Improving Forage Quality from Permanent Grasslands to Enhance Ruminant Productivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Characteristics of Forage from Permanent Grasslands
4. Forage Quality Evaluation
4.1. Chemical Composition of Forage
4.2. Energy and Forage Value Calculations
4.3. Parameters for Silage Evaluation
4.4. Microbiological Assessment of Forages
4.5. Methods for Forage Evaluation
5. Factors Affecting Forage Quality from Grasslands
5.1. Environmental Factors
5.2. Soil Fertility and Nutrient Availability
5.3. Botanical Composition and Species Richness
5.4. Developmental Stage and Harvest Date
5.5. Conservation Method
5.5.1. Hay Production
5.5.2. Silage Production
5.6. Negative Compounds
5.7. Fungal Contaminants in Forage
5.8. Interactions Between Factors
6. Methods for Improving Forage Quality
6.1. Breeding Methods for Grasses and Legumes
6.2. Renovation Methods
6.2.1. Overseeding
6.2.2. Reseeding
6.2.3. Simplified Tillage Methods
6.2.4. Species for Grassland Renovation
6.2.5. Weed Control
6.3. Fertilisation Strategies
6.3.1. Soil pH Optimisation
6.3.2. Macronutrients
6.3.3. Micronutrients
6.3.4. Beneficial Elements
6.3.5. Organic Fertilisers
6.3.6. Plant-Growth-Promoting Bacteria
6.4. Mowing Intensity
6.5. Grazing Management Strategies
6.6. Forage Preservations
6.7. Enhancing Forage Quality Through Smart Agriculture and Intelligent Grazing
7. Effects of Forage Quality Improvement
7.1. Improvement of Animal Performance and Welfare
7.2. Environment Protection
7.3. Reduction of Production Costs
8. Directions of Future Study
9. Conclusions
- -
- Breeding and selection of grass and legume cultivars with enhanced digestibility, reduced fibre fractions, and greater tolerance to environmental stress.
- -
- Optimization of mowing and grazing regimes to balance yield, forage quality, and long-term sward persistence.
- -
- Diversification of sward composition, including legumes and functional forbs, to boost protein content, palatability, and mineral availability.
- -
- Targeted fertilization and soil management that maintain nutrient supply while preserving forage quality.
- -
- Effective weed control and sward renovation to ensure dominance of productive and palatable species.
- -
- Use of precision technologies for real-time monitoring, assessment, and management of forage systems.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huyghe, C.; De Vliegher, A.; Golinski, P. European grasslands overview: Temperate region. Grassl. Sci. Eur. 2014, 19, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Regulation (EU) No 1307/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 December 2013 Establishing Rules for Direct Payments to Farmers Under Support Schemes Within the Framework of the Common Agricultural Policy and Repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 637/2008 and Council Regulation (EC) No 73/2009. Off. J. Eur. Union 2013, 347, 608. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2013:347:0608:0670:EN:PDF (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- FAOSTAT. Agri-Environmental Indicators, Land Use; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2019; ISBN 978-3-9525031-4-0. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/EL (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Statistics Poland. Statistical Yearbook of Agriculture 2024. Available online: https://stat.gov.pl/en/topics/statistical-yearbooks/statistical-yearbooks/statistical-yearbook-of-agriculture-2024,6,19.html (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Hejcman, M.; Hejcmanova, P.; Pavlů, V.; Beneš, J. Origin and history of grasslands in Central Europe–A review. Grass Forage Sci. 2013, 68, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milazzo, F.; Fernández, P.; Peña, A.; Vanwalleghem, T. The Resilience of Soil Erosion Rates under Historical Land Use Change in Agroecosystems of Southern Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schils, R.L.M.; Bufe, C.; Rhymer, C.M.; Francksen, R.M.; Klaus, V.H.; Abdalla, M.; Milazzo, F.; Lellei-Kovács, E.; ten Berge, H.; Bertora, C.; et al. Permanent Grasslands in Europe: Land Use Change and Intensification Decrease Their Multifunctionality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 330, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, F.; Gierus, M.; Hermann, A.; Loges, R.; Schönbach, P. Grasslands and globalization—Challenges for the north-west European grass and forage research. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 69, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, L.; Rotar, I.; Vlahova, M.; Vidican, R. Importance and Functions of Grasslands. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. 2009, 37, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Pol-Van Dasselaar, A.; Bastiaansen-Aantjes, L.; Bogue, F.; O’Donovan, M.; Huyghe, C. Grassland Use in Europe: A Syllabus for Young Farmers; Inno4Grass: Versailles, France, 2019; p. 264. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, P.C.F.; Bremm, C.; Mezzalira, J.C.; Da Trindade, J.K.; Nascimento, D., Jr. How can grazing behavior research at the bite to patch scales contribute to enhance sustainability of rangeland livestock production systems? In Proceedings of the IX International Rangeland Congress—Diverse Rangelands for a Sustainable Society, Rosario, Argentina, 2–8 April 2011; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, P.; Herrero, M. Potential for reduced methane and carbon dioxide emissions from livestock and pasture management in the tropics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19667–19672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billen, G.; Le Noë, J.; Garnier, J. Two contrasted future scenarios for the French agro-food system. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mara, F.P. The role of grasslands in food security and climate change. Review: Part of a highlight on breeding strategies for forage and grass improvement. Ann. Bot. 2012, 110, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinenberg, M.H.; Valk, H.; Korevaar, H.; Struik, P.C. Factors affecting digestibility of temperate forages from seminatural grasslands: A review. Grass Forage Sci. 2002, 57, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejcman, M.; Szaková, J.; Schellberg, J.; Tlustoš, P. The Rengen Grassland Experiment: Relationship between soil and biomass chemical properties, amount of elements applied, and their uptake. Plant Soil 2010, 333, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitra, A.; Deléglise, C.; Meisser, M.; Risch, A.C.; Signarbieux, C.; Lamacque, L.; Delzon, S.; Buttler, A.; Mariotte, P. Responses of plant leaf economic and hydraulic traits mediate the effects of early—And late season—Drought on grassland productivity. AoB Plants 2019, 11, plz023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dindová, A.; Hakl, J.; Hrevušová, Z.; Nerušil, P. Relationships between long-term fertilization management and forage nutritive value in grasslands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 279, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deléglise, C.; Meisser, M.; Mosimann, E.; Spiegelberger, T.; Signarbieux, C.; Jeangros, B.; Buttler, A. Drought-induced shifts in plants traits, yields and nutritive value under realistic grazing and mowing managements in a mountain grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 213, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, B.; Zielewicz, W.; Staniak, M. Challenges of Pasture Feeding Systems—Opportunities and Constraints. Agriculture 2023, 13, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradus, J.; Roldan, M.; Voisey, C.; Woodfield, D. White clover (Trifolium repens L.) benefits in grazed pastures and potential improvements. In Production and Utilization of Legumes: Progress and Prospects; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Navarrete, S.; Horne, D.J.; Donaghy, D.J.; Kemp, P.D. Incorporating Plantain with Perennial Ryegrass-White Clover in a Dairy Grazing System: Dry Matter Yield, Botanical Composition, and Nutritive Value Response to Sowing Rate, Plantain Content and Season. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Li, C.; Zeng, T.; Xin, Y.; Chen, C.; Javed, H.H.; Yang, W.; Yan, Y. Mixture Composition Influenced the Biomass Yield and Nutritional Quality of Legume–Grass Pastures. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fynn, R.W.; Kirkman, K.P.; Dames, R. Optimal grazing management strategies: Evaluating key concepts. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2017, 34, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittarello, M.; Probo, M.; Perotti, E.; Lonati, M.; Lombardi, G.; Ravetto Enri, S. Grazing Management Plans improve pasture selection by cattle and forage quality in sub-alpine and alpine grasslands. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 2126–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wims, C.M.; Deighton, M.H.; Lewis, E.; O’Loughlin, B.; Delaby, L.; Boland, T.M.; O’Donovan, M. Effect of pregrazing herbage mass on methane production, dry matter intake, and milk production of grazing dairy cows during the mid-season period. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 4976–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.; Nelson, C.J.; Moore, K.J.; Barnes, R.F. Forages. An Introduction to Grassland Agriculture, 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 1, 432p. [Google Scholar]
- Scarbrough, D.A.; Coblentz, W.K.; Humphry, J.B.; Coffey, K.P.; Daniel, T.C.; Sauer, T.J.; Jennings, J.A.; Turner, J.E.; Kellogg, D.W. Evaluation of dry matter loss, nutritive value, and in situ dry matter disappearance for wilting orchardgrass and bermudagrass forages damaged by simulated rainfall. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, L.; Du, S.; Si, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, K.; Jia, Y. Effects of storage time on nutritive qualities, volatile components, and microbial community of native grass hay. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 109, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, W.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y.; Du, S. Insights into the microbiome and metabolome assembly during short-term storage of native grass hay. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 106, 102283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, B.; Nowak, J.; Fabiszewska, A.; Paszkiewicz-Jasińska, A.; Przystupa, W. Dry Matter Losses in Silages Resulting From Epiphytic Microbiota Activity—A Comprehensive Study. Agronomy 2023, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radkowski, A.; Radkowska, I.; Bocianowski, J. Quality of silages made from meadow sward from south–eastern Poland. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2020, 27, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumont, R.; Sauvant, D.; Maxin, G.; Chapoutot, P.; Tran, G.; Boudon, A.; Lemosquet, S.; Nozière, P. Calculations of feed values in INRA system: Feed tables and prediction equations. In INRA Feeding System for Ruminants; Nozière, P., Sauvant, D., Delaby, L., Eds.; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 411–440. [Google Scholar]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Nutrient Requirements of Dairy Cattle: Eighth Revised Edition; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volden, H. (Ed.) NorFor—The Nordic Feed Evaluation System; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2011; p. 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzas, C.; Broderick, G.A.; Fox, D.G. Improved feed protein fractionation schemes for formulating rations with the cornell net carbohydrate and protein system. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4881–4891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmunds, B.; Südekum, K.-H.; Bennett, R.; Schröder, A.; Spiekers, H.; Schwarz, F.J. The Amino Acid Composition of Rumen-Undegradable Protein: A Comparison between Forages. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 4568–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Cai, C.; Lei, X.; Yao, J. Physically Effective Neutral Detergent Fiber Improves Chewing Activity, Rumen Fermentation, Plasma Metabolites, and Milk Production in Lactating Dairy Cows Fed a High-Concentrate Diet. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 5631–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, M.V.G.; Ítavo, L.C.V.; Ítavo, C.C.B.F.; Dias, A.M.; dos Santos Difante, G.; Longhini, V.Z.; da Costa Gomes, R.; Vedovatto, M.; Gurgel, A.L.C.; de Moraes, G.J.O.; et al. Effect of physically effective neutral detergent fiber on nutrient intake and digestibility, ruminal and blood parameters, and ingestive behavior of confined beef cattle. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, M.; Allen, M.S. Evaluation of the Importance of the Digestibility of Neutral Detergent Fiber from Forage: Effects on Dry Matter Intake and Milk Yield of Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getachew, G.; DePeters, E.J.; Robinson, P.H.; Fadel, J.G. Use of an in vitro rumen gas production technique to evaluate microbial fermentation of ruminant feeds and its impact on fermentation products. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2005, 123, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, S.R.; Prostko, E.P. Understanding Forage Quality Analysis, Produced by AgriLife Communications & Marketing. The Texas A&M System, 1998. Available online: https://lubbock.tamu.edu/files/2011/10/forageanalysis_6.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Rayburn, E. Use Forage Test to Diagnose Management Problems. 2002. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/239552821 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Schroeder, J.W. Forage Nutrition for Ruminants AS-1250. 2004. Available online: https://library.ndsu.edu/ir/items/49fb44cb-1457-403a-89c3-d91f359ecdc7 (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Linn, J.G.; Martin, N.P. Forage Quality Tests and Interpretations; University of Minnesota, Agricultural Extension Service: Retrieved from the University of Minnesota Digital Conservancy, 1989. Available online: https://conservancy.umn.edu/handle/11299/207442 (accessed on 2 December 2024).
