Combinatorial Approaches to Image Processing and MGIDI for the Efficient Selection of Superior Rice Grain Quality Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- To develop and implement an image processing technique to rapidly assess appearance quality in a large rice population.
- 2.
- To utilize the MGIDI for selecting the best lines from the assessed rice population based on multiple traits related to the appearance quality of head rice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Field Experiment
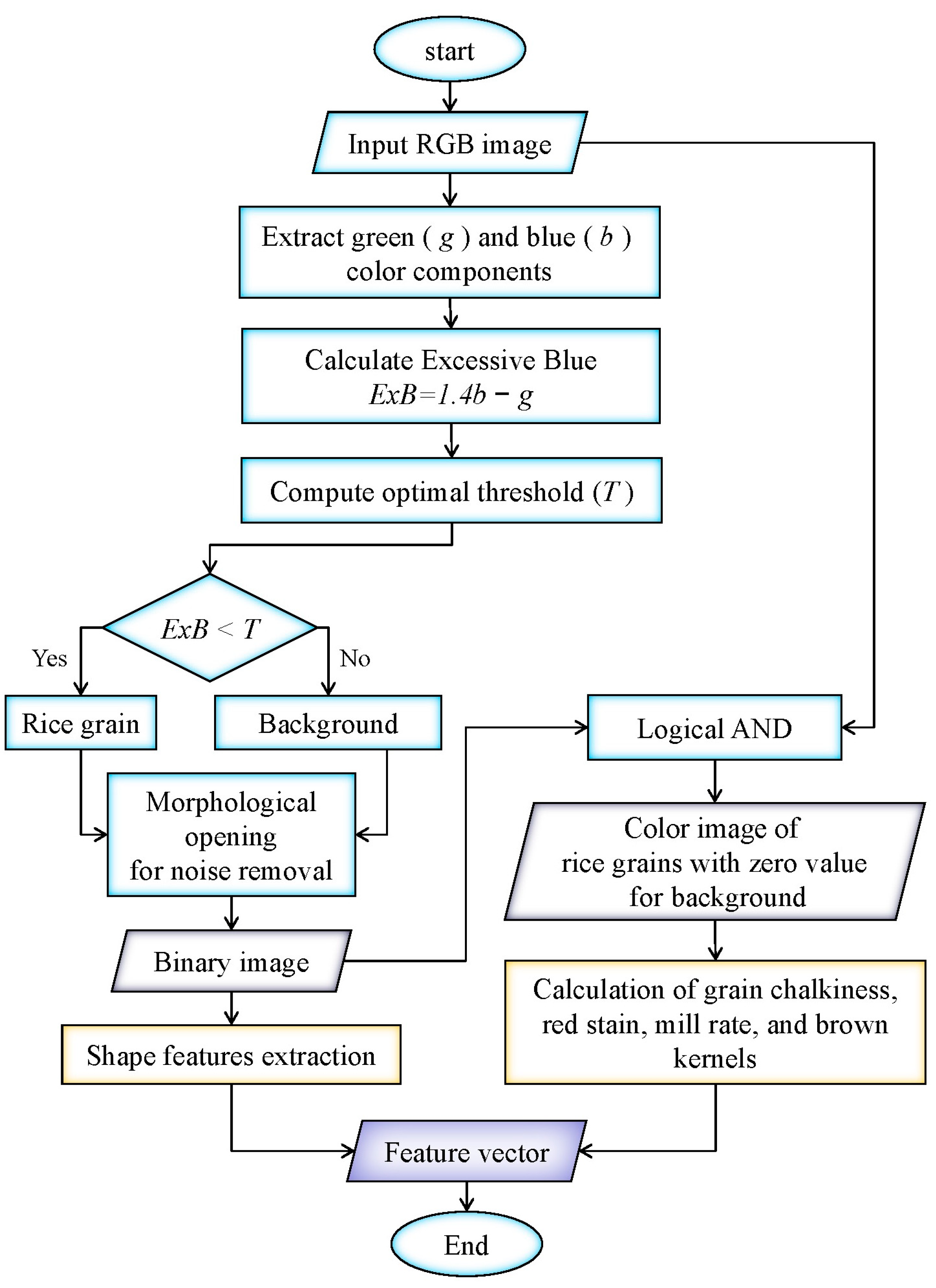
2.2. Methods System and Appearance Quality Trait Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.3.1. Descriptive Statistics and Correlation Coefficient Calculation
2.3.2. MGIDI
- 1.
- Rescaling the traits:
- 2.
- Factor analysis:
- 3.
- Definition of ideal genotype (Ideotype):
- 4.
