Lab- and Pilot-Scale Effects of Spirulina (Limnospira sp.) Biomass Produced from Brewery Wastewater Treatment as a Biofertilizer for Barley (Hordeum vulgare) in Passo Fundo, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microalgae-Based Biofertilizer
2.2. Soil Characterization
2.3. Lab-Scale Barley Cultivation and Characterization
2.4. Pilot-Scale Barley Cultivation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Granulometry and Composition
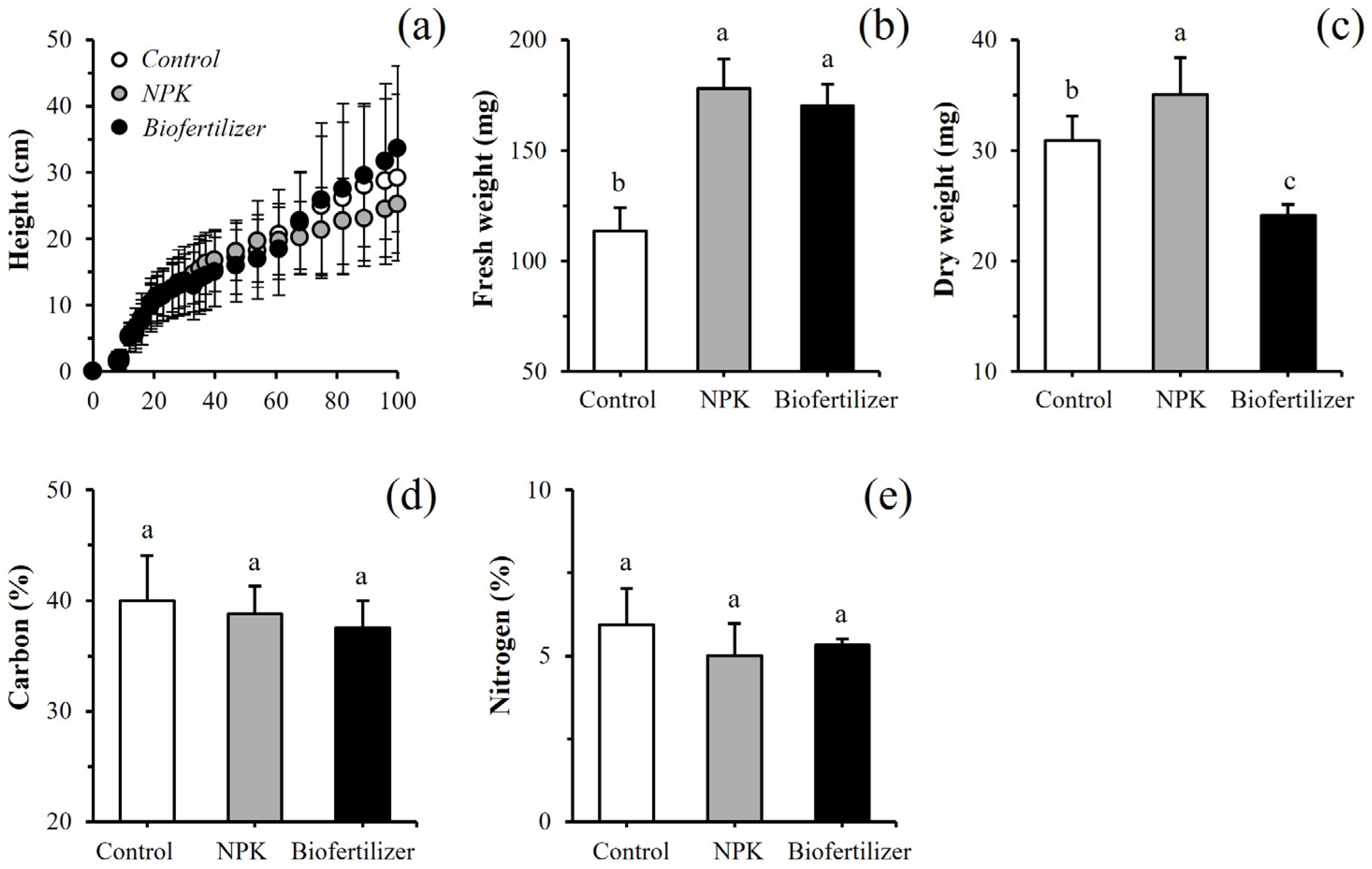
3.2. Lab-Scale Barley Growth and Composition
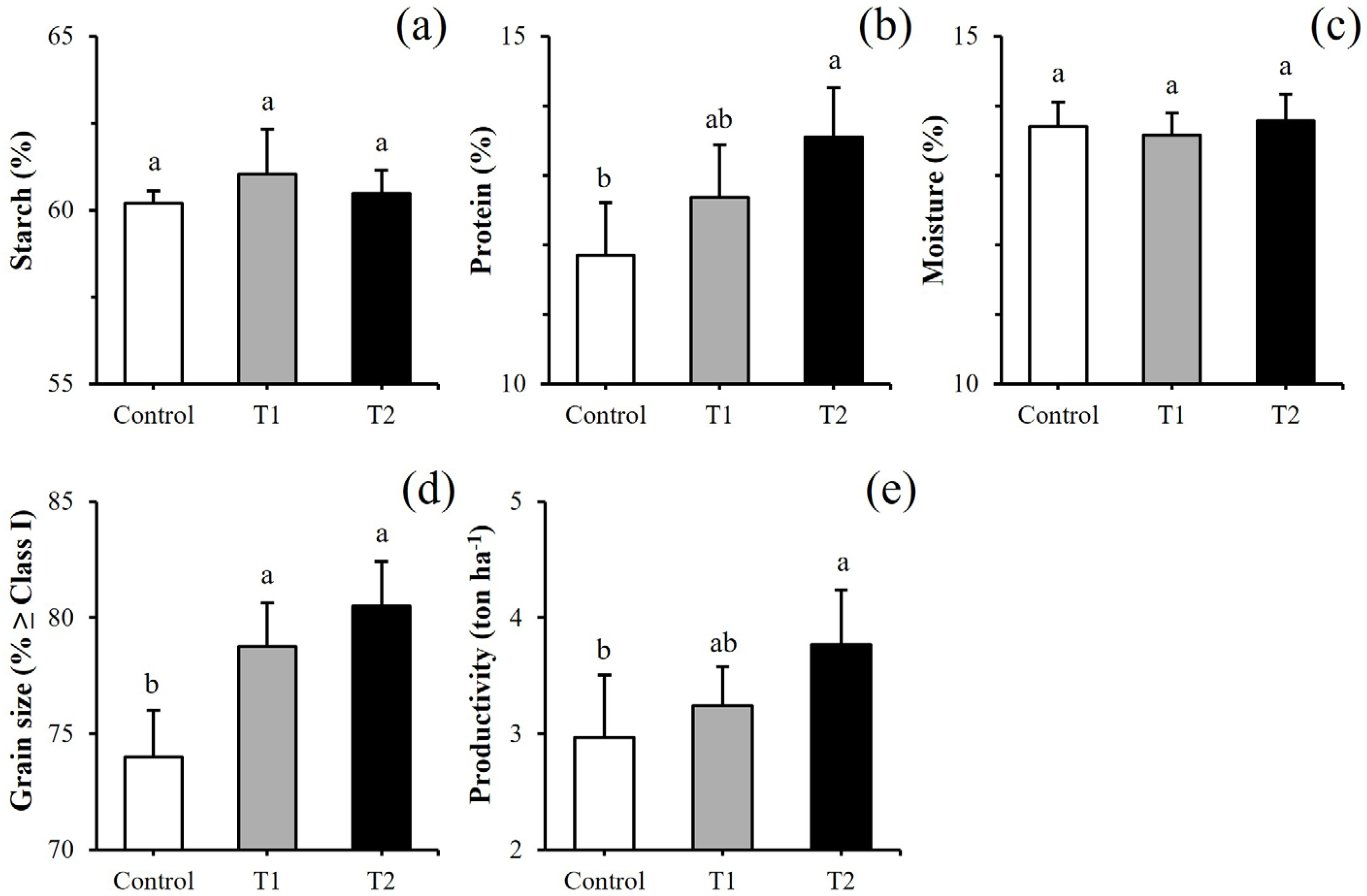
3.3. Pilot-Scale Growth and Composition of Barley Using Limnospira sp.-Based Biofertilizer for Base and/or Top Dressing
4. Discussion
4.1. Passo Fundo Soil Under Controlled Conditions (Lab-Scale Trials)
4.2. Limnospira sp.-Based Biofertilization in the Field (Pilot-Scale Trials)
4.3. Microalgae Wastewater Treatment and Safe Use of the Biomass
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samoraj, M.; Chojnacka, K.; Skrzypczak, D.; Mikula, K.; Mironiuk, M.; Calis, D. Microalgae as Biobased Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture. In Advances in Sustainable Applications of Microalgae; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 263–281. ISBN 978-0-443-22127-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rouphael, Y.; Colla, G. Toward a Sustainable Agriculture Through Plant Biostimulants: From Experimental Data to Practical Applications. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arahou, F.; Lijassi, I.; Wahby, A.; Rhazi, L.; Arahou, M.; Wahby, I. Spirulina-Based Biostimulants for Sustainable Agriculture: Yield Improvement and Market Trends. Bioenergy Res. 2023, 16, 1401–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisti, Y. Biodiesel from Microalgae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2007, 25, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borowitzka, M.A. High-Value Products from Microalgae—Their Development and Commercialisation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieti, M.G.; Petrucciani, A.; Mollo, L.; Gerotto, C.; Eusebi, A.L.; Fatone, F.; Norici, A.; González-Camejo, J. Acclimated Green Microalgae Consortium to Treat Sewage in an Alternative Urban WWTP in a Coastal Area of Central Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 945, 174056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.C.; Ghazaryan, L.; Poodiack, B.; Zorin, B.; Gross, A.; Gillor, O.; Khozin-Goldberg, I.; Gelfand, I. The Effects of Microalgae-Based