- Undersander, D.; Moore, J.E.; Schneider, N. Relative Forage Quality. Forage Focus 2010, 12, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, Y.C.; Lambert, B.; Muir, J.P. Defining Forage Quality. Subtitle: Nutritive Value of Southern Forages. 2024. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/636718643.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Driehius, F.; Elferink, S.J.W.H.O. The Impact of The Quality of Silage On Animal Health and Food Safety: A Review. Vet. Quart. 2000, 22, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driehuis, F.; van Wikselaar, P.G. Effects of formic, acetic or propionic acid to maize silage and low dry matter grass silage on the microbial flora and aerobic stability. In Proceedings of the 11th International Silage Conference, Aberystwyth, UK, 8–11 September 1996; pp. 256–257. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Solano, B.; Lizarraga Pérez, E.; González-Peñas, E. Monitoring mycotoxin exposure in food-producing animals (cattle, pig, poultry, and sheep). Toxins 2024, 16, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudamore, K.A.; Livese, C.T. Occurrence and Significance of Mycotoxins in Forage Crops and Silage: A Review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1998, 77, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlow, L.W. Molds and Mycotoxins in Feedstuffs—Prevention and Treatment. In Proceedings of the Florida Ruminant Nutrition Symposium, Gainesville, FL, USA, 1–2 February 2005; pp. 123–142. Available online: https://animal.ifas.ufl.edu/apps/dairymedia/rns/2005/Whitlow.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2024).
- Fulgueira, C.L.; Amigot, S.L.; Gaggiotti, M.; Romero, L.A.; Basílico, J.C. Forage Quality: Techniques for Testing. Fresh Prod. Glob. Sci. Books 2007, 1, 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, W.P.; Hall, M.B. Laboratory Methods for Evaluating Forage Quality. In Forages; Moore, K.J., Collins, M., Nelson, C.J., Redfearn, D.D., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 36, pp. 659–672. [Google Scholar]
- Cozzolino, D.; Fassio, A.; Fernández, E. Use of near Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy to Analyze Corn Silage Quality. Agric. Técnica 2003, 63, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Deaville, E.R.; Flinn, P.C. Near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy: An alternative approach for the estimation of forage quality and voluntary intake. In Forage Evaluation in Ruminant Nutrition; Givens, D.I., Owen, E., Axford, R.F.E., Omedi, H.M., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2000; pp. 301–320. [Google Scholar]
- Reeves, J.B., III; van Kessel, J.S. Near-infrared spectroscopic determination of carbon, total nitrogen, and ammonium-N in dairy manures. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 1829–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Kaul, H.-P. Monitoring Yield and Quality of Forages and Grassland in the View of Precision Agriculture Applications—A Review. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrini, S.; Acciaioli, A.; Crovetti, A.; Bozzi, R. Use of FT-NIRS for determination of chemical components and nutritional value of natural pasture. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 17, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, J.C.J.; Lantinga, E.A.; Neuteboom, J.H.; Deinum, B. Analysis of the temperature effect on the components of plant digestibility in two populations of perennial ryegrass. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.; Andueza, D.; Picard, F.; Plantureux, S.; Baumont, R. Seasonal dynamics of biomass production and herbage quality of three grasslands with contrasting functional compositions: Production and quality of permanent grasslands. Grass Forage Sci. 2012, 67, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, A.; Plantureux, S.; Pottier, E.; Baumont, R. Links between functional composition, biomass production and forage quality in permanent grasslands over a broad gradient of conditions. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 153, 891–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedbała, G.; Wróbel, B.; Piekutowska, M.; Zielewicz, W.; Paszkiewicz-Jasińska, A.; Wojciechowski, T.; Niazian, M. Application of Artificial Neural Networks Sensitivity Analysis for the Pre-Identification of Highly Significant Factors Influencing the Yield and Digestibility of Grassland Sward in the Climatic Conditions of Central Poland. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignol, N.; Andueza, D.; Carrère, P.; Cruz, P.; Duru, M.; Fiorelli, J.-L.; Michaud, A.; Plantureux, S.; Pottier, E.; Baumont, R. Assessing population maturity of three perennial grass species: Influence of phenology and tiller demography along latitudinal and altitudinal gradients. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 69, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanzant, E.S.; Cochran, R.C.; Coblentz, W.K. Animal Methods for Evaluating Forage Quality. Forages: Sci. Grassl. Agric. 2020, 2, 673–685. [Google Scholar]
- Buttler, A.; Mariotte, P.; Meisser, M.; Guillaume, T.; Signarbieux, C.; Vitra, A.; Preux, S.; Mercier, G.; Quezada, J.; Bragazza, L.; et al. Drought-induced decline of productivity in the dominant grassland species Lolium perenne L. depends on soil type and prevailing climatic conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 132, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotte, P.; Cresswell, T.; Johansen, M.; Harrison, J.; Keitel, C.; Dijkstra, F. Plant Uptake of Nitrogen and Phosphorus among Grassland Species Affected by Drought along a Soil Available Phosphorus Gradient. Plant Soil 2020, 448, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisser, M.; Vitra, A.; Deléglise, C.; Dubois, S.; Probo, M.; Mosimann, E.; Buttler, A.; Mariotte, P. Nutrient limitations induced by drought affect forage N and P differently in two permanent grasslands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 280, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadodin, I.; Corral, D.E.F.; Reinsch, T.; Kluß, C.; Taube, F. Climate change effects on temperate grassland and its implication for forage production: A case study from northern Germany. Agriculture 2021, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.A.; Davis, A.P.; Chagunda, M.G.; Manning, P. Forage quality declines with rising temperatures, with implications for livestock production and methane emissions. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordheim-Viken, H.; Volden, H.; Jørgensen, M. Effects of maturity stage, temperature and photoperiod on growth and nutritive value of timothy (Phleum pratense L.). Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 152, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, B.; Andueza, D.; Niderkorn, V.; Lüscher, A.; Porqueddu, C.; Picon-Cochard, C. A meta-analysis of climate change effects on forage quality in grasslands: Specificities of mountain and Mediterranean areas. Grass Forage Sci. 2015, 70, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisser, M.; Vitra, A.; Stévenin, L.; Mosimann, E.; Mariotte, P.; Buttler, A. Impact of drought on the functioning of grassland systems. Rech. Agron. Suisse 2018, 9, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, K.; Kreyling, J.; Dienstbach, L.F.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Jentsch, A. Water stress due to increased intra-annual precipitation variability reduced forage yield but raised forage quality of a temperate grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 186, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroche, B.; Pradel, P.; Baumont, R. Long-term evolution and prediction of feed value for permanent mountain grassland hay: Analysis of a 32-year data set in relation to climate change. Grass Forage Sci. 2020, 75, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, L.J.; Hughes, L.; Pitman, A.J. Why is the choice of future climate scenarios for species distribution modelling important? Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreyling, J.; Jentsch, A.; Beierkuhnlein, C. Stochastic trajectories of succession initiated by extreme climatic events. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, C.D.; Maduro Dias, C.S.A.M.; Wallon, S.; Borba, A.E.S.; Madruga, J.; Borges, P.A.V.; Ferreira, M.T.; Elias, R.B. Influence of Climate Variability and Soil Fertility on the Forage Quality and Productivity in Azorean Pastures. Agriculture 2022, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, P.A.; Prober, S.M.; Harpole, W.S.; Knops, J.M.H.; Bakker, J.D.; Borer, E.T.; Lind, E.M.; MacDougall, A.S.; Seabloom, E.W.; Wragg, P.D.; et al. Grassland Productivity Limited by Multiple Nutrients. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijneveld, J.A.; Abbink, G.W.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; Oenema, O. Relationships between soil fertility, herbage quality and manure composition on grassland-based dairy farms. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 56, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boob, M.; Elsaesser, M.; Thumm, U.; Hartung, J.; Lewandowski, I. Harvest Time Determines Quality and Usability of Biomass from Lowland Hay Meadows. Agriculture 2019, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čop, J.; Vidrih, M.; Hacin, J. Influence of cutting regime and fertilizer application on the botanical composition, yield and nutritive value of herbage of wet grasslands in Central Europe. Grass Forage Sci. 2009, 64, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štýbnarová, M.; Hakl, J.; Mičová, P.; Karabcová, H.; Látal, O.; Fiala, K.; Pozdíšek, J. Species Diversity and Botanical Composition of Permanent Grassland as a Response to Different Grazing Management Practices. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2015, 63, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukač, B.; Kramberger, B.; Meglič, V.; Verbič, J. Importance of non-leguminous forbs in animal nutrition and their ensiling properties: A review. Zemdirb. Agric. 2012, 99, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, F.; Morris, C.; Chamane, S.; Ntuli, N.; Siebert, S.J. The functional importance of forbs in grassland ecosystems. In The Joint XXIV International Grassland and XI Rangeland 2021 Congress, Proceedings XXIV; UKnowledge: Nairobi, Kenya, 2022; p. 35. Available online: https://uknowledge.uky.edu/igc/24/1-2/35 (accessed on 18 June 2025).
