Synergistic Purification of Flue Gas from Straw Combustion Using Ammonia Method and Electrostatic Charged Spray
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Primary reaction: 4NO + 4NH3 + O2 → 4N2 + 6H2O |
| Secondary reactions: 2NO2 + 4NH3 + O2 → 3N2 + 6H2O |
| NO + NO2 + 2NH3 → 2N2 + 3H2O |
| NO oxidation reaction: 2NO + O2 → 2NO2 |
| Absorption reactions: NO2 + H2O → HNO3 + HNO2 |
| HNO3 + NH3 → NH4NO3 |
| HNO2 + NH3 → NH4NO2 |
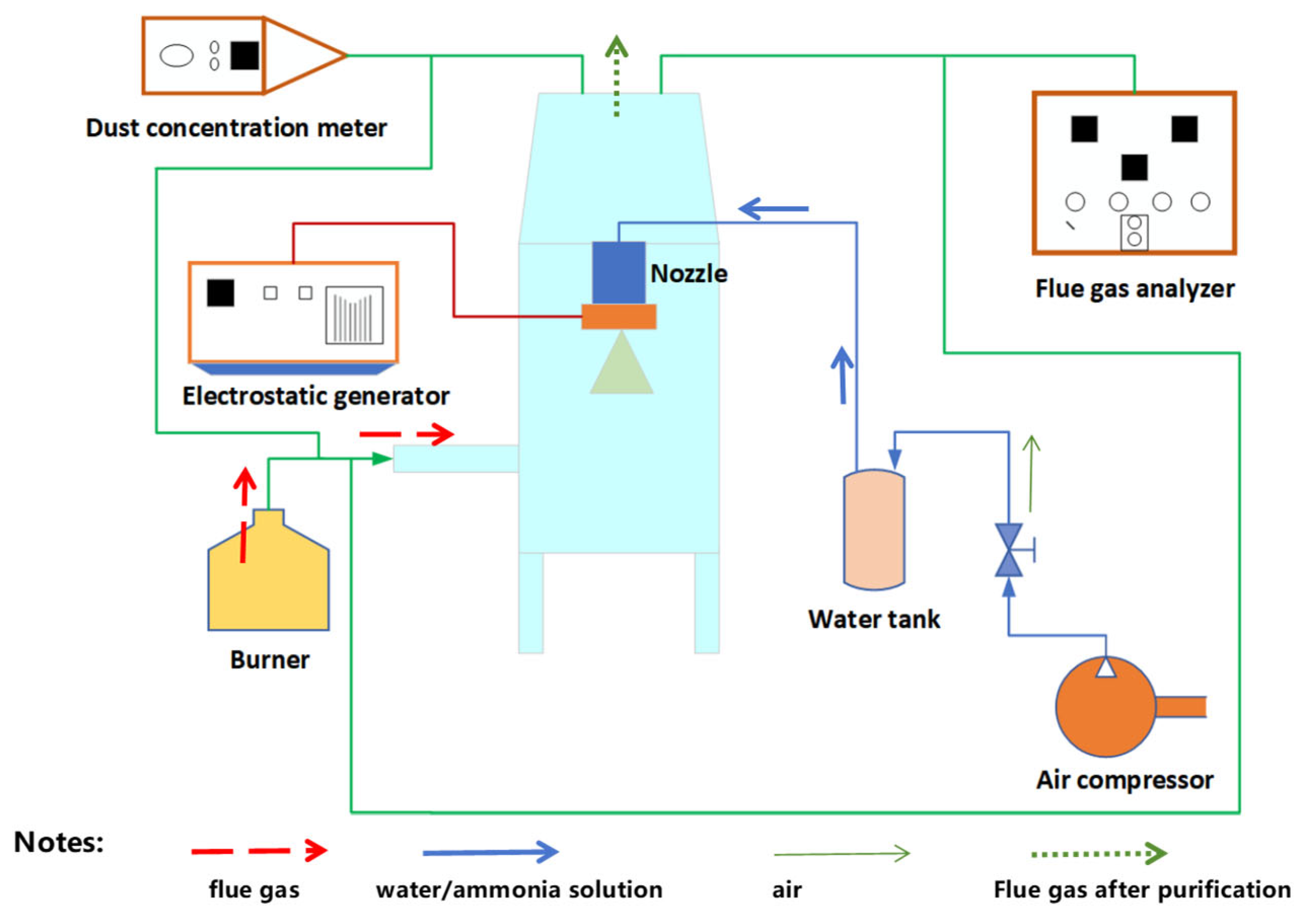
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Materials
2.2. Measurement Method of Charge–Mass Ratio
2.3. Measurement Method of Straw Flue Gas Purification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Straw Combustion Flue Gas
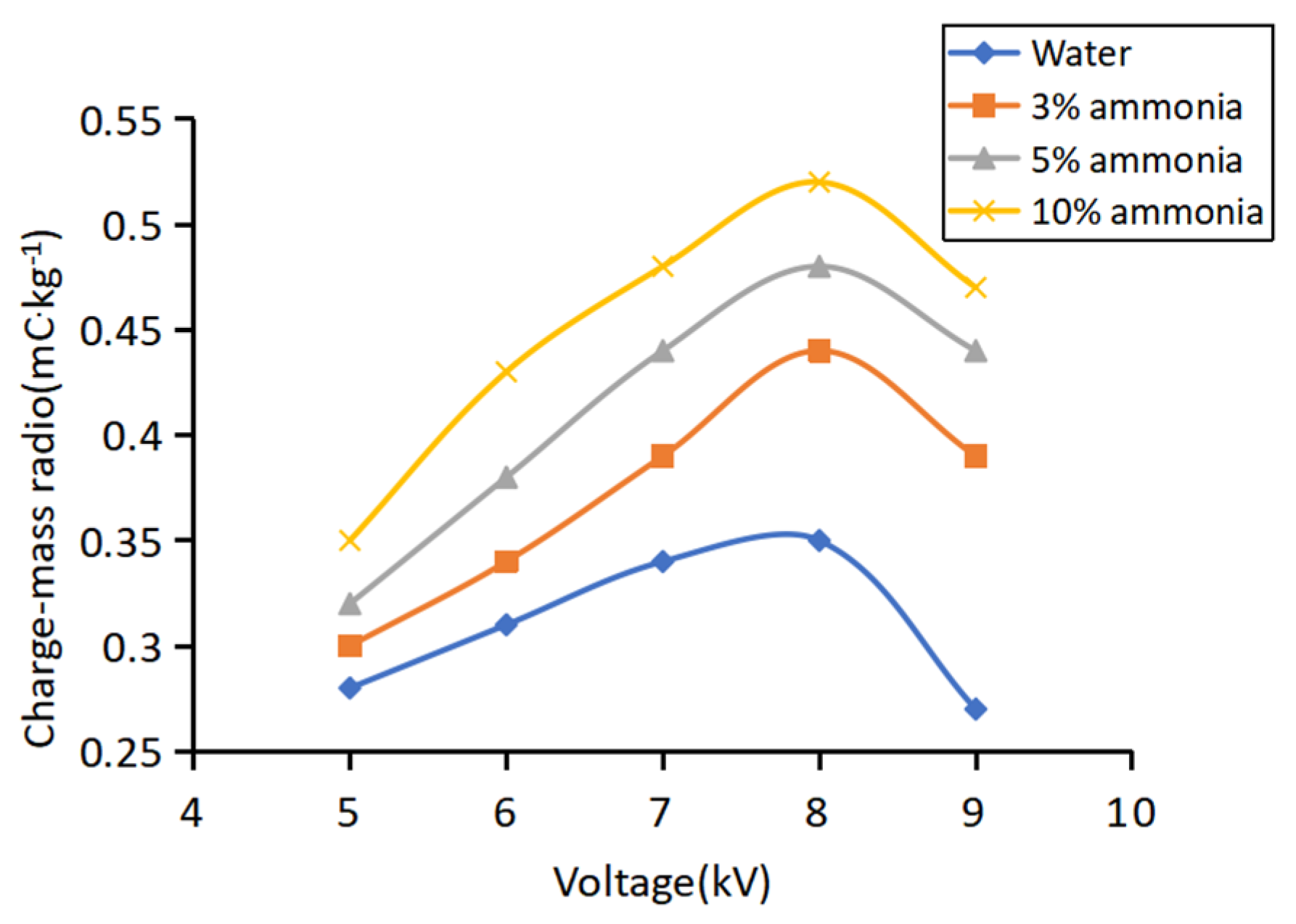
3.2. Effect of Different Operating Parameters on the Charge–Mass Ratio
3.2.1. Effect of Spray Pressure on Charge–Mass Ratio
3.2.2. Effect of Ammonia Concentration on Charge–Mass Ratio
3.2.3. Effect of Charging Voltage on Charge–Mass Ratio
3.3. Purification Effect of Straw Flue Gas
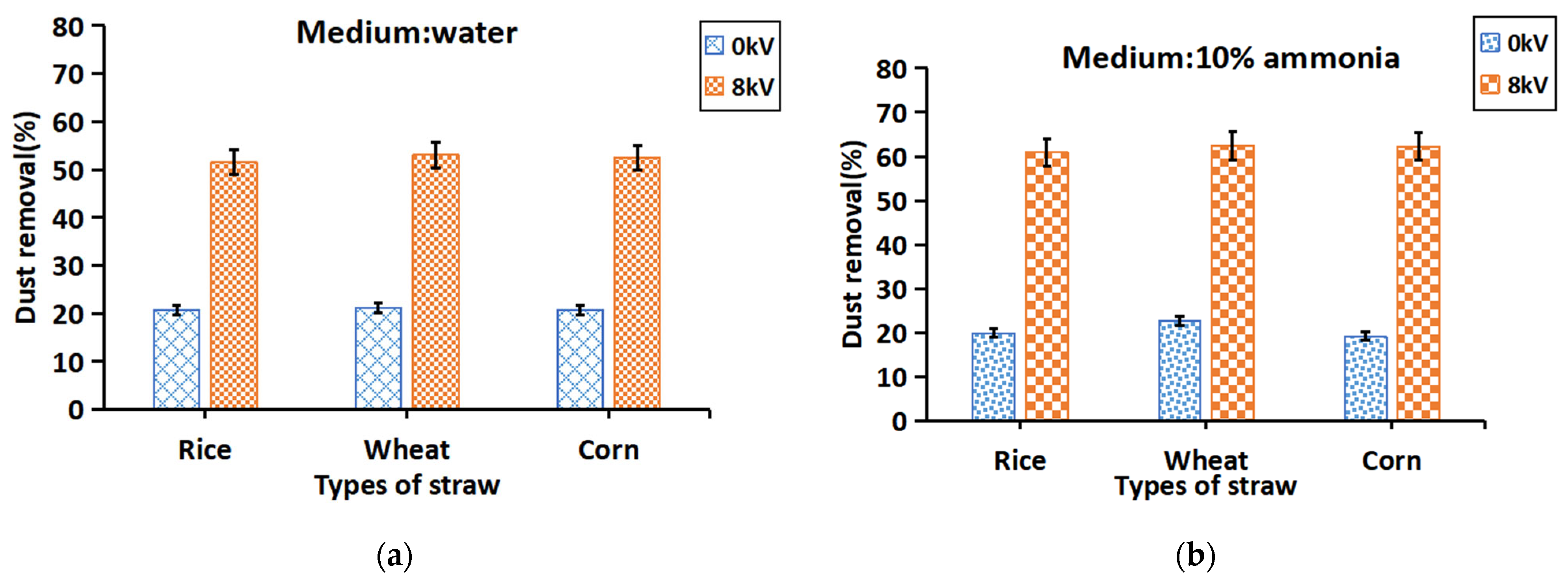
3.3.1. Electrostatic Charging Effects on Dust Removal
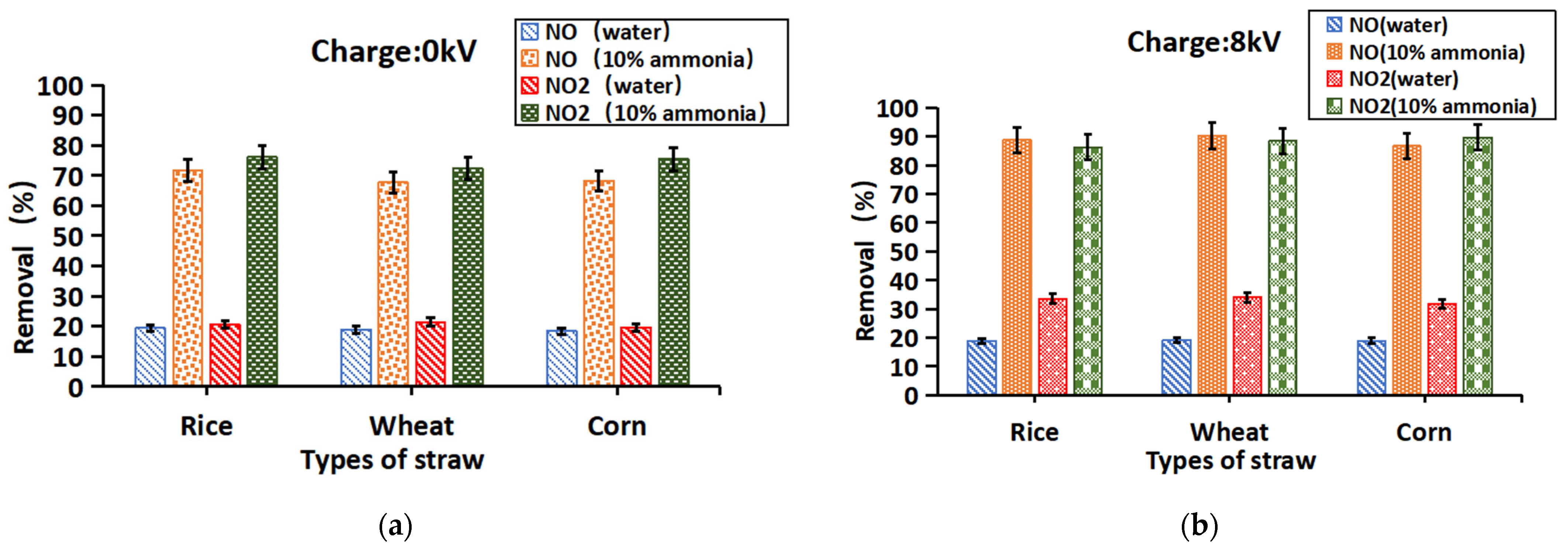
3.3.2. Electrostatic Charging Effects on Nitrogen Oxide Removal
3.3.3. Electrostatic Charging and Ammonia on Dust Removal
3.3.4. Electrostatic Charging and Ammonia on Nitrogen Oxide Removal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.; Chang, J.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J. Energy, Environmental, and Socioeconomic Potential Benefit of Straw Resources Utilization under Water Availability Limit Condition. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 392, 136274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, N.; Chen, S. Effects of Straw Incorporation on Soil Erosion Resistance along a Land Degradation Gradient in the Black Soil Region of China. Catena 2023, 231, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, D.; Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Lu, J.; Nie, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J. Bio-straw resource recycling systems: Agricultural productivity and green development. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Guo, R.; Yang, Q.; Naseer, M.A.; Sun, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, X.; Chen, X.; Jia, Z. Can straw recycling achieve sustainable agriculture at the smallholder level? A case in a semi-arid region. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 439, 140859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, Y.A.; Asfaw, S.L.; Terfie, T.A. Exposure to urban particulate matter and its association with human health risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 27491–27506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, D.L.; Crosman, E.T.; Benney, T.M.; Anderson, C.; Gonzales, S.A. A Preliminary Case Study on the Compounding Effects of Local Emissions and Upstream Wildfires on Urban Air Pollution. Fire 2024, 7, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jo, S.; Woo, J.; Jeon, E.-C. Studies on characteristics of fine particulate matter emissions from agricultural residue combustion. Energy Environ. 2021, 32, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatkal, N.R.; Nalawade, S.M.; Sahni, R.K.; Walunj, A.A.; Kadam, P.B.; Bhanage, G.B.; Datta, R. Present trends, sustainable strategies and energy potentials of crop residue management in India: A review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurets, L.; Izmodenova, T.; Vakal, V.; Vakal, S.; Malovanyy, M. Utilization of Renewable Energy Waste (Wood Ash and Straw) in the Production of Mineral Fertilizers. J. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 25, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Li, A.; Tian, X.