SLW-YOLO: A Hybrid Soybean Parent Phenotypic Consistency Detection Model Based on Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Based on the YOLOv5s network, the hybrid soybean parent phenotypic consistency detection model, SLW-YOLO, was proposed, which could be used to identify soybean phenotypic traits instead of using manual identification in the field.
- (2)
- A self-propelled image acquisition platform was designed for acquiring image data from different soybean growth stages in the field, which laid a foundation for the development of a hybrid soybean seed production field off-type plant-cutting robot in the future.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Site
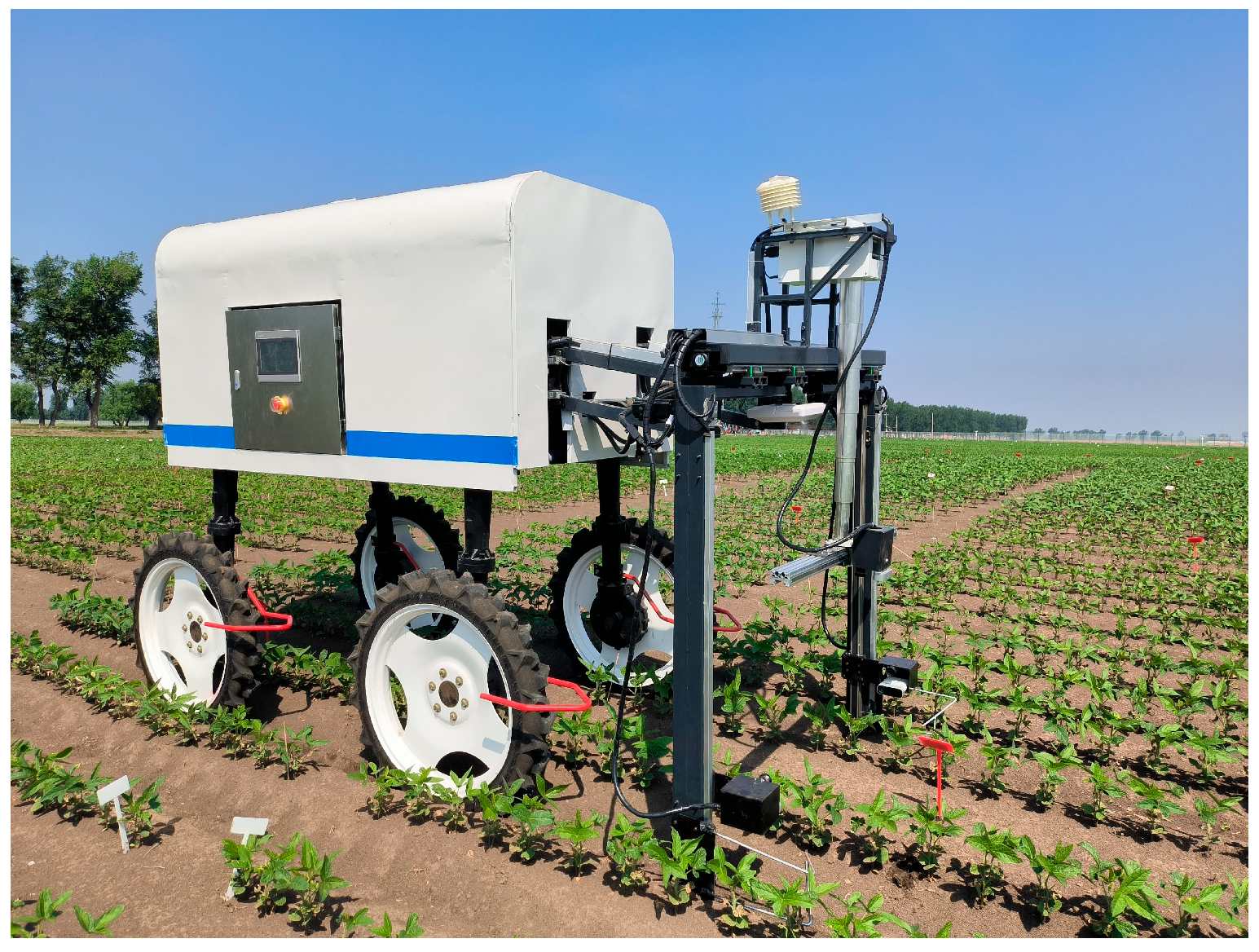
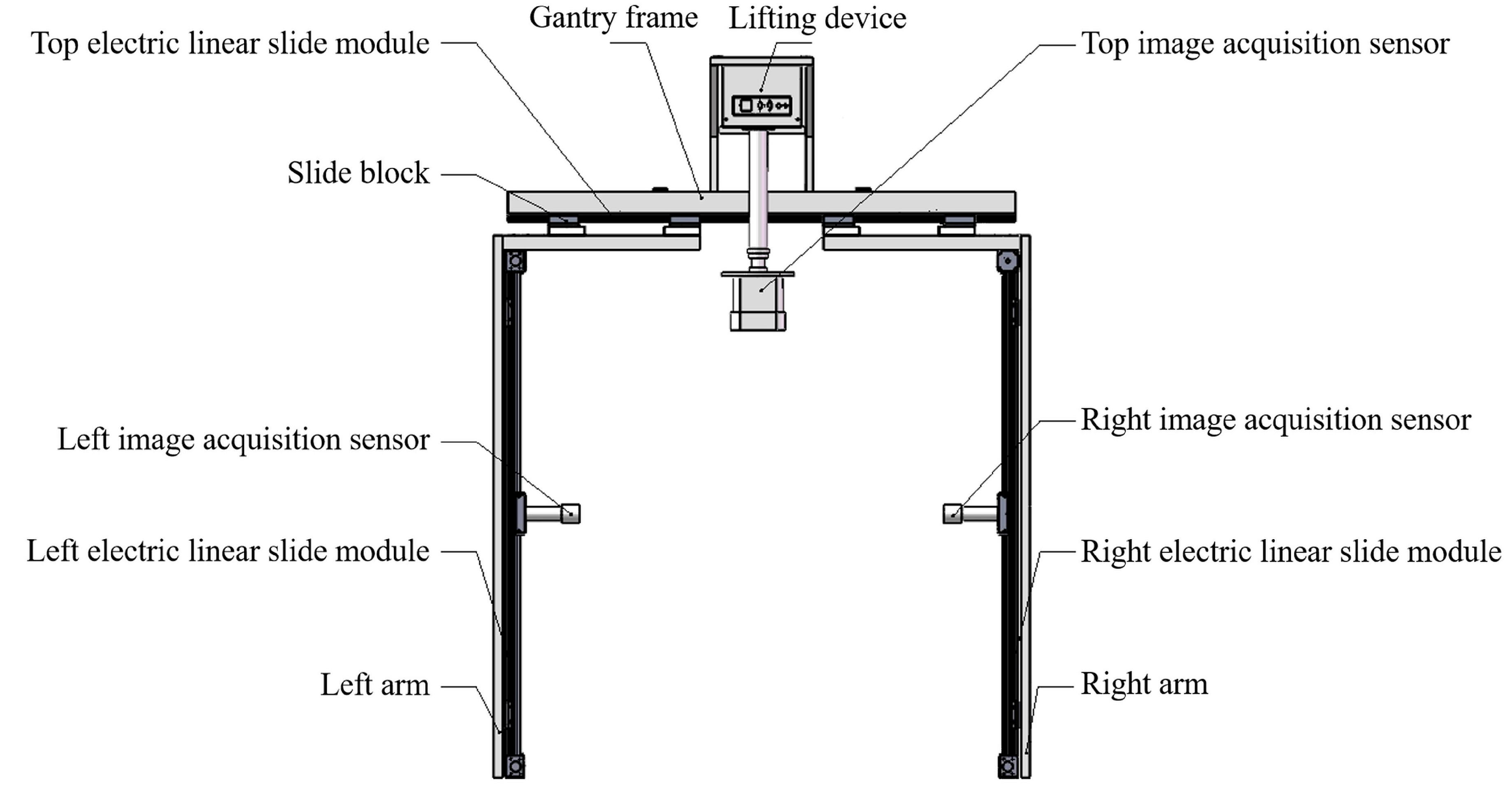
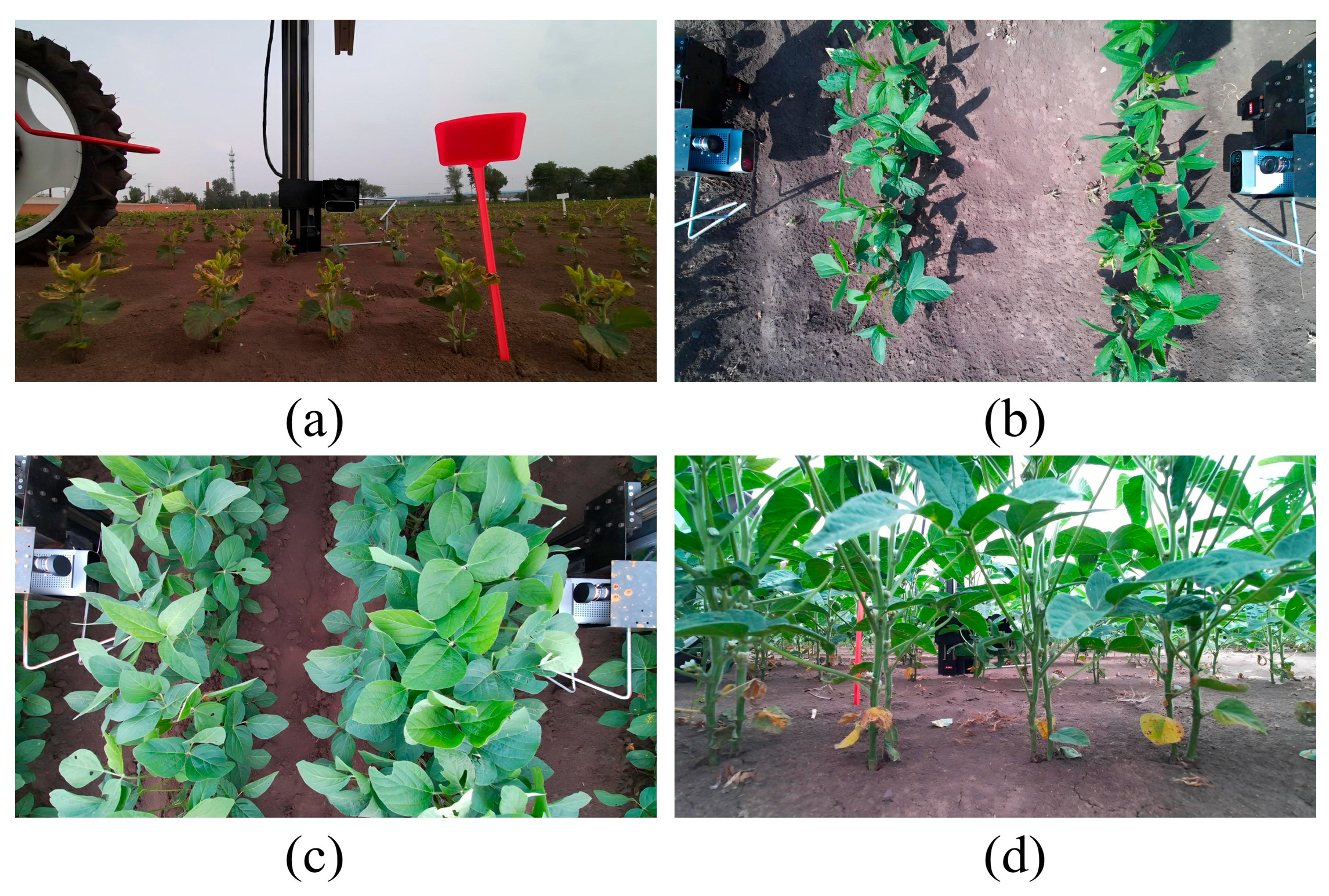
