Passion Fruit Disease Detection Using Sparse Parallel Attention Mechanism and Optical Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Introduction of sparse parallel attention mechanism: This paper innovatively introduces a sparse parallel attention mechanism, optimizing the efficiency of attention computation in the Transformer model. By sparsifying the attention matrix, the computational complexity is reduced, enabling the model to focus more on feature extraction from key areas.
- Design of parallel differential loss: The proposed parallel differential loss guides the model to learn across multiple scales during training, enhancing its adaptability to diseases of varying sizes and forms. This innovative design helps the model learn features of diseases of different scales from multiple dimensions simultaneously, especially in handling multi-scale, complex-background disease data, which effectively improves detection accuracy and robustness.
- Adaptation to the diversity and complexity of agricultural greenhouse environments: The proposed method is optimized for the practical conditions in agricultural greenhouse environments, capable of handling changes in the greenhouse environment, the diversity of diseases, and the growth states of plants.
2. Related Work
2.1. CNN-Based Object Detection
2.1.1. Single-Stage Object Detection
2.1.2. Two-Stage Object Detection
2.2. Transformer-Based Object Detection
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset Collection
3.2. Dataset Annotation and Augmentation
3.2.1. Dataset Annotation
3.2.2. Data Augmentation
3.3. Proposed Method
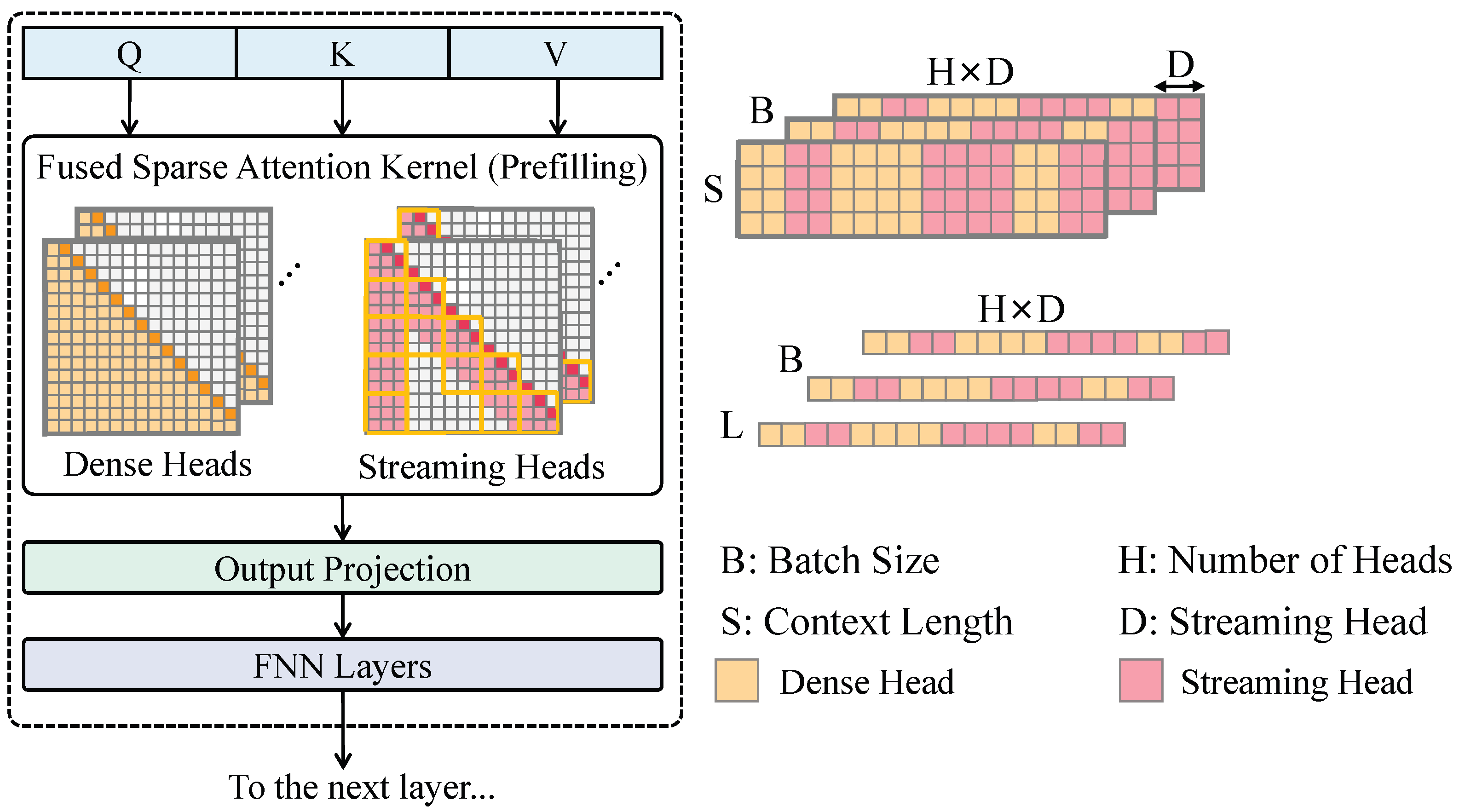
3.3.1. Disease Detection Network Based on Sparse Parallel Attention Mechanism
3.3.2. Sparse Parallel Attention Mechanism
3.3.3. Parallel Differential Loss
3.4. Experimental Setup
3.4.1. Hardware/Software Platforms and Hyperparameters
3.4.2. Dataset Split
3.4.3. Evaluation Metrics
3.5. Baseline Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Experimental Results of Disease Detection Models
4.2. Experimental Results of Disease Detection Models for Each Disease Type
4.3. Ablation Experiment of Different Attention Mechanisms
4.4. Ablation Experiment of Different Loss Functions
4.5. Limitation and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asande, L.K.; Ombori, O.; Oduor, R.O.; Nchore, S.B.; Nyaboga, E.N. Occurrence of passion fruit woodiness disease in the coastal lowlands of Kenya and screening of passion fruit genotypes for resistance to passion fruit woodiness disease. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Long, X. Passion fruit plants alter the soil microbial community with continuous cropping and improve plant disease resistance by recruiting beneficial microorganisms. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0281854. [Google Scholar]
- Do, D.H.; Chong, Y.H.; Ha, V.C.; Cheng, H.W.; Chen, Y.K.; Bui, T.N.L.; Nguyen, T.B.N.; Yeh, S.D. Characterization and detection of Passiflora mottle virus and two other potyviruses causing passionfruit woodiness disease in Vietnam. Phytopathology® 2021, 111, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, C. TinySegformer: A lightweight visual segmentation model for real-time agricultural pest detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108740. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, M.; Zhao, Q.; Jing, B.; Yang, N.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y. Chemical composition, pharmacological effects, and parasitic mechanisms of Cistanche deserticola: An update. Phytomedicine 2024, 132, 155808. [Google Scholar]
