Genomic Inference Unveils Population Bottlenecks and a North-to-South Migration Pattern of Wild Cordyceps militaris Across China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
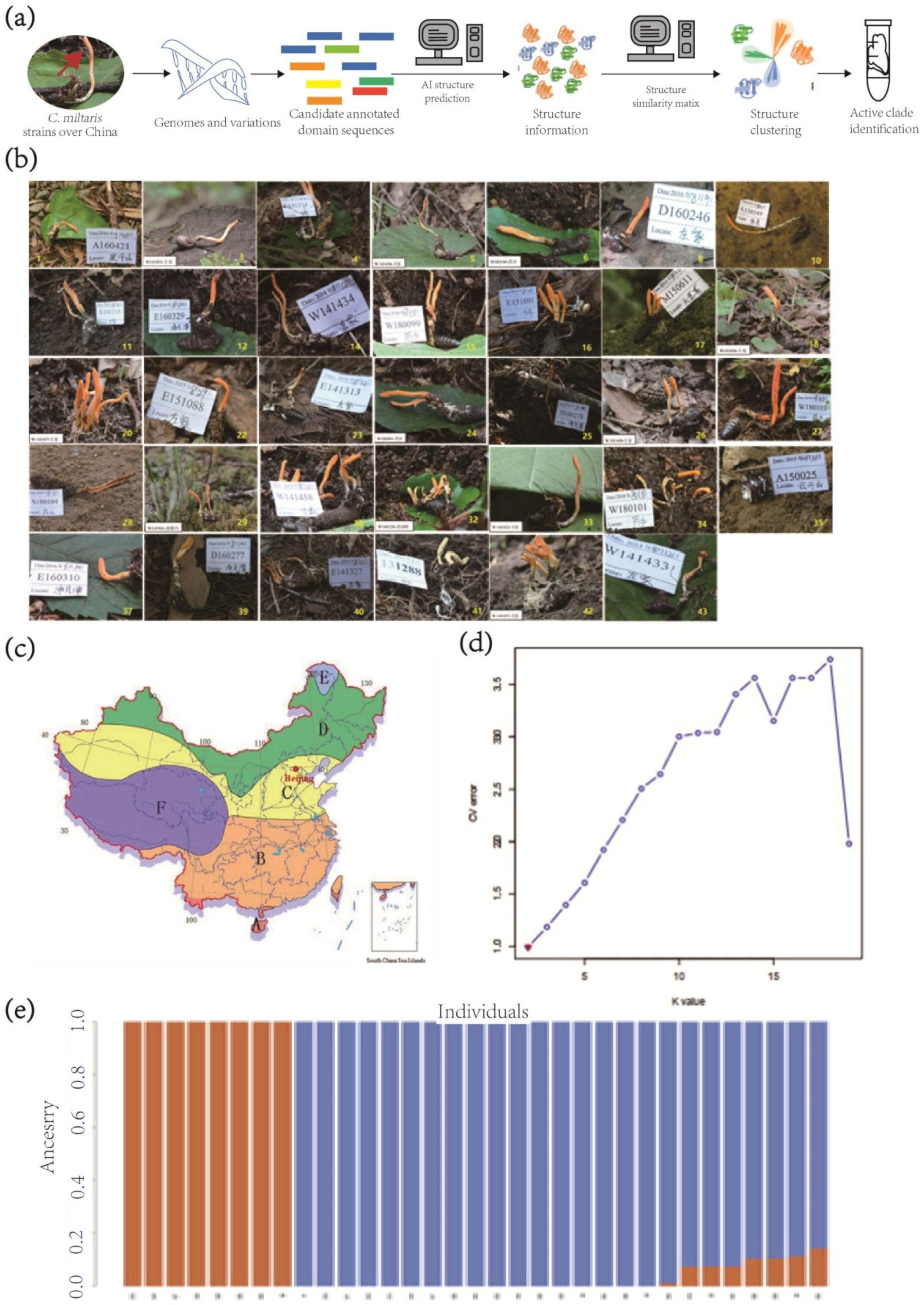
2.1. Collection of C. militaris Strains
2.2. Trans-Inoculation of Strains and Their DNA Extraction
2.3. Construction of a DNA Library
2.4. Whole-Genome Re-Sequencing and SNP Calling
2.5. Population Structure Analyses
2.6. Demographic History
2.7. Population Genetic Statistics
2.8. Protein Clustering and Analysis of Cytosine Deaminase of C. militaris
3. Results
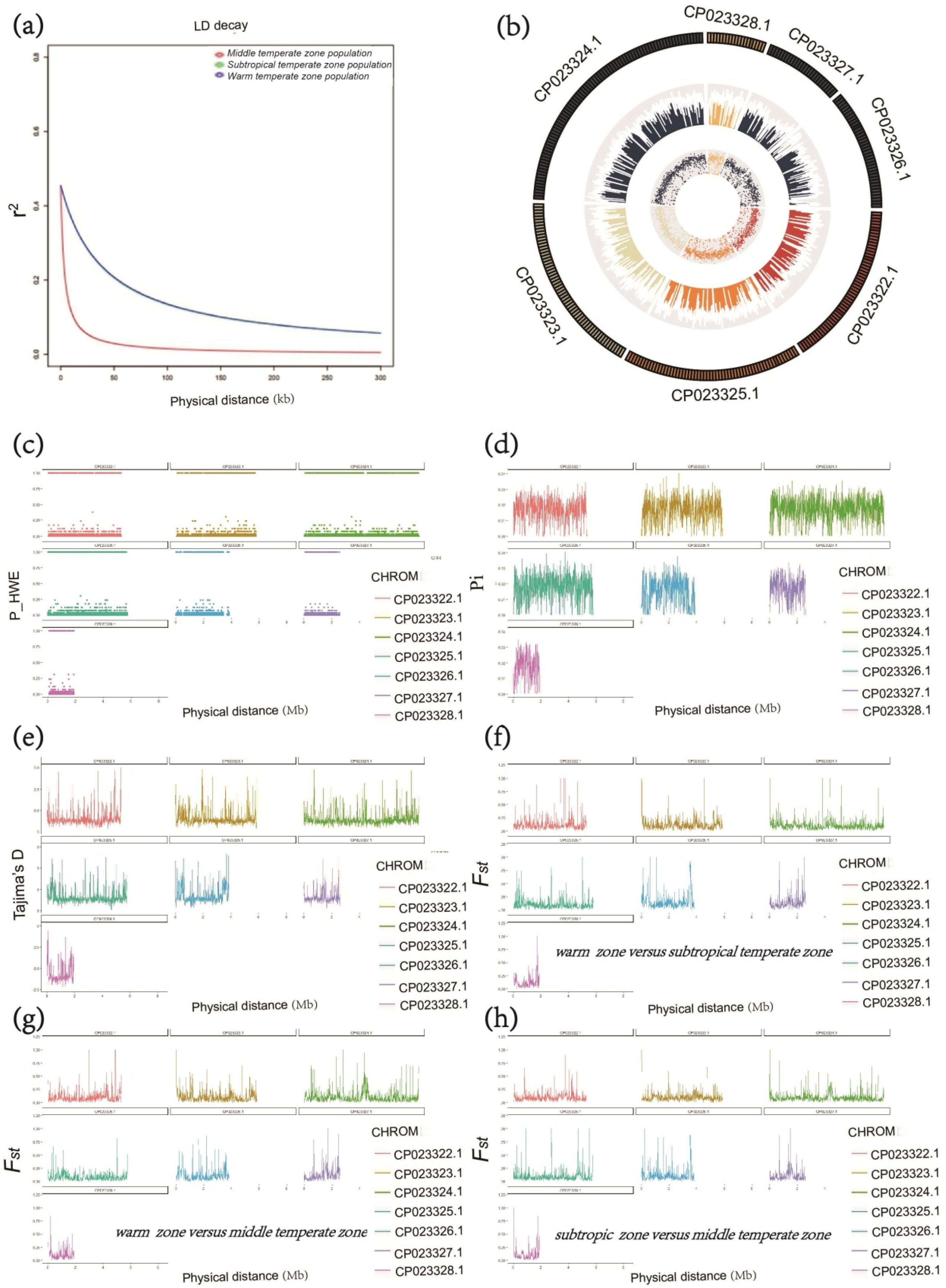
3.1. Population Structure and Demographic History of the Three Populations of C. militaris
3.2. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
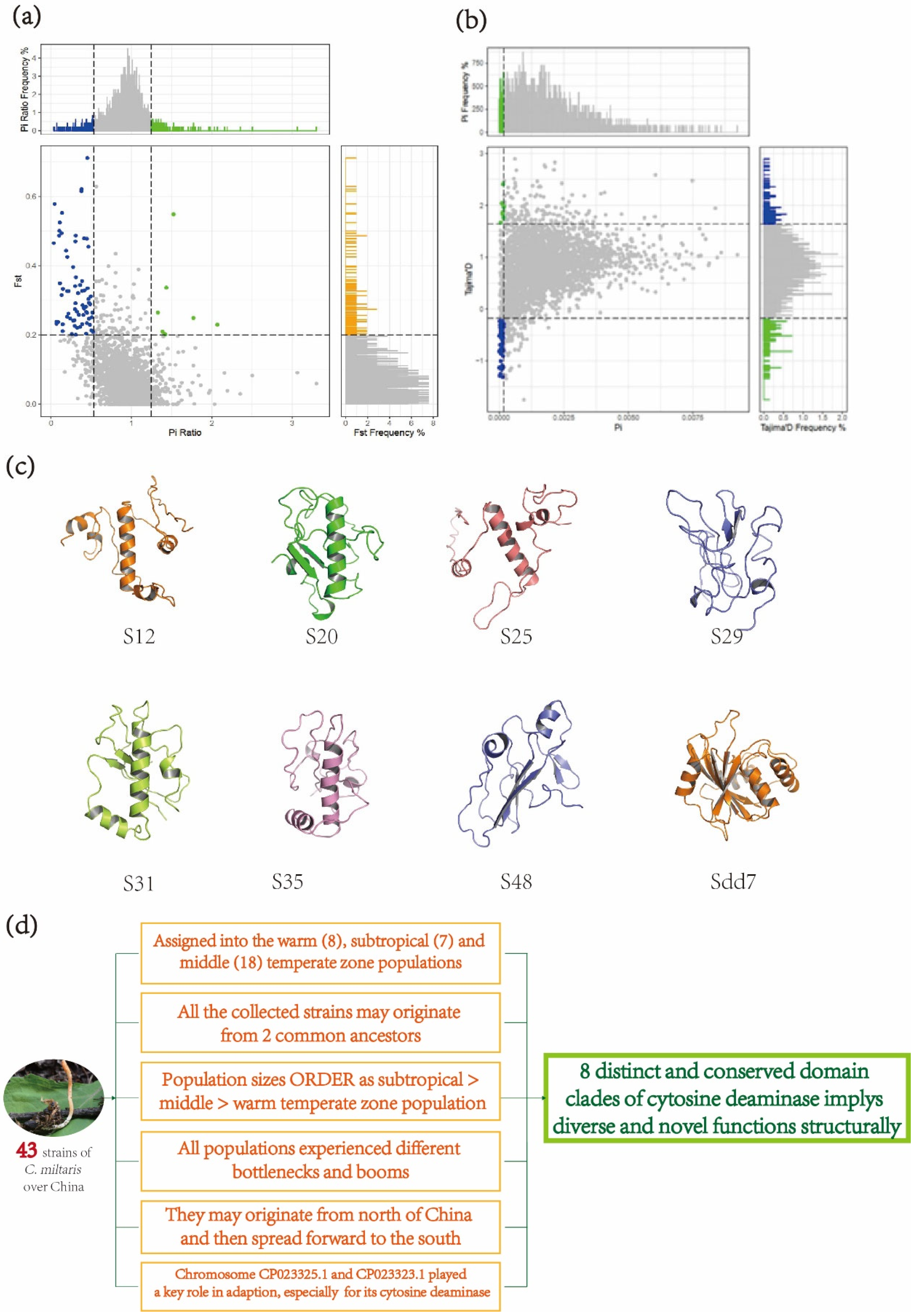
3.3. Population Diversity of C. militaris
3.4. Representative Predicted Structures for Eight Deaminase Clades
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, M.H.; Nguyen, T.M.; Huynh, V.B.; Sridhar, K.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Fung, S.-Y.; Mahadevakumar, S. Diversity evaluation of Cordyceps spp. in Bidoup Nui Ba, Lam Dong province, Vietnam. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Sustainable Agriculture and Environment, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 17–19 November 2022; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2023; Volume 1155, p. 012003. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, M.; Saraf, A.; Khelkar, T. Exploring the world of Cordyceps: Ecology, cultivation, biotechnology, and future horizons. In Futuristic Trends in Biotechnology; Iterative International Publishers (IIP), Selfypage Developers Pvt Ltd.: Novi, MI, USA, 2024; Volume 3, pp. 112–126. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Han, Y. Taxonomy, phylogeny, and genetics of Cordyceps. In Advances in Cordyceps Research, 1st ed.; Sridhar, K., Deshmukh, S.K., Fung, S.-Y., Mahadevakumar, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, P.; Xia, Y.; Xiao, G.; Xiong, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Genome sequence of the insect pathogenic fungus Cordyceps militaris, a valued traditional Chinese medicine. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevakumar, S.; Sridhar, K.R. An overview of the phylogeny of Cordyceps. In Advances in Cordyceps Research, 1st ed.; Sridhar, K., Deshmukh, S.K., Fung, S.-Y., Mahadevakumar, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Roberson, R.W. Subcellular structure and behaviour in fungal hyphae. J. Microsc. 2020, 280, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woolley, V.C.; Teakle, G.R.; Prince, G.; de Moor, C.H.; Chandler, D. Cordycepin, a metabolite of Cordyceps militaris, reduces immune-related gene expression in insects. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 177, 107480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.-Y.; Luo, R.; Fan, Q.; Duan, D.-E.; Dao, V.-M.; Wang, Y.