Tillage Effects on Bacterial Community Structure and Ecology in Seasonally Frozen Black Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Illumina Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
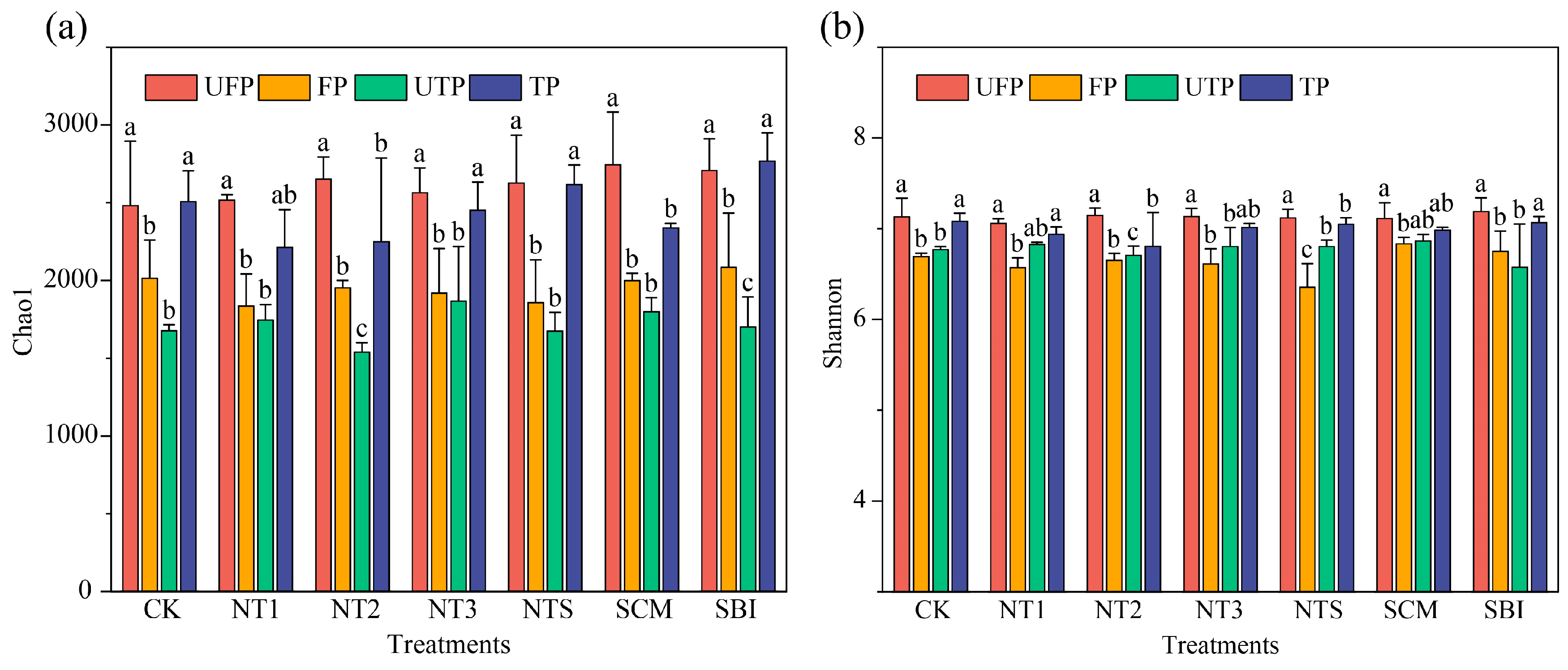
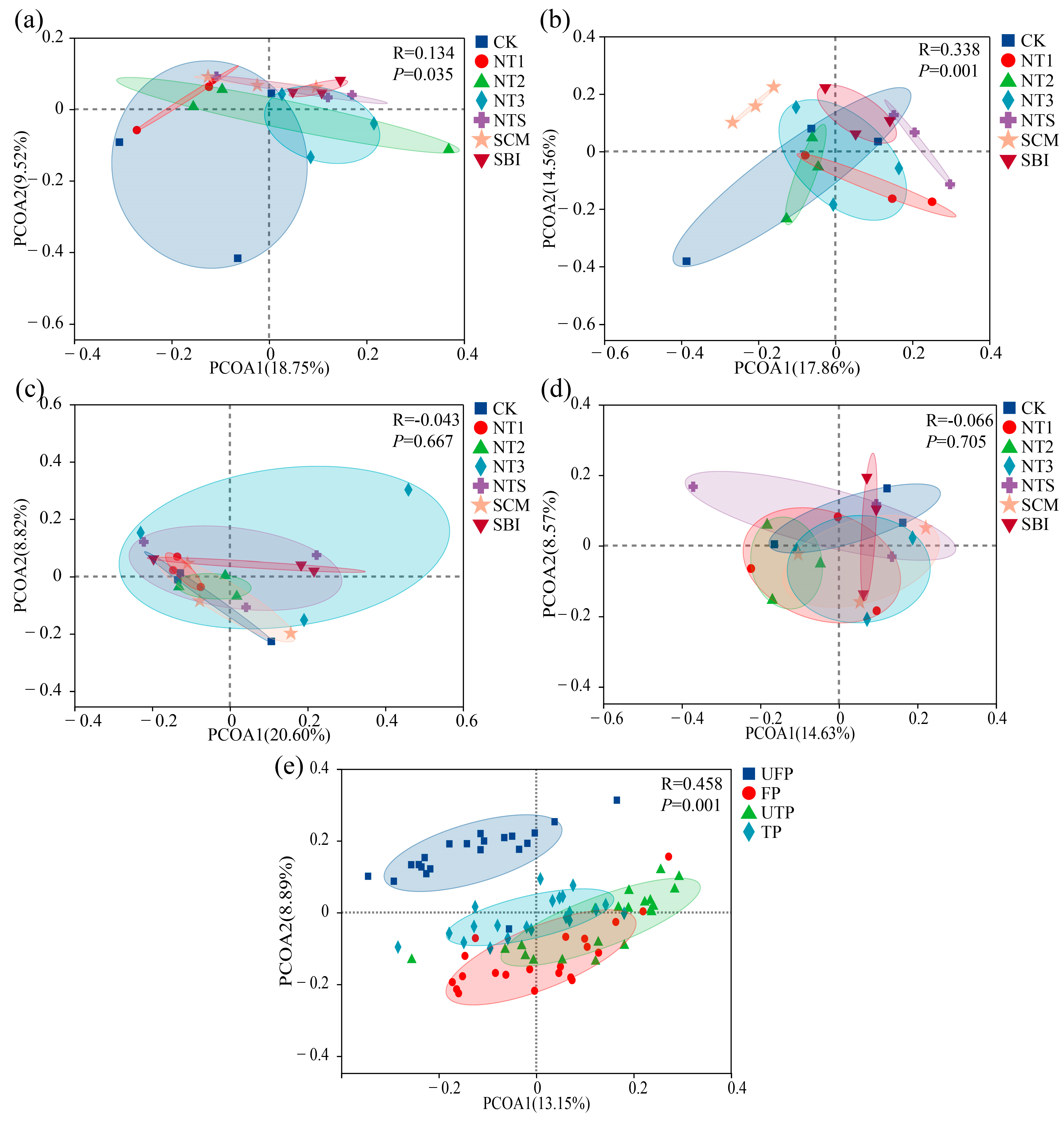
3.1. α- and β-Diversity of Freeze–Thaw Soil Bacterial Communities
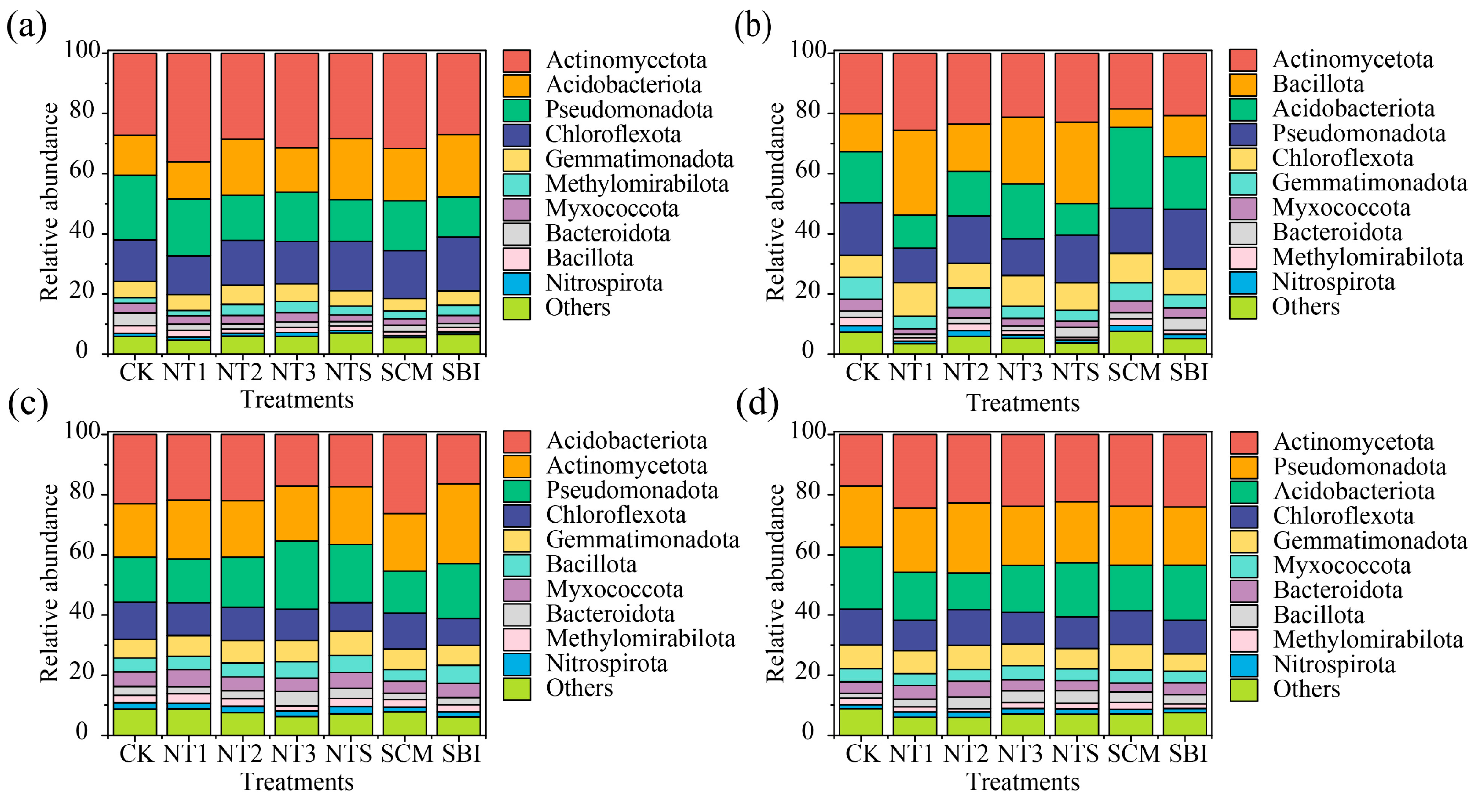
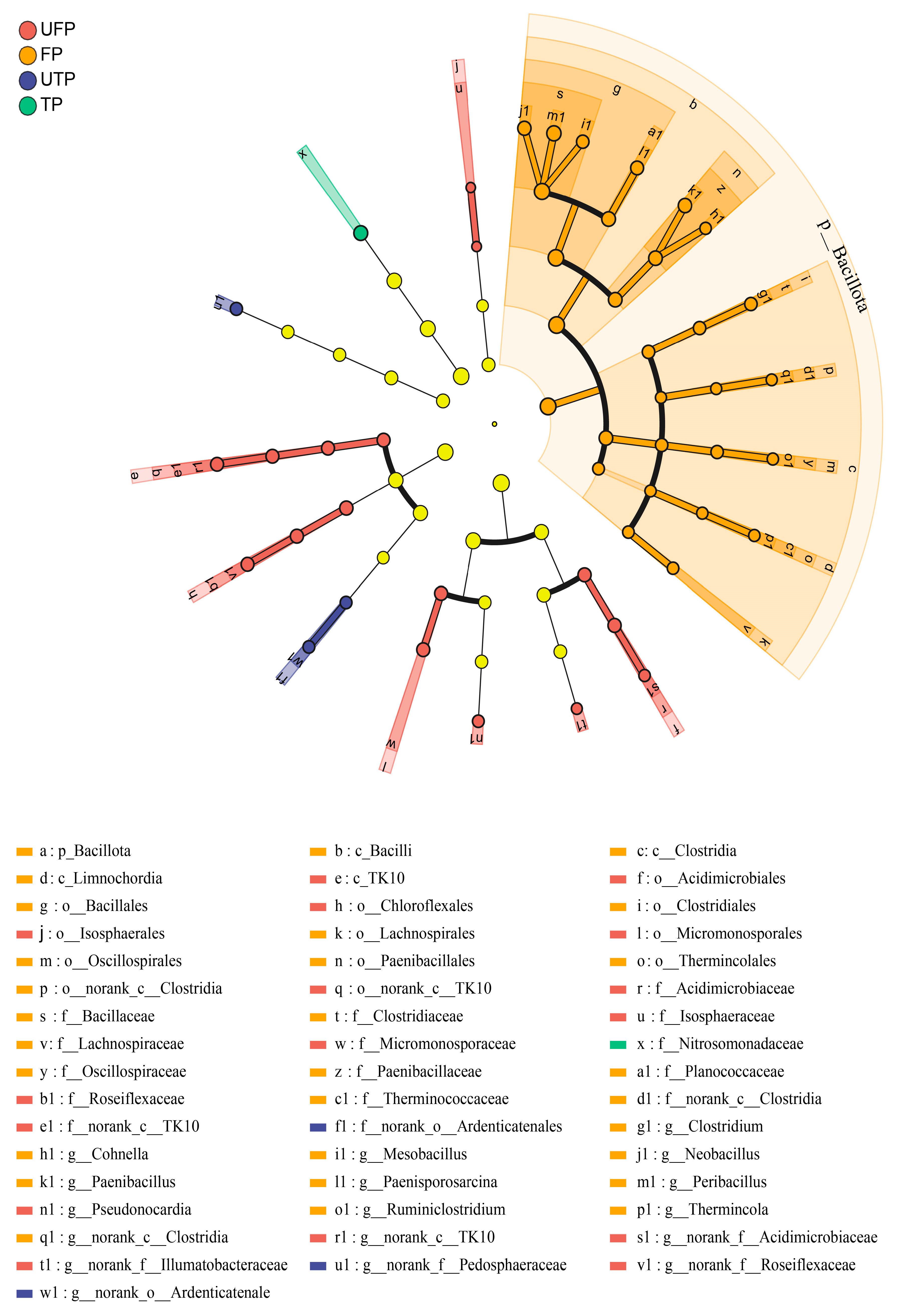
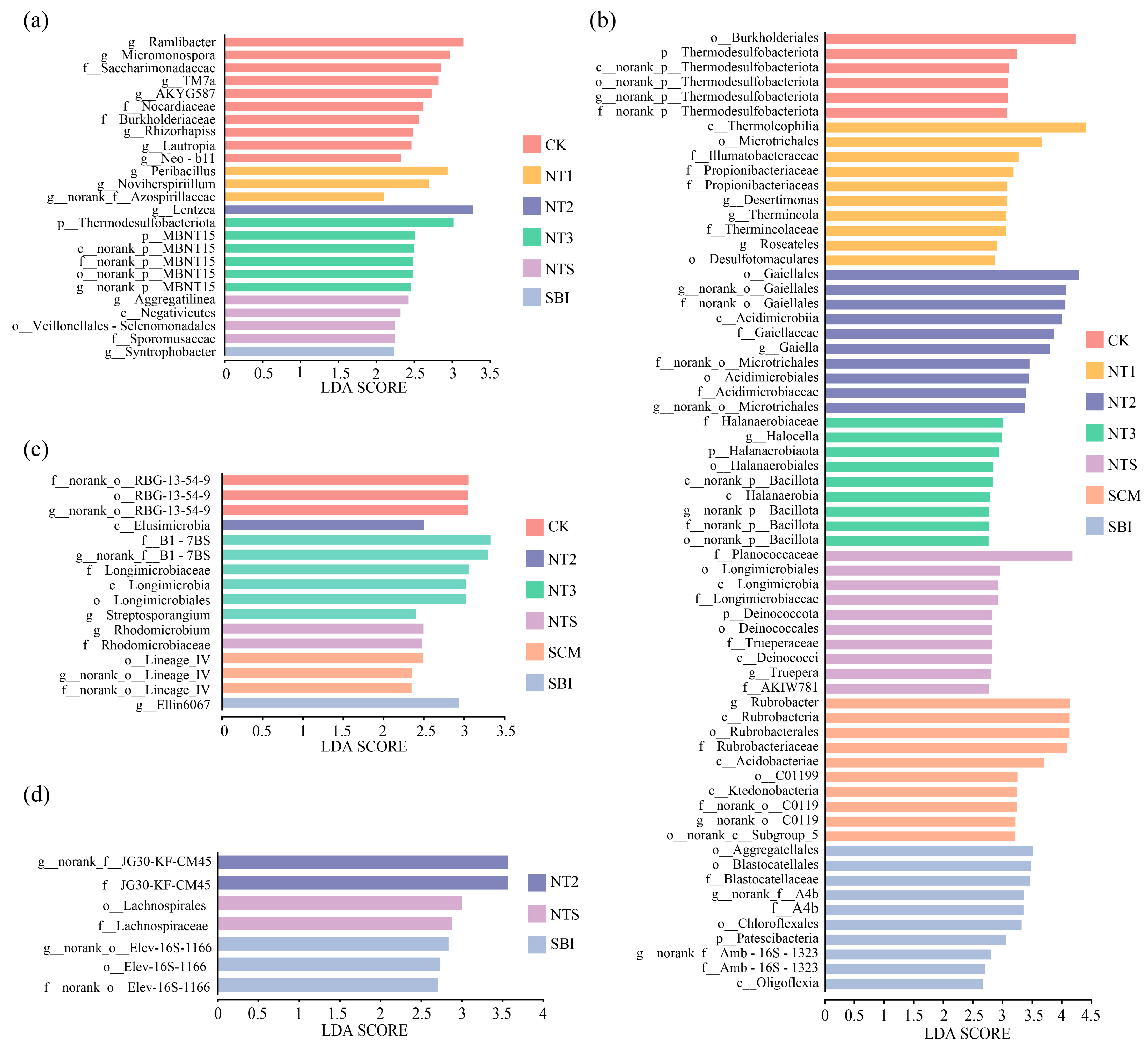
3.2. Composition and Differential Analysis of Freeze–Thaw Soil Bacterial Communities
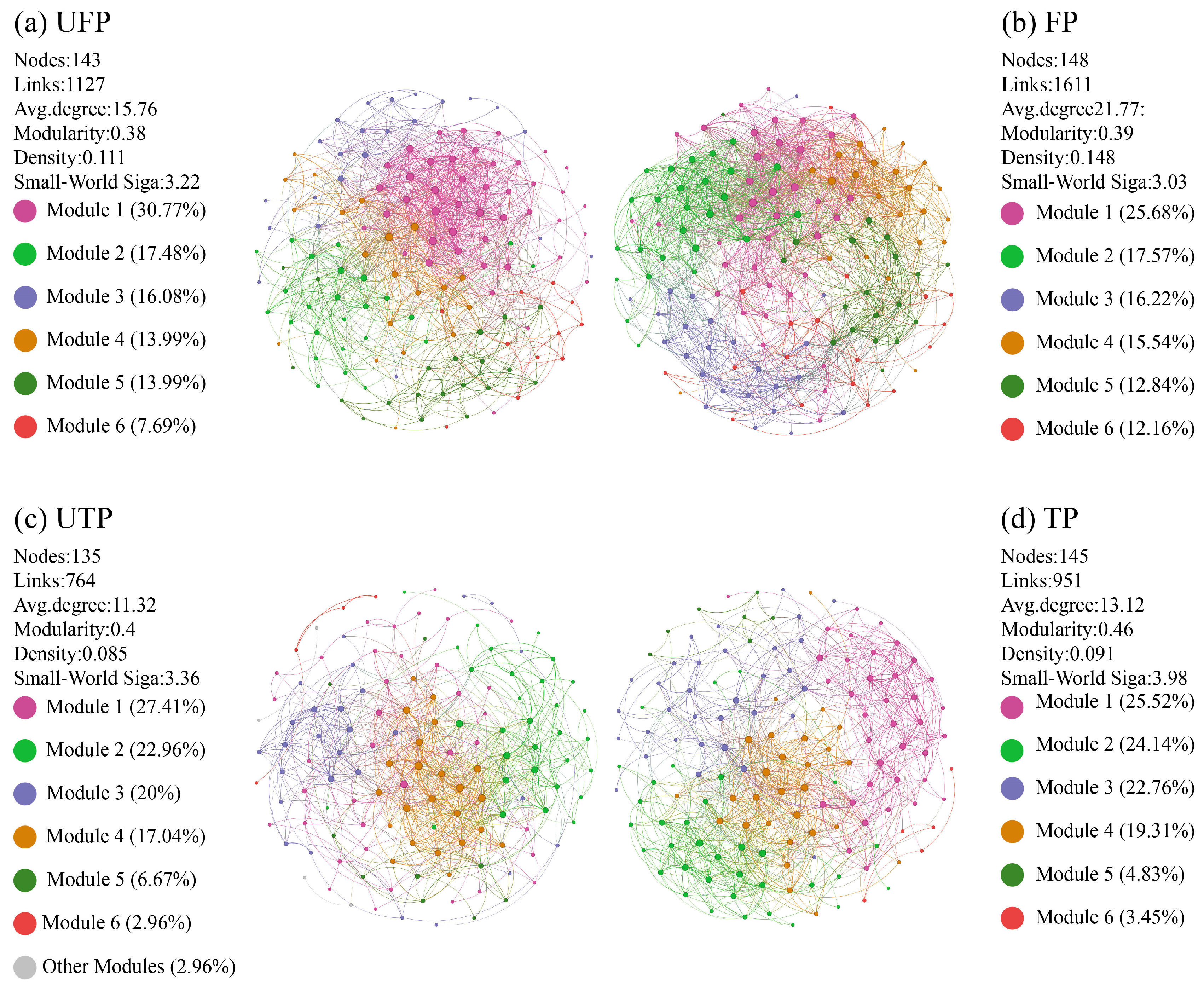
3.3. Co-Occurrence Networks of Freeze–Thaw Soil Bacterial Communities
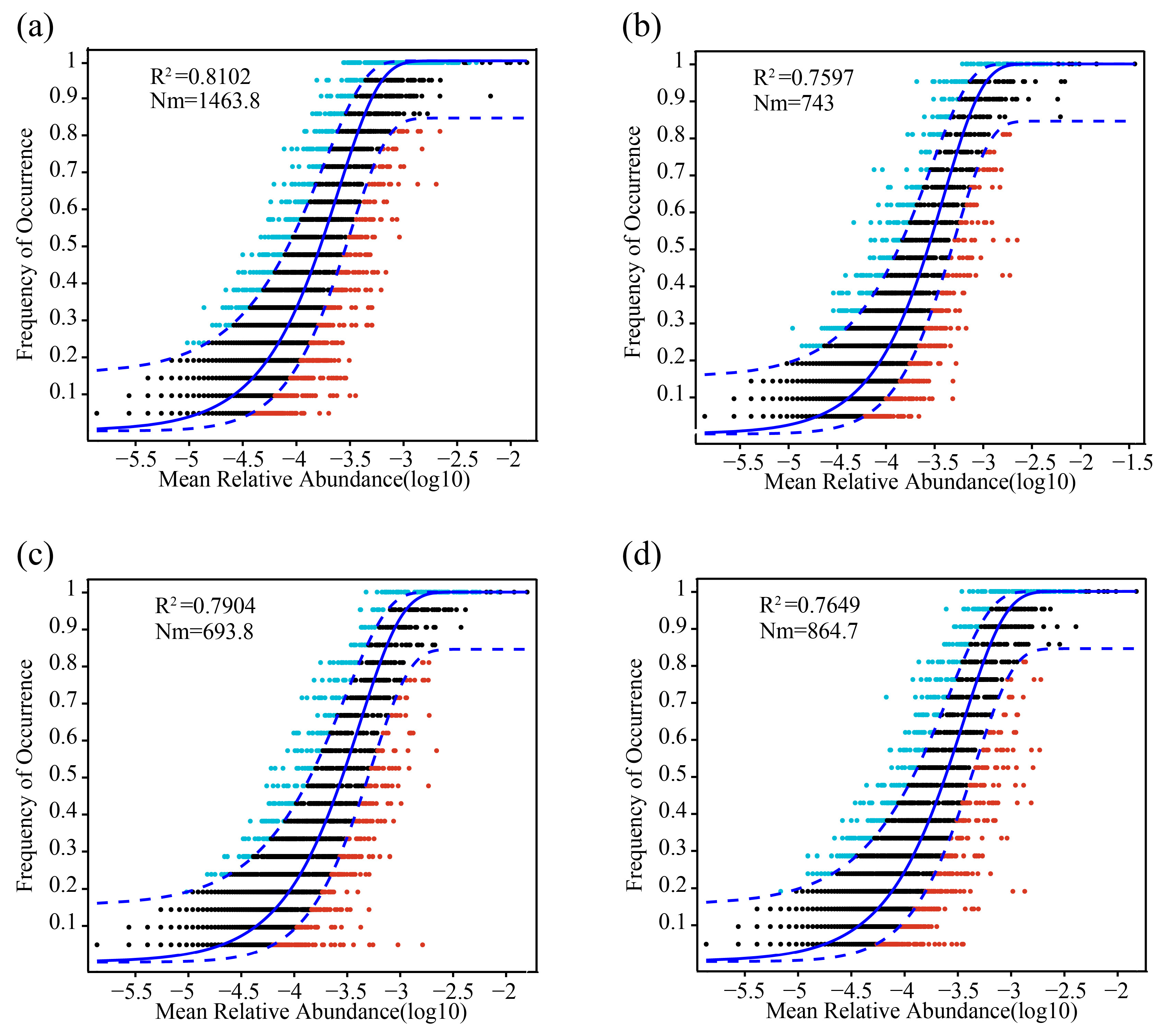
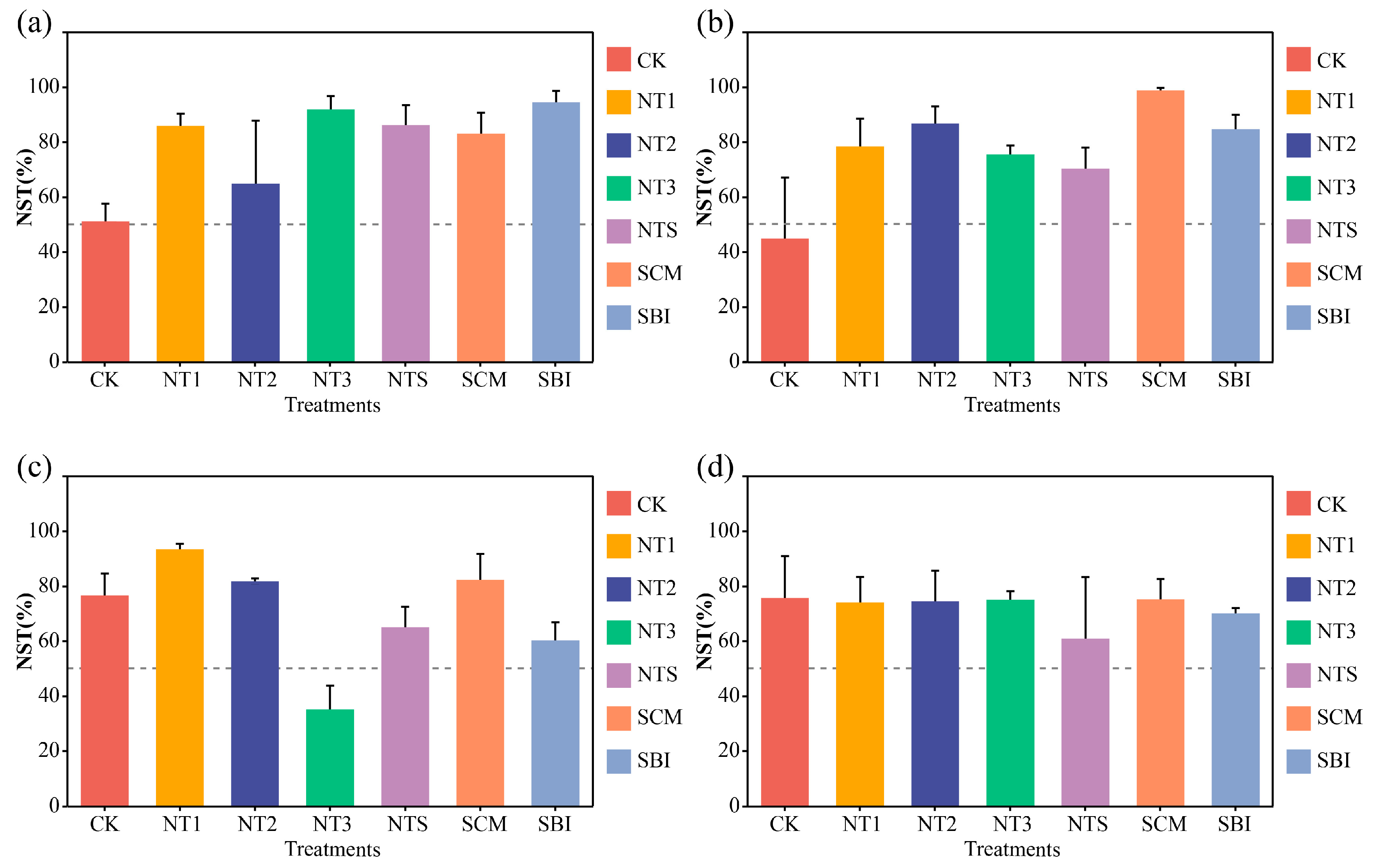
3.4. Ecological Assembly Processes of Freeze–Thaw Soil Bacterial Communities
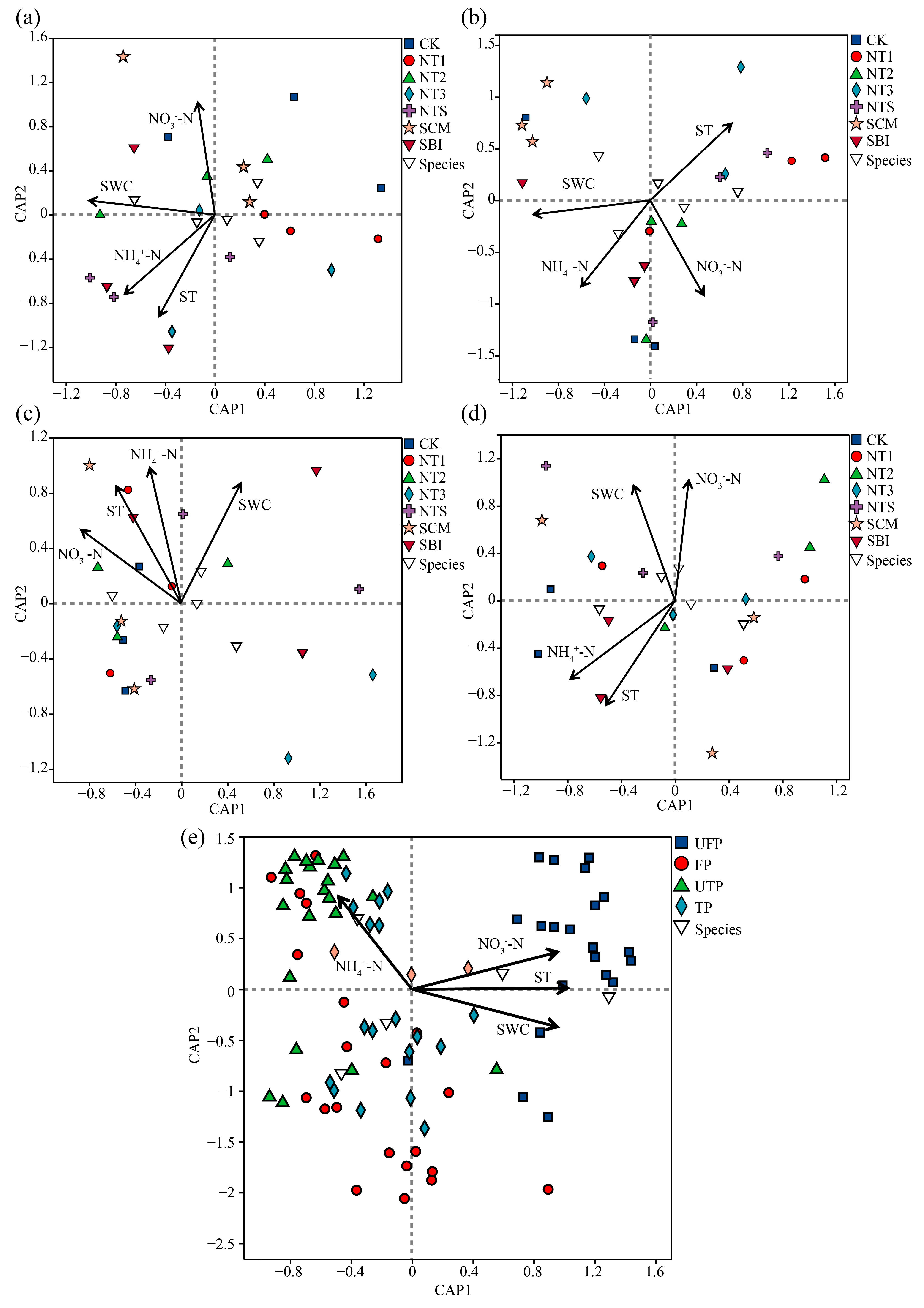
3.5. The Relationship Between Freeze–Thaw Soil Bacterial Communities and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Seasonal Freeze–Thaw and Tillage on Bacterial Diversity
4.2. Shifts in Bacterial Community Composition and Taxon-Specific Responses
4.3. Adaptive Changes in Bacterial Co-Occurrence Networks
4.4. Bacterial Community Assembly Under Seasonal Freeze–Thaw and Tillage
4.5. Key Environmental Drivers of Bacterial Community Dynamics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UFP | Unstable freezing period |
| FP | Frozen period |
| UTP | Unstable thawing period |
| TP | Thawed period |
| CK | Conventional tillage without straw |
| NT1 | No-Tillage 1 Year |
| NT2 | No-Tillage 2 Years |
| NT3 | No-Tillage 3 Years |
| NTS | No-tillage with straw mulching |
| SCM | Straw chopped-and-mixed incorporation |
| SBI | Straw burial incorporation |
| NCM | Neutral community model |
| NST | Normalized stochasticity ratio |
| SWC | Soil water content |
| ST | Soil temperature |
References
- Osterkamp, T.E. Characteristics of the Recent Warming of Permafrost in Alaska. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth Surf. 2007, 112, F02S02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurylyk, B.L.; MacQuarrie, K.T.B.; McKenzie, J.M. Climate Change Impacts on Groundwater and Soil Temperatures in Cold and Temperate Regions: Implications, Mathematical Theory, and Emerging Simulation Tools. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Jin, H.; Wu, Q.; Bense, V.F.; He, R.; Ma, Q.; Gao, S.; Jin, X.; Lu, L. Thermal Regime of Warm-Dry Permafrost in Relation to Ground Surface Temperature in the Source Areas of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, SW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Feng, F. Meta-Analysis of the Impact of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Soil Microbial Diversity and C and N Dynamics. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2022, 168, 108608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Hou, J.; Xiao, L.; Ren, Z.; Xu, G.; Yu, K.; Su, Y. The Effects of Freeze-Thaw Process on Soil Water Migration in Dam and Slope Farmland on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, L.; Bao, K.; Mao, L.; Klamt, A.-M.; Pratte, S.; Shen, J. Anthropogenic and Climate-Driven Environmental Change in the Songnen Plain of Northeastern China over the Past 200 Years. Paleogeogr. Paleoclimatol. Paleoecol. 2018, 511, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Xue, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Y. Biochar-Based Fertilizer Amendments Improve the Soil Microbial Community Structure in a Karst Mountainous Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöler, A.; Jacquiod, S.; Vestergaard, G.; Schulz, S.; Schloter, M. Analysis of Soil Microbial Communities Based on Amplicon Sequencing of Marker Genes. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Nielsen, L.L.; Simpson, M.J. Responses of Soil Organic Matter and Microorganisms to Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, Y.; Toyota, K.; Okazaki, M. Effects of Successive Soil Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Soil Microbial Biomass and Organic Matter Decomposition Potential of Soils. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2004, 50, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-D.; Hu, X. Seasonal Freeze-Thaw Processes Regulate and Buffer the Distribution of Microbial Communities in Soil Horizons. Catena 2023, 231, 107348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Gu, Y.; Liu, E.; Wu, M.; Cheng, X.; Yang, P.; Bahadur, A.; Bai, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. Freeze-Thaw Strength Increases Microbial Stability to Enhance Diversity-Soil Multifunctionality Relationship. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Hou, R.; Li, T.; Fu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Su, Z.; Shen, W.; Wang, Y. Effects of Biochar and Freeze-Thaw Cycles on the Bacterial Community and Multifunctionality in a Cold Black Soil Area. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.-L.; Gu, Y.-J.; Kong, M.; Hu, L.-W.; Jia, Y.; Li, F.-M.; Sun, G.-J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Responses of Soil Microorganisms, Carbon and Nitrogen to Freeze Thaw Cycles in Diverse Land-Use Types. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2018, 124, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.; Mitchell, J.; Scow, K. Cover Cropping and No-till Increase Diversity and Symbiotroph:Saprotroph Ratios of Soil Fungal Communities. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2019, 129, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, A.; Whalen, J.K.; McLaughlin, N.B. Greater Fungal and Bacterial Biomass in Soil Large Macropores under No-Tillage than Mouldboard Ploughing. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2020, 97, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Sun, R.; He, T.; Sun, Y.; Wu, M.; Xue, Y.; Meng, F.; Wang, J. Disentangling the Impact of Straw Incorporation on Soil Microbial Communities: Enhanced Network Complexity and Ecological Stochasticity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, Q.; Wen, J.; Ding, X.; Agathokleous, E. Straw Addition Decreased the Resistance of Bacterial Community Composition to Freeze–Thaw Disturbances in a Clay Loam Soil Due to Changes in Physiological and Functional Traits. Geoderma 2022, 424, 116007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Deng, M.; Yuan, A.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Ma, J. Vertical Variation of a Black Soil’s Properties in Response to Freeze-Thaw Cycles and Its Links to Shift of Microbial Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Li, T.; Du, S.; Li, A.; Liu, J. No-Tillage with Straw Mulching Increased Maize Yield and Nitrogen Fertilizer Recovery Rate in Northeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 292, 108687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, D.; Ma, W.; Guo, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, Q.; Lee, D.-J. Denitrifying Sulfide Removal Process on High-Salinity Wastewaters in the Presence of Halomonas sp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly Accurate OTU Sequences from Microbial Amplicon Reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberan, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using Network Analysis to Explore Co-Occurrence Patterns in Soil Microbial Communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, A.; Lan, W.; Woo, S.P.; Shau-Hwai, A.T.; Fan, J. Bacteria versus Fungi for Predicting Anthropogenic Pollution in Subtropical Coastal Sediments: Assembly Process and Environmental Response. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 134, 108484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Huang, T.; Mei, C.; Wu, F.; Cheng, B.; Li, X.; et al. Synergistic Mechanisms of AMF and Biochar Driving Rhizosphere Fungal Community in Shallot in Barren Soil. Hortic. Plant J. 2024, 10, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhong, S.; Luo, K.; Yang, S.; Xia, J.; Chen, Q. Effect of Metal Pollution on the Distribution and Co-Occurrence Pattern of Bacterial, Archaeal and Fungal Communities throughout the Soil Profiles. Chemosphere 2023, 315, 137692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, W.T.; Lunn, M.; Woodcock, S.; Head, I.M.; Nee, S.; Curtis, T.P. Quantifying the Roles of Immigration and Chance in Shaping Prokaryote Community Structure. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, D.; Yuan, M.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Arkin, A.P.; Firestone, M.K.; Zhou, J. A Quantitative Framework Reveals Ecological Drivers of Grassland Microbial Community Assembly in Response to Warming. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Jiao, Y.; Lyu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Soil Characteristics and Response Mechanism of the Microbial Community in a Coal–Grain Compound Area with High Groundwater Levels. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, W.; Wu, F. Effect of Seasonal Soil Freeze–Thaw Cycles on Bacterial Diversity in the Process of Fine Root Decomposition at Different Critical Periods. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.P.; Clein, J.S. Microbial Response to Freeze-Thaw Cycles in Tundra and Taiga Soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Szele, Z.; Schilling, R.; Munch, J.C.; Schloter, M. Influence of Freeze-Thaw Stress on the Structure and Function of Microbial Communities and Denitrifying Populations in Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 2148–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, D.; Liao, Y. Tillage Practices with Different Soil Disturbance Shape the Rhizosphere Bacterial Community throughout Crop Growth. Soil. Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, L.; Xie, J.; Coulter, J.A.; Zhang, R.; Luo, Z.; Cai, L.; Wang, L.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Soil Bacterial Diversity and Potential Functions Are Regulated by Long-Term Conservation Tillage and Straw Mulching. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Lin, X.; Guan, S.; Dou, S. Deep Incorporation of Corn Straw Benefits Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Community Composition in a Black Soil of Northeast China. Soil. Use Manage. 2022, 38, 1266–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wei, Z.; Schaeffer, S.M.; Liang, A.; Ding, X. Recovery of Bacterial Communities and Functions of Soils under Ridge Tillage and No-Tillage after Different Intensities and Frequencies of Drying-Wetting Disturbances in Agroecosystems of Northeastern China. Catena 2021, 203, 105367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sansupa, C.