- Calculation of MGIDI:
2.3.3. Selection Differential and Selection Gain
3. Results
3.1. Enhanced Efficiency and Accuracy with Image Processing
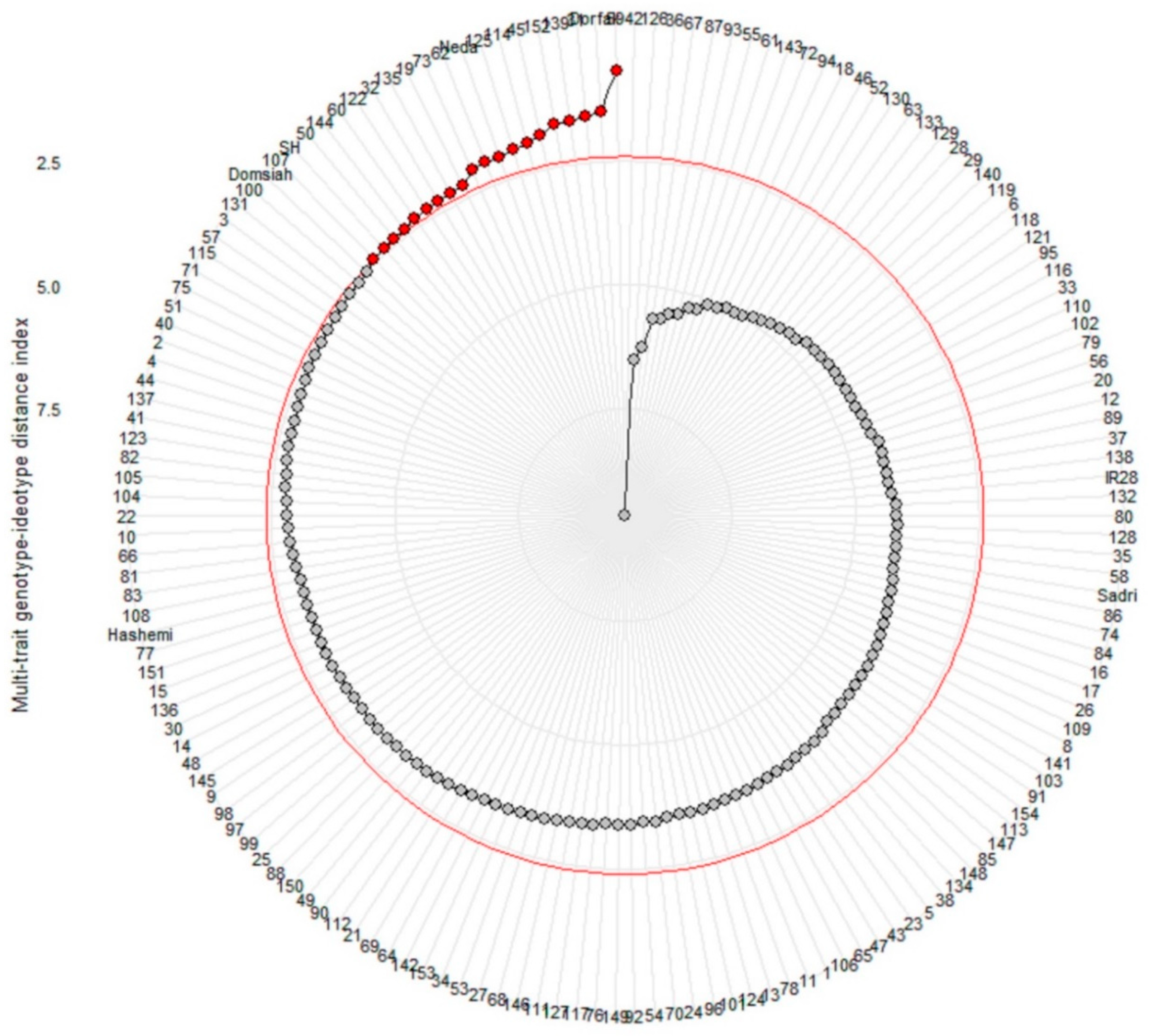
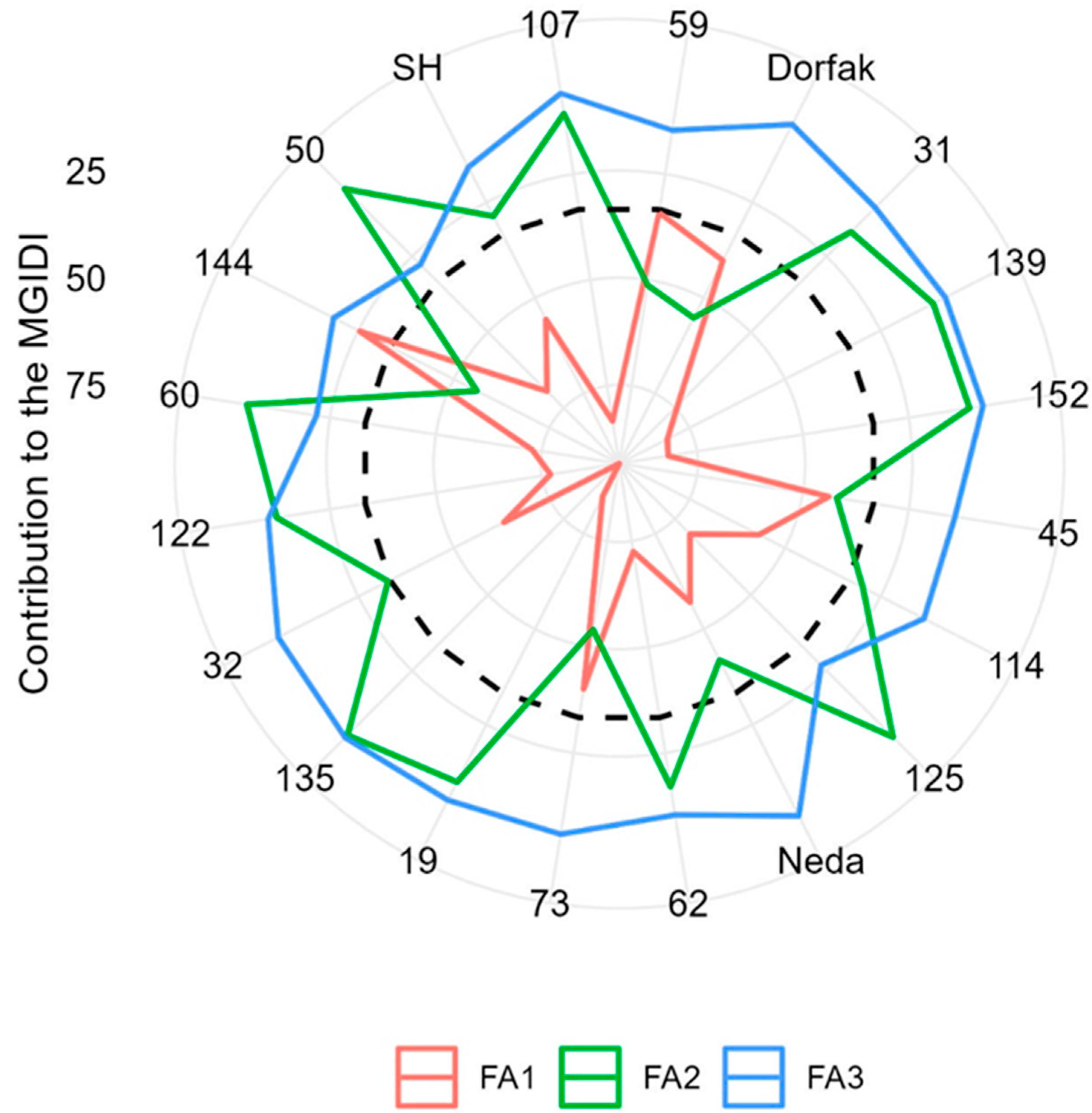
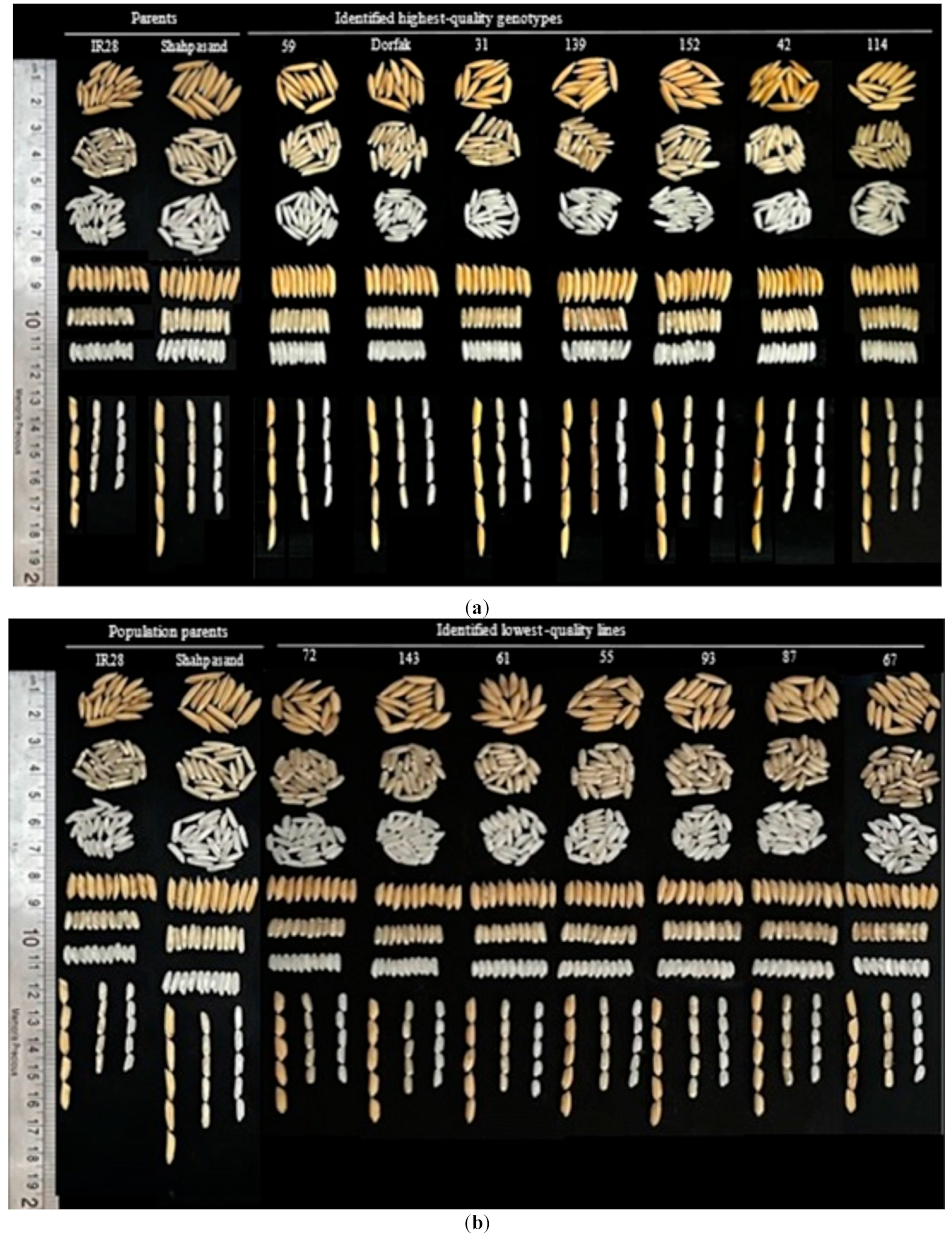
3.2. Selection of Genotypes Based on the MGIDI
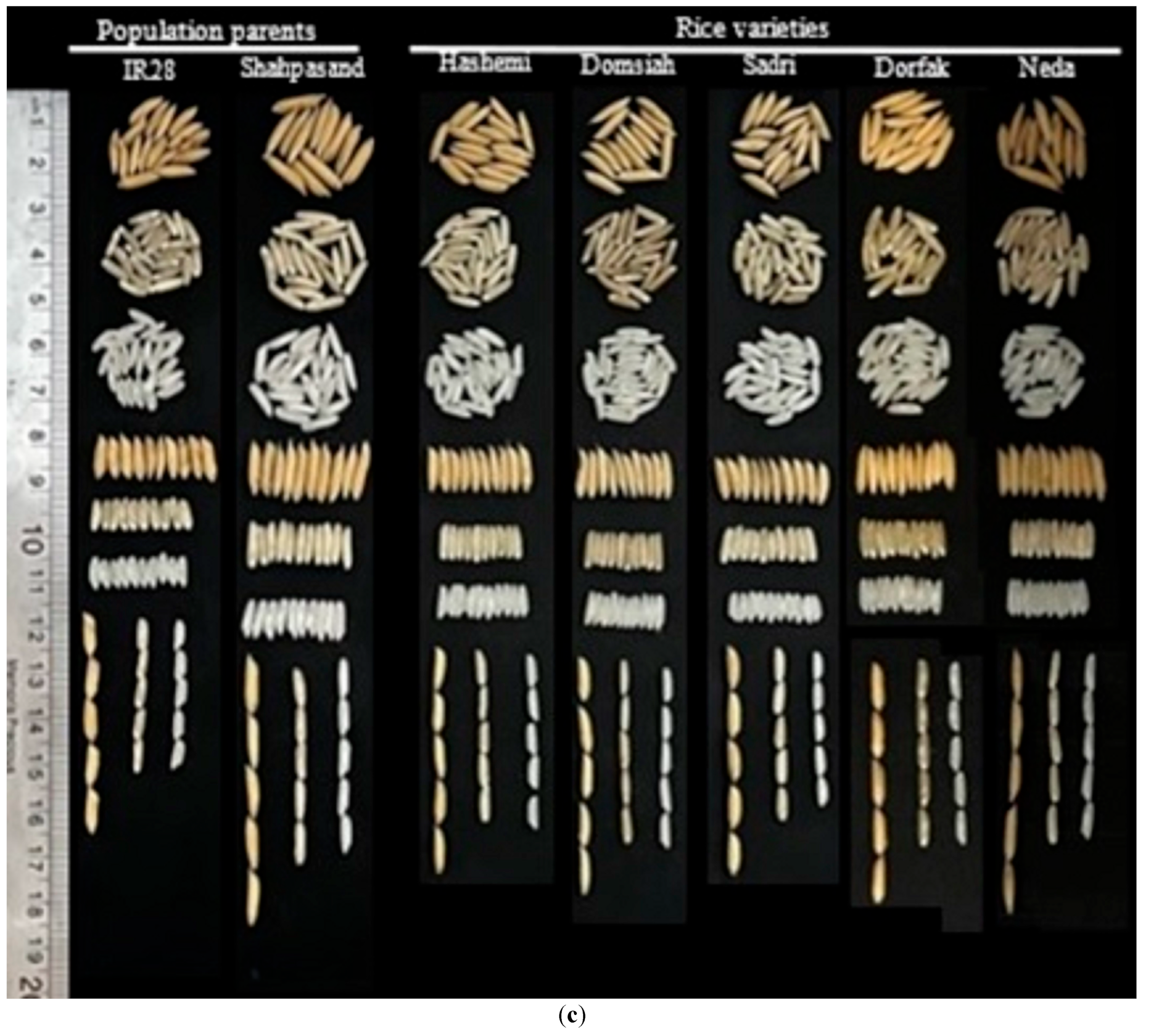
3.3. Comparison of RILs with Varieties and Population Parents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, M.A.; Sunooj, K.V.; Mir, S.A. Cereal-Based Food Products; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Lara, K.I. Temperate japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.) breeding: History, present and future challenges. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 80, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.W.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.J.; Wan, G.P. Nutrient accumulation and transcriptome patterns during grain development in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2023, 74, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, J.; Zhang, C.Q.; Liu, Q.Q.; Li, Q.F. Genes and their molecular functions determining seed structure, components, and quality of rice. Rice 2022, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J. Genes and QTLs for Rice Grain Quality Improvement. In Genes and QTLs for Rice Grain Quality Improvement; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2014; Volume 9, pp. 239–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xu, R.; Li, Y. Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 435–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Seo, J.; Lar, S.M.; Jang, S.G.; Zhang, H.; Lee, A.R.; Kwon, S.W. QTL analysis of rice grain size using segregating populations derived from the large grain line. Agriculture 2021, 11, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septiningsih, E.M.; Prasetiyono, J.; Lubis, E.; Tai, T.H.; Tjubaryat, T.; Moeljopawiro, S.; McCouch, S.R. Identification of quantitative trait loci for yield and yield components in an advanced backcross population derived from the Oryza sativa variety IR64 and the wild relative O. rufipogon. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, M.A.; McCouch, S.R.; Hall, R.D. Not just a grain of rice: The quest for quality. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; He, N.; Pang, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Zheng, W. QTL Detection for Rice Grain Length and Fine Mapping of a Novel Locus qGL6. 1. Rice 2022, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hu, L.; Xiao, Z.; Cao, F. Low-temperature stress during the flowering period alters the source–sink relationship and grain quality in field-grown late-season rice. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2021, 207, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, J.; Lohumi, S.; Ahmed, M.R.; Kandpal, L.M.; Faqeerzada, M.A.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, B.K. Improvement in purity of healthy tomato seeds using an image-based one-class classification method. Sensors 2020, 20, 2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznan, A.; Viejo, C.G.; Pang, A.; Fuentes, S. Review of technology advances to assess rice quality traits and consumer perception. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payman, S.H.; Bakhshipour, A.; Zareiforoush, H. Development of an expert vision-based system for inspecting rice quality indices. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2018, 10, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashaswini, S.; Dubey, P.; Kumar, S.R. Rice Quality Analysis Based on Physical Attributes Using Image Processing and Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Electronics, Communication, Computing and Intelligent Information Systems (ICAECIS), Bangalore, India, 19–21 April 2023; pp. 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Choudhury, S.; Samal, A.; Awada, T. Leveraging image analysis for high-throughput plant phenotyping. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 436562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznan, A.; Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Pang, A.; Fuentes, S. Rapid assessment of rice quality traits using low-cost digital technologies. Foods 2022, 11, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurade, C.; Meenu, M.; Kalra, S.; Miglani, A.; Neelapu, B.C.; Yu, Y.; Ramaswamy, H.S. An automated image processing module for quality evaluation of milled rice. Foods 2023, 12, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour-Aboughadareh, A.; Koohkan, S.; Zali, H.; Marzooghian, A.; Gholipour, A.; Kheirgo, M.; Askari-Kelestani, A. Identification of high-yielding genotypes of barley in the warm regions of Iran. Plants 2023, 12, 3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivoto, T.; Licio, A.D.C.; da Silva, J.A.G.; Marchioro, V.S.; de Souza, V.Q.; Jost, E. Mean performance and stability in multi-environment trials I: Combining features of AMMI and BLUP techniques. Agronomy 2019, 111, 2949–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivoto, T.; Lucio, A.D. metan: An R package for multi-environment trial analysis. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivoto, T.; Nardino, M. MGIDI: Toward an effective multivariate selection in biological experiments. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour-Aboughadareha, A.; Poczaib, P. Dataset on the use of MGIDI index in screening drought -tolerant wild wheat accessions at the early growth stage. Data Brief 2021, 36, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour-Aboughadareha, A.; Poczaib, P. A dataset on multi -trait selection approaches for screening desirable wild relatives of wheat. Data Brief 2021, 39, 107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Iran (Islamic Republic of). Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/392ee95b-6852-42cd-a8ec-1a8d8ad6eaf8/content/y4347e0y.htmk (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Sabouri, A.; Dadras, A.R.; Azari, M.; Saberi Kouchesfahani, A.; Taslimi, M.; Jalalifar, R. Screening of rice drought-tolerant lines by introducing a new composite selection index and competitive with multivariate methods. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khush, G.S.; Virk, P.S. IR Varieties and Their Impact; International Rice Research Institute (IRRI): Los Baños, Philippines, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Biró, L.; Kozma-Bognár, V.; Berke, J. Comparison of RGB Indices used for Vegetation Studies based on Structured Similarity Index (SSIM). J. Plant Sci. Phytopathol. 2024, 8, 007–012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, M.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Sultana, M.S.; Igathinathane, C.; Ziauddin, A.T.M.; Grift, T.E. Geometry-based mass grading of mango fruits using image processing. Inf. Process. Agric. 2017, 4, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.rproject.org (accessed on 16 June 2024).
- Selvaraj, R.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, V.K.; Abbai, R.; Habde, S.V.; Singh, U.M. Superior haplotypes towards development of low glycemic index rice with preferred grain and cooking quality. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandiya, M.; Christy, S. Estimation of Varietal Classification and Quality Analysis in Rice Seeds Using Digital Image Processing—A Survey. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Res Methodologies in Knowledge Management, Artificial Intelligence and Telecommunication Engineering (RMKMATE), Chennai, India, 1–2 November 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, P.; Chen, W.; Hao, Y.; Ma, X.; Xu, S.; Jia, J.; Kong, L.; et al. QTL mapping for yield-related traits in wheat based on four RIL populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2020, 133, 917–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalifar, R.; Sabouri, A.; Mousanejad, S.; Dadras, A.R. Estimation of genetic parameters and identification of leaf blast-resistant rice RILs using cluster analysis and MGIDI. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstic, M.; Mladenov, V.; Cuk, N.; Ovuka, J.; Gvozdenac, S.; Krstic, J.; Miklic, V. Agro-morphological traits of inbred sunflower lines and their genetic assessment. Contemp. Agric. 