Ecological Responses of Mercury to Selenium in Farmland: Insights from Metal Transport in Crops, Soil Properties, Enzyme Activities, and Microbiome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.4.1. Plant Elemental Analysis
2.4.2. Analysis of Soil Properties
2.5. Microbial Community Structure and Diversity Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
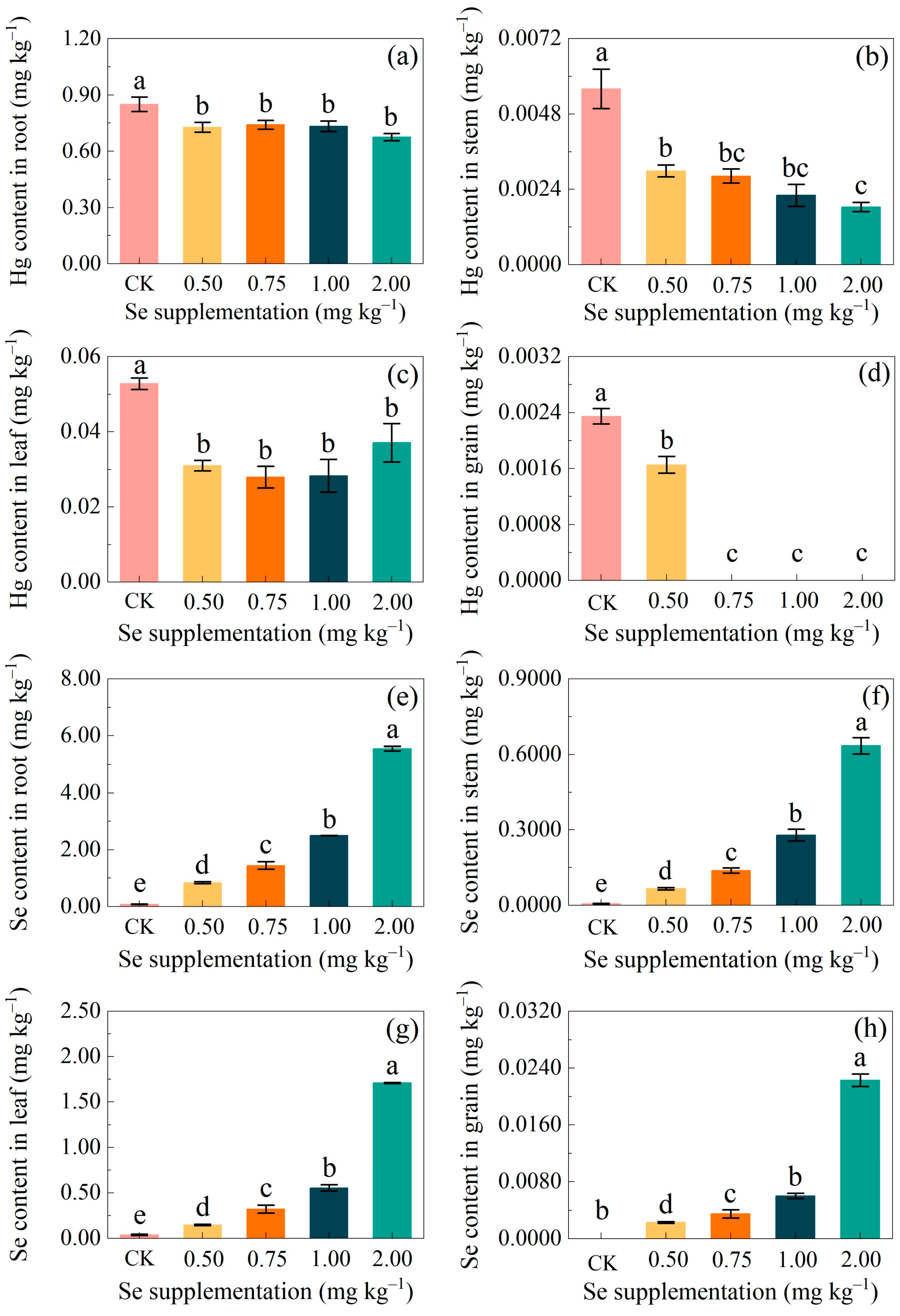
3.1. The Effectiveness of Exogenous Se on the Uptake of Hg and Se in Maize
3.1.1. Changes in the Hg Concentration in Maize
3.1.2. Changes in the Se Concentration in Maize
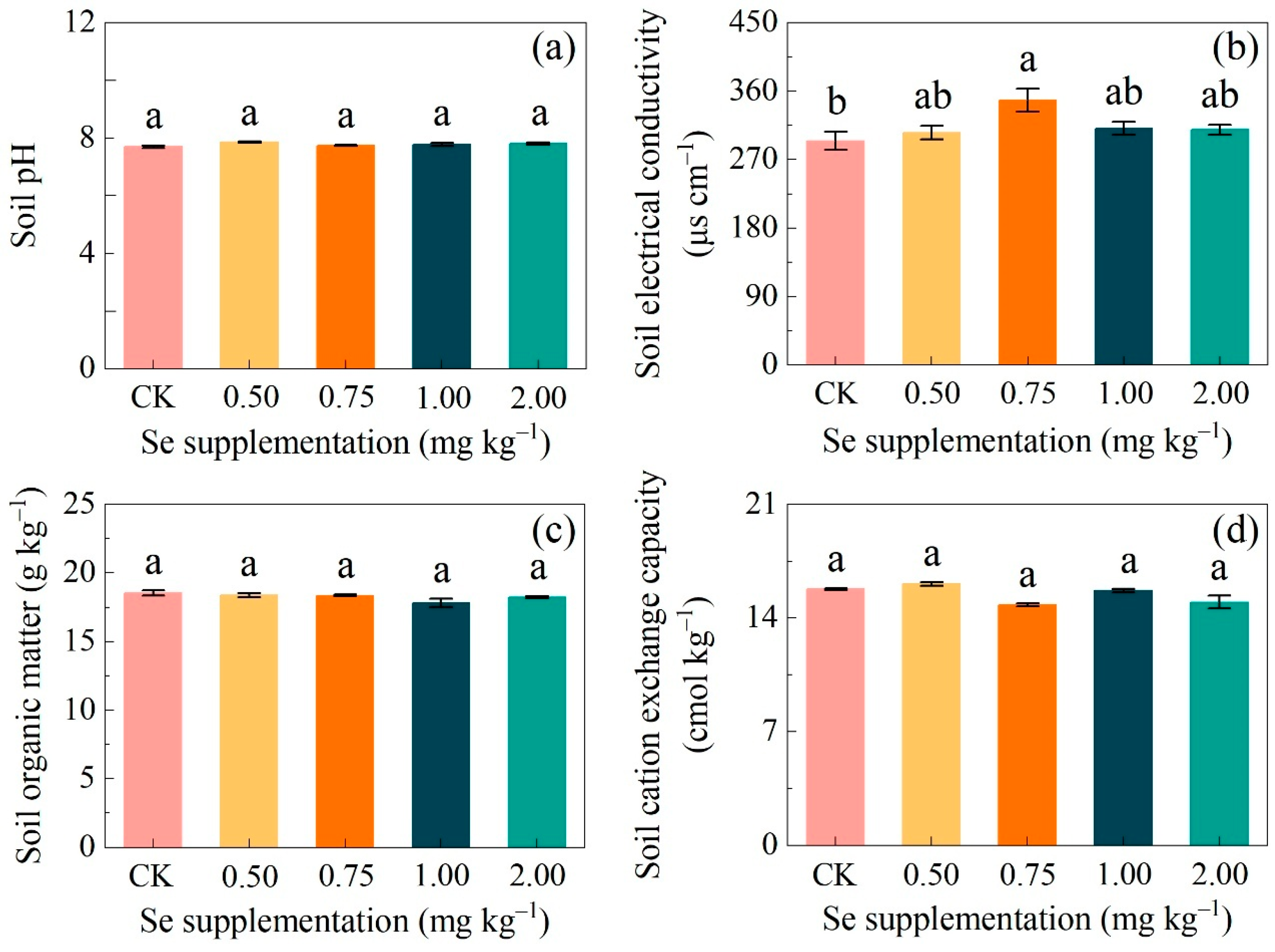
3.2. The Effectiveness of Exogenous Se on the Soil Properties
3.2.1. Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Soil
3.2.2. Changes in the Activities of Soil Enzymes
3.3. The Effectiveness of Exogenous Se on the Diversity and Community of Soil Microorganisms
3.3.1. Sequencing Statistics
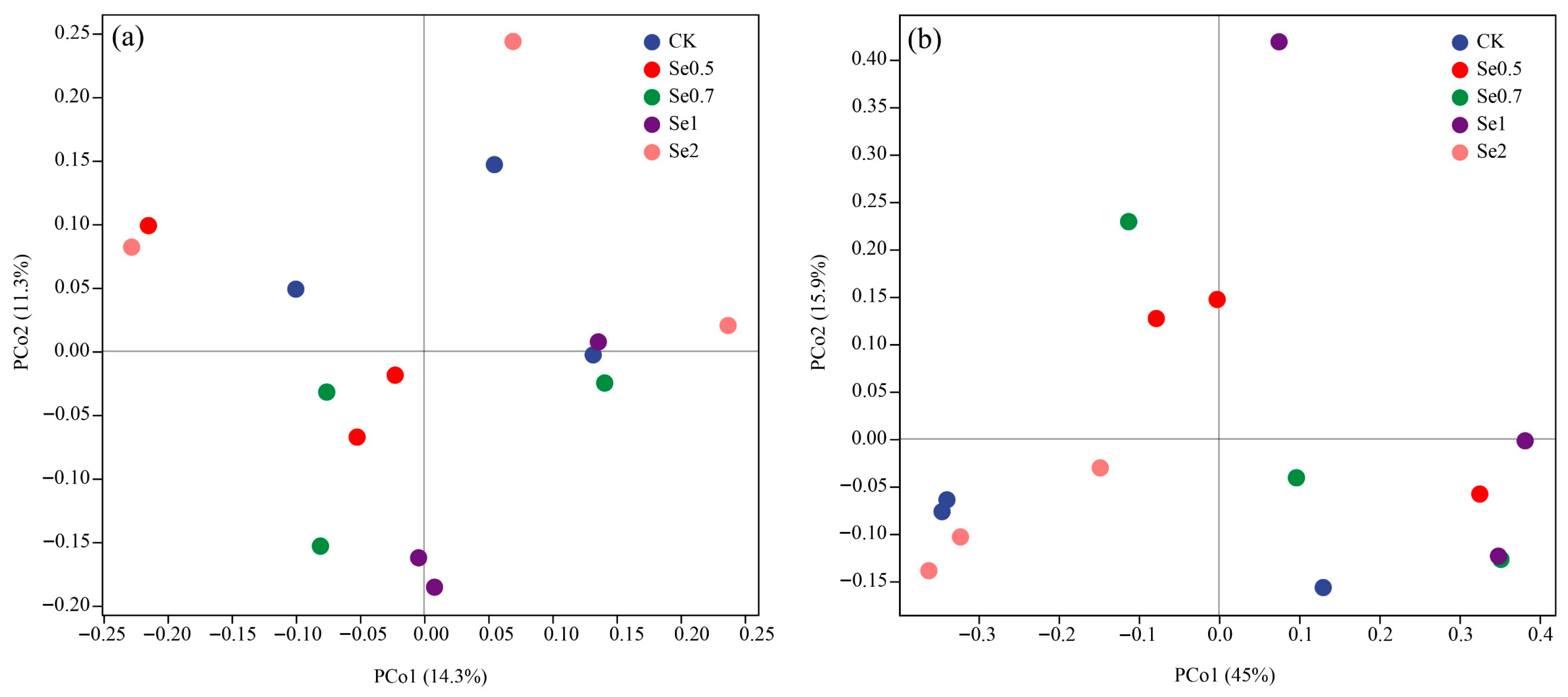
3.3.2. Changes in the Microbial Diversity
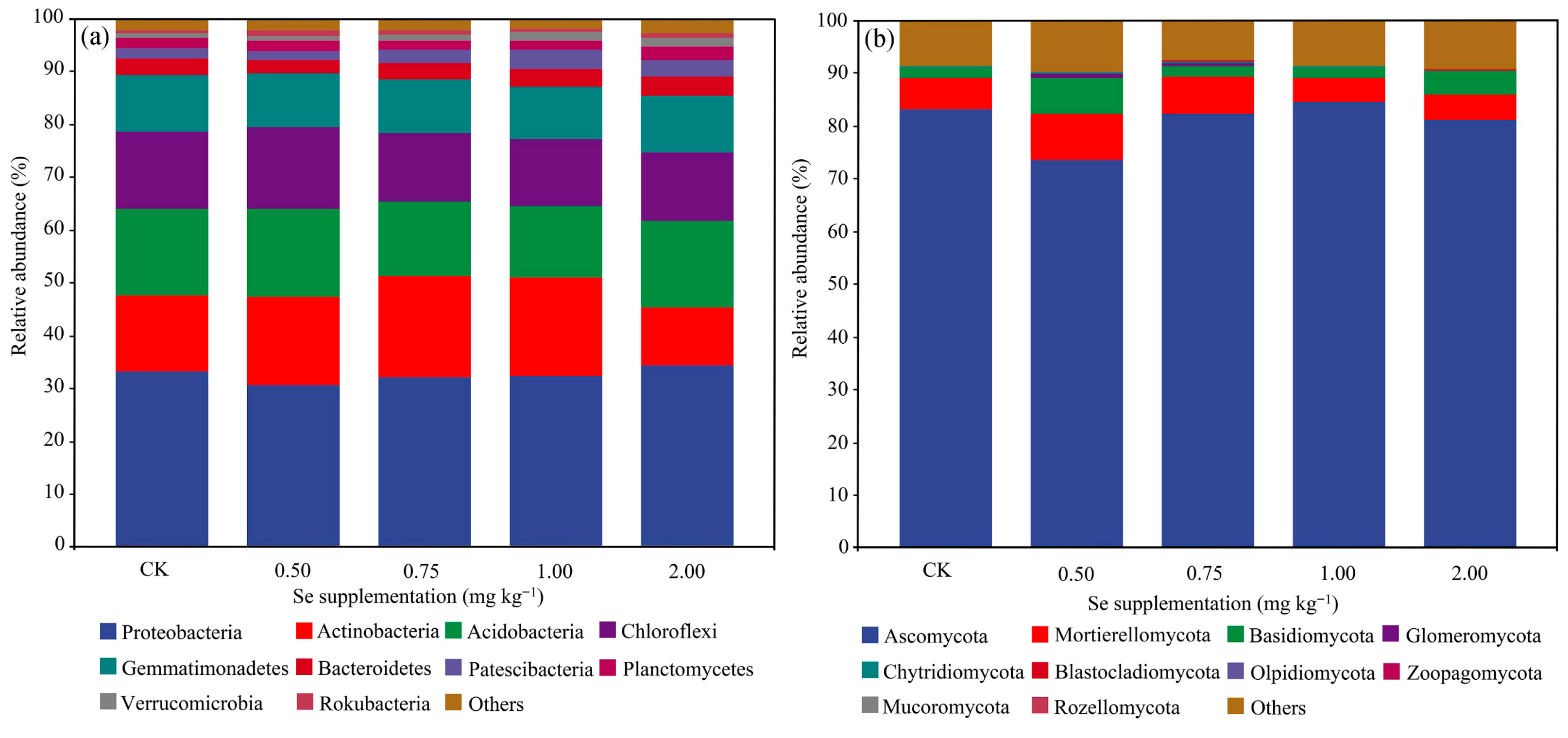
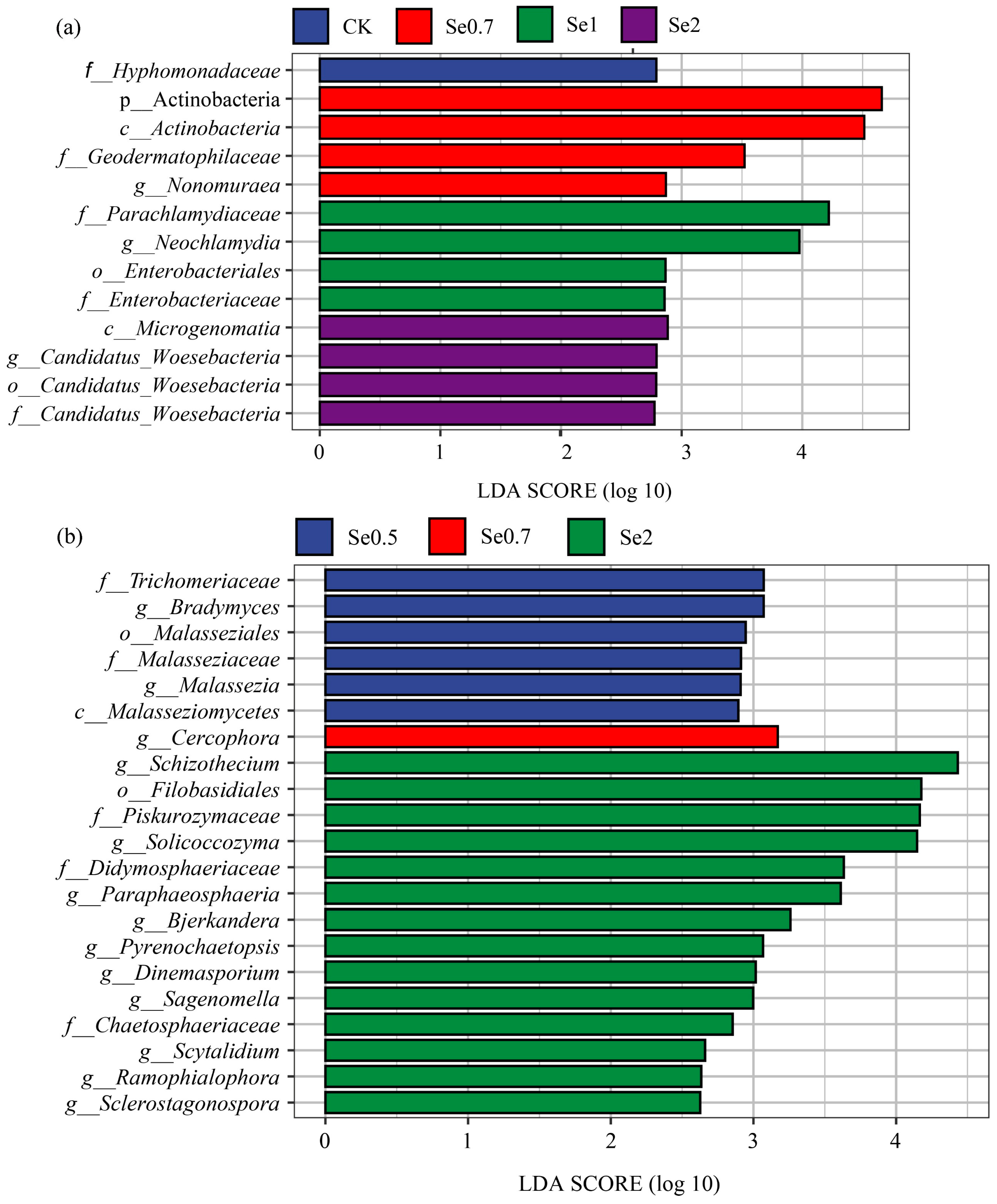
3.3.3. Changes in the Microbial Community
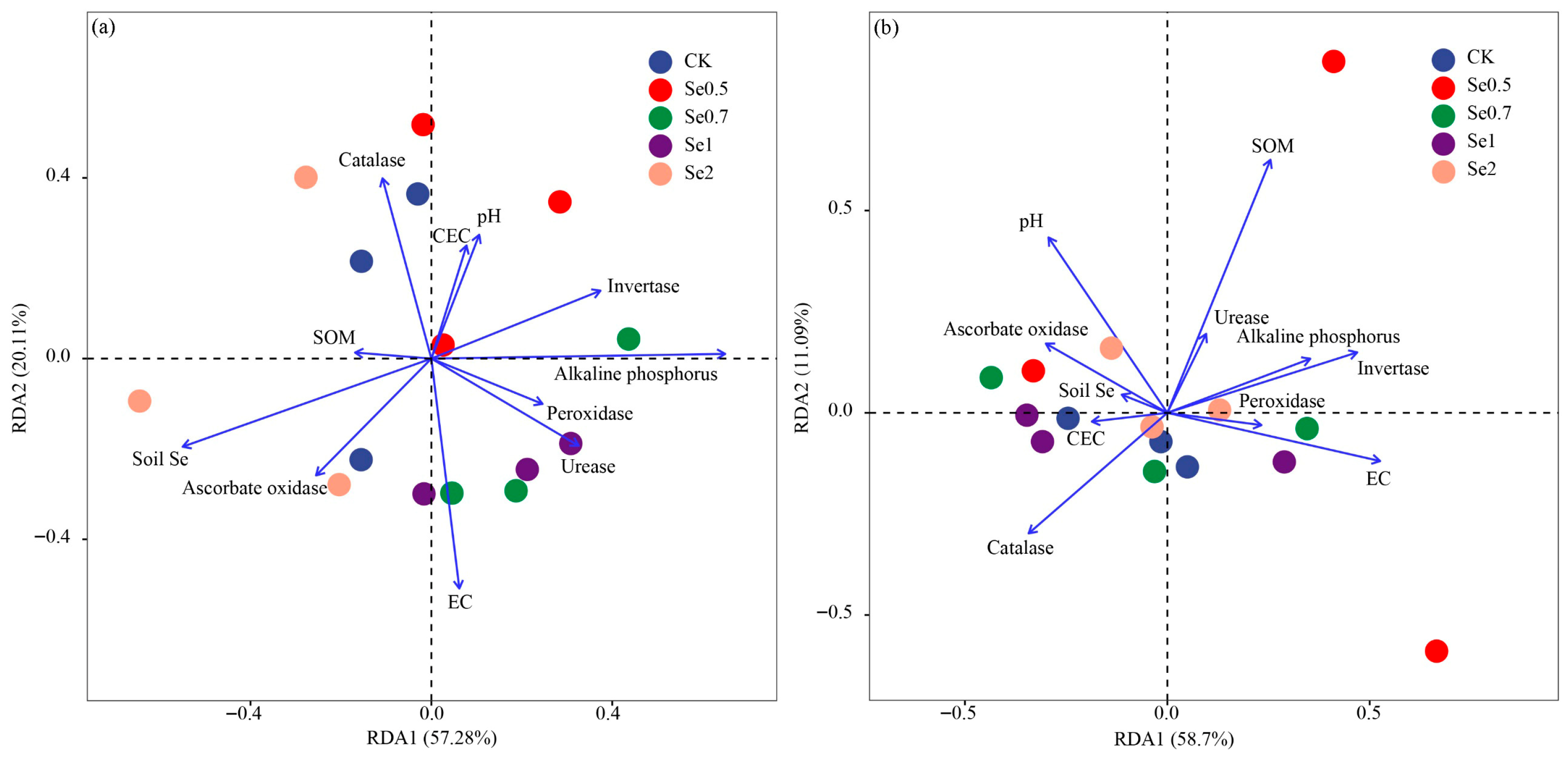
3.4. Relative Influences of Soil Properties on the Microbial Community
3.5. The Effectiveness of Exogenous Se on the Predicted Functions of the Microbial Community
4. Discussion
4.1. Selenium Applications Reduce the Uptake of Hg and Increase the Uptake of Se by Maize
4.2. The Impact of Se on Soil Enzyme Activities
4.3. The Regulatory Effect of Se on Soil Microorganisms
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lang, T.; Hussain, M.; Ishfaq, M.; Shakoor, N.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Pan, M.; Zhu, Z.J.; Xin, S.; Zhou, H.C. Mercury-induced alterations in soil microbiome: A potential for microbiome stewardship to remediate contaminated soils. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 512, 145717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, Z.D.; Luo, K.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X.H.; Xu, C.X.; Qiu, G.L. Biomagnification and trophic transfer of total mercury and methylmercury in a sub-tropical montane forest food web, southwest China. Chemosphere 2021, 277, 130371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Obrist, D.; Dastoor, A.; Jiskra, M.; Ryjkov, A. Vegetation uptake of mercury and impacts on global cycling. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.C.; Xia, T.X.; Zhang, L.N.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.A.; Jia, X.Y.; Jia, L.; Zhu, X.Y.; Li, G.B. Mercury pollution risks of agricultural soils and crops in mercury mining areas in Guizhou province, China: Effects of large mercury slag piles. Environ. Geochem. Hlth. 2024, 46, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natasha; Shahid, M.; Khalid, S.; Bibi, I.; Bundschuh, J.; Niazi, N.K.; Dumat, C. A critical review of mercury speciation, bioavailability, toxicity and detoxification in soil–plant environment: Ecotoxicology and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A.T.; Dinh, Q.T.; Zhou, F.; Zhai, H.; Xue, M.Y.; Du, Z.K.