Using APSIM Model to Optimize Nitrogen Application for Alfalfa Yield Under Different Precipitation Regimes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Items and Methods
2.3.1. Hay Yield (Y, t·ha−1)
2.3.2. Nitrogen Use Efficiency (NUE)
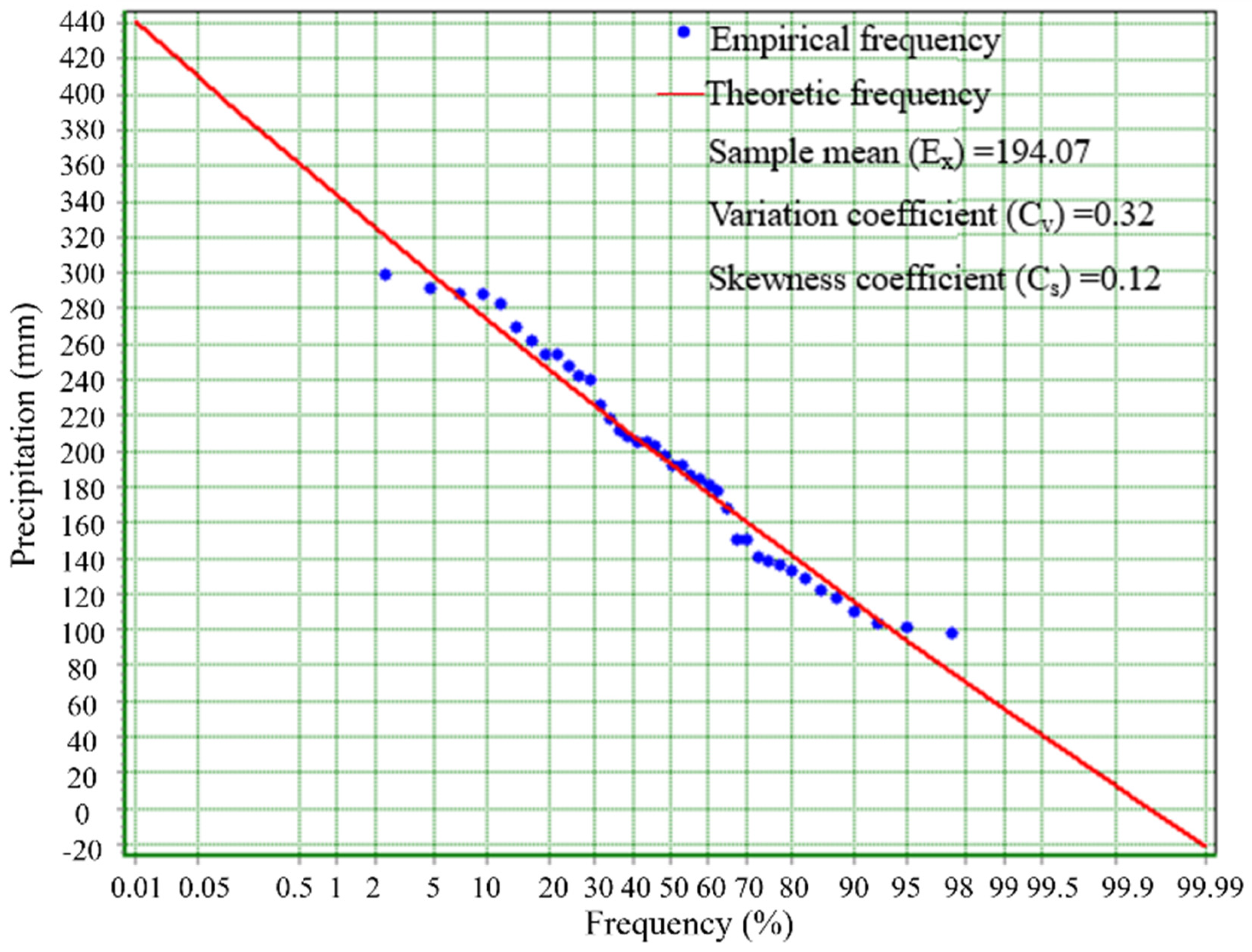
2.4. Classification of Different Precipitation Year Types
2.5. Scenario Design
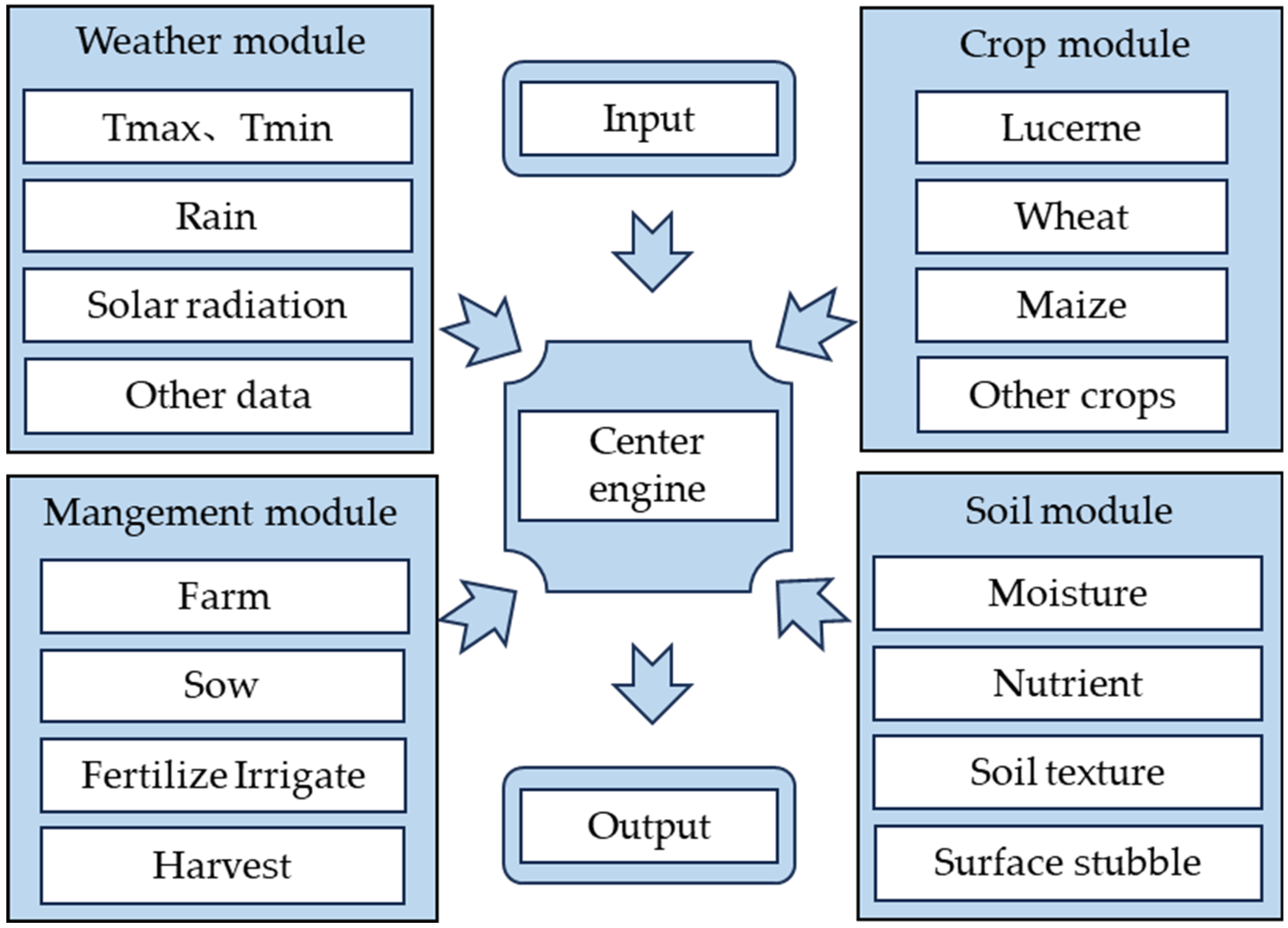
2.6. Model Construction and Verification
2.6.1. Construction of the APSIM-Lucerne Model
2.6.2. Model Verification Methods
2.7. Entropy Weight-TOPSIS Model
- (1)
- Determination of Indicator Weights Using the Entropy Weight Method
- (2)
- Entropy Weight-TOPSIS Model
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
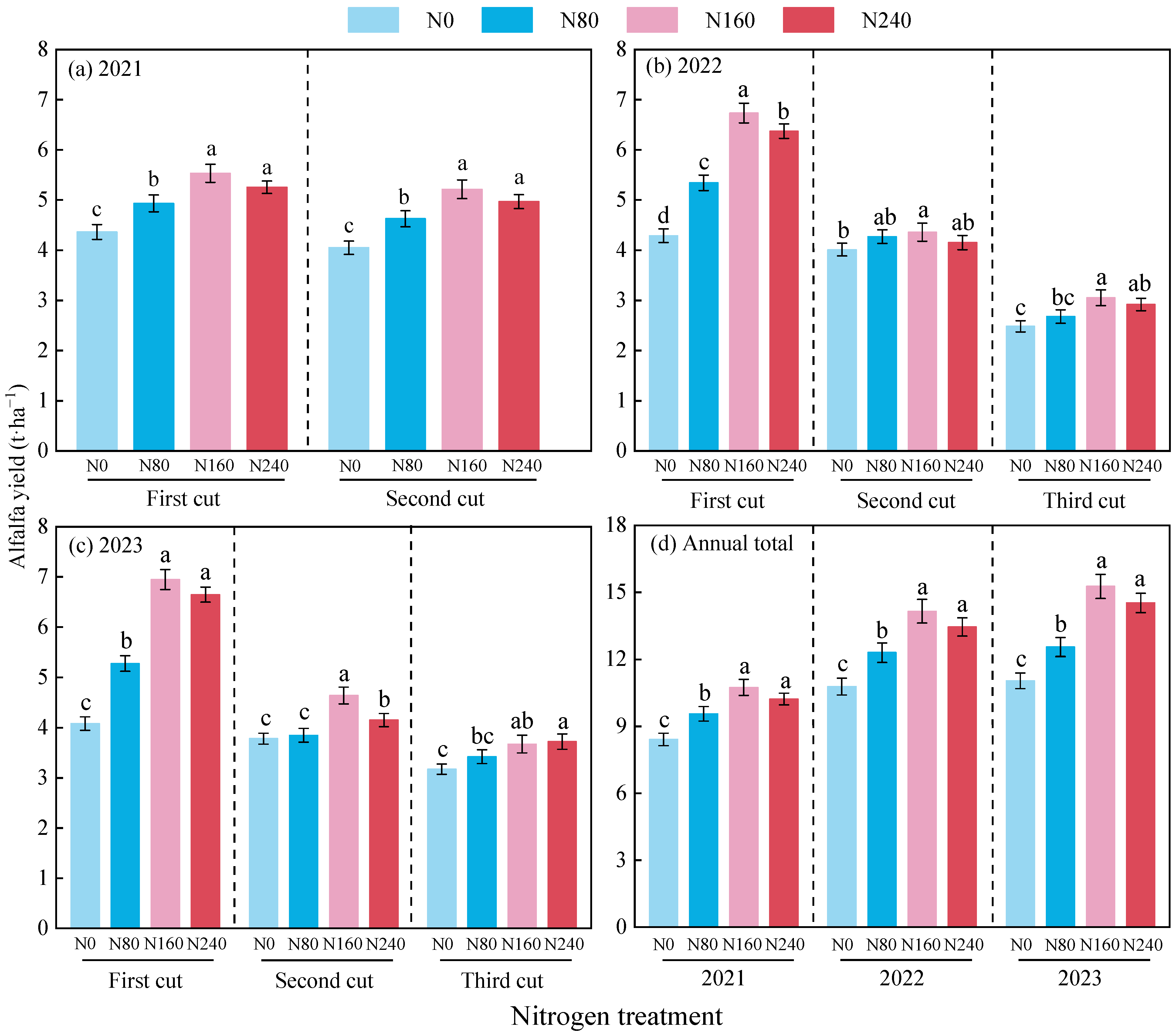
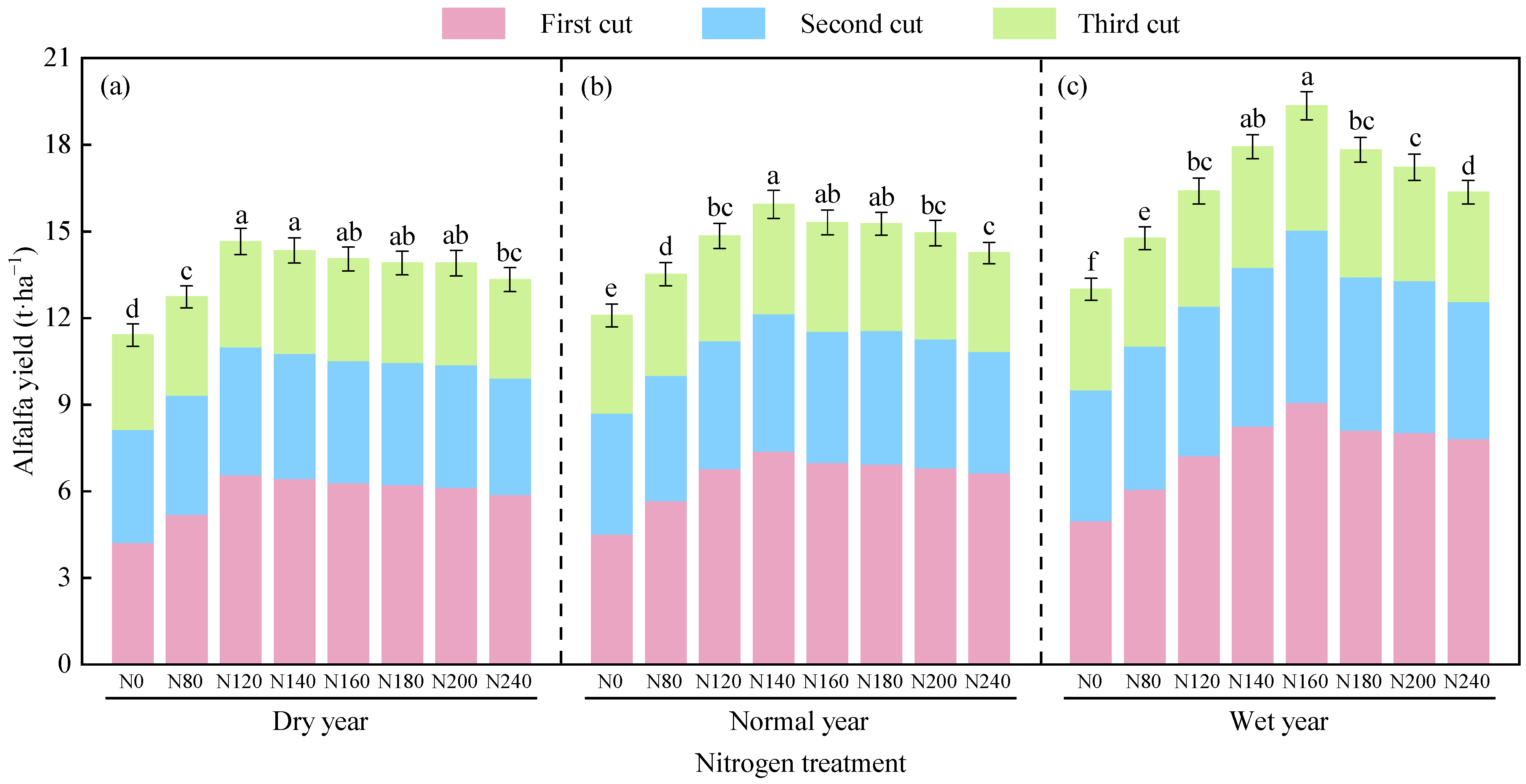
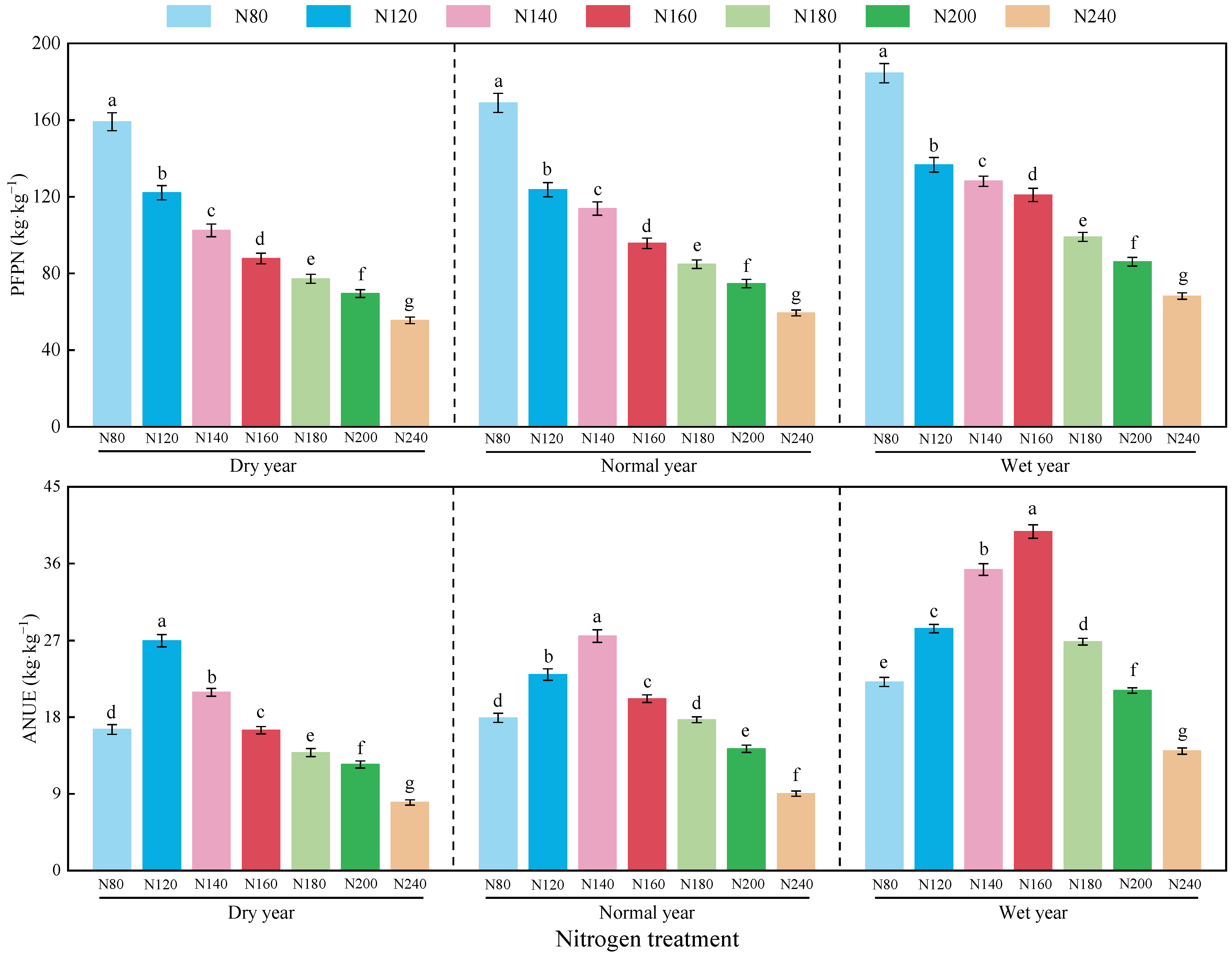
3.1. Effects of Nitrogen Application on Alfalfa Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
3.1.1. Yield
3.1.2. Nitrogen Use Efficiency
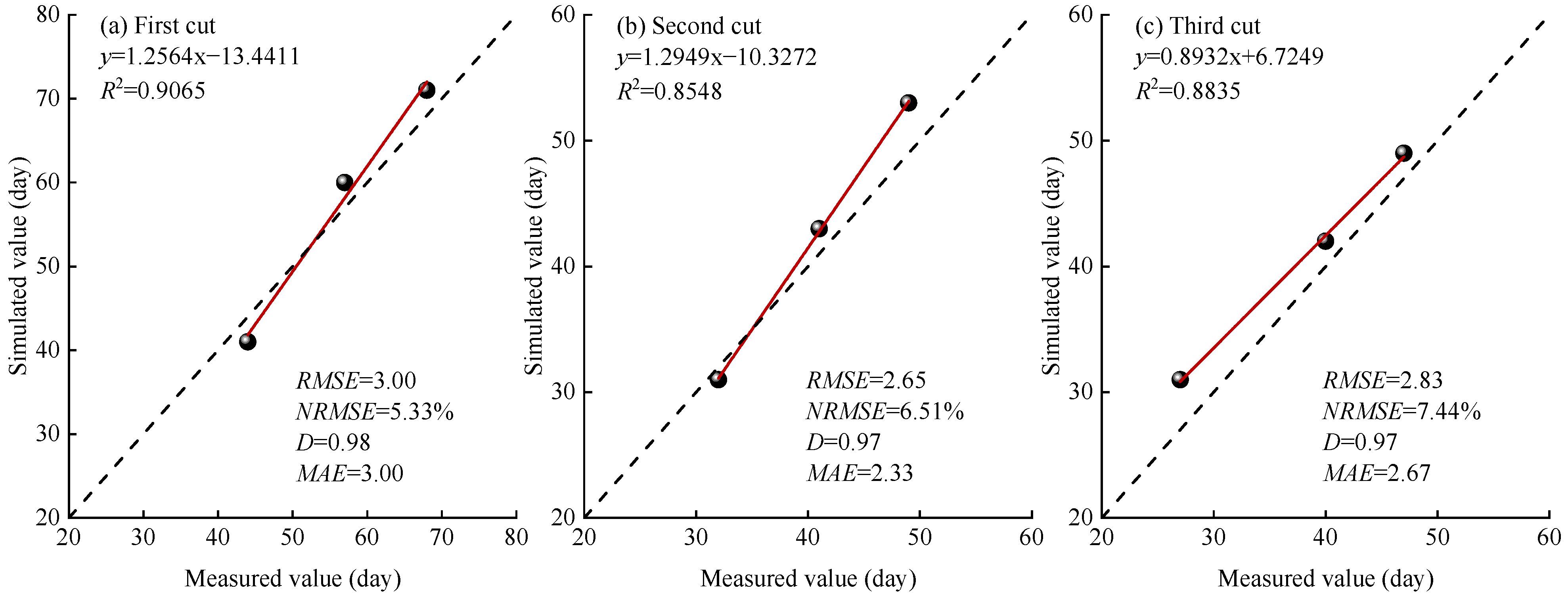
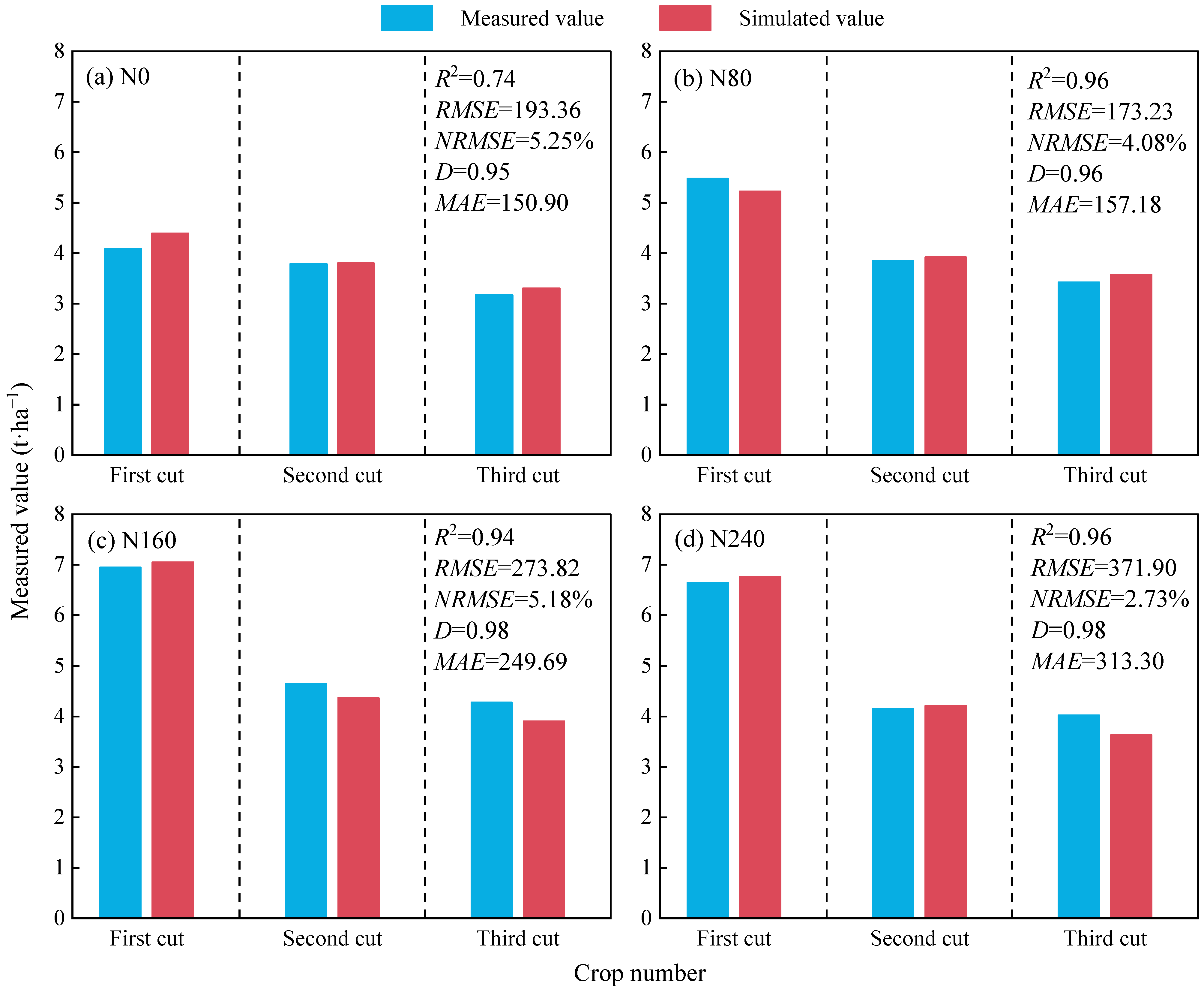
3.2. Verification of the APSIM-Lucerne Model
3.2.1. Verification of the Reproductive Period
3.2.2. Verification of Yield
3.3. Selection of Typical Precipitation Year Types
3.4. Simulation of Alfalfa Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency Under Different Precipitation Year Types
3.4.1. Simulation of Yield
3.4.2. Simulation of Nitrogen Use Efficiency
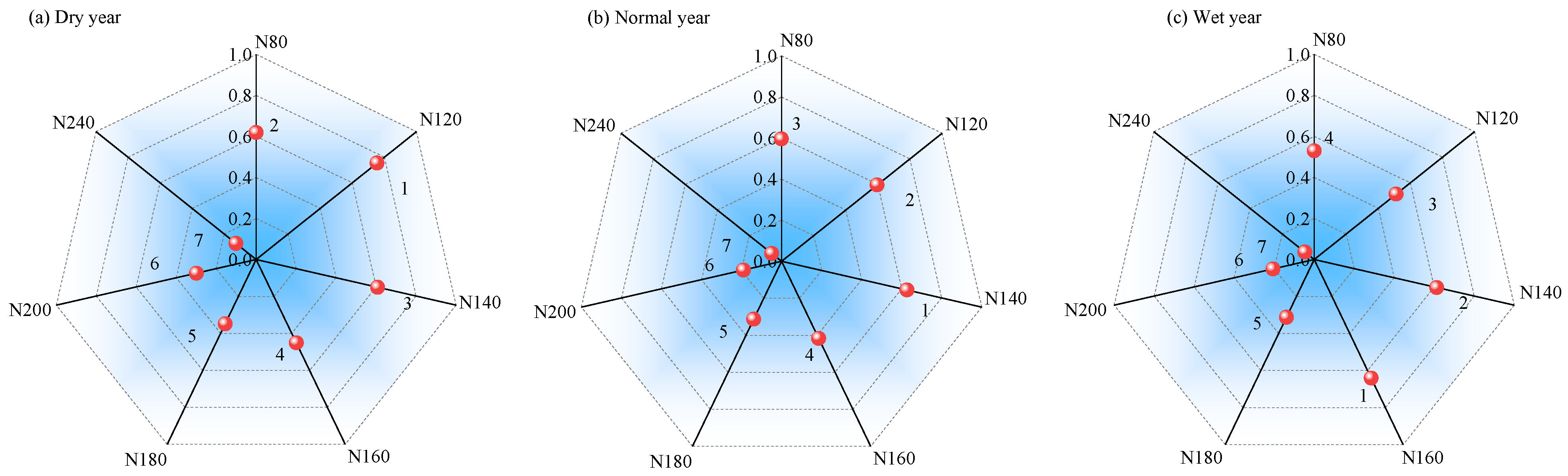
3.5. Comprehensive Evaluation Based on the Entropy Weight-TOPSIS Model
4. Discussion
4.1. Applicability of APSIM-Lucerne Model for Simulating Alfalfa
4.2. Effect of Precipitation Year Type and Nitrogen Application Level on Alfalfa Yield
4.3. Effects of Precipitation Year Type and Nitrogen Application Level on Alfalfa Nitrogen Use Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, X.W.; Wu, K.; Fu, X.D.; Liu, Q. Improving coordination of plant growth and nitrogen metabolism for sustainable agriculture. aBIOTECH 2020, 1, 255–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Z.; Hao, G.; Li, H.Y. Research progress on the effectiveness and form of exogenous nitrogen input and its impact on plant growth and physiology. J. Ecol. 2024, 43, 878–887. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Ou, E.L.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Fang, X.W.; Zhang, J.L. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GB03 augmented tall fescue growth by regulating phytohormone and nutrient homeostasis under nitrogen deficiency. Front Plant Sci. 2022, 13, e979883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.Y.; Yao, L.; Zhong, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.F.