Design of a Predictive Digital Twin System for Large-Scale Varroa Management in Honeybee Apiaries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method
3. Results
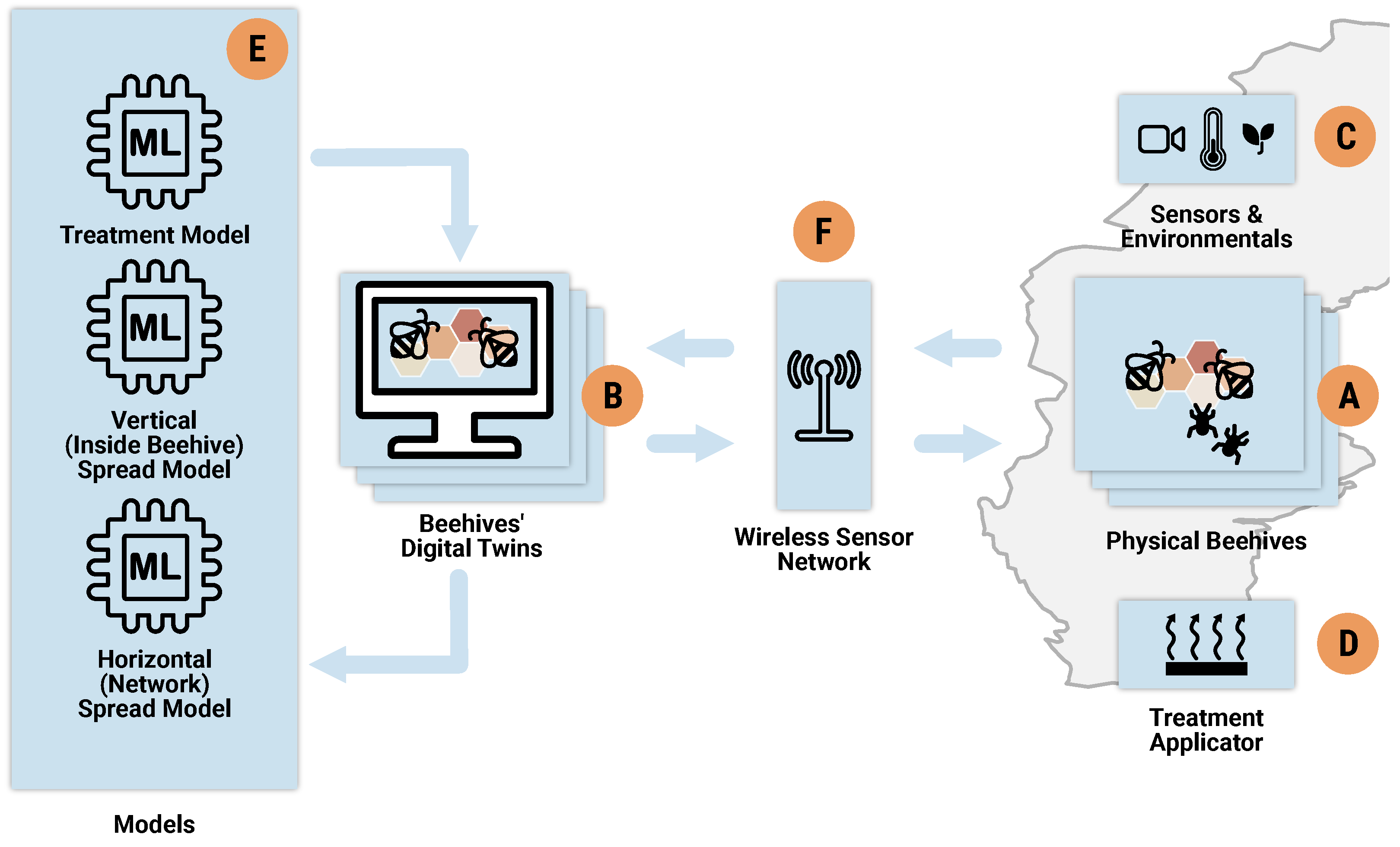
3.1. Architecture and Components
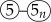 ).