-B.; Yu, H. Molecular phylogeny and morphology reveal cryptic species in the Cordyceps militaris complex from Vietnam. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Leger, R.S.; Wang, C. Advances in genomics of entomopathogenic fungi. Adv. Genet. 2016, 94, 67–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Hussain, A.; Guan, Z.; Wang, D.; Jaleel, W.; Lyu, L.; He, Y. Unraveling the mode of action of Cordyceps fumosorosea: Potential biocontrol agent against Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Insects 2021, 12, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, C.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H. Advance in Cordyceps militaris (Linn) Link polysaccharides: Isolation, structure, and bioactivities: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 906–914. [Google Scholar]
- Avery, P.B.; Kumar, V.; Francis, A.; McKenzie, C.L.; Osborne, L.S. Compatibility of the predatory beetle, delphastus catalinae, with an entomopathogenic fungus, Cordyceps fumosorosea, for biocontrol of invasive pepper whitefly, Aleurothrixus trachoides, in Florida. Insects 2020, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Nishimura, K.; Misu, S.; Ikeo, K.; Park, E.Y. Changes of the gene expression in silkworm larvae and Cordyceps militaris at late stages of the pathogenesis. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 111, e21968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Yin, Y.Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, B.Y.; Ma, Y.C.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, G.Q. Chitinase is involved in the fruiting body development of medicinal fungus Cordyceps militaris. Life 2023, 13, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Chang, P.S. Heterologous expression, purification, and characterization of a recombinant Cordyceps militaris lipase from Candida rugosa-like family in Pichia pastoris. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 168, 110254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterson, R.R.M. Cordyceps—A traditional Chinese medicine and another fungal therapeutic biofactory? Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1469–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Ye, M.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, W.; Lin, X. The genus Cordyceps: A chemical and pharmacological review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 65, 474–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, K.G.; Manson, W.; Spring, F.S.; Hutchinson, S.A. Cordycepin, a metabolic product isolated from cultures of Cordyceps militaris (Linn.) Link. Nature 1950, 166, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Luo, F.; Shang, Y.; Chen, P.; Lu, Y.; Wang, C. Fungal cordycepin biosynthesis is coupled with the production of the safeguard molecule pentostatin. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 1479–1489.e1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, S.; Tan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Fu, J.; Li, T.; Wei, C.; Liu, X.; Mei, Z.; Cheng, J.; et al. Antiviral potential of small molecules cordycepin, thymoquinone, and n6, n6-dimethyladenosine targeting SARS-CoV-2 entry protein ADAM17. Molecules 2022, 27, 9044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Ling, J.; Zhang, G.; Liu, F.; Tao, S.; Han, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, Z.; Le, H. Cordycepin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by inducing DNA damage and up-regulation of p53 in Leukemia cells. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Weng, Q.; Jiang, S.; Tian, S.; Xu, T.; Hu, S.; Yang, G.; et al. Cordycepin ameliorates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by activation of the amp-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Hepatology 2021, 74, 686–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirithep, K.; Xiao, F.; Raethong, N.; Zhang, Y.; Laoteng, K.; Hu, G.; Vongsangnak, W. Probing carbon utilization of Cordyceps militaris by sugar transportome and protein structural analysis. Cells 2020, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Xu, P.; Faure, G.; Maguire, S.; Kannan, S.; Altae-Tran, H.; Vo, S.; Desimone, A.; Macrae, R.K.; Zhang, F. Fanzor is a eukaryotic programmable RNA-guided endonuclease. Nature 2023, 620, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakireva, A.V.; Kuznetsova, N.V.; Petushkova, A.I.; Savvateeva, L.V.; Zamyatnin, A.A., Jr. Trends and prospects of plant proteases in therapeutics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 465–486. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Zeng, C.; Huang, F.; Yuan, F.; Yan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hankey, W.; Jin, V.X.; Huang, J.; et al. Cas13d knockdown of lung protease Ctsl prevents and treats SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Chen, H.; Myung, S.; Sathitsuksanoh, N.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.-Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.H.P. Enzymatic transformation of nonfood biomass to starch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7182–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; You, C.; Fan, C.; Ji, W.; Park, J.-T.; Kwak, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.-H.P.J.; Ma, Y. Biosynthesis of artificial starch and microbial protein from agricultural residue. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Lin, Q.; Fei, H.; He, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Qu, K.; Han, P.; Gao, Q.; Li, B.; et al. Discovery of deaminase functions by structure-based protein clustering. Cell 2023, 186, 3182–3195.e3114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.; Hu, H.; Yong, T.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, C.; Huang, L.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Q. Induction of sexual fruiting-body formation by pairing the opposite mating-type isolates of Cordyceps militaris. Mycosystema 2023, 42, 344–352. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, T. Integrated enzymes activity and transcriptome reveal the effect of exogenous melatonin on the strain degeneration of Cordyceps militaris. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1112035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.E.; Qiu, W.; Sa, F.; Feng, Y.; Ge, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Effects of mating-type ratio imbalance on the degeneration of Cordyceps militaris subculture and preventative measures. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Lin, J.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.; Tian, S.; Liu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, R. Advances in research on Cordyceps militaris degeneration. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7835–7841. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, T.; Zhang, M.; Chen, D.; Shuai, O.; Chen, S.; Su, J.; Jiao, C.; Feng, D.; Xie, Y. Actions of water extract from Cordyceps militaris in hyperuricemic mice induced by potassium oxonate combined with hypoxanthine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, T.; Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; Chen, D.; Su, J.; Shuai, O.; Jiao, C.; Zuo, D. Cordycepin, a characteristic bioactive constituent in Cordyceps militaris, ameliorates hyperuricemia through URAT1 in hyperuricemic mice. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y. Genomic and transcriptome analysis reveals the biosynthesis network of cordycepin in Cordyceps militaris. Genes 2024, 15, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; Gosling, A.L.; Gaffo, A.; Abhishek, A. Gout. Lancet 2021, 397, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Luo, J.; Liao, H.; Zheng, F.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Tian, J.; et al. Pharmacological evaluation of a novel skeleton compound isobavachin (4′,7-dihydroxy-8-prenylflavanone) as a hypouricemic agent: Dual actions of URAT1/GLUT9 and xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 133, 106405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wei, F.; Wang, G.-L.; Ma, S.-C.; Lin, R.-C. Identification of geographical origins of Cordyceps based on data of amino acids with self-organizing map neural network. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021, 46, 4765–4773. [Google Scholar]
- Zeb, U.; Aziz, T.; Azizullah, A.; Zan, X.Y.; Khan, A.A.; Bacha, S.A.S.; Cui, F.J. Complete mitochondrial genomes of edible mushrooms: Features, evolution, and phylogeny. Physiol. Plant 2024, 176, e14363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-P.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chan, Y.; El-Shazly, M.; Wu, T.-Y.; Lo, I.-W.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Lai, K.-H.; Hou, M.-F.; Yuan, S.-S.; et al. Research and development of Cordyceps in Taiwan. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 177–185. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Wong, K.K.; Tseng, Y. Editorial: A new frontier for traditional medicine research-multi-omics approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1203097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J.; et al. From fastq data to high-confidence variant calls: The genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from next-generation sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meisner, J.; Albrechtsen, A. Inferring population structure and admixture proportions in low-depth NGS data. Genetics 2018, 210, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Obbard, D.J. Experimental estimates of germline mutation rate in eukaryotes: A phylogenetic meta-analysis. Evol. Lett. 2023, 7, 216–226. [Google Scholar]
- Korneliussen, T.S.; Albrechtsen, A.; Nielsen, R. ANGSD: Analysis of next generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 356. [Google Scholar]
- Kofler, R.; Schlötterer, C. Gowinda: Unbiased analysis of gene set enrichment for genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2084–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.; DiMaio, F.; Anishchenko, I.; Dauparas, J.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Lee, G.R.; Wang, J.; Cong, Q.; Kinch, L.N.; Schaeffer, R.D.; et al. Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Science 2021, 373, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kempen, M.; Kim, S.S.; Tumescheit, C.; Mirdita, M.; Lee, J.; Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Söding, J.; Steinegger, M. Fast and accurate protein structure search with Foldseek. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Feng, L.; Mu, S.; Dong, A.; Gan, J.; Wen, Z.; Meng, J.; Li, M.; Wu, R.; Sun, L. Asymptotic tests for Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium in hexaploids. Hort. Res. 2022, 9, uhac104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneliussen, T.S.; Moltke, I.; Albrechtsen, A.; Nielsen, R. CalcuFlation of Tajima’s D and other neutrality test statistics from low depth next-generation sequencing data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 289. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, H.; Whibley, A.; Field, D.L.; Bradley, D.; Couchman, M.; Copsey, L.; Elleouet, J.; Burrus, M.; Andalo, C.; Li, M.; et al. Selection and gene flow shape genomic islands that control floral guides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 11006–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinsky, M.; Challis, R.J.; Tyers, A.M.; Schiffels, S.; Terai, Y.; Ngatunga, B.P.; Miska, E.A.; Durbin, R.; Genner, M.J.; Turner, G.F. Genomic islands of speciation separate cichlid ecomorphs in an East African crater lake. Science 2015, 350, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Guo, M.; Liu, G.; Zhao, K.T.; Gao, C. Strand-preferred base editing of organellar and nuclear genomes using CyDENT. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 936–945. [Google Scholar]