- Kibriya, H.; Abdullah, I.; Nasrullah, A. Plant disease identification and classification using convolutional neural network and SVM. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 13–14 December 2021; pp. 264–268. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wa, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Sun, P.; Ma, Q. High-accuracy detection of maize leaf diseases CNN based on multi-pathway activation function module. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, P.; He, C.; Song, Q.; Chen, J.; Kong, X.; Luo, Z. A lightweight and high-precision passion fruit YOLO detection model for deployment in embedded devices. Sensors 2024, 24, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preanto, S.A.; Ahad, M.T.; Emon, Y.R.; Mustofa, S.; Alamin, M. A Semantic Segmentation Approach on Sweet Orange Leaf Diseases Detection Utilizing YOLO. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.06671. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wa, S.; Zhang, L.; Lv, C. Automatic plant disease detection based on tranvolution detection network with GAN modules using leaf images. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 875693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Chen, M.; Peng, Z. Yolov8-g: An improved yolov8 model for major disease detection in dragon fruit stems. Sensors 2024, 24, 5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Lin, F.; Lu, C.; Zhuang, J.; Su, H.; Zhang, D.; He, J. YOLOv8-MDN-Tiny: A lightweight model for multi-scale disease detection of postharvest golden passion fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2025, 219, 113281. [Google Scholar]
- Huangfu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Shi, J.; Yang, L. HHS-RT-DETR: A Method for the Detection of Citrus Greening Disease. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Dang, M. PD-TR: End-to-end plant diseases detection using a transformer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Q. A time-series neural network for pig feeding behavior recognition and dangerous detection from videos. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108710. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Lv, T.; Zhang, X. Using a Hybrid Convolutional Neural Network with a Transformer Model for Tomato Leaf Disease Detection. Agronomy 2024, 14, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Jain, N.; Jain, P.; Kayal, P.; Kumawat, S.; Batra, N. PlantDoc: A dataset for visual plant disease detection. In Proceedings of the 7th ACM IKDD CoDS and 25th COMAD, New York, NY, USA, 15 January 2020; pp. 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J. PL-DINO: An improved transformer-based method for plant leaf disease detection. Agriculture 2024, 14, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q.; Zou, H.; Kuang, Y. IMLL-DETR: An intelligent model for detecting multi-scale litchi leaf diseases and pests in complex agricultural environments. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 273, 126816. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, R.; Singh, S. A comprehensive review of object detection with deep learning. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 132, 103812. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Wergeles, N.; Shang, Y. A survey and performance evaluation of deep learning methods for small object detection. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 172, 114602. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2025, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Vairavasundaram, S. Yolo-based object detection models: A review and its applications. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 83535–83574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ji, J.; Xing, Z.; Miao, Q. Attention and feature fusion SSD for remote sensing object detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, X.; Cao, G.; Yang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Liu, F. ViT-YOLO: Transformer-based YOLO for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 2799–2808. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, X. Yolo-firi: Improved yolov5 for infrared image object detection. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 141861–141875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Tang, W.; Jiang, L.; Fu, C.W. SE-SSD: Self-ensembling single-stage object detector from point cloud. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 14494–14503. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Ji, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Fang, G. Improved SSD network for fast concealed object detection and recognition in passive terahertz security images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Analysis of object detection performance based on Faster R-CNN. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. Iop Publ. 2021, 1827, 012085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Qiu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C. Defrcn: Decoupled faster r-cnn for few-shot object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 8681–8690. [Google Scholar]
- Avola, D.; Cinque, L.; Diko, A.; Fagioli, A.; Foresti, G.L.; Mecca, A.; Pannone, D.; Piciarelli, C. MS-Faster R-CNN: Multi-stream backbone for improved Faster R-CNN object detection and aerial tracking from UAV images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Huang, S.; Ma, J.; He, Y.; Chang, S.F. Meta faster r-cnn: Towards accurate few-shot object detection with attentive feature alignment. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 780–789. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Miao, N.; Ma, L.; Shuang, F.; Huang, X. Transformer for object detection: Review and benchmark. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; Ni, L.M.; Shum, H.Y. Dino: Detr with improved denoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.03605. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Y.; Liang, W.; Hao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, H.; Huang, G. Rank-DETR for high quality object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 16100–16113. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Ai, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, C. Efficient detr: Improving end-to-end object detector with dense prior. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.01318. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, H. Deyo: Detr with yolo for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.16370. [Google Scholar]
- DeVries, T.; Taylor, G.W. Improved Regularization of Convolutional Neural Networks with Cutout. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.04552. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.J.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. CutMix: Regularization Strategy to Train Strong Classifiers With Localizable Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Aldakheel, E.A.; Zakariah, M.; Alabdalall, A.H. Detection and identification of plant leaf diseases using YOLOv4. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1355941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 213–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.T.; Wu, X. Object Detection With Deep Learning: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, A.; Zaki, M. Comparison of Deep Learning Models for Agricultural Disease Detection. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2020, 175, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, Y.; Bahri, D.; Yang, L.; Metzler, D.; Juan, D.C. Sparse Sinkhorn Attention. In Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Red Hook, NY, USA, 13–18 July 2020; Daume, H., III, Singh, A., Eds.; ACM Digital Library: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 119, pp. 9438–9447. [Google Scholar]
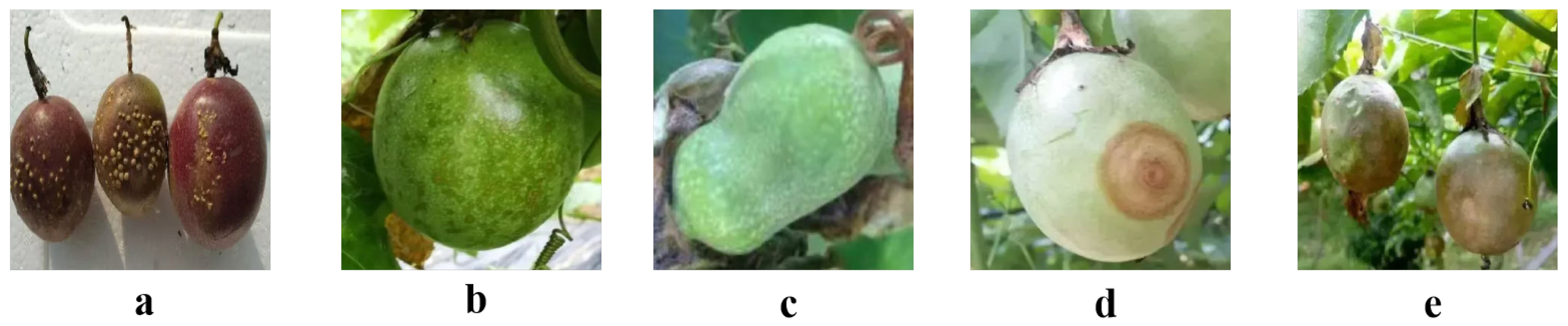





| Disease | Data |
|---|---|
| Ulcer disease | 1092 |
| Brown rot | 1781 |
| Gray mold | 1267 |
| Anthracnose | 1514 |
| Late blight | 1339 |