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, H.; et al. Use of the PSCF method to analyze the variations of potential sources and transports of NO2, SO2, and HCHO observed by MAX-DOAS in Nanjing, China during 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-N.; Deng, J.; Xiao, Y. Comprehensive review of spray and ventilation technologies for coal dust control at mining faces. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 195, 106799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Shao, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X. Enhancing fine particle removal by electrostatic precipitation from flue gas with a high PM concentration: Effect of various electrode configurations. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353 Pt B, 128459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gonze, E.; Ondarts, M.; Outin, J.; Gonthier, Y. Electrostatic precipitator for fine and ultrafine particle removal from indoor air environments. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Fan, X.; Li, J. Effect of charged water drop atomization on particle removal performance in plate type wet electrostatic precipitator. J. Electrost. 2020, 104, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hu, C.; He, J. Performance evaluation of a three-stage composite wet scrubber for removing particulate matter. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 615, 012117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.; Holz, L.I.V.; Fernandes, C.; Ribeirinha, P.; Mendes, D.; Fagg, D.P.; Mendes, A. A comprehensive review of NOx and N2O mitigation from industrial streams. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 155, 111916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, X.; Xue, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, F. Simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification from flue gas by catalytic ozonation combined with NH3/(NH4)2S2O8 absorption: Mechanisms and recovery of compound fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, T.; Tam, I.; Yin, C.