2022, 71, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singamsetti, A.; Zaidi, P.H.; Seetharam, K.; Vinayan, M.T.; Olivoto, T.; Mahato, A.; Madankar, K.; Kumar, M.; Shikha, K. Genetic gains in tropical maize hybrids across moisture regimes with multi-trait-based index selection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1147424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.M.; Mezzomo, H.C.; Ribeiro, J.P.O.; de Freitas, D.S.; Nardino, M. Multi-trait selection of wheat lines under drought-stress condition. Bragantia 2023, 82, e20220254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandru, A.M.; Mihai, G.; Stoica, E.; Curtu, A.L. Multi-trait selection and stability in Norway Spruce (Picea abies) provenance trials in Romania. Forests 2023, 14, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, N.H.; Thai-Nghe, N. Deep Learning for Rice Quality Classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Applications (ACOMP), Nha Trang, Vietnam, 26–28 November 2019; pp. 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, G.; Anacleto, R.; Badoni, S.; Butardo, V.; Molina, L.; Graner, A. Dissecting the genome-wide genetic variants of milling and appearance quality traits in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5115–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çınarer, G.; Erbaş, N.; Öcal, A. Rice classification and quality detection success with artificial intelligence technologies. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2024, 67, e24220754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
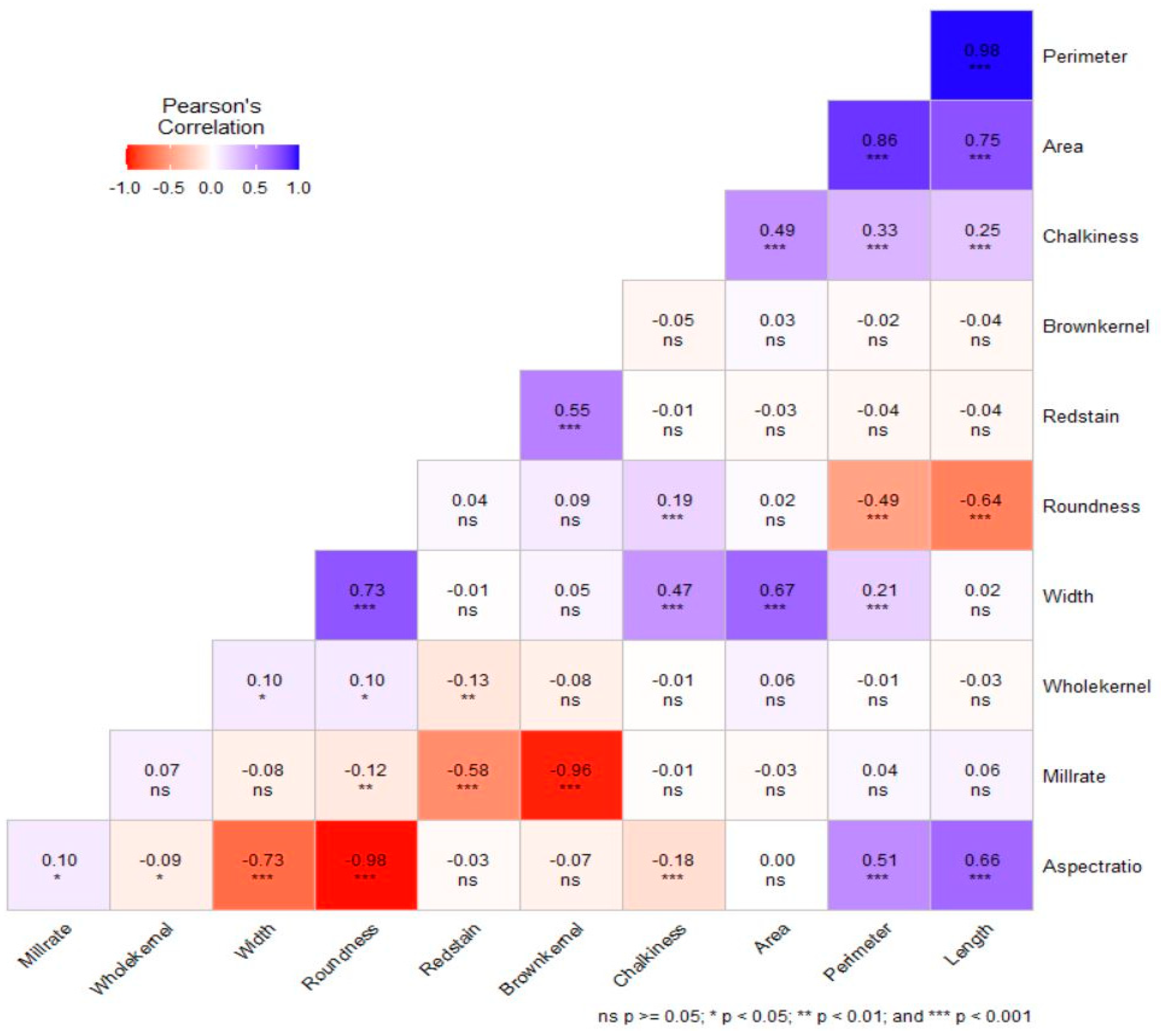
| Traits | FA1 | FA2 | FA3 | Communality | Uniquenesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area | 0.08 | −0.98 | −0.025 | 0.96 | 0.038 |
| Perimeter | −0.44 | −0.88 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.02 |
| Length | −0.60 | −0.80 | 0.04 | 0.99 | 0.01 |
| Width | −0.77 | 0.60 | 0.05 | 0.96 | 0.04 |
| Aspect ratio | −0.98 | −0.09 | 0.07 | 0.98 | 0.02 |
| Roundness | −0.98 | −0.07 | 0.09 | 0.98 | 0.02 |
