Meta-Analysis on Criteria and Forecasting Models for Potato Late Blight Pathosystem: Assessing Robustness and Temporal Consistency
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Review Protocol
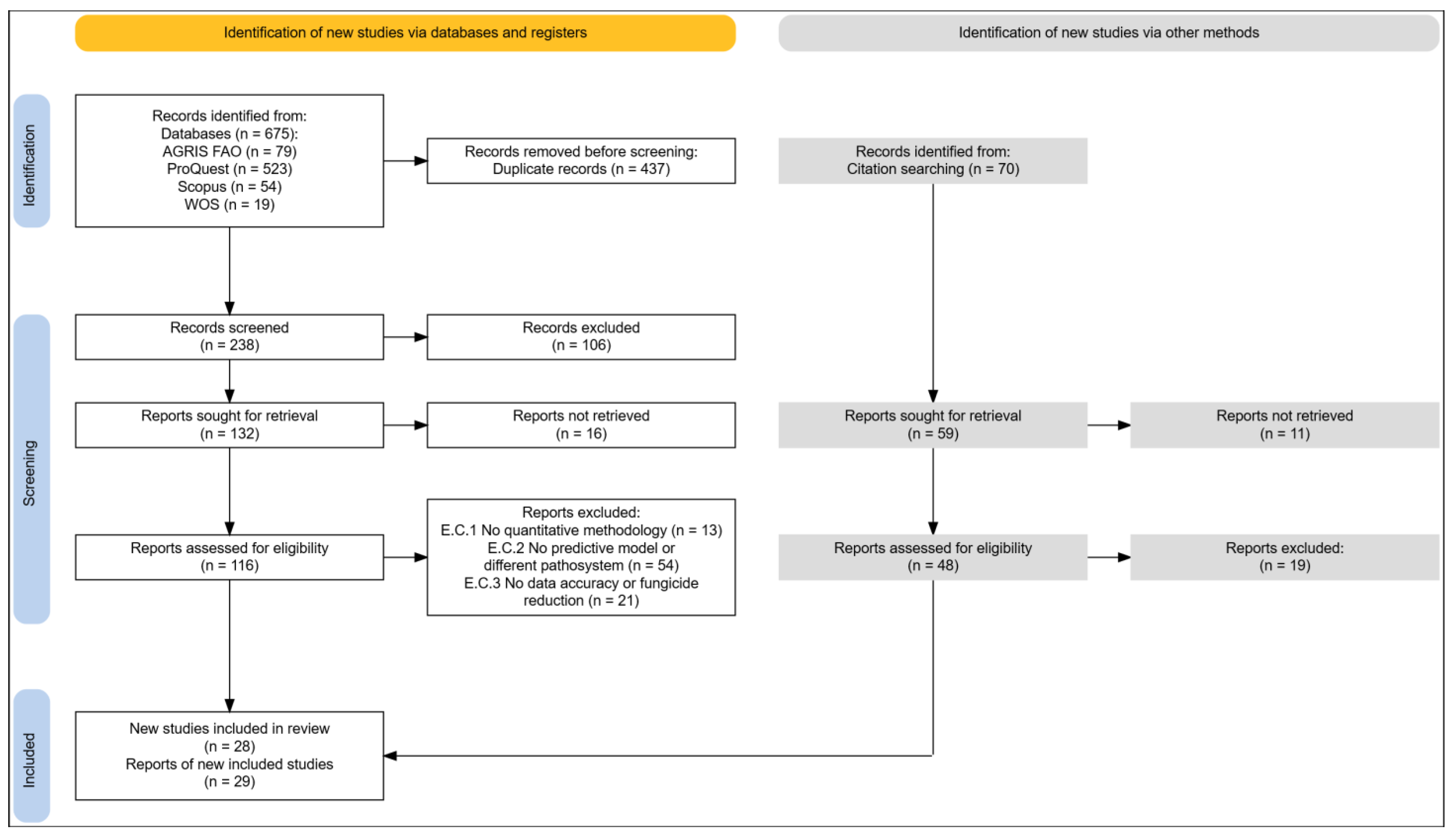
2.1.1. Identification Phase
2.1.2. Screening Phase
2.1.3. Included Phase
2.2. Classification and Structuring of Data
2.3. Bibliometric Analysis
3. Results
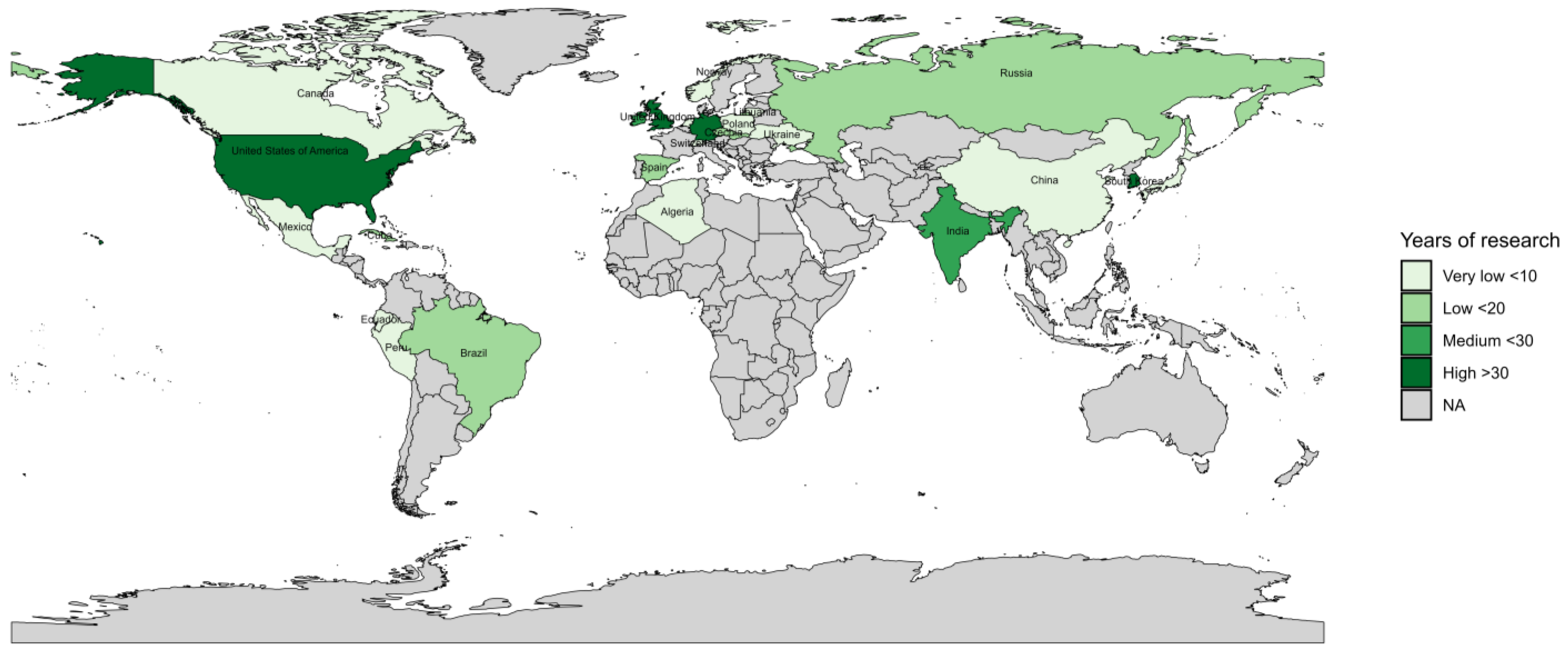
3.1. Overview of Research
3.2. Bibliometric Results
3.2.1. Data Distribution of Accuracy and Fungicide Reduction of Forecasting Models
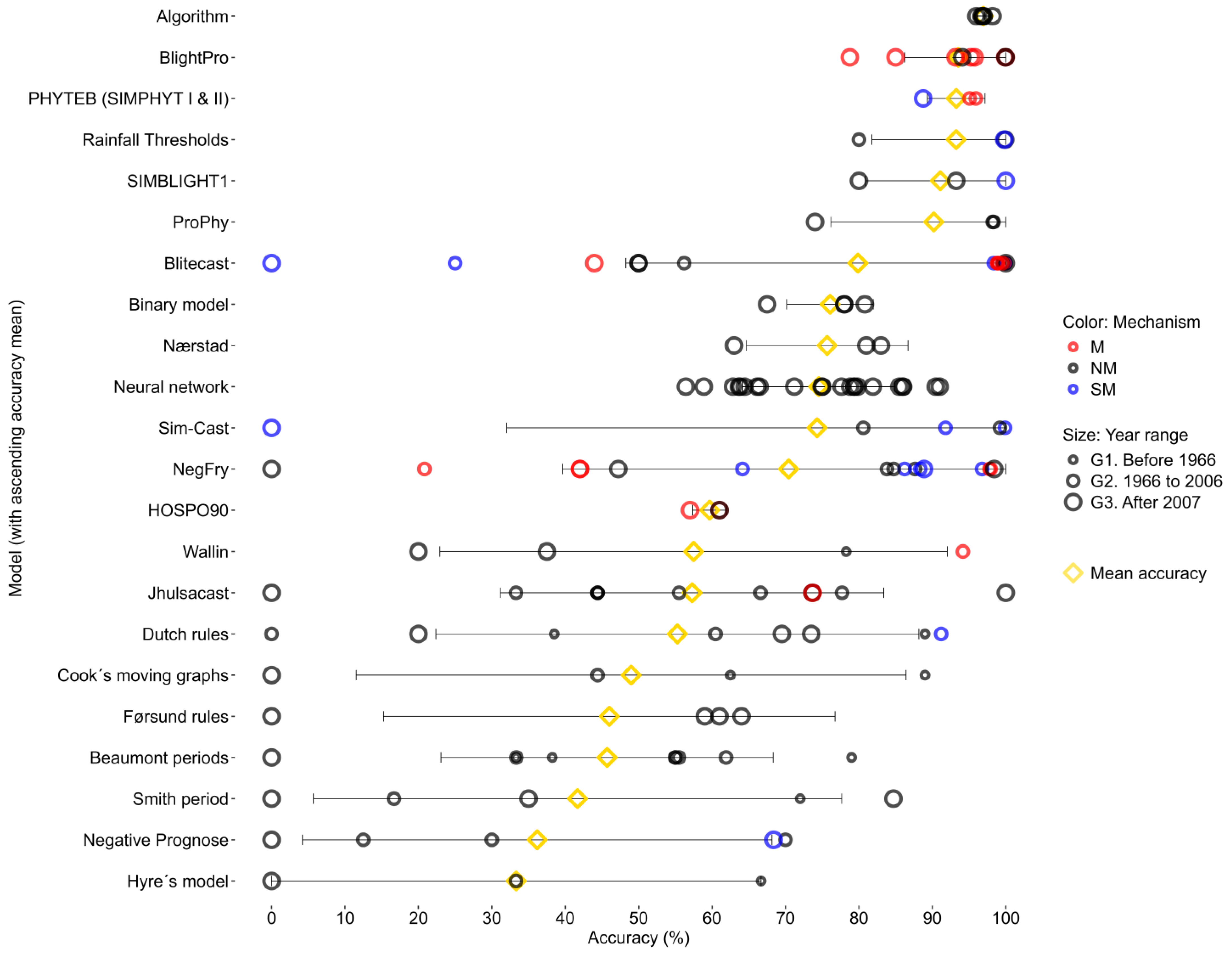
3.2.2. Accuracy of Criteria and Models According to Generation and Mechanism Classification
3.2.3. Fungicide Reduction of Models According to Generation and Mechanism Classification
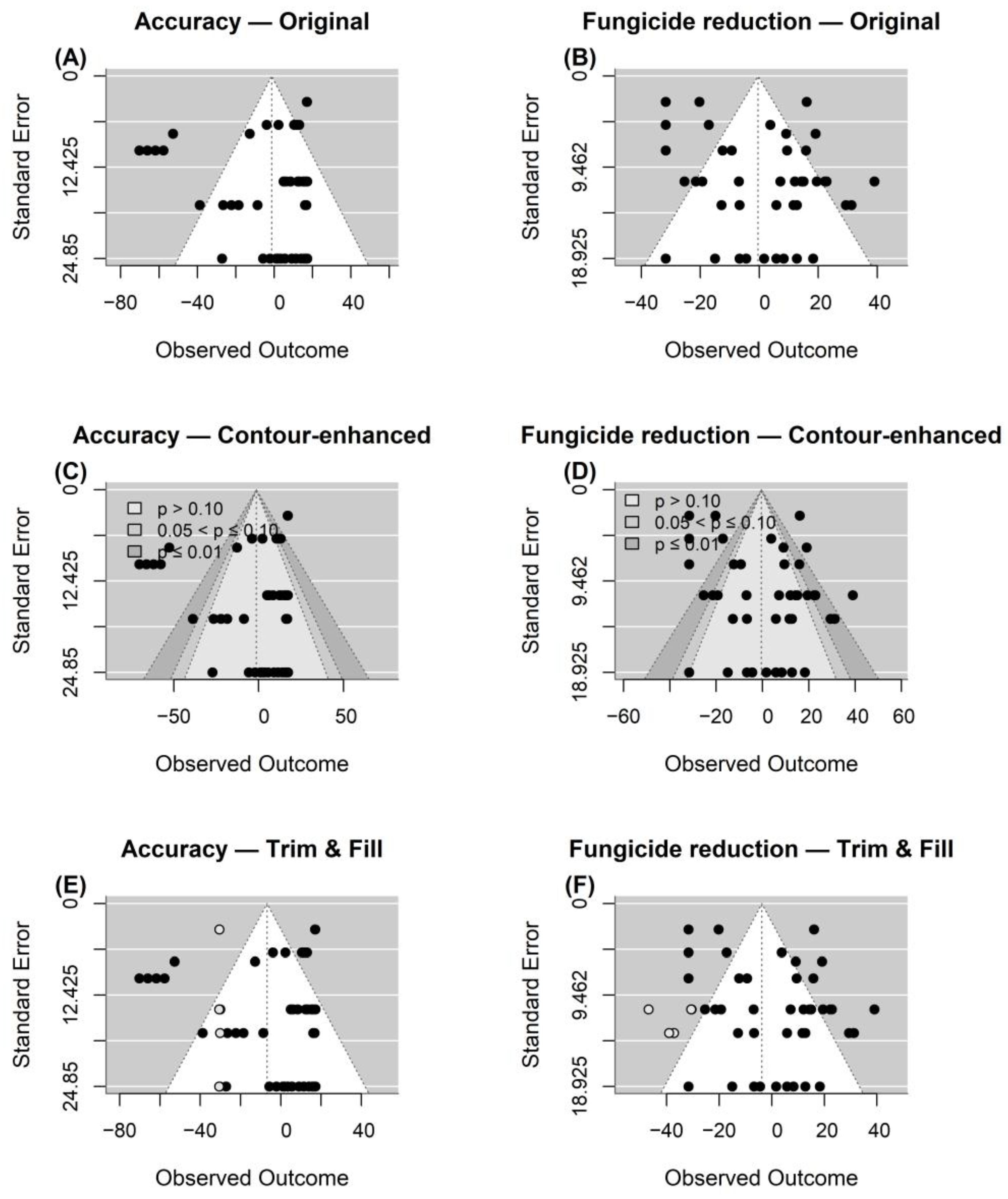
3.2.4. Meta-Analytical Results
3.3. Analysis of the Consistency of Criteria and Forecasting Models over Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO; FIDA; OMS; PMA; UNICEF. El Estado de La Seguridad Alimentaria y La Nutrición En El Mundo 2023. Urbanización, Transformación de Los Sistemas Agroalimentarios y Dietas Saludables a Lo Largo Del Continuo Rural-Urbano, 1st ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- FAO; FIDA; OMS; PMA; UNICEF. El Estado de La Seguridad Alimentaria y La Nutrición En El Mundo 2024: Financiación Para Acabar Con El Hambre, La Inseguridad Alimentaria y La Malnutrición En Todas Sus Formas, 1st ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024; ISBN 978-92-5-139096-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sawicka, B.; Barbaś, P.; Pszczółkowski, P.; Skiba, D.; Yeganehpoor, F.; Krochmal-Marczak, B. Climate Changes in Southeastern Poland and Food Security. Climate 2022, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juroszek, P.; Bartsch, L.; Fontaine, J.F.; Racca, P.; Kleinhenz, B. Summary of the Worldwide Available Crop Disease Risk Simulation Studies That Were Driven by Climate Change Scenarios and Published during the Past 20 Years. Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 1815–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, B.; Qi, A.; Fitt, B.D.L. Control of Crop Diseases through Integrated Crop Management to Deliver Climate-Smart Farming Systems for Low- and High-Input Crop Production. Plant Pathol. 2022, 71, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, K.A.; Bebber, D.P.; Etherton, B.A.; Gold, K.M.; Plex Sulá, A.I.; Selvaraj, M.G. Climate Change Effects on Pathogen Emergence: Artificial Intelligence to Translate Big Data for Mitigation. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2022, 60, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bois, B.; Zito, S.; Calonnec, A. Climate vs Grapevine Pests and Diseases Worldwide: The First Results of a Global Survey. OENO One 2017, 51, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, J. Pathogens Which Threaten Food Security: Phytophthora infestans, the Potato Late Blight Pathogen. Food Secur. 2021, 13, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meno, L.; Abuley, I.K.; Escuredo, O.; Seijo, M.C. Factors Influencing the Airborne Sporangia Concentration of Phytophthora infestans and Its Relationship with Potato Disease Severity. Sci. Hortic. 2023, 307, 111520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylor, D.E.; Schmale, D.G.; Shields, E.J.; Newcomb, M.; Nappo, C.J. Tracking the Potato Late Blight Pathogen in the Atmosphere Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and Lagrangian Modeling. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, P.H.; Lekshmanan, D.K.; Palanisamy, V.E.; Bairwa, A.; Sharma, S. Management of the Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) Disease of Potato in the Southern Hills of India. J. Phytopathol. 2021, 169, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meno, L.; Escuredo, O.; Seijo, M.C. Opportunity of the NEGFRY Decision Support System for the Sustainable Control of Potato Late Blight in A Limia (NW of Spain). Agriculture 2024, 14, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuredo, O.; Seijo-Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez-Flores, M.S.; Seijo, M.C. Decision Support Systems for Detecting Aerial Potato Phytophthora infestans Sporangia in Northwestern Spain. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meno, L.; Escuredo, O.; Abuley, I.K.; Seijo, M.C. Predicting Daily Aerobiological Risk Level of Potato Late Blight Using C5.0 and Random Forest Algorithms under Field Conditions. Sensors 2023, 23, 3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doster, M.A.; Fry, W.E. Evaluation by Computer Simulation of Strategies to Time Metalaxyl Applications for Improved Control of Potato Late Blight. Crop Prot. 1991, 10, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadafora, V.J.; Bruhn, J.A.; Fry, W.E. Influence of Selected Protectant Fungicides and Host Resistance on Simple and Complex Potato Late Blight Forecasts. Phytopathology 1984, 74, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EuroBlight: A Potato Late Blight Network for Europe. Available online: https://agro.au.dk/forskning/internationale-platforme/euroblight/ (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Krause, R.A.; Massie, L.B.; Hyre, R.A. Blitecast: A Computerized Forecast of Potato Late Blight. Plant Dis. Report. 1975, 59, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.G. Effects of the Aerial Environment on Late Blight of Potato Foliage—A Review. Plant Pathol. 1992, 41, 384–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everdingen, E. Het Verband Tusschen De Weersgesteldheid En De Aardappelziekte (Phytophthora infestans). Tijdschr. Over Plantenziekten 1926, 32, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, A. The Dependence on the Weather of the Dates of Outbreak of Potato Blight Epidemics. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1947, 31, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grainger, J. Potato Blight Forecasting and Its Mechanization. Nature 1953, 171, 1012–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.P. Potato Blight Forecasting By 90 Per Cent Humidity Criteria. Plant Pathol. 1956, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, J.R. Summary of Recent Progress in Predicting Late Blight Epidemics in United States and Canada. Am. Pot J. 1962, 39, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maito, G.; Bortoluzzi, M.P.; Magro, S.Z.D.; Maldaner, L.V.C. Potato Late Blight Control Based on the Blitecast Forecast System on the Rio Grande Do Sul Plateau, Brazil. Cienc. Rural 2025, 55, e20230691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhn, J.A.; Fry, W.E. Analysis of Potato Late Blight Epidemiology by Simulation Modeling. Phytopathology 1981, 71, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünwald, N.J.; Rubio-Covarrubias, O.A.; Fry, W.E. Potato Late-Blight Management in the Toluca Valley: Forecasts and Resistant Cultivars. Plant Dis. 2000, 84, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.C.; Hardwick, N.V.; Bradshaw, N.J.; Hall, A.M. Relative Performance of Five Forecasting Schemes for Potato Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) I. Accuracy of Infection Warnings and Reduction of Unnecessary, Theoretical, Fungicide Applications. Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowley, L.J.; Burke, J.J. Field Validation of Four Decision Support Systems for the Control of Late Blight of Potatoes in Ireland. Pot. Res. 2004, 47, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorn, B.; Musa, T.; Krebs, H.; Fried, P.M.; Forrer, H.R. Control of Late Blight in Organic Potato Production: Evaluation of Copper-Free Preparations under Field, Growth Chamber and Laboratory Conditions. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2007, 119, 217–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narouei-Khandan, H.A.; Shakya, S.K.; Garrett, K.A.; Goss, E.M.; Dufault, N.S.; Andrade-Piedra, J.L.; Asseng, S.; Wallach, D.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. BLIGHTSIM: A New Potato Late Blight Model Simulating the Response of Phytophthora infestans to Diurnal Temperature and Humidity Fluctuations in Relation to Climate Change. Pathogens 2020, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödter, H.; Ullrich, J. Weitere Untersuchungen Zur Biometeorologie Und Epidemiologie von Phytophthora Infestans (Mont.) de By. Ein Neues Konzept Zur Lösung Des Problems Der Epidemiologischen Prognose. J. Phytopathol. 1966, 56, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, W.E. Integrated Control of Potato Late Blight—Effects of Polygenic Resistance and Techniques of Timing Fungicide Applications. Phytopathology 1977, 77, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Shimanuki, T. Validation of Potato Late Blight Forecasts in Hokkaido [Japan]. Annu. Rep. Soc. Plant Prot. North. Jpn. 2001, 52, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, D.C.; Lima, M.A.; Haddad, F.; Maffia, L.A.; Mizubuti, E.S.G. Validation of Decision Support Systems for Tomato Early Blight and Potato Late Blight, under Brazilian Conditions. Crop Prot. 2006, 25, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trentin, G.; Heldwein, A.B.; Streck, L.; Maass, G.F.; Radons, S.Z.; Trentin, R. Controlling Potato Cv. “Asterix” Late Blight Base on Forecast Systems. Cienc. Rural 2009, 39, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, L.C.; Heldwein, A.B.; Blume, E.; Trentin, G.; Grimm, E.L.; Lucas, D.D.P.; Loose, L.H.; Radons, S.Z. Sistemas de Previsão de Requeima Em Cultivos de Batata Em Santa Maria, RS. Bragantia 2010, 69, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Singh, B.P.; Ahmad, I.; Sharma, S. Forecasting Late Blight of Potato in Plains of West Bengal Using Jhulsacast Model. Pot. J. 2015, 42, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Colturato, A.B.; Chavier, L.F.C. Decision Support System for Late Blight in Tomato and Potato. Acta Hortic. 2019, 1233, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, R.; Wilks, D.S.; Fry, W.E. Evaluation of Potato Late Blight Forecasts Modified to Include Weather Forecasts: A Simulation Analysis. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanya, O.M.; Honeycutt, C.W.; Tschöepe, B.; Kleinhenz, B.; Lambert, D.H.; Johnson, S.B. Effectiveness of SIMBLIGHT1 and SIMPHYT1 Models for Predicting Phytophthora infestans in North-Eastern United States. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2012, 45, 1558–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litschmann, T.; Hausvater, E.; Dolezal, P. A New Method of Potato Late Blight Forecasting in the Czech Republic. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2020, 60, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünwald, N.J.; Romero Montes, G.; Lozoya Saldaña, H.; Rubio Covarrubias, O.A.; Fry, W.E. Potato Late Blight Management in the Toluca Valley: Field Validation of SimCast Modified for Cultivars with High Field Resistance. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 1163–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fohner, G.R.; Fry, W.E.; White, G.B. Computer Simulation Raises Question About Timing Protectant Fungicide Application Frequency According to a Potato Late Blight Forecast. Phytopathology 1984, 74, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutsche, V. PROGEB—A Model-Aided Forecasting Service for Pest Management in Cereals and Potatoes. Bull. OEPP/EPPO Bull. 1993, 23, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.P.; Ahmad, I.; Sharma, V.C.; Shekhawat, G.S. JHULSACAST: A Computerized Forecast of Potato Late Blight in Western Uttar Pradesh. J. Indian Pot. Assoc. 2000, 27, 25–34. Available online: https://krishikosh.egranth.ac.in/server/api/core/bitstreams/d635cad4-77ea-4ecf-bfdc-dd36955efd3b/content#page=26 (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Leonard, R.; Dowley, L.J.; Rice, B.; Ward, S. Comparison of the NegFry Decision Support System with Routine Fungicide Application for the Control of Potato Late Blight in Ireland. Pot. Res. 2001, 44, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, G.; Suárez, M.; Suárez, I.; Montero, J.; Arredondo, M.E.; Rivero, T.; Hernández, A.; Díaz, E.; Martínez, E. Pronóstico Del Tizón Tardío (Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary) de La Papa En Cuba. V. Evaluación de La Efectividad Del Método Umbral de Lluvias Para La Predicción de Epifitotias. Fitosanidad 2003, 7, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hermansen, A.; Amundsen, T. Evaluation of Old Potato Late Blight Forecasting Rules during 1994-1999 in Fields with the New Phytophthora infestans Population in Norway. Acta Agric. Scand. B Soil Plant Sci. 2003, 53, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsa, J.; Osowski, J.; Bernat, E. NegFry-Decision Support System for Late Blight Control in Potato Crops-Results of Validation Trials in North Poland. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2003, 43, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, D.; Williams, C.J.; Miller, J.S. Forecasting Late Blight in Potato Crops of Southern Idaho Using Logistic Regression Analysis. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.M.; Kirk, W.W. Comparative Analysis of Models Integrating Synoptic Forecast Data into Potato Late Blight Risk Estimate Systems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2007, 57, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinhenz, B.; Falke, K.; Kakau, J.; Rossberg, D. SIMBLIGHT1 a New Model to Predict First Occurrence of Potato Late Blight. EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kromann, P.; Taipe, A.; Perez, W.G.; Forbes, G.A. Rainfall Thresholds as Support for Timing Fungicide Applications in the Control of Potato Late Blight in Ecuador and Peru. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skelsey, P.; Kessel, G.J.T.; Holtslag, A.A.M.; Moene, A.F.; van der Werf, W. Regional Spore Dispersal as a Factor in Disease Risk Warnings for Potato Late Blight: A Proof of Concept. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, K.M.; Lake, T.; Benston, S.F.; Trenary, R.; Wharton, P.; Duynslager, L.; Kirk, W. Improved Weather-Based Late Blight Risk Management: Comparing Models with a Ten Year Forecast Archive. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 153, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelkrem, A.G.R.; Eikemo, H.; Le, V.H.; Hermansen, A.; Nærstad, R. A Process-Based Model to Forecast Risk of Potato Late Blight in Norway (The Nærstad Model): Model Development, Sensitivity Analysis and Bayesian Calibration. Ecol. Modell. 2021, 450, 109565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelsey, P. Forecasting Risk of Crop Disease with Anomaly Detection Algorithms. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abderrahmane, O.; Berdja, R.; Ammad, F.; Bensaci, O.A.; Benchabane, M. Potato Late Blight (Phytophthora infestans) Disease Forecasting Using an Auto-Encoded Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Networks in North-Western Algeria. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2022, 55, 1542–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, G.; Suárez, M.; Figueroa, M.; Rivero, T.; Hernández, A. Pronóstico Del Tizón Tardío (Phytophthora infestans (MONT.) de BARY) de La Papa En Cuba. II. Evaluación de La Efectividad Del Modelo Naumova Modificado. Fitosanidad 2002, 6, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Filippov, A.; Rogozhin, A.; Kuznetsova, M.; Statsyuk, N.; Ronis, A.; (Bud)Platt, H.W. Sprendimų Priėmimo Kompiuterinės Programos Efektyvumo Nustatymas, Siekiant Sumažinti Bulvių Pasėlių Purškimą Fungicidais. Zemdirbyste 2015, 102, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Langemeier, M.R.; Small, I.M.; Joseph, L.; Fry, W.E. Risk Management Strategies Using Precision Agriculture Technology to Manage Potato Late Blight. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucak, M.; de Andrade Moral, R.; Fealy, R.; Lambkin, K.; Kildea, S. Opportunities for Improved Potato Late Blight Management in the Republic of Ireland: Field Evaluation of the Modified Irish Rules Crop Disease Risk Prediction Model. Phytopathology 2021, 111, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.C.S.; Frost, K.E.; Rouse, D.I.; Gevens, A.J. Effect of Temperature on Growth and Sporulation of US-22, US-23, and US-24 Clonal Lineages of Phytophthora infestans and Implications for Late Blight Epidemiology. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skelsey, P.; Kessel, G.J.T.; Rossing, W.A.H.; Van Der Werf, W. Parameterization and Evaluation of a Spatiotemporal Model of the Potato Late Blight Pathosystem. Anal. Theor. Plant Pathol. 2009, 99, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, I.M.; Joseph, L.; Fry, W.E. Evaluation of the BlightPro Decision Support System for Management of Potato Late Blight Using Computer Simulation and Field Validation. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oijen, M. Selection and Use of a Mathematical Model to Evaluate Components of Resistance to Phytophthora infestans in Potato. Neth. J. Plant Pathol. 1992, 98, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessel, G.J.T.; Mullins, E.; Evenhuis, A.; Stellingwerf, J.; Cortes, V.O.; Phelan, S.; van den Bosch, T.; Förch, M.G.; Goedhart, P.; van der Voet, H.; et al. Development and Validation of IPM Strategies for the Cultivation of Cisgenically Modified Late Blight Resistant Potato. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 96, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; 500p. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R Package and Shiny App for Producing PRISMA 2020-compliant Flow Diagrams, with Interactivity for Optimised Digital Transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croaxall, H.E.; Smith, L.P. The Epidemiology of Potato Blight in the East Midlands 1923–74. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1976, 82, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bootsma, A. Potato Late Blight Forecasting in Prince Edward Island in 1978. Can. Plant Dis. Surv. 1979, 59, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.P.; Govindakrishnan, P.M.; Ahmad, I.; Rawat, S.; Sharma, S.; Sreekumar, J. INDO-BLIGHTCAST—A Model for Forecasting Late Blight across Agroecologies. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2016, 62, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Ding, J.; Wang, S.; Hou, X.; Jia, S.; Hou, Y. Forecast Model for Potato Late Blight in Northern My Country Based on Meteorological Conditions and Its Validation. Chin. J. Ecol. 2018, 37, 2856. [Google Scholar]
- Cucak, M.; Sparks, A.; De Andrade Moral, R.; Kildea, S.; Lambkin, K.; Fealy, R. Evaluation of the ‘Irish Rules’: The Potato Late Blight Forecasting Model and Its Operational Use in the Republic of Ireland. Agronomy 2019, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, I.A. The Sources and Development of Potato Blight in Kent 1966–69. Plant Pathol. 1971, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaner, G. The Effect of Nitrogen Fertilization on the Expression of Slow-Mildewing Resistance in Knox Wheat. Phytopathology 1977, 77, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.H.; Yoo, S.J.; Park, C.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, S.K.; Kim, J.S.; Lim, J.H. BLITE-SVR: New Forecasting Model for Late Blight on Potato Using Support-Vector Regression. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 130, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ooms, J. writexl: Export Data Frames to Excel ‘xlsx’ Format. R package version 1.5.1. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=writexl (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Bryan, J. readxl: Read Excel Files. R package version 1.4.5. 2025. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=readxl (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K.; Vaughan, D. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. R package version 1.1.4. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Vaughan, D.; Girlich, M. tidyr: Tidy Messy Data. R package version 1.3.1. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=tidyr (accessed on 26 October 2025).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Pedersen, T.L. patchwork: The Composer of Plots. R package version 1.3.0. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=patchwork (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Pebesma, E. Simple Features for R: Standardized Support for Spatial Vector Data. R. J. 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massicotte, P.; South, A. rnaturalearth: World Map Data from Natural Earth. R package version 1.0.1. 2025. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rnaturalearth (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- South, A.; Schramm, M.; Massicotte, P. rnaturalearthdata: World Vector Map Data from Natural Earth Used in ‘rnaturalearth’. R package version 1.0.0. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rnaturalearthdata (accessed on 26 March 2025).