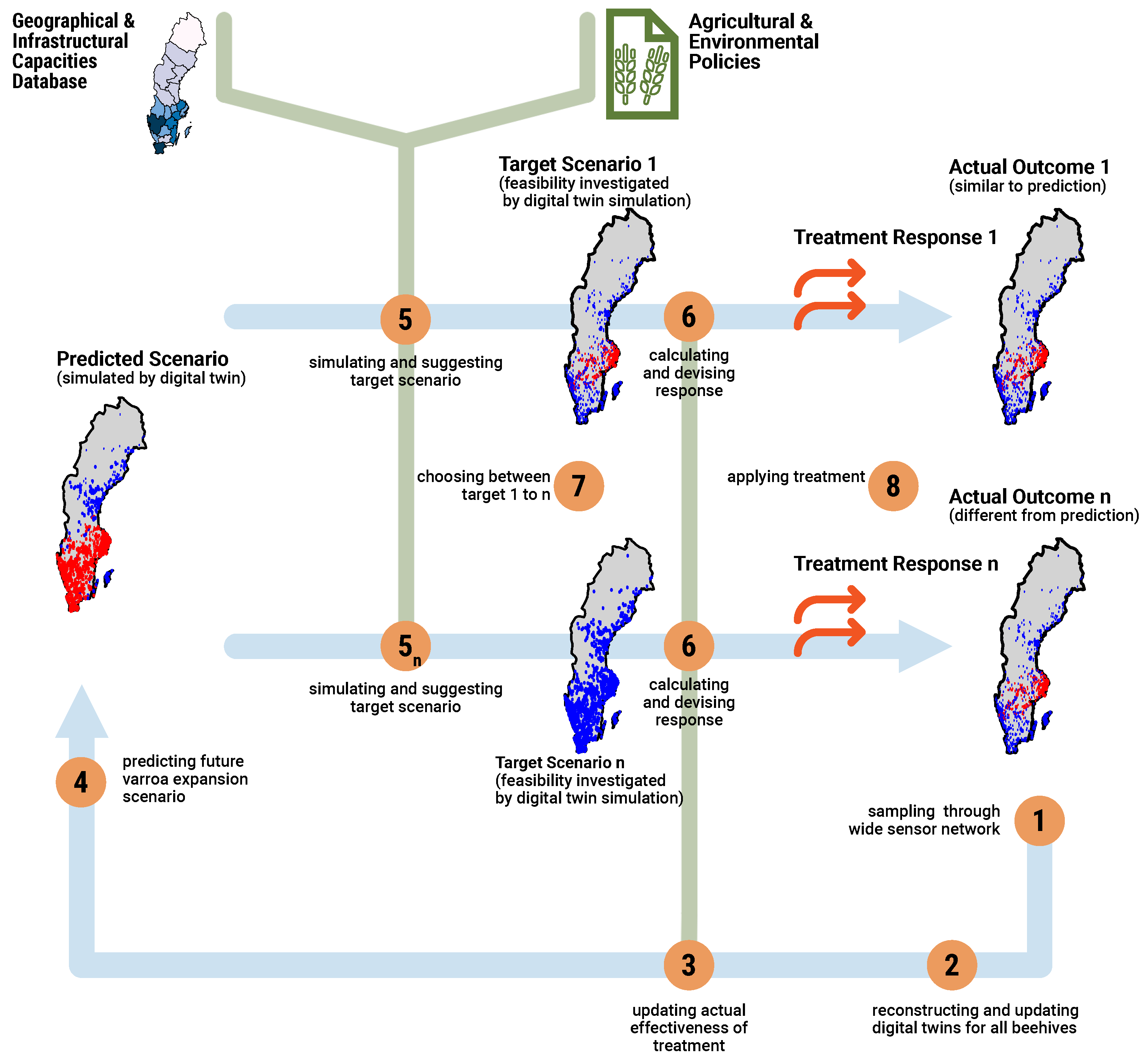
).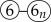 ). After the initial cycle in the workflow, the effectiveness of prior interventions—as reflected in the actual outcomes—becomes an additional parameter (⑥) that is updated alongside other parameters (③).
). After the initial cycle in the workflow, the effectiveness of prior interventions—as reflected in the actual outcomes—becomes an additional parameter (⑥) that is updated alongside other parameters (③).3.2. Mite Detection System
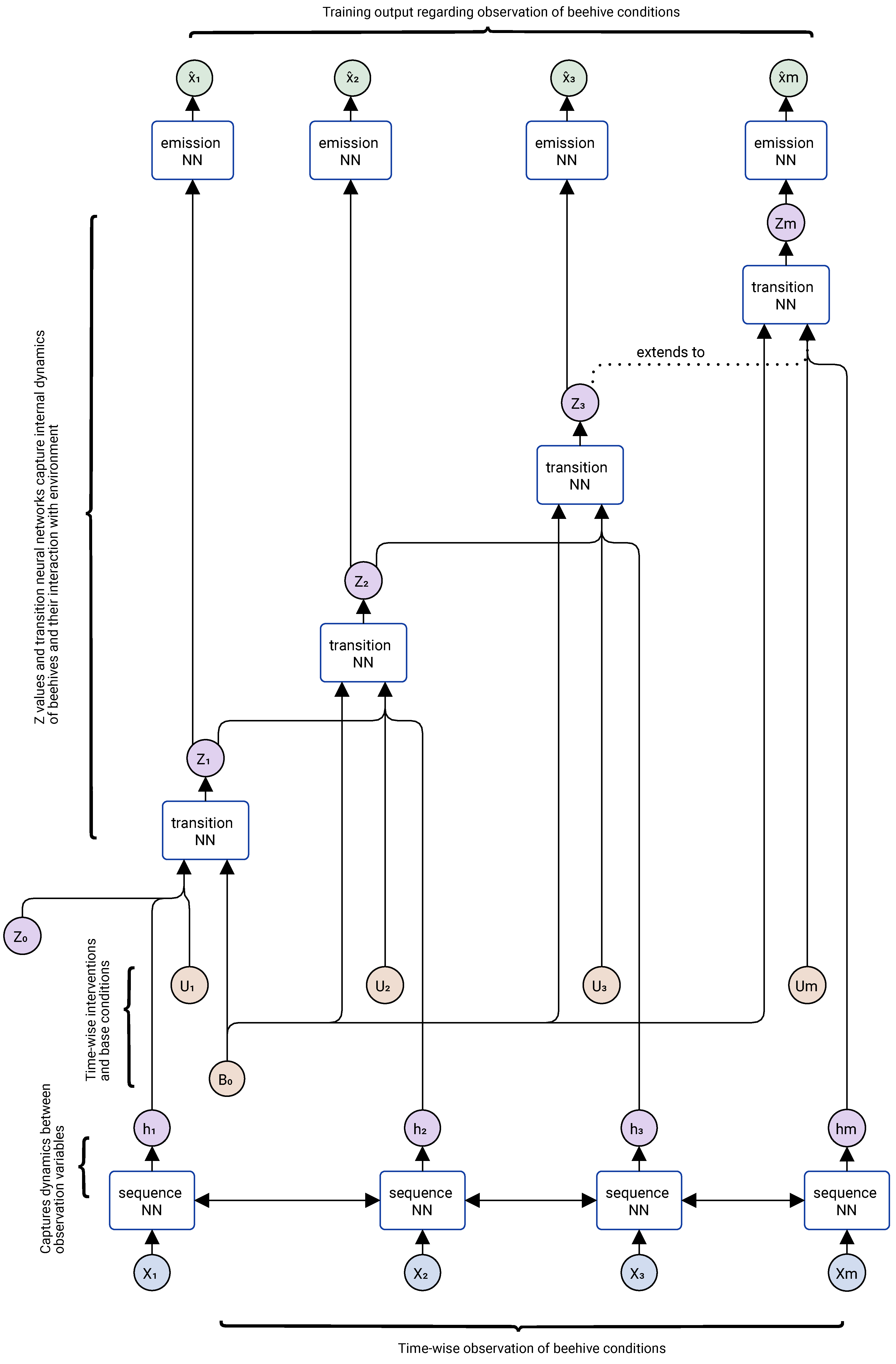
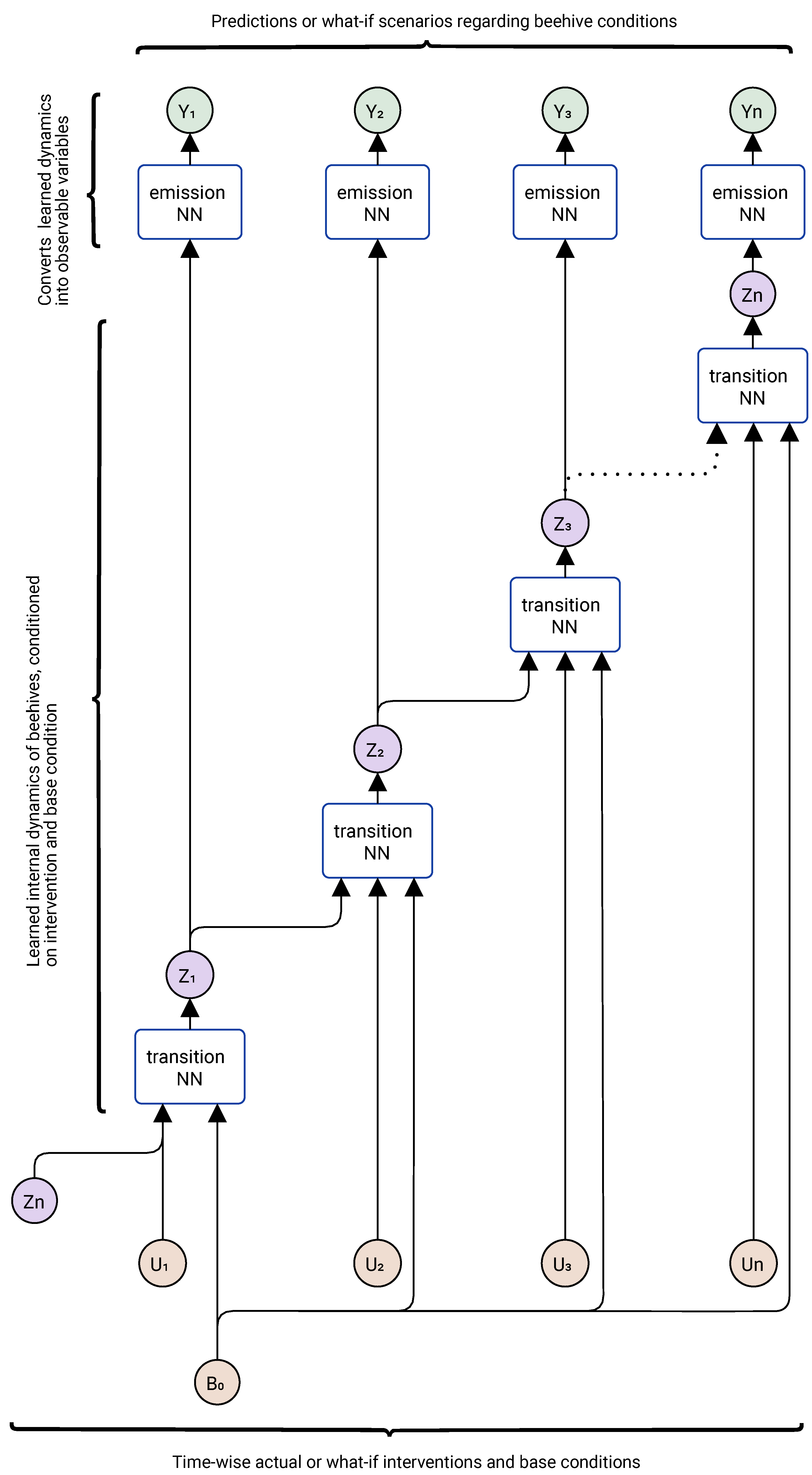
3.3. Modeling Vertical and Horizontal Dynamics
3.4. Pretraining the Models for Population Dynamics and Mite Spread
3.4.1. Vertical Spread Model: Within a Colony
3.4.2. Horizontal Spread Model: Among Colonies
3.4.3. Pretraining the Models for Treatment Effects
3.5. Dynamic Monitoring Strategy for Mitigating Disease Spread
3.6. Feasibility of Implementing Digital Twins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenkranz, P.; Aumeier, P.; Ziegelmann, B. Biology and Control of Varroa Destructor. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103, S96–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Steen, J.; Vejsnæs, F. Varroa Control: A Brief Overview of Available Methods. Bee World 2021, 98, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government. Varroa Mite (Varroa Destructor) | Outbreak, 2023. September 2023. Available online: https://www.outbreak.gov.au/current-outbreaks/varroa-mite (accessed on 13 February 2024).
