Functional Prediction of Bacteria–Enzyme Co-Regulation on Rapeseed Straw Silage: Fermentation Quality and Fiber Degradation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Rapeseed Straw Raw Material
2.2. Analytical Methods for Silage Quality Assessment
2.3. Bacterial Community Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Impact of Additives on the Quality of Silage from Rapeseed Straw
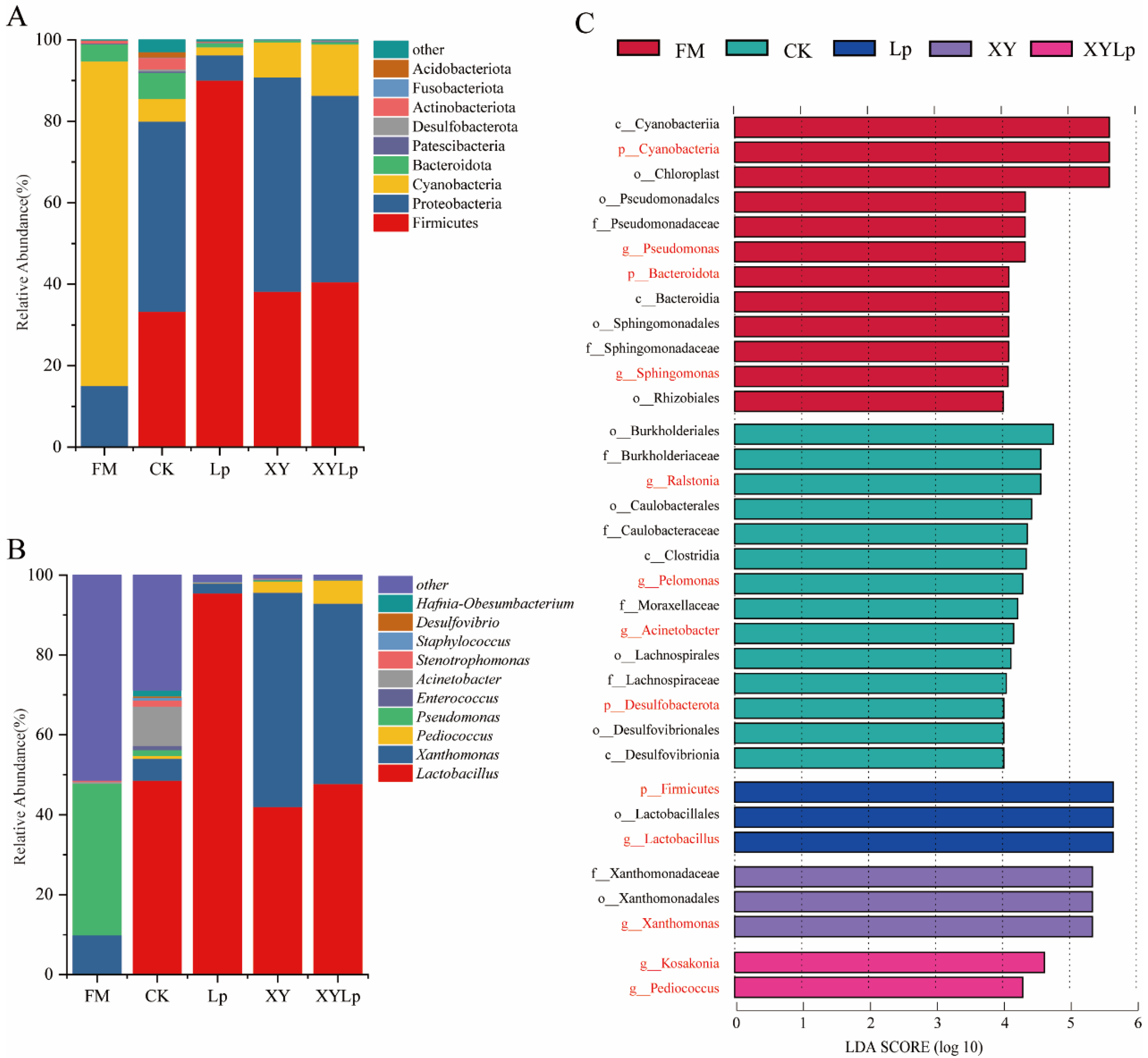
3.2. The Influence of Additives on the Microbial Consortia in Rapeseed Straw
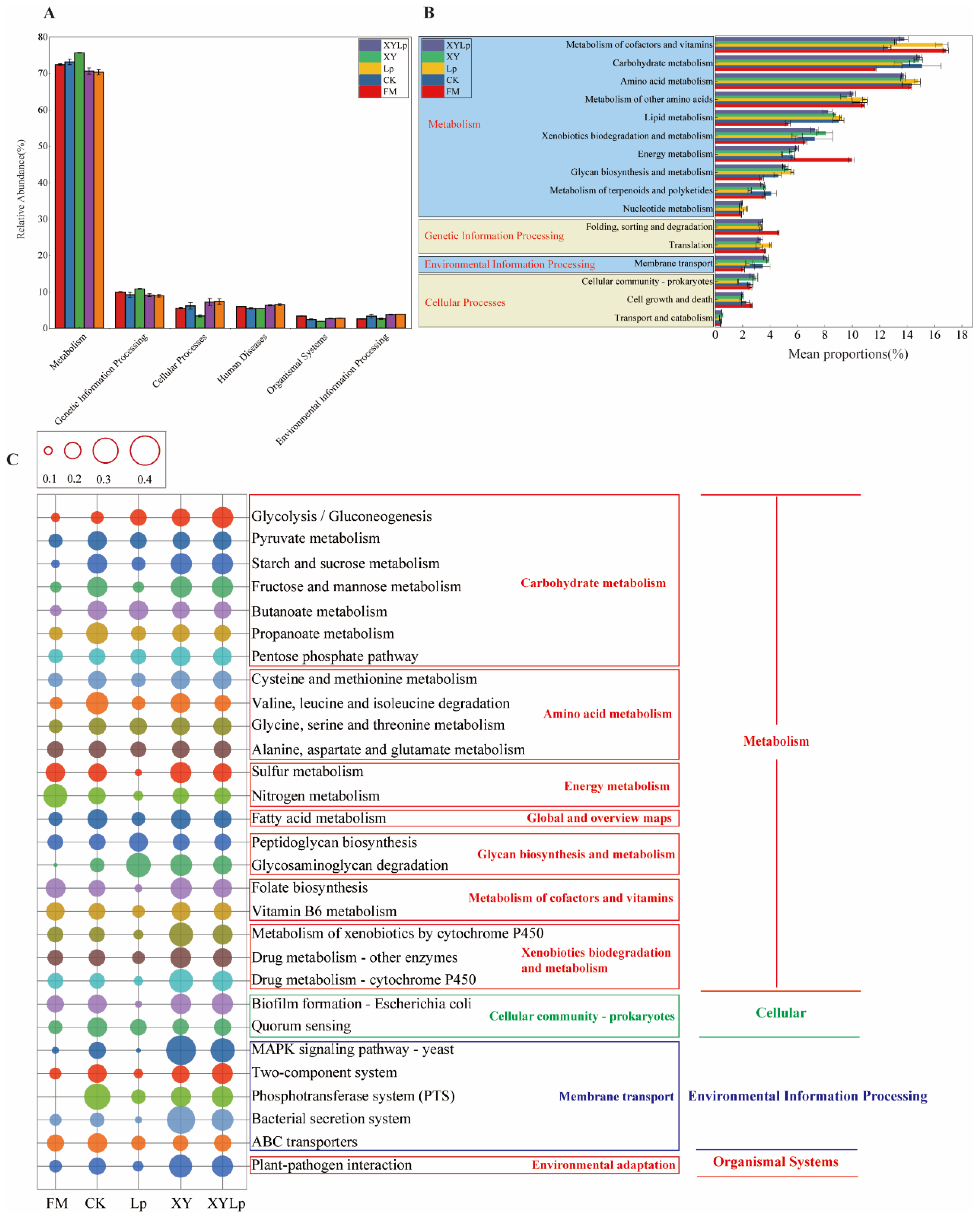
3.3. Bacterial Community Function Prediction Analysis
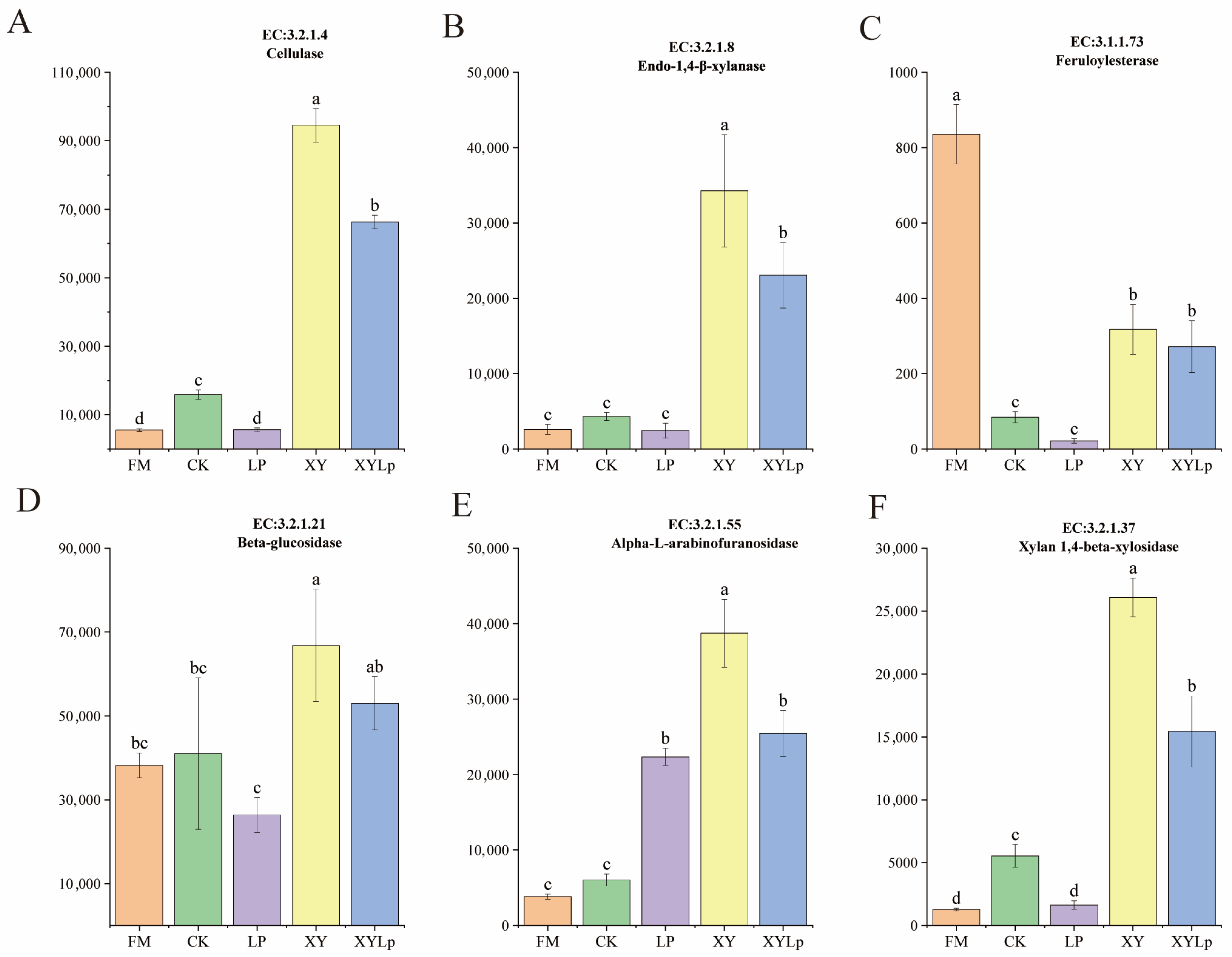
3.4. Enzyme Function Prediction of Microbial Communities Using the KEGG Database
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, L.-Y.; Mason, A.S.; Huang, C.-H. Research progress and strategies for multifunctional rapeseed: A case study of China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1673–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Cui, M.; Gao, D.; Yao, J.; Qi, Z. The Role of Rapeseed Straw in Soil Fertility and Crop Productivity. Mol. Soil Biol. 2024, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.W.; Gordon, A.H.; Lomax, J.A.; Chesson, A. Composition and rumen degradability of straw from three varieties of oilseed rape before and after alkali, hydrothermal and oxidative treatment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1987, 41, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.; Aldhalmi, A.K.; Abd El-Hack, M.E.; Elsherbeni, A.I.; Youssef, I.M.; Hussein, S.; Bai, B.; Xu, Z.; Hao, L.; Mahrose, K.M. Enhancing the Feed Efficiency of Crop Residues in Ruminants–A Comprehensive Review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2025, 25, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zuo, J. Nutritional and anti-nutritional composition of rapeseed meal and its utilization as a feed ingredient for animal. Agric. Food Sci. 2007, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Alegbeleye, O.O.; Strateva, M.; Stratev, D. Understanding spoilage microbial community and spoilage mechanisms in foods of animal origin. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 311–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svärd, A.; Brännvall, E.; Edlund, U. Rapeseed straw as a renewable source of hemicelluloses: Extraction, characterization and film formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Xu, L.; Jiang, C.; Xiao, Y. Novel strategy to understand the bacteria-enzyme synergy action regulates the ensiling performance of wheat straw silage by multi-omics analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 289, 138864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Feng, H.; Guo, G.; Huo, W.; Li, Q.