Response of Maize Yield and Water Productivity to Different Long-Term Fertilization Strategies in Semi-Arid Regions in Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Maize Yield
2.3.2. Soil Bulk Density
2.3.3. Soil Water Storage Before Sowing and After Harvesting and Water Consumption During the Growth Period
2.3.4. Maize Water Productivity (WP)
2.3.5. Soil Organic Carbon (SOC)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
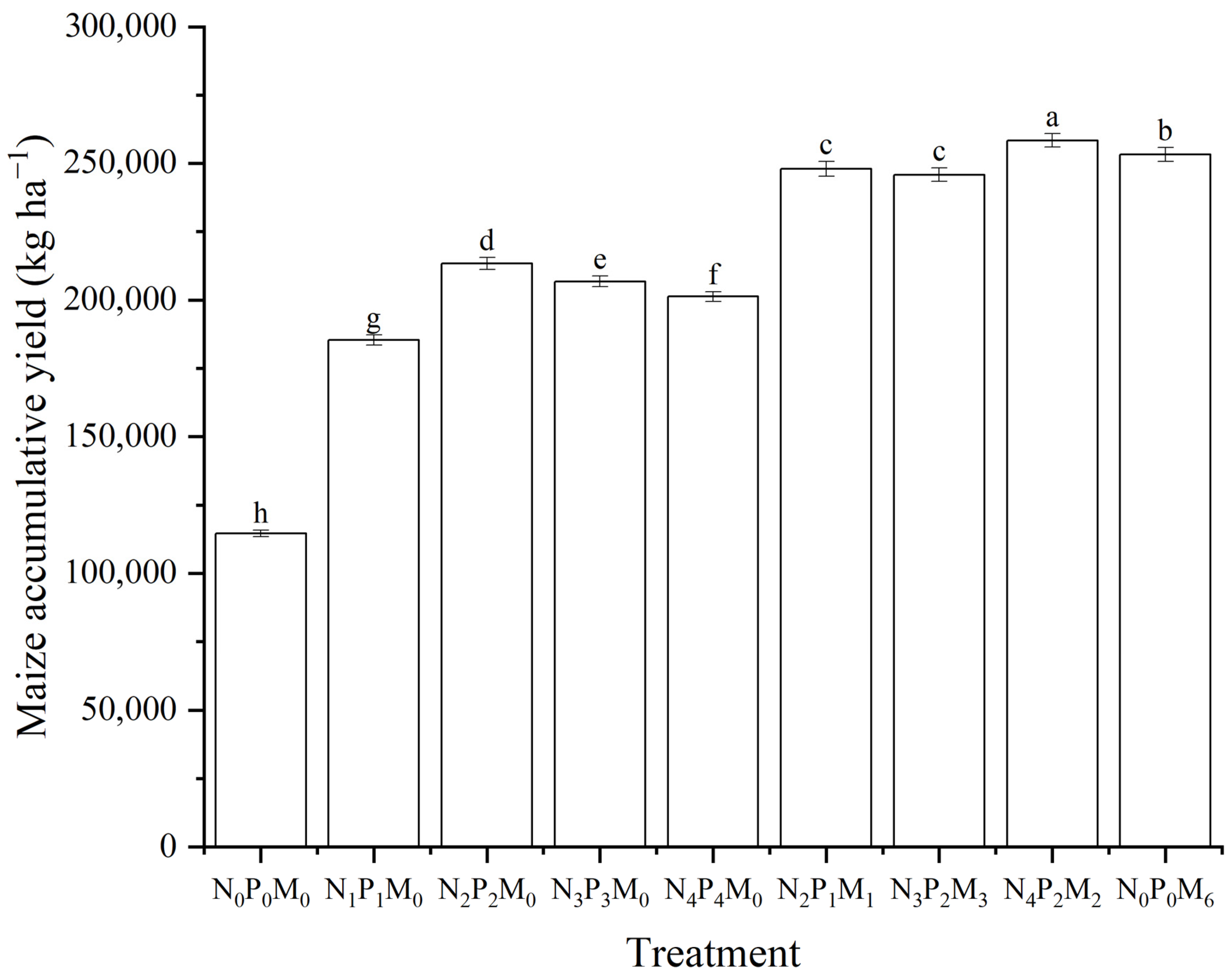
3.1. Effect of Fertilization on Maize Yield
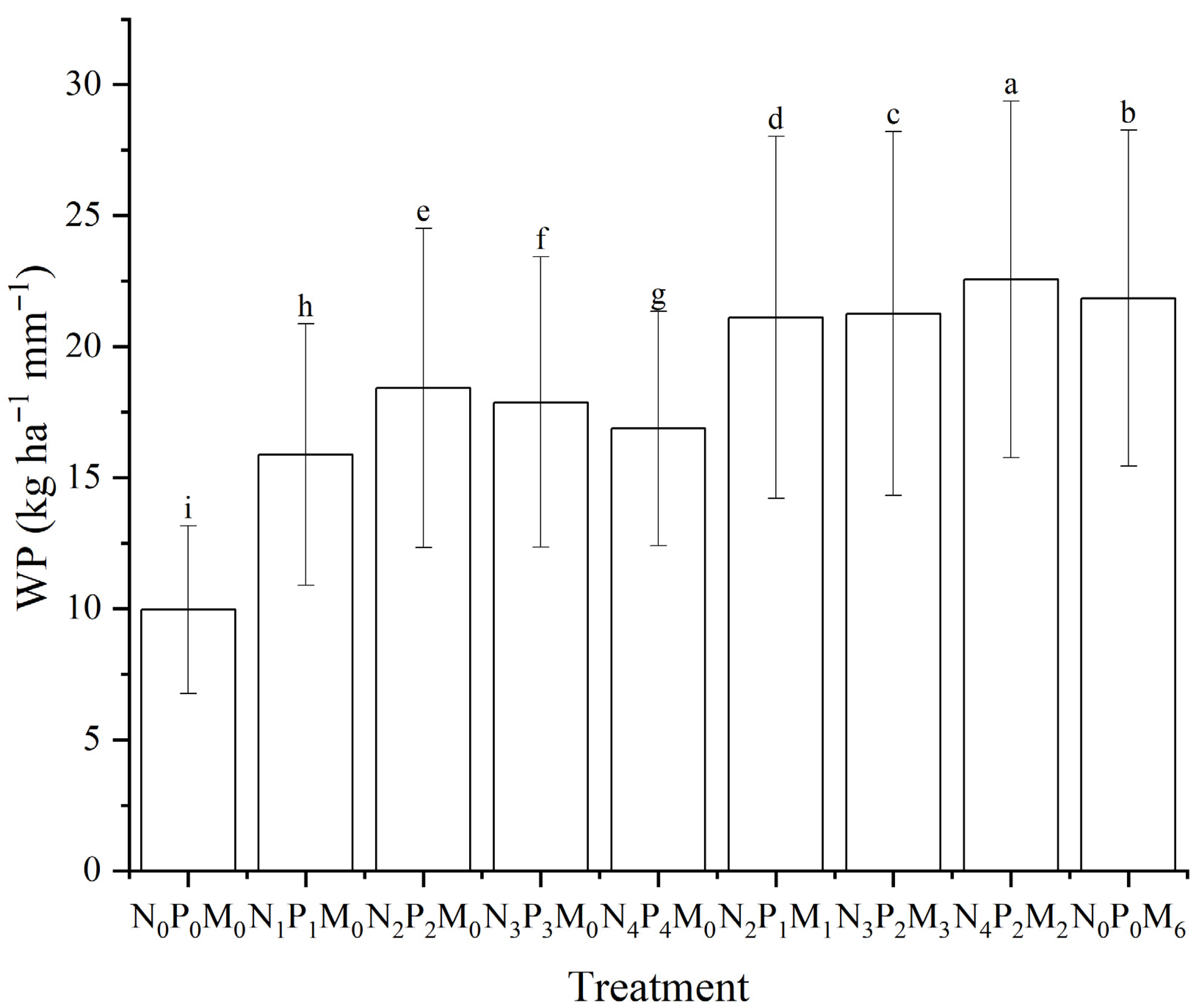
3.2. Effect of Fertilization on WP
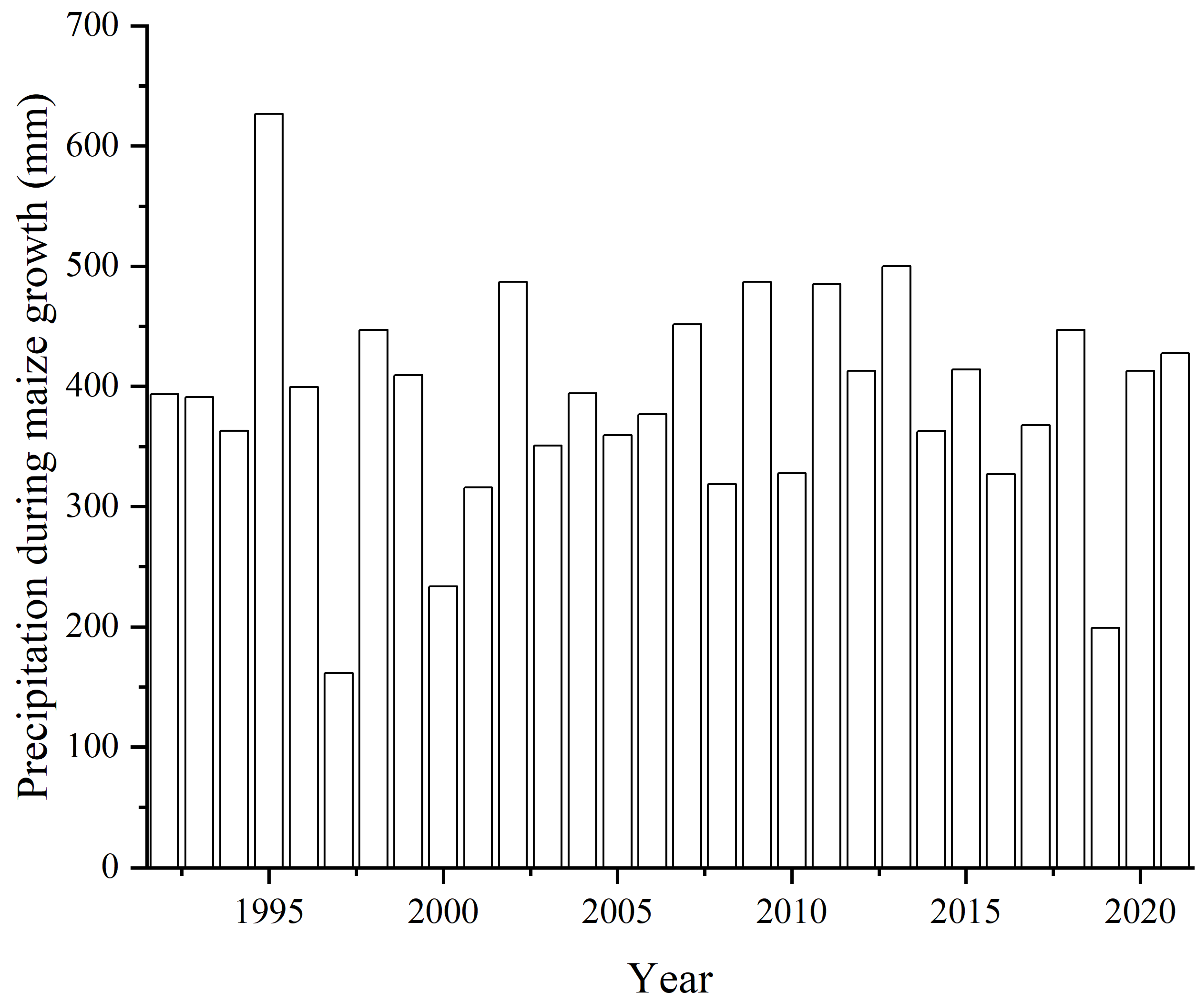
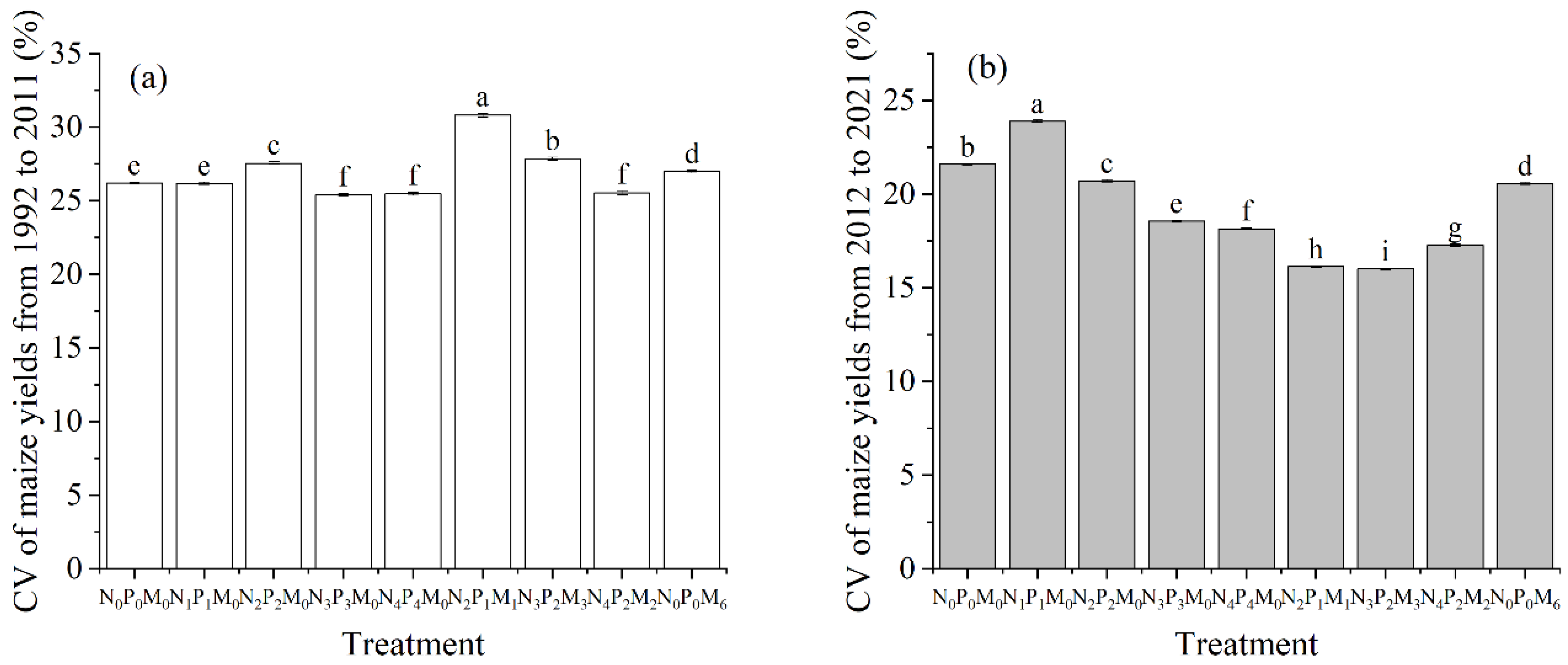
3.3. Effect of Fertilization and Precipitation on Yield and WP
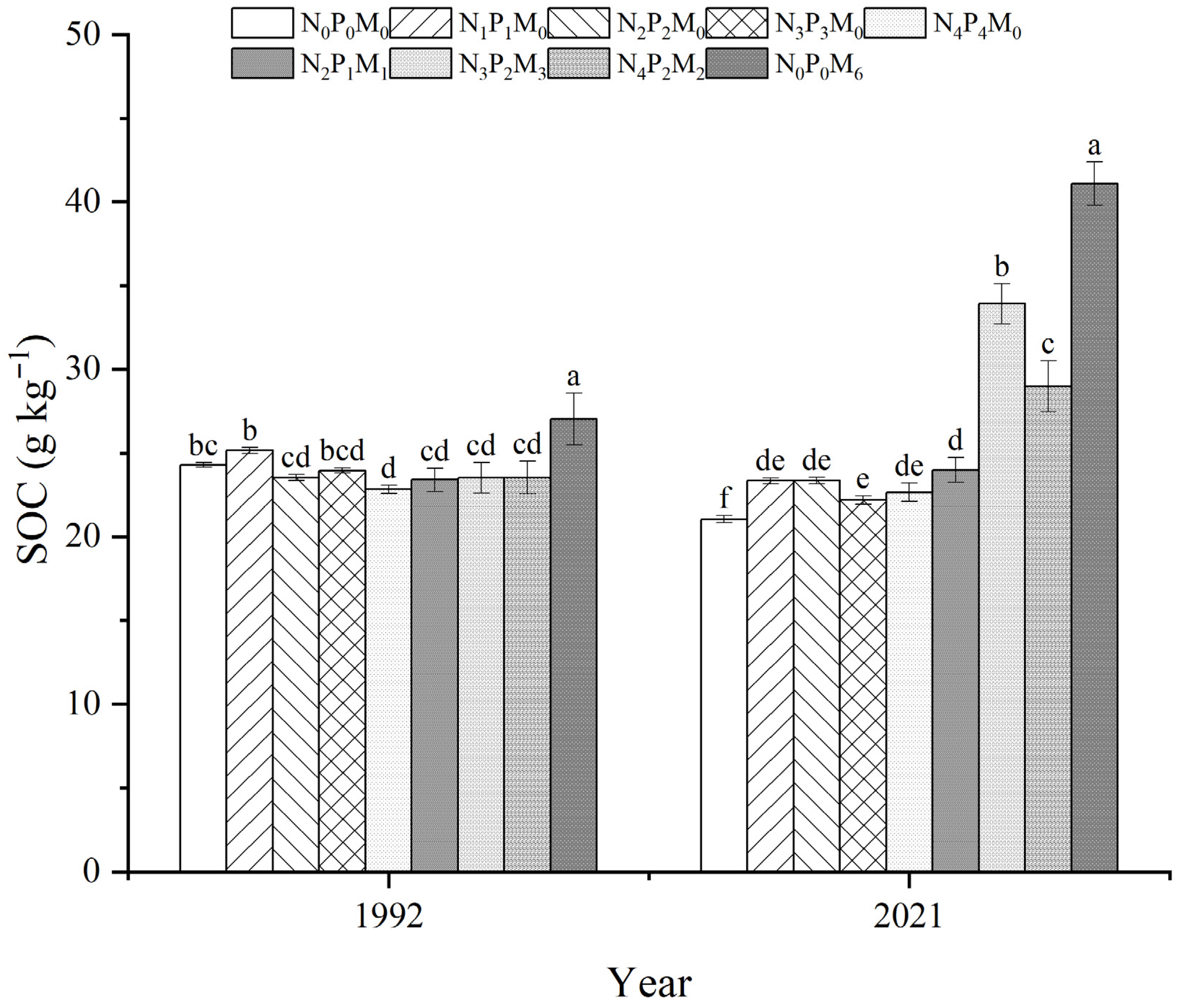
3.4. Effect of Fertilization on SOC
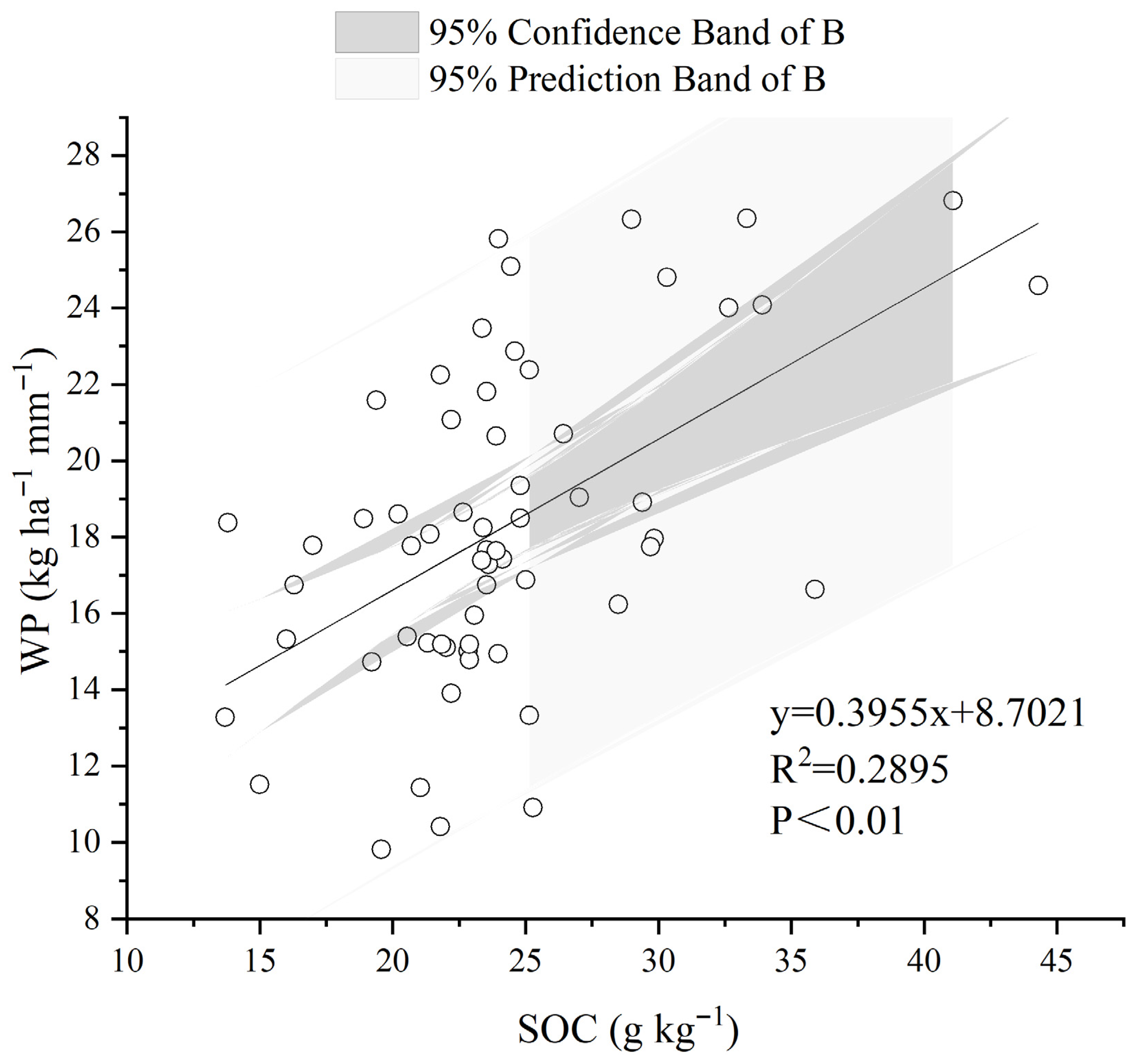
3.5. Correlations Among Maize Yield, WP, SOC, and Water Consumption During Growth
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Fertilization on Maize Yield
4.2. Effect of Fertilization on WP
4.3. Effect of Precipitation on Maize Yield
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Malhi, S.S.; Li, S.Q.; Gao, Y.J.; Tian, X.H. Nutrient and water management effects on crop production, and nutrient and water use efficiency in dryland areas of China. Adv. Agron. 2009, 102, 223–265. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Du, Y.; Chen, P.; Hu, H. Evapotranspiration, water use efficiency, and yield for film mulched maize under different nitrogen-fertilization rates and climate conditions. Agric. Water. Manag. 2024, 301, 108935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Zhu, H.; Dang, T.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Hao, M.; Li, Y.; Syers, J.K. Winter wheat grain yield associated with precipitation distribution under long-term nitrogen fertilization in the semiarid Loess Plateau in China. Geoderma 2012, 189–190, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, X.; Xie, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xu, M. Response of maize yield and water efficiency to long-term fertilization patters in dryland of Shanxi Province. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2023, 41, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Celik, I.; Gunal, H.; Budak, M.; Akpinar, C. Effects of long-term organic and mineral fertilizers on bulk density and penetration resistance in semi-arid Mediterranean soil conditions. Geoderma 2010, 160, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhang, T.; Yan, S.; Wang, C.; Dong, Q.G.; Feng, H.; Zhang, T.; Kisekka, I. Organic substitution improves soil structure and water and nitrogen status to promote sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) growth in an arid saline area. Agric. Water. Manag. 2023, 283, 108320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, S.Q.; Gao, Y.J. Effect of nitrogen fertilization under plastic mulched and non-plastic mulched conditions on water use by maize plants in dryland areas of China. Agric. Water. Manag. 