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.J.; Liu, R.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.F. Nitrogen fertilizer demand in China in the context of green development. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2025, 62, 308–321. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.; Wu, T.X.; Wang, S.D.; Sang, S.; Zhao, Y.T. Phenology–gross primary productivity (GPP) method for crop information extraction in areas sensitive to non-point source pollution and its influence on pollution intensity. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Hu, S.; Guo, Z.; Cui, T.; Jin, Y. Effect of balanced nutrient fertilizer: A case study in pinggu district, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 754, 142069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabuba, J.; Lephallo, J.; Rutto, H. Comparison of various technologies used to eliminate nitrogen from wastewater: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 48, 102885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.L.; Yu, Y.D. Optimizing the irrigation schedule for winter wheat-summer maize using APEX model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2025, 41, 118–126. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.X.; Su, J.Y.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, W.H. State and parameter estimation of the AquaCrop model for winter wheat using sensitivity informed particle filter. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 180, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.P. Discussion on problems in the development and application of crop growth model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2025, 36, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.L.; Zeng, W.Z.; Ma, T.; Lei, G.Q.; Zha, Y.Y.; Fang, Y.H.; Wu, J.W.; Huang, J.S. Testing and improving the WOFOST model for sunflower simulation on saline soils of inner mongolia, China. Agronomy 2018, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strer, M.; Svoboda, N.; Herrmann, A. Abundance of adverse environmental conditions during critical stages of crop production in Northern Germany. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palosuo, T.; Hoffmann, M.; Rtter, R.; Lehtonen, H. Sustainable intensification of crop production under alternative future changes in climate and technology: The case of the North Savo region. Agric. Syst. 2021, 190, 103135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzworth, D.P.; Huth, N.I.; Devoil, P.G.; Zurcher, E.J.; Herrmann, N.I. APSIM—Evolution towards a new generation of agricultural systems simulation. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 62, 327–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, H.; Levia, D.F.; Herrick, J.E.; Lydiasari, H.; Schütze, N. Water requirements for oil palm grown on marginal lands: A simulation approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 260, 107292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Wang, E.L.; He, D.; Liu, X.; Archontoulis, S.V.; Huth, N.I.; Zhao, Z.G.; Gong, W.Z.; Yang, W.Y. Combine observational data and modelling to quantify cultivar differences of soybean. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 111, 125940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaki, A.K.; Gaydon, D.S.; Dalal, R.C.; Bellotti, W.D.; Gathala, M.K.; Hossain, A.; Menzies, N.W. How we used APSIM to simulate conservation agriculture practices in the rice–wheat system of the Eastern Gangetic Plains. Field Crop. Res. 2022, 275, 108344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcedo, A.; Bastos, L.M.; Yadav, S.; Mondal, M.K.; Jagadish, S.V.K.; Kamal, F.A.; Sutradhar, A.; Prasad, P.; Ciampitti, I.A. Assessing impact of salinity and climate scenarios on dry season field crops in the coastal region of Bangladesh. Agric. Syst. 2022, 200, 1034281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Cui, S.; Shen, Y. Modelling the effects of conservation tillage on crop water productivity, soil water dynamics and evapotranspiration of a maize–winter wheat–soybean rotation system on the Loess Plateau of China using APSIM. Agric. Syst. 2018, 166, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.H.; Jiang, Y.B.; Ling, Y.; Ma, Y.L.; Qi, G.P.; Kang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lu, Q.; Shang, Y.J.; Fan, X.R.; et al. Optimizing lucerne productivity and resource efficiency in China’s Yellow River irrigated region: Synergistic effects of ridge-film mulchingand controlled-release nitrogen fertilization. Agriculture 2025, 15, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, F.G.; Zhu, Y.M.; Wu, H.; Ahmad, I.; Dong, G.C.; Zhou, G.S.; Wu, Y.Q. The effects of planting density and nitrogen application on the growth quality of alfalfa forage in saline soils. Agriculture 2024, 14, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterholz, W.R.; Renz, M.J.; Jokela, W.E.; Grabber, J.H. Interseeded alfalfa reduces soil and nutrient runoff losses during and after corn silage production. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 12, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.D.; Wang, Y.R.; Han, Y.H. Effects of irrigation frequency and fertilizer rate on alfalfa seed yields in the Yellow River irrigated region. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2016, 25, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.J.; Han, C.L.; Kong, M.; Shi, X.Y.; Zdruli, P.; Li, F.M. Plastic film mulch promotes high alfalfa production with phosphorus saving and low risk of soil nitrogen loss. Field Crops Res. 2018, 229, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Qi, G.P.; Yin, M.H.; Kang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.L.; Jia, Q.; Wang, J.H.; Jiang, Y.B.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.L. Alfalfa cultivation patterns in the Yellow River irrigation area on soil water and nitrogen use efficiency. Agronomy 2024, 14, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.R.; Wang, J.H.; Yin, M.H.; Kang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.L.; Jia, Q.; Qi, G.P.; Jiang, Y.B.; Lu, Q.; Chen, X.L. Effects of planting and nitrogen application patterns on alfalfa yield, quality, water–nitrogen use efficiency, and economic benefits in the Yellow River irrigation region of Gansu Province, China. Water 2023, 15, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, X.H.; Wang, J. Response simulation of CO2 concentration and temperature onspring wheat yield in dryland under different precipitation types. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2023, 41, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Huang, G.B.; Bellotti, W.; Chen, W. Adaptation research of APSIM model under different tillage systems in the Loess hill-gullied region. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 2655–2663. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R.R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?—Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbakov, M.V.; Brebels, A.; Shcherbakova, N.L.; Tyukov, A.P.; Janovsky, T.A.; Kamaev, V.A. A survey of forecast error measures. World Appl. Sci. J. 2013, 24, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, R.R.; Wang, J.H.; Yin, M.H.; Ma, Y.L.; Jia, Q.; Kang, Y.X.; Qi, G.P.; Gao, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.B.; Li, H.Y.; et al. Investigation of the regulatory effects of water and nitrogen supply on nitrogen transport and distribution in wolfberry fields. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1385980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ech–Chatir, L.; Er–Raki, S.; Rodriguez, J.C.; Meddich, A. Advances in crop growth modeling: A review of perennial crop and beneficial soil microorganism approaches. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 315, 109548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornet, D.; Marcos, J.; Tournebize, R.; Sierra, J. Observed and modeled response of water yam (Dioscorea alata L.) to nitrogen supply: Consequences for nitrogen fertilizer management in the humid tropics. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 138, 126536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, J. The adaptability of APSIM-wheat model in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Plain of China: A case study of winter wheat in Hubei Province. Agronomy 2020, 10, 981. [Google Scholar]
- Gulnazar, A.l.I.; Tao, H.M.; Wang, Z.K.; Shen, Y.Y. Evaluating the deep-horizon soil water content and water use efficiency in the alfalfa–wheat rotation system on the dryland of Loess Plateau using APSIM. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2021, 30, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, L.J.; Archontoulis, S.V.; Puntel, L.A. Simulating within-field spatial and temporal corn yield response to nitrogen with APSIM mode. Precis. Agric. 2024, 25, 2421–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, C.; Yang, F.Y.; Fan, D.L.; Luo, J.M.; Han, J.R.; Wang, T.S.; Guo, E.J. Optimization of water and nitrogen management mode for spring wheat under different precipitation year types based on APSIM model. J. Triticeae Crops. 2025, 45, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, W.L.; Zhao, Y.H.; Li, X.F.; Xu, J.; Liu, K.G.; Chai, Y.Q.; Xu, H.J.; Cui, H.X.; Chen, X.J.; Wu, P.; et al. A moderate reduction in irrigation and nitrogen improves water–nitrogen use efficiency, productivity, and profit under new type of drip irrigated spring wheat system. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1005945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Wang, Q.; Shi, S.L.; Zhang, N.H.; Wang, T.T.; Liu, Q.L.; Liu, C.W.; Yu, H.L. Effect of irrigation and nitrogen supply levels on hay yield and water use efficiency and soil total nitrogen of Medicage sativa. Grassl. Turf. 2012, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.L.; Zhao, J.W.; Liu, X.S.; Li, S.Y.; Ma, C.H.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhang, Q.B. Effect of nitrogen application on photosynthetic daily variation, leaf morphology and dry matter yield of alfalfa at the early flowering growth stage. Acta Pratacult. Sin. 2022, 31, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.T.; Wang, Y.Q.; Sun, S.N.