| Item | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Hardware | NVIDIA A100 Tensor Core GPU |
| Operating system | Ubuntu 20.04 |
| Software | TensorFlow 2.4, PyTorch 1.7 |
| Development environment | Python 3.8 |
| Training time | 50 h (using a single GPU for training) |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Learning rate | 0.0001 |
| Optimizer | Adam optimizer |
| Hyperparameters | Dropout rate: 0.3; weight decay: 1 × 10 |
| Dataset | Custom passion fruit disease dataset, 10,000 images |
| Image resolution | 512 × 512 |
| Training epochs | 50 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | mAP@50 | mAP@50–95 | F1-Score | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Faster R-CNN | 0.84 | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.82 | 29 |
| SSD | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.52 | 0.83 | 25 |
| RetinaNet | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.56 | 0.85 | 34 |
| YOLOv10 | 0.88 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 0.86 | 41 |
| DETR | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.54 | 0.86 | 39 |
| YOLOv11 | 0.91 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.57 | 0.87 | 42 |
| Proposed method | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.90 | 47 |
| Disease Type | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | mAP@50 | mAP@50–95 | F1-Score | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ulcer disease | 0.89 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.86 | 0.56 | 0.87 | 46 |
| Brown rot | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 0.89 | 44 |
| Gray mold | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.90 | 49 |
| Anthracnose | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.63 | 0.92 | 48 |
| Late blight | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.65 | 0.95 | 48 |
| Attention | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | mAP@50 | mAP@50–95 | F1-Score | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBAM | 0.85 | 0.81 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.44 | 0.81 | 34 |
| Standard self-attention | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.52 | 0.76 | 39 |
| Proposed method | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.90 | 47 |
| Loss | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | mAP@50 | mAP@50–95 | F1-Score | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-entropy loss | 0.67 | 0.63 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.32 | 0.63 | 31 |
| Focal loss | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.43 | 0.82 | 35 |
| Proposed method | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.90 | 0.60 | 0.90 | 47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ge, X.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Kong, M.; Guo, Y.; Lv, C. Passion Fruit Disease Detection Using Sparse Parallel Attention Mechanism and Optical Sensing. Agriculture 2025, 15, 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070733
He Y, Zhang N, Ge X, Li S, Yang L, Kong M, Guo Y, Lv C. Passion Fruit Disease Detection Using Sparse Parallel Attention Mechanism and Optical Sensing. Agriculture. 2025; 15(7):733. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070733
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Yajie, Ningyi Zhang, Xinjin Ge, Siqi Li, Linfeng Yang, Minghao Kong, Yiping Guo, and Chunli Lv. 2025. "Passion Fruit Disease Detection Using Sparse Parallel Attention Mechanism and Optical Sensing" Agriculture 15, no. 7: 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070733
APA StyleHe, Y., Zhang, N., Ge, X., Li, S., Yang, L., Kong, M., Guo, Y., & Lv, C. (2025). Passion Fruit Disease Detection Using Sparse Parallel Attention Mechanism and Optical Sensing. Agriculture, 15(7), 733. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070733