2.2. Data Acquisition Equipment
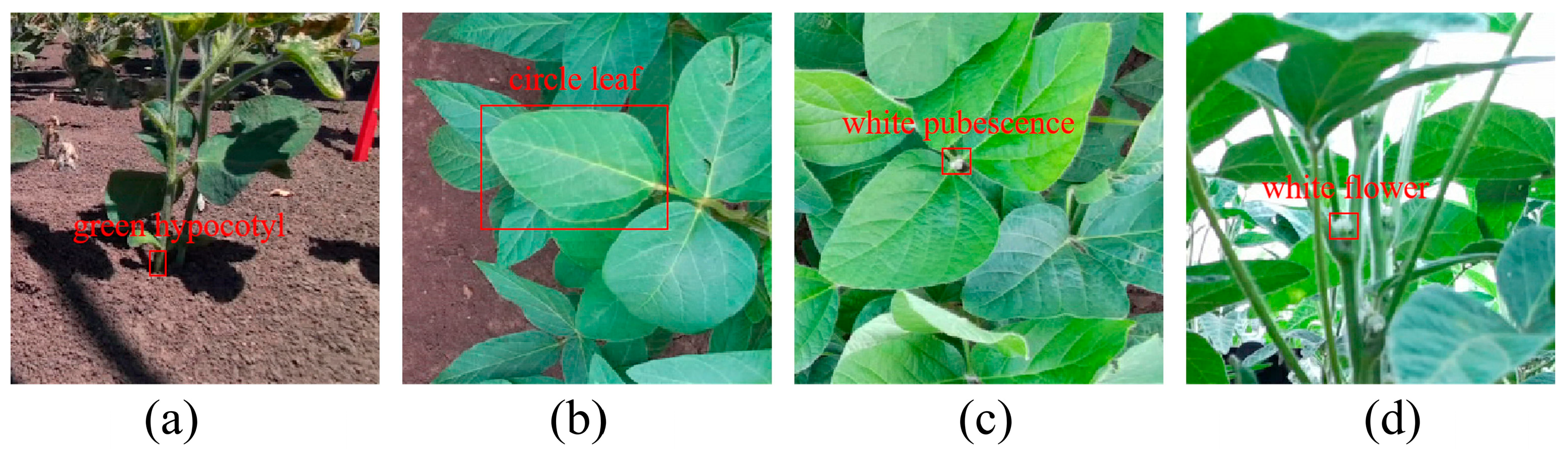
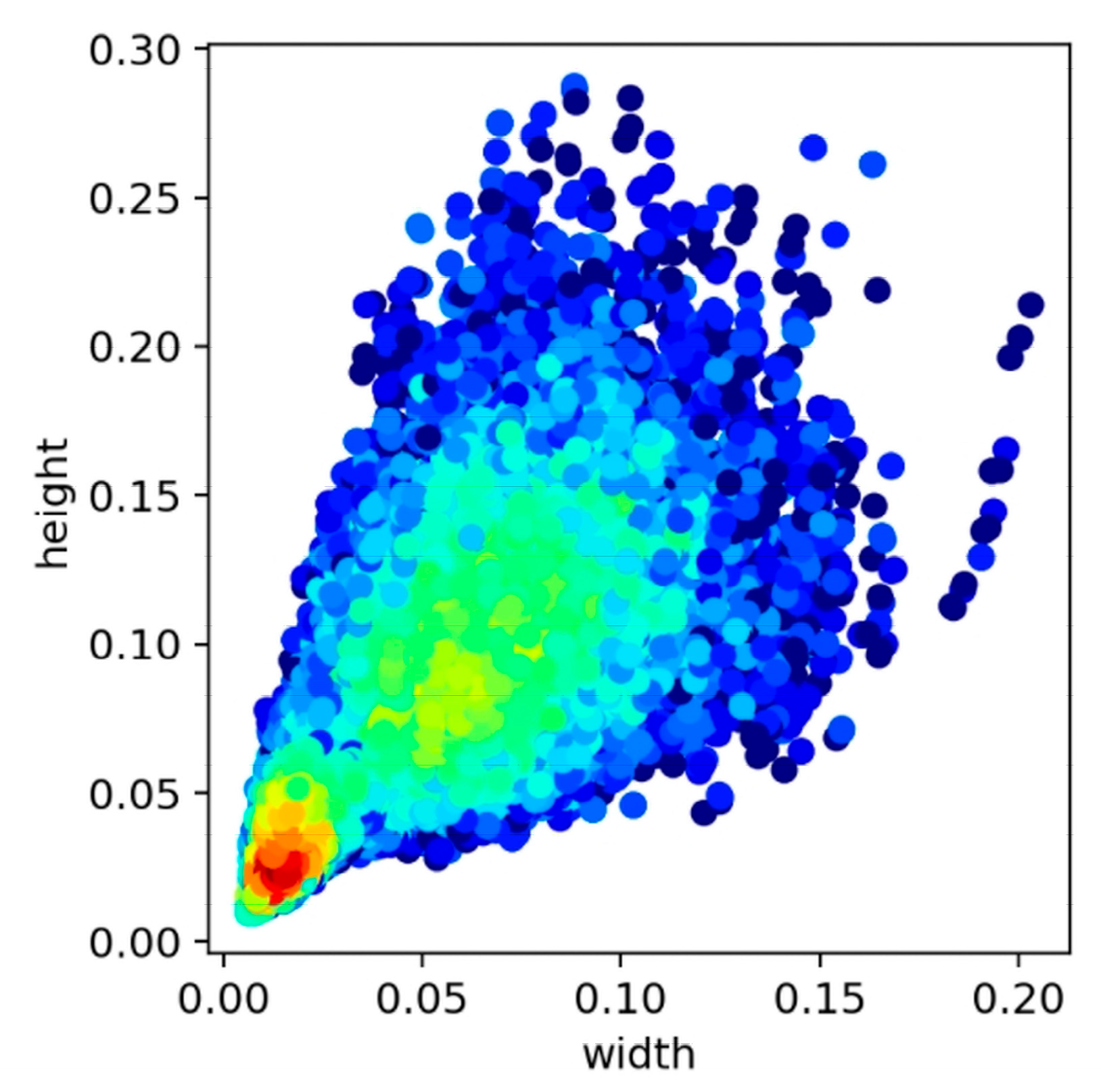
2.3. Dataset Construction
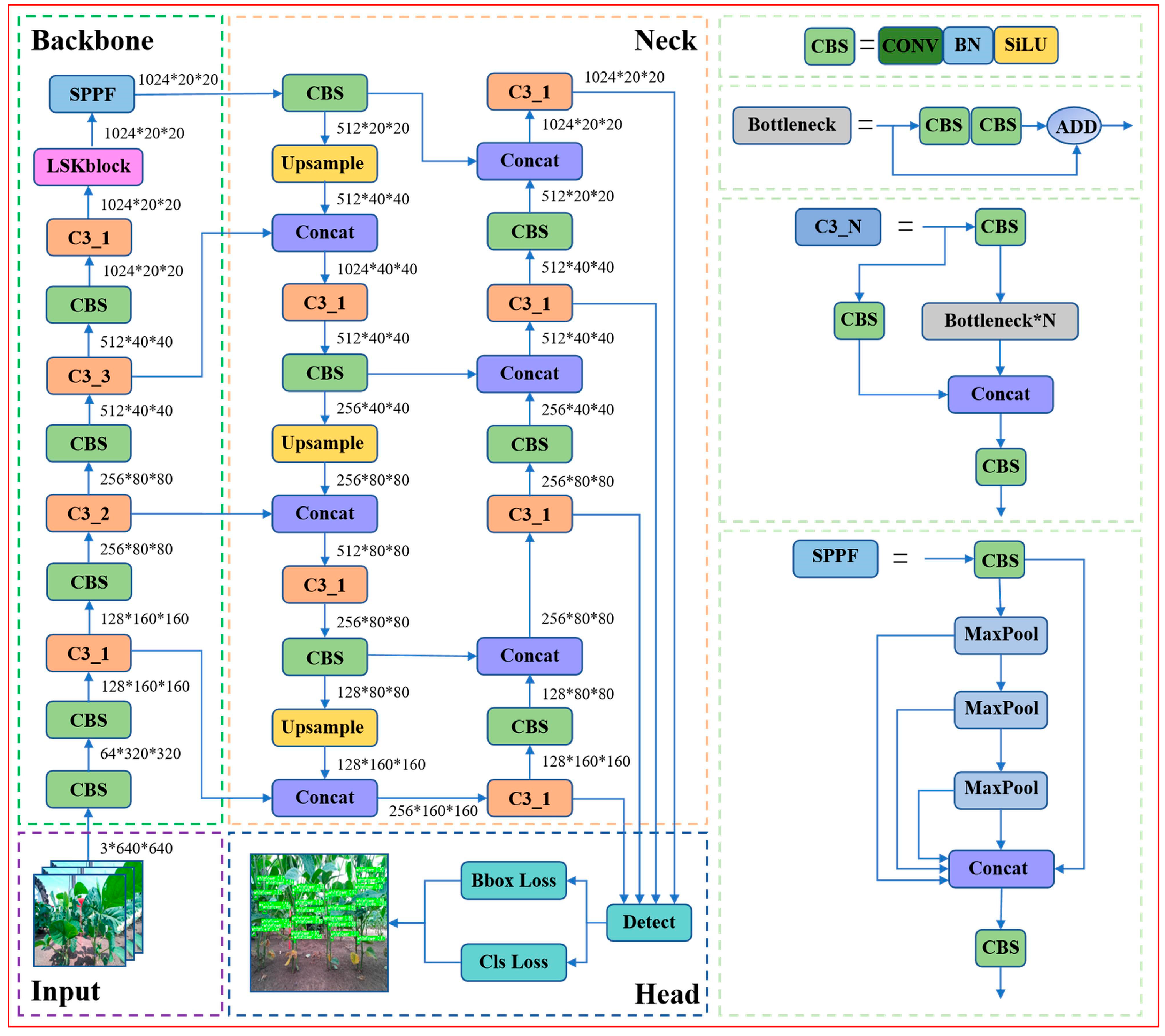
2.4. Construction of SLW-YOLO Model
2.4.1. SNet Detection Layer
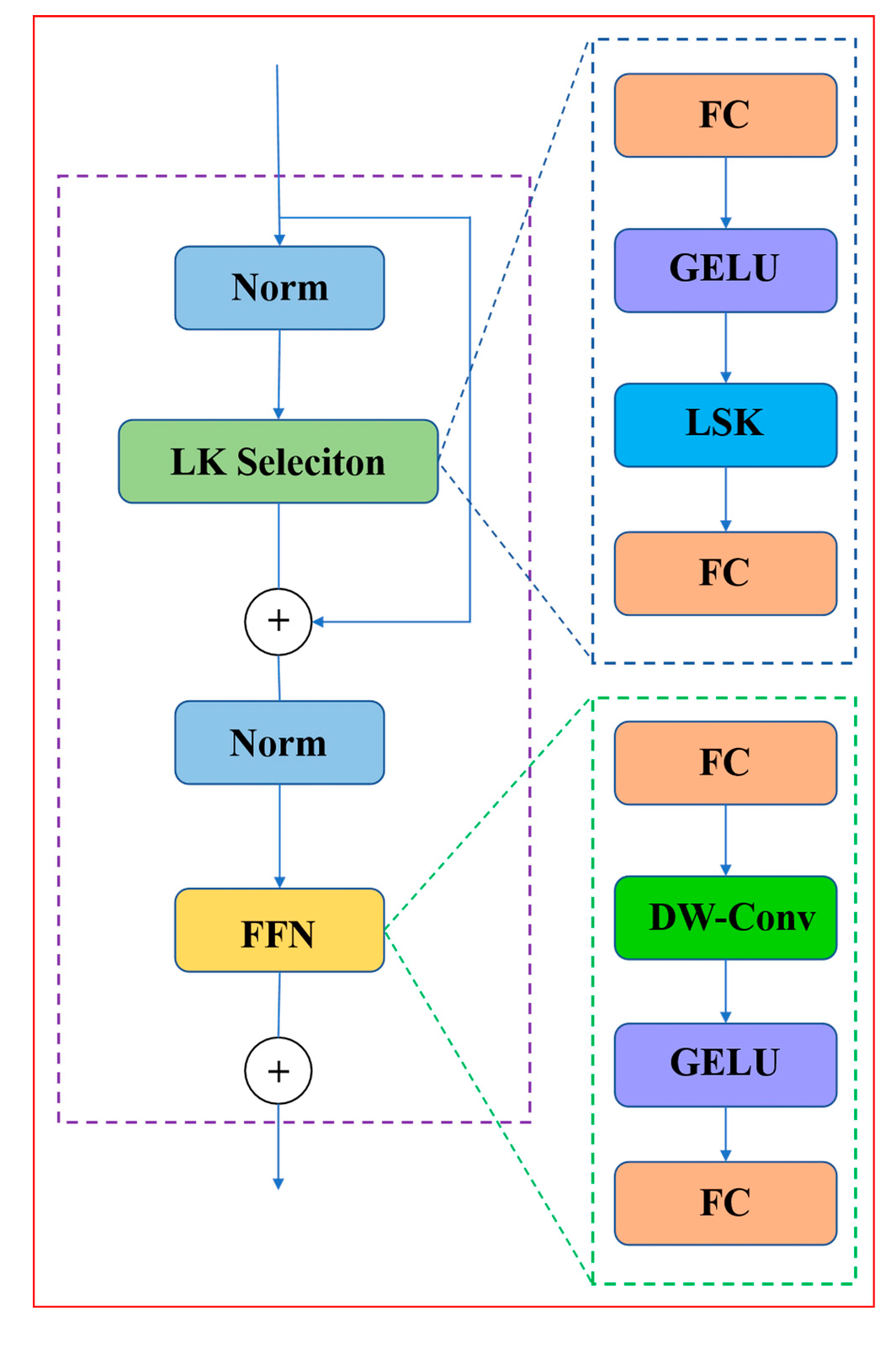
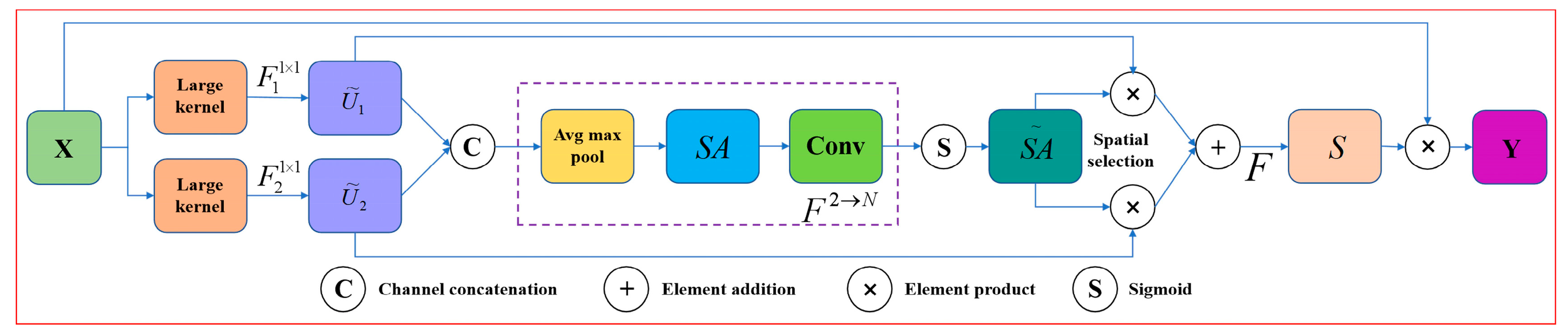
2.4.2. LSKNet Attention Mechanism Module
