Nitrogen Availability Level Controlling the Translocation and Stabilization of Maize Residue Nitrogen in Soil Matrix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Samples, Maize Residue, and Laboratory Incubation
2.2. Soil Particle Size Fractionation
2.3. Determination of Total N, 15N Enrichment, and Organic C in Bulk Soil and Sub-Fractions
2.4. Calculations
2.4.1. Maize Residue N Concentration
2.4.2. Enrichment Factors of Total N and Maize Residue N in Particle-Size Fractions
2.4.3. Stock of Total N and Maize Residue N
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Concentrations of Organic C in Bulk Soil
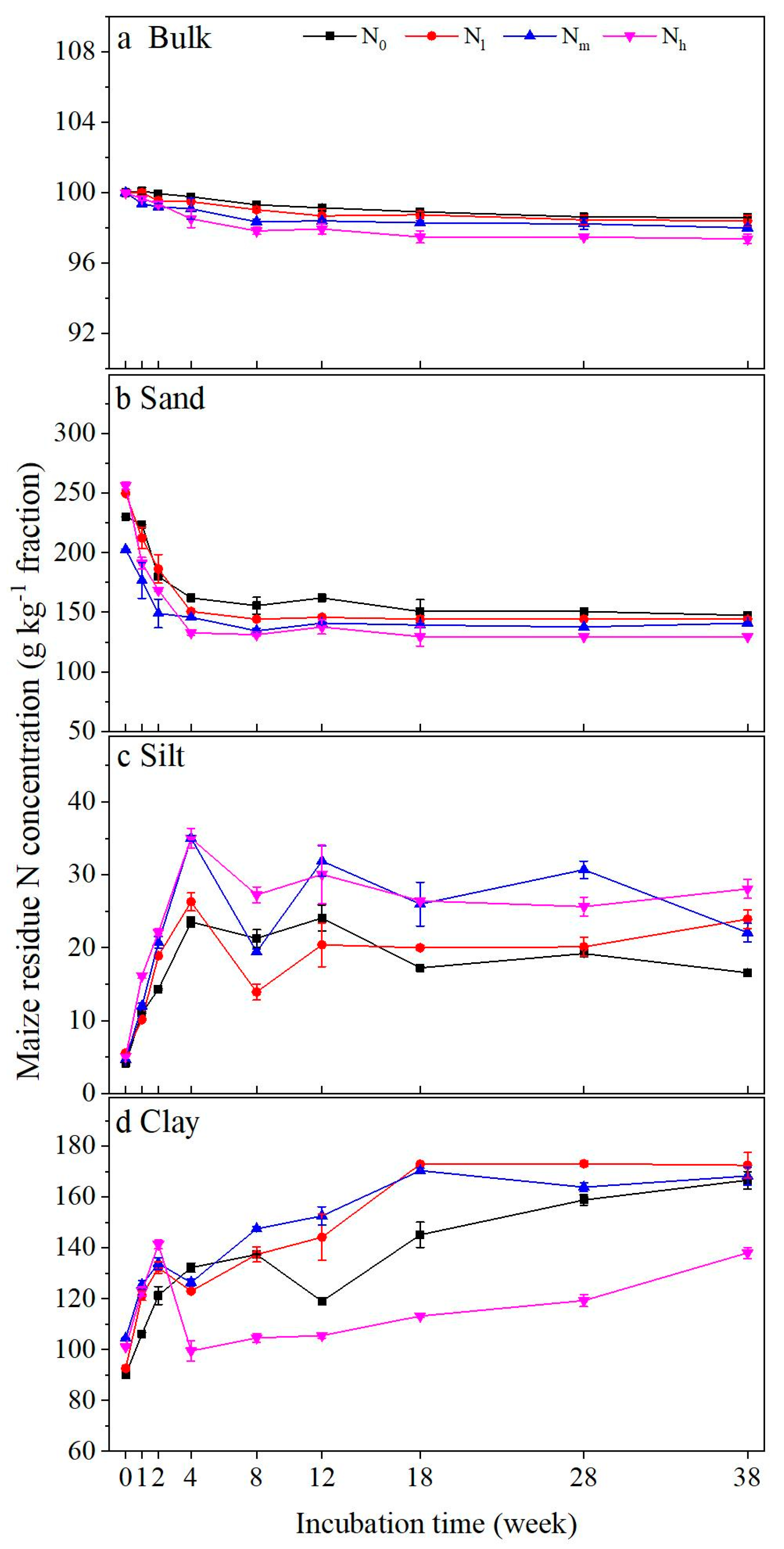
3.2. Concentrations of Total and Maize Residue N in Bulk Soil and Different Particle-Size Fractions
3.3. Enrichment Factors of Total N and Maize Residue N in Soil Particle Size Fractions
3.4. Relative Distribution of Total N and Maize Residue N in Soil Particle Size Fractions
4. Discussion
4.1. Distinct Transformation of Total N and Maize Residue N Among Different Soil Particle Size Fractions
4.2. Effects of N Availability on Transformation Dynamics of Maize Residue N
4.3. Distribution and Stabilization of Maize Residue N Influenced by Inorganic N Availability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Hill, P.W.; Jones, D.L. Root exudate components change litter decomposition in a simulated rhizosphere depending on temperature. Plant Soil 2007, 290, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, Y.M.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Ok, Y.S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of polyacrylamide, biopolymer and biochar on the decomposition of 14C-labelled maize residues and on their stabilization in soil aggregates. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, A.W.; Diochon, A.; Ma, B.L.; Morrison, M.J.; Kellman, L.; Walley, F.L.; Regier, T.Z.; Chevrier, D.; Dynes, J.J.; Gregorich, E.G. Nitrogen input quality changes the biochemical composition of soil organic matter stabilized in the fine fraction: A long-term study. Biogeochemistry 2014, 117, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.B.; Wang, H.J.; Xie, H.T.; Bao, X.L.; He, H.B.; Zhang, X.D.; Liang, C. Low-disturbance farming regenerates healthy deep soil toward sustainable agriculture-Evidence from long-term no-tillage with stover mulching in Mollisols. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 153929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.M.F.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Cambardella, C.A.; Barbour, N.W. Crop and Soil Responses to Using Corn Stover as a Bioenergy Feedstock: Observations from the Northern US Corn Belt. Agriculture 2013, 3, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.K.; Tahir, M.M.; Sabir, N.; Khurshid, M. Impact of the addition of different plant residues on nitrogen mineralization-immobilization turnover and carbon content of a soil incubated under laboratory conditions. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.Q.; Liu, X.; He, H.B.; Zhang, W.; Xie, H.T.; Wu, Y.Y.; Cui, J.H.