YOLO-MSLT: A Multimodal Fusion Network Based on Spatial Linear Transformer for Cattle and Sheep Detection in Challenging Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The work proposes a multimodal fusion network, YOLO-MSLT, based on the spatial linear transformer, which allows efficient collaboration of RGB and infrared modalities to detect cattle and sheep in complex scenes with precision.
- Our prime innovation resides in the CFFT module, which performs efficiently in cross-modal feature interaction and deep feature enhancement, thereby drastically enhancing object detection performance under variably difficult conditions.
- We evaluated our method on the self-constructed multi-modal cattle and sheep dataset MRDS, and compared it with the advanced fusion modules CSCA and CFT.
- Our technique exhibits a high level of both accuracy and efficiency, indicating its efficacy for reliable livestock detection in complex environments within Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) applications.
2. Materials and Methods
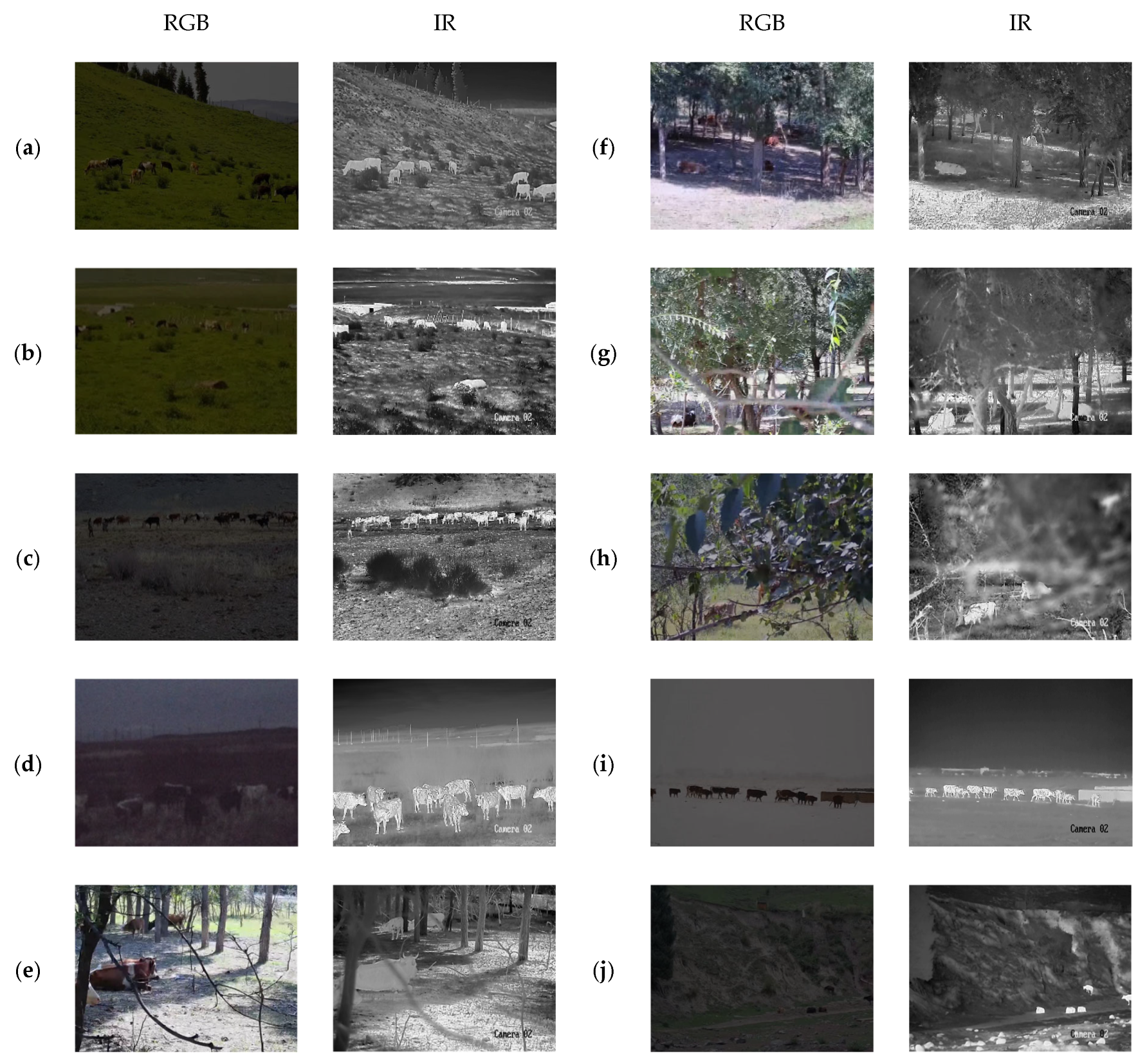
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Dataset Construction
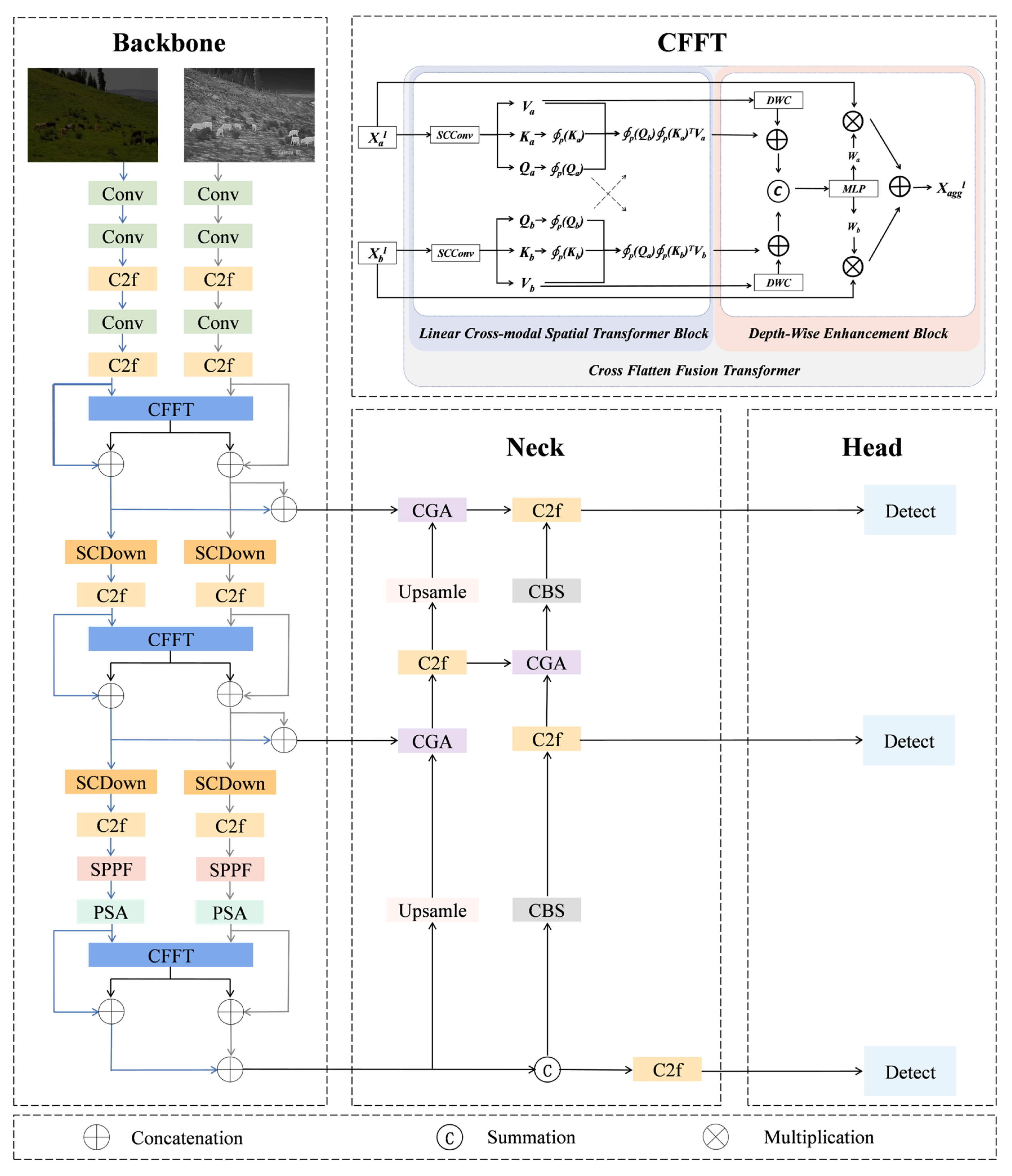
2.3. YOLO-MSLT
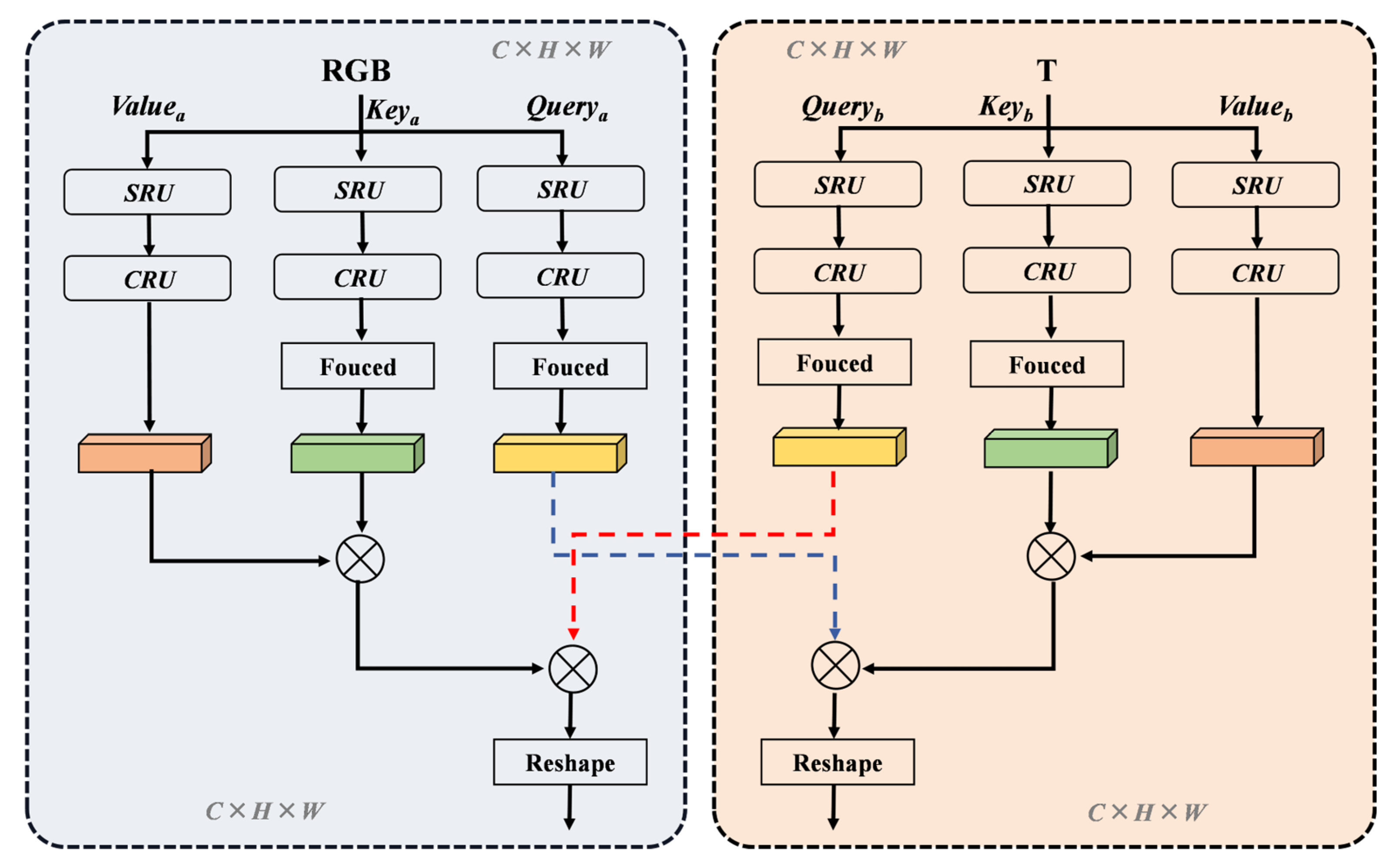
2.4. Linear Cross-Modal Spatial Transformer
2.5. Depth-Wise Enhancement
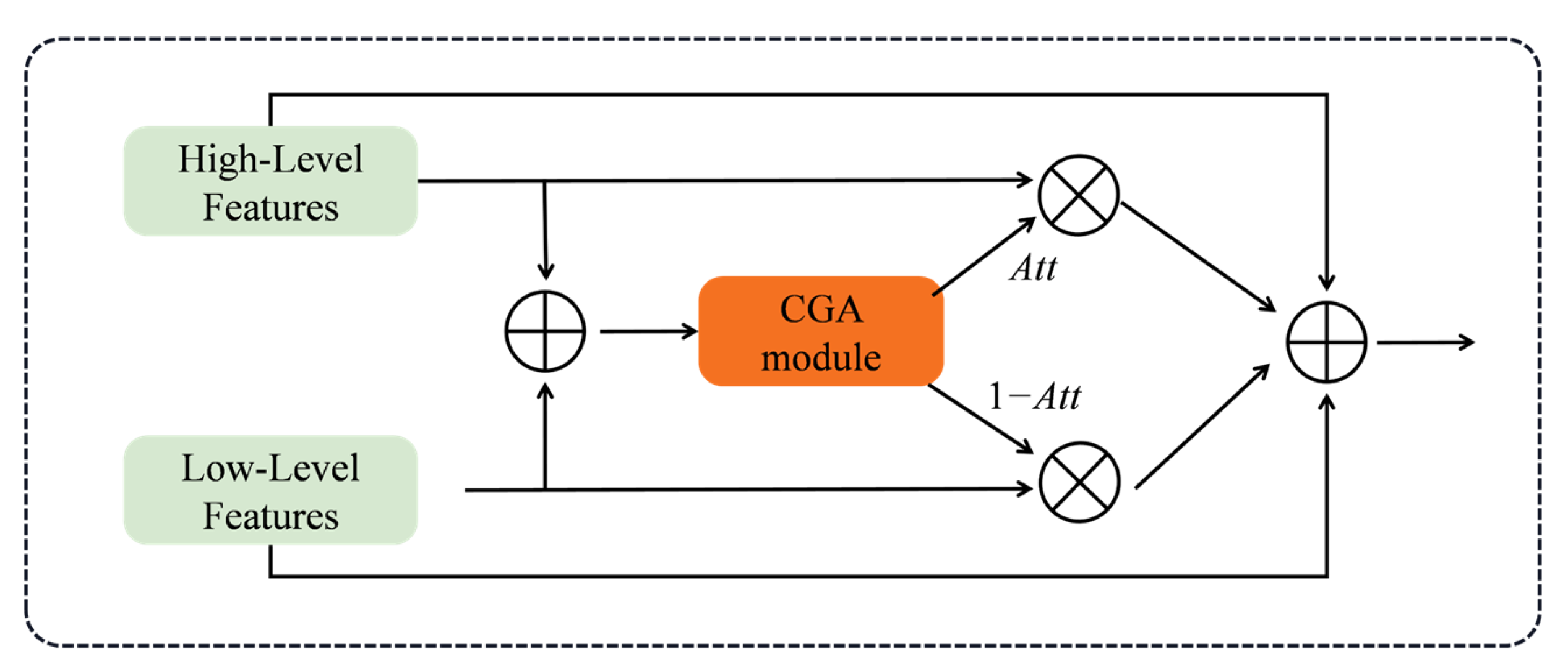
2.6. Content-Guided Attention Feature Pyramid Network
2.7. Network Training Implementation Details
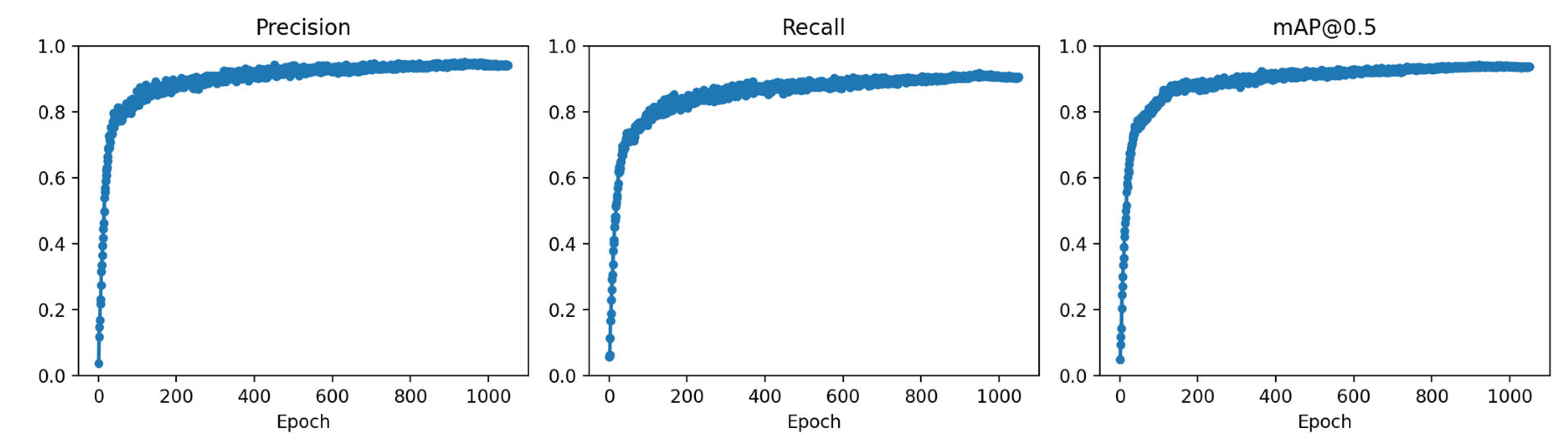
2.8. Performance Evaluation
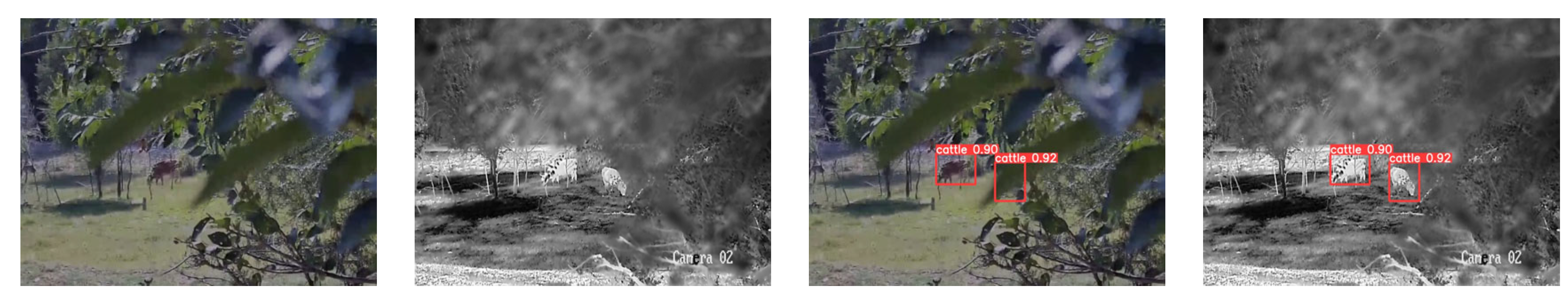
3. Results
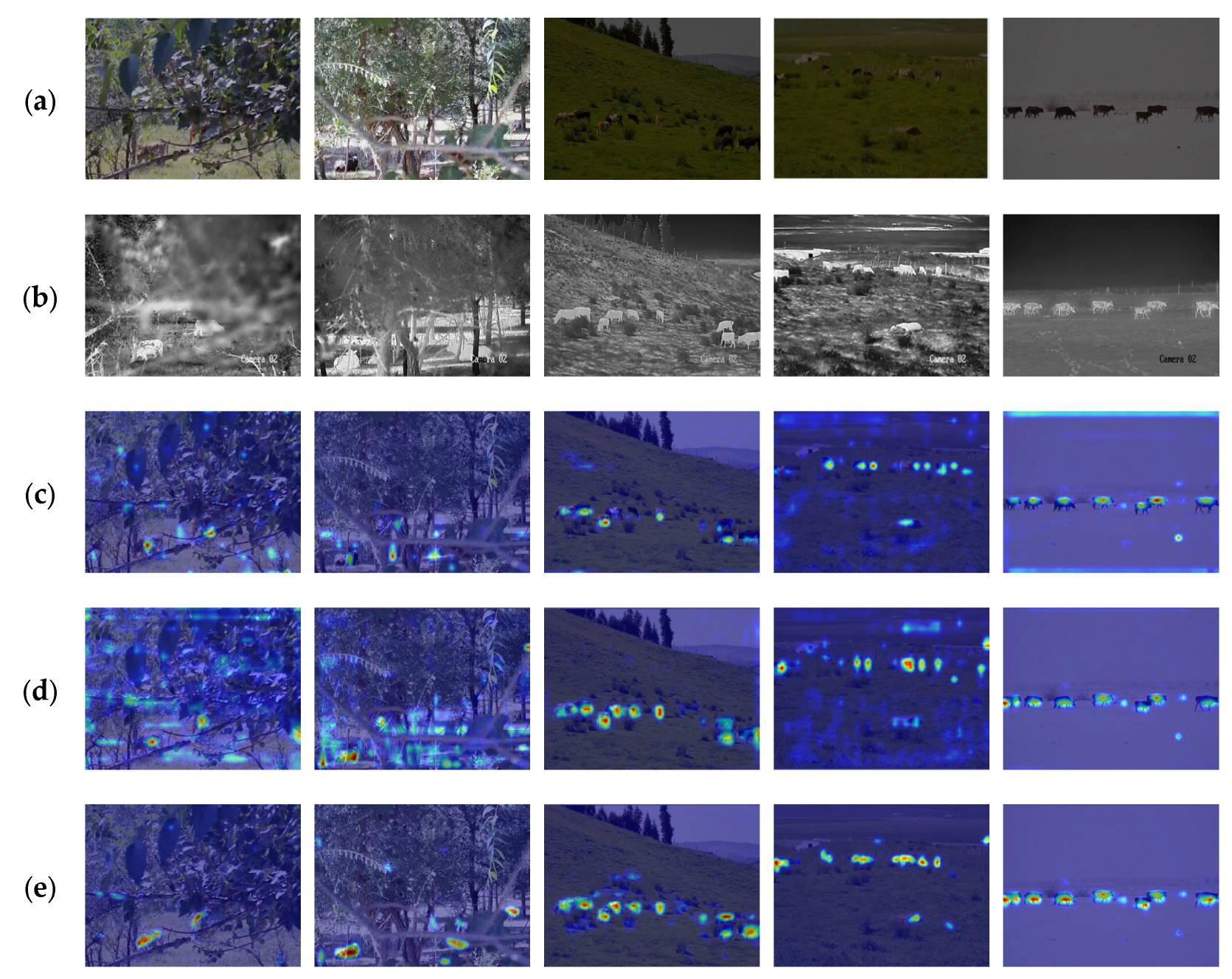
3.1. Comparison with Other Methods
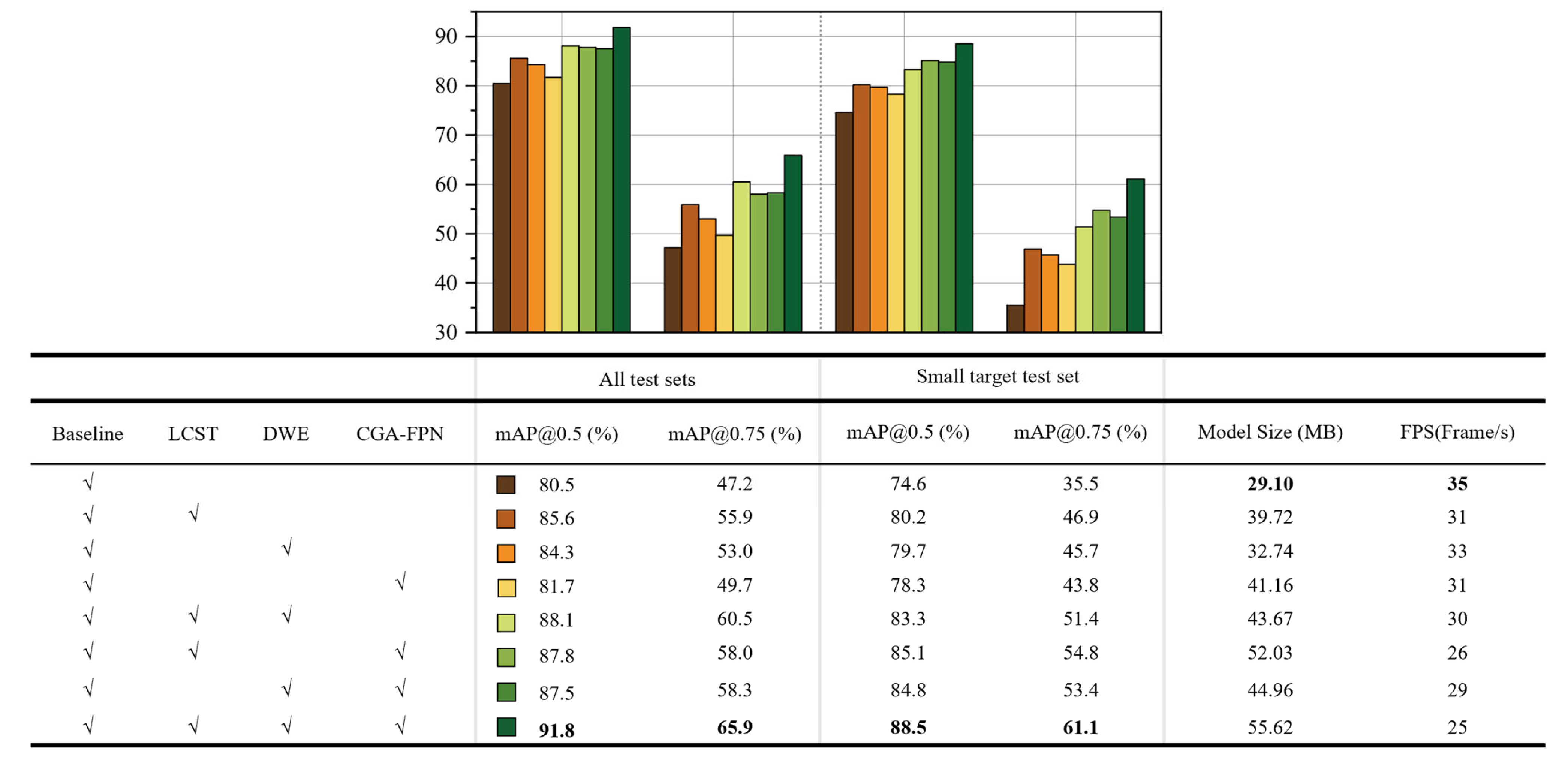
3.2. Ablation Study
4. Discussion
- exploring GAN-based [60] image enhancement and super-resolution techniques to further improve ultra-small object detection;
- developing lightweight variants of YOLO-MSLT through pruning, knowledge distillation, and quantization to improve suitability for edge deployment;