- Reiné, R.; Ascaso, J.; Barrantes, O. Nutritional Quality of Plant Species in Pyrenean Hay Meadows of High Diversity. Agronomy 2020, 10, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhurst, R.J.; Delaby, L.; Moloney, A.; Boland, T.; Lewis, E. Nutritive value of forage legumes used for grazing and silage. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2009, 48, 167–187. [Google Scholar]
- Bovolenta, S.; Spanghero, M.; Dovier, S.; Orlandi, D.; Clementel, F. Chemical composition and net energy content of alpine pasture species during the grazing season. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 140, 164–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinas, A.; García-González, R.; Fondevila, M. The Nutritive Value of Five Pasture Species Occurring in the Summer Grazing Ranges of the Pyrenees. Anim. Sci. 2003, 76, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vondrášková, B.; Čermák, B.; Martínková, L.; Brouček, J. Examination of the nutritional quality of forbs from mountainous pastures in the Southwestern Bohemia region. Ekológia 2012, 31, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misztal, A.; Zarzycki, J. The effect of botanical composition on mineral content in hay from extensively managed mountain grassland. In Proceeding of the 22th General Meeting of the European Grassland Federation, Uppsala, Sweden, 9–12 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanizadeh, H.; Harrington, K.C. Weed Management in New Zealand Pastures. Agronomy 2019, 9, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortinovis, C.; Caloni, F. Alkaloid-Containing Plants Poisonous to Cattle and Horses in Europe. Toxins 2015, 7, 5301–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, S.; Penker, M.; Kriechbaum, M. Integrating farmers’ knowledge on toxic plants and grassland management: A case study on Colchicum autumnale in Austria. Biodivers. Conserv. 2011, 20, 1763–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, J.A.; Provenza, F.D.; Panter, K.E.; Stegelmeier, B.L.; Launchbaugh, K.L. Risk management to reduce livestock losses from toxic plants. J. Range Manag. 2002, 55, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlström, A.; Lennartsson, T.; Wissman, J.; Frycklund, I. Biodiversity and Traditional Land Use in South-Central Sweden: The Significance of Management Timing. Environ. Hist. 2008, 14, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpole, W.S.; Sullivan, L.L.; Lind, E.M.; Firn, J.; Adler, P.B.; Borer, E.T.; Chase, J.; Fay, P.A.; Hautier, Y.; Hillebrand, H.; et al. Addition of Multiple Limiting Resources Reduces Grassland Diversity. Nature 2016, 537, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladouceur, E.; Blowes, S.A.; Chase, J.M.; Clark, A.T.; Garbowski, M.; Alberti, J.; Arnillas, C.A.; Bakker, J.D.; Barrio, I.C.; Bharath, S.; et al. Linking Changes in Species Composition and Biomass in a Globally Distributed Grassland Experiment. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 25, 2699–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautier, Y.; Niklaus, P.A.; Hector, A. Competition for Light Causes Plant Biodiversity Loss After Eutrophication. Science 2009, 324, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francksen, R.M.; Turnbull, S.; Rhymer, C.M.; Hiron, M.; Bufe, C.; Klaus, V.H.; Newell-Price, P.; Stewart, G.; Whittingham, M.J. The Effects of Nitrogen Fertilisation on Plant Species Richness in European Permanent Grasslands: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalsa, J.; Fricke, T.; Weisser, W.W.; Weigelt, A.; Wachendorf, M. Effects of functional groups and species richness on biomass constituents relevant for combustion: Results from a grassland diversity experiment. Grass Forage Sci. 2012, 67, 569–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, K.E. Species composition determines forage quality and medicinal value of high diversity grasslands in lowland England. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 241, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fychan, R.; Sanderson, R.; Marley, C. Effects of harvesting red clover/ryegrass at different stage of maturity on forage yield and quality. Grassl. Sci. Eur. 2016, 21, 323–325. [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier, S.; Tremblay, G.F.; Bélanger, G.; Bertrand, A.; Castonguay, Y.; Pageau, D.; Drapeau, R. Forage nonstructural carbohydrates and nutritive value as affected by time of cutting and species. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poetsch, E.; Resch, R.; Krautzer, B. Variability of forage quality between and within three maturity groups of Lolium perenne L. during the first growth. Grassl. Sci. Eur. 2016, 21, 293–295. [Google Scholar]
- Rinne, M.; Nykänen, A. Timing of primary growth harvest affects the yield and nutritive value of timothy-red clover mixtures. Agric. Food Sci. Finl. 2000, 9, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, B.; Zielewicz, W.; Paszkiewicz-Jasińska, A.; Spychalski, B.; Jakubowska, Z. Effect of Harvest Date on Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin Content in Meadow Sward in Different Pluvio-Thermal Conditions. J. Water Land Dev. 2022, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andueza, D.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Picard, F.; Rossignol, N.; Baumont, R.; Cecato, U.; Farruggia, A. Relationships between botanical composition, yield and forage quality of permanent grasslands over the first growth cycle. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 71, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgersma, A.; Søegaard, K. Changes in nutritive value and herbage yield during extended growth intervals in grass-legume mixtures: Effects of species, maturity at harvest, and relationships between productivity and components of feed quality. Grass Forage Sci. 2018, 73, 78–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulli, S. Growth factors and management technique used in relation to the developmental rhythm and yield formation pattern of a pure grass stand. Agric. Food Sci. 1980, 52, 281–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne, M. Influence of the Timing of the Harvest of Primary Grass Growth on Herbage Quality and Subsequent Digestion and Performance in the Ruminant Animal. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, K.B.; Harrison, P.; Chatterton, N.J.; Bushman, B.S.; Creech, J.E. Seasonal Trends in Nonstructural Carbohydrates in Cool- and Warm-season Grasses. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 2328–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszkiewicz-Jasińska, A.; Wróbel, B.; Stopa, W.; Jakubowska, Z.; Steinhoff-Wrześniewska, A.; Zielewicz, W. Nutritional Status of Wood Melick (Melica Uniflora Retz.) in a Natural Forest Stand in South-Western Poland. Forests 2023, 14, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, C.A.; Abrams, S.M. Losses and quality changes during alfalfa hay harvest and storage. Trans. ASAE 1988, 31, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroche, B.; Morvan-Bertrand, A.; Le Morvan, A.; Wyss, U.; Aoun, M.; Baumont, R. Prediction of water-soluble carbohydrate contents in hay from their content in fresh forage and drying time. Grassland at the heart of circular and sustainable food systems. Grassl. Sci. Eur. 2022, 27, 128–130. [Google Scholar]
- Buckmaster, D.R.; Rotz, C.A.; Black, J.R. Value of alfalfa losses on dairy farms. Trans. ASAE 1990, 33, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driehuis, F.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Jiang, Y.; Ogunade, I.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage Review: Animal and Human Health Risks from Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4093–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borreani, G.; Tabacco, E.; Schmidt, R.J.; Holmes, B.J.; Muck, R.E. Silage Review: Factors Affecting Dry Matter and Quality Losses in Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3952–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, C.A.; Muck, R.E. Changes in forage quality during harvest and storage. In Forage Quality, Evaluation, and Utilization; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 828–868. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, J.M.; Davies, D.R. The aerobic stability of silage: Key findings and recent developments. Grass Forage Sci. 2013, 68, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oetzel, G.R. Herd-level ketosis—Diagnosis and risk factors. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Conference American Association of Bovine Practitioners, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 19 September 2007; Available online: https://www.aghost.net/images/E0153801/ketosis_AABP_GarrettOetzel_UWMadison.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Gardini, F.; Özogul, Y.; Suzzi, G.; Tabanelli, G.; Özogul, F. Technological Factors Affecting Biogenic Amine Content in Foods: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, Z.; Muck, R.; Weimer, P. The Survival of Silage Inoculant Lactic Acid Bacteria in Rumen Fluid. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.; Nadeau, E.; McAllister, T.; Contreras, F.; Santos, M.; Kung, L. Silage Review: Recent Advances and Future Uses of Silage Additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, C.J.; Gleeson, D.; Jordan, K.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. Anaerobic sporeformers and their significance with respect to milk and dairy products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 197, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.; Peck, M. Genomes, Neurotoxins and Biology of Clostridium Botulinum Group I and Group II. Res. Microbiol. 2014, 166, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driehuis, F. Silage and the Safety and Quality of Dairy Foods: A Review. Agric. Food Sci. 2013, 22, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walser, V.; Kranzler, M.; Dawid, C.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Stark, T.D.; Hofmann, T.F. Distribution of the Emetic Toxin Cereulide in Cow Milk. Toxins 2021, 13, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, M.; Christiansson, A.; Svensson, B. Bacillus Cereus Spores During Housing of Dairy Cows: Factors Affecting Contamination of Raw Milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majowicz, S.E.; Scallan, E.; Jones-Bitton, A.; Sargeant, J.M.; Stapleton, J.; Angulo, F.J.; Yeung, D.H.; Kirk, M.D. Global Incidence of Human Shiga Toxin–Producing Escherichia coli Infections and Deaths: A Systematic Review and Knowledge Synthesis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, L.H.; Mody, R.K.; Ong, K.L.; Clogher, P.; Cronquist, A.B.; Garman, K.N.; Lathrop, S.; Medus, C.; Spina, N.L.; Webb, T.H.; et al. for the Emerging Infections Program Foodnet Working Group. Increased recognition of non-O157 Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli infections in the United States during 2000–2010: Epidemiologic features and comparison with E. coli O157 infections. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2013, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprioli, A.; Morabito, S.; Scavia, G. Bacteria: Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia Coli and Other Pathogenic Escherichia Coli. In Encyclopedia of Food Safety; Motarjemi, Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.H.; Ward, D.; Shrader, A.M. Salivary tannin-binding proteins: A foraging advantage for goats? Livest. Sci. 2020, 234, 103974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Hu, T.; Wang, Y. Potential and Challenges of Tannins as an Alternative to In-Feed Antibiotics for Farm Animal Production. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Kemp, P.D. A Review of Factors Affecting and Prevention of Pasture-Induced Nitrate Toxicity in Grazing Animals. ProNZG 2003, 65, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasby, R.J.; Kononoff, P.J. Nitrates in Livestock Feeding. 2007. Available online: https://rangemanagement.extension.colostate.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/42/2018/08/Nitrates-UNL.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2025).