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Qian, J.; Yan, X.B. Effects of nitrogen Forms on nitrogen accumulation and utilization of alfalfa in different stubbles. Pratac. Sci. 2021, 38, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.F.; Sun, X.C.; Tian, R.; Li, K.X.; Ni, M.; Ying, J.L.; Xu, L.A.; Liu, L.W.; Wang, Y. Genome-Wide Characterization of the Aquaporin Gene Family in Radish and Functional Analysis of RsPIP2-6 Involved in Salt Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 860742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delevatti, L.M.; Cardoso, A.S.; Barbero, R.P.; Leite, R.G.; Reis, R.A. Effect of nitrogen application rate on yield, forage quality, and animal performance in a tropical pasture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Z.P.; Wang, L. Relationship between soil moisture dynamics, crop growth and precipitation in rain-fed area of the Loess Tableland, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Xiao, D.P.; Bai, H.Z.; Tang, J.Z. Climatic suitability of winter wheat and summer maize in the North China Plain. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 2251–2262. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.R.; Zhong, R.; Sun, M.; Kong, W.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Hafeez, N.; Ren, A.X.; Lin, W.; Gao, Z.Q. Nitrogen application rates at rainfall gradients regulate water and nitrogen use efficiency in dryland winter wheat. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 2022, 28, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar]
- García-López, J.; Lorite, I.J.; García-Ruiz, R.; Ordoñez, R.; Dominguez, J. Yield response of sunflower to irrigation and fertilization under semi-arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Tong, C.; Wu, Y. Effect of root interaction on nodulation and nitrogen fixation ability of alfalfa in the simulated alfalfa/triticale intercropping in pots. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 61234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.X.; Wang, J.; Tang, J.Z.; Fang, Q.X.; Zhang, J.P.; Bai, H.Q.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Wu, B.J.; Zheng, J.Q.; et al. Analysis of interaction of sowing date, irrigation and nitrogen application on yield of oilsunflower based on APSIM model. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Li, C.; Li, W.M.; Ye, C.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhao, C.S.; Ding, F.H.; Jin, A.F.; Feng, L.P.; Li, Z.F. Optimal path of the simulation model in horticultural crop development and harvest period. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 158. [Google Scholar]