- expanding cross-species generalization via transfer learning and adaptive multimodal alignment, particularly for animals such as horses and deer.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernabucci, G.; Evangelista, C.; Girotti, P.; Viola, P.; Spina, R.; Ronchi, B.; Bernabucci, U.; Basiricò, L.; Turini, L.; Mantino, A. Precision livestock farming: An overview on the application in extensive systems. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2025, 24, 859–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Scott, S.; Mancini, C.; Boivin, X.; Strand, E. Human-computer interactions with farm animals—Enhancing welfare through precision livestock farming and artificial intelligence. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1490851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ren, F.; Nie, L.; Aodemu; Feng, W. Analysis of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Characteristics and Emissions Reduction Measures of Animal Husbandry in Inner Mongolia. Processes 2023, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesschen, J.P.; van den Berg, M.; Westhoek, H.; Witzke, H.; Oenema, O. Greenhouse gas emission profiles of European livestock sectors. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2011, 166, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteny, G.; Groenestein, C.; Hilhorst, M. Interactions and coupling between emissions of methane and nitrous oxide from animal husbandry. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2001, 60, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Kong, H.; Clark, C.; Lomax, S.; Su, D.; Eiffert, S.; Sukkarieh, S. Intelligent perception for cattle monitoring: A review for cattle identification, body condition score evaluation, and weight estimation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 185, 106143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Syed, D.F.; Ploughe, M.; Zhang, W. Autonomous vision-guided object collection from water surfaces with a customized multirotor. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanidakis, C.; Tzamaloukas, O.; Simitzis, P.; Panagakis, P. Precision livestock farming applications (PLF) for grazing animals. Agriculture 2023, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Chen, K.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ye, J. Object Detection in 20 Years: A Survey. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Shi, C.; Liu, J.; Ma, P.; Ma, J. Behavior recognition and maternal ability evaluation for sows based on triaxial acceleration and video sensors. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 65346–65360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.; Große-Butenuth, K.; Junge, W.; Maassen-Francke, B.; Renner, C.; Sparenberg, H.; Krieter, J. Using the XGBoost algorithm to classify neck and leg activity sensor data using on-farm health recordings for locomotor-associated diseases. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 173, 105404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, J.; Yubero, R.; Visitación, B.; Navarro-García, J.; Algar, M.J.; Cano, E.L.; Ortega, F. Analysis of accelerometer and GPS data for cattle behaviour identification and anomalous events detection. Entropy 2022, 24, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wu, P.; Cui, H.; Xuan, C.; Su, H. Identification and classification for sheep foraging behavior based on acoustic signal and deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, K.; Du, R.; Wu, Z.; Firkat, E.; Li, D. Deformable convolution and coordinate attention for fast cattle detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 211, 108006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tang, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, H.; Xin, J.; He, D. Dairy goat detection based on Faster R-CNN from surveillance video. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 154, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekert, M.; Klein, A.; Adrion, F.; Hoffmann, C.; Gallmann, E. Automatically detecting pig position and posture by 2D camera imaging and deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 174, 105391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Kawakami, R.; Yoshihashi, R.; You, S.; Kawase, H.; Naemura, T. Cattle detection and counting in UAV images based on convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, A.; Kumar, A.; Singh, D.P.; Karn, A.K.; Gola, K.K.; Suyal, P. Advancements in Animal Behaviour Monitoring and Livestock Management: A Review. In Proceedings of the 2024 7th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), Greater Noida, India, 18–20 September 2024; pp. 