- Toaima, S.A.; Lamlom, M.M.; Abdel-Wahab, T.I.; Abdel-Wahab, S.I. Allelopathic Effects of Sorghum and Sudan Grass on Some Following Winter Field Crops. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2014, 3, 599–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, V.; Carbone, K.; Spirito, F.; Iacurto, M.; Terzano, M.G.; Verna, M.; Vincenti, F.; Settineri, D. The Effects of Subterranean Clover Phytoestrogens on Sheep Growth, Reproduction and Carcass Characteristics. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branca, F.; Lorenzetti, S. Health Effects of Phytoestrogens. Forum Nutr. 2005, 57, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkies, A.L.; Wilcox, G.; Davis, S.R. Phytoestrogens. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravcová, J.; Kleinová, T.; Loučka, R.; Tyrolová, I.; Kvasnička, F.; Dušek, M.; Čeřovský, M.; Matucha, P. Coumestrol content of alfalfa following ensilage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2004, 115, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, N.R. Detection of the effects of phytoestrogens on sheep and cattle. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallela, K.; Heinonen, K.; Saloniemi, H. Plant oestrogens; the cause of decreased fertility in cows: A case report. Nord. Vet. Med. 1984, 36, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Cheeke, P.R. Toxicity and metabolism of pyrrolizidine alkaloids. J. Anim. Sci. 1988, 66, 2343–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Xia, Q.; Lin, G.; Chou, M. Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids—Genotoxicity, Metabolism Enzymes, Metabolic Activation, and Mechanisms. Drug Metab. Rev. 2004, 36, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, E.K. The toxic actions of pyrrolizidine (Senecio) alkaloids. Pharmacol. Rev. 1970, 22, 429–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaman, J.T.; Walker, K.H. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid poisoning of cattle and horses in New South Wales. In Plant Toxicology, Proceedings of the Australia-USA Poisonous Plants Symposium, Brisbane, Australia, 14–18 May 1984; Animal Research Institute: Yeerongpilly, QLD, Australia, 1985; pp. 235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Seaman, J.T. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid poisoning of sheep in New South Wales. Aust. Vet. J. 1987, 64, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Martinez-Tuppia, C.; Queiroz, O.C.M.; Jiang, Y.; Drouin, P.; Wu, F.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A.T. Silage review: Mycotoxins in silage: Occurrence, effects, prevention, and mitigation. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4034–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostrom, M.S.; Jacobsen, B.J. Ruminant Mycotoxicosis. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2011, 27, 315–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crews, C. Analysis of Ergot Alkaloids. Toxins 2015, 7, 2024–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molloy, J.; Moore, C.; Bruyeres, A.; Murray, S.-A.; Blaney, B. Determination of dihydroergosine in sorghum ergot using an immunoassay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3916–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comis, D. The grass farmers love to hate. Agric. Res. 2000, 48, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lean, I.J. Association between feeding perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne cultivar Grasslands Impact) containing high concentrations of ergovaline, and health and productivity in a herd of lactating dairy cows. Aust. Vet. J. 2001, 79, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, B.J.; McKenzie, R.A.; Walters, J.R.; Taylor, L.F.; Bewg, W.S.; Ryley, M.J.; Maryam, R. Sorghum ergot (Claviceps africana) associated with agalactia and feed refusal in pigs and dairy cattle. Aust. Vet. J. 2000, 78, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikołajczak, J.; Podkówka, L.; Podkówka, Z.; Staszak, E. Effects of endophyte infection of grasses on the chemical composition, quality and stability of silage. Folia Biol. 2005, 53, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaney, B.J.; Ryley, M.J.; Boucher, B.D. Early harvest and ensilage of forage sorghum infected with ergot (Claviceps africana) reduces the risk of livestock poisoning. Aust. Vet. J. 2010, 88, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conaghan, P.; Casler, M.D. A theoretical and practical analysis of the optimum breeding system for perennial ryegrass. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2011, 50, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Katoch, R. Biotechnological techniques for nutritional quality improvement in forages. In Nutritional Quality Management of Forages in the Himalayan Region; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haremza, J. Selected breeding methods used by DANKO Hodowla Roślin Sp. z o.o. and the company’s expectations towards Polish scientists. Biul. Inst. Hod. I Aklim. Roślin 2019, 287, 47–49. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Fu, C. The Progress of Genetic Improvement of Forage Grasses through Transgenic Approaches. Grass Res. 2024, 4, e027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Geng, J.; Chen, L.; García-Caparros, P.; Hu, T. Genome Editing for Grass Improvement and Future Agriculture. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhae293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.B. Double haploid induction in ryegrass and other grasses. In Doubled Haploid Production in Crop Plants: A Manual; Maluszynski, M., Kasha, K.J., Forster, B.P., Szarejko, I., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummer, E.C.; Caler, M.D. Cool-Season Forages. In Yield Gains in Major U.S. Field Crops; Smith, S., Diers, B., Specht, J., Carver, B., Eds.; CSSA Special Publication 33; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2014; pp. 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, T.J.; Ball, T.; Hennessy, D. Opportunities and challenges for breeding perennial ryegrass cultivars with improved livestock production potential. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 59, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.F.; Bryant, J.R.; Olayemi, M.E.; Edwards, G.R.; Thorrold, B.S.; McMillan, W.H.; Kerr, G.A.; Judson, G.; Cookson, T.; Moorhead, A.; et al. An economically based evaluation index for perennial and short-term ryegrasses in New Zealand dairy farm systems. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 72, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, M.; O’Donovan, M.; Shalloo, L. Development and application of an economic ranking index for perennial ryegrass cultivars. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capstaff, N.M.; Miller, A.J. Improving the Yield and Nutritional Quality of Forage Crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesquière, M.; Humphreys, M.W.; Zwierzykowski, Z. Festulolium. In Fodder Crops and Amenity Grasses; Boller, B., Posselt, U., Veronesi, F., Eds.; Handbook of Plant Breeding; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 5, pp. 288–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.G.; Gwak, S.C.; Baek, E.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Choi, B.R.; Hwang, T.Y. The Current Status of Breeding Research in Lolium Genus. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 26, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Hayes, R. Ryegrass breeding—Balancing trait priorities. Ir. J. Agric. Food Res. 2011, 50, 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Katova, A. Breeding assessment of leafiness for species, varieties and ecotypes of genus Festuca. J. Mt. Agric. Balk. 2023, 26, 141–161. [Google Scholar]
- Little, V.; Reed, K.; Smith, K. Variation for Concentrations of Various Phytoestrogens and Agronomic Traits Among a Broad Range of Red Clover (Trifolium pratense) Cultivars and Accessions. Agronomy 2017, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucak, M.; Ravlić, M.; Horvat, D.; Čupić, T. Improvement of Forage Nutritive Quality of Alfalfa and Red Clover through Plant Breeding. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumball, W.; Keogh, R.G.; Miller, J.E.; Claydon, R.B. “Grasslands G27” red clover (Trifolium pratense L.). N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 1997, 40, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghorn, G. Beneficial and detrimental effects of dietary condensed tannins for sustainable sheep and goat production—Progress and challenges. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 147, 116–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognli, O.A.; Pecetti, L.; Kovi, M.R.; Annicchiarico, P. Grass and Legume Breeding Matching the Future Needs of European Grassland Farming. Grass Forage Sci. 2021, 76, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.A.; Hume, D.; McCulley, R. Forages and pastures symposium: Fungal endophytes of tall fescue and perennial ryegrass: Pasture friend or foe? J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 2379–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fribourg, H.A.; Hannaway, D.B.; West, C.P. (Eds.) Tall Fescue for the Twenty-First Century; American Society of Agronomy, Crop Science Society of America, Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2009; Available online: http://forages.oregonstate.edu/tallfescuemonograph (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Bouton, J.H.; Latch, G.C.; Hill, N.S.; Hoveland, C.S.; McCann, M.A.; Watson, R.H. Reinfection of tall fescue cultivars with non-ergot alkaloid–producing endophytes. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 567–574. [Google Scholar]