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Stability of Soil Bacteria in Undisturbed Soil and Continuous Maize Cultivation in Northern Thailand. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1285445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.; Song, W.; Qi, R.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Chang, Z. Land Use Types Drive the Distinct Patterns of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Soils from the Semi-Arid Area. Microb. Ecol. 2025, 88, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landesman, W.J.; Freedman, Z.B.; Nelson, D.M. Seasonal, Sub-Seasonal and Diurnal Variation of Soil Bacterial Community Composition in a Temperate Deciduous Forest. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; Abulaizi, M.; Hu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhu, X.; Yu, P.; Jia, H. Soil Bacterial Communities in Alpine Wetlands in Arid Central Asia Remain Stable during the Seasonal Freeze-Thaw Period. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bore, E.K.; Halicki, S.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Dippold, M.A. Structural and Physiological Adaptations of Soil Microorganisms to Freezing Revealed by Position-Specific Labeling and Compound-Specific 13C Analysis. Biogeochemistry 2019, 143, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, H.L. Bacterial Community Composition under Long-Term Reduced Tillage and No till Management. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 126, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Gu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Jia, Y. Effects of Autumn Diurnal Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Soil Bacteria and Greenhouse Gases in the Permafrost Regions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1056953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic Biomarker Discovery and Explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.; Kobabe, S.; Pfeiffer, E.-M.; Hubberten, H.-W. Microbial Controls on Methane Fluxes from a Polygonal Tundra of the Lena Delta, Siberia. Permafr. Periglac. Process. 2003, 14, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, J.; Balser, T.C.; Wallenstein, M. Microbial Stress-Response Physiology and Its Implications for Ecosystem Function. Ecology 2007, 88, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, Y.; Baker, N.R.; Herman, D.; Fossum, C.; Hale, L.; Zhang, X.; Nuccio, E.; Saha, M.; Zhou, J.; Pett-Ridge, J.; et al. Microbial Extracellular Polysaccharide Production and Aggregate Stability Controlled by Switchgrass (Panicum Virgatum) Root Biomass and Soil Water Potential. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.M.; Pimm, S.L.; Sole, R.V. Ecological Networks and Their Fragility. Nature 2006, 442, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Klenk, H.-P.; Clément, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, Physiology, and Natural Products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.E.; Ho, L.; Rees, C.A.; Hill, J.E.; Nodwell, J.R.; Elliot, M.A. Streptomyces Exploration Is Triggered by Fungal Interactions and Volatile Signals. eLife 2017, 6, e21738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F. Compositional Shifts and Co-Occurrence Patterns of Topsoil Bacteria and Micro-Eukaryotes across a Permafrost Thaw Gradient in Alpine Meadows of the Qilian Mountains, China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e0195524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latora, V.; Marchiori, M. Efficient Behavior of Small-World Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, M.; Kimothi, A.; Sharma, A.; Pandey, A. Cold Adapted Pseudomonas: Ecology to Biotechnology. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1218708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, B.; Bashir, Z.; Yatoo, A.M.; Mohiddin, F.; Majeed, N.; Bansal, M.; Poczai, P.; Almalki, W.H.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Shati, A.A.; et al. Cold-Active Enzymes and Their Potential Industrial Applications—A Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and Deterministic Assembly Processes in Subsurface Microbial Communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ren, K.; Isabwe, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, J. Stochastic Processes Shape Microeukaryotic Community Assembly in a Subtropical River across Wet and Dry Seasons. Microbiome 2019, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Ni, B.; Zou, Y.; Freeman, C.; Peng, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, G.; Jiang, M. Deciphering Soil Environmental Regulation on Reassembly of the Soil Bacterial Community during Wetland Restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mu, Y.; Ma, W.; Kong, X.; Yang, C. Dynamic Characteristics of Soil Pore Structure and Water-Heat Variations during Freeze-Thaw Process. Eng. Geol. 2024, 343, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Wang, C. Water Storage Effect of Soil Freeze-Thaw Process and Its Impacts on Soil Hydro-Thermal Regime Variations. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 265, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottos, E.M.; Kennedy, D.W.; Romero, E.B.; Fansler, S.J.; Brown, J.M.; Bramer, L.M.; Chu, R.K.; Tfaily, M.M.; Jansson, J.K.; Stegen, J.C. Dispersal Limitation and Thermodynamic Constraints Govern Spatial Structure of Permafrost Microbial Communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechesne, A.; Wang, G.; Gulez, G.; Or, D.; Smets, B.F. Hydration-Controlled Bacterial Motility and Dispersal on Surfaces. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14369–14372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.N.; Or, D. Microbial Dispersal in Unsaturated Porous Media: Characteristics of Motile Bacterial Cell Motions in Unsaturated Angular Pore Networks. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7406–7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecon, R.; Or, D. Biophysical Processes Supporting the Diversity of Microbial Life in Soil. Fems Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 599–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Dang, P.; Qin, X.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Straw Incorporation with Ridge-Furrow Plastic Film Mulch Alters Soil Fungal Community and Increases Maize Yield in a Semiarid Region of China. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2021, 167, 104038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; An, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Biogeography and the Driving Factors Affecting Forest Soil Bacteria in an Arid Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 680, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Ma, B. The Influence of Wheat Straw Mulching and Straw Length on Infiltration, Runoff and Soil Loss. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Norton, J.M.; Stark, J.M. Ammonium Availability and Temperature Control Contributions of Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria and Archaea to Nitrification in an Agricultural Soil. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

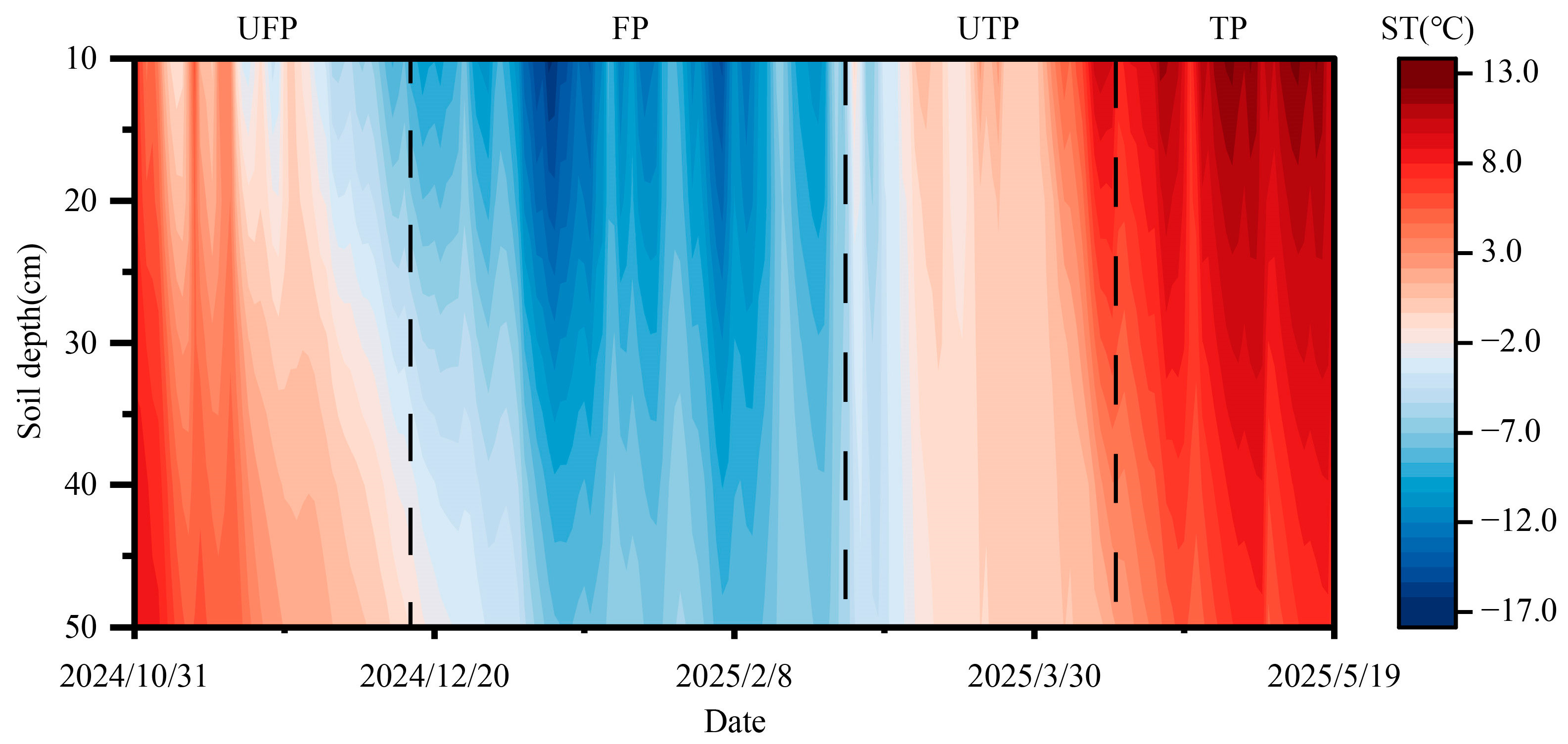
| Soil Depth (cm) | Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | pH | Available Nitrogen (mg·kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg·kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg·kg−1) | Organic Matter Content (g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5–20 | 1.17 | 7.27 | 154.4 | 40.1 | 376.8 | 30.31 |
| Treatment | Treatment Content | Treatment Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tillage Method | Straw Management | ||
| NT1 | One-year flat no-tillage, maize straw removed. | Flat cultivation with no-tillage for one year, no tillage operations. | Maize straw was removed from the field after harvest. |
| NT2 | Continuous two-year flat no-tillage, maize straw removed. | Continuous flat cultivation with no-tillage for two years, no tillage operations. | Maize straw was removed from the field after harvest. |