Fertilization of Wheat on Yield, Soil Microbiome and Nitrogen Oxides Emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Using Microalgae to Reduce the Use of Conventional Fertilizers in Hydroponics and Soil-Based Cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, A.K.A.; Lourenço, K.S.; Clark, C.; Luz, R.L.; Da Silva, G.H.R.; Vet, L.E.M.; Cantarella, H.; Fernandes, T.V.; Kuramae, E.E. From Toilet to Agriculture: Fertilization with Microalgal Biomass from Wastewater Impacts the Soil and Rhizosphere Active Microbiomes, Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Plant Growth. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, M.; Swain, D.K.; Sen, R. Strategic Valorization of De-Oiled Microalgal Biomass Waste as Biofertilizer for Sustainable and Improved Agriculture of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Crop. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 682, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, E.; Ripa, M.; Catone, C.M.; Ulgiati, S. A Review about Microalgae Wastewater Treatment for Bioremediation and Biomass Production—A New Challenge for Europe. Environments 2021, 8, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Wei, L.; Xiong, Q.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Lv, S.; Zhou, W. Use of microalgae based technology for the removal of antibiotics from wastewater: A review. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hena, S.; Gutierrez, L.; Crou’e, J.P. Removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) from wastewater using microalgae: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillas-España, A.; López-Serna, R.; Rodríguez Chikri, L.Y.; Jiménez, J.J.; Lafarga, T.; Uggetti, E.; Acién, G.; González-López, C.V. Microalgae Wastewater Treatment: Pharmaceutical Removal and Biomass Valorization. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 380, 124942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarga, T.; Fernández-Sevilla, J.M.; González-López, C.; Acién-Fernández, F.G. Spirulina for the Food and Functional Food Industries. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dineshbabu, G.; Goswami, G.; Kumar, R.; Sinha, A.; Das, D. Microalgae–Nutritious, Sustainable Aqua- and Animal Feed Source. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 62, 103545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirne-Santos, C.C.; Barros, C.S.; Da Silva, A.C.R.; Kurpan, D.; Da Silva Cunha Oliveira, W.; Vasconcellos, B.M.; De Palmer Paixão, I.C.N.; Moreira, M.F.; Do Valle, A.F. Arthrospira maxima Extract Prevents and Cures Zika Virus Infection: In Vitro Analysis with VERO Cells. Algal Res. 2024, 79, 103479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Araújo, S.P.; De Assis, L.C.; Kurpan, D.; Telles, M.; De Carvalho, A.G.A.; Carneiro, G.R.A.; Nogueira, F.C.S.; Santos, P.; Barbarino, E.; Torres, A.G.; et al. Screening Microalgae Strains for Fish Feed of Juvenile Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and Their Zootechnical Performance. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 2665–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Encinas, J.P.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Juárez, J.; Ornelas-Paz, J.D.J.; Del Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Márquez-Ríos, E. Proteins from Microalgae: Nutritional, Functional and Bioactive Properties. Foods 2025, 14, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima E Silva, A.; Kurpan, D.; Ribeiro De Moura, M.; Costa Dos Santos, A.; De Souza Silva, T.; De Lemos Novo, B.; De Oliveira Santo, I.; Balata, L.Q.; Carvalho De Assis, L.; Barbarino, E.; et al. Bioremediation of Brewery Wastewater Using Arthrospira sp.: Preliminary Assessment of Biomass as a Biofertilizer toward Circular Economy. J. Appl. Phycol. 2025, 37, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, A.; Marsaro Júnior, A.L.; Pasinato, A.; Vilarinho, A.A.; do Amaral, A.J.; Sbalcheiro, C.C.; Lau, D.; da Cunha, G.R.; Maciel, J.L.N.; Denardim, J.E.; et al. Indicações Técnicas Para a Produção de Cevada Cervejeira Nas Safras de 2023 e 2024. In 33a Reunião Nacional de Pesquisa de Cevada; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2023; Volume 33, pp. 9–88. ISBN 978-65-89957-76-8. [Google Scholar]
- ICDD. PDF-2 2025 Phase Identification + Value. 2022. Available online: https://www.icdd.com/pdf-2/#1510774252214-10a99f93-2ae1e7b3-24d8 (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- EBC. Analytica, Analytica EBC Methods. 1997. Available online: https://brewup.eu/ebc-analytica (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- INMETRO. Orientação Sobre Validação de Métodos Analíticos. 2020. Available online: https://www.gov.br/cdtn/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/documentos-cgcre-abnt-nbr-iso-iec-17025/doq-cgcre-008/view (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Jurado-Flores, A.; Heredia-Martínez, L.G.; Torres-Cortes, G.; Díaz-Santos, E. Harnessing microalgae and cyanobacteria for sustainable agriculture: Mechanistic insights and applications as biostimulants, biofertilizers, and biocontrol agents. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mógor, Á.F.; De Oliveira Amatussi, J.; Mógor, G.; Bocchetti De Lara, G. Bioactivity of Cyanobacterial Biomass Related to Amino Acids Induces Growth and Metabolic Changes on Seedlings and Yield Gains of Organic Red Beet. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2018, 09, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, H.M.; Marrez, D.A.; Salama, A.B.; Wahba, H.E.; Khalid, K.A. Growth and Chemical Constituents of Cardoon Plant in Response to Foliar Application of Various Algal Extracts. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, K.V.; Buneshree, B.; Balasubramanian, P. Efficacy of Microalgal Extracts as Biostimulants through Seed Treatment and Foliar Spray for Tomato Cultivation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytryk, A.; Samoraj, M.; Moustakas, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A.; Chojnacka, K. Bioactive Fatty Acids and Compounds from Spirulina (Arthrospira) platensis: Potential as Biostimulants for Plant Growth. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 30, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaró, S.; Acién, G.; Alarcón, J.; Ruiz, Á.; Rodríguez-Chikri, L.; Viviano, E.; Lafarga, T. A Zero-Waste Approach for the Production and Use of Arthrospira platensis as a Protein Source in Foods and as a Plant Biostimulant in Agriculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 2619–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akgül, F. Effect of Spirulina platensis (Gomont) Geitler Extract on Seed Germination of Wheat and Barley. Alınteri J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 34, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, G.A.; Rocha, R.H.C.; Araújo, J.L.; Lima, J.F.; Guedes, W.A. Growth, Yield, and Postharvest Quality in Eggplant Produced under Different Foliar Fertilizer (Spirulina platensis) Treatments. Softw. Compos. Anal. 2016, 37, 3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, B.M.; Gómez-Serrano, C.; Acién-Fernández, F.G.; Jimenez-Becker, S. Effect of Microalgae Hydrolysate Foliar Application (Arthrospira platensis and Scenedesmus sp.) on Petunia x hybrida Growth. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2359–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodosio, A.E.M.D.M.; Araujo, R.H.C.R.; Lima, J.F.D.; Onias, E.A.; Ferreira, A.P.N.; Santos, B.G.F.L.; Rodrigues, M.H.B.S.; Oliveira, L.M.D.; Oliveira, Á.M.F.D.; Medeiros, M.L.D.S.; et al. Effect of the Biodegradable Coatings the Base on Microalgae and Oil of the Seed of the Pomegranate in the Conservation Powder-Crop of the Papaya ‘Golden’. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAGB. Barley Requirements. 2025. Available online: https://www.ukmalt.com/uk-malting-industry/barley-requirements/ (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Rani, H.; Bhardwaj, R.D. Quality Attributes for Barley Malt: “The Backbone of Beer”. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 3322–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, A.; Zannini, E.; Sahin, A.W.; Arendt, E.K. Barley Protein Properties, Extraction and Applications, with a Focus on Brewers’ Spent Grain Protein. Foods 2021, 10, 1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Gallaghar, E. Barley for Brewing: Characteristic Changes during Malting, Brewing and Applications of Its By-Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagles, H.; Bedggood, A.; Panozzo, J.; Martin, P. Cultivar and Environmental Effects on Malting Quality in Barley. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiki, S.Y.A.; Mofijur, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Ahmed, S.F.; Inayat, A.; Kusumo, F.; Badruddin, I.A.; Khan, T.M.Y.; Nghiem, L.D.; Ong, H.C.; et al. Microalgae Biomass as a Sustainable Source for Biofuel, Biochemical and Biobased Value-Added Products: An Integrated Biorefinery Concept. Fuel 2022, 307, 121782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuang, S.C.; Khin, M.C.; Chua, P.Q.D.; Luo, Y.D. Use of Spirulina Biomass Produced from Treatment of Aquaculture Wastewater as Agricultural Fertilizers. Algal Res. 2016, 15, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Oxides | Composition (%) |
|---|---|
| SiO2 | 40.5 |
| Al2O3 | 17.9 |
| Fe2O3 | 17.0 |
| K2O | 7.00 |
| TiO2 | 3.70 |
| MgO | 0.32 |
| CaO | 0.32 |
| P2O5 | 0.21 |
| MnO | 0.17 |
| SO3 | <0.1 |
| ZrO2 | <0.1 |
| LOI * | 12.7 |
| Treatment | Macrominerals (g kg−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca | Mg | Na | K | P | |
| Control | 6.16 ± 2.39 | 1.90 ± 0.36 | 2.61 ± 1.42 | 44.09 ± 9.57 | 2.52 ± 0.82 |
| NPK | 4.28 ± 1.16 | 2.03 ± 0.06 | 3.31 ± 0.83 | 49.60 ± 5.81 | 2.17 ± 0.87 |
| Biofertilizer | 8.50 ± 3.44 | 2.35 ± 0.35 | 3.52 ± 0.35 | 32.86 ± 15.6 | 2.48 ± 1.02 |
| Treatment | Trace Minerals | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe (g kg−1) | Zn (ppm) | Cr (ppm) | Cu (ppm) | Mn (ppm) | |
| Control | 1.39 ± 0.70 | 43.22 ± 4.19 | 34.31 ± 7.61 | <LOD * | 63.20 ± 35.18 |