- Marei, H.; Tsai, W.-T.K.; Kee, Y.-S.; Ruiz, K.; He, J.; Cox, C.; Sun, F.T.; Penikalapati, S.; Dwivedi, P.; Choi, M.; et al. Antibody targeting of E3 ubiquitin ligases for receptor degradation. Nature 2022, 610, 182–189. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lisanza, S.; Juergens, D.; Tischer, D.; Watson, J.L.; Castro, K.M.; Ragotte, R.; Saragovi, A.; Milles, L.F.; Baek, M.; et al. Scaffolding protein functional sites using deep learning. Science 2022, 377, 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Mosalaganti, S.; Obarska-Kosinska, A.; Siggel, M.; Taniguchi, R.; Turoňová, B.; Zimmerli, C.E.; Buczak, K.; Schmidt, F.H.; Margiotta, E.; Mackmull, M.-T.; et al. AI-based structure prediction empowers integrative structural analysis of human nuclear pores. Science 2022, 376, eabm9506. [Google Scholar]

| Group and Temperate Zone | Seq. No. | Strain No. | Collection Location | Latitude | Longitude | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| subtropical temperate zone | S1 | A160421 | Xingdou Moutain, Hubei | 30°01′29″ | 109°06′10″ | 23 September 2016 |
| S10 | A150549 | Huangsang, Hunan | 26°28′21″ | 110°06′23″ | 13 May 2015 | |
| S17 | M150611 | Tiantangzhai, Anhui | 31°07′19″ | 115°54′58″ | 12 August 2015 | |
| S29 | W141904 | Hailuogou, Sichuan | 29°34′27″ | 101°59′57″ | 17 September 2014 | |
| S32 | W180129 | Qingliang Peak, Zhejiang | 30°06′39″ | 118°53′28″ | 07 November 2018 | |
| S58 | A200293 | Tianma, Anhui | 31°09′32″ | 115°45′57″ | 14 September 2020 | |
| S59 | A200332 | Tianma, Anhui | 31°17′32″ | 115°41′07″ | 16 September 2020 | |
| warm temperate zone | S6 | W180100 | Yaoxiang, Shandong | 36°19′43″ | 117°07′15″ | 15 August 2018 |
| S15 | W180099 | Yaoxiang, Shandong | 36°19′43″ | 117°07′15″ | 15 August 2018 | |
| S24 | W180091 | Yaoxiang, Shandong | 36°19′43″ | 117°07′15″ | 15 August 2018 | |
| S27 | W180103 | Yaoxiang, Shandong | 36°19′43″ | 117°07′15″ | 15 August 2018 | |
| S28 | S180104 | Yaoxiang, Shandong | 36°19′35″ | 117°06′56″ | 15 August 2018 | |
| S48 | A200181 | Yaoxiang, Shandong | 36°19′38″ | 117°07′22″ | 18 August 2020 | |
| S50 | A200168 | Yaoxiang, Shandong | 36°19′45″ | 117°07′16″ | 18 August 2020 | |
| S54 | A200190 | Yaoxiang, Shandong | 36°19′49″ | 117°06′58″ | 18 August 2020 | |
| middle temperate zone | S3 | W141451 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′56″ | 126°04′17″ | 12 August 2014 |
| S4 | E141314 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′43″ | 126°04′12″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S5 | W141436 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′44″ | 126°04′13″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S8 | D160246 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′45″ | 126°04′14″ | 09 August 2016 | |
| S11 | E141315 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′43″ | 126°04′12″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S12 | E160329 | Jingyue Lake, Jilin | 43°46′32″ | 125°27′50″ | 10 August 2016 | |
| S14 | W141434 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′44″ | 126°04′13″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S16 | E151091 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′46″ | 126°04′30″ | 29 August 2015 | |