- Guichard, M.; Dietemann, V.; Neuditschko, M.; Dainat, B. Advances and Perspectives in Selecting Resistance Traits against the Parasitic Mite Varroa Destructor in Honey Bees. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2020, 52, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamiduzzaman, M.M.; Sinia, A.; Guzman-Novoa, E.; Goodwin, P.H. Entomopathogenic Fungi as Potential Biocontrol Agents of the Ecto-Parasitic Mite, Varroa destructor, and Their Effect on the Immune Response of Honey Bees (Apis mellifera L.). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 111, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël, A.; Le Conte, Y.; Mondet, F. Varroa Destructor: How Does It Harm Apis Mellifera Honey Bees and What Can Be Done about It? Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2020, 4, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, S.; Howlett, B.G.; Donovan, B.J.; Nelson, W.R.; van Toor, R.F. Culturing Chelifers (Pseudoscorpions) That Consume Varroa Mites. J. Appl. Entomol. 2014, 138, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.J.; Ellis, J.D. Integrated Pest Management Control of Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae), the Most Damaging Pest of (Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera: Apidae)) Colonies. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.V.; Moon, R.D.; Burkness, E.C.; Hutchison, W.D.; Spivak, M. Practical Sampling Plans for Varroa destructor (Acari: Varroidae) in Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae) Colonies and Apiaries. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietemann, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Neumann, P. (Eds.) The COLOSS BEEBOOK Volume I: Standard Methods for Apis Mellifera Research; International Bee Research Association IBRA: Treforest, UK, 2013; Volume 52. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Cui, M.; Xu, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Xu, X.; Yan, Y. Detection of Varroa Destructor Infestation of Honeybees Based on Segmentation and Object Detection Convolutional Neural Networks. AgriEngineering 2023, 5, 1644–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yániz, J.; Casalongue, M.; Martinez-de-Pison, F.J.; Silvestre, M.A.; Consortium, B.; Santolaria, P.; Divasón, J. An AI-Based Open-Source Software for Varroa Mite Fall Analysis in Honeybee Colonies. Agriculture 2025, 15, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutaru, D.; Bergonzoli, S.; Costa, C.; Violino, S.; Costa, C.; Albertazzi, S.; Capano, V.; Kostić, M.M.; Scarfone, A. An AI-Based Digital Scanner for Varroa Destructor Detection in Beekeeping. Insects 2025, 16, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlinghaus, P.; Gülzow, J.M.; Odemer, R. In-Hive Flatbed Scanners for Non-Destructive, Long-Term Monitoring of Honey Bee Brood, Pathogens and Pests. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 9, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, Z.S.; Zemcik, T.; Bilik, S.; Sihvonen, T.; Honec, P.; Reinikainen, S.P.; Horak, K. Varroa Destructor Detection on Honey Bees Using Hyperspectral Imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Ardekani, I.; Sharifzadeh, H.; Varastehpour, S. A CNN-Based Identification of Honeybees’ Infection Using Augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical, Computer, Communications and Mechatronics Engineering (ICECCME), Maldives, 16–18 November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudiotis, G.; Moraiti, A.; Kontogiannis, S. Deep Learning Beehive Monitoring System for Early Detection of the Varroa Mite. Signals 2022, 3, 506–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurischuster, S.; Kampel, M. Image-Based Classification of Honeybees. In Proceedings of the 2020 Tenth International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), Paris, France, 9–12 November 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerge, K.; Frigaard, C.E.; Mikkelsen, P.H.; Nielsen, T.H.; Misbih, M.; Kryger, P. A Computer Vision System to Monitor the Infestation Level of Varroa Destructor in a Honeybee Colony. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 164, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannesi, L.; Russo, P.; Beraldi, R. Vit4v: A Video Classification Method for the Detection of Varroa Destructor from Honeybees. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 5343–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.; Oh, H.; Lee, Y.; Seo, H.; Jo, G.; Jeong, J.; Park, G.; Choi, J.; Seo, Y.D.; Jeong, J.H.; et al. IoT and AI Systems for Enhancing Bee Colony Strength in Precision Beekeeping: A Survey and Future Research Directions. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 362–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, H.; Bencsik, M.; Newton, M. Automated, Non-Invasive Varroa Mite Detection by Vibrational Measurements of Gait Combined with Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczurek, A.; Maciejewska, M.; Bąk, B.; Wilk, J.; Wilde, J.; Siuda, M. Detecting Varroosis Using a Gas Sensor System as a Way to Face the Environmental Threat. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards-Murphy, F.; Magno, M.; Whelan, P.M.; O’Halloran, J.; Popovici, E.M. b+WSN: Smart Beehive with Preliminary Decision Tree Analysis for Agriculture and Honey Bee Health Monitoring. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 124, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senger, D.; Johannsen, C.; Kluss, T. Anomaly Detection at the Apiary: Predicting State and Swarming Preparation Activity of Honey Bee Colonies Using Low-Cost Sensor Technology. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech), Virtual, 21–23 April 2022; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasyam, V.; Eivazzadeh, S.; Pokuri, S.; Zhao, J.; Khatibi, S. Designing a Wireless Sensor Network Solution for Varroa Control in Bee Colonies. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Tenth International Conference on Communications and Electronics (ICCE), Da Nang, Vietnam, 31 July–2 August 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.A.; Dénes, A. A Mathematical Model for the Spread of Varroa Mites in Honeybee Populations: Two Simulation Scenarios with Seasonality. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, M.A.; Grimm, V.; Thorbek, P.; Horn, J.; Kennedy, P.J.; Osborne, J.L. BEEHAVE: A Systems Model of Honeybee Colony Dynamics and Foraging to Explore Multifactorial Causes of Colony Failure. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, D.J.; Torres, N.A. Modeling the Influence of Mites on Honey Bee Populations. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiga, A.; Palmer, N.; Baek, Y.Y.; Mortveit, H.; Ravi, S.S. Network Models and Simulation Analytics for Multi-scale Dynamics of Biological Invasions. Front. Big Data 2022, 5, 796897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Valk, H.; Haße, H.; Möller, F.; Otto, B. Archetypes of Digital Twins. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2022, 64, 375–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, D.; Gonsard, A. Definitions and Characteristics of Patient Digital Twins Being Developed for Clinical Use: Scoping Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e58504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirahmadi, A.; Hensel, O. Toward the Next Generation of Digitalization in Agriculture Based on Digital Twin Paradigm. Sensors 2022, 22, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gund, R.; Badgujar, C.M.; Samiappan, S.; Jagadamma, S. Application of Digital Twin Technology in Smart Agriculture: A Bibliometric Review. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdouw, C.; Tekinerdogan, B.; Beulens, A.; Wolfert, S. Digital Twins in Smart Farming. Agric. Syst. 2021, 189, 103046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawn, N.; Ghosh, S.; Saha, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Ghosh, T.; Guha, S.; Sarkar, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Sanyal, T. A Review on Digital Twins Technology: A New Frontier in Agriculture. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2024, 2, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z. Digital Twins’ Technology for Smart Agriculture. In Encyclopedia of Digital Agricultural Technologies; Zhang, Q., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneveld, J.; Martinovic, T.; Rossi, T.; Salamon, O.; Sara-aho, K.; Grimm, V. Prototype Biodiversity Digital Twin: Honey Bees in Agricultural Landscapes. Res. Ideas Outcomes 2024, 10, e125167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, M. BEEHAVE. 2023. Available online: https://beehave-model.net/ (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Senger, D.; Kluss, T.; Förster, A. Towards a Warning System for Beekeepers: Detecting Anomalous Changes in Sensor Data from Honey Bee Colonies. In Proceedings of the EnviroInfo 2023. Gesellschaft für Informatik e.V., Garching, Germany, 11–13 October 2023; pp. 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Johannsen, C.; Senger, D.; Kluss, T. A Digital Twin of the Social-Ecological System Urban Beekeeping. In Advances and New Trends in Environmental Informatics; Kamilaris, A., Wohlgemuth, V., Karatzas, K., Athanasiadis, I.N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Progress in IS is series; pp. 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudragada, S.C.M.; Vendrapu, S. Feasibility of Having a Digital Twin of Sensor Network for Varroa Control in Bee Colonies with Hardware Integration and Digital Twin Platform. Master’s Thesis, Blekinge Institute of Technology, Karlskrona, Sweden, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Blessing, L.T.M.; Chakrabarti, A. DRM, a Design Research Methodology; Springer: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liljeberg, C. The Apiary Map-Beekeepers and Apiaries on a Map. 2024. Available online: https://apiarymap.com/ (accessed on 23 February 2024).