1206–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, W.; Ren, C.; Han, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, F.; Liu, Z. Cattle Body Detection Based on YOLOv5-EMA for Precision Livestock Farming. Animals 2023, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Weng, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, C. Algorithm for cattle identification based on locating key area. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 228, 120365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Du, S.; Liu, C.; Cao, Z. Interior attention-aware network for infrared small target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5002013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Huang, Z.; Wu, G.; Liu, R.; Zhong, W.; Luo, Z. Target-aware dual adversarial learning and a multi-scenario multi-modality benchmark to fuse infrared and visible for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5802–5811. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Q. Multi-modal gated mixture of local-to-global experts for dynamic image fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 23555–23564. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Kang, Y. Multi-modal gait recognition via effective spatial-temporal feature fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17949–17957. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Zhao, H.; Xie, H.; Gao, B. Multi-sensor decision-level fusion network based on attention mechanism for object detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 31466–31480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Xie, S.; Zhao, F.; He, Y.; Lu, H. Metafusion: Infrared and visible image fusion via meta-feature embedding from object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 13955–13965. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Luo, X.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M.Y. Locality guided cross-modal feature aggregation and pixel-level fusion for multispectral pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2022, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Leung, H.; Gong, K.; Xiao, G. Object Fusion Tracking Based on Visible and Infrared Images: A Comprehensive Review. Inf. Fusion 2020, 63, 166–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Han, M. Cattle identification based on multiple feature decision layer fusion. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Tang, J. Learning soft-consistent correlation filters for RGB-T object tracking. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision: First Chinese Conference, PRCV 2018, Guangzhou, China, 23–26 November 2018; pp. 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.Y.; Peng, L.; Zhang, X.X. A complementary and precise vehicle detection approach in RGB-T images via semi-supervised transfer learning and decision-level fusion. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 196–214. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Jing, Y.; Wu, G. Decision-level fusion detection method of visible and infrared images under low light conditions. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2023, 2023, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, S.; Gao, S.; Ma, Y. Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D. Csrnet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1091–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Ge, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, W. Cross-modal feature fusion for field weed mapping using RGB and near-infrared imagery. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Yang, C.; Sun, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, X.; Fan, J. An object detection algorithm based on infrared-visible dual modal feature fusion. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2024, 137, 105107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, X.; Clifton, D.A. Multimodal learning with transformers: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 12113–12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Gavrilyuk, K.; Sanford, R.; Javan, M.; Snoek, C.G. Actor-transformers for group activity recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Ren, S.; Lu, S.; Feng, Z.; Tang, D.; Liu, S.; Zhou, L.; Duan, N.; Svyatkovskiy, A.; Fu, S. Graphcodebert: Pre-training code representations with data flow. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.08366. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, B.; Hsu, W.