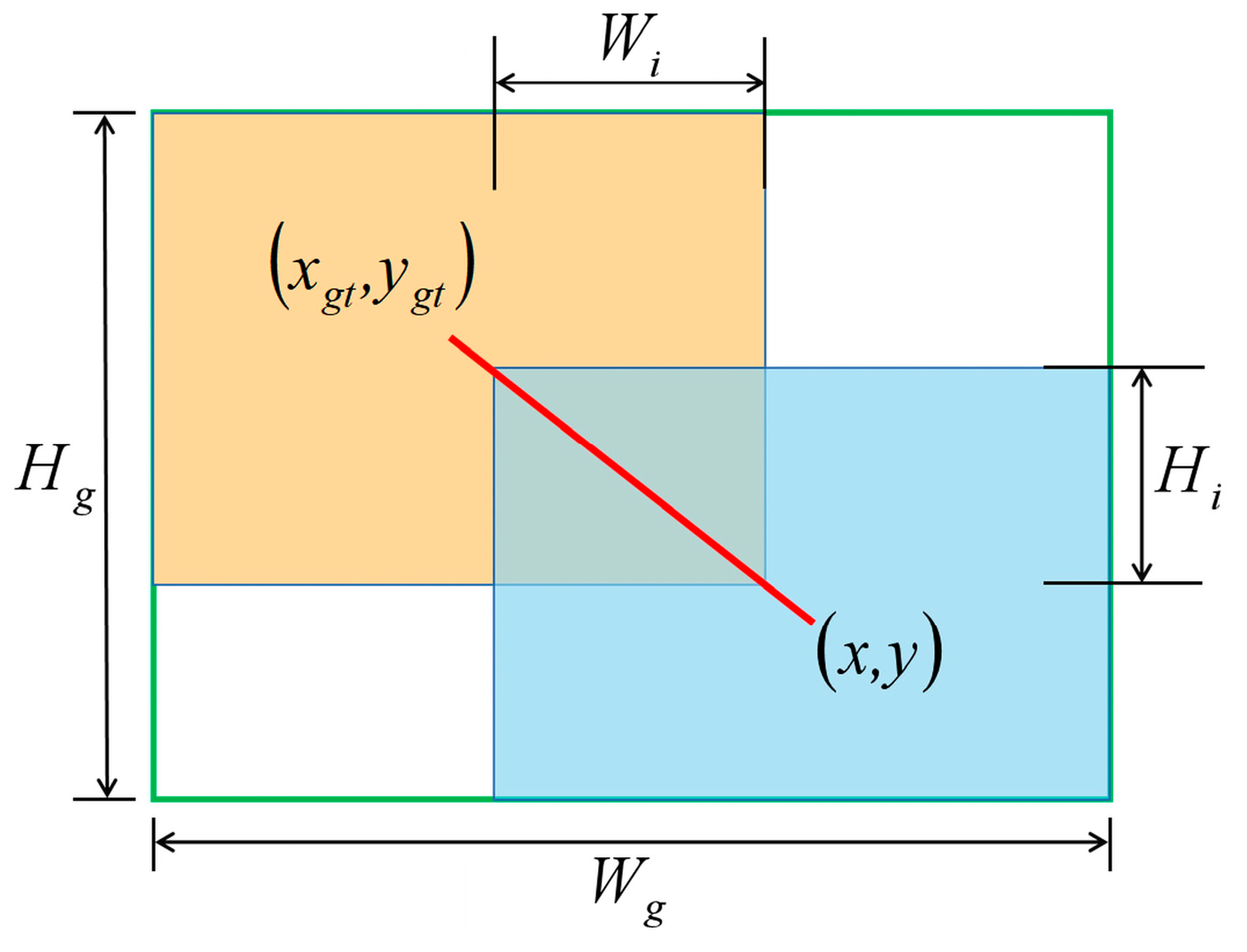
2.4.3. Wise-IoU Loss Function
2.5. Image Test Platform
2.6. Evaluation Metrics
2.7. Hybrid Soybean Parents’ Phenotypic Consistency
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Model Comparison and Ablation Test
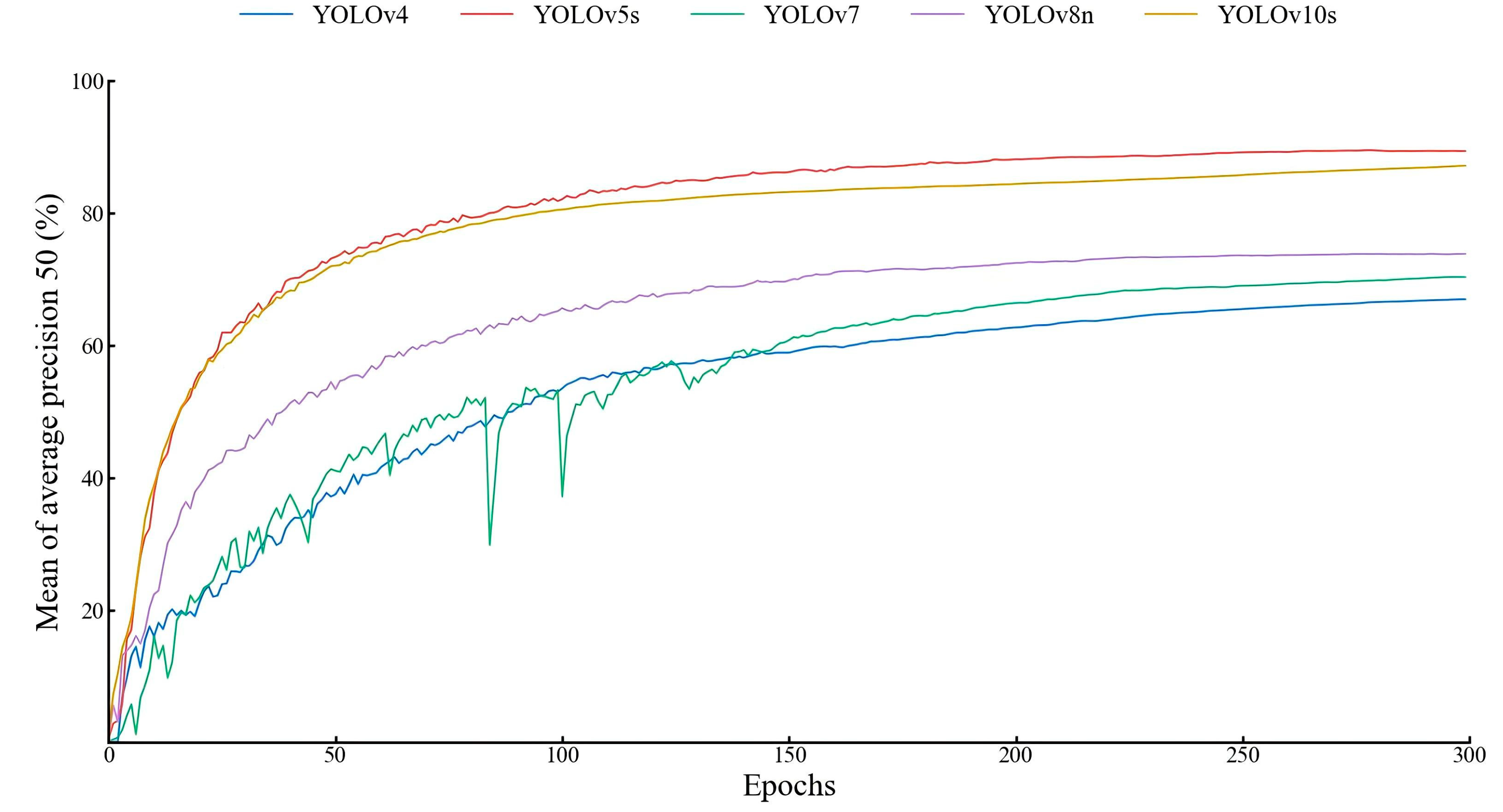
3.1.1. Comparative Test of YOLO Model
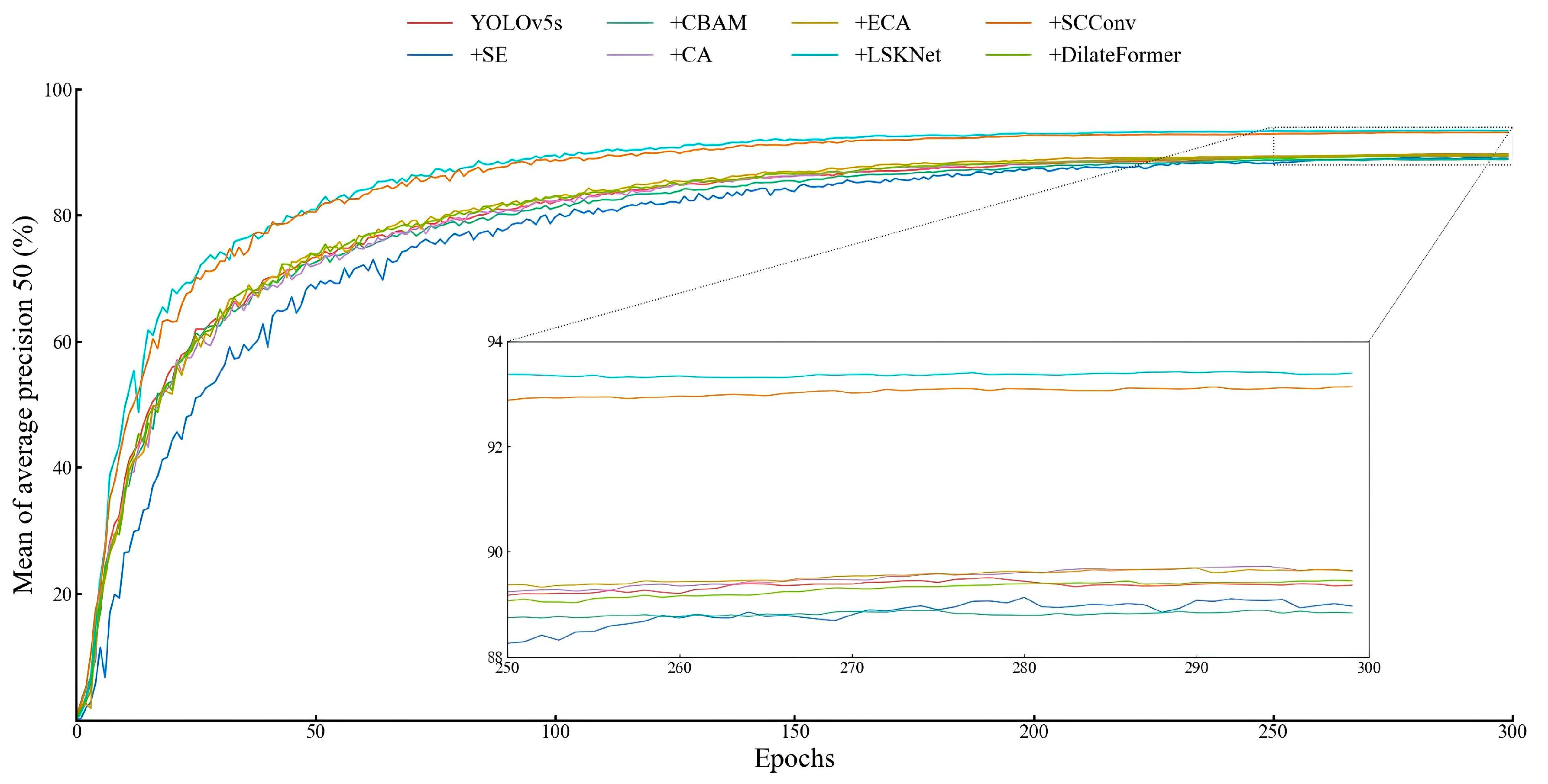
3.1.2. Comparative Test of Attention Mechanism