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in Meta-Analysis Detected by a Simple, Graphical Test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and Fill: A Simple Funnel-Plot–Based Method of Testing and Adjusting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting Meta-Analyses in R with the Metafor Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Farm to Fork Strategy. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2020-05/f2f_action-plan_2020_strategy-info_en.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- FAO. High Level Expert Forum–How to Feed the World in 2050. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/wsfs/docs/Issues_papers/HLEF2050_Global_Agriculture.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2025).
- Hijmans, R.J.; Forbes, G.A.; Walker, T.S. Estimating the Global Severity of Potato Late Blight with GIS-Linked Disease Forecast Models. Plant Pathol. 2000, 49, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, A.H.; Forbes, G.A.; Hijmans, R.J.; Garrett, K.A. Climate Change May Have Limited Effect on Global Risk of Potato Late Blight. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 3621–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwiczewska, M.; Janiszewska, M.; Yin, Z.; Śliwka, J. Populations of Phytophthora Infestans in Northern and Eastern Europe. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2024, 171, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, W.E.; Goodwin, S.B.; Matuszak, J.M.; Spielman, L.J.; Milgroom, M.G.; Drenth, A. Population Genetics and Intercontinental Migrations of Phytophthora infestans. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1992, 30, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziero, J.M.N.; Maffia, L.A.; Mizubuti, E.S.G. Effects of Temperature on Events in the Infection Cycle of Two Clonal Lineages of Phytophthora infestans Causing Late Blight on Tomato and Potato in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Keywords | Database | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAO AGRIS | ProQuest a,b | Scopus a,c | WoS a | |
| “solanum AND tuberosum AND phytophthora AND infestans AND predictive AND model” | 3 | 73 | 3 | 1 |
| “solanum AND tuberosum AND phytophthora AND infestans AND disease AND forecasting” | 51 | 55 | 24 | 9 |
| “solanum AND tuberosum AND phytophthora AND infestans AND decision AND support AND system” | 25 | 198 | 22 | 8 |
| “solanum AND tuberosum AND phytophthora AND infestans AND predictive AND model AND climate AND change” | 0 | 42 | 1 | 0 |
| “solanum AND tuberosum AND phytophthora AND infestans AND disease AND forecasting AND climate AND change” | 0 | 36 | 3 | 1 |
| “solanum AND tuberosum AND phytophthora AND infestans AND decision AND support AND system AND climate AND change” | 0 | 119 | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 675 | |||
| Number | Reference | Model or Criteria Used for Prognosis | Generation Class | Mechanism Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [20,38,46,63,76] | Dutch rules | G1 | NM |
| 2 | [21,38,46,72,77] | Beaumont periods | G1 | NM |
| 3 | [13,23,28,38,58] | Smith period | G1 | NM |
| 4 | [24,38] | Hyre’s model | G1 | NM |
| 5 | [24] | Cook’s moving graphs | G1 | NM |
| 6 | [13,24,38] | Wallin | G1 | NM |
| 7 | [32] | Negative Prognose | G2 | NM |
| 8 | [25,27,28,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] | Blitecast | G2 | NM |
| 9 | [73] | BWI index | G2 | NM |
| 10 | [26] | Computational Simulation | G2 | M |
| 11 | [45] | PHYTEB (SIMPHYT I and II) | G2 | NM |
| 12 | [40] | Blitecast Computational | G2 | SM |
| 13 | [27] | Blitecast-Modified | G2 | M |
| 14 | [27] | Tom-Cast | G2 | NM |
| 15 | [27] | Sim-Cast | G2 | SM |
| 16 | [46] | Bhattacharya method | G2 | NM |
| 17 | [46] | Cumulative blight severity value | G1 | NM |
| 18 | [46] | Jhulsacast | G2 | NM |
| 19 | [34] | PhytoPRE | G2 | SM |
| 20 | [47] | Dutch rules ME | G1 | SM |
| 21 | [47] | NegFry | G2 | SM |
| 22 | [60] | Naumova Mod | G2 | NM |
| 23 | [43] | Sim-Cast Mod | G2 | SM |
| 24 | [43] | Rainfall Thresholds | G1 | NM |
| 25 | [49] | Førsund rules | G2 | NM |
| 26 | [49] | NEGFRY-P | G2 | SM |
| 27 | [49] | NEGFørsund rules | G2 | SM |
| 28 | [28] | Sparks | G2 | M |