| S18 | W141456 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°05′04″ | 126°04′14″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S20 | W141457 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°05′04″ | 126°04′14″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S22 | E151088 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′52″ | 126°04′35″ | 29 August 2015 | |
| S23 | E141313 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′43″ | 126°04′12″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S25 | D160278 | Jingyue Lake, Jilin | 43°46′41″ | 125°28′02″ | 10 August 2016 | |
| S26 | W141449 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′53″ | 126°04′15″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S30 | W141458 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°05′04″ | 126°04′14″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S33 | W141432 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′44″ | 126°04′13″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S40 | E141327 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′56″ | 126°04′18″ | 12 August 2014 | |
| S43 | W141433 | Zuojia, Jilin | 44°04′44″ | 126°04′13″ | 12 August 2014 |
| Pop ID a | Private b | Num InDv c | Obs Het d | Obs Hom e | Exp Het f | Exp Hom g | Pi h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Middle | 21,786 | 18 | 0.068 | 0.932 | 0.253 | 0.747 | 0.261 |
| Subtropical | 12,924 | 8 | 0.041 | 0.959 | 0.258 | 0.742 | 0.275 |
| Warm | 4433 | 7 | 0.104 | 0.896 | 0.213 | 0.787 | 0.229 |
| Fsta | Warm Temperate Zone | Middle Temperate Zone |
|---|---|---|
| Subtropical temperate zone | 0.109 | 0.083 |
| Warm temperate zone | 0.092 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yong, T.; Liu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhuo, L.; Wu, X.; Guo, H.; Hu, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; et al. Genomic Inference Unveils Population Bottlenecks and a North-to-South Migration Pattern of Wild Cordyceps militaris Across China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070686
Yong T, Liu Y, Cai M, Zhuo L, Wu X, Guo H, Hu H, Gao Y, Chen S, Xie Y, et al. Genomic Inference Unveils Population Bottlenecks and a North-to-South Migration Pattern of Wild Cordyceps militaris Across China. Agriculture. 2025; 15(7):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070686
Chicago/Turabian StyleYong, Tianqiao, Yuanchao Liu, Manjun Cai, Lijun Zhuo, Xiaoxian Wu, Huiyang Guo, Huiping Hu, Yichuang Gao, Shaodan Chen, Yizhen Xie, and et al. 2025. "Genomic Inference Unveils Population Bottlenecks and a North-to-South Migration Pattern of Wild Cordyceps militaris Across China" Agriculture 15, no. 7: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070686
APA StyleYong, T., Liu, Y., Cai, M., Zhuo, L., Wu, X., Guo, H., Hu, H., Gao, Y., Chen, S., Xie, Y., & Zhong, W. (2025). Genomic Inference Unveils Population Bottlenecks and a North-to-South Migration Pattern of Wild Cordyceps militaris Across China. Agriculture, 15(7), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15070686