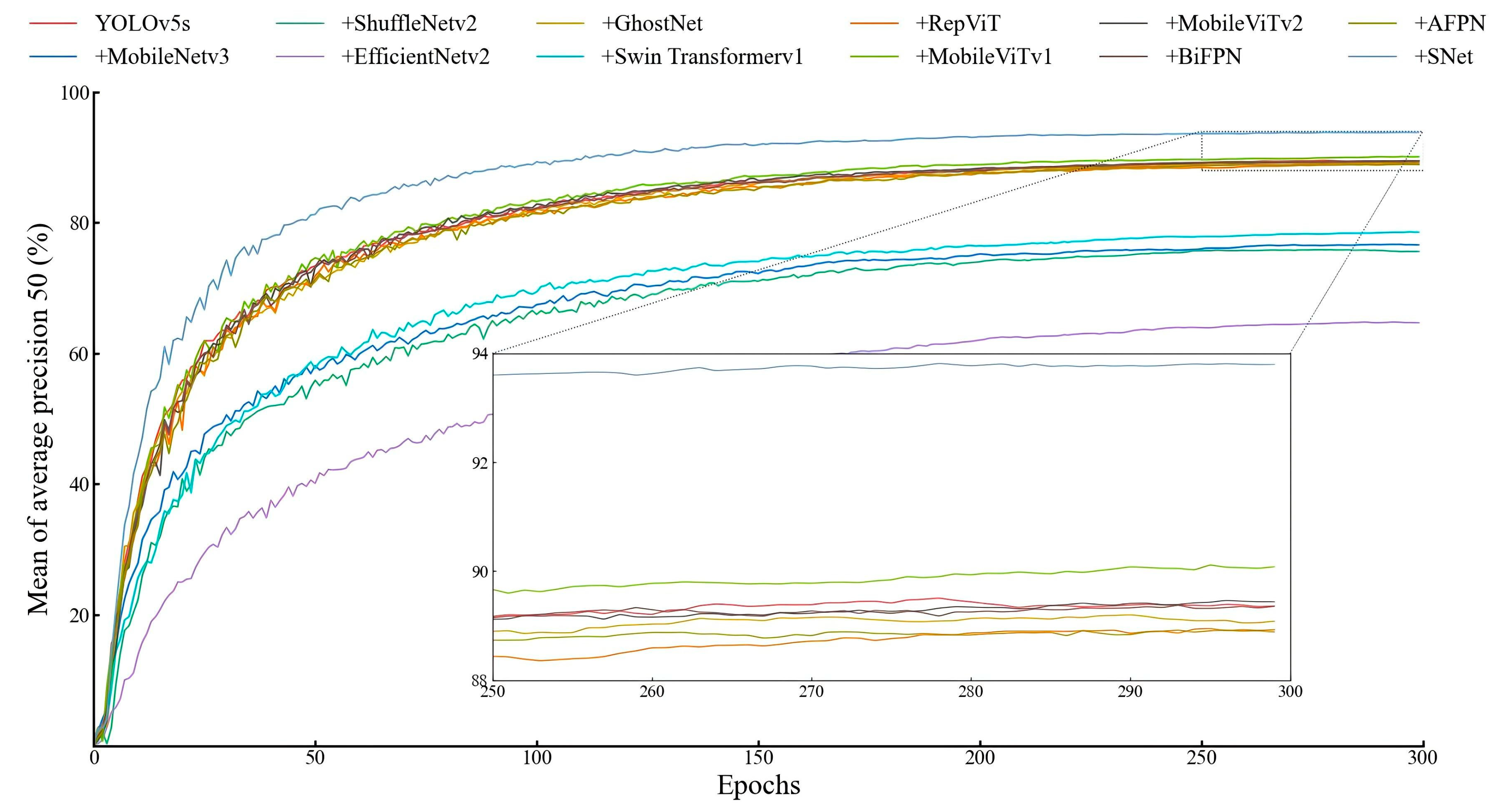
3.1.3. Comparative Test of Network Structure
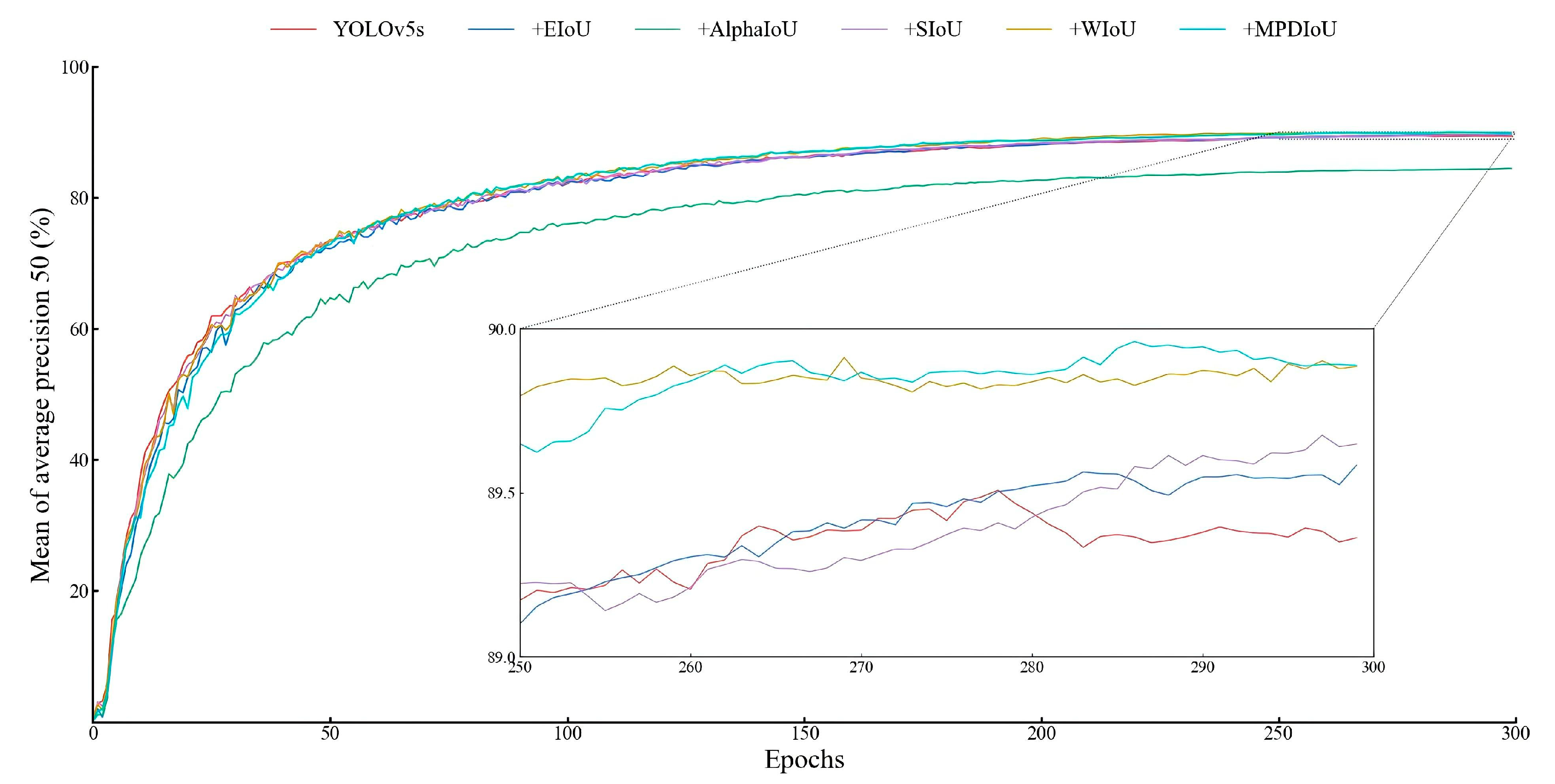
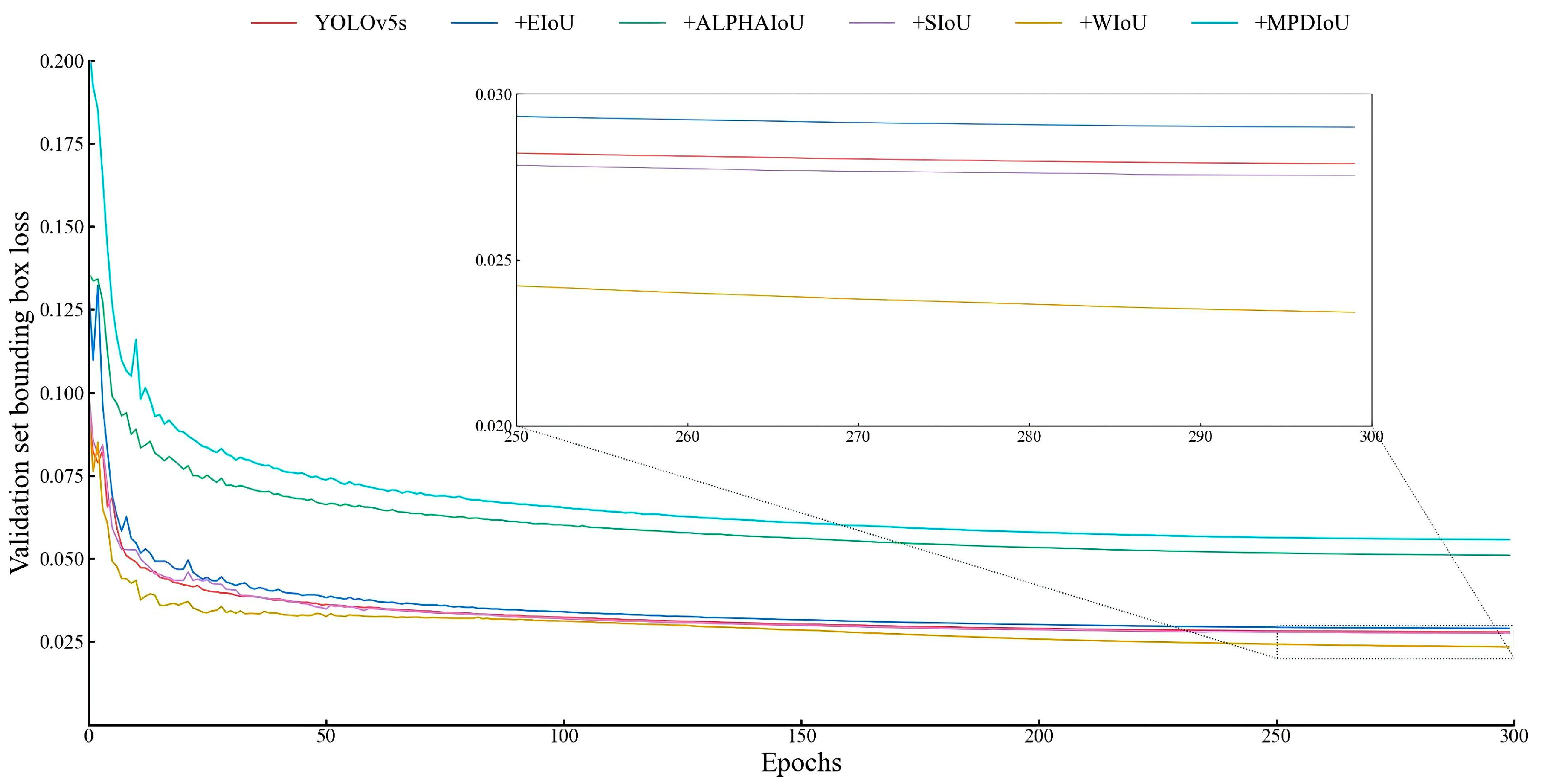
3.1.4. Comparative Test of Loss Function
3.1.5. Ablation Test
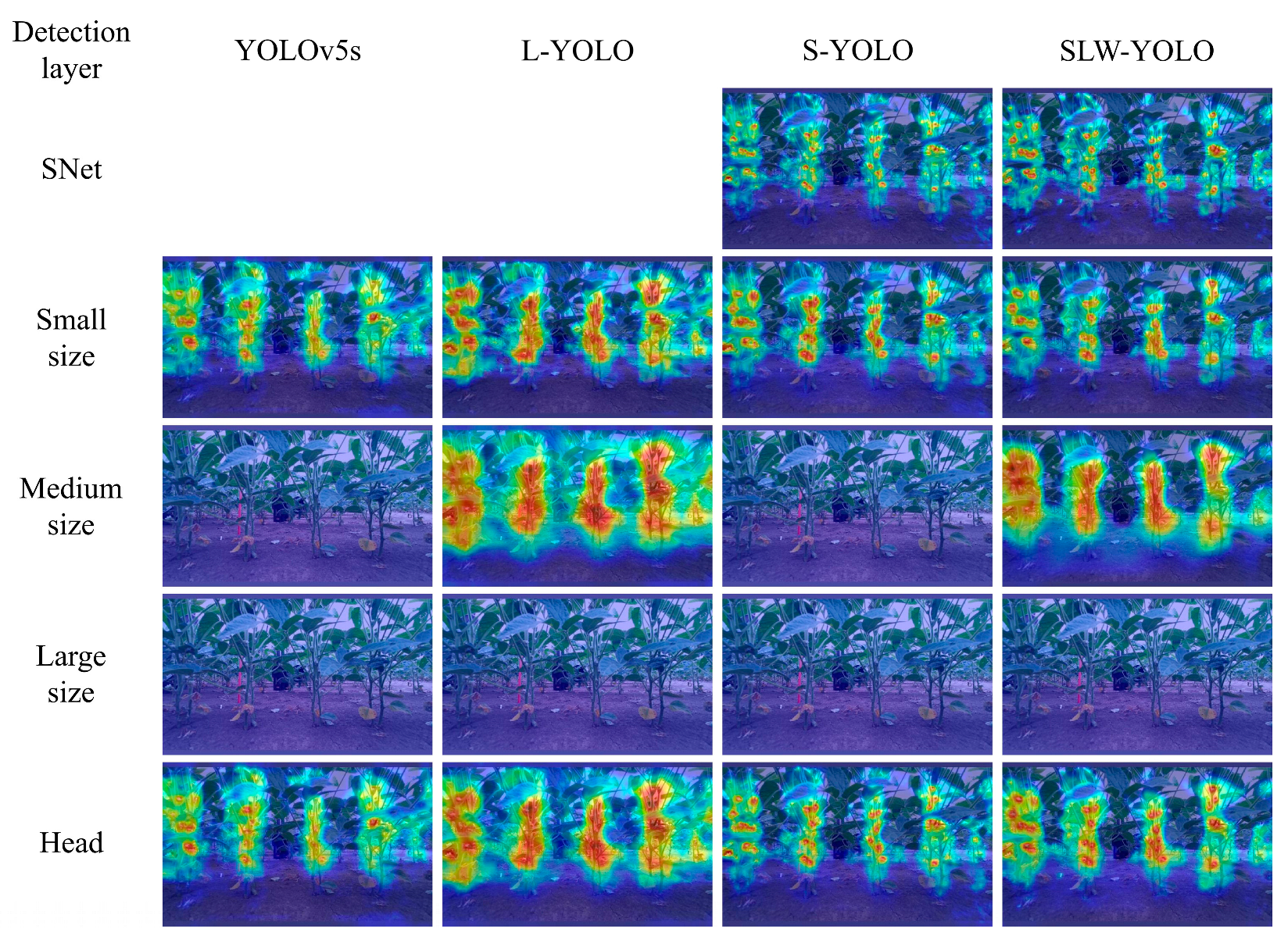
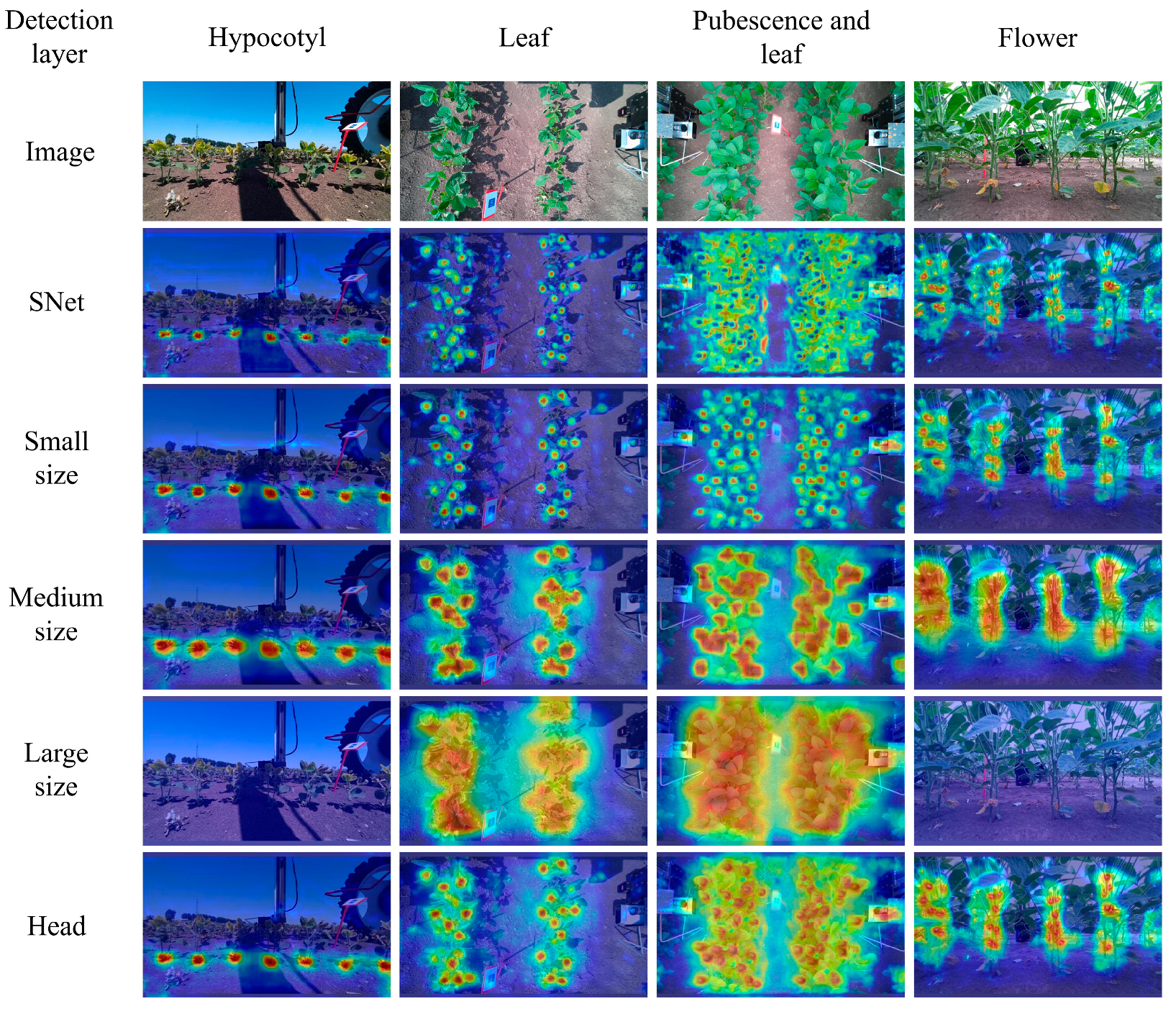
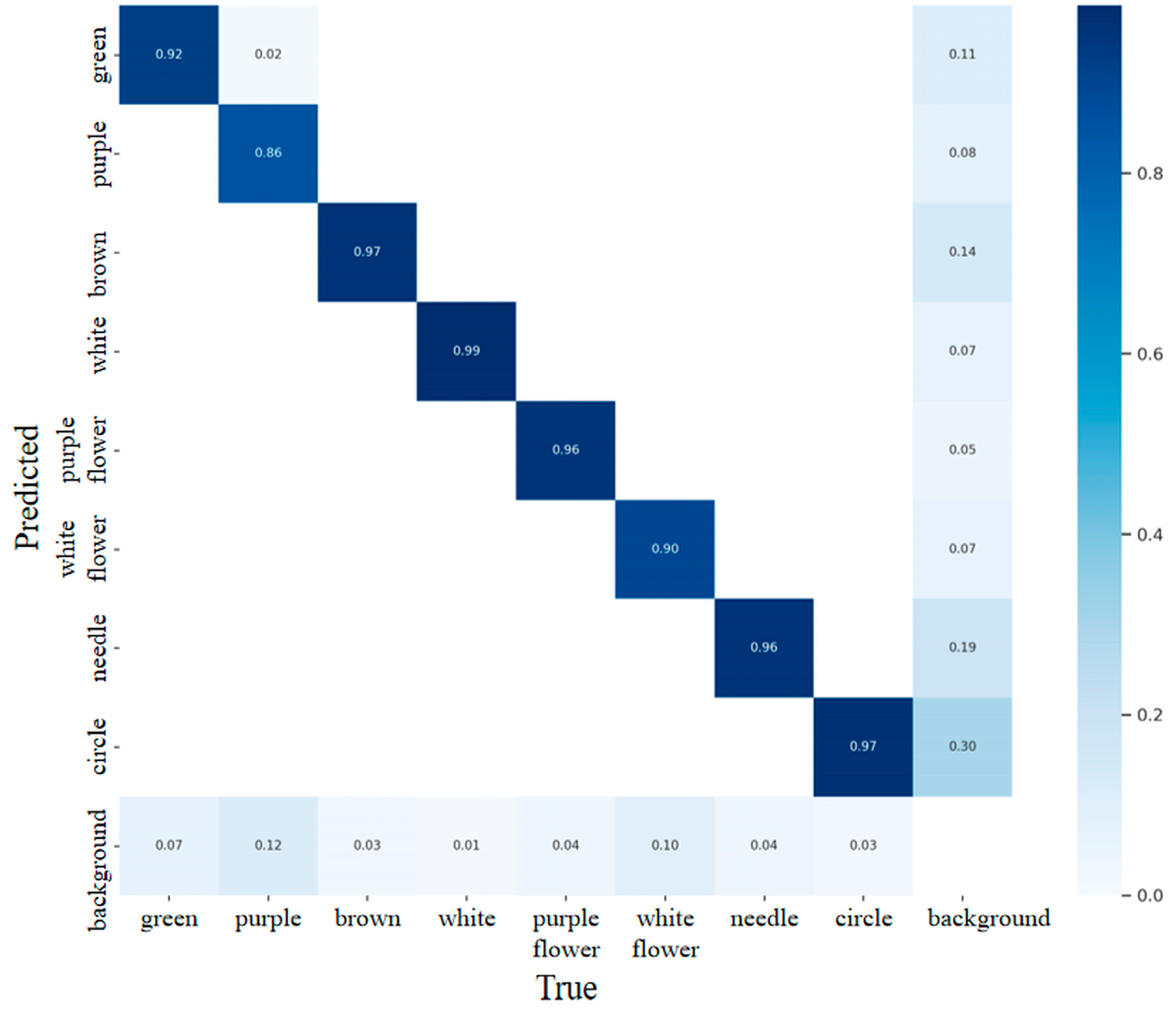
3.2. Heat Map Analysis
