Predicting Long-Term Maize Straw Decomposition from Incorporation Amount and Depth in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
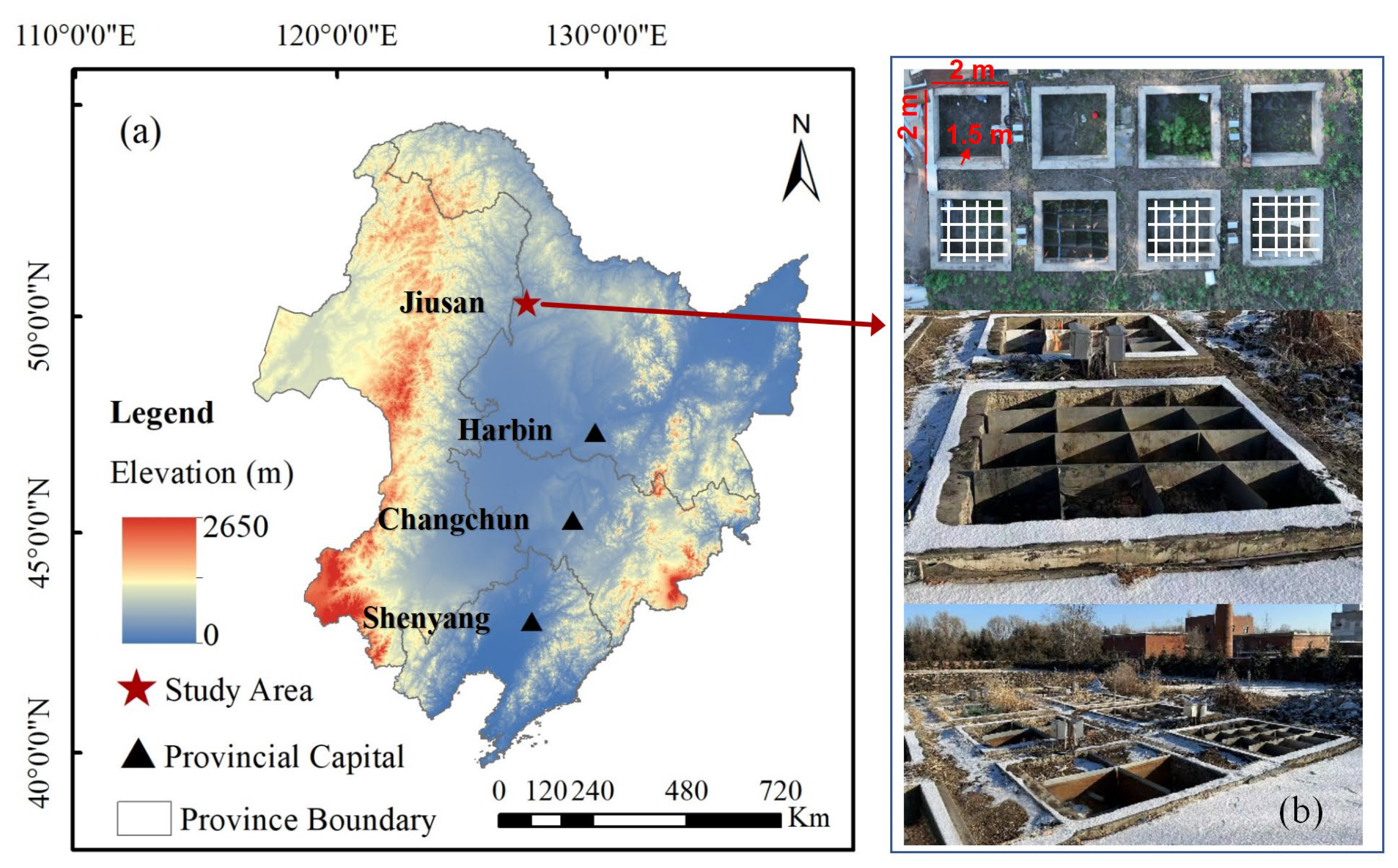
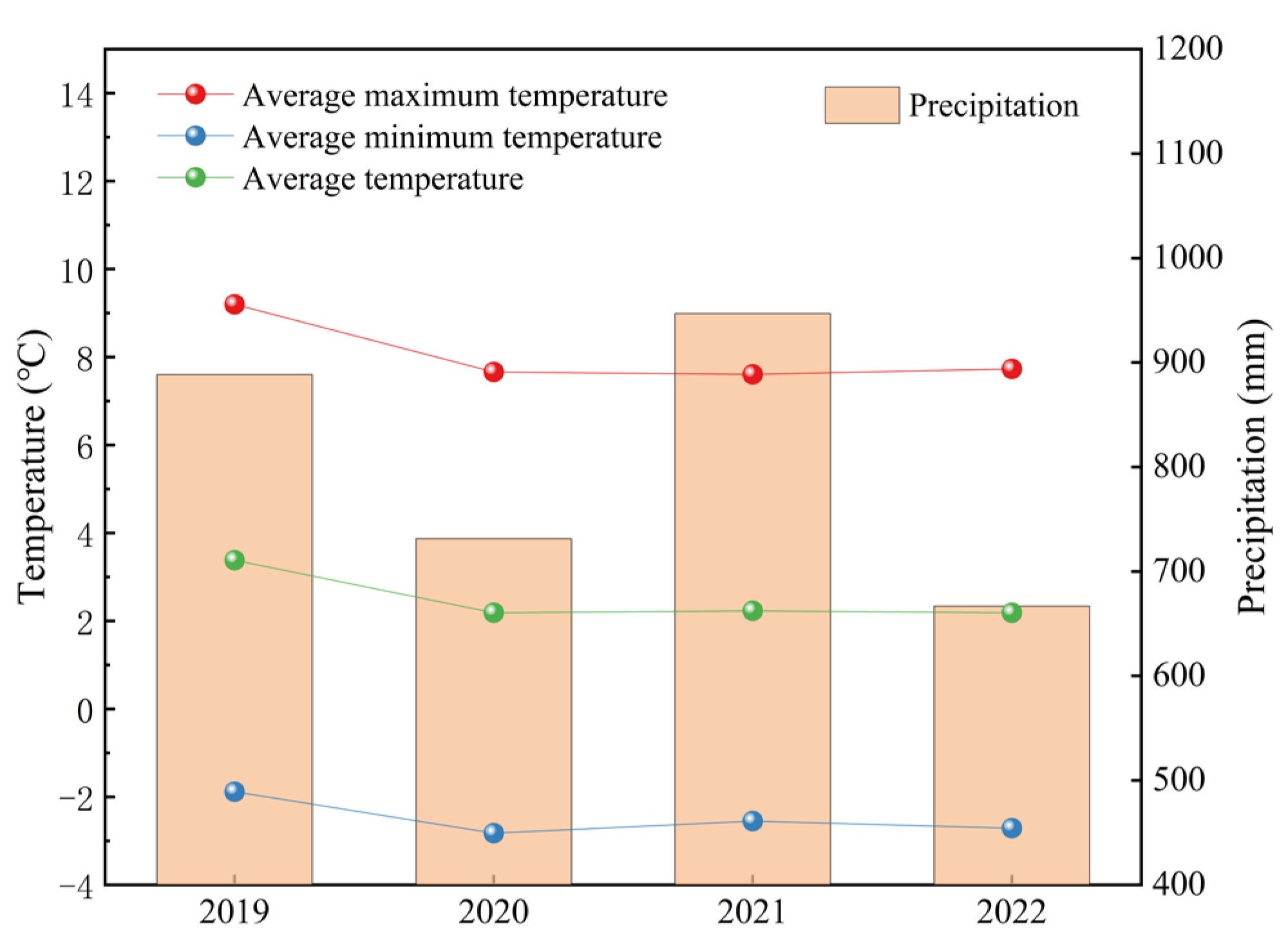
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
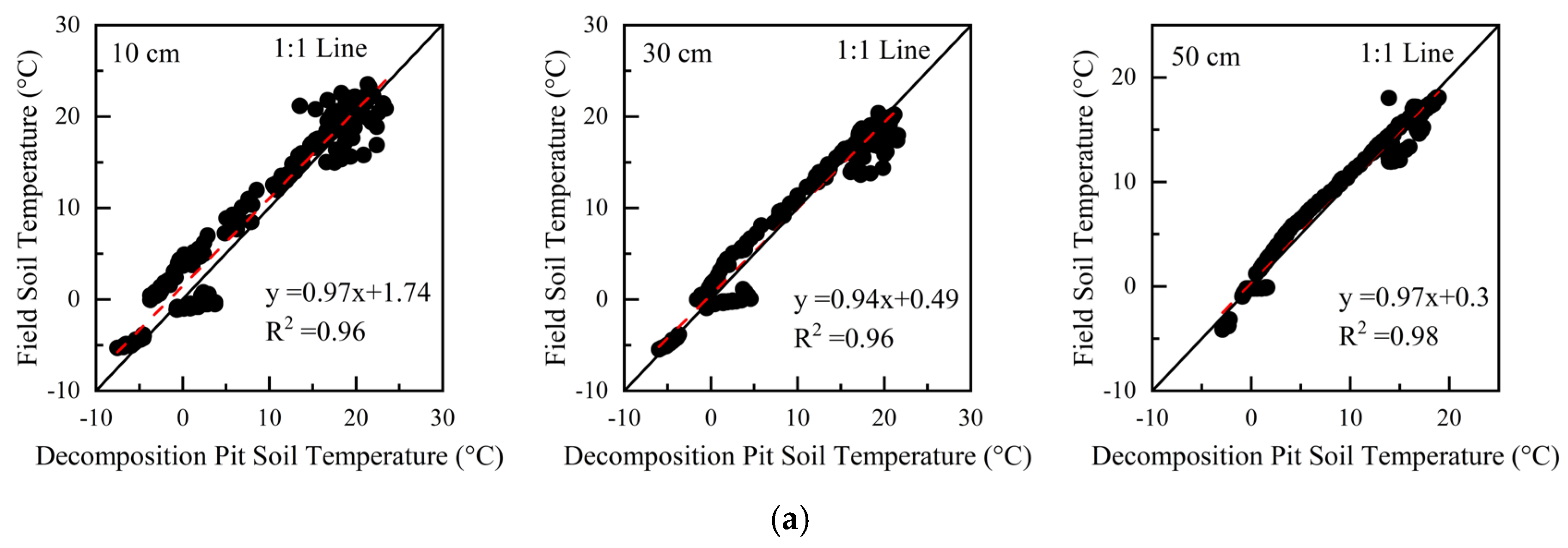
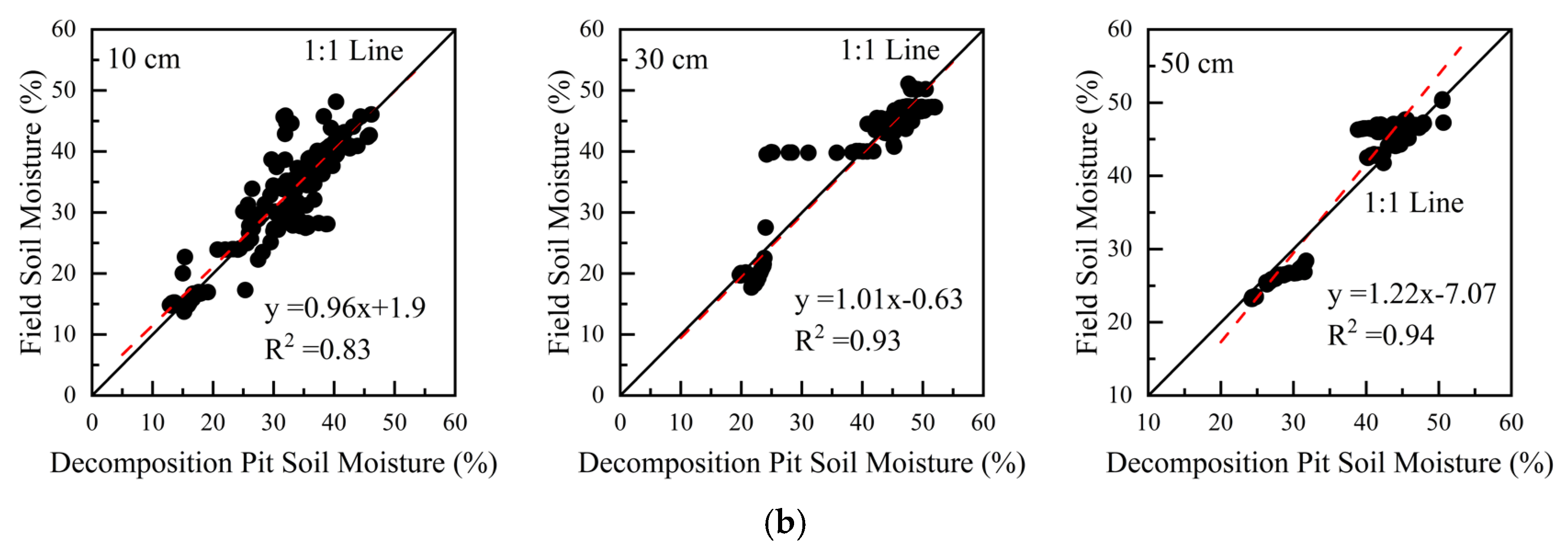
2.3. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Data Statistical Analysis, Development and Validation of a Predictive Equation for RSR
2.5. Scenario Analysis of Soil Loss Ratios Under Slope Cropland
3. Results
3.1. Results of Statistical Analysis
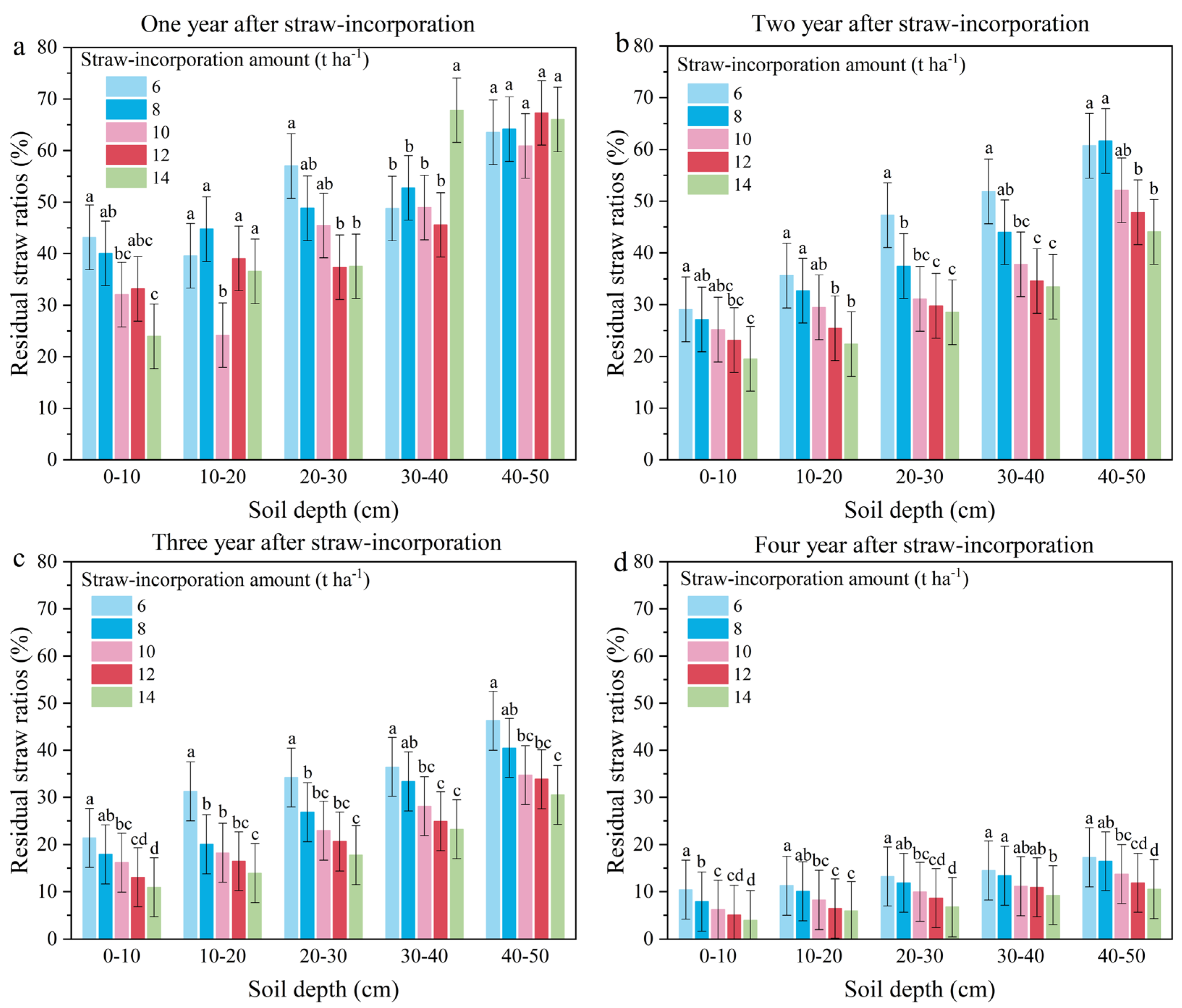
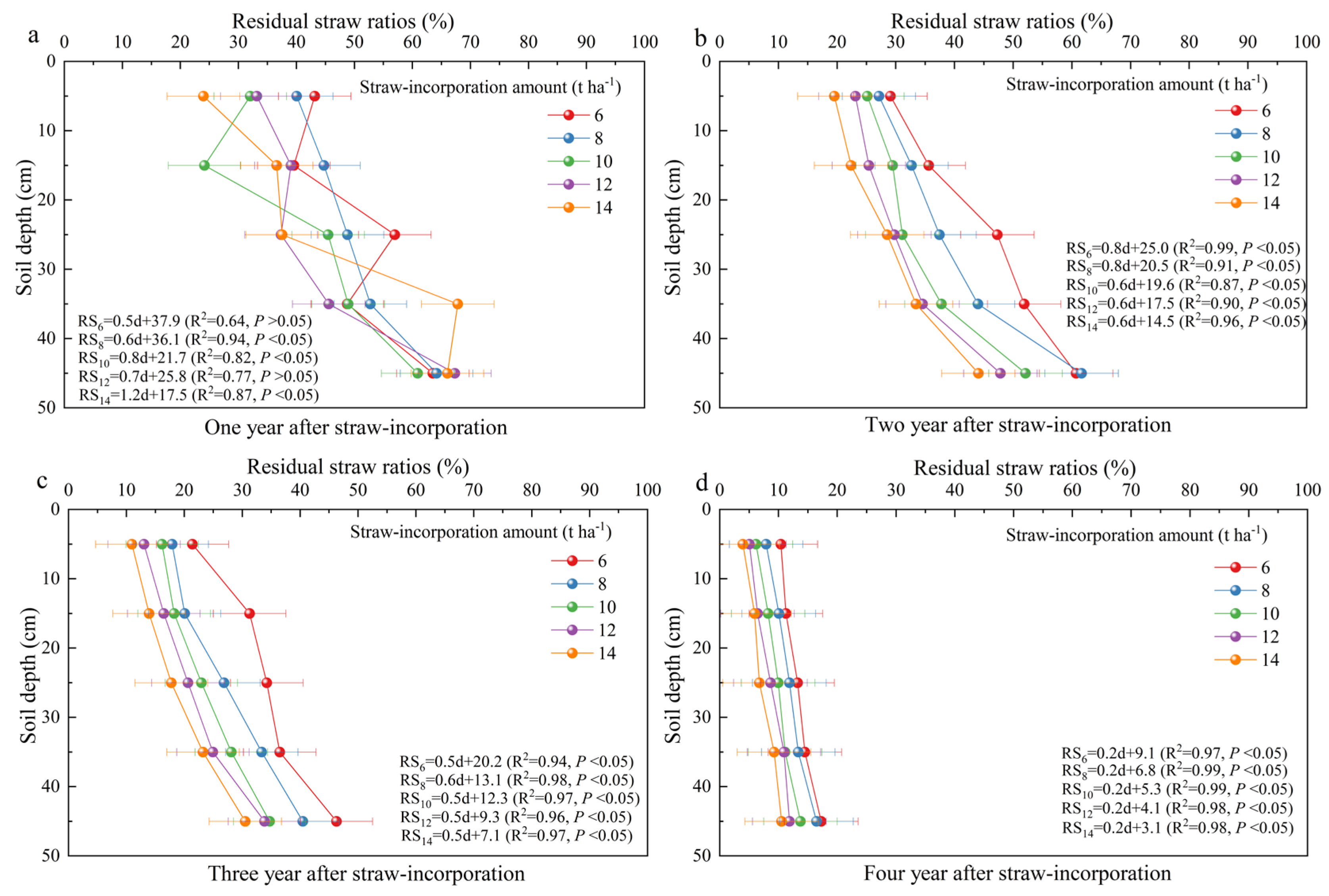
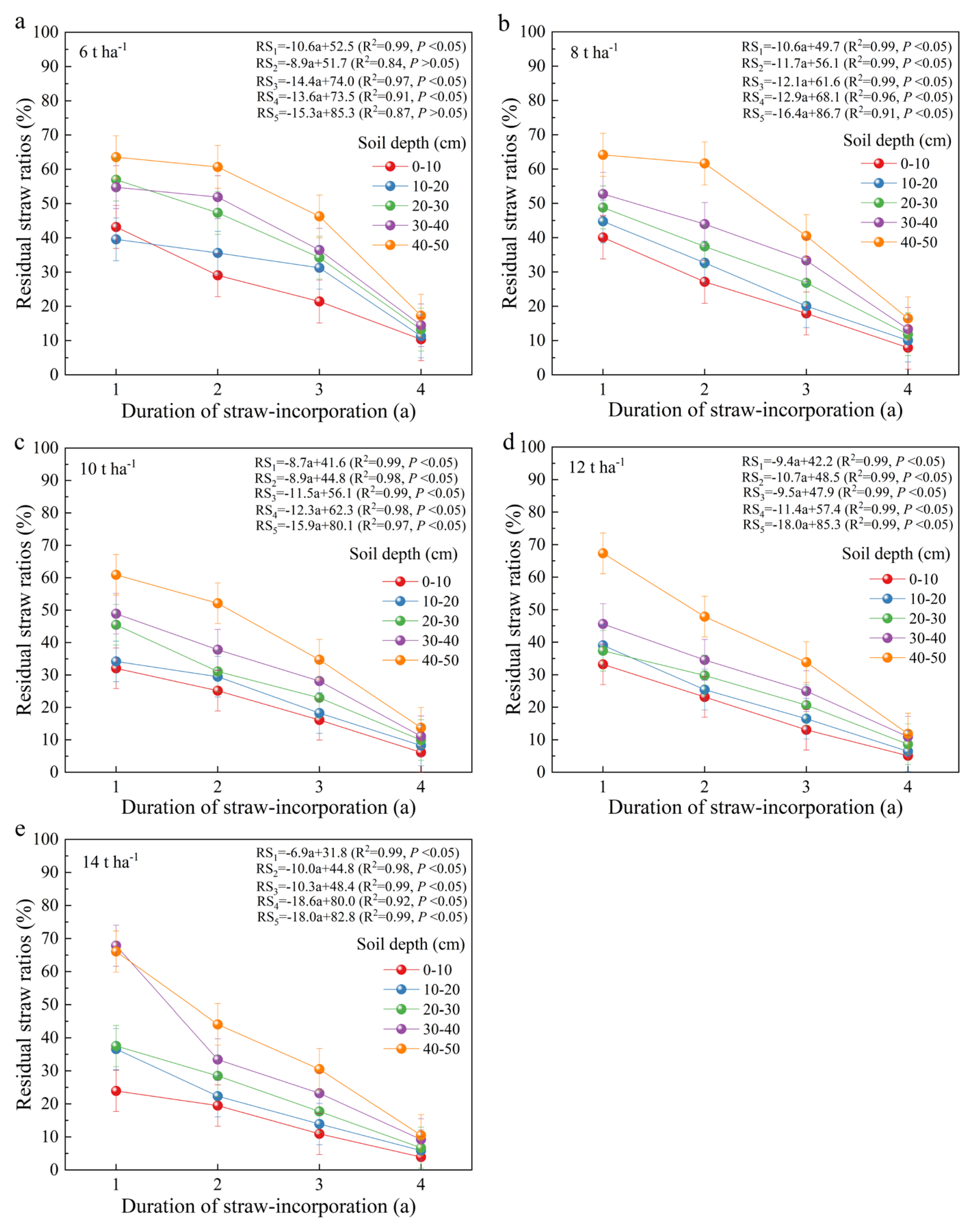
3.2. RSR Under Different Landfill Amounts, Burial Depths and Landfill Years
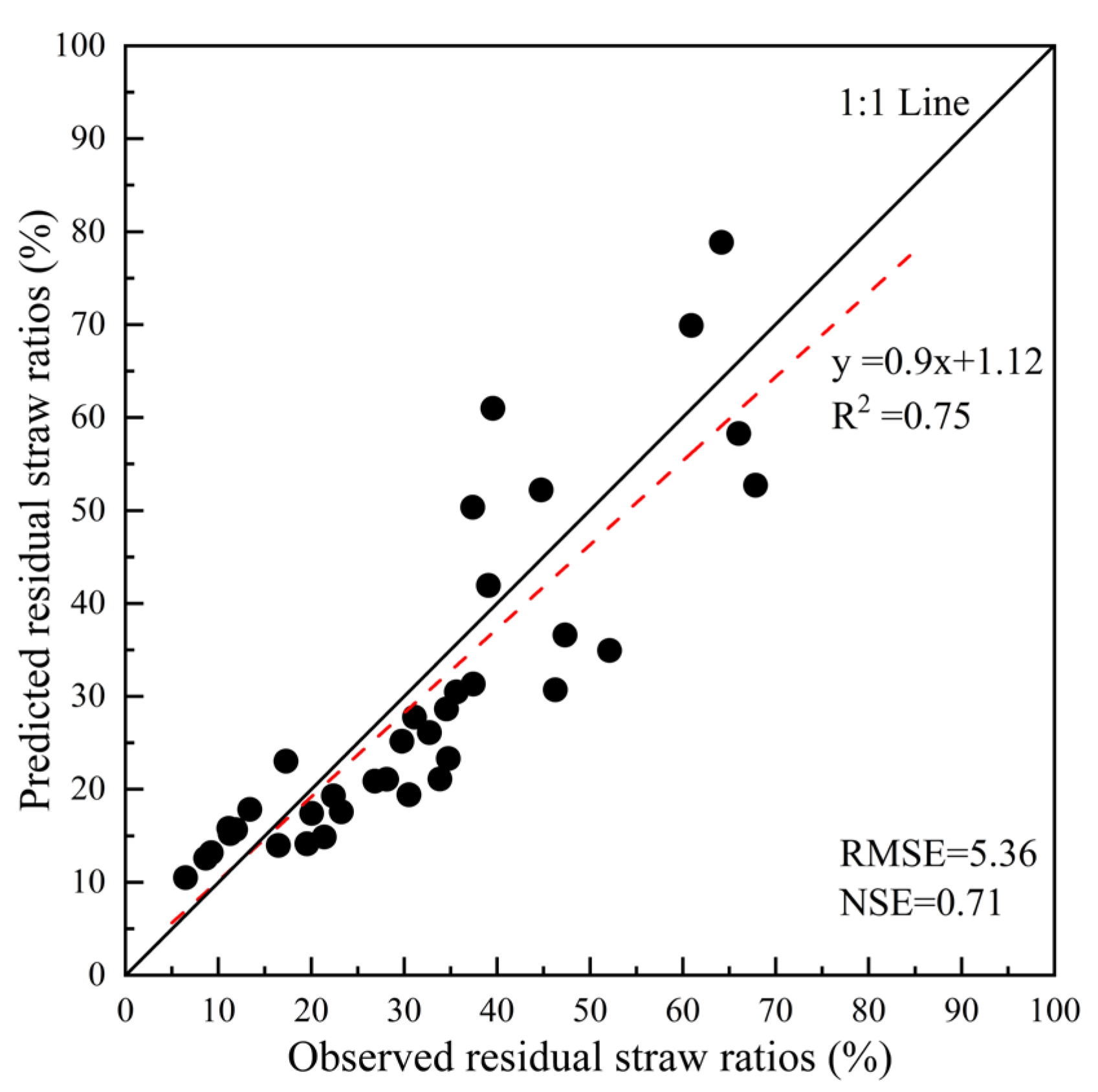
3.3. Development and Validation of a Predictive Equation for RSR
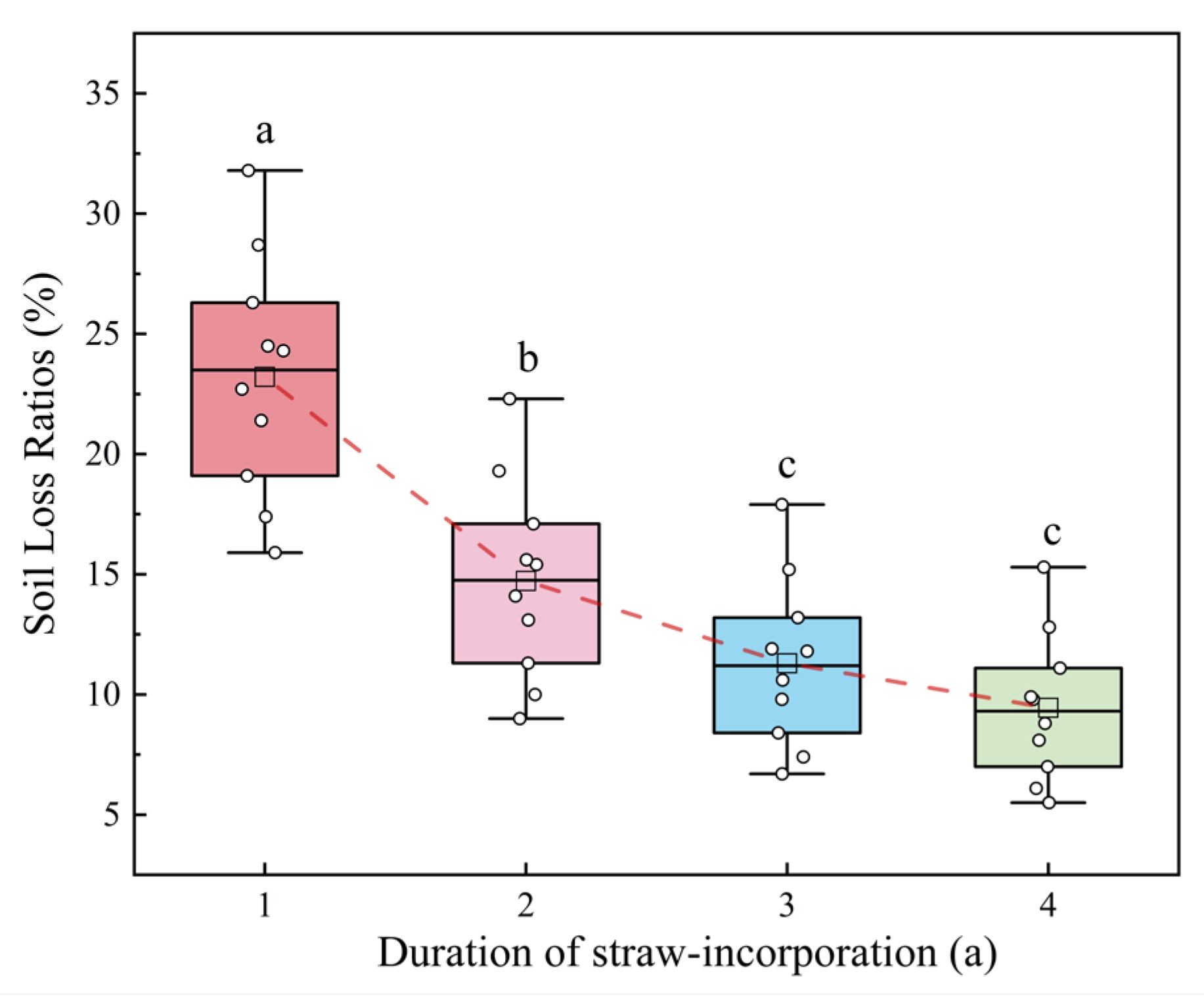
3.4. Soil Loss Assessment for Slope Cropland Under Straw Incorporation
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Landfill Amounts, Burial Depths, and Durations on Straw Decomposition
4.2. Effect of Continuous Straw Incorporation on Soil Loss
4.3. The Limitations of the Predictive Equation for RSR
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, N.; Bai, L.; Wei, X.; Li, T.; Tang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lei, Z.; Wen, J.; Su, S. Promoted decomposition in straw return to double-cropped rice fields controls soil acidity, increases soil fertility and improves rice yield. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 509, 161309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C. How does straw-incorporation rate reduce runoff and erosion on sloping cropland of black soil region? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 357, 108676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, B. The influence of wheat straw mulching and straw length on infiltration, runoff and soil loss. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Geng, J.; Wang, L. Key soil properties influencing infiltration capacity after long-term straw incorporation in a wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)–maize (Zea mays L.) rotation system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 344, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting rainfall erosion losses—A guide toconservation planning. In United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Handbook, No. 537; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting soil erosion by water, a guild to conservation planning with the revised universal soil loss equation (rusle). In United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Handbook, No. 703; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, T.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, B.; Han, Y.; Yao, S. Effects of size and amount and burial depth on early decomposition of maize straw and the links to microbial and nematode communities in the mollisol of china. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e70003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Chaudhary, A.; Ahlawat, O.P.; Naorem, A.; Upadhyay, G.; Chhokar, R.S.; Gill, S.C.; Khippal, A.; Tripathi, S.C.; Singh, G.P. Crop residue management challenges, opportunities and way forward for sustainable food-energy security in India: A review. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 228, 105641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, B.; Mao, J.; Sui, Y.; Cao, X. Structural convergence of maize and wheat straw during two-year decomposition under different climate conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7159–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorich, E.G.; Janzen, H.; Ellert, B.H.; Helgason, B.L.; Qian, B.; Zebarth, B.J.; Angers, D.A.; Beyaert, R.P.; Drury, C.F.; Duguid, S.D.; et al. Litter decay controlled by temperature, not soil properties, affecting future soil carbon. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Liang, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Rui, Y.; Xu, M.; Luo, Y. Long-term straw decomposition in agro-ecosystems described by a unified three-exponentiation equation with thermal time. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, M.; Yang, L.; Gu, X.; Jin, J.; Fu, M. Regulation of straw decomposition and its effect on soil function by the amount of returned straw in a cool zone rice crop system. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Chen, S. Soil surface roughness of sloping croplands affected by land degradation degree and residual of incorporated straw. Geoderma 2024, 444, 116872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hui, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, G. Rates of litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: Global patterns and controlling factors. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiura, M.; Wagai, R.; Hayashi, K. Optimal thermolysis conditions for soil carbon storage on plant residue burning: Modeling the trade-off between thermal decomposition and subsequent biodegradation. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, C.L.; Rickman, R.W. Estimating crop residue decomposition from air temperature, initial nitrogen content, and residue placement. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, E.C.; Parton, W.J.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Silver, W.L.; Harmon, M.E.; Hall, S.A.; Burke, I.C.; Hart, S.C. Simple three-pool model accurately describes patterns of long-term litter decomposition in diverse climates. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2636–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Teng, P.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Li, N. Decomposition and driving factor of organic materials in the black soil belt of northeast china. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2024, 40, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Song, M.; Han, M.; Li, Z. Prediction and evaluation of different crop straw decomposition laws and models. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2023, 37, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Z. Effects of warming on the decomposition rates of the straw of different crops in soils and modelling. J. Plant Nutr. Fertitizer 2021, 27, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Pan, H.; Lei, H.; Tong, W.; Shi, L.; Chen, H. Dissolved organic matter evolution and straw decomposition rate characterization under different water and fertilizer conditions based on three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum and deep learning. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.M.; Yu, W.T.; Ma, Q.; Xu, Y.G.; Zou, H. Alleviating global warming potential by soil carbon sequestration: A multi-level straw incorporation experiment from a maize cropping system in northeast china. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Guo, Z.; Li, D.; Hua, L.; Li, W. Cover-management impacts on runoff and sediment dynamics at different slope positions in northeast china. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 310, 109373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, G.; Xie, Y.; Dun, X.W.; Wang, D.A.; Zhang, S. Annual variation of ephemeral gully erosion in a cultivated catchment. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C. Temporal variation in soil erodibility indicators of sloping croplands with different straw-incorporation rates. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Duan, X. Productivity assessment for black soil region in northeastern china using black soil thickness a case study of hebei watershed. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 34, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhu, M.; Mady, A.Y.; Huang, M.; Yan, X.; Guo, T. Effects of different long-term fertilization and cropping systems on crop yield, water balance components and water productivity in dryland farming. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 292, 108689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM-Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows (Version 26.0) [Software]; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Ren, X.Y. Residue cover effects on soil erosion and the infiltration in black soil under simulated rainfall experiments. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifmanesh, H.; Deng, A.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Bao, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, W. How incorporation depth of corn straw affects straw decomposition rate and c&n release in the wheat-corn cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 300, 107000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Sanaullah, M.; Heitkamp, F.; Zelenev, V.; Kumar, A.; Blagodatskaya, E. Microbial decomposition of soil organic matter is mediated by quality and quantity of crop residues: Mechanisms and thresholds. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandick, A.K.; Dick, R.P. Field management effects on soil enzyme activities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Cao, Y.; Xie, W.; He, W.; Tian, X. Effects of maize straw returning on soil enzyme activity. J. Northwest Univ. Agric. For. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2015, 43, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, S.; Xu, Y.; Qin, X.; Tian, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Cao, Z.; Wang, D.; Wu, M.; Wu, Z.; et al. Building microbial consortia to enhance straw degradation, phosphorus solubilization, and soil fertility for rice growth. Microb. Cell Factories 2024, 23, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Chang, Z.; Huang, H.; Ye, X.; Ma, Y.; Qian, Y. Effect of microbial inoculants for straw decomposing on soil microorganisms and the nutrients. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 563–570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; Xu, X.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Zhang, S.; He, P. Change in straw decomposition rate and soil microbial community composition after straw addition in different long-term fertilization soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 138, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guo, X.; Lu, J.; Wan, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X. Decomposition characteristics of wheat straw and effects on soil biological properties and nutrient status under different rice cultivation. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Liu, S.; Ni, G.; Rong, Q.; Huang, H.; Zhou, C.; Yin, X. Effects of different soil moisture contents on rumen fluids in promoting straw decomposition after straw returning. Agronomy 2023, 13, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, C.; Yan, W.; Sun, N.; Zhao, H.; Feng, Y.; Tan, G.; Bian, S. The effect of irrigation quota on straw decomposition, nitrogen release, and maize nitrogen uptake. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharayil, N.; Suseela, V.; Triebwasser, D.J.; Preston, C.M.; Gerard, P.D.; Dukes, J.S. Changes in the structural composition and reactivity of Acer rubrum leaf litter tannins exposed to warming and altered precipitation: Climatic stress-induced tannins are more reactive. New Phytol. 