| NPK | 1.56 ± 0.74 | 761.33 ± 913.98 | 32.07 ± 4.75 | <LOD * | 122.19 ± 68.04 |
| Biofertilizer | 1.36 ± 0.52 | 56.65 ± 28.57 | 32.89 ± 7.88 | <LOD * | 103.21 ± 17.20 |
| Treatment | Toxic Elements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al (g kg−1) | As (ppm) | Cd (ppm) | Sn (ppm) | Hg (ppm) | |
| Control | 1.29 ± 0.78 | 9.17 ± 0.92 | <LOD * | 19.70 ± 0.00 | <LOD * |
| NPK | 1.46 ± 0.65 | <LOD * | <LOD * | 9.29 ± 0.38 | <LOD * |
| Biofertilizer | 1.26 ± 0.72 | 13.9 ± 6.08 | <LOD * | 18.45 ± 12.51 | <LOD * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lima e Silva, A.; Kurpan, D.; dos Santos, A.C.; Silva, T.d.S.; Santo, I.d.O.; de Oliveira, V.R.L.; Novo, B.d.L.; de Assis, L.C.; Amario, M.; Ribeiro, R.d.O.; et al. Lab- and Pilot-Scale Effects of Spirulina (Limnospira sp.) Biomass Produced from Brewery Wastewater Treatment as a Biofertilizer for Barley (Hordeum vulgare) in Passo Fundo, Brazil. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222397
Lima e Silva A, Kurpan D, dos Santos AC, Silva TdS, Santo IdO, de Oliveira VRL, Novo BdL, de Assis LC, Amario M, Ribeiro RdO, et al. Lab- and Pilot-Scale Effects of Spirulina (Limnospira sp.) Biomass Produced from Brewery Wastewater Treatment as a Biofertilizer for Barley (Hordeum vulgare) in Passo Fundo, Brazil. Agriculture. 2025; 15(22):2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222397
Chicago/Turabian StyleLima e Silva, Arthur, Daniel Kurpan, Arthur Costa dos Santos, Thalia de Souza Silva, Isadora de Oliveira Santo, Victor Rafael Leal de Oliveira, Bruna de Lemos Novo, Layon Carvalho de Assis, Michelle Amario, Raphael de Oliveira Ribeiro, and et al. 2025. "Lab- and Pilot-Scale Effects of Spirulina (Limnospira sp.) Biomass Produced from Brewery Wastewater Treatment as a Biofertilizer for Barley (Hordeum vulgare) in Passo Fundo, Brazil" Agriculture 15, no. 22: 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222397
APA StyleLima e Silva, A., Kurpan, D., dos Santos, A. C., Silva, T. d. S., Santo, I. d. O., de Oliveira, V. R. L., Novo, B. d. L., de Assis, L. C., Amario, M., Ribeiro, R. d. O., Braz, B. F., Cincotto, F. H., Santelli, R. E., Barbarino, E., Nunes, R. d. O., Perrone, D., Teixeira, R. S. S., Bertolino, L. C., Freire, D. M. G., & Valle, A. F. d. (2025). Lab- and Pilot-Scale Effects of Spirulina (Limnospira sp.) Biomass Produced from Brewery Wastewater Treatment as a Biofertilizer for Barley (Hordeum vulgare) in Passo Fundo, Brazil. Agriculture, 15(22), 2397. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222397







