Exogenous Catalase Supplementation Alleviates Fusarium graminearum Mycotoxins-Induced Oxidative Stress in Weaned Piglets
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Diet, and Experimental Design
2.2. Assessment of Growth Performance, Diarrhea Index and Organ Indexes
2.3. Detection of Oxidative Status
2.4. Analysis of Gene Expression
2.5. Analysis of Ileal Microbiota and Metabolome Analysis of Hepatic Portal Vein Blood
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Exogenous CAT on Growth Performance and Organ Indexes of FGM-Exposed Piglets
3.2. Effects of Exogenous CAT on the Oxidative Status of the Intestine and Liver of FGM-Exposed Piglets
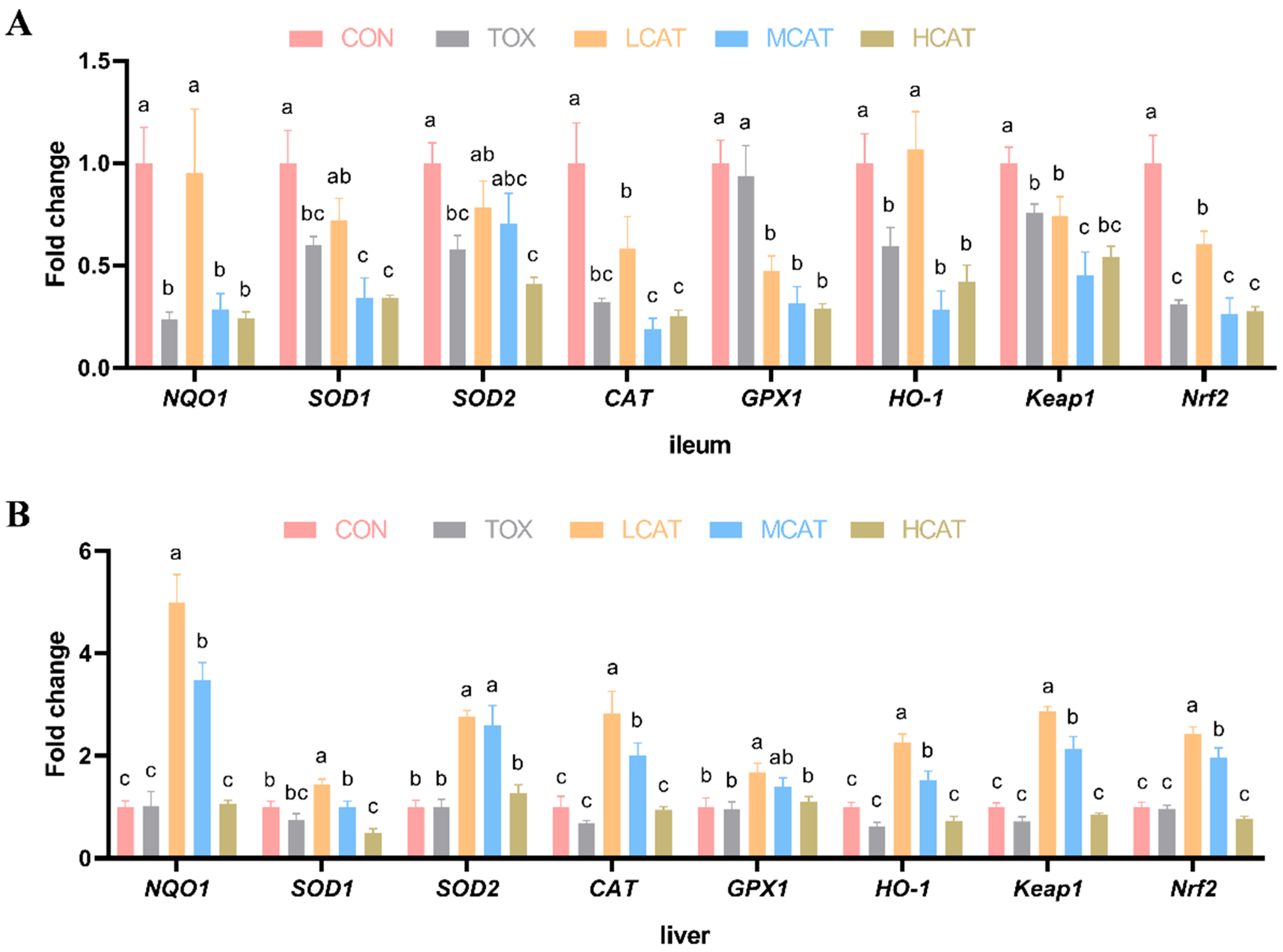
3.3. Effects of Exogenous CAT on the Relative mRNA Expression of Antioxidation-Related Genes of FGM-Exposed Piglets
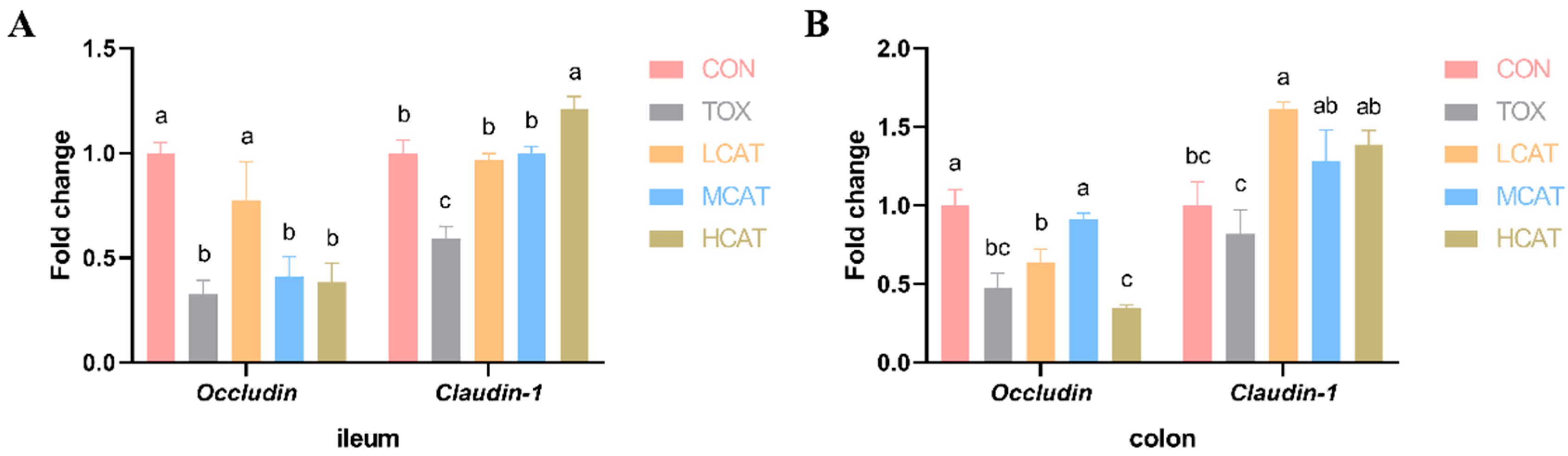
3.4. Effects of Exogenous CAT on the Relative mRNA Expression of Tight Junction Proteins of FGM-Exposed Piglets
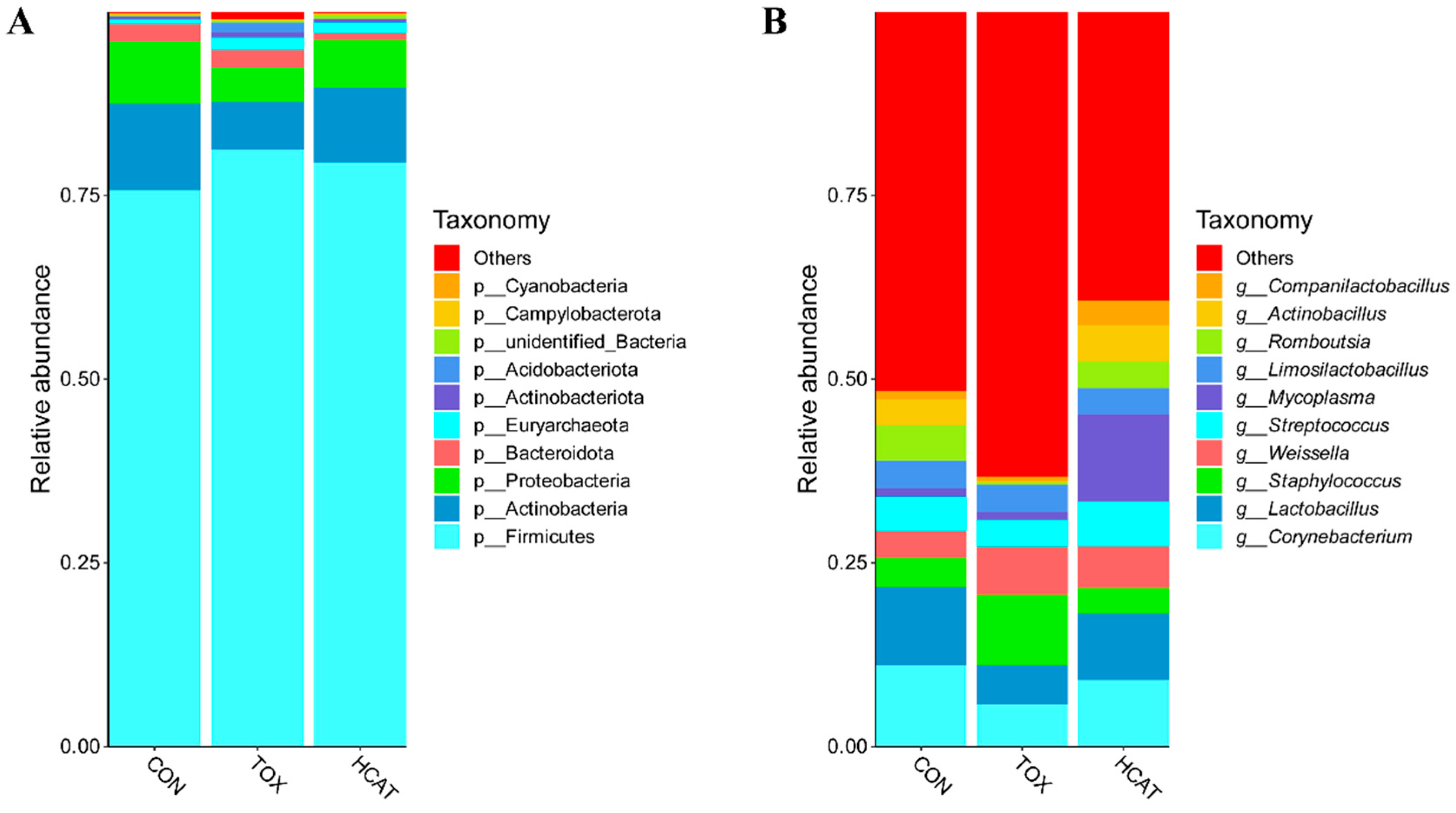
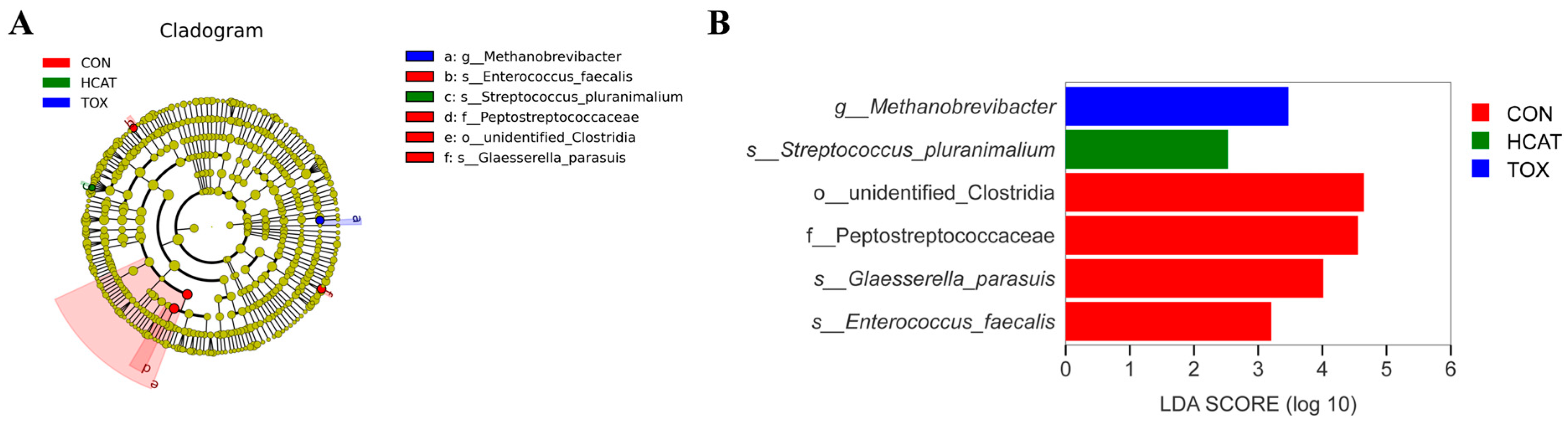
3.5. Effects of Exogenous CAT on the Ileal Microbiota of FGM-Exposed Piglets
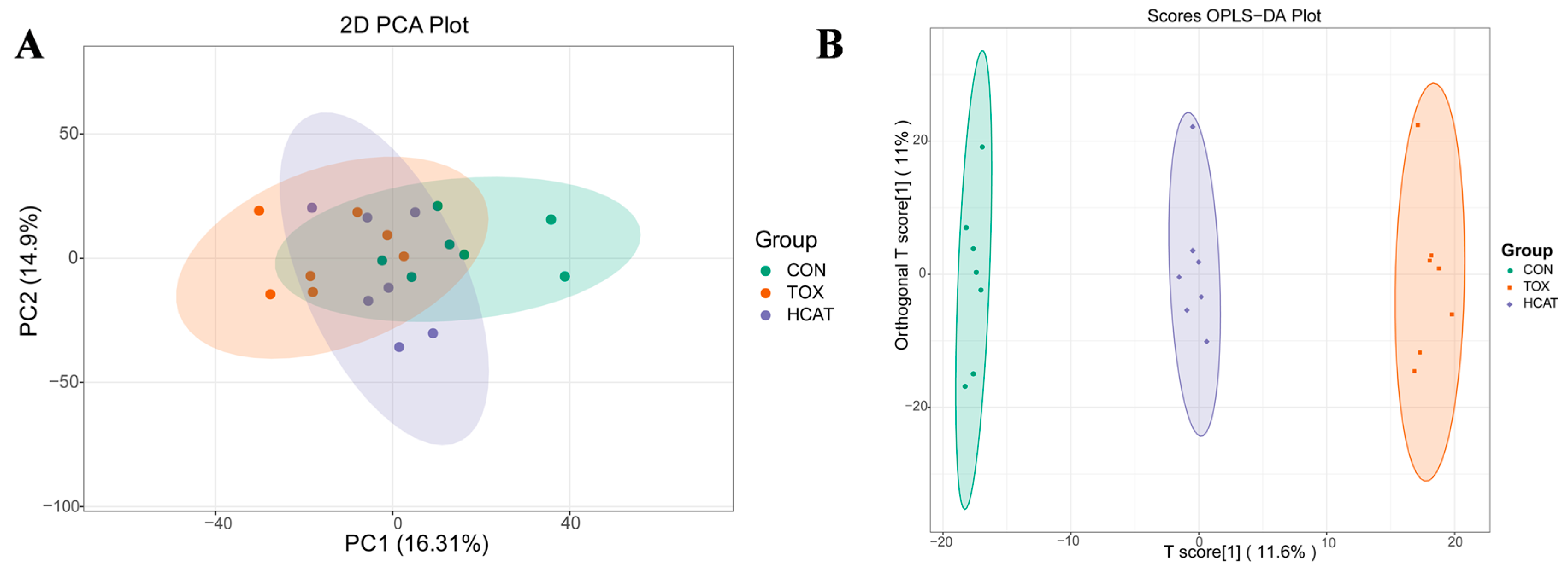
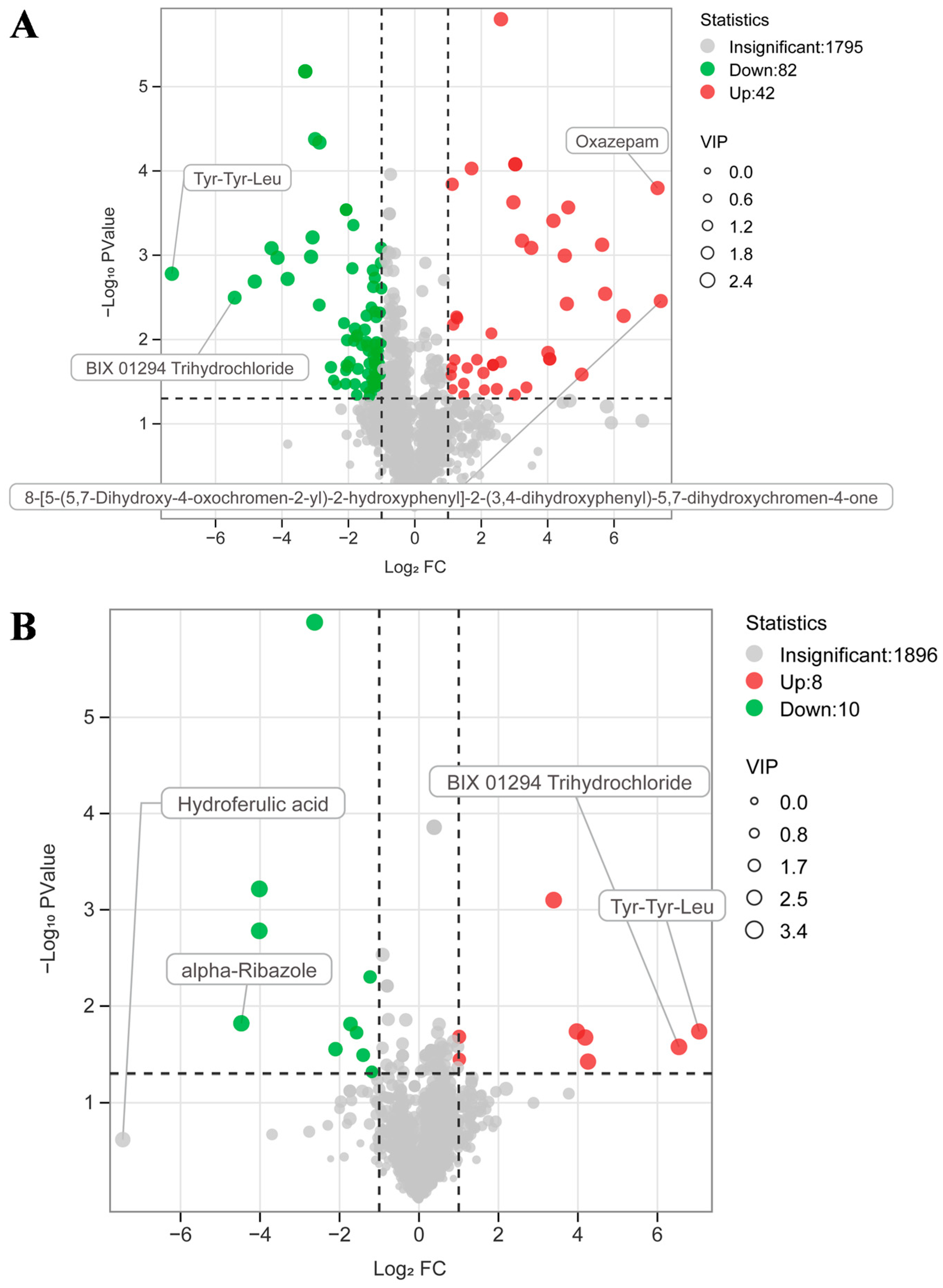
3.6. Effects of Exogenous CAT on the Metabolome of Hepatic Portal Vein Blood of FGM-Exposed Piglets
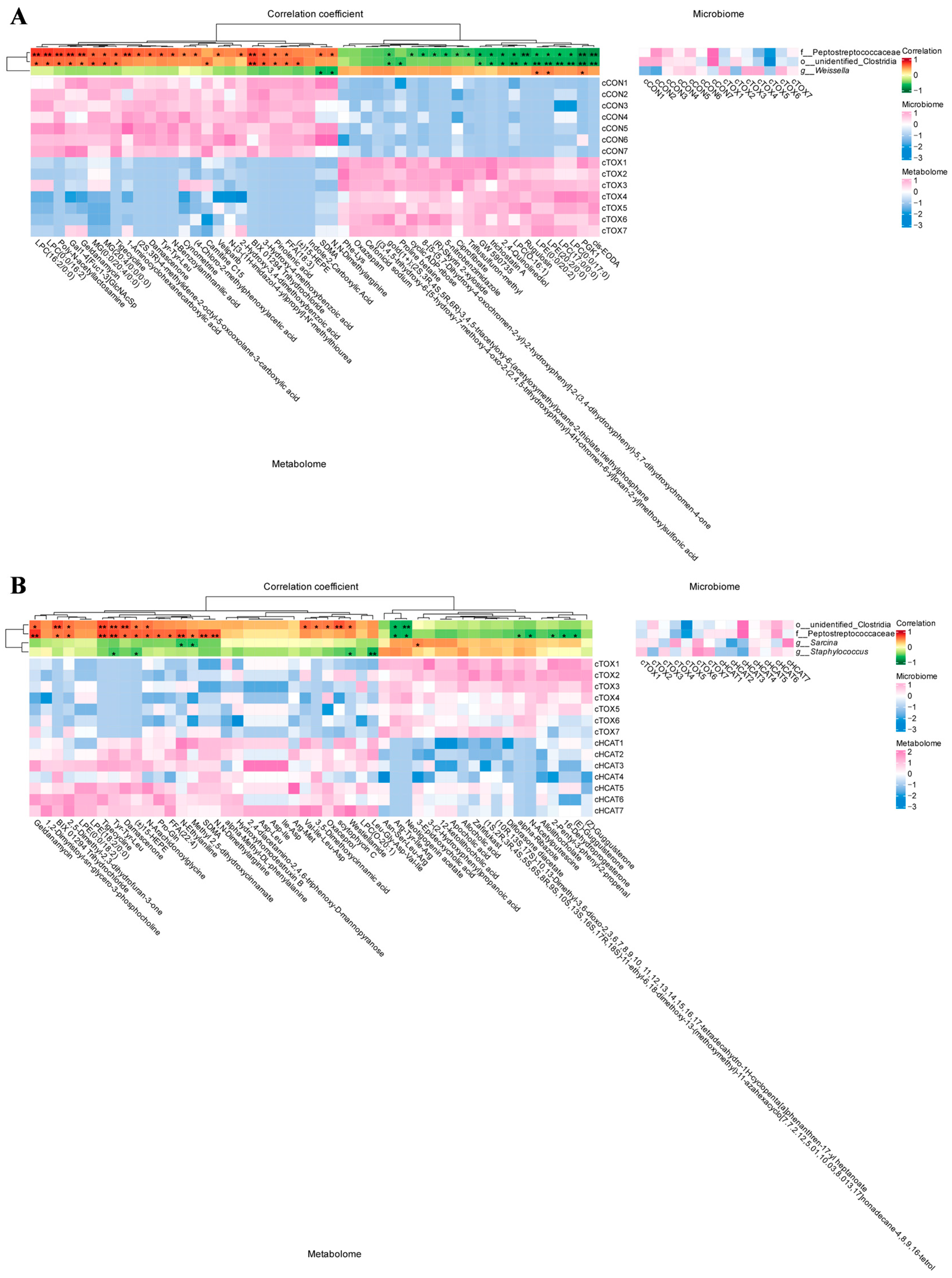
3.7. Effects of Exogenous CAT on Correlations Between Ileal Microbiota and Metabolome of FGM-Exposed Piglets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADFI | Average daily feed intake |
| ADG | Average daily gain |
| AFB1 | Aflatoxin B1 |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CON | Basal diet |
| DON | Deoxynivalenol |
| FBW | Final body weight |
| FC | Fold change |
| FCR | Feed conversion ratio |
| FGM | Fusarium graminearum mycotoxins |
| GPX1 | Glutathione peroxidase 1 |
| HCAT | FGM-contaminated diet + 400 U/kg CAT |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| IBW | Initial body weight |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| LCAT | FGM-contaminated diet + 100 U/kg CAT |
| LEfSe | LDA combined effect size |
| MCAT | FGM-contaminated diet + 200 U/kg CAT |
| NQO1 | NAD(P)H oxidoreductase 1 |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid-2-related factor |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TOX | FGM-contaminated diet |