- Quigley, P.E. Effects of Neotyphodium lolii infection and sowing rate of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) on the dynamics of ryegrass/subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum) swards. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2000, 51, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatley, W.M. Endophytes, quality assurance and the seed trade in eastern Australia. In Neotyphodium in Cool-Season Grasses; Roberts, C.A., West, C.P., Spiers, D.E., Eds.; Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2005; pp. 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C.A.; Clark, S.G.; Reed, K.F.M.; Nie, Z.N.; Smith, K.F. Novel Festuca arundinacea Shreb. and Dactylis glomerata L. germplasm to improve adaptation for marginal environments. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2008, 48, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hume, D.E.; Cooper, B.M.; Pankhurst, K.A. The role of endophyte in determining the persistence and productivity of ryegrass, tall fescue and meadow fescue in northland. Proc. N. Z. Grassl. Assoc. 2009, 71, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.A.; Young, C.A.; Panaccione, D.G.; Simpson, W.R.; Mittal, S.; Bouton, J.H. Agronomic performance and lamb health among several tall fescue novel endophyte combinations in the south-central USA. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, P.W.; Humphreys, M.O. Progress in breeding perennial forage grasses for temperate agriculture. J. Agric. Sci. 2003, 140, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.G.; Török, P.; Hermann, J.-M.; Kiehl, K.; Kirmer, A.; Kollmann, J.; Overbeck, G.E.; Tischew, S.; Allen, E.B.; Bakker, J.D.; et al. Challenges and Opportunities for Grassland Restoration: A Global Perspective of Best Practices in the Era of Climate Change. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 46, e02612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hou, F. Principle, technique and application of grassland improvement. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 369, 122–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaurena, M.; Lezama, F.; Salvo, L.; Cardozo, G.; Ayala, W.; Terra, J.; Nabinger, C. The Dilemma of Improving Native Grasslands by Overseeding Legumes: Production Intensification or Diversity Conservation. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 69, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermenean, I.; Mocanu, V. New mechanization alternatives with low inputs for over sowing degraded grasslands. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 41, 423–437. [Google Scholar]
- Golka, W.; Żurek, G.; Kamiński, J.R. Permanent grassland restoration techniques—An overview. Agric. Eng. 2016, 20, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badowski, M.; Sekutowski, T. Chemiczna renowacja zaniedbanych trwałych użytków zielonych. Inżynieria Rol. 2007, 3, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Ma, S.; Rao, X.; Liao, S.; Zhu, J.; Yang, C. Effects of Land Use on the Mineralization of Organic Matter in Ultisol. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQueen, J.P.; Gendron, E.M.S.; Solon, A.J.; Bueno de Mesquita, C.P.; Hufft, R.A.; Shackelford, N.; Suding, K.N.; Schmidt, S.K.; Porazinska, D.L. Glyphosate-based restoration of a degraded grassland threatens soil health and the diversity of nematode communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 191, 109350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badowski, M.; Rola, H. Ocena przydatności herbicydu Fernando 225 EC do zwalczania Rumex crispus i Urtica dioica na użytkach zielonych. Prog. Plant Prot. 2003, 43, 521–523. [Google Scholar]
- Rayburn, A.P.; Laca, E. Strip-seeding for grassland restoration: Past successes and future potential. Restor. Ecol. 2013, 31, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, D.M.; Sheridan, H.; Soder, K.; Dubeux, J.C.B. Enhancing the Sustainability of Temperate Pasture Systems through More Diverse Swards. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.L.; Malisch, C.S.; Thers, H.; Eriksen, J. Adding Forbs and Legumes to a Grass-Clover Mixture Suppressed Weeds and Maintained Herbage Yield and Crude Protein Content across Slurry Application Rates. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezequel, A.; Delaby, L.; Finn, J.A.; McKay, Z.C.; Horan, B. Sward Species Diversity Impacts on Pasture Productivity and Botanical Composition Under Grazing Systems. Grass Forage Sci. 2024, 79, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, M.; Labreveux, M.; Hall, M.; Elwinger, G. Nutritive Value of Chicory and English Plantain Forage. Crop Sci. 2003, 43, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordon, M.; Willis, K.; Bürkner, P.-C.; Petrokofsky, G. Rotational Grazing and Multispecies Herbal Leys Increase Productivity in Temperate Pastoral Systems–A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 337, 108075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weggler, K.; Thumm, U.; Elsaesser, M. Development of legumes after reseeding in permanent grassland, as affected by nitrogen fertilizer applications. Agriculture 2019, 9, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.; Santos, S. Sustainable Approach to Weed Management: The Role of Precision Weed Management. Agronomy 2022, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozer, K.; Barker, G.; Cameron, C.; Wilson, D.; Loick, N. Effects of Including Forage Herbs in Grass–Legume Mixtures on Persistence of Intensively Managed Pastures Sampled across Three Age Categories and Five Regions. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 59, 250–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, Z.K.; De Silva, A.G.S.D.; Hassouni, A.A.; Vona, V.M.; Bede, L.; Stencinger, D.; Horváth, B.; Zsebő, S.; Kulmány, I.M. Effects of Various Herbicide Types and Doses, Tillage Systems, and Nitrogen Rates on CO2 Emissions from Agricultural Land: A Literature Review. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pywell, R.F.; Hayes, M.J.; Tallowin, J.R.B.; Walker, K.J.; Meek, W.R.; Carvell, C.; Warman, L.A.; Bullock, J.M. Minimizing environmental impacts of grassland weed management: Can Cirsium arvense be controlled without herbicides? Grass Forage Sci. 2010, 65, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheepens, P.C.; Müller-Schärer, H.; Kempenaar, C. Opportunities for biological weed control in Europe. BioControl 2001, 46, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinková, Z.; Honěk, A. Gastrophysa viridula (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and Biocontrol of Rumex—A Review. Plant Soil Environ. 2004, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.V.; Gourlay, A.H.; Hill, R. Biological Control of Ragwort in the New Zealand Dairy Sector: An Ex-Post Economic Analysis. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 59, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, M.; Sumner, M.E.; Weeks, G.; Saigusa, M. Long-term Effects of Gypsum on Crop Yield and Subsoil Chemical Properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaretto, N.; Norton, L.D.; Joern, B.C.; Brouder, S.M. Gypsum amendment and exchangeable Calcium and Magnesium affecting Phosphorous and Nitrogen Runoff. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Espenberg, M.; Zavattaro, L.; Lellei-Kovacs, E.; Mander, U.; Smith, K.; Thorman, R.; Damatirca, C.; Schils, R.; ten-Berge, H.; et al. Does Liming Grasslands Increase Biomass Productivity without Causing Detrimental Impacts on Net Greenhouse Gas Emissions? Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielewicz, W.; Swędrzyńska, D.; Swędrzyński, A.; Grzebisz, W.; Goliński, P. The Influence of Calcium Sulfate and Different Doses of Potassium on the Soil Enzyme Activity and the Yield of the Sward with a Mixture of Alfalfa and Grasses. Agriculture 2022, 12, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.E.; Bennett, A.E.; Newton, A.C.; White, P.J.; McKenzie, B.M.; George, T.S.; Pakeman, R.J.; Bailey, J.S.; Fornara, D.A.; Hayes, R.C. Liming impacts on soils, crops and biodiversity in the UK: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochon, I.; Carrère, P.; Yvin, J.-C.; Houdusse-Lemenager, D.; Bloor, J.M.G. Impacts of low-level liming on soil respiration and forage production in a fertilized upland grassland in Central France. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 697, 98–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bide, T.; Ander, E.L.; Broadley, M.R. A spatial analysis of lime resources and their potential for improving soil magnesium concentrations and pH in grassland areas of England and Wales. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, J.H.; Cherney, D.J.R. Impact of Fertilization on Forage Production and Animal Performance. In Proceedings of the Colloque sur les Plantes Fourrageres, Drummondville, QC, Canada, 9 December 2015; pp. 1–7. Available online: https://www.craaq.qc.ca/documents/files/EPLF1501/Cherney_resume_va.pdf (accessed on 21 April 2025).
- Malafaia, P.; Barbosa, J.D.; Brito, M.F.; Souza, V.C.d.S.; Costa, D.F.A. Phosphorus for Cattle and Buffaloes in Brazil: Clinical Signs and Diagnosis of Its Deficiency and Relevance, and Recommended Strategies to Alleviate Issues Observed under Grazing Conditions. Ruminants 2023, 3, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinotti, L.; Manoni, M.; Ferrari, L.; Tretola, M.; Cazzola, R.; Givens, I. The Contribution of Dietary Magnesium in Farm Animals and Human Nutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayland, H.F.; Hankins, J.L. Mineral Imbalances and Animal Health: A Management Puzzle, 2001. Available online: https://eprints.nwisrl.ars.usda.gov/id/eprint/1106/1/1048.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2025).