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Chen, L. Effects of laccase and lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality, nutrient composition, enzymatic hydrolysis, and bacterial community of alfalfa silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1035942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, D.; Ge, Q.; Yang, B.; Li, S. Effects of harvest period and mixed ratio on the characteristic and quality of mixed silage of alfalfa and maize. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2023, 306, 115796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd-Setapar, S.; Abd-Talib, N.; Aziz, R. Review on crucial parameters of silage quality. APCBEE Procedia 2012, 3, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.G.; Murray, R. The volatility of components of grass silage on oven drying and the inter-relationship between dry-matter content estimated by different analytical methods. Grass Forage Sci. 2001, 56, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magomya, A.; Kubmarawa, D.; Ndahi, J.; Yebpella, G. Determination of plant proteins via the Kjeldahl method and amino acid analysis: A comparative study. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 3, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyang’au, J.O.; Møller, H.B.; Larsen, S.U.; Sørensen, P. Brown juice assisted ensiling of straw and press cake for enhanced biogas production and nutrient availability in digestates. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Du, S.; Ge, G.; Wan, T.; Jia, Y. Microbial community and fermentation characteristics of native grass prepared without or with isolated lactic acid bacteria on the Mongolian Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 731770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.A. An automated procedure for the determination of soluble carbohydrates in herbage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1977, 28, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of lactic acid bacteria and molasses additives on the microbial community and fermentation quality of soybean silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, Y.; Kong, X.; Dong, P.; Zhang, J. A reused method for molasses-processed wastewater: Effect on silage quality and anaerobic digestion performance of Pennisetum purpereum. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Guo, G.; Shao, T. Effects of applying lactic acid bacteria and propionic acid on fermentation quality, aerobic stability and in vitro gas production of forage-based total mixed ration silage in Tibet. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2019, 59, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinschmit, D.; Schmidt, R.; Kung, L., Jr. The effects of various antifungal additives on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, J.; Davies, D. The aerobic stability of silage: Key findings and recent developments. Grass Forage Sci. 2013, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, W.; Do Nascimento, W.; Magalhães, A.; Silva, D.; Silva, W.; Santana, A.; Soares, G. Nutritive value, total losses of dry matter and aerobic stability of the silage from three varieties of sugarcane treated with commercial microbial additives. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2015, 204, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, T.C.; da Silva, L.D.; Santos, E.M.; Oliveira, J.S.; Perazzo, A.F. Importance of the fermentation to produce high-quality silage. In Fermentation Processes; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, B.; Qiu, R.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Bao, J.; Sun, L.; Liu, T.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y. Effects of cellulase and lactic acid bacteria on ensiling performance and bacterial community of Caragana korshinskii silage. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y. Cellulase interacts with lactic acid bacteria to affect fermentation quality, microbial community, and ruminal degradability in mixed silage of soybean residue and corn stover. Animals 2021, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Xie, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Bao, J. Rapid prediction of acid detergent fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and acid detergent lignin of rice materials by near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Wang, J.; Lv, J.; Sun, X.; Kong, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Cao, Z.; Li, S. Comparison of ruminal degradability, indigestible neutral detergent fiber, and total-tract digestibility of three main crop straws with alfalfa hay and corn silage. Animals 2021, 11, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-J.G. Analysis of forage fiber and cell walls in ruminant nutrition. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 810S–813S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, J., Jr.; Van Soest, P.; Young, E. Comparative study of the digestibility of forage cellulose and hemicellulose in ruminants and nonruminants. J. Anim. Sci. 1969, 29, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yi, C.; Quan, K.; Lin, B. Chemical composition, structure, physicochemical and functional properties of rice bran dietary fiber modified by cellulase treatment. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effect of cellulase and Lactobacillus casei on ensiling characteristics, chemical composition, antioxidant activity, and digestibility of mulberry leaf silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9919–9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Synergistic Effects of Exogenous Lactobacillus plantarum and Fibrolytic Enzymes on Fermentation Quality, Fiber Degradation, and In Vitro Digestibility of Napiergrass (Pennisetum purpureum) Silage. Agronomy 2025, 15, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Ensiling as pretreatment of rice straw: The effect of hemicellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on hemicellulose degradation and cellulose conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. Dynamics of microbial community and fermentation quality during ensiling of sterile and nonsterile alfalfa with or without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gou, W.; Cheng, Q.; Bai, S.; Cai, Y. Silage fermentation and bacterial community of bur clover, annual ryegrass and their mixtures prepared with microbial inoculant and chemical additive. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 247, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Pang, H. Natural lactic acid bacteria population and silage fermentation of whole-crop wheat. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Sun, B. Effects of Cellulase, Lactobacillus plantarum, and Sucrose on Fermentation Parameters, Chemical Composition, and Bacterial Community of Hybrid Pennisetum Silage. Ferment.-Basel 2022, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Deng, M.; Tian, H.C.; Liu, D.W.; Li, Y.K.; Liu, G.B.; Sun, B.L.; Guo, Y.Q. Effects of Mulberry Leaves and Pennisetum Hybrid Mix-Silage on Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Community. Ferment.-Basel 2022, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.Z.; Na, N.; Wu, N.R.; Sun, L.; Li, Z.Q.; Qili, M.; Han, H.Y.; Xue, Y.L. Impact of Additives and Packing Density on Fermentation Weight Loss, Microbial Diversity, and Fermentation Quality of Rape Straw Silage. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda Ramulu, H.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D490–D495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Niu, H. Diversity of bacterial community during ensiling and subsequent exposure to air in whole-plant maize silage. Asian-Australasian J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ni, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Yang, F. Fermentation characteristics, chemical composition and microbial community of tropical forage silage under different temperatures. Asian-Australasian J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 32, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Tong, X.; Wang, S. Dynamic analysis of fermentation quality, microbial community, and metabolome in the whole plant soybean silage. Fermentation 2024, 10, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.; Pirttiniemi, J.; Tapio, I.; Rinne, M. Modulation of Bacterial Communities of Grass Silage by Additives, Compaction and Soil Contamination; Mendel University in Brno: Brno, Czech Republic, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, H.; Pan, G.; Yin, H.; Sun, J.; Yu, Z.; Bai, C.; Xue, Y. Effect of exogenous microorganisms on the fermentation quality, nitrate degradation and bacterial community of sorghum-sudangrass silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1052837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Ma, J.; Wu, H.