| Whole kernel | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.92 |
| Chalkiness | −0.30 | 0.62 | −0.01 | 0.47 | 0.53 |
| Red stain | 0.03 | −0.04 | 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.33 |
| Mill rate | −0.05 | 0.02 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 0.07 |
| Brown kernel | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.09 |
| Eigenvalue | 3.53 | 2.91 | 2.48 | ||
| Variance (%) | 32.13 | 26.46 | 22.52 | ||
| Cumulative (%) | 32.13 | 58.59 | 81.11 |
| Traits | Factor | Goal | Xo | Xs | SD | SD% | h2 | SG | SG% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width | FA1 | decrease | 2.27 | 2.19 | −0.08 | −3.53 | 0.99 | −0.08 | −3.50 |
| Aspect ratio | FA1 | increase | 3.16 | 3.52 | 0.36 | 11.37 | 0.99 | 0.36 | 11.30 |
| Roundness | FA1 | decrease | 0.33 | 0.29 | −0.03 | −9.57 | 0.99 | −0.03 | −9.52 |
| Whole kernel | FA1 | increase | 0.95 | 0.94 | −0.01 | −1.10 | 0.63 | −0.007 | −0.69 |
| Area | FA2 | increase | 12.92 | 13.56 | 0.64 | 4.98 | 0.99 | 0.64 | 4.95 |
| Perimeter | FA2 | increase | 16.16 | 17.19 | 1.03 | 6.40 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 6.35 |
| Length | FA2 | increase | 7.13 | 7.67 | 0.54 | 7.62 | 0.99 | 0.54 | 7.57 |
| Chalkiness | FA2 | decrease | 14.27 | 14.48 | −0.02 | 1.42 | 0.99 | 0.20 | 1.40 |
| Red stain | FA3 | decrease | 0.07 | 0.05 | −0.02 | −32.08 | 0.72 | −0.02 | −23.11 |
| Mill rate | FA3 | increase | 99.81 | 99.94 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.93 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| Brown kernel | FA3 | decrease | 0.01 | 0.002 | −0.004 | −65.27 | 0.87 | −0.003 | −56.84 |
| Total (Increase) | 31.69 | ||||||||
| Total (Decrease) | −93.66 |
| Trait | Selected Line/Variety Mean | RIL Mean | RILs Min | RILs Max | Varieties | Parents | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dorfak | Neda | Hashemi | Domsiah | Sadri | SH | IR28 | |||||
| Area (mm2) | 13.49 | 12.94 | 9.61 | 15.65 | 12.60 | 12.92 | 12.25 | 11.45 | 11.00 | 15.19 | 11.96 |
| Perimeter (mm) | 17.13 | 16.16 | 14.14 | 18.40 | 16.92 | 16.76 | 16.05 | 16.18 | 14.76 | 18.16 | 15.35 |