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.D. Multi-Seasonal Nitrogen Recoveries from Crop Residue in Soil and Crop in a Temperate Agro-Ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryals, R.; Kaiser, M.; Torn, M.S.; Berhe, A.A.; Silver, W.L. Impacts of organic matter amendments on carbon and nitrogen dynamics in grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajan, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Tian, G.; Naidu, R.; Kunhikrishnan, A. Role of organic amendment application on greenhouse gas emission from soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 72–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, W.; Shao, S.; He, H.B.; Zhang, X.D. Comparing microbial transformation of maize residue-N and fertilizer-N in soil using amino sugar-specific 15N analysis. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalhais, N.; Forkel, M.; Khomik, M.; Bellarby, J.; Jung, M.; Migliavacca, M.; Mu, M.; Saatchi, S.; Santoro, M.; Thurner, M.; et al. Global covariation of carbon turnover times with climate in terrestrial ecosystems. Nature 2014, 514, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Xie, H.T.; Mao, Z.; Bao, X.L.; He, H.B.; Zhang, X.D.; Liang, C. Fungi determine increased soil organic carbon more than bacteria through their necromass inputs in conservation tillage croplands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 167, 108587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.B.; Li, X.B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.D. Differentiating the dynamics of native and newly immobilized amino sugars in soil frequently amended with inorganic nitrogen and glucose. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 62, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, S.S.; Nyborg, M.; Solberg, E.D.; McConkey, B.; Dyck, M.; Puurveen, D. Long-term straw management and N fertilizer rate effects on quantity and quality of organic C and N and some chemical properties in two contrasting soils in Western Canada. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalos, D.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Garcia-Torres, L.; van Groenigen, J.W.; Vallejo, A. Role of maize stover incorporation on nitrogen oxide emissions in a non-irrigated Mediterranean barley field. Plant Soil 2013, 364, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.R.; Li, Q.; Fang, Y.; Luo, Y.C.; Duan, C.J.; Chen, Q.; Song, X.Z.; Tian, X.J. Enlarging interface reverses the dominance of fungi over bacteria in litter decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 198, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Horwath, W.R.; Joergensen, R.G.; Ludwig, B. Pathways of nitrogen utilization by soil microorganisms—A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2058–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.T. Physical fractionation of soil and structural and functional complexity in organic matter turnover. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 52, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Luetzow, M.; Koegel-Knabner, I.; Ekschmitt, K.; Flessa, H.; Guggenberger, G.; Matzner, E.; Marschner, B. SOM fractionation methods: Relevance to functional pools and to stabilization mechanisms. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2183–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, M.; Bourg, I.C.; Coward, E.K.; Hansel, C.M.; Myneni, S.C.B.; Nunan, N. Dynamic interactions at the mineral-organic matter interface. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.F.; Yu, W.T.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, C.M.; Xu, Y.G.; Ren, J.F. Influence of 15N-labeled ammonium sulfate and straw on nitrogen retention and supply in different fertility soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.L.; He, H.B.