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, K. Evaluation of pH regulation in carbohydrate-type municipal waste anaerobic co-fermentation: Roles of pH at acidic, neutral and alkaline conditions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 853, 158327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bao, J.; Zhao, M.; Si, Q.; Sun, P.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y. Effects of different types of LAB on dynamic fermentation quality and microbial community of native grass silage during anaerobic fermentation and aerobic exposure. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, G.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, T. Characteristics of isolated lactic acid bacteria and their effects on the silage quality. Asian-Australasian J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 30, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koc, F.; Aksoy, S.O.; Okur, A.A.; Celikyurt, G.; Korucu, D.; Ozduven, M. Effect of pre-fermented juice, Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus buchneri on the fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of high dry matter alfalfa bale silage. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2017, 27, 1426–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Alhaag, H.; Yuan, X.; Mala, A.; Bai, J.; Shao, T. Fermentation characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus species isolated from sweet sorghum silage and their application as silage inoculants. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, M.C.W.; Kuniyoshi, T.M.; Azevedo, P.; Vitolo, M.; Oliveira, R.P.S. Pediococcus spp.: An important genus of lactic acid bacteria and pediocin producers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, X. Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: Ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Usman, S.; Li, F.; Bai, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Lignocellulose conversion of ensiled Caragana korshinskii Kom. facilitated by Pediococcus acidilactici and cellulases. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.T.; Zhao, M.Q.; Sun, P.B.; Zhu, L.; Yan, X.Q.; Hao, J.F.; Si, Q.; Wang, Z.J.; Jia, Y.S.; Wang, M.J.; et al. Effects of different additives on fermentation characteristics, nutrient composition and microbial communities of Leymus chinensis silage. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.Q.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z.J.; Du, S.; Gao, C.P.; Nan, D.H.; Yan, X.Q.; Ge, G.T. Evaluation of the fermentation performance and functional properties of bacterial communities of amaranth silage supplemented with Limosilactobacillus fermentum and Latilactobacillus graminis. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemble, A.R. Studies on the nitrogen metabolism of the ensilage process. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1956, 7, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R. Factors influencing silage quality and their implications for management. J. Dairy Sci. 1988, 71, 2992–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Items | Content | SD |