2011, 191, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomberg, H.H.; Foster, G.R.; Steiner, J.L.; Stott, D.E. An improved temperature function for modeling crop residue decomposition. Trans. ASAE 2002, 45, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Han, X.; Wang, C.; Yan, J.; Lu, X.; Chen, X.; Zou, W. Temporal dynamics of density separated soil organic carbon pools as revealed by d13c changes under 17 years of straw return. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 356, 108656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, V.L.; Schmer, M.R.; Wienhold, B.J.; Stewart, C.E.; Varvel, G.E.; Sindelar, A.J.; Follett, R.F.; Mitchell, R.B.; Vogel, K.P. Twelve years of stover removal increases soil erosion potential without impacting yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2015, 79, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Song, K.; Zhu, B.; Tao, Z.; Wang, C.M. Changes in cropland soil color in northeast china’s black soils region over the past 30 years. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 254, 106750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Deng, N.; Song, Q.; Li, Z. Decomposing characteristics of maize straw returning in songnen plain in long-time located experiment. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Depth (cm) | BD (g cm−3) |
|---|---|
| 0–10 | 0.85 |
| 10–20 | 1.05 |
| 20–30 | 1.05 |
| 30–40 | 1.14 |
| 40–50 | 1.10 |
| Average BD (g cm−3) | 1.04 |
| 10 cm depth required fill soil weight for each cell (kg) | 127.92 |
| Landfill amounts (t ha−1) | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| 10 cm depth required straw air-dry weight for each cell (g) | 54 | 72 | 90 | 108 | 126 |
| Residue Cover (%) | Soil Loss Ratios (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Tilled Seedbed 1 | No-Till | |