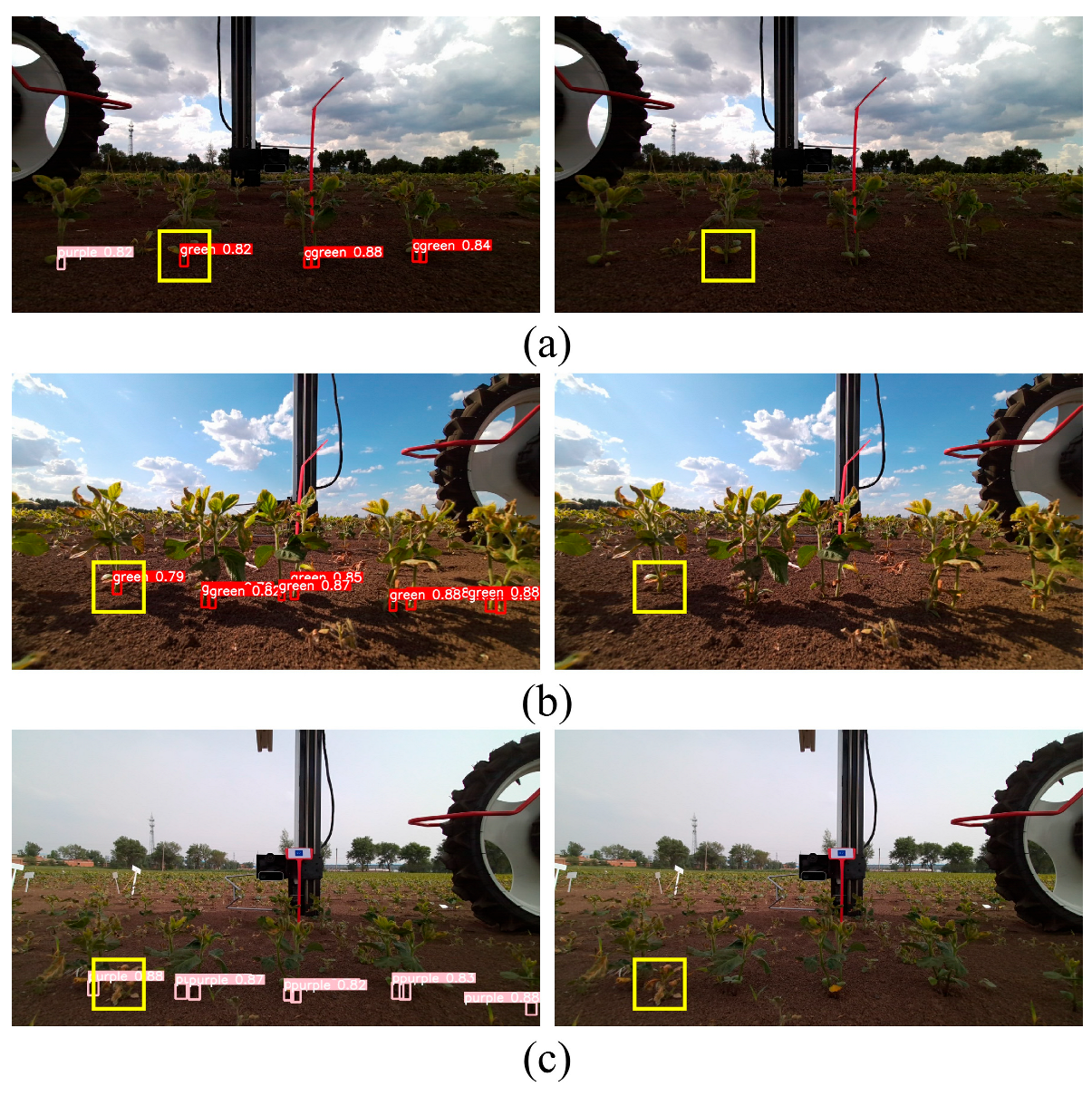
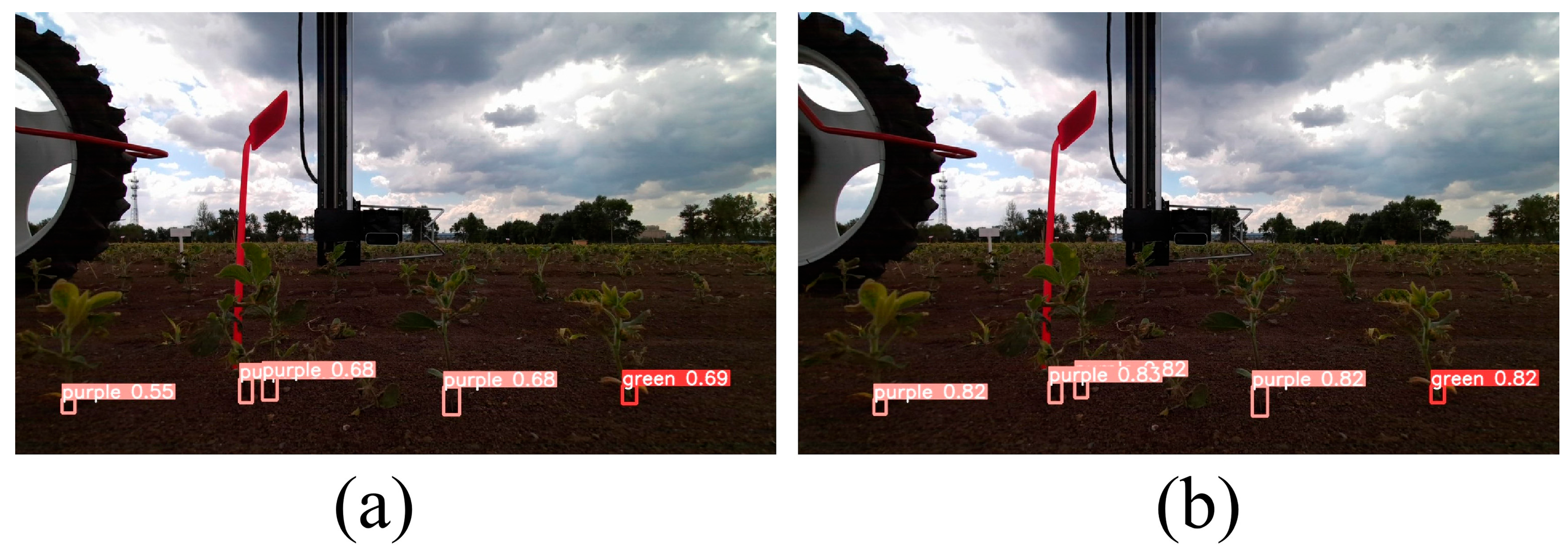
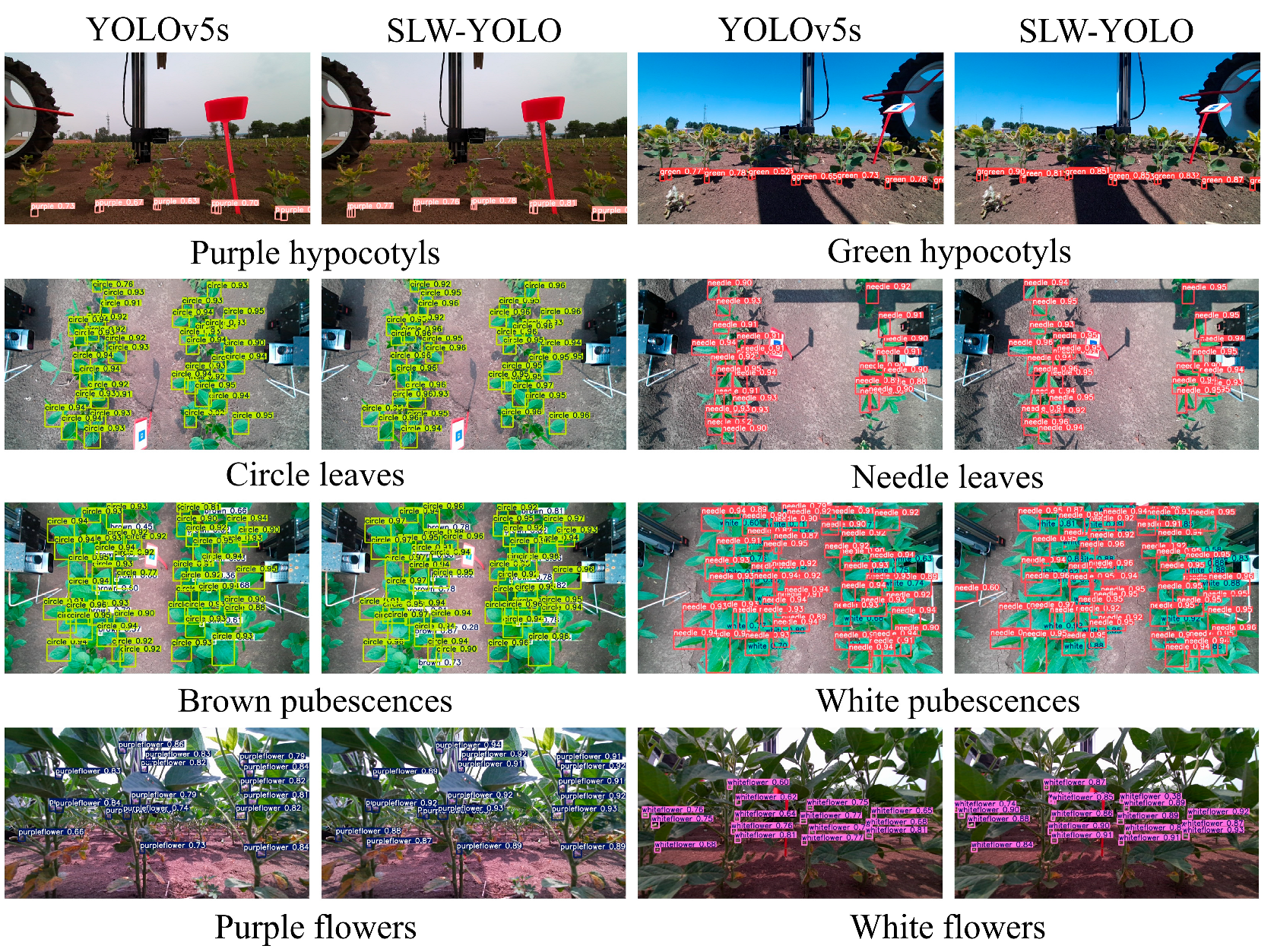
3.3. Model Performance Verification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- A hybrid soybean parent phenotypic consistency detection model, SLW-YOLO, was established based on the YOLOv5s network. The model achieved the following: F1 score: 92.3%; mAP: 94.8%; detection speed: 88.3 FPS; and model size: 45.1 MB. Compared to the YOLOv5s model, SLW-YOLO showed improvements in F1 score by 6.1% and mAP by 5.4%, while the detection speed decreased by 42.1 FPS and the model size increased by 31.4 MB.
- (2)
- To obtain field soybean plant image datasets, a self-propelled image acquisition platform was designed, which is suitable for field hybrid soybean cultivation mode.