| VIP | Variable importance in projection |
| ZEA | Zearalenone |
References
- Iqbal, S.Z. Mycotoxins in food, recent development in food analysis and future challenges; a review. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozewicz, M.; Wyzinska, M.; Grabinski, J. The Most Important Fungal Diseases of Cereals-Problems and Possible Solutions. Agronomy 2021, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, J.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ruiz, M.J.; Vila-Donat, P. Multi-mycotoxin occurrence in feed, metabolism and carry-over to animal-derived food products: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 158, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; He, Z.Q.; Xiong, D.W.; Long, M. Mechanisms by which microbial enzymes degrade four mycotoxins and application in animal production: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 15, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escrivá, L.; Font, G.; Manyes, L. In vivo toxicity studies of Fusarium mycotoxins in the last decade: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Mu, P.Q.; Lin, R.Q.; Wen, J.K.; Deng, Y.Q. Toxicokinetics and metabolism of deoxynivalenol in animals and humans. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 2639–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; He, H.Y.; Zuo, Z.C.; Xu, Z.W.; Wei, Z.Y.; Deng, J.L. ROS: Trichothecenes’ handy weapon? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 142, 111438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MatÉs, J.M.; Pérez-Gómez, C.; De Castro, I. Antioxidant enzymes and human diseases. Clin. Biochem. 1999, 32, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veal, E.A.; Day, A.M.; Morgan, B.A. Hydrogen peroxide sensing and signaling. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamocky, M.; Furtmüller, P.G.; Obinger, C. Evolution of catalases from bacteria to humans. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1527–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.S.; Ahsan, H.; Zia, M.K.; Siddiqui, T.; Khan, F.H. Understanding oxidants and antioxidants: Classical team with new players. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.L.; Li, F.C.; Yang, W.R.; Jiang, S.Z.; Li, Y. Supplementation with exogenous catalase from Penicillium notatum in the diet ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal oxidative damage through affecting intestinal antioxidant capacity and microbiota in weaned pigs. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, H.; Payros, D.; Pinton, P.; Théodorou, V.; Mercier-Bonin, M.; Oswald, I.P. Impact of mycotoxins on the intestine: Are mucus and microbiota new targets? Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2017, 20, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.P.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zuo, M.Y.; Ding, S.X.; Li, J.J.; Feng, S.K.; Xiao, Y.P.; Tao, S.Y. Novel mechanism by which extracellular vesicles derived from Lactobacillus murinus alleviates deoxynivalenol-induced intestinal barrier disruption. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Li, J.Y.; Kang, W.L.; Liu, S.P.; Liu, J.Y.; Shi, M.D.; Wang, Y.B.; Liu, X.J.; Chen, X.X.; Huang, K.H. Aflatoxin B1 induces liver injury by disturbing gut microbiota-bile acid-FXR axis in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 176, 113751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.W.; Zhu, J.Q.; Cao, Q.Y.; Zhang, C.M.; Dong, Z.M.; Feng, D.Y.; Ye, H.; Zuo, J.J. Dietary catalase supplementation alleviates deoxynivalenol-induced oxidative stress and gut microbiota dysbiosis in broiler chickens. Toxins 2022, 14, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 39235-2020; Nutrient Requirements of Swine. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 6432-2018; Determination of Crude Protein in Feeds—Kjeldahl method. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 6436-2018; Determination of Calcium in Feeds. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 6437-2018; Determination of Phosphorus in Feeds—Spectrophotometry. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB/T 6438-2007; Animal Feeding Stuffs—Determination of Crude Ash. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2007.
- GB/T 20806-2006; Determination of Neutral Detergent Fiber in Feedstuffs. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- NY/T 1459-2022; Determination of Acid Detergent Fiber in Feed. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Li, M.; Sun, M.N.; Hong, X.; Duan, J.S.; Du, D.L. Survey of deoxynivalenol contamination in agricultural products in the Chinese market using an ELISA kit. Toxins 2019, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, V.; Schulthess, J.; Molist, F.; Santos, R.R. Effect of a Yeast β-Glucan on the performance, intestinal integrity, and liver function of broiler chickens fed a diet naturally contaminated with Fusarium mycotoxins. Toxins 2025, 17, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.B.; Cui, Z.J.; Hao, X.Y.; Cheng, C.H.; Chen, J.Z.; Wu, D.Y.; Luo, H.F.; Deng, J.P.; Tan, C.Q. Dietary fibers with low hydration properties exacerbate diarrhea and impair intestinal health and nutrient digestibility in weaned piglets. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhou, H.N.; Wang, K.S.; Shi, W.G.; Qin, L.; Guan, J.H.; Li, L.S.; Long, B.; et al. Targeting UBE2T potentiates gemcitabine efficacy in pancreatic cancer by regulating pyrimidine metabolism and replication stress. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 1232–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 13078-2017; Hygienical Standard for Feeds. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Wu, C.M.; Song, J.P.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Thomas, D.G.; Wu, B.; Yan, X.R.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.N.; et al. Effect of iron-manganese oxide on the degradation of deoxynivalenol in feed and enhancement of growth performance and intestinal health in weaned piglets. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wu, M.M.; Tan, B.E.; Yin, Y.L.; Li, T.J.; Xiao, D.F.; Li, L. Effects of composite antimicrobial peptides in weanling piglets challenged with deoxynivalenol: I. growth performance, immune function, and antioxidation capacity1. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4772–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.J.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Q.; Du, W.C.; Wei, Q.W.; Yao, W. Hydrogen-rich water and lactulose protect against growth suppression and oxidative stress in female piglets fed Fusarium toxins contaminated diets. Toxins 2018, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Tang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liang, H.M.; Chen, D.W.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Mao, X.B.; Huang, Z.Q.; Yan, H.; et al. Eugenol attenuates transmissible gastroenteritis virus-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via ROS-NRF2-ARE signaling. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magesh, S.; Chen, Y.; Hu, L.Q. Small molecule modulators of Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as potential preventive and therapeutic agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2012, 32, 687–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Iwata, M.; Warabi, E.; Oishi, H.; Lira, V.A.; Okutsu, M. p62/SQSTM1 and Nrf2 are essential for exercise-mediated enhancement of antioxidant protein expression in oxidative muscle. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8022–8032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.F.; Gao, K.G.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, Z.Y. Dietary resveratrol attenuation of intestinal inflammation and oxidative damage is linked to the alteration of gut microbiota and butyrate in piglets challenged with deoxynivalenol. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Tang, Z.Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, F.; Wu, Y.J.; Wu, D. Dietary taurine supplementation counteracts deoxynivalenol-induced liver injury via alleviating oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, apoptosis, and inflammation in piglets. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Cai, P.R.; Shan, T.Z. Global distribution, toxicity to humans and animals, biodegradation, and nutritional mitigation of deoxynivalenol: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 3951–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoultz, I.; Keita, Å.V. The intestinal barrier and current techniques for the assessment of gut permeability. Cells 2020, 9, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Shen, Y.; Cheng, D.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, C.; Liu, M.; Yao, W.H.; Ran, R.R.; et al. Macrophage AHR-TLR4 cross-talk drives p-STAT3 (Ser727)-mediated mitochondrial oxidative stress and upregulates IDO/ICAM-1 in the steatohepatitis induced by aflatoxin B1. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 923, 171377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.O.; Loeffler, A.; Davis, M.F.; Guardabassi, L.; Weese, J.S. Recommendations for approaches to meticillin-resistant staphylococcal infections of small animals: Diagnosis, therapeutic considerations and preventative measures. Vet. Dermatol. 