- Ryant, P.; Skládanka, J. The effect of applications of various forms of sulfur on the yields and quality of grass forage. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B–Soil Plant Sci. 2009, 59, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, U.C.; Monteiro, F.A.; Werner, J.C. Micronutrients in grassland production. In Proceedings of the XIX International Grassland Congress, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 11–21 February 2021; Volume 28. Available online: https://uknowledge.uky.edu/igc/19/4/28/ (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Fordyce, F. Selenium Geochemistry and Health. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2007, 36, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radujković, D.; Verbruggen, E.; Seabloom, E.W.; Bahn, M.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Boughton, E.H.; Catford, J.A.; Campioli, M.; Donohue, I.; et al. Soil properties as key predictors of global grassland production: Have we overlooked micronutrients? Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 2713–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darch, T.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Hood, J.; Lee, M.R.F.; Storkey, J.; Beaumont, D.A.; McGrath, S.P. The Effect of Soil Type on Yield and Micronutrient Content of Pasture Species. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radkowski, A.; Radkowska, I.; Bocianowski, J.; Wolski, K.; Bujak, H. Effect of Amino Acid and Titanium Foliar Application on Smooth-Stalked Meadow Grass (Poa pratensis L.) Macronutrient Content. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastalerczuk, G.; Borawska-Jarmułowicz, B.; Dąbrowski, P.; Szara, E.; Perzanowska, A.; Wróbel, B. Can the Application the Silicon Improve the Productivity and Nutritional Value of Grass–Clover Sward in Conditions of Rainfall Shortage in Organic Management? Agronomy 2020, 10, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borawska-Jarmułowicz, B.; Mastalerczuk, G.; Janicka, M.; Wróbel, B. Effect of Silicon-Containing Fertilizers on the Nutritional Value of Grass–Legume Mixtures on Temporary Grasslands. Agriculture 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowski, J.; Wróbel, B.; Truba, M. Effect of Tytanit on Selected Morphological, Physiological and Chemical Characteristics of Lolium multiflorum Dry Matter. J. Water Land Dev. 2023, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalor, S.T.J.; Hoekstra, N.J.; Murphy, P.N.C.; Richards, K.G.; Lanigan, G.J. Practical Advice for Slurry Application Strategies for Grassland Systems; Proceedings of the International Fertiliser Society; International Fertiliser Society: Chester, UK, 2012; Volume 712, ISBN 978-0-85310-349-3. [Google Scholar]
- Brummerloh, A.; Kuka, K. The Effects of Manure Application and Herbivore Excreta on Plant and Soil Properties of Temperate Grasslands—A Review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štýbnarová, M.; Mičová, P.; Fiala, K.; Karabcová, H.; Látal, O.; Pozdíšek, J. Effect of organic fertilizers on botanical composition of grassland, herbage yield and quality. Agriculture (Pol’nohospodárstvo) 2014, 60, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khan, M.T.; Aleinikoviene, J.; Butkeviciene, L.-M. Innovative Organic Fertilizers and Cover Crops: Perspectives for Sustainable Agriculture in the Era of Climate Change and Organic Agriculture. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, A.; Stojanović, B.; Vučković, S.; Marković, J.; Božičković, A.; Bijelić, Z.; Mandić, V. Application of farmyard manure in grassland production. AGROFOR Int. J. 2016, 1, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, W.; Kasperczyk, M.; Kacorzyk, P. Role of farmyard manure on upland meadows. Grassl. Sci. Eur. 2004, 9, 714–716. [Google Scholar]
- Vîntu, V.; Samuil, C.; Trofin, A.; Popovici, I.C. The influence of organic and mineral fertilizers on fodder quality in NE Romania. Grassl. Sci. Eur. 2008, 13, 637–639. [Google Scholar]
- Duffková, R.; Hejcman, M.; Libichová, H. Effect of Cattle Slurry on Soil and Herbage Chemical Properties, Yield, Nutrient Balance and Plant Species Composition of Moderately Dry Arrhenatherion Grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 213, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampere, M.; Viiralt, R. The Efficiency of Biogas Digestate on Grassland Compared to Mineral Fertilizer and Cattle Slurry. Res. Rural Dev. 2014, 1, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Simić, A.; Marković, J.; Vučković, S.; Stojanović, B.; Bijelić, Z.; Mandić, V.; Dželetović, Ž. The Use of Different N Sources for the Treatment of Permanent Grassland and Effect on Forage Quality. Emir J. Food Agric. 2019, 31, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walie, M.; Amogne, F.T.; Mekuriaw, Y.; Tsunekawa, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Ichinohe, T.; Haregeweyn, N.; Wolde, A.; Mekuriaw, S.; Masunaga, T.; et al. Biomass Yield, Quality, and Soil Nutrients of Pasture Influenced by Farmyard Manure and Enrichment Planting. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 88, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacorzyk, P.; Głąb, T. Effect of Ten Years of Mineral and Organic Fertilization on the Herbage Production of a Mountain Meadow. J. Elem. 2012, 22, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Groves, S.J.; Chambers, B.J. Pathogen survival during livestock manure storage and following land application. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ploeg, J.D.; Groot, J.; Verhoeven, F.; Lantinga, E.A. Interpretation of results from on-farm experiments: Manure-nitrogen recovery on grassland as affected by manure quality and application technique. 2. A sociological analysis. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2007, 54, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdin, F.; Sakrabani, R.; Kibblewhite, M.G.; Lanigan, G.J. Effect of slurry dry matter content, application technique and timing on emissions of ammonia and greenhouse gas from cattle slurry applied to grassland soils in Ireland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 188, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huijsmans, J.; Hol, J.; Hendriks, M. Effect of application technique, manure characteristics, weather and field conditions on ammonia volatilization from manure applied to grassland. NJAS-Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2001, 49, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, J.F.; Young, E.O.; Jokela, W.E.; Cavadini, J. Impacts of low-disturbance dairy manure incorporation on ammonia and greenhouse gas fluxes in a corn-winter rye cover crop system. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, J.; van der Ploeg, J.D.; Verhoeven, F.; Lantinga, E.A. Interpretation of results from on-farm experiments: Manure-nitrogen recovery on grassland as affected by manure quality and application technique. 1. An agronomic analysis. NJAS-Wageningen. J. Life Sci. 2007, 54, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangueiro, D.; Hjorth, M.; Gioelli, F. Acidification of animal slurry—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 149, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Huf, M.; Reinsch, T.; Zutz, M.; Essich, C.; Ruser, R.; Buchen-Tschiskale, C.; Flessa, H.; Olfs, H.-W. Effects of Liquid Manure Application Techniques on Ammonia Emission and Winter Wheat Yield. Agronomy 2023, 13, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbarao, G.V.; Ito, O.; Sahrawat, K.L.; Berry, W.L.; Nakahara, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Watanabe, T.; Suenaga, K.; Rondon, M.; Rao, I.M. Scope and strategies for regulation of nitrification in agricultural systems—Challenges and opportunities. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2006, 25, 303–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keidel, L.; Lenhart, K.; Moser, G.; Müller, C. Depth-dependent response of soil aggregates and soil organic carbon content to long-term elevated CO2 in a temperate grassland soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusi-Kämppä, J.; Mattila, P.K. Nitrogen losses from grass ley after slurry application surface broadcasting vs. injection. Agric. Food Sci. 2010, 19, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Beckwith, C.P.; Chalmers, A.G.; Jackson, D.R. Nitrate leaching following autumn and winter application of animal manures to grassland. Soil Use Manag. 2002, 18, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Dutta, B.; Grant, B.B.; Chantigny, M.H.; Hunt, D.; Bittman, S.; Tenuta, M.; Worth, D.; VanderZaag, A.; Desjardins, R.L.; et al. Assessing the effects of manure application rate and timing on nitrous oxide emissions from managed grasslands under contrasting climate in Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 716, 135374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.; Pain, B.; Bittman, S.; Morgan, J. The impacts of manure application methods on emissions of ammonia, nitrous oxide and on crop response—A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perala, P.; Kapuinen, P.; Esala, M.; Tyynela, S.; Regina, K. Influence of slurry and mineral fertiliser application techniques on N2O and CH4 fluxes from a barley field in southern Finland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 117, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzyński, J.; Jakubowska, Z.; Dybek, B. Potential of Bacillus Pumilus to Directly Promote Plant Growth. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1069053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkova, I.; Dobrzyński, J.; Kowalczyk, P.; Bełżecki, G.; Kramkowski, K. Plant Growth Promotion Using Bacillus Cereus. IJMS 2023, 24, 9759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkova, I.; Wróbel, B.; Dobrzyński, J. Serratia spp. as Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Alleviating Salinity, Drought, and Nutrient Imbalance Stresses. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1342331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Díaz, S.; Romero-Perdomo, F.; Mendoza-Labrador, J.; Delgadillo-Duran, D.; Castro-Rincon, E.; Silva, A.M.M.; Rojas-Tapias, D.F.; Cardoso, E.J.B.N.; Estrada-Bonilla, G.A. Endophytic PGPB Improves Plant Growth and Quality, and Modulates the Bacterial Community of an Intercropping System. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 715270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzani, H.; Zohdi, M.; Fish, E.; Amiri, G.; Nikkhah, A.; Wester, D. Phenological Effects on Forage Quality of Five Grass Species. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 57, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, L.; Häusler, J.; Steinwidder, A.; Schauer, A.; Maierhofer, G. Influence of cutting frequency in Alpine permanent grassland on nutritive value, DM yield and agronomic parameters. Slovak J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 39, 26–42. [Google Scholar]