2015, 162, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Kong, T.; Xie, J.; Yang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, Z. Appropriate water and fertilizer supply can increase yield by promoting growth while ensuring the soil ecological environment in melon production. Agric. Water. Manag. 2023, 289, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, M.; Yao, H.; Lv, L.; Shen, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Y.; et al. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic fertilizer benefits grain yield, water use efficiency, and economic return of summer maize. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 217, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Meng, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, X.; Jiang, G. Effects of cattle manure compost combined with chemical fertilizer on topsoil organic matter, bulk density and earthworm activity in a wheat–maize rotation system in Eastern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 156, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, S.; Fan, J.; Feng, H.; He, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of bio-organic fertilizer derived from agricultural waste resources on soil properties and winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yield in semi-humid drought-prone regions. Agric. Water. Manag. 2023, 289, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, M.; Gao, S.; Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, B. Nitrogen use efficiency in a wheat–corn cropping system from 15 years of manure and fertilizer applications. Field Crops Res. 2014, 157, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, G.; Lalor, S.T.J.; Cabe, T.M. An evaluation of the combined usage of separated liquid pig manure and inorganic fertiliser in nutrient programmes for winter wheat production. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Fang, H.; Mooney, S.J.; Peng, X. Effects of long-term inorganic and organic fertilizations on the soil micro and macro structures of rice paddies. Geoderma 2016, 266, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Liang, G.; Hou, E.; Luo, Y. Manure acts as a better fertilizer for increasing crop yields than synthetic fertilizer does by improving soil fertility. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 189, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, J.; Xie, D.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic materials changed the abundance, diversity, and activity of nirS-type denitrifying bacterial communities in a vegetable soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 152, 103589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiboi, M.N.; Ngetich, K.F.; Fliessbach, A.; Muriuki, A.; Mugendi, D.N. Soil fertility inputs and tillage influence on maize crop performance and soil water content in the Central Highlands of Kenya. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 217, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Kundu, S.; Prakash, V.; Gupta, H.S. Sustainability under combined application of mineral and organic fertilizers in a rainfed soybean–wheat system of the Indian Himalayas. Eur. J. Agron. 2008, 28, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Zhou, P.; Li, Z.; Smith, P.; Li, L.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Shen, S.; Chen, X. Combined inorganic/organic fertilization enhances N efficiency and increases rice productivity through organic carbon accumulation in a rice paddy from the Tai Lake region, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 131, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M. Chemical fertilizer reduction with organic fertilizer effectively improve soil fertility and microbial community from newly cultivated land in the Loess Plateau of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 165, 103966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, A.; Kaleem Abbasi, M. Improvements in the physical and chemical characteristics of degraded soils supplemented with organic–inorganic amendments in the Himalayan region of Kashmir, Pakistan. Catena 2015, 126, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Song, D.; Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; Liang, G.; He, P.; Sun, G.; Yuan, F.; Liu, Z.; Yao, Y.; et al. Partial substitution of chemical nitrogen with organic nitrogen improves rice yield, soil biochemical indictors and microbial composition in a double rice cropping system in south China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Dai, X.Q.; Fu, X.L.; Yang, F.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Sun, X.M.; Wen, X.F.; Schaeffer, S. Changes in soil microbial community composition in response to fertilization of paddy soils in subtropical China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 84, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Liang, G.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W. Responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community in both the rhizosphere and bulk soil to long-term fertilization practices in a fluvo-aquic soil. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Singh Chauhan, P.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.; Sa, T. Community level functional diversity and enzyme activities in paddy soils under different long-term fertilizer management practices. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2010, 47, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Yan, C.; Mei, X.; He, W.; Bing, S.H.; Ding, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Fan, T. Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure on soil chemical and biological properties in northwest China. Geoderma 2010, 158, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xie, W.; Yang, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H. Effects of manure and chemical fertilizer on bacterial community structure and soil enzyme activities in North China. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2006. In A Framework for International Classification, Correlation and Communication, 2nd ed.; World Soil Resources Reports No. 103; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, N.Q.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, L.X. The Study on Dryland Agriculture in North China; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tsimba, R.; Edmeades, G.O.; Millner, J.P.; Kemp, P.D. The effect of planting date on maize grain yields and yield components. Field Crops Res. 2013, 150, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Analysis Method of Soil and Agricultural Chemistry, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 25–108. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.; Xu, B.C.; Lin, L.; Gu, Y.J.; Liu, Q.Q.; Turner, N.C.; Li, F.M. Does a mixture of old and modern winter wheat cultivars increase yield and water use efficiency in water-limited environments? Field Crops Res. 2014, 156, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.L.; Li, P.R.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Chen, X.P. Effects of tillage and plastic mulch on soil water, growth and yield of spring-sown maize. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 112, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, K.; Dass, A.; Sudhishri, S.; Kaur, R.; Rain, A. Yield components, yield and nutrient uptake pattern in maize (Zea mays) under varying irrigation and nitrogen levels. Indian J. Agron. 2017, 62, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Evgenia, B. Improved nitrogen use efficiency, carbon sequestration and reduced environmental contamination under a gradient of manure application. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufert, V.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture. Nature 2012, 485, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezahegn, A.M. Effect of organic fertilizers on maize (Zea mays L.) production and soil physical and chemical properties. World Appl. Sci. J. 2021, 39, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, T.E.; Peoples, M.B. Can the Synchrony of Nitrogen Supply and Crop Demand be Improved in Legume and Fertilizer-based Agroecosystems? A Review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 72, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Liang, Y.; Wakelin, S.A.; Chu, G. Supplementing chemical fertilizer with an organic component increases soil biological function and quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 96, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ni, T.; Li, J.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, R.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q. Effects of organic–inorganic compound fertilizer with reduced chemical fertilizer application on crop yields, soil biological activity and bacterial community structure in a rice–wheat cropping system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 99, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Deng, A.