| 20 | 48 | 34 |
| 30 | 37 | 26 |
| 40 | 30 | 21 |
| 50 | 22 | 15 |
| 60 | 17 | 12 |
| 70 | 12 | 8 |
| 80 | 7 | 5 |
| 90 | 4 | 3 |
| 95 | 3 | 2 |
| Source of Variation | df | F-Value | p-Value | Partial η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Landfill year | 3 | 609.34 | 0.00 | 0.90 |
| Landfill amount | 4 | 36.01 | 0.00 | 0.42 |
| Burial depth | 4 | 146.51 | 0.00 | 0.75 |
| Landfill year × Landfill amount | 12 | 2.93 | 0.00 | 0.15 |
| Landfill year × Burial depth | 12 | 8.93 | 0.00 | 0.35 |
| Landfill amount × Burial depth | 16 | 1.31 | 0.20 | 0.10 |
| Landfill year × Landfill amount × Burial depth | 48 | 1.56 | 0.02 | 0.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Chen, P.; Xie, Y.; Lin, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, G. Predicting Long-Term Maize Straw Decomposition from Incorporation Amount and Depth in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232448
Zhang R, Chen P, Xie Y, Lin H, Tang J, Liu G. Predicting Long-Term Maize Straw Decomposition from Incorporation Amount and Depth in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agriculture. 2025; 15(23):2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232448
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Peiyan Chen, Yun Xie, Honghong Lin, Jie Tang, and Gang Liu. 2025. "Predicting Long-Term Maize Straw Decomposition from Incorporation Amount and Depth in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China" Agriculture 15, no. 23: 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232448
APA StyleZhang, R., Chen, P., Xie, Y., Lin, H., Tang, J., & Liu, G. (2025). Predicting Long-Term Maize Straw Decomposition from Incorporation Amount and Depth in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. Agriculture, 15(23), 2448. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15232448