- Bilik, S.; Kratochvila, L.; Ligocki, A.; Bostik, O.; Zemcik, T.; Hybl, M.; Horak, K.; Zalud, L. Visual Diagnosis of the Varroa Destructor Parasitic Mite in Honeybees Using Object Detector Techniques. Sensors 2021, 21, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odemer, R. Approaches, Challenges and Recent Advances in Automated Bee Counting Devices: A Review. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2022, 180, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriouile, Y.; Ancourt, C.; Wegrzyn-Wolska, K.; Bougueroua, L. Nested Object Detection Using Mask R-CNN: Application to Bee and Varroa Detection. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 22587–22609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divasón, J.; Martinez-de-Pison, F.J.; Romero, A.; Santolaria, P.; Yániz, J.L. Varroa Mite Detection Using Deep Learning Techniques. In Hybrid Artificial Intelligent Systems; García Bringas, P., Pérez García, H., Martínez de Pisón, F.J., Martínez Álvarez, F., Troncoso Lora, A., Herrero, Á., Calvo Rolle, J.L., Quintián, H., Corchado, E., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehzadi, T.; Hashmi, K.A.; Stricker, D.; Afzal, M.Z. Object Detection with Transformers: A Review. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.04670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M. Towards Efficient Vision Transformer Inference: A First Study of Transformers on Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, New York, NY, USA, 9–10 March 2022; HotMobile ’22. pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Bulat, A.; Tan, F.; Zhu, X.; Dudziak, L.; Li, H.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Martinez, B. EdgeViTs: Competing Light-Weight CNNs on Mobile Devices with Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2022, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cissé, M., Farinella, G.M., Hassner, T., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 294–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N. Enhancing Honeybee Hive Health Monitoring: Vision Transformer-Based Non-Invasive Classification. In Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Ambient Intelligence in Health Care (ICAIHC), Raipur, India, 10–11 January 2025; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Ratti, V.; Kang, Y.; Chen, J.; DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Ratti, V.; Kang, Y. Review on Mathematical Modeling of Honeybee Population Dynamics. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2021, 18, 9606–9650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassly, N.C.; Fraser, C. Mathematical Models of Infectious Disease Transmission. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, M.T.; Ehrhardt, M. Differential Equation Models for Infectious Diseases: Mathematical Modeling, Qualitative Analysis, Numerical Methods and Applications. SeMA J. 2025, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Guo, G.; Qiu, X. Mathematical and Computational Approaches to Epidemic Modeling: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Comput. Sci. 2015, 9, 806–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Peng, J.; He, T.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Pan, S.; Chen, S. Compatible Transformer for Irregularly Sampled Multivariate Time Series. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, K.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, D. ContiFormer: Continuous-Time Transformer for Irregular Time Series Modeling. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.10635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Goel, K.; Ré, C. Efficiently Modeling Long Sequences with Structured State Spaces. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2111.00396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-Time Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidger, P.; Morrill, J.; Foster, J.; Lyons, T. Neural Controlled Differential Equations for Irregular Time Series. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 33, pp. 6696–6707. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, R.G.; Shalit, U.; Sontag, D. Structured Inference Networks for Nonlinear State Space Models. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; AAAI’17. pp. 2101–2109. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, P.; Freymuth, N.; Neumann, G. KalMamba: Towards Efficient Probabilistic State Space Models for RL under Uncertainty. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.15131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, P.; Campitelli, P.; Shepherd, D.P.; Ozkan, S.B.; Pressé, S. Mamba Time Series Forecasting with Uncertainty Quantification. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2025, 6, 035012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Winata, G.I.; Xu, P.; Liu, Z.; Fung, P. Variational Transformers for Diverse Response Generation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.12738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liu, A.; Dong, F.; Gu, F.; Gama, J.; Zhang, G. Learning under Concept Drift: A Review. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2019, 31, 2346–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, M.U.G.; Tsui, J.L.H.; Chang, S.Y.; Lytras, S.; Khurana, M.P.; Vanderslott, S.; Bajaj, S.; Scheidwasser, N.; Curran-Sebastian, J.L.; Semenova, E.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Modelling Infectious Disease Epidemics. Nature 2025, 638, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wan, G.; Prakash, B.A.; Lau, M.S.; Jin, W. A Review of Graph Neural Networks in Epidemic Modeling. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Barcelona, Spain, 25–29 August 2024; pp. 6577–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; White, S. Neural Posterior Estimation on Exponential Random Graph Models: Evaluating Bias and Implementation Challenges. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.09349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, A. Estimating Network Models Using Neural Networks. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.01810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messan, K.; Rodriguez Messan, M.; Chen, J.; DeGrandi-Hoffman, G.; Kang, Y. Population Dynamics of Varroa Mite and Honeybee: Effects of Parasitism with Age Structure and Seasonality. Ecol. Model. 2021, 440, 109359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasyam, V.S.A.; Pokuri, S. Wireless Sensor Network for Controlling the Varroasis Spread within Bee Colonies across a Geographical Region. Master’s Thesis, Blekinge Institute of Technology, Karlskrona, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kablau, A.; Berg, S.; Rutschmann, B.; Scheiner, R. Short-Term Hyperthermia at Larval Age Reduces Sucrose Responsiveness of Adult Honeybees and Can Increase Life Span. Apidologie 2020, 51, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SunFounder. ESP32 CAM—SunFounder GalaxyRVR Kit for Arduino 1.0 Documentation. 2025. Available online: https://docs.sunfounder.com/projects/galaxy-rvr/en/latest/hardware/cpn_esp_32_cam.html (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Quectel. LPWA BC660K-GL NB2|Quectel. 2025. Available online: https://www.quectel.com/product/lpwa-bc660k-gl-nb2/ (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Industries, A. DHT22 Temperature-Humidity Sensor + Extras. 2025. Available online: https://www.adafruit.com/product/385 (accessed on 21 August 2025).