2017, 28, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Singh, A. Gut microbiome and human health: Exploring how the probiotic genus Lactobacillus modulate immune responses. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1042189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.X.; Chang, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, C.Q.; Liu, M.J.; Zhou, T.; Yin, Q.Q.; Yan, G.R. Glycyrrhizic acid and compound probiotics supplementation alters the intestinal transcriptome and microbiome of weaned piglets exposed to deoxynivalenol. Toxins 2022, 14, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, S.J.; Cheng, S.S.; Li, Y.; Wen, Z.S.; Ma, X.; Jiang, X.M.; Wang, Y.Z.; Han, X.Y. Faecal microbiota transplantation reduces susceptibility to epithelial injury and modulates tryptophan metabolism of the microbial community in a piglet model. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 1359–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Trauner, M. Gut-liver axis: Pathophysiological concepts and clinical implications. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; De Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.J.; Liu, C.; Wan, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.W.; Duan, J.A. Enterohepatic circulation of bile acids and their emerging roles on glucolipid metabolism. Steroids 2021, 165, 108757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningrum, A.; Wardani, D.W.; Vanidia, N.; Manikhaeda; Sarifudin, A.; Kumalasari, R.; Ekafitri, R.; Kristanti, D.; Setiaboma, W.; Munawaroh, H.S.H. Evaluation of antioxidant activities from a sustainable source of okara protein hydrolysate using enzymatic reaction. Molecules 2023, 28, 4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohwer, N.; Chiu, C.Y.; Huang, D.; Smyl, C.; Rothe, M.; Rund, K.M.; Schebb, N.H.; Kühn, H.; Weylandt, K.H. Omega-3 fatty acids protect from colitis via an Alox15-derived eicosanoid. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Zhou, W.J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, F.H.; Dang, Y.Q. Quantitative profiling of oxylipin reveals the mechanism of pien-tze-huang on alcoholic liver disease. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.L.; Xiong, Y.N.; Jie, Z.W.; Li, C.Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Cai, J.W.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, J.H.; Yao, Y.H.; Chang, M.Z.; et al. Damascenone inhibits osteoclastogenesis by epigenetically modulating Nrf2-mediated ROS scavenge and counteracts OVX-induced osteoporosis. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ingredients | Content (%) | Nutrient Levels | Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 57.83 | Analyzed nutrient level | |
