumber leaves visualized by digital infrared thermography. Phytopathology 2005, 95, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beschreibende Sortenliste 2012–Getreide, Mais, Öl- und Faserpflanzen, Leguminosen, Rüben, Zwischenfrüchte; Bundessortenamt: Hannover, Deutschland, 2012.
- Ding, L.; Xu, H.; Yi, H.; Yang, L.; Kong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xue, S.; Jia, H.; Ma, Z. Resistance to hemi-biotrophic F. graminearum infection is associated with coordinated and ordered expression of diverse defense signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuc, J. Phytoalexins, stress metabolism, and disease resistance in plants. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 1995, 33, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kema, G.H.J.; Sayoud, R.; Annone, J.G.; Van Silfhout, C.H. Genetic variation for virulence and resistance in the wheat–Mycosphaerella graminicola pathosystem. II: Analysis of interactions between pathogen isolates and host cultivars. Phytopathology 1996, 8, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosyara, R.U.; Subedi, S.; Duveiller, E.; Sharma, R.C. The effect of spot blotch and heat stress on variation of canopy temperature depression, chlorophyll fluorescence and chlorophyll content of hexaploid wheat genotypes. Euphytica 2010, 174, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbinge, R.; Jorritsma, I.T.M.; Schans, J. Damage components of powdery mildew in winter wheat. Neth. J. Plant. Pathol. 1985, 91, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtienberg, D. Effect of Folia Diseases on Gas Exchange Processes: A comparative Study. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerke, E.C.; Steiner, U.; Dehne, H.W.; Lindenthal, M. Thermal imaging of cucumber leaves affected by downy mildew and environmental conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 2121–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.G.; Idso, S.B.; Reginato, R.J.; Pinter, P.J. Canopy temperature as a crop water stress indicator. Water Resour. Res. 1981, 17, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balota, M.; Payne, A.W.; Evett, R.S.; Lazar, D.M. Canopy Temperature Depression Sampling to Assess Grain Yield and Genotypic Differentiation in Winter Wheat. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 1518–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variety | Country of Origin | Susceptibility |
|---|---|---|
| Akratos | G | 5 |
| Apache | F | n.i. |
| Arina | CH | n.i. |
| Batis | G | 4 |
| Biscay | G | 7 |
| Bussard | G | 7 |
| Cubus | G | 6 |
| Dream | G | n.i. |
| Egoist | G | 4 |
| F201-R | ROM | n.i. |
| Florett | G | n.i. |
| History | G | n.i. |
| Impression | G | 4 |
| Julius | G | 3 |
| MES130 | C | n.i. |
| Meteor | G | 4 |
| Naturastar | G | 6 |
| Nelson | G | 3 |
| Pamier | G | 3 |
| Rubens | G | n.i. |
| Sailor | G | 5 |
| Skalmeje | G | 4 |
| Solitär | G | n.i. |
| Toras | G | 4 |
| Tuareg | G | 5 |
| Variety | First Visual Symptoms | ANOVA Test | Maximum Difference from Control | First Significant Difference from Control | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAI | CTD | MTD | ∆CTDmax | DAI | ∆MTDmax | DAI | ∆CTD | DAI | ∆MTD | DAI | |
| Akratos | 23 | - | ** | 2.74 | 7 | 5.42 | 38 | - | - | 1.06 | 3 |
| Apache | 23 | ** | - | 3.23 | 9 | 1.06 | 5 | 2.06 | 4 | - | - |
| Arina | 28 | ** | *** | 3.28 | 5 | 2.33 | 28 | 2.87 | 7 | 1.92 | 7 |
| Batis | 23 | ** | *** | 4.6 | 7 | 2.12 | 28 | 4.60 | 7 | 0.91 | 5 |
| Biscay | 28 | ** | ** | 4.09 | 9 | 1.64 | 38 | 3.82 | 8 | 0.51 | 4 |
| Bussard | 23 | ** | *** | 4.31 | 28 | 2.35 | 38 | 2.61 | 7 | 0.90 | 5 |
| Cubus | 23 | ** | ** | 3.74 | 12 | 1.35 | 38 | 1.91 | 5 | 0.78 | 4 |
| Dream | 23 | - | *** | 4.88 | 3 | 2.05 | 29 | - | - | 0.81 | 4 |
| Egoist | 23 | *** | *** | 3.63 | 5 | 2.21 | 28 | 2.98 | 4 | 0.45 | 3 |
| F201-R | 23 | *** | * | 4.25 | 7 | 1.51 | 38 | 2.34 | 4 | 0.29 | 3 |
| Florett | 23 | ** | - | 3.20 | 9 | 1.06 | 5 | 1.70 | 4 | - | - |
| History | 23 | ** | * | 3.45 | 9 | 1.69 | 38 | 1.75 | 5 | 1.04 | 5 |
| Impression | 23 | ** | - | 3.50 | 8 | 0.98 | 26 | 1.52 | 3 | - | - |
| Julius | 28 | - | ** | 1.69 | 9 | 1.43 | 8 | - | - | 1.09 | 4 |
| MES130 | 23 | *** | ** | 3.45 | 38 | 2.12 | 38 | 1.83 | 4 | 0.86 | 7 |
| Meteor | 23 | ** | ** | 3.41 | 3 | 1.91 | 38 | 2.24 | 1 | 1.04 | 5 |
| Naturastar | 23 | ** | *** | 4.03 | 7 | 2.72 | 3 | 2.22 | 4 | 1.65 | 4 |
| Nelson | 23 | *** | *** | 4.54 | 9 | 2.57 | 12 | 3.51 | 4 | 1.17 | 4 |
| Pamier | 23 | ** | ** | 3.35 | 8 | 1.86 | 5 | 2.27 | 4 | 1.86 | 5 |
| Rubens | 23 | * | * | 3.06 | 29 | 1.7 | 29 | 1.34 | 1 | 0.84 | 3 |
| Sailor | 23 | *** | ** | 3.78 | 9 | 1.15 | 9 | 3.77 | 7 | 0.95 | 5 |
| Skalmeje | 28 | - | ** | 2.86 | 26 | 1.49 | 1 | - | - | 1.23 | 3 |
| Solitär | 28 | * | - | 2.67 | 26 | 1.28 | 38 | 2.03 | 4 | - | - |
| Toras | 23 | * | ** | 3.24 | 3 | 1.91 | 12 | 2.50 | 8 | 0.90 | 4 |
| Tuareg | 23 | - | ** | 2.76 | 38 | 2.01 | 7 | - | - | 1.87 | 5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zia-Khan, S.; Owusu-Adu, S.; Miedaner, T.; Müller, J. Early Detection of Zymoseptoria tritici in Winter Wheat by Infrared Thermography. Agriculture 2019, 9, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9070139
Wang Y, Zia-Khan S, Owusu-Adu S, Miedaner T, Müller J. Early Detection of Zymoseptoria tritici in Winter Wheat by Infrared Thermography. Agriculture. 2019; 9(7):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9070139
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuxuan, Shamaila Zia-Khan, Sebastian Owusu-Adu, Thomas Miedaner, and Joachim Müller. 2019. "Early Detection of Zymoseptoria tritici in Winter Wheat by Infrared Thermography" Agriculture 9, no. 7: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9070139
APA StyleWang, Y., Zia-Khan, S., Owusu-Adu, S., Miedaner, T., & Müller, J. (2019). Early Detection of Zymoseptoria tritici in Winter Wheat by Infrared Thermography. Agriculture, 9(7), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture9070139