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Liang, D.L. Mechanisms underlying mercury detoxification in soil–plant systems after selenium application: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46852–46876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Luo, Z.D.; Guo, S.J.; Strähle, U. Toxicity of mercury: Molecular evidence. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, D.; Hou, D.Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Mulder, J.; Duan, L.; Wu, Q.R.; Wang, S.X.; Tack, F.M.G.; Rinklebe, J. Mercury speciation, transformation, and transportation in soils, atmospheric flux, and implications for risk management: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2019, 126, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Yen, J.H. On-site mercury-contaminated soils remediation by using thermal desorption technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, D.Y.; Mao, K.; Ali, W.; Xu, G.M.; Huang, G.P.; Niazi, N.K.; Feng, X.B.; Zhang, H. Describing the toxicity and sources and the remediation technologies for mercury-contaminated soil. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23221–23232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, H.B.; Wang, H.J.; Li, Q.C.; Li, Y. Effect of soil washing on heavy metal removal and soil quality: A two-sided coin. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2020, 203, 110981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, J.C.; Banna, K.M.; Reed, M.N.; Pesek, E.F.; Cole, N.; Li, J.; Newland, M.C. Dietary selenium protects against selected signs of aging and methylmercury exposure. Neurotoxicology 2010, 31, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, X.F.; Ning, Z.P.; Kwon, S.Y.; Li, M.L.; Tack, F.M.G.; Kwon, E.E.; Rinklebe, J.; Yin, R.S. The beneficial and hazardous effects of selenium on the health of the soil–plant-human system: An overview. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 422, 126876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyer, R.A. Toxic and essential metal interactions. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1997, 17, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parízek, J.; Ostádalová, I. The protective effect of small amounts of selenite in sublimate intoxication. Experientia 1967, 23, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boszke, L.; Kowalski, A.; Astel, A.; Barański, A.; Gworek, B.; Siepak, J. Mercury mobility and bioavailability in soil from contaminated area. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syversen, T.; Kaur, P. The toxicology of mercury and its compounds. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2012, 26, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornberg, A.; Hakanson, L.; Lundbergh, K. A theory on the mechanisms regulating the bioavailability of mercury in natural waters. Environ. Pollut. 1988, 49, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, X.B.; Zhu, J.M.; Sapkota, A.; Meng, B.; Yao, H.; Qin, H.B.; Larssen, T. Selenium in soil inhibits mercury uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10040–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.A.; Ralston, N.V.C.; Peck, D.V.; Sickle, J.V.; Robertson, J.D.; Spate, V.L.; Morris, J.S. How might selenium moderate the toxic effects of mercury in stream fish of the western US? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørmo, E.G.; Ciesielski, T.M.; Øverjordet, I.B.; Lierhagen, S.; Eggen, G.S.; Berg, T.; Jenssen, B.M. Selenium moderates mercury toxicity in free-ranging freshwater fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6561–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a global pollutant: Sources, pathways, and effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ahsan, M.Z.; Luo, D.; Panhwar, F.H.; Li, L.; Su, Y.; Jia, X.M.; Ye, X.Y.; Chen, R.J.; Li, L.H.; et al. Dynamics of selenium-mercury interaction under mercury stress in high and low selenium rice genotypes. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 224, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.A.T.; Dinh, Q.T.; Cui, Z.W.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Wei, T.J.; Liang, D.L.; Sun, X.; Ning, P. Comparing the influence of selenite (Se4+) and selenate (Se6+) on the inhibition of the mercury (Hg) phytotoxicity to pak choi. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounicou, S.; Shah, M.; Meijia, J.; Caruso, J.A.; Vonderheide; Shann, J. Localization and speciation of selenium and mercury in Brassica juncea-implications for Se–Hg antagonism. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2006, 21, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNear, D.H.J.; Afton, S.E.; Caruso, J.A. Exploring the structural basis for selenium/mercury antagonism in Allium fistulosum. Metallomics 2012, 4, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Hu, W.J.; Zhao, J.T.; Chen, Q.M.; Wang, W.; Li, B.; Li, Y.F. Selenium decreases methylmercury and increases nutritional elements in rice growing in mercury-contaminated farmland. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 182, 109447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Dang, F.; Zhao, J.T.; Zhong, H. Selenium inhibits sulfate-mediated methylmercury production in rice paddy soil. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.H.; Yan, M.; Liang, L.C.; Lu, Q.H.; Han, J.L.; Liu, L.; Feng, X.B.; Guo, J.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Qiu, G.L. Impacts of selenium supplementation on soil mercury speciation, and inorganic mercury and methylmercury uptake in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Q.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ji, Y.Y.; Tian, L.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T. Natural organic matter facilitates formation and microbial methylation of mercury selenide nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.X.; He, L.N.; Tian, X.; Zhang, W.; Cui, L.W.; Shang, L.H.; Zhao, J.T.; Li, B.; Li, Y.F. Nano mercury selenide as a source of mercury for rice. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 318, 120918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Yin, R.S.; Shen, Y.; Mao, K.; Yang, Z.G.; Feng, X.B.; Zhang, H. Bioaccumulation of Hg in rice leaf facilitates selenium bioaccumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) leaf in the Wanshan mercury mine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3228–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, G.S.; Oliveira, J.R.; Curi, N.; Schulze, D.G.; Marques, J.J. Selenium and mercury in Brazilian Cerrado soils and their relationships with physical and chemical soil characteristics. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, G.G.; Wang, K.T.; Zhuang, H.M.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, W.; Lan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Fu, F.F.; Yang, G.D. Effect of selenium in soil on the toxicity and uptake of arsenic in rice plant. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.M.; Hu, C.X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Jia, W.; Sun, X.C.; Elyamine, A.M.; Zhao, X.H. Selenium induces changes of rhizosphere bacterial characteristics and enzyme activities affecting chromium/selenium uptake by pak choi (Brassica campestris L. ssp. Chinensis Makino) in chromium contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Liang, L.Y.; Gu, B.H. Mercury reduction and oxidation by reduced natural organic matter in anoxic environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Shao, S.W.; Ai, L.H.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, L. Influences of biochar with selenite on bacterial community in soil and Cd in peanut. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 255, 114742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhao, Z.W. Colonization characteristics and composition of dark septate endophytes (DSE) in a lead and zinc slag heap in Southwest China. Soil Sediment Contam. 2013, 22, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manici, L.M.; Caputo, F.; De Sabata, D.; Fornasier, F. The enzyme patterns of Ascomycota and Basidiomycota fungi reveal their different functions in soil. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.17-2014; Determination of Total Mercury and Organic Mercury in Food According to the National Food Safety Standard. China Standard Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Ding, Y.H.; Li, C.J.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Zou, Y.F.; Gao, X.D.; Cai, Y.H.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Wu, P.; Zhao, X.N. Greenhouse gas emission responses to different soil amendments on the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.93-2017; National Food Safety Standard Determination of Selenium in Food. China Standard Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Nie, L.L.; Zhou, B.Q.; Hong, B.; Wang, X.D.; Chang, T.; Guan, C.Y.; Guan, M. Application of selenium can alleviate the stress of cadmium on rapeseed at different growth stages in soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.S. Soil Agrochemical Analysis Method; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- HJ 802-2016; Soil Quality-Determination of Conductivity-Electrode Method. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- HJ 889-2017; Soil Quality-Determination of Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)-Hexamminecobalt Trichloride Solution-Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Guan, S.Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z. Soil Enzyme and Its Research Methods; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1986; pp. 274–297. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 1, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 3, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kõljalg, U.; Nilsson, R.H.; Abarenkov, K.; Tedersoo, L.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bahram, M.; Bates, S.T.; Burns, T.D.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Callaghan, T.M.; et al. Towards a unified paradigm for sequence-based identification of fungi. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5271–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.F.; Hao, S.Y.; Bañuelos, G.; Zhou, X.B. A quantitative review of the effects of Se application on the reduction of Hg concentration in plant: A meta-analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1199721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yathavakilla, S.K.V.; Caruso, J.A. A study of Se–Hg antagonism in Glycine max (soybean) roots by size exclusion and reversed phase HPLC-ICPMS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, M. Selenium in agriculture, food, and nutrition. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masscheleyn, P.H.; Delaune, R.D.; Patrick Jr, W.H. Arsenic and selenium chemistry as affected by sediment redox potential and pH. J. Environ. Qual. 1991, 20, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.X.; Chen, Q.W.; Jiang, L.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Rao, S.; Zhang, W.W.; Xu, F. Physiological mechanism of exogenous selenium in alleviating mercury stress on pakchoi (Brassica campestris L.). Phyton-int. J. Exp. Bot 2024, 9, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.P.; Li, Y.X.; Li, H. Impacts of selenium supplementation on soil mercury speciation, soil properties and mercury-resistant microorganisms and resistant genes. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Hussain, S.; Noor, Y.; Khanam, T.; Xia, X.; Darma, A.I.; Feng, Y.; Yang, J.J. Influencing factors and prediction models of mercury phytoavailability and transference in a soil-lettuce system under chinese agricultural soils. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Wuriyanghan, H.; Lei, Z.; Tang, Y.N.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.H. Exogenous selenium endows salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive soybeans with salt tolerance through plant-microbial coactions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.N.; Wang, M.; Zhou, F.; Zhai, H.; Qi, M.X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.N.; Zhang, N.C.; Ma, Y.Z.; Huang, J.; et al. Selenium bioavailability in soil-wheat system and its dominant influential factors: A field study in Shaanxi province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 144664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feudis, M.D.; D’Amato, R.; Businelli, D.; Guiducci, M. Fate of selenium in soil: A case study in a maize (Zea mays L.) field under two irrigation regimes and fertilized with sodium selenite. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 659, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroczek-Zdyrska, M.; Wójcik, M. The influence of selenium on root growth and oxidative stress induced by lead in Vicia faba L. minor plants. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 147, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Hu, C.X.; Wu, Z.C.; Liu, X.W.; Cai, M.M.; Jia, W.; Zhao, X.H. Selenium reduces cadmium accumulation in seed by increasing cadmium retention in root of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 158, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GH/T 1135-2024; Selenium-Enriched Agricultural Products. All China Federation of Supply and Marketing Cooperatives: Beijing, China, 2024.
- Li, J.W.; Wu, J.Z.; Yu, J.Y.; Wang, K.B.; Li, J.P.; Cui, Y.X.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Deng, L. Soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry in response to precipitation changes in terrestrial ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vithanage, M.; Bandara, T.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Abduljabbar, A.; Usman, A.R.A.; Ahmad, M.; Ok, Y.S. Soil enzyme activities in waste biochar amended multi-metal contaminated soil; effect of different pyrolysis temperatures and application rates. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 4, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.F.; Ji, Q.; Rizwan, M.; Li, H.S.; Li, D.Q.; Chen, G.K. Effects of biochar and foliar application of selenium on the uptake and subcellular distribution of chromium in Ipomoea aquatica in chromium-polluted soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, B.J.; Wu, D.S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, G.Q.; Wang, X.L.; Hu, S.M.; Fan, H.B.; Fang, H.Y. Effects of different exogenous selenium on enzyme activities and microorganisms in arsenic contaminated soil. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 4237–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.X.; Zheng, W.Z.; Lin, J.Y.; Shi, Y.; Xie, W.Z.; Zhou, H.M. Effect of metal ions on the activity of green crab (Scylla serrata) alkaline phosphatase. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2000, 32, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, W.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Kuang, Z.Y.; Yuan, J. Application of selenocysteine increased soil nitrogen content, enzyme activity, and microbial quantity in Camellia oleifera Abel. Forests. Forests 2023, 1, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.X.; Zhu, M.E.; Zhang, Y.P. Recent advance in relationship between soil enzymes and heavy metals. Soil Environ. Sci. 2000, 9, 139–142. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Hu, H.Q.; Ye, X.J.; Xia, P.L.; Deng, J.Q. Effects of exogenous selenium with different valences on Se forms, enzyme activities, and microbial quantity of soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 29, 137–171. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fierer, N. Embracing the unknown: Disentangling the complexities of the soil microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Geng, Q.; Xu, L.F.; Li, X.; Pan, X.M.; Zheng, J.J.; He, R.Q.; He, M.D.; Xu, X.X.; Zhang, S.R. Rice husk biochar resuscitates the microecological functions of heavy-metal contaminated soil after washing by enriching functional bacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Cho, K.S. Enhancement of the phytoremediation performance in heavy metal-contaminated soil using a multifunctional EPS-producing bacterium Kosakonia sp. W18. Environ. Res. 2025, 274, 121355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qi, W.Y.; Chen, H.; Song, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.G. Selenium nanoparticles as an innovative selenium fertilizer exert less disturbance to soil microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 746046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Ming, J.J.; Fu, W.; Long, L.; Wen, X.L.; Zhang, Q.H.; Xiang, J.Q.; Zhu, Y.F.; Yin, H.Q. Selenium fertilizer improves microbial community structure and diversity of rhizospheric soil and selenium accumulation in tomato plants. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2024, 55, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Yang, J.J.; Finn, D.R.; Brunotte, J.; Tebbe, C.C. Distinct seasonal and annual variability of prokaryotes, fungi and protists in cropland soil under different tillage systems and soil texture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 203, 109732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.P.; Bi, Y.L.; Tian, L.X.; Li, M.C.; Yin, K.J. Enhancing infiltration characteristics of compact soil in open-pit dumps through arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation in Amorpha fruticosa: Mechanisms and effects. Catena 2024, 247, 108515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Cai, M.M.; Hu, C.X.; Sun, X.C.; Cheng, Q.; Jia, W.; Yang, T.; Nie, M.; Zhao, X.H. Selenium (Se) reduces Sclerotinia stem rot disease incidence of oilseed rape by increasing plant Se concentration and shifting soil microbial community and functional profiles. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Q.; Kuzyakov, Y. Mechanisms and implications of bacterial-fungal competition for soil resources. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Wang, H.Q.; Nie, Z.J.; Tao, Z.K.; Peng, H.Y.; Shi, H.Z.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.E. Combined application of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and selenium fertilizer increased wheat biomass under cadmium stress and shapes rhizosphere soil microbial communities. Bmc Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Adebayo, A.; Jia, J.L.; Xing, Y.; Deng, S.Q.; Guo, L.M.; Liang, Y.T.; Zhang, D.Y. Impacts of heavy metals and soil properties at a Nigerian e-waste site on soil microbial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.K.; Wang, C.; Xie, Y.L.; Luo, Y.; Sheng, M.P.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Ecological responses of soil microbial abundance and diversity to cadmium and soil properties in farmland around an enterprise-intensive region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feris, K.; Ramsey, P.; Frazar, C.; Moore, J.N.; Gannon, J.E.; Holben, W.E. Differences in hyporheic-zone microbial community structure along a heavy-metal contamination gradient. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5563–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Q.; Meng, D.L.; Li, J.; Yin, H.Q.; Liu, H.W.; Liu, X.D.; Cheng, C.; Xiao, Y.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Yan, M.L. Response of soil microbial communities and microbial interactions to long-term heavy metal contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 908–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrålstad, T.; Myhre, E.; Schumacher, T. Molecular diversity and phylogenetic affinities of symbiotic root-associated ascomycetes of the Helotiales in burnt and metal polluted habitats. New Phytol. 2002, 155, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Microorganism | Se Supplementation (mg kg−1) | Alpha Diversity Indices | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chao1 | Shannon | Pielou’s Evenness | Good’s Coverage | ||
| Bacterial | Control | 292 ± 14 a | 5.33 ± 0.44 a | 0.6516 ± 0.0490 a | 0.9994 ± 0.0001 b |
| 0.50 | 319 ± 71 a | 5.05 ± 0.76 a | 0.6100 ± 0.0775 a | 0.9995 ± 0.0002 ab | |
| 0.75 | 263 ± 37 a | 4.73 ± 0.94 a | 0.5856 ± 0.1022 a | 0.9998 ± 0.0000 a | |
| 1.00 | 250 ± 38 a | 4.09 ± 0.78 a | 0.5117 ± 0.0828 a | 0.9998 ± 0.0001 ab | |
| 2.00 | 375 ± 18 a | 5.99 ± 0.23 a | 0.7032 ± 0.0040 a | 0.9990 ± 0.0002 c | |
| Fungi | Control | 1584 ± 33 a | 9.72 ± 0.03 a | 0.9248 ± 0.0032 a | 0.9869 ± 0.0008 a |
| 0.50 | 1366 ± 43 b | 9.50 ± 0.03 b | 0.9223 ± 0.0003 a | 0.9893 ± 0.0007 a | |
| 0.75 | 1420 ± 59 ab | 9.60 ± 0.05 ab | 0.9253 ± 0.0016 a | 0.9890 ± 0.0008 a | |
| 1.00 | 1591 ± 25 a | 9.68 ± 0.04 ab | 0.9195 ± 0.0020 a | 0.9865 ± 0.0004 a | |
| 2.00 | 1563 ± 112 a | 9.71 ± 0.10 a | 0.9249 ± 0.0009 a | 0.9873 ± 0.0015 a | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Guan, S.; Pei, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Lv, Y.; Li, H. Ecological Responses of Mercury to Selenium in Farmland: Insights from Metal Transport in Crops, Soil Properties, Enzyme Activities, and Microbiome. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161753
Li Y, Guan S, Pei G, Zhang X, Zhang Y, Huang J, Lv Y, Li H. Ecological Responses of Mercury to Selenium in Farmland: Insights from Metal Transport in Crops, Soil Properties, Enzyme Activities, and Microbiome. Agriculture. 2025; 15(16):1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161753
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuxin, Shuyun Guan, Guangpeng Pei, Xiaorong Zhang, Yongbing Zhang, Junbao Huang, Yingzhong Lv, and Hua Li. 2025. "Ecological Responses of Mercury to Selenium in Farmland: Insights from Metal Transport in Crops, Soil Properties, Enzyme Activities, and Microbiome" Agriculture 15, no. 16: 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161753
APA StyleLi, Y., Guan, S., Pei, G., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Huang, J., Lv, Y., & Li, H. (2025). Ecological Responses of Mercury to Selenium in Farmland: Insights from Metal Transport in Crops, Soil Properties, Enzyme Activities, and Microbiome. Agriculture, 15(16), 1753. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15161753