- Pontes, L.D.S.; Carrere, P.; Andueza, D.; Louault, F.; Soussana, J.F. Seasonal productivity and nutritive value of temperate grasses found in semi-natural pastures in Europe: Responses to cutting frequency and N supply. Grass Forage Sci. 2007, 62, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berça, A.S.; Romanzini, E.P.; da Silva Cardoso, A.; Ferreira, L.E.; D’Aurea, A.P.; Fernandes, L.B.; Reis, R.A. Advances in Pasture Management and Animal Nutrition to Optimize Beef Cattle Production in Grazing Systems. In Animal Feed Science and Nutrition-Production, Health and Environment; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, M.; Schmidt, A.; Hölzel, N.; Baasch, A.; Tischew, S. Positive long-term effects of year-round horse grazing in orchid-rich dry calcareous grasslands–Results of a 12-year study. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1107987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, K.; von Oheimb, G.; Härdtle, W.; Fichtner, A.; Tischew, S. The reproductive potential and importance of key management aspects for successful Calluna vulgaris rejuvenation on abandoned Continental heaths. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 2091–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, Z.; Nippert, J.B.; Ocheltree, T.W. Abrupt transition of mesic grassland to shrubland: Evidence for thresholds, alternative attractors, and regime shifts. Ecology 2014, 95, 2633–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesléard, F.; Yavercovski, N.; Lefebvre, G.; Willm, L.; Bonis, A. High stocking density controls Phillyrea angustifolia in Mediterranean Grasslands. Environ. Manag. 2017, 59, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrigo, J.K.; Ataide, P.F.; Filho, J.A.; Oliveira, L.V.; Jaurena, M.; Laca, E.A.; Overbeck, G.E.; Nabinger, C. Temporary grazing exclusion promotes rapid recovery of species richness and productivity in a long-term overgrazed Campos grassland. Restor. Ecol. 2018, 26, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root-Bernstein, M.; Guerrero-Gatica, M.; Piña, L.; Bonacic, C.; Svenning, J.-C.; Jaksic, F.M. Rewilding-inspired transhumance for the restoration of semiarid silvopastoral systems in Chile. Reg. Environ. Change 2017, 17, 1381–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metara, E.; Sakowski, T.; Słoniewski, K.; Romanowicz, B. Grazing as a tool to maintain biodiversity of grassland–A review. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 2010, 28, 315–334. [Google Scholar]
- Wätzold, F.; Jauker, F.; Komainda, M.; Schöttker, O.; Horn, J.; Sturm, A.; Isselstein, J. Harnessing Virtual Fencing for More Effective and Adaptive Agri-Environment Schemes to Conserve Grassland Biodiversity. Biol. Conserv. 2024, 297, 110736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.G.; Garnick, S.; Elgar, M.A.; Coulson, G. Parasite and predator risk assessment: Nuanced use of olfactory cues. Proc. R. Soc. B 2015, 282, 20151941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricarello, P.A.; Longo, C.; da Rocha, R.A.; Hötzel, M.J. Understanding Animal-PlantParasite Interactions to Improve the Management of Gastrointestinal Nematodes in Grazing Ruminants. Pathogens 2023, 12, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, G.; Gorlier, A.; Lonati, M.; Probo, M. Pastoral Plans to support mountain farming in SW Alps. In Proceedings of the 16th Meeting of the FAO-CIHEAM Mountain Pastures Network. Contribution of Mountain Pastures to Agriculture and Environment, Kraków, Poland, 25–27 May 2011; pp. 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Conway-Cunningham, T.; Ajayi, H.J.; Gyawali, B.; Gebremedhin, M.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y. Effects of Continuous and Rotational Grazing Practices on Forage Production and Goat Performance. Preprints 2024, 2024050090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probo, M.; Lonati, M.; Pittarello, M.; Bailey, D.W.; Garbarino, M.; Gorlier, A.; Lombardi, G. Implementation of a rotational grazing system with large paddocks changes the distribution of grazing cattle in the south-western Italian Alps. Rangel. J. 2014, 36, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, A.D.; McIntosh, B.J.; Plunk, J.D.; Webb, M.; McIntosh, D.; Parks, A.G. Effects of rotational grazing on water-soluble carbohydrate and energy content of horse pastures. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2015, 35, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, M.; Kardyńska, S.; Wieczorek, A.; Kryszak, J.; Biniaś, J. Przestrzenne zróżnicowanie składu botanicznego i wysokości spasanej runi a strategia spożywania zielonki pastwiskowej przez bydło. Zesz. Nauk. Akad. Rol. W Krakowie 2000, 73, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, S.; Lynch, M.B.; Godwin, F.; Boland, T.M.; Kelly, A.K.; Evans, A.C.O.; Murphy, P.N.C.; Sheridan, H. Multispecies Swards Outperform Perennial Ryegrass under Intensive Beef Grazing. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 345, 108335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, H.; Reinsch, T.; Kluß, C.; Taube, F.; Loges, R. Does the Admixture of Forage Herbs Affect the Yield Performance, Yield Stability and Forage Quality of a Grass Clover Ley? Sustainability 2020, 12, 5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirhofer-Walzl, K.; Søegaard, K.; Høgh-Jensen, H.; Eriksen, J.; Sanderson, M.A.; Rasmussen, J. Forage herbs improve mineral composition of grassland herbage. Grass Forage Sci. 2011, 66, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killerby, M.A.; Reyes, D.C.; White, R.; Romero, J.J. Meta-analysis of the effects of chemical and microbial preservatives on hay spoilage during storage. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Oude-Elferink, S.J.W.H.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of ensiling. In Silage Science and Technology; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, J.H., Eds.; The American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; pp. 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L. Silage fermentation and additives. Arch. Latinoam. Prod. Anim. 2018, 26, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, M.; Rinne, M. Dry Matter Content and Additives with Different Modes of Action Modify the Preservation Characteristics of Grass Silage. Fermentation 2023, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridla, M.; Albarki, H.R.; Risyahadi, S.T.; Sukarman, S. Effects of Wilting on Silage Quality: A Meta-Analysis. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, T.M.; Lingvall, P. Effects of Mechanical Forage Treatment and Surfactants on Fermentation of Grass Silage. Acta Agric. Scand. A Anim. Sci. 1999, 49, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Holmes, B.J. Factors Affecting Bunker Silo Densities. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2000, 16, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiszewska, A.U.; Zielińska, K.J.; Wróbel, B. Trends in Designing Microbial Silage Quality by Biotechnological Methods Using Lactic Acid Bacteria Inoculants: A Minireview. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, S.; Sun, L.; Cheng, Q.; Hao, J.; Lu, Q.; Ge, G.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Molasses Additives on Dynamic Fermentation Quality and Microbial Community of Native Grass Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 830121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bao, J.; Zhao, M.; Si, Q.; Sun, P.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y. Effects of Different Types of LAB on Dynamic Fermentation Quality and Microbial Community of Native Grass Silage during Anaerobic Fermentation and Aerobic Exposure. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, M.; Tapio, I.; Pirttiniemi, J.; Stefański, T.; Jalava, T.; Huuskonen, A.; Rinne, M. Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Ecology of Grass Silage Modulated by Additive Treatments, Extent of Compaction and Soil Contamination. Fermentation 2022, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zheng, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, X. Novel intelligent grazing strategy based on remote sensing, herd perception and UAVs monitoring. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.J.; Murphy, M.D.; O’Brien, B.; O’Donovan, M. A Review of Precision Technologies for Optimising Pasture Measurement on Irish Grassland. Agriculture 2021, 11, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J. An Intelligent Grazing Development Strategy for Unmanned Animal Husbandry in China. Drones 2023, 7, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, H.; Savkin, A.; Zhang, J. Robotic Herding of Farm Animals Using a Network of Barking Aerial Drones. Drones 2022, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, L.; Huguenin-Elie, O.; Latsch, R.; Simmler, M.; Dubois, S.; Umstatter, C. Comparison of Spectral Reflectance-Based Smart Farming Tools and a Conventional Approach to Determine Herbage Mass and Grass Quality on Farm. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Cawkwell, F.; Dwyer, E.; Barrett, B.; Green, S. Satellite Remote Sensing of Grasslands: From Observation to Management. JPECOL 2016, 9, 649–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachendorf, M.; Fricke, T.; Möckel, T. Remote sensing as a tool to assess botanical composition, structure, quantity and quality of temperate grasslands. Grass Forage Sci. 2018, 73, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Bi, Y.; Du, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, T.; Pi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Research on deep learning method recognition and a classification model of grassland grass species based on unmanned aerial vehicle hyperspectral remote sensing. Grassl. Sci. 2023, 69, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, H.; Honkavaara, E.; Lucieer, A.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J. Quantitative Remote Sensing at Ultra-High Resolution with UAV Spectroscopy: A Review of Sensor Technology, Measurement Procedures, and Data Correction Workflows. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendig, J.; Yu, K.; Aasen, H.; Bolten, A.; Bennertz, S.; Broscheit, J.; Gnyp, M.; Bareth, G. Combining UAV-based plant height from crop surface models, visible, and near infrared vegetation indices for biomass monitoring in barley. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 39, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näsi, R.; Viljanen, N.; Kaivosoja, J.; Alhonoja, K.; Hakala, T.; Markelin, L.; Honkavaara, E. Estimating Biomass and Nitrogen Amount of Barley and Grass Using UAV and Aircraft Based Spectral and Photogrammetric 3D Features. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesingha, J.; Astor, T.; Schulze-Brüninghoff, D.; Wengert, M.; Wachendorf, M. Predicting Forage Quality of Grasslands Using UAV-Borne Imaging Spectroscopy. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.A.; Näsi, R.; Niemeläinen, O.; Nyholm, L.; Alhonoja, K.; Kaivosoja, J.; Jauhiainen, L.; Viljanen, N.; Nezami, S.; Markelin, L.; et al. Machine learning estimators for the quantity and quality of grass swards used for silage production using drone-based imaging spectrometry and photogrammetry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, J.S.; Pampolini, L.F.; Jackson, J.J.; Seyyedhasani, H.; Sama, M.P.; Goff, B. Predicting Quality and Yield of Growing Alfalfa from a UAV. Trans. ASABE 2021, 64, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, M.S.; McCarthy, T.; Magee, A.; Murphy, D.J. Evaluation of Grass Quality under Different Soil Management Scenarios Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, K.; He, Y.; Chen, D.; Sui, M.; Zhang, G.; Zang, L.; Liu, Q. Aerial Seeding Promotes the Restoration of Ecosystem Health in Mu Us Sandy Grasslands in China. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewhurst, R.J.; Fisher, W.J.; Tweed, J.K.S.; Wilkins, R.J. Comparison of Grass and Legume Silages for Milk Production. 1. Production Responses with Different Levels of Concentrate. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2598–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorby, J.M.; Evans, R.T.; Scollan, N.D.; MacRae, J.C.; Theodorou, M.K. Increased concentration of water-soluble carbohydrate in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). Evaluation in dairy cows in early lactation. Grass Forage Sci. 2006, 61, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.G.; Allen, M.S. Characteristics of plant cell walls affecting intake and digestibility of forages by ruminants. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 2774–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingfield, K.J.; Chilliard, Y.; Toivonen, V.; Kairenius, P.; Givens, D.I. Trans fatty acids and bioactive lipids in ruminant milk. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 606, 3–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suttle, N. Mineral Nutrition of Livestock; Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux International: Oxfordshire, UK, 2010; 579p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.G.; Peng, H.H.; Schwab, C.G. Enhancing the productivity of dairy cows using amino acids. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2013, 53, 1156–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutter, S.M.; Orr, R.J.; Yarrow, N.H.; Champion, R.A. Dietary Preference of Dairy Cows Grazing Ryegrass and White Clover. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, M.; Lynch, M.B.; Hennessy, D. Including White Clover In Nitrogen Fertilized Perennial Ryegrass Swards: Effects on Dry Matter Intake and Milk Production of Spring Calving Dairy Cows. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 155, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClearn, B.; Shalloo, L.; Gilliland, T.J.; Coughlan, F.; McCarthy, B. An economic comparison of pasture-based production systems differing in sward type and cow genotype. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 4455–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmemies-Beauchet-Filleau, A.; Vanhatalo, A.; Toivonen, V.; Heikkilä, T.; Lee, M.R.F.; Shingfield, K.J. Effect of Replacing Grass Silage with Red Clover Silage on Nutrient Digestion, Nitrogen Metabolism, and Milk Fat Composition in Lactating Cows Fed Diets Containing a 60:40 Forage-to-Concentrate Ratio. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 3761–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.; Lund, P.; Weisbjerg, M. Feed Intake and Milk Production in Dairy Cows Fed Different Grass and Legume Species: A Meta-Analysis. Animal 2018, 12, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhatalo, A.; Gäddnäs, T.; Heikkilä, T. Microbial Protein Synthesis, Digestion and Lactation Responses of Cows to Grass or Grass-Red Clover Silage Diet Supplemented with Barley or Oats. AFSci 2008, 15, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, A.; Jayanegara, A.; Niderkorn, V. Impacts of Red Clover and Sainfoin Silages on the Performance, Nutrient Utilization and Milk Fatty Acids Profile of Ruminants: A Meta-Analysis. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 108, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, G.; Natalello, A.; Mattioli, S.; Pauselli, M.; Sebastiani, B.; Niderkorn, V.; Copani, G.; Benhissi, H.; Amanpour, A.; Valenti, B. Feeding Lambs with Silage Mixtures of Grass, Sainfoin and Red Clover Improves Meat Oxidative Stability under High Oxidative Challenge. Meat Sci. 2019, 156, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, K.; McAloon, C.; Lynch, M.; Pierce, K.; Mulligan, F. Herb species inclusion in grazing swards for dairy cows—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 1416–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorini, P.; Minnee, E.; Griffiths, W.; Lee, J. Dairy cows increase ingestive mastication and reduce ruminative chewing when grazing chicory and plantain. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 7798–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorini, P.; Gunter, S.A.; Masino, C.A.; Beck, P. Effects of ruminal fill on short-term herbage intake rate and grazing dynamics of beef heifers. Grass Forage Sci. 2007, 62, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooledge, E.; Kendall, N.; Leake, J.; Chadwick, D.; Jones, D. Herbal Leys Increase Forage Macro-and Micronutrient Content, Spring Lamb Nutrition, Liveweight Gain, and Reduce Gastrointestinal Parasites Compared to a Grass-Clover Ley. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 367, 108991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, M.; Delaby, L. A comparison of perennial ryegrass cultivars differing in heading date and grass ploidy with spring calving dairy cows grazed at two different stocking rates. Anim. Res. 2005, 54, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wims, C.; McEvoy, M.; Delaby, L.; Boland, T.; O’Donovan, M. Effect of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) cultivars on the milk yield of grazing dairy cows. Animal 2013, 7, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, T.J.; Barrett, P.D.; Mann, R.L.; Agnew, R.E.; Fearon, A.M. Canopy morphology and nutritional quality traits as potential grazing value indicators for Lolium perenne varieties. J. Agric. Sci. 2002, 139, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Lesama, M.; Hazard, L.; Betin, M.; Emile, J.C. Differences in sward structure of ryegrass cultivars and impact on milk production of grazing dairy cows. Anim. Res. 2006, 55, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novobilský, A.; Mueller-Harvey, I.; Thamsborg, S.M. Condensed tannins act against cattle nematodes. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 182, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Harvey, I. Unravelling the conundrum of tannins in animal nutrition and health. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 2010–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugène, M.; Klumpp, K.; Sauvant, D. Methane mitigating options with forages fed to ruminants. Grass Forage Sci. 2021, 76, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, D.; Bannink, A.; Hatew, B.; van Laar, H.; Dijkstra, J. Effects of grass silage quality and level of feed intake on enteric methane production in lactating dairy cows. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 3687–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herron, J.; Hennessy, D.; Curran, T.P.; Moloney, A.; O’Brien, D. The simulated environmental impact of incorporating white clover into pasture-based dairy production systems. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7902–7918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouton, J. The economic benefits of forage improvement in the United States. Euphytica 2007, 154, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradus, J.R.; Woodfield, D.R.; Stewart, A.V. Overview and vision for white clover. In White Clover: New Zealand’s Competitive Edge; Woodfield, D., Ed.; NZ Grassland Association Grassland Research and Practice Series; Lincoln University: Lincoln, New Zealand, 1995; Volume 6, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

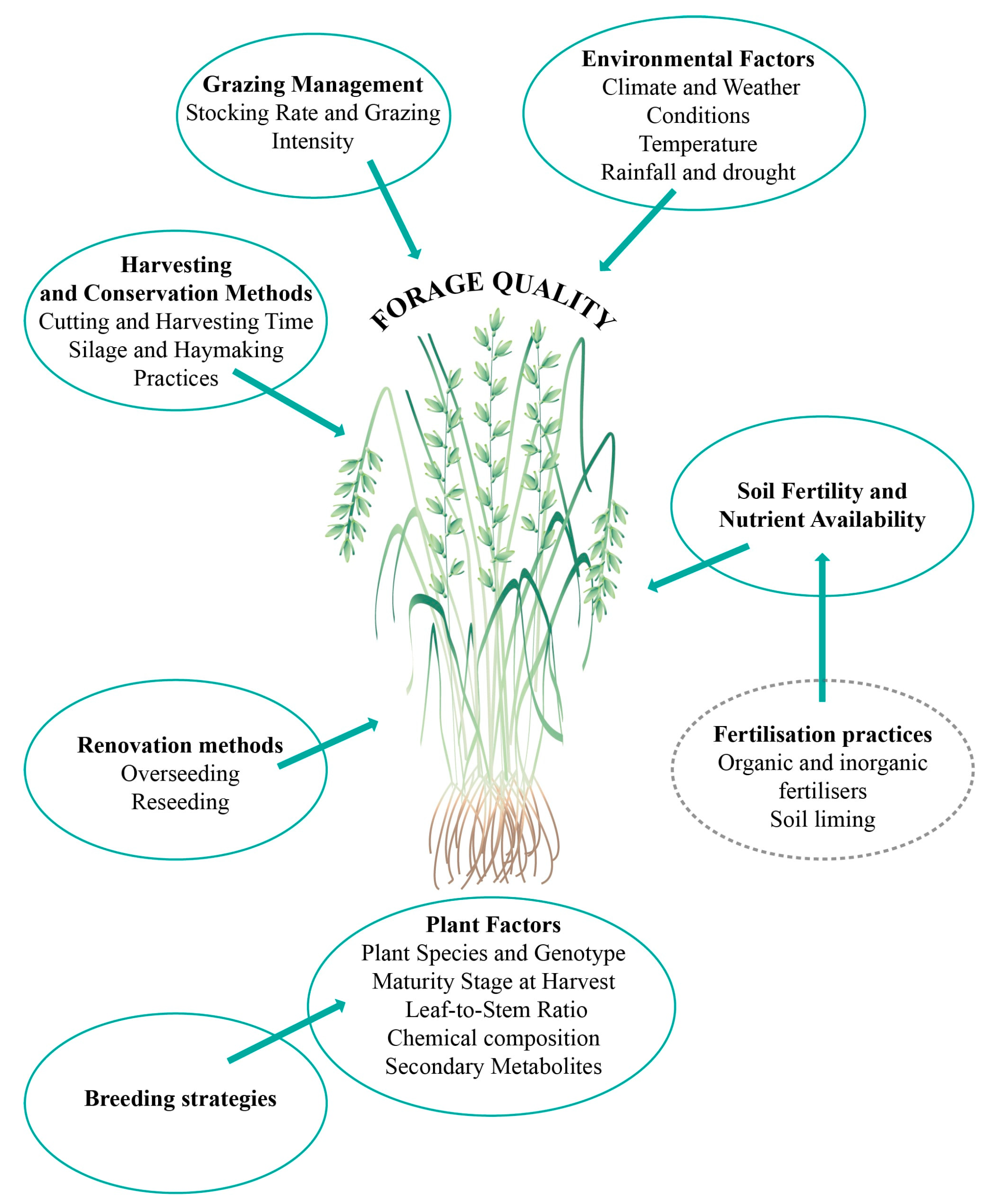


| Forage Trait | Mechanism of Action | Effect on Animal Productivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude protein | Supplies nitrogen for microbial protein synthesis | Supports milk yield, growth, reproduction | [310] |
| Fiber digestibility (e.g., NDFD, TTNDFD) | Determines rate of digestion and intake potential | Higher energy availability, improved milk and meat production | [40] |
| Water-soluble carbohydrates | Enhance microbial efficiency and rumen fermentation | Improved nutrient utilization, better nitrogen balance | [311] |
| Lignin content | Indigestible; binds to cellulose and hemicellulose | Reduces overall digestibility and intake potential | [312] |
| Fat content (PUFA, CLA) | Modifies rumen fermentation and milk fatty acid profile | Improves milk fat quality, can suppress methane, but may reduce fibre digestion if excessive | [313] |
| Mineral composition | Supplies essential macro- and microelements | Supports bone health, fertility, immune function; imbalance may limit productivity | [314] |
| Amino acid profile | Determines efficiency of absorbed protein use | Influences milk protein synthesis and muscle accretion | [315] |
| Anti-nutritional factors | Toxins or inhibitors affecting metabolism or intake | Reduced feed intake, digestibility, possible toxicity (e.g., alkaloids, tannins, mycotoxins) | [134] |
| Forage palatability | Influences voluntary feed intake | Determines actual nutrient consumption and grazing selectivity | [316] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wróbel, B.; Zielewicz, W.; Paszkiewicz-Jasińska, A. Improving Forage Quality from Permanent Grasslands to Enhance Ruminant Productivity. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131438
Wróbel B, Zielewicz W, Paszkiewicz-Jasińska A. Improving Forage Quality from Permanent Grasslands to Enhance Ruminant Productivity. Agriculture. 2025; 15(13):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131438
Chicago/Turabian StyleWróbel, Barbara, Waldemar Zielewicz, and Anna Paszkiewicz-Jasińska. 2025. "Improving Forage Quality from Permanent Grasslands to Enhance Ruminant Productivity" Agriculture 15, no. 13: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131438
APA StyleWróbel, B., Zielewicz, W., & Paszkiewicz-Jasińska, A. (2025). Improving Forage Quality from Permanent Grasslands to Enhance Ruminant Productivity. Agriculture, 15(13), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131438