| Length (mm) | 7.65 | 7.12 | 6.28 | 8.15 | 7.65 | 7.51 | 7.14 | 7.35 | 6.54 | 8.04 | 6.71 |
| Width (mm) | 2.19 | 2.28 | 1.88 | 2.64 | 2.04 | 2.12 | 2.16 | 1.95 | 2.15 | 2.36 | 2.28 |
| Aspect ratio | 3.56 | 3.15 | 2.62 | 3.97 | 3.76 | 3.55 | 3.32 | 3.79 | 3.05 | 3.43 | 2.96 |
| Roundness | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 0.34 |
| Whole kernel | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.82 | 0.99 | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| Chalkiness (%) | 14.24 | 14.56 | 0.22 | 44.74 | 8.54 | 6.32 | 4.34 | 1.22 | 2.74 | 26.01 | 7.07 |
| Red stain (%) | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.012 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.02 |
| Mill rate (%) | 99.86 | 99.81 | 95.63 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 99.78 | 100.00 | 99.88 | 99.88 |
| Brown kernel | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feizi, N.; Sabouri, A.; Bakhshipour, A.; Abedi, A. Combinatorial Approaches to Image Processing and MGIDI for the Efficient Selection of Superior Rice Grain Quality Lines. Agriculture 2025, 15, 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060615
Feizi N, Sabouri A, Bakhshipour A, Abedi A. Combinatorial Approaches to Image Processing and MGIDI for the Efficient Selection of Superior Rice Grain Quality Lines. Agriculture. 2025; 15(6):615. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060615
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeizi, Nahid, Atefeh Sabouri, Adel Bakhshipour, and Amin Abedi. 2025. "Combinatorial Approaches to Image Processing and MGIDI for the Efficient Selection of Superior Rice Grain Quality Lines" Agriculture 15, no. 6: 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060615
APA StyleFeizi, N., Sabouri, A., Bakhshipour, A., & Abedi, A. (2025). Combinatorial Approaches to Image Processing and MGIDI for the Efficient Selection of Superior Rice Grain Quality Lines. Agriculture, 15(6), 615. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15060615