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.D. Plant-N incorporation into microbial amino sugars as affected by inorganic N addition: A microcosm study of 15N-labeled maize residue decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Drury, C.F.; Reynolds, W.D.; MacTavish, D.C. Use of sonication to determine the size distributions of soil particles and organic matter. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 89, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, B.T. Physical Fractionation of Soil and Organic Matter in Primary Particle Size and Density Separates. In Advances in Soil Science: Volume 20; Stewart, B.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- North, P.F. Towards an Absolute Measurement of Soil Structural Stability Using Ultrasound. J. Soil Sci. 1976, 27, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, W.; Zech, W.; Zhang, X.; Follett, R.F.; Tiessen, H.; Knox, E.; Flach, K.W. Carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur pools in particle-size fractions as influenced by climate. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Luetzow, M.; Koegel-Knabner, I.; Ekschmitt, K.; Matzner, E.; Guggenberger, G.; Marschner, B.; Flessa, H. Stabilization of organic matter in temperate soils: Mechanisms and their relevance under different soil conditions—A review. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2006, 57, 426–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungait, J.A.J.; Hopkins, D.W.; Gregory, A.S.; Whitmore, A.P. Soil organic matter turnover is governed by accessibility not recalcitrance. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 1781–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Boot, C.M.; Denef, K.; Paul, E. The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilization: Do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, G.; Skipper, N.T.; Sutton, R.; Park, S.H.; Soper, A.K.; Greathouse, J.A. Surface geochemistry of the clay minerals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3358–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinz, H. Clay minerals for nanocomposites and biotechnology: Surface modification, dynamics and responses to stimuli. Clay Miner. 2012, 47, 205–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adisa, S.J.; Nortcliff, S. Carbon Fractions Associated with Silt-Size Particles in Surface and Subsurface Soil Horizons. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kaisi, M.M.; Guzman, J.G. Effects of tillage and nitrogen rate on decomposition of transgenic Bt and near-isogenic non-Bt maize residue. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 129, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.D.; Xie, H.T.; Zhuang, J. Temporal responses of soil microorganisms to substrate addition as indicated by amino sugar differentiation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiem, R.; Kögel-Knabner, I. Contribution of lignin and polysaccharides to the refractory carbon pool in C-depleted arable soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recous, S.; Robin, D.; Darwis, D.; Mary, B. Soil inorganic N availability: Effect on maize residue decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; LeBauer, D.S.; Ofrecio, M.R.; Reyes, R.; Ta, A.-M.; Tran, T.M. Low levels of nitrogen addition stimulate decomposition by boreal forest fungi. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chapin, F.S.; Firestone, M.K.; Field, C.B.; Chiariello, N.R. Nitrogen limitation of microbial decomposition in a grassland under elevated CO2. Nature 2001, 409, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolardot, B.; Recous, S.; Mary, B. Simulation of C and N mineralisation during crop residue decomposition:: A simple dynamic model based on the C:N ratio of the residues. Plant Soil 2001, 228, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.R.; Senbayram, M.; Blagodatsky, S.; Myachina, O.; Dittert, K.; Lin, X.G.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y. Soil C and N availability determine the priming effect: Microbial N mining and stoichiometric decomposition theories. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, D.L.D.; Schneider, R.J.; Scherer, H.W.; Duarte, A.C.; Santos, E.B.H.; Esteves, V.I. Sorption-Desorption Behavior of Atrazine on Soils Subjected to Different Organic Long-Term Amendments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3101–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhao, M.Q.; Chi, G.Y.; Huang, B. Fixation of labeled (15NH4)2SO4 and its subsequent release in black soil of Northeast China over consecutive crop cultivation. Soil Tillage Res. 2010, 106, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Chen, X.; Jia, J.C.; Chen, H.H.; Shi, Y.; Ma, J.; Liang, C.; Liu, Y.; Xie, H.T.; He, H.B.; et al. Stover mulching and inhibitor application maintain crop yield and decrease fertilizer N input and losses in no-till cropping systems in Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 312, 107360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassink, J. The capacity of soils to preserve organic C and N by their association with clay and silt particles. Plant Soil 1997, 191, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Week | Distribution (%) | Recovery Rate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | ||
| 0th week | 12.9 ± 0.8 a | 48.6 ± 0.7 a | 35.8 ± 0.5 a | 97.3 ± 0.9 a |
| 38th week | 14.1 ± 0.8 a | 46.9 ± 0.8 a | 35.2 ± 0.3 a | 96.2 ± 0.3 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Ma, S.; Deng, F.; Zhou, F.; Liang, X.; Yuan, L.; Lü, H.; Ding, X.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Nitrogen Availability Level Controlling the Translocation and Stabilization of Maize Residue Nitrogen in Soil Matrix. Agriculture 2025, 15, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15040403
Liu S, Ma S, Deng F, Zhou F, Liang X, Yuan L, Lü H, Ding X, He H, Zhang X. Nitrogen Availability Level Controlling the Translocation and Stabilization of Maize Residue Nitrogen in Soil Matrix. Agriculture. 2025; 15(4):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15040403
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuzhe, Sicong Ma, Fangbo Deng, Feng Zhou, Xiaona Liang, Lei Yuan, Huijie Lü, Xueli Ding, Hongbo He, and Xudong Zhang. 2025. "Nitrogen Availability Level Controlling the Translocation and Stabilization of Maize Residue Nitrogen in Soil Matrix" Agriculture 15, no. 4: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15040403
APA StyleLiu, S., Ma, S., Deng, F., Zhou, F., Liang, X., Yuan, L., Lü, H., Ding, X., He, H., & Zhang, X. (2025). Nitrogen Availability Level Controlling the Translocation and Stabilization of Maize Residue Nitrogen in Soil Matrix. Agriculture, 15(4), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15040403