| NT3 | Continuous three-year flat no-tillage, maize straw removed. | Continuous flat cultivation with no-tillage for three years, no tillage operations. | Maize straw was removed from the field after harvest. |
| NTS | Flat no-tillage with full straw mulching. | Flat cultivation with no-tillage, no tillage operations. | After harvest, maize straw was chopped (particle size < 10 cm) and evenly distributed on the soil surface. |
| SCM | Straw chopped-and-mixed incorporation, ridge tillage. | Conventional ridge tillage combined with topsoil plowing. | After harvest, maize straw was chopped (particle size < 10 cm) and uniformly mixed into the 0–30 cm soil layer during plowing. |
| SBI | Straw burial incorporation, ridge tillage. | Conventional ridge tillage combined with topsoil plowing. | After harvest, maize straw was chopped (particle size < 10 cm) and buried in the soil layer at a depth of 30 cm. |
| CK | Conventional ridge tillage. | Conventional ridge tillage with plowing. | All maize straw was removed from the field after harvest. |
| Period | SWC | ST | NO3−-N | NH4+-N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UFP | R2 | 0.435 | 0.333 | 0.545 | 0.287 |
| p-value | 0.01 ** | 0.033 * | 0.003 ** | 0.051 | |
| FP | R2 | 0.427 | 0.107 | 0.357 | 0.277 |
| p-value | 0.008 ** | 0.383 | 0.018 * | 0.047 * | |
| UTP | R2 | 0.363 | 0.227 | 0.257 | 0.053 |
| p-value | 0.02 * | 0.087 | 0.066 | 0.633 | |
| TP | R2 | 0.463 | 0.151 | 0.392 | 0.449 |
| p-value | 0.005 ** | 0.237 | 0.008 ** | 0.003 ** | |
| ALL | R2 | 0.227 | 0.653 | 0.422 | 0.118 |
| p-value | 0.001 *** | 0.001 *** | 0.001 *** | 0.009 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Si, Z.; Huang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, B.; Ren, A. Tillage Effects on Bacterial Community Structure and Ecology in Seasonally Frozen Black Soils. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202132
Liu B, Si Z, Huang Y, Sun Y, Wang B, Ren A. Tillage Effects on Bacterial Community Structure and Ecology in Seasonally Frozen Black Soils. Agriculture. 2025; 15(20):2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202132
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bin, Zhenjiang Si, Yan Huang, Yanling Sun, Bai Wang, and An Ren. 2025. "Tillage Effects on Bacterial Community Structure and Ecology in Seasonally Frozen Black Soils" Agriculture 15, no. 20: 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202132
APA StyleLiu, B., Si, Z., Huang, Y., Sun, Y., Wang, B., & Ren, A. (2025). Tillage Effects on Bacterial Community Structure and Ecology in Seasonally Frozen Black Soils. Agriculture, 15(20), 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202132