| 29 | [29] | ProPhy | G2 | M |
| 30 | [29] | Plant-Plus | G2 | M |
| 31 | [30] | Bio-PhytoPRE | G2 | M |
| 32 | [51] | Binary model | G1 | NM |
| 33 | [52] | Determinacy analysis | G2 | NM |
| 34 | [52] | Logistic regression | G2 | NM |
| 35 | [52] | Discriminant analysis | G2 | NM |
| 36 | [52,59] | Neural network | G3 | NM |
| 37 | [53] | SIMBLIGHT1 | G2 | SM |
| 38 | [38] | Winstel | G1 | NM |
| 39 | [41] | SIMPHYT I | G2 | NM |
| 40 | [41] | SIMPHYT I (US) | G2 | SM |
| 41 | [41] | Noblight | G2 | NM |
| 42 | [56] | NWN07 | G3 | NM |
| 43 | [56] | THOM | G3 | NM |
| 44 | [61] | VNIIFBlight | G2 | SM |
| 45 | [62] | BlightPro | G3 | M |
| 46 | [79] | Linear regression | G2 | NM |
| 47 | [79] | Pace regression | G2 | NM |
| 48 | [79] | BLITE-SVR | G2 | NM |
| 49 | [74] | INDO-BLIGHTCAST | G2 | NM |
| 50 | [68] | IPM 2.0 | G3 | M |
| 51 | [42] | Index | G2 | NM |
| 52 | [31] | BLIGHTSIM | G3 | M |
| 53 | [63] | Blight Management | G2 | M |
| 54 | [63] | Dutch rules (MIR) | G2 | M |
| 55 | [57] | Nærstad | G2 | M |
| 56 | [57] | HOSPO90 | G1 | NM |
| 57 | [58] | Hutton Criteria | G1 | NM |
| 58 | [58] | Algorithm | G3 | NM |
| 59 | [14] | ML Algorithms | G3 | NM |
| Country | Model or Criteria |
|---|---|
| Algeria | Neural network |
| Brazil | Blitecast, ProPhy, Sim-Cast, NegFry, Wallin |
| Canada | BWI, VNIIFBlight |
| China | Binary model |
| Cuba | Naumova Mod, Rain Threshold |
| Czechia | NegFry, Noblight, Index |
| Ecuador | BLIGHTSIM, Rainfall Thresholds |
| Germany | Negative Prognose, PHYTEB (SIMPHYT I and II), SIMBLIGHT1 |
| India | Beaumont periods, Bhattacharya method, Blitecast, Cook’s moving graphs, Cumulative blight severity value, Dutch rules, Førsund rules, Hyre’s model, INDO-BLIGHTCAST, Jhulsacast, Negative Prognose, NegFry, Sim-Cast, Smith period, Wallin, Winstel |
| Ireland | Blight Management, Dutch rules, Dutch rules ME, Dutch rules (MIR), IPM 2.0, NegFry, PHYTEB (SIMPHYT I and II), Plant-Plus, ProPhy |
| Japan | Blitecast, PhytoPRE, Sim-Cast |
| Lithuania | VNIIFBlight |
| Mexico | Blitecast, Blitecast-Modified, Sim-Cast, Sim-Cast Mod, Tom-Cast |
| Netherlands | Dutch rules, IPM 2.0, Sim-Cast, VNIIFBlight |
| Norway | Førsund rules, HOSPO90, Nærstad, NEGFørsund rules, NegFry-P |
| Peru | Rainfall Thresholds |
| Poland | NegFry, VNIIFBlight |
| Russia | VNIIFBlight |
| Slovakia | Index, NegFry, Noblight |
| South Korea | Blitecast, BLITE-SVR, Cook’s moving graphs, Linear regression, Pace regression |
| Spain | ML Algorithms, Negative Prognose, NegFry, Smith period, Wallin, Winstel |
| Switzerland | Bio-PhytoPRE |
| Ukraine | VNIIFBlight |
| United Kingdom | Algorithm, Beaumont periods, Blitecast, Dutch rules, Hutton Criteria, Negative Prognose, Negfry, Smith period, Sparks |
| USA | Binary model, Blitecast, BlightPro, Computational Blitecast, Computational Simulation, Cook’s moving graphs, Determinacy analysis, Discriminant analysis, Hyre’s model, Logistic regression, Neural network, Noblight, NWN07, SIMBLIGHT1, SIMPHYT I, SIMPHYT I (US), THOM, Wallin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castaño-Serna, J.S.; Meno, L.; Seijo, M.C.; Escuredo, O. Meta-Analysis on Criteria and Forecasting Models for Potato Late Blight Pathosystem: Assessing Robustness and Temporal Consistency. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212242
Castaño-Serna JS, Meno L, Seijo MC, Escuredo O. Meta-Analysis on Criteria and Forecasting Models for Potato Late Blight Pathosystem: Assessing Robustness and Temporal Consistency. Agriculture. 2025; 15(21):2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212242
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastaño-Serna, Jonathan S., Laura Meno, M. Carmen Seijo, and Olga Escuredo. 2025. "Meta-Analysis on Criteria and Forecasting Models for Potato Late Blight Pathosystem: Assessing Robustness and Temporal Consistency" Agriculture 15, no. 21: 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212242
APA StyleCastaño-Serna, J. S., Meno, L., Seijo, M. C., & Escuredo, O. (2025). Meta-Analysis on Criteria and Forecasting Models for Potato Late Blight Pathosystem: Assessing Robustness and Temporal Consistency. Agriculture, 15(21), 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15212242