-N.; Lakhotia, K.; Mohamed, A. Learning audio-visual speech representation by masked multimodal cluster prediction. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.02184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. Vilbert: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NIPS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 32, pp. 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, H.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Lee, K.; Kim, G. Pano-avqa: Grounded audio-visual question answering on 360deg videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2031–2041. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, Y.; Ding, W.; Wang, Z. Cross on cross attention: Deep fusion transformer for image captioning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 4257–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, V.M.; Rili, I.; Gisiger, T.; Gambs, S.; Vasseur, E.; Cellier, M.; Diallo, A.B. AI-Powered Cow Detection in Complex Farm Environments. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 10, 100770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, W.; Burge, M.J. Scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT). In Digital Image Processing: An Algorithmic Introduction; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 709–763. [Google Scholar]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, 6–13 October 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; He, Z.; Lu, Z.-M. DEA-Net: Single image dehazing based on detail-enhanced convolution and content-guided attention. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; He, L. Scconv: Spatial and channel reconstruction convolution for feature redundancy. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6153–6162. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.-Y.; Dollár, G. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Sohan, M.; Sai Ram, T.; Rami Reddy, C.V. A review on yolov8 and its advancements. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics, Tirunelveli, India, 18–20 November 2024; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; NIPS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2024; Volume 37, pp. 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Choi, S.; Hong, S. Spatio-channel attention blocks for cross-modal crowd counting. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Macau, China, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 90–107. [Google Scholar]