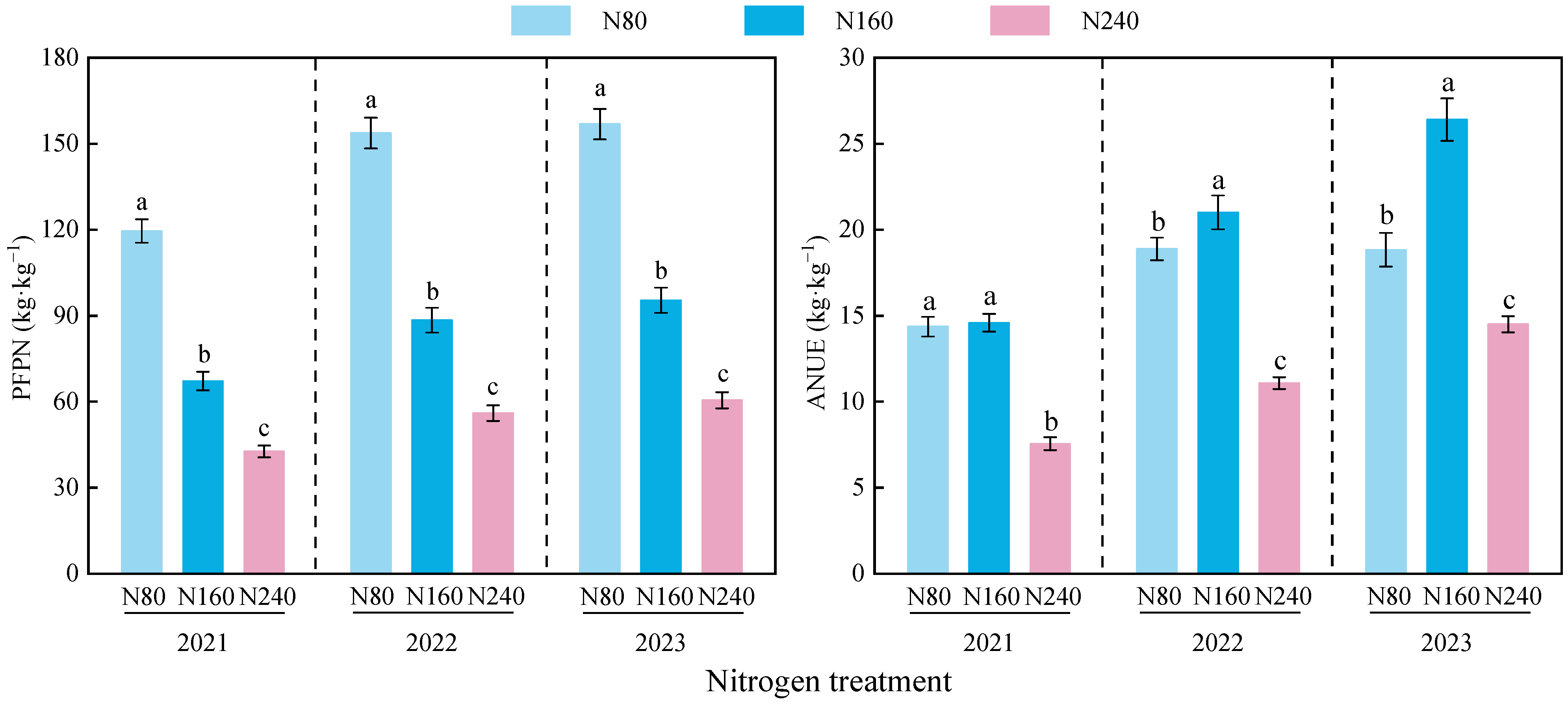
| Model Year | Average Precipitation (mm) | Total (Year) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wet year | 267.33 | 12 | 1985, 1994, 2002, 2003, 2007, 2011, 2014, 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2024 |
| Normal year | 208.08 | 8 | 1988, 1992, 1993, 1995, 1997, 1998, 2001, 2021 |
| Dry year | 144.50 | 20 | 1986, 1987, 1989, 1990, 1991, 1996, 1999, 2000, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2012, 2013, 2015, 2020, 2022, 2023 |
| Parameters | Soil Depth (cm) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–10 | 10–20 | 20–30 | 30–40 | 40–60 | 60–80 | 80–100 | 100–120 | |
| BD (g·cm−1) | 1.260 | 1.340 | 1.360 | 1.390 | 1.280 | 1.140 | 1.240 | 1.300 |
| Air_dry (mm·mm−1) | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.050 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.070 | 0.070 |
| LL15 (mm·mm−1) | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.016 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.022 |
| DUL (mm·mm−1) | 0.184 | 0.210 | 0.215 | 0.225 | 0.241 | 0.278 | 0.233 | 0.253 |
| SAT (mm·mm−1) | 0.134 | 0.160 | 0.165 | 0.175 | 0.191 | 0.228 | 0.183 | 0.203 |
| Swcon (0–1) | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.600 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.500 |
| Soil pH | 8.080 | 8.110 | 8.130 | 8.300 | 8.410 | 8.540 | 8.700 | 8.700 |
| LucerneLL (mm·mm−1) | 0.290 | 0.290 | 0.290 | 0.290 | 0.300 | 0.310 | 0.320 | 0.330 |
| LucerneKL (d−1) | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.090 |
| LucerneXF (0–1) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.000 |
| Parameters | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal time from emergence to end of juvenile | 550 | °C·d |
| Thermal time from end of juvenile to floral initiation | 610 | °C·d |
| Photoperiod required for floral initiation | >10 | h |
| Thermal time from initiation to full-blooming | 260 | °C·d |
| Radiation use efficiency | 1.8 | g·MJ−1 |
| Stem weight | 0~5 | g·plant−1 |
| Plant height | 0~5000 | mm |
| Treatment | Dry Year | Normal Year | Wet Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield | PFPN | ANUE | Yield | PFPN | ANUE | Yield | PFPN | ANUE | |