| Soybean meal | 18.60 | Crude protein | 18.69 |
| Soybean oil | 1.40 | Organic matter | 80.94 |
| Extruded soybean meal | 8.00 | Neutral detergent fiber | 7.12 |
| Whey powder | 10.00 | Acid detergent fiber | 3.60 |
| Salt | 0.32 | Calcium | 0.61 |
| Limestone | 0.50 | Total phosphorus | 0.55 |
| Dicalcium phosphate | 1.23 | Calculated nutrient level | |
| Choline chloride (50%) | 0.16 | Metabolizable energy, MJ/kg | 13.81 |
| L-lysine (99%) | 0.58 | Total lysine | 1.30 |
| DL-methionine (98%) | 0.17 | Total methionine + cystine | 0.73 |
| L-threonine (98.5%) | 0.17 | Total tryptophan | 0.23 |
| L-tryptophan (98%) | 0.05 | Total threonine | 0.83 |
| Premix (1) | 1.00 | ||
| Total | 100.00 |
| Items | CON (1) | TOX | LCAT | MCAT | HCAT | SEM | p-Value (2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Linear | Quadratic | |||||||
| IBW (kg) | 7.93 | 7.89 | 7.89 | 7.91 | 7.91 | 0.113 | 1.000 | 0.943 | 0.997 |
| FBW (kg) | 17.07 | 15.54 | 16.95 | 17.08 | 18.85 | 0.312 | 0.067 | 0.009 | 0.035 |
| ADG (g) | 332.37 ab | 268.36 b | 314.22 ab | 327.05 ab | 381.96 a | 9.945 | 0.039 | 0.004 | 0.016 |
| ADFI (g) | 559.08 ab | 462.29 b | 555.74 ab | 549.03 ab | 695.91 a | 14.146 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.003 |
| FCR | 1.69 | 1.75 | 1.77 | 1.68 | 1.83 | 0.026 | 0.387 | 0.762 | 0.445 |
| Diarrhea rate (%) | 12.95 c | 30.61 a | 24.49 ab | 16.96 b | 16.07 b | 2.533 | <0.001 | / | / |
| Diarrhea index | 0.50 c | 0.99 a | 0.76 b | 0.65 b | 0.58 b | 0.059 | <0.001 | / | / |
| Items | CON (1) | TOX | LCAT | MCAT | HCAT | SEM | p-Value (2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Linear | Quadratic | |||||||
| Liver index (g/kg) | 27.76 | 26.82 | 25.68 | 27.83 | 29.14 | 0.349 | 0.110 | 0.044 | 0.066 |
| Thymus index (g/kg) | 2.59 | 2.54 | 2.08 | 2.97 | 2.55 | 0.099 | 0.170 | 0.462 | 0.760 |
| Spleen index (g/kg) | 2.09 | 2.07 | 1.83 | 2.09 | 2.14 | 0.038 | 0.460 | 0.227 | 0.214 |
| Items | CON (1) | TOX | LCAT | MCAT | HCAT | SEM | p-Value (2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Linear | Quadratic | |||||||