- Qingyun, F.; Dapeng, H.; Zhaokui, W. Cross-modality fusion transformer for multispectral object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00273. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Wang, M.; Hua, X.; Sun, Q. Feature pyramid transformer. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 323–339. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Pang, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, J.; Han, J. Latent feature pyramid network for object detection. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 2153–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhu, C.; Li, M.; Tang, W.; Zhou, W. LLVIP: A visible-infrared paired dataset for low-light vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 3496–3504. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, D.; Olaniyi, E.; Huang, Y. Generative adversarial networks (GANs) for image augmentation in agriculture: A systematic review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





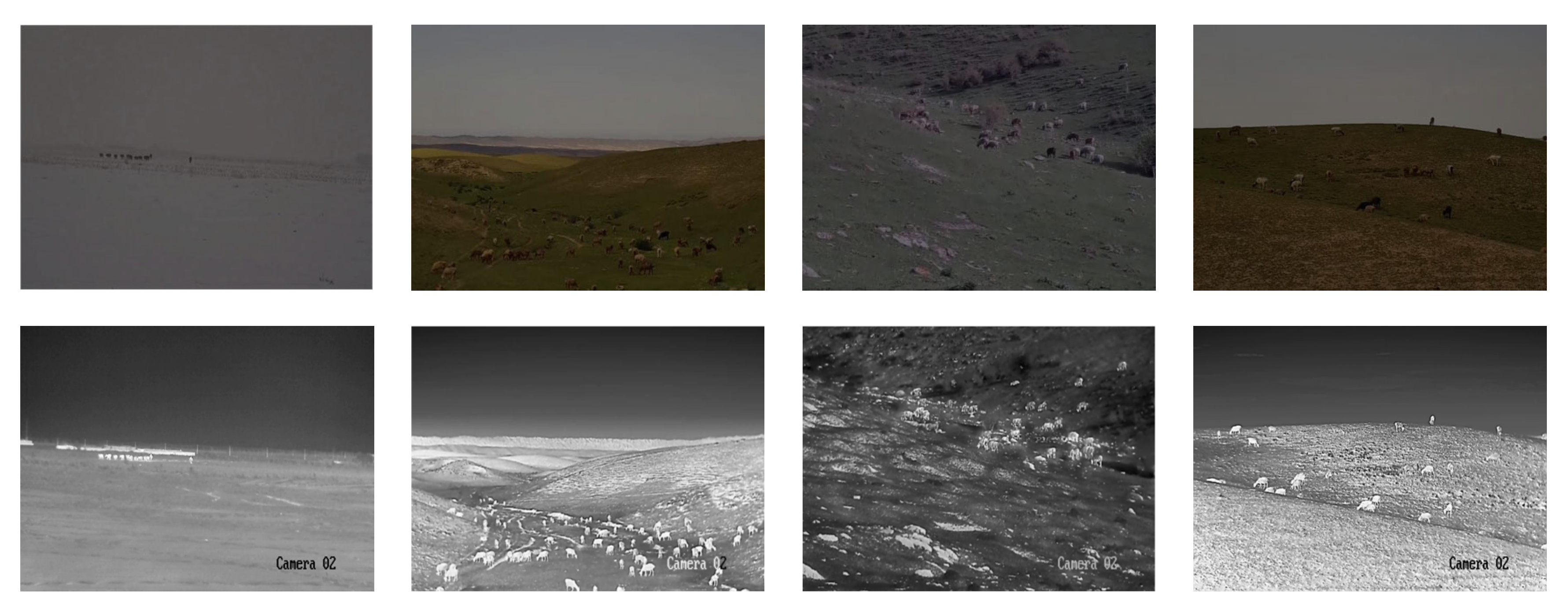





| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Thermal Imaging Sensor | VOx uncooled focal plane array |
| Thermal Imaging Resolution | 640 × 512 |
| Thermal Pixel Pitch | 17 μm |
| Thermal Spectral Range | 8–14 μm |
| NETD | ≤35 mK (at 25 °C, F# = 1.0) |
| Thermal Focal Length | 35 mm |
| Thermal Aperture | F1.0 |
| Visible Light Sensor | 1/2.7″ progressive scan CMOS |
| Visible Light Resolution | 2688 × 1520 (4 MP) |
| Visible Light Focal Length | 8 mm |
| Visible Light Aperture | F1.6 |
| Visible Light Wide Dynamic Range | 120 dB |
| Maximum Infrared Illumination Distance | 40 m |
| Frame Rate | 20 fps |
| Detectors | Modality | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | FPS (Frame/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | RGB | 64.5 | 57.1 | 61.0 | 17 |
| RetinaNet | RGB | 56.2 | 64.6 | 59.8 | 15 |
| YOLOv8 | RGB | 64.4 | 69.3 | 66.5 | 31 |
| YOLOv10 | RGB | 66.1 | 71.4 | 68.1 | 37 |
| Faster R-CNN | IR | 69.9 | 59.3 | 64.4 | 17 |