-Y. Wet scrubbing process with oxidation and reduction in series for removal of SO2 and NO from marine diesel engine exhaust. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, H.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Nishioka, R.; Fukuda, Y.; Kuroki, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Okubo, M. Pilot-Scale NOx and SOx Aftertreatment by Semi-Dry Plasma-Chemical Hybrid Process in Glass-Melting-Furnace Exhaust Gas. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2021, 42, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, B. Purification Technologies for NOx Removal from Flue Gas: A Review. Separations 2022, 9, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Zhang, J.; Jia, W.; Ou, M.; Zhou, H.; Dong, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. Experimental Study on the Droplet Size and Charge-to-Mass Ratio of an Air-Assisted Electrostatic Nozzle. Agriculture 2022, 12, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Environmental Protection Administration. Determination of Particulate Matter in Exhaust from Stationary Pollution Sources and Sampling Method for Gaseous Pollutants; GB/T 16157-1996; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xian, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, M. Sulfur release behavior and sulfur fixation mechanism during biomass microwave co-pyrolysis of Ascophyllum and rice straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 407, 131073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Tan, Y.; Lin, F.; Su, Z.; Liao, W.; Wang, H. Pilot design of experiment study: Effect of stirring duration and guest particle loading on electrostatic adsorption of Ti-6Al-4V composite powder formation. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 1949–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, L. Dielectric constant, dielectric loss, conductivity, capacitance and model analysis of electronic electroactive polymers. Polym. Test. 2023, 120, 107965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Purakayastha, T.J.; Pendall, E.; Dey, S.; Jain, N.; Kumar, S. Nitrification and urease inhibitors mitigate global warming potential and ammonia volatilization from urea in rice-wheat system in India: A field to lab experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 898, 65479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaddi, R.S.; Guan, Y.; Novosselov, I. Behavior of Ultrafine Particles in Electro-Hydrodynamic Flow Induced by Corona Discharge. J. Aerosol Sci. 2020, 148, 105587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ou, M.; Dong, X.; Zhou, W.; Dai, S.; Jia, W. Spraying performance and deposition characteristics of an improved air-assisted nozzle with induction charging. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1309088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, M.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y.; Jia, W.; Dai, S. Analysis and experiment research on droplet coverage and deposition measurement with capacitive sensor. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badami, M.M.; Tohidi, R.; Aldekheel, M.; Farahani, V.J.; Verma, V.; Sioutas, C. Design, optimization, and evaluation of a wet electrostatic precipitator (ESP) for aerosol collection. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 308, 119858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Veerasamy, V.S.; St. John, J.P.; Orlov, A. A comprehensive review on dust removal using electrodynamic shield: Mechanism, influencing factors, performance, and progress. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine. Emission Standard of Air Pollutants for Boilers; GB 13271-2014; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi Rizi, H.A.; Shin, D. Development of Ammonia Combustion Technology for NOx Reduction. Energies 2025, 18, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlocon, L.J.S.; Zhao, L.; Wyslouzil, B.E.; Zhu, H. Semi-mechanistic modelling of ammonia absorption in an acid spray wet scrubber based on mass balance. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 136, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Medium | Resistance (Ω) | Conductivity (mS·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Water (0%) | 3226 | 0.31 |
| 3% ammonia solution | 821 | 1.21 |
| 5% ammonia solution | 775 | 1.29 |
| 10% ammonia solution | 711 | 1.41 |
| Types of Straw | Gas Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (/%) |
|---|---|---|
| rice straw | 40.3 | 50.0 |
| wheat straw | 59.3 | 39.3 |
| corn straw | 56.9 | 38.4 |
| Types of Straw | NO | NO2 | NOx | Dust |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rice straw | 1.48 ± 0.23 | 0.69 ± 0.10 | 2.17 | 26.49 |
| wheat straw | 2.18 ± 0.21 | 0.79 ± 0.14 | 2.97 | 25.34 |
| corn straw | 2.75 ± 0.21 | 0.57 ± 0.07 | 3.32 | 28.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Hu, X.; Zhang, C.; Xu, X.; Wu, C. Synergistic Purification of Flue Gas from Straw Combustion Using Ammonia Method and Electrostatic Charged Spray. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15091001
Zhang B, Hu X, Zhang C, Xu X, Wu C. Synergistic Purification of Flue Gas from Straw Combustion Using Ammonia Method and Electrostatic Charged Spray. Agriculture. 2025; 15(9):1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15091001
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bo, Xinkang Hu, Congyang Zhang, Xiaohong Xu, and Chundu Wu. 2025. "Synergistic Purification of Flue Gas from Straw Combustion Using Ammonia Method and Electrostatic Charged Spray" Agriculture 15, no. 9: 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15091001
APA StyleZhang, B., Hu, X., Zhang, C., Xu, X., & Wu, C. (2025). Synergistic Purification of Flue Gas from Straw Combustion Using Ammonia Method and Electrostatic Charged Spray. Agriculture, 15(9), 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15091001