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, T.; Zheng, C.; Cao, C.; Chen, F. Long-term inorganic plus organic fertilization increases yield and yield stability of winter wheat. Crop J. 2018, 6, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Fan, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z. Crop yield stability and sustainability in a rice-wheat cropping system based on 34-year field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 113, 125965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macholdt, J.; Piepho, H.P.; Honermeier, B. Mineral NPK and manure fertilisation affecting the yield stability of winter wheat: Results from a long-term field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 102, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, C.; Elliott, J.; Pugh, T.A.M.; Ruane, A.C.; Ciais, P.; Balkovic, J.; Deryng, D.; Folberth, C.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Jones, C.D.; et al. Global patterns of crop yield stability under additional nutrient and water inputs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, P.M.; Sylvester-Bradley, R.; Philipps, L.; Hatch, D.J.; Cuttle, S.P.; Rayns, F.W.; Gosling, P. Is the productivity of organic farms restricted by the supply of available nitrogen? Soil Use Manag. 2006, 18, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.P.; Letey, J. Organic Farming Challenge of Timing Nitrogen Availability to Crop Nitrogen Requirements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Nie, J.; Wang, P.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Z.; Zang, H. Does the replacement of chemical fertilizer nitrogen by manure benefit water use efficiency of winter wheat—Summer maize systems? Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, N. Applications of organic manure increased maize (Zea mays L.) yield and water productivity in a semi-arid region. Agric. Water. Manag. 2017, 187, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Jia, Z.K.; Liang, L.Y.; Kang, S.Z. Effect of manure management on the temporal variations of dryland soil moisture and water use efficiency of maize. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2013, 15, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Uwimpaye, F.; Yan, Z.; Shao, L.; Chen, S.; Sun, H.; Liu, X. Water productivity improvement in summer maize—A case study in the North China Plain from 1980 to 2019. Agric. Water. Manag. 2021, 247, 106728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bu, L.; Zhu, L.; Luo, S.; Chen, X.; Li, S. Optimizing Plant Density and Plastic Film Mulch to Increase Maize Productivity and Water-Use Efficiency in Semiarid Areas. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzoma, K.C.; Inoue, M.; Andry, H.; Fujimaki, H.; Zahoor, A.; Nishihara, E. Effect of cow manure biochar on maize productivity under sandy soil condition. Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yan, Z.; Qin, J.; Xiao, Z. Effects of long-term cattle manure application on soil properties and soil heavy metals in corn seed production in Northwest China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7586–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Sui, F.; Bai, L.; Tong, C.; Sun, N. Effects of water stress on growth, biomass partitioning, and water-use efficiency in summer maize (Zea mays L.) throughout the growth cycle. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 34, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.A.; Li, F.R.; Zhou, L.M.; Zhang, R.H.; Yu, J.; Lin, S.L.; Wang, L.J.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Li, F.M. Effect of organic manure and fertilizer on soil water and crop yields in newly-built terraces with loess soils in a semi-arid environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerge, T. Safely delaying the first irrigation of corn. In Crop Insights; Pioneer Hi-Bred: Johnston, IA, USA, 2008; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
| Soil Depth (cm) | Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Porosity (%) | Particle Size Distribution (%) | Wilting Moisture (Dry Soil %) | Field Capacity (Dry Soil %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >0.05 mm | 0.05–0.01 mm | 0.01–0.005 mm | 0.005–0.001 mm | <0.001 mm | |||||
| 0–10 | 1.18 | 55.5 | 45.5 | 23.5 | 10.5 | 12.5 | 8.0 | 5.1 | 25.7 |
| 10–20 | 1.24 | 53.2 | 44.5 | 26.5 | 11.0 | 10.0 | 8.0 | 6.1 | 24.8 |
| 20–40 | 1.33 | 49.8 | 37.5 | 32.5 | 9.5 | 8.3 | 12.2 | 5.5 | 25.1 |
| 40–60 | 1.36 | 48.7 | 44.5 | 30.0 | 12.0 | 4.0 | 9.5 | 5.3 | 23.4 |
| 60–80 | 1.28 | 51.7 | 41.7 | 33.2 | 8.5 | 7.3 | 9.3 | 5.0 | 24.0 |
| 80–100 | 1.28 | 51.7 | 43.0 | 33.0 | 8.2 | 6.8 | 9.0 | 6.5 | 24.2 |
| 100–120 | 1.37 | 48.3 | 43.0 | 30.5 | 11.0 | 6.0 | 9.5 | 7.2 | 25.4 |
| 120–140 | 1.36 | 48.7 | 44.5 | 27.0 | 10.5 | 9.5 | 8.5 | 8.0 | 26.2 |
| 140–160 | 1.40 | 47.2 | 40.5 | 38.0 | 7.5 | 6.5 | 7.5 | 7.9 | 26.4 |
| 160–180 | 1.39 | 47.5 | 37.5 | 35.0 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 9.0 | 8.8 | 27.3 |
| 180–200 | 1.32 | 50.2 | 37.5 | 32.0 | 10.5 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 9.5 | 30.7 |
| Treatment | N (kg·ha−1) | P2O5 (kg·ha−1) | Cattle Manure (t·ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N0P0M0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| N1P1M0 | 60.0 | 37.5 | 0.0 |
| N2P2M0 | 120.0 | 75.0 | 0.0 |
| N3P3M0 | 180.0 | 112.5 | 0.0 |
| N4P4M0 | 240.0 | 150.0 | 0.0 |
| N2P1M1 | 120.0 | 37.5 | 22.5 |
| N3P2M3 | 180.0 | 75.0 | 67.5 |
| N4P2M2 | 240.0 | 75.0 | 45.0 |
| N0P0M6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 135.0 |
| Precipitation Pattern | Frequency | Precipitation (mm) | Drying Index | Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very wet year | 3 | 613.7–668.2 | 1.4–2.0 | 1995, 2007, 2021 |