| RetinaNet | IR | 59.8 | 65.9 | 62.9 | 15 |
| YOLOv8 | IR | 70.4 | 77.7 | 73.3 | 31 |
| YOLOv10 | IR | 71.9 | 80.3 | 76.6 | 37 |
| Baseline | RGB + IR | 76.5 | 83.1 | 80.5 | 35 |
| Baseline + CFT | RGB + IR | 87.8 | 82.5 | 85.5 | 28 |
| Baseline + CSCA | RGB + IR | 88.5 | 84.0 | 86.7 | 30 |
| YOLO-MSLT | RGB + IR | 93.2 | 89.3 | 91.8 | 25 |
| Detectors | Modality | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | FPS (Frame/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline (PAN-FPN) | RGB + IR | 90.5 | 85.1 | 88.1 | 30 |
| Baseline + LFPN | RGB + IR | 91.4 | 87.1 | 90.3 | 27 |
| Baseline + FPT | RGB + IR | 92.9 | 90.8 | 91.4 | 15 |
| YOLO-MSLT | RGB + IR | 93.2 | 89.3 | 91.8 | 25 |
| Detectors | Modality | Recall (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | mAP@0.75 (%) | FPS (Frame/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | RGB + IR | 90.6 | 94.3 | 65.7 | 35 |
| Baseline + CFT | RGB + IR | 91.3 | 95.6 | 67.5 | 28 |
| Baseline + CSCA | RGB + IR | 93.2 | 95.9 | 71.3 | 30 |
| YOLO-MSLT | RGB + IR | 93.5 | 96.3 | 74.3 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Di, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Gao, P. YOLO-MSLT: A Multimodal Fusion Network Based on Spatial Linear Transformer for Cattle and Sheep Detection in Challenging Environments. Agriculture 2026, 16, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010035
Bai Y, Li Y, Di R, Liu J, Wang X, Li C, Gao P. YOLO-MSLT: A Multimodal Fusion Network Based on Spatial Linear Transformer for Cattle and Sheep Detection in Challenging Environments. Agriculture. 2026; 16(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yixing, Yongquan Li, Ruoyu Di, Jingye Liu, Xiaole Wang, Chengkai Li, and Pan Gao. 2026. "YOLO-MSLT: A Multimodal Fusion Network Based on Spatial Linear Transformer for Cattle and Sheep Detection in Challenging Environments" Agriculture 16, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010035
APA StyleBai, Y., Li, Y., Di, R., Liu, J., Wang, X., Li, C., & Gao, P. (2026). YOLO-MSLT: A Multimodal Fusion Network Based on Spatial Linear Transformer for Cattle and Sheep Detection in Challenging Environments. Agriculture, 16(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture16010035