| ileal tissue | |||||||||
| ROS | 1.00 a | 0.74 b | 0.93 a | 0.90 a | 0.93 a | 0.018 | 0.006 | 0.026 | 0.021 |
| H2O2 (mmol/g prot) | 8.69 | 10.47 | 8.35 | 9.41 | 9.43 | 0.315 | 0.301 | 0.633 | 0.349 |
| SOD (U/mg prot) | 23.27 | 22.34 | 22.49 | 20.56 | 21.88 | 0.272 | 0.057 | 0.208 | 0.288 |
| CAT (U/mg prot) | 7.35 a | 3.44 c | 4.21 bc | 4.90 b | 3.65 c | 0.115 | <0.001 | 0.280 | 0.002 |
| ileal chyme | |||||||||
| ROS | 1.00 b | 1.95 a | 0.98 b | 1.17 b | 1.17 b | 0.086 | 0.018 | 0.068 | 0.026 |
| H2O2 (mmol/g prot) | 1.11 | 2.61 | 1.93 | 2.41 | 1.97 | 0.175 | 0.072 | 0.408 | 0.661 |
| liver | |||||||||
| ROS | 1.00 | 1.06 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.040 | 0.940 | 0.907 | 0.944 |
| H2O2 (mmol/g prot) | 2.83 | 4.28 | 3.93 | 3.55 | 3.22 | 0.204 | 0.214 | 0.086 | 0.237 |
| SOD (U/mg prot) | 80.61 c | 88.56 bc | 98.14 ab | 108.04 a | 105.10 a | 1.600 | <0.001 | 0.005 | 0.006 |
| CAT (U/mg prot) | 52.80 c | 48.20 c | 42.03 c | 127.95 b | 154.94 a | 2.930 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Ling, C.; Xian, M.; Ye, H.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Z.; Wang, W.; Zuo, J. Exogenous Catalase Supplementation Alleviates Fusarium graminearum Mycotoxins-Induced Oxidative Stress in Weaned Piglets. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171892
Liang S, Jiang Y, Ling C, Xian M, Ye H, Cao Q, Zhang C, Dong Z, Wang W, Zuo J. Exogenous Catalase Supplementation Alleviates Fusarium graminearum Mycotoxins-Induced Oxidative Stress in Weaned Piglets. Agriculture. 2025; 15(17):1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171892
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Shujie, Yunfei Jiang, Chong Ling, Meitian Xian, Hui Ye, Qingyun Cao, Changming Zhang, Zemin Dong, Weiwei Wang, and Jianjun Zuo. 2025. "Exogenous Catalase Supplementation Alleviates Fusarium graminearum Mycotoxins-Induced Oxidative Stress in Weaned Piglets" Agriculture 15, no. 17: 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171892
APA StyleLiang, S., Jiang, Y., Ling, C., Xian, M., Ye, H., Cao, Q., Zhang, C., Dong, Z., Wang, W., & Zuo, J. (2025). Exogenous Catalase Supplementation Alleviates Fusarium graminearum Mycotoxins-Induced Oxidative Stress in Weaned Piglets. Agriculture, 15(17), 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15171892