| Relatively wet year | 7 | 518.7–572.4 | 0.4–1.0 | 2002, 2003, 2009, 2011, 2013, 2015, 2017 |
| Normal year | 11 | 447.8–504.1 | −0.3–0.3 | 1992, 1993, 1994, 1996, 1998, 2004, 2006, 2008, 2012, 2016, 2018 |
| Relatively dry year | 5 | 380.9–440.5 | −1.0–−0.4 | 1999, 2005, 2010, 2014, 2020 |
| Very dry year | 4 | 250.7–368.7 | −2.3–−1.1 | 1997, 2000, 2001, 2019 |
| Treatment | Very Wet Year | Relative Wet Year | Normal Year | Relative Dry Year | Very Dry Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Maize Yield (kg ha−1) | Increasing Rate (%) * | Average Maize Yield (kg ha−1) | Increasing Rate (%) | Average Maize Yield (kg ha−1) | Increasing Rate (%) | Average Maize Yield (kg ha−1) | Increasing Rate (%) | Average Maize Yield (kg ha−1) | Increasing Rate (%) | |
| N0P0M0 | 4352.6 | - | 4143.7 | - | 3839.2 | - | 3602.2 | - | 3067.3 | - |
| N1P1M0 | 7663.3 | 76.06 | 6677.8 | 58.22 | 6180.2 | 60.98 | 6332.2 | 75.79 | 4005.0 | 30.57 |
| N2P2M0 | 8391.0 | 92.78 | 7641.6 | 80.36 | 7405.0 | 92.88 | 6958.9 | 93.18 | 4589.1 | 49.61 |
| N3P3M0 | 8752.4 | 101.08 | 7376.6 | 74.28 | 6913.9 | 80.09 | 6889.3 | 91.25 | 4596.1 | 49.84 |
| N4P4M0 | 8438.9 | 93.88 | 7032.3 | 66.36 | 6956.5 | 81.20 | 6592.5 | 83.01 | 4295.0 | 40.03 |
| N2P1M1 | 9869.8 | 126.76 | 9065.6 | 113.08 | 8364.5 | 117.87 | 8288.5 | 130.10 | 5358.1 | 74.68 |
| N3P2M3 | 9903.0 | 127.52 | 8704.4 | 104.78 | 8571.2 | 123.25 | 7845.9 | 117.81 | 5403.3 | 76.16 |
| N4P2M2 | 10,138.6 | 132.93 | 9006.7 | 111.73 | 9019.5 | 134.93 | 8453.7 | 134.68 | 5842.0 | 90.46 |
| N0P0M6 | 10,236.2 | 135.17 | 8744.4 | 105.70 | 8885.8 | 131.45 | 8513.1 | 136.33 | 5239.4 | 70.81 |
| Average | 8638.42 | 110.77 | 7599.23 | 89.31 | 7348.42 | 102.83 | 7052.92 | 107.77 | 4710.59 | 60.27 |
| Treatment | Very Wet Year | Relative Wet Year | Normal Year | Relative Dry Year | Very Dry Year | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average of Water Productivity (kg ha−1 mm−1) | Increasing Rate (%) * | Average of Water Productivity (kg ha−1 mm−1) | Increasing Rate (%) | Average of Water Productivity (kg ha−1 mm−1) | Increasing Rate (%) | Average of Water Productivity (kg ha−1 mm−1) | Increasing Rate (%) | Average of Water Productivity (kg ha−1 mm−1) | Increasing Rate (%) | |
| N0P0M0 | 9.33 | - | 10.97 | - | 9.34 | - | 10.15 | - | 10.09 | - |
| N1P1M0 | 16.80 | 0.80 | 17.51 | 0.60 | 14.69 | 0.57 | 18.50 | 0.82 | 12.31 | 0.22 |
| N2P2M0 | 17.56 | 0.88 | 20.03 | 0.83 | 17.72 | 0.90 | 21.24 | 1.09 | 14.68 | 0.46 |
| N3P3M0 | 17.87 | 0.92 | 19.33 | 0.76 | 16.26 | 0.74 | 22.08 | 1.18 | 14.57 | 0.44 |
| N4P4M0 | 17.90 | 0.92 | 18.49 | 0.69 | 16.20 | 0.73 | 18.30 | 0.80 | 13.41 | 0.33 |
| N2P1M1 | 21.36 | 1.29 | 23.19 | 1.11 | 19.76 | 1.11 | 23.95 | 1.36 | 17.42 | 0.73 |
| N3P2M3 | 21.60 | 1.32 | 22.97 | 1.09 | 20.29 | 1.17 | 23.65 | 1.33 | 17.70 | 0.75 |
| N4P2M2 | 22.69 | 1.43 | 23.70 | 1.16 | 21.67 | 1.32 | 25.60 | 1.52 | 19.15 | 0.90 |
| N0P0M6 | 23.73 | 1.54 | 22.30 | 1.03 | 21.11 | 1.26 | 24.15 | 1.38 | 18.78 | 0.86 |