- Sandrock, C.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Brunner, W.; Brunner, P. Efficacy and Trade-Offs of an Innovative Hyperthermia Device to Control Varroa Destructor in Honeybee Colonies. J. Pest Sci. 2024, 97, 1433–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porporato, M.; Manino, A.; Cuttini, D.; Lorenzon, S.; Ciaudano, S.; Parodi, V. Varroa Control by Means of a Hyperthermic Device. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kablau, A.; Berg, S.; Härtel, S.; Scheiner, R. Hyperthermia Treatment Can Kill Immature and Adult Varroa Destructor Mites without Reducing Drone Fertility. Apidologie 2020, 51, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinanis, G.; Lambropoulos, G. Beehive Frame and Comb Foundation for Controlling Varroa Mites. US. US8272921B2, 25 September 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Chen, Y.; Mao, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yu, M. Forecasting Spatio-Temporal Renewable Scenarios: A Deep Generative Approach. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.05274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
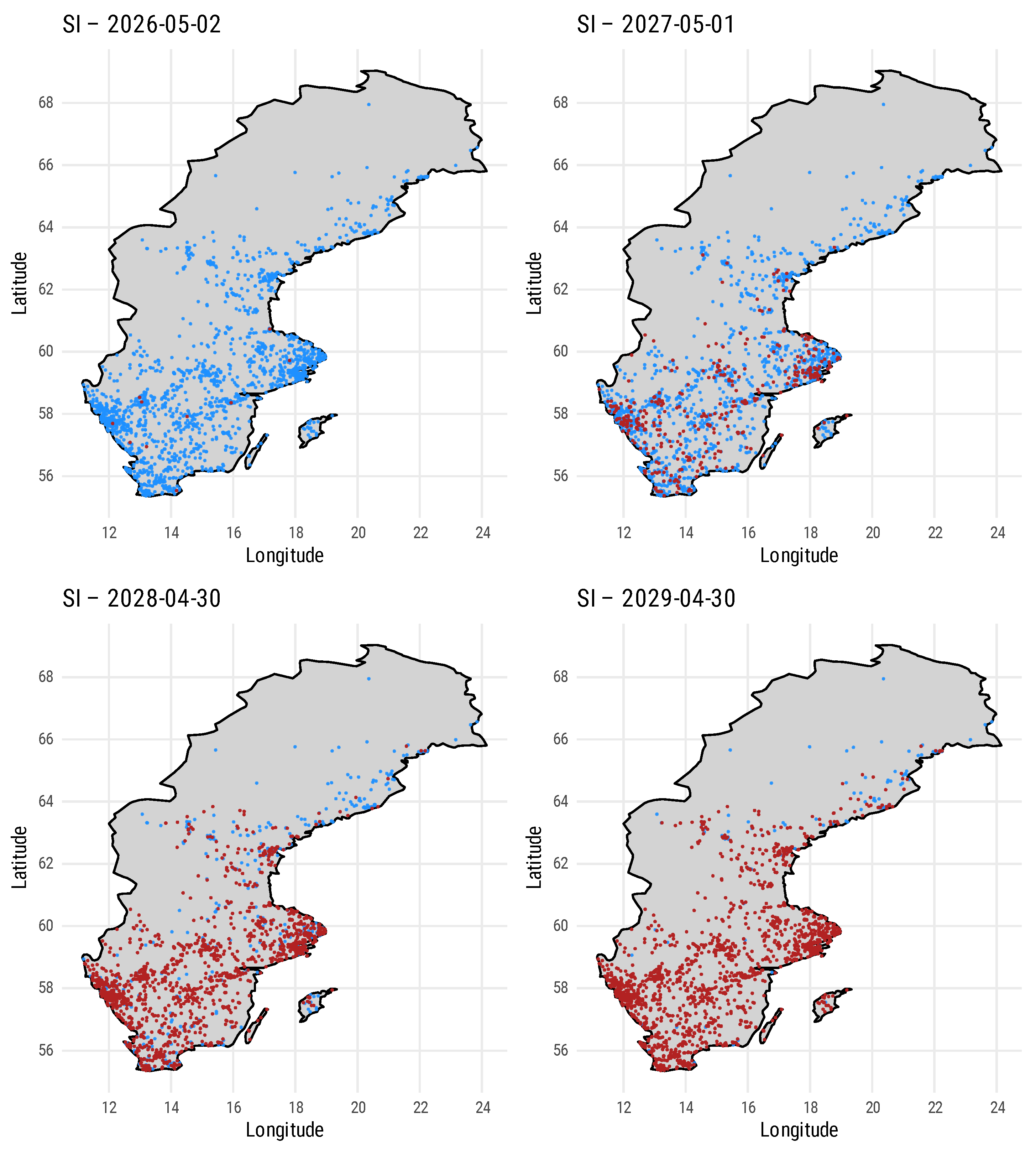
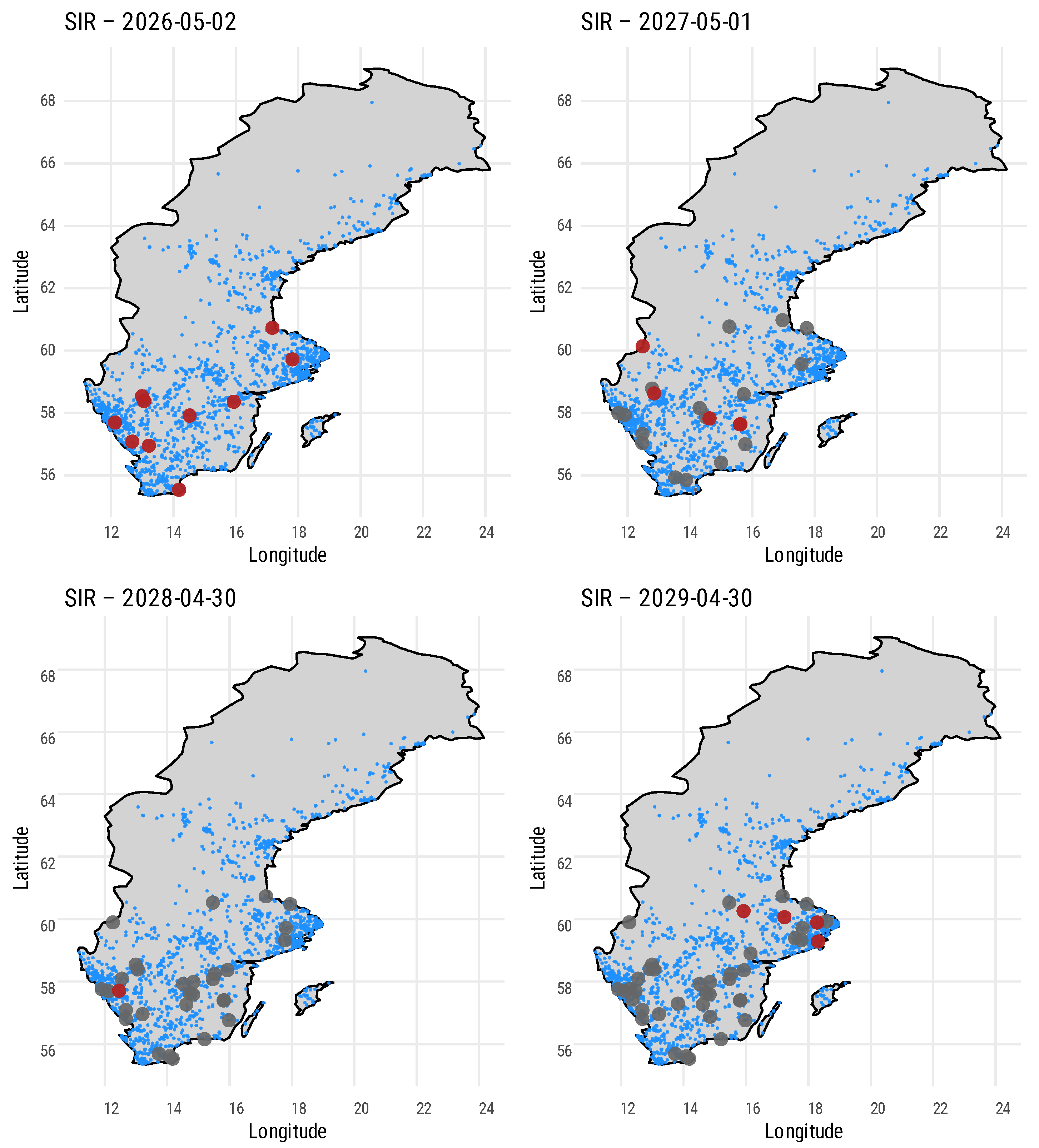
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Nodes | 619 |
| Average Distance Between Nodes | 243.90 km |
| Distance Variability (SD) | 122.85 km |
| Maximum Distance Between Nodes | 658.68 km |
| Minimum Distance Between Nodes | 0 km |
| Component | Operation | Power (W) | Duration (s) | Energy (W-s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Camera Module (ESP32-CAM) | Capturing 5 images | 0.90 | 20 | 18.00 |