| N80 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.5658 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4808 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.3153 |
| N120 | 1.0000 | 0.6418 | 1.0000 | 0.5476 | 0.5868 | 0.7550 | 0.3564 | 0.5886 | 0.5582 |
| N140 | 0.8384 | 0.4522 | 0.8434 | 1.0000 | 0.4968 | 1.0000 | 0.6910 | 0.5151 | 0.8269 |
| N160 | 0.6855 | 0.3111 | 0.5605 | 0.7414 | 0.3313 | 0.6025 | 1.0000 | 0.4536 | 1.0000 |
| N180 | 0.6112 | 0.2094 | 0.3866 | 0.7232 | 0.2321 | 0.4678 | 0.5808 | 0.2463 | 0.4128 |
| N200 | 0.6096 | 0.1347 | 0.2948 | 0.5887 | 0.1399 | 0.2845 | 0.5349 | 0.1541 | 0.2760 |
| N240 | 0.3108 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3033 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3480 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Parameter | Dry Year | Normal Year | Wet Year | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield | PFPN | ANUE | Yield | PFPN | ANUE | Yield | PFPN | ANUE | |
| Information entropy value (Ej) | 0.8945 | 0.8214 | 0.8803 | 0.8932 | 0.8310 | 0.8846 | 0.8868 | 0.8448 | 0.8662 |
| Information utility value (Dj) | 0.1055 | 0.1786 | 0.1197 | 0.1068 | 0.1690 | 0.1154 | 0.1132 | 0.1552 | 0.1338 |
| Weight coefficient (Wj, %) | 0.2614 | 0.4423 | 0.2963 | 0.2730 | 0.4321 | 0.2949 | 0.2815 | 0.3859 | 0.3326 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Ling, Y.; Yin, M.; Ma, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qi, G.; et al. Using APSIM Model to Optimize Nitrogen Application for Alfalfa Yield Under Different Precipitation Regimes. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161789
Wang Y, Li H, Jiang Y, Duan Y, Ling Y, Yin M, Ma Y, Kang Y, Wang Y, Qi G, et al. Using APSIM Model to Optimize Nitrogen Application for Alfalfa Yield Under Different Precipitation Regimes. Agriculture. 2025; 15(16):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161789
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanbiao, Haiyan Li, Yuanbo Jiang, Yaya Duan, Yi Ling, Minhua Yin, Yanlin Ma, Yanxia Kang, Yayu Wang, Guangping Qi, and et al. 2025. "Using APSIM Model to Optimize Nitrogen Application for Alfalfa Yield Under Different Precipitation Regimes" Agriculture 15, no. 16: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161789
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, H., Jiang, Y., Duan, Y., Ling, Y., Yin, M., Ma, Y., Kang, Y., Wang, Y., Qi, G., Shen, G., Li, B., Chen, J., & Lv, H. (2025). Using APSIM Model to Optimize Nitrogen Application for Alfalfa Yield Under Different Precipitation Regimes. Agriculture, 15(16), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161789