|---|---|---|
| Dry matter (% of FM) | 55.26 | 1.53 |
| Crude protein (% of DM) | 3.26 | 0.22 |
| Acid detergent fiber (% of DM) | 32.40 | 1.32 |
| Neutral detergent fiber (% of DM) | 48.33 | 1.94 |
| Water-soluble carbohydrates (% of DM) | 4.64 | 0.15 |
| Lactic acid bacteria (log10 CFU/g FM) | 4.46 | 0.16 |
| Aerobic bacteria (log10 CFU/g FM) | 5.38 | 0.24 |
| Yeasts (log10 CFU/g FM) | 5.86 | 0.16 |
| Coliform bacteria (log10 CFU/g FM) | 6.63 | 0.26 |
| Mold (log10 CFU/g FM) | 6.75 | 0.22 |
| Items | CK | Lp | XY | XYLp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation quality | ||||
| pH | 5.40 ± 0.17 a | 4.27 ± 0.04 c | 4.79 ± 0.08 b | 4.52 ± 0.11 bc |
| Lactic acid (% of DM) | 1.35 ± 0.06 c | 1.84 ± 0.07 a | 1.59 ± 0.03 b | 1.77 ± 0.08 a |
| Acetic acid (% of DM) | 1.06 ± 0.02 a | 0.76 ± 0.05 b | 1.09 ± 0.11 a | 1.01 ± 0.05 a |
| Chemical compositions | ||||
| Dry matter (%) | 40.22 ± 0.69 | 41.78 ± 1.17 | 41.84 ± 0.94 | 41.44 ± 0.61 |
| Crude protein (% of DM) | 5.02 ± 0.10 b | 5.65 ± 0.44 a | 5.30 ± 0.12 a | 5.42 ± 0.34 a |
| ADF (% of DM) | 15.25 ± 0.60 a | 13.02 ± 0.83 ab | 12.56 ± 1.63 ab | 10.31 ± 0.28 b |
| NDF (% of DM) | 45.27 ± 1.28 a | 45.06 ± 0.87 a | 44.50 ± 2.79 a | 42.18 ± 0.94 b |
| Cellulose (% of DM) | 16.49 ± 1.85 b | 17.75 ± 2.16 a | 12.20 ± 0.57 b | 13.78 ± 0.70 b |
| Hemicellulose (% of DM) | 16.00 ± 1.50 a | 8.63 ± 1.03 a | 10.22 ± 1.26 b | 9.20 ± 2.28 b |
| Holocellulose (% of DM) | 32.49 ± 1.81 b | 33.37 ± 2.29 a | 21.42 ± 1.28 c | 23.99 ± 1.63 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Sun, L.; Dong, H.; Song, W.; Han, Z.; Zong, S.; Zhou, X.; Du, S.; Jia, Y.; Wang, S. Functional Prediction of Bacteria–Enzyme Co-Regulation on Rapeseed Straw Silage: Fermentation Quality and Fiber Degradation. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222398
Xiao Y, Sun L, Dong H, Song W, Han Z, Zong S, Zhou X, Du S, Jia Y, Wang S. Functional Prediction of Bacteria–Enzyme Co-Regulation on Rapeseed Straw Silage: Fermentation Quality and Fiber Degradation. Agriculture. 2025; 15(22):2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222398
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yanzi, Lin Sun, He Dong, Weiqiang Song, Zhaorui Han, Sen Zong, Xingzhao Zhou, Shuai Du, Yushan Jia, and Siran Wang. 2025. "Functional Prediction of Bacteria–Enzyme Co-Regulation on Rapeseed Straw Silage: Fermentation Quality and Fiber Degradation" Agriculture 15, no. 22: 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222398
APA StyleXiao, Y., Sun, L., Dong, H., Song, W., Han, Z., Zong, S., Zhou, X., Du, S., Jia, Y., & Wang, S. (2025). Functional Prediction of Bacteria–Enzyme Co-Regulation on Rapeseed Straw Silage: Fermentation Quality and Fiber Degradation. Agriculture, 15(22), 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222398