| DHT22 Sensor | Measuring temperature and humidity | 0.0125 | 20 | 0.25 |
| Microcontroller (ESP32) | Modem/light sleep | 0.10 | 20 | 2.00 |
| NB-IoT Modem (Quectel BC66) | Uplink transmission | 0.36 | 5 | 1.80 |
| NB-IoT Modem (Quectel BC66) | Idle/paging | 0.0008 | 15 | 0.012 |
| Total per Cycle | 22.06 W-s |
| Component | Operation | Power (W) | Duration (s) | Energy (W-h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcontroller (ESP32) | Temperature regulation (active) | 0.10 | 9000 | 0.25 |
| Heater (12 W low-power pad) | Hyperthermia heating | 12 | 9000 | 30.00 |
| Total per cycle (10 frames) | 300.25 W-h | |||
| Heater (65 W medium pad) | Hyperthermia heating | 65 | 9000 | 162.25 |
| Total per cycle (10 frames) | 1620.25 W-h |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eivazzadeh, S.; Khatibi, S. Design of a Predictive Digital Twin System for Large-Scale Varroa Management in Honeybee Apiaries. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202126
Eivazzadeh S, Khatibi S. Design of a Predictive Digital Twin System for Large-Scale Varroa Management in Honeybee Apiaries. Agriculture. 2025; 15(20):2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202126
Chicago/Turabian StyleEivazzadeh, Shahryar, and Siamak Khatibi. 2025. "Design of a Predictive Digital Twin System for Large-Scale Varroa Management in Honeybee Apiaries" Agriculture 15, no. 20: 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202126
APA StyleEivazzadeh, S., & Khatibi, S. (2025). Design of a Predictive Digital Twin System for Large-Scale Varroa Management in Honeybee Apiaries. Agriculture, 15(20), 2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15202126