- (3)
- The SLW-YOLO model is capable of completing the task of phenotypic consistency detection of hybrid soybean parents in a complicated field environment, accelerating seed production, improving the efficiency of phenotypic consistency detection, and thereby providing technical support for breeding experts to engage in soybean hybrid breeding and large-scale seed production.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gai, J.; Ding, D.; Cui, Z.; Qiu, J. Development and performance of the cytoplasmic-nuclear male sterile line NJCMS1A of soybean. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1999, 32, 23–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Peng, B.; Zhang, J.; Yan, H.; Zhang, W.; Lin, C.; Wang, P.; Ding, X. DB22/T 3177-2020; Code of Practice of Cytoplasmic-Nuclear Interaction Male Sterile Line of Hybrid Soybean. Jilin Provincial Market Supervision and Administration Bureau: Changchun, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Nadeem, M.; Sun, G.; Wang, X.; Qiu, L. Male sterility in soybean: Occurrence, molecular basis and utilization. Plant Breed. 2019, 138, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Y. Research progress of image sensing and deep learning in agriculture. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 1–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Jiang, T.; Peng, H.; Jin, H.; Sun, H.; Chai, D.; Huang, J. Coffee flower identification using binarization algorithm based on convolutional neural network for digital images. Plant Phenomics 2020, 2020, 6323965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, R.; Sun, S.; Robertson, J.S.; Paterson, A.H. DeepFlower: A deep learning-based approach to characterize flowering patterns of cotton plants in the field. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, S.; Wa, S.; Zong, Z.; Liu, Y. Using generative module and pruning inference for the fast and accurate detection of apple flower in natural environments. Information 2021, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Suo, R.; Zhao, G.; Gao, C.; Fu, L.; Shi, F.; Dhupia, J.; Li, R.; Cui, Y. Real-time detection of kiwifruit flower and bud simultaneously in orchard using YOLOv4 for robotic pollination. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Yang, Z.; Li, K.; Hao, W.; He, Z.; Ding, X.; Cui, Y. Detecting kiwi flowers in natural environments using an improved YOLOv5s. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 177–185. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Lin, G.; He, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y. Study on pear flowers detection performance of YOLO-PEFL model trained with synthetic target images. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 911473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Z.; Song, H. Using lightweight deep learning algorithm for real-time detection of apple flowers in natural environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 207, 107765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Wu, D.; Zheng, X. Detection of chrysanthemums inflorescence based on improved CR-YOLOv5s algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, K.; Yahata, S.; Ozawa, S.; Ohkawa, T.; Chonan, Y.; Tsuji, H.; Murakami, N. An image sensing method to capture soybean growth state for smart agriculture using single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Miyazaki, Japan, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1693–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratama, M.T.; Kim, S.; Ozawa, S.; Ohkawa, T.; Chona, Y.; Tsuji, H.; Murakami, N. Deep learning-based object detection for crop monitoring in soybean fields. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, H.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Xin, D.; et al. Exploring soybean flower and pod variation patterns during reproductive period based on fusion deep learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 922030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhang, W. Detection and Counting Model of Soybean at the Flowering and Podding Stage in the Field Based on Improved YOLOv5. Agriculture 2025, 15, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liang, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, P.; Wan, L.; Zheng, Q. An improved YOLOv5-based approach to soybean phenotype information perception. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 106, 108582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, J.; Shi, W.; Qi, L.; Yu, C.; Zhang, W. Field-based soybean flower and pod detection using an improved YOLOv8-VEW method. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.S.; Nelson, R.L. Relationship between plant height and flowering date in determinate soybean. Crop Sci. 1988, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C. Research Progress on Utilization of Soybean Heterosis. Soybean Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 26–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Hou, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Cheng, M.M.; Yang, J.; Li, X. Large selective kernel network for remote sensing object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Tan, D.; Sui, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, R. Wolfberry recognition and picking-point localization technology in natural environments based on improved Yolov8n-Pose-LBD. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 227, 109551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, J.; Shi, W.; Qi, L.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C. Color detection model of hybrid soybean hypocotyl based on an improved YOLOv7 object detection model. J. China Agric. Univ. 2024, 29, 11–22. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Li, H. DHSW-YOLO: A duck flock daily behavior recognition model adaptable to bright and dark conditions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yu, R. Wise-IoU: Bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism. arXiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Cheng, H.; Ma, Z.; Lu, W.; Wang, M.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, C.; Hong, F. DSW-YOLO: A detection method for ground-planted strawberry fruits under different occlusion levels. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 214, 108304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, T.; Han, K.; Jin, X.; Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Yu, J. TSP-yolo-based deep learning method for monitoring cabbage seedling emergence. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 157, 127191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Su, T.; Li, K.; Dai, J. Small Target-YOLOv5: Enhancing the Algorithm for Small Object Detection in Drone Aerial Imagery Based on YOLOv5. Sensors 2023, 24, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Image Tag | Training Set | Validation Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypocotyl | 2000 | 500 | 100 |
| Leaf | 2000 | 500 | 100 |
| Pubescence | 2000 | 500 | 100 |
| Flower | 2000 | 500 | 100 |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | mAP50 (%) | Detection Speed (FPS) | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv4 | 46.4 | 89.7 | 61.2 | 67.0 | 22.6 ± 2.9 | 491.0 |
| YOLOv5s | 89.4 | 83.3 | 86.2 | 89.4 | 130.4 ± 9.4 | 13.7 |
| YOLOv7 | 69.7 | 66.3 | 68.0 | 70.3 | 19.3 ± 1.9 | 71.3 |
| YOLOv8n | 74.5 | 68.4 | 71.3 | 73.8 | 211.1 ± 5.1 | 6.0 |
| YOLOv10s | 87.1 | 79.6 | 83.2 | 87.2 | 209.3 ± 5.6 | 15.7 |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | mAP50 (%) | Detection Speed (FPS) | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 89.4 | 83.3 | 86.2 | 89.4 | 130.4 ± 9.4 | 13.7 |
| +SE | 89.1 | 82.3 | 85.6 | 89.0 | 129.5 ± 2.3 | 13.7 |
| +CBAM | 89.0 | 82.5 | 85.6 | 88.9 | 124.7 ± 5.9 | 13.7 |
| +CA | 89.7 | 83.5 | 86.5 | 89.6 | 126.8 ± 6.3 | 13.7 |
| +ECA | 89.5 | 83.7 | 86.5 | 89.7 | 131.3 ± 2.6 | 13.7 |
| +LSKNet | 91.9 | 89.0 | 90.4 | 93.4 | 123.4 ± 5.3 | 56.9 |
| +SCConv | 92.1 | 88.3 | 90.2 | 93.0 | 113.5 ± 2.7 | 58.7 |
| +DilateFormer | 89.3 | 83.6 | 86.4 | 89.4 | 118.5 ± 2.3 | 16.0 |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | mAP50 (%) | Detection Speed (FPS) | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 89.4 | 83.3 | 86.2 | 89.4 | 130.4 ± 9.4 | 13.7 |
| +MobileNetV3 | 79.8 | 71.3 | 75.3 | 76.8 | 80.0 ± 4.6 | 10.0 |
| +ShuffleNetV2 | 78.7 | 70.7 | 74.5 | 75.7 | 92.8 ± 3.8 | 7.6 |
| +EfficientNetv2 | 73.2 | 61.5 | 66.8 | 64.7 | 80.4 ± 3.5 | 10.9 |
| +GhostNet | 90.6 | 83.8 | 78.1 | 89.1 | 80.1 ± 4.4 | 43.1 |
| +Swin TransformerV1 | 79.7 | 73.0 | 76.2 | 78.4 | 105.8 ± 9.9 | 6.7 |
| +RepViT | 89.1 | 82.5 | 85.7 | 88.9 | 119.8 ± 5.0 | 16.2 |
| +MobileViTv1 | 89.8 | 83.7 | 86.6 | 90.1 | 123.2 ± 7.6 | 16.7 |
| +MobileViTv2 | 89.4 | 83.7 | 86.5 | 89.4 | 123.0 ± 4.8 | 14.4 |
| +BiFPN | 89.0 | 83.3 | 86.1 | 89.2 | 123.6 ± 8.4 | 14.0 |
| +AFPN | 89.0 | 83.3 | 86.1 | 89.0 | 93.1 ± 3.1 | 14.8 |
| +SNet | 93.3 | 89.1 | 91.2 | 93.8 | 93.8 ± 5.1 | 41.5 |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | mAP50 (%) | Detection Speed (FPS) | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 89.4 | 83.3 | 86.2 | 89.4 | 130.4 ± 9.4 | 13.7 |
| +EIoU | 90.1 | 83.1 | 86.5 | 89.6 | 127.7 ± 4.0 | 13.7 |
| +AlphaIoU | 85.2 | 78.0 | 81.4 | 84.5 | 129.5 ± 2.2 | 13.7 |
| +SIoU | 89.2 | 83.5 | 86.3 | 89.5 | 130.7 ± 5.9 | 13.7 |
| +WIoU v3 | 89.4 | 84.0 | 86.6 | 89.9 | 124.9 ± 3.2 | 13.7 |
| +MPDIoU | 89.6 | 83.6 | 86.5 | 89.9 | 128.1 ± 4.3 | 13.7 |
| Model | LSKNet | SNet | WIoU v3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LW-YOLO | √ | √ | |
| SL-YOLO | √ | √ | |
| SW-YOLO | √ | √ | |
| SLW-YOLO | √ | √ | √ |
| Model | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | mAP50 (%) | Detection Speed (FPS) | Model Size (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 89.4 | 83.3 | 86.2 | 89.4 | 130.4 ± 9.4 | 13.7 |
| LW-YOLO | 93.2 | 89.2 | 91.2 | 93.8 | 120.3 ± 2.7 | 56.9 |
| SL-YOLO | 93.7 | 89.8 | 91.7 | 94.1 | 84.7 ± 3.4 | 45.1 |
| SW-YOLO | 93.1 | 90.5 | 91.8 | 94.6 | 92.6 ± 3.8 | 41.5 |
| SLW-YOLO | 94.0 | 90.6 | 92.3 | 94.8 | 88.3 ± 6.7 | 45.1 |
| Phenotypic Trait | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1 Score (%) | AP50 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green hypocotyl | 0.903 | 0.878 | 0.890 | 0.918 |
| Purple hypocotyl | 0.895 | 0.765 | 0.825 | 0.860 |
| Needle leaf | 0.947 | 0.941 | 0.944 | 0.971 |
| Circle leaf | 0.954 | 0.966 | 0.860 | 0.984 |
| Brown pubescence | 0.943 | 0.932 | 0.937 | 0.964 |
| White pubescence | 0.959 | 0.966 | 0.963 | 0.985 |
| Purple flower | 0.972 | 0.921 | 0.946 | 0.971 |
| White flower | 0.952 | 0.877 | 0.913 | 0.928 |
| Detection Method | Number of Observed Parent Samples (Plant) | Number of Observed Off-Type Samples (Plant) | Phenotypic Consistency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual record | 567 | 7 | 98.9% |
| YOLOv5s | 554 | 6 | 98.9% |
| SLW-YOLO | 560 | 6 | 98.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.; Li, J.; Shi, W.; Qi, L.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C. SLW-YOLO: A Hybrid Soybean Parent Phenotypic Consistency Detection Model Based on Deep Learning. Agriculture 2025, 15, 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192001
Yu C, Li J, Shi W, Qi L, Guan Z, Zhang W, Zhang C. SLW-YOLO: A Hybrid Soybean Parent Phenotypic Consistency Detection Model Based on Deep Learning. Agriculture. 2025; 15(19):2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192001
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Chuntao, Jinyang Li, Wenqiang Shi, Liqiang Qi, Zheyun Guan, Wei Zhang, and Chunbao Zhang. 2025. "SLW-YOLO: A Hybrid Soybean Parent Phenotypic Consistency Detection Model Based on Deep Learning" Agriculture 15, no. 19: 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192001
APA StyleYu, C., Li, J., Shi, W., Qi, L., Guan, Z., Zhang, W., & Zhang, C. (2025). SLW-YOLO: A Hybrid Soybean Parent Phenotypic Consistency Detection Model Based on Deep Learning. Agriculture, 15(19), 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15192001