| Average | 18.76 | 1.14 | 19.83 | 0.91 | 17.45 | 0.98 | 20.84 | 1.19 | 15.34 | 0.59 |
| Yield | WP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Value | p Value | F Value | p Value | |
| Fertilization | 13.180 | <0.001 | 10.966 | <0.001 |
| Precipitation | 17.764 | <0.001 | 5.888 | <0.001 |
| Fertilization × Precipitation | 0.191 | 1.000 | 0.123 | 1.000 |
| Yield | SOC | WP | Water Consumption | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield | 1 | |||
| SOC | 0.644 ** | 1 | ||
| WP | 0.838 ** | 0.585 ** | 1 | |
| Water consumption | 0.495 ** | 0.223 | −0.039 | 1 |
| Period | N0P0M0 | N1P1M0 | N2P2M0 | N3P3M0 | N4P4M0 | N2P1M1 | N3P2M3 | N4P2M2 | N0P0M6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annual precipitation (January–December) | 0.104 | * 0.011 | 0.059 | ** 0.006 | ** 0.006 | 0.053 | * 0.026 | * 0.035 | * 0.020 |
| Precipitation during maize growth period (May–September) | 0.323 | * 0.035 | 0.124 | * 0.017 | * 0.017 | 0.174 | 0.103 | * 0.049 | * 0.045 |
| Precipitation during the leisure period before sowing (October–December of the previous year + January–April of the current year) | * 0.02 | 0.087 | * 0.04 | 0.106 | 0.059 | * 0.038 | ** 0.007 | * 0.046 | ** 0.006 |
| Precipitation of the previous year and precipitation before sowing (January–December of the previous year + January–April of the current year) | 0.128 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.101 | 0.095 | 0.065 | * 0.032 | 0.164 | * 0.027 |
| Precipitation in the fallow period and growth period (October–December of the previous year + January–September of the current year) | * 0.042 | ** 0.004 | * 0.013 | ** 0.002 | ** 0.001 | * 0.021 | ** 0.004 | ** 0.004 | ** 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xie, W.; Yang, Z.; He, L.; Chen, D.; Wu, X.; Zhou, H. Response of Maize Yield and Water Productivity to Different Long-Term Fertilization Strategies in Semi-Arid Regions in Northern China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222396
Liu Z, Guo Z, Wang Z, Xie W, Yang Z, He L, Chen D, Wu X, Zhou H. Response of Maize Yield and Water Productivity to Different Long-Term Fertilization Strategies in Semi-Arid Regions in Northern China. Agriculture. 2025; 15(22):2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222396
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhiping, Ziyuan Guo, Zongyi Wang, Wenyan Xie, Zhenxing Yang, Liyan He, Deli Chen, Xueping Wu, and Huaiping Zhou. 2025. "Response of Maize Yield and Water Productivity to Different Long-Term Fertilization Strategies in Semi-Arid Regions in Northern China" Agriculture 15, no. 22: 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222396
APA StyleLiu, Z., Guo, Z., Wang, Z., Xie, W., Yang, Z., He, L., Chen, D., Wu, X., & Zhou, H. (2025). Response of Maize Yield and Water Productivity to Different Long-Term Fertilization Strategies in Semi-Arid Regions in Northern China. Agriculture, 15(22), 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15222396








