Impact of Coastal Beach Reclamation on Seasonal Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Study of Diversified Saline–Alkaline Land Use Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Sampling Sites
2.2. Gas Flux Measurements
2.3. Vegetation Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Description of Soil and Vegetation Traits
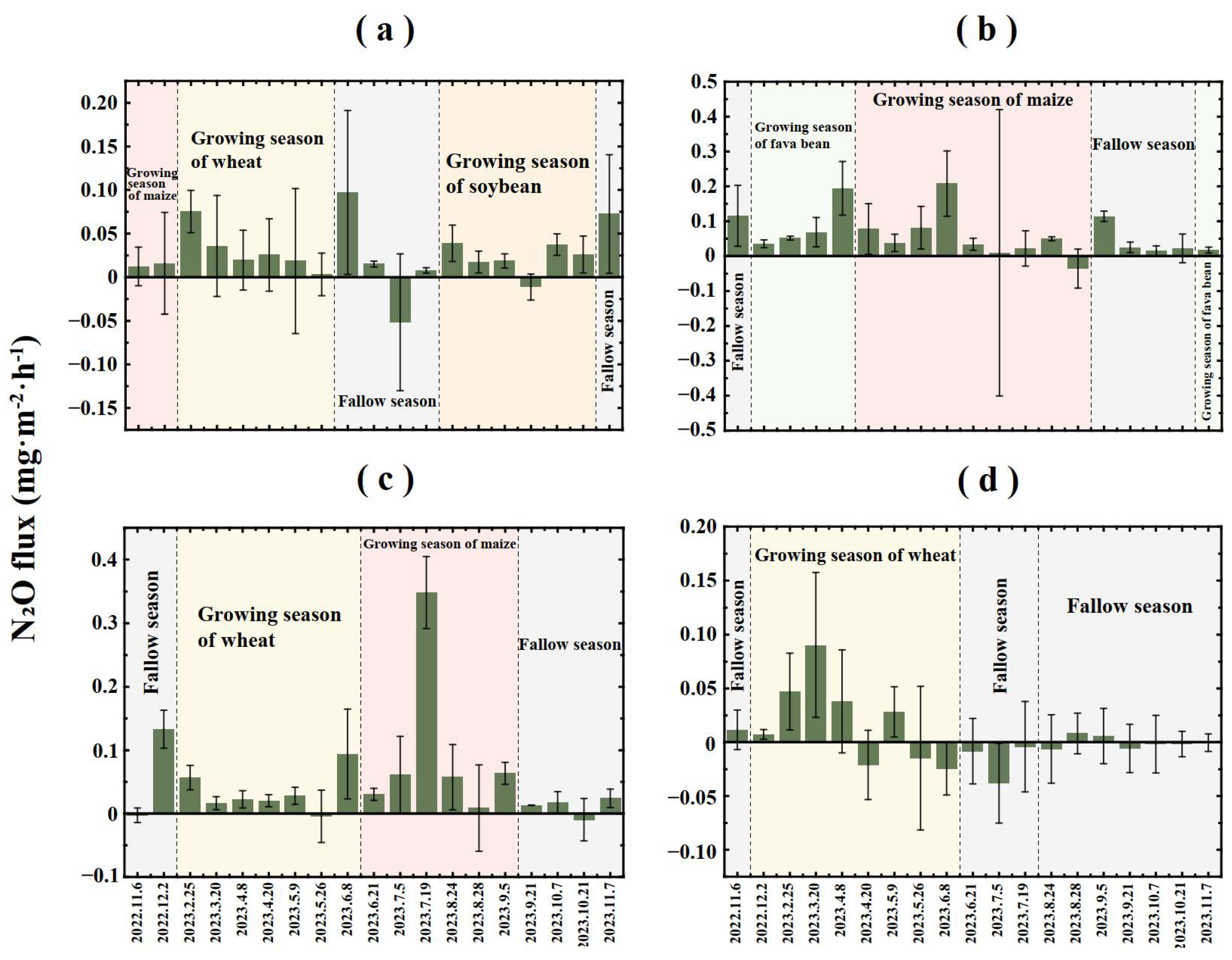
3.2. Analyses of the Dynamic Seasonal-Scale Gas Carbon Fluxes and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
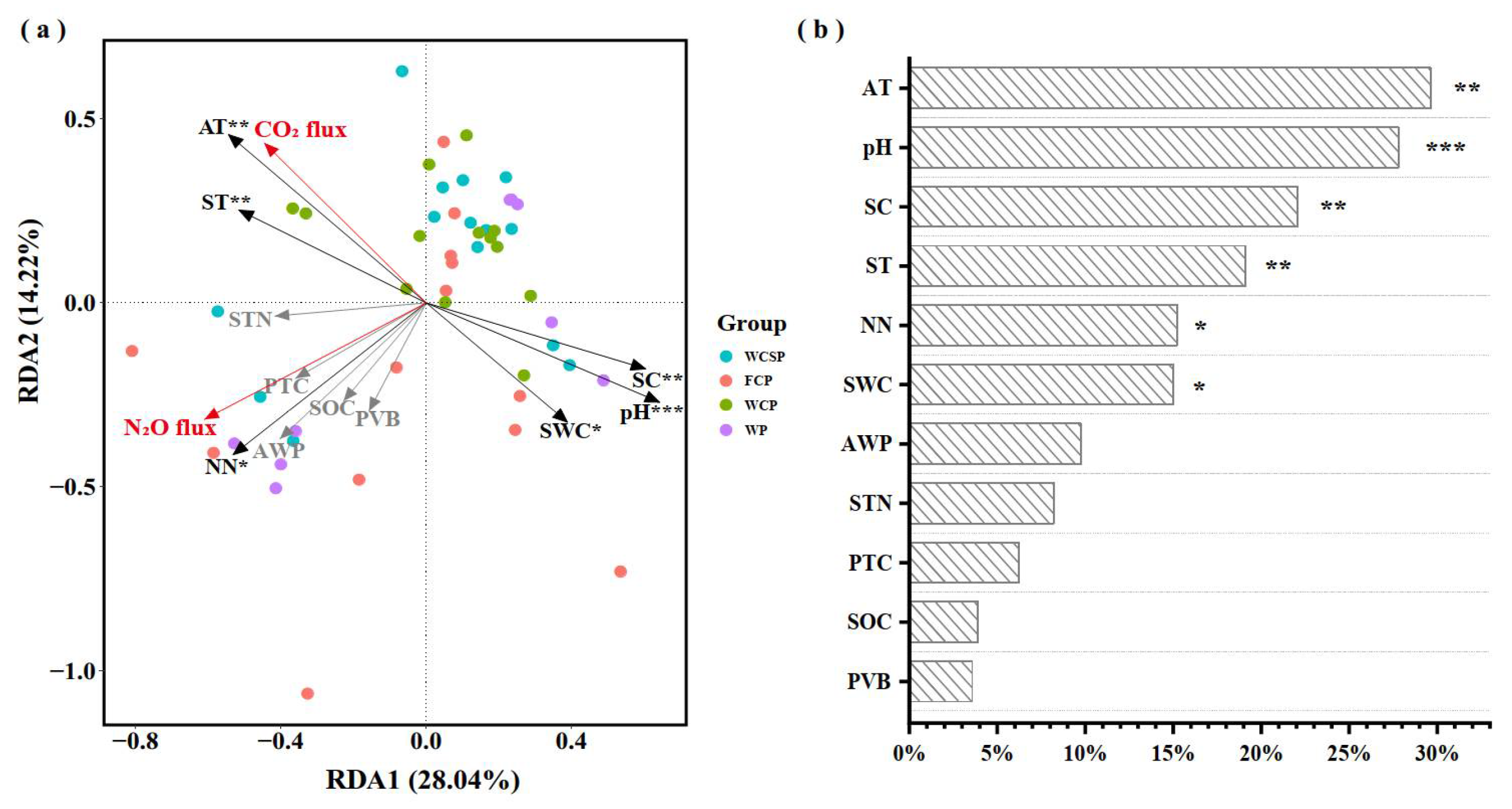
3.3. Environmental Drivers of GHG Flux Exchange in Coastal Reclamation Areas
4. Discussion
4.1. Responses of CO2 and N2O Emissions to Wetland Reclamation and Saline–Alkali Dynamics
4.2. Responses of GHG and Soil–Vegetation Carbon and Nitrogen Pools Under Different Years of Reclamation
4.3. Insights and Perspectives on Sustainable Planting in Coastal Wetland Development and Reclaimed Areas
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC—Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Nguyen, H.-D.; Youn, Y.-C.; Bui, D.T.; Nguyen, T.H.Y.; Dinh, D.T.; Ho, Q.T. Optimal Forest Management for Carbon Sequestration, Timber, and Bioenergy Production in Vietnam Using an Extended Full-Cycle Carbon Accounting Method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 101192–101207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, O.; Probert, S.D. Sources of Atmospheric Nitrous Oxide. Appl. Energy 1992, 42, 129–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Peng, S.; Canadell, J.G.; Piao, S. Inventory of Methane and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Freshwater Aquaculture in China. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Jia, G.; Xu, X. Weakening greenhouse gas sink of pristine wetlands under warming. Nat. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Xu, R.; Canadell, J.G.; Thompson, R.L.; Winiwarter, W.; Suntharalingam, P.; Davidson, E.A.; Ciais, P.; Jackson, R.B.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; et al. A Comprehensive Quantification of Global Nitrous Oxide Sources and Sinks. Nature 2020, 586, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Hu, Y.; Qian, L.; Yan, J.; Gao, L.; Mei, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, P.; Sun, Y.; et al. Preliminary Manifestation of the Yangtze River Protection Strategy in Improving the Carbon Sink Function of Estuary Wetlands. iScience 2024, 27, 108974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkinson, C.S.; Cai, W.-J.; Hu, X. Carbon Sequestration in Wetland Dominated Coastal Systems—A Global Sink of Rapidly Diminishing Magnitude. Curr. Opin. Env. Sustain. 2012, 4, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhao, W.; Ye, J.; Muroki, M.; Pereira, P. Ecosystem Carbon Sequestration Service Supports the Sustainable Development Goals Progress. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 330, 117155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haonan, Q.; Shihong, Y.; Guangmei, W.; Xiaoling, L.; Jie, Z.; Yi, X.; Shide, D.; Hanwen, L.; Zewei, J. Analysis of carbon flux characteristics in saline-alkali soil under global warming. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2024, 210, e12720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Pu, L.; Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Kong, F. Coupling Mechanism of C:N:P Stoichiometry between Plant and Soil after Long-Term Reclamation in the Coastal Area, Eastern China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 68, 103178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Tang, J.; Song, X.-P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Anthropogenic Transformation of Yangtze Plain Freshwater Lakes: Patterns, Drivers and Impacts. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, B.; Wen, Z.; Wu, J.; Xia, J. The Comprehensive Evaluation of How Water Level Fluctuation and Temperature Change Affect Vegetation Cover Variations at a Lake of Ecological Importance (Poyang Lake), China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, R.C.; Robinson, D.T.; Petrone, R. Megaproject Reclamation and Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.-S.; Ge, Z.-M.; Li, S.-H.; Li, Y.-L.; Xie, L.-N.; Tang, J.-W. Reclamation-Induced Tidal Restriction Increases Dissolved Carbon and Greenhouse Gases Diffusive Fluxes in Salt Marsh Creeks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 773, 145684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Sheng, X.; Wang, M.; Wu, M.; Shao, X. Comparative Study of Methane Emission in the Reclamation-Restored Wetlands and Natural Marshes in the Hangzhou Bay Coastal Wetland. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 175, 106473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, S.; Sun, Z.; Wang, H.; Qu, S.; Lei, N.; He, J.; Dong, Q. Tillage Effects on Soil Properties and Crop Yield after Land Reclamation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Gao, S.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.P. Evolution Modeling and Protection Scheme for Tidal Flats under Natural Change and Human Pressure, Central Jiangsu Coast. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF003913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Lu, M.; Jin, H.; Sheng, X.; Wei, H.; Yang, Q.; Qi, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Dou, X. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Environmental Drivers in Different Natural Wetland Regions of China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 330, 121754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zou, X.; Cao, L.; Zhamangulova, N.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, D.; Liu, D. Seasonal and Spatial Dynamics of Greenhouse Gas Emissions under Various Vegetation Covers in a Coastal Saline Wetland in Southeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hussain, S.; Liu, Y.; Mustafa, G.; Hu, B.; Qin, Z.; Wang, X. Responses of Soil Seed Bank and Its Above-Ground Vegetation to Various Reclamation Patterns. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 196, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Wang, K.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, G.; Van Den Bosch, C.K.; Wang, J. Agroforestry Reclamations Decreased the CO2 Budget of a Coastal Wetland in the Yangtze Estuary. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 296, 108212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mei, W.; Yin, Q.; Guan, Y.; Le, Y.; Fu, X. The Variability in CO2 Fluxes at Different Time Scales in Natural and Reclaimed Wetlands in the Yangtze River Estuary and Their Key Influencing Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Han, G.; Xing, Q.; Xia, J.; Sun, B.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Li, D.; Song, W. Changes in Plant Biomass Induced by Soil Moisture Variability Drive Interannual Variation in the Net Ecosystem CO2 Exchange over a Reclaimed Coastal Wetland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2019, 264, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, K.W.; Whitbeck, J.L. Soil Greenhouse Gas Fluxes during Wetland Forest Retreat along the Lower Savannah River, Georgia (USA). Wetlands 2012, 32, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wei, C.; Li, X.; Cui, S.; Zhong, J. New Insight into Blue Carbon Stocks and Natural-Human Drivers under Reclamation History Districts for Sustainable Coastal Development: A Case Study from Liaohe River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Tang, K.W.; Yang, H.; Tong, C.; Zhang, L.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Hong, Y.; Tan, L.; Zhu, W.; Tang, C. Contrasting Effects of Aeration on Methane (CH4) and Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Emissions from Subtropical Aquaculture Ponds and Implications for Global Warming Mitigation. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Pu, L.; Xie, J.; Yao, J.; Qie, L.; He, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhai, J.; Gong, Z.; et al. Carbon Storage in Typical Ecosystems of Coastal Wetlands in Jiangsu, China: Spatiotemporal Patterns and Mechanisms. Catena 2025, 254, 108882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, S. Tracking Annual Changes in the Distribution and Composition of Saltmarsh Vegetation on the Jiangsu Coast of China Using Landsat Time Series–Based Phenological Parameters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 284, 113370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Li, Y. China’s Conservation and Restoration of Coastal Wetlands Offset Much of the Reclamation-Induced Blue Carbon Losses. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Van Vliet, J.; Verburg, P.H.; Pu, L. Land Use Change and Farmer Behavior in Reclaimed Land in the Middle Jiangsu Coast, China. Ocean Coast. Manage. 2017, 137, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Pu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y. Landscape Ecological Security Response to Land Use Change in the Tidal Flat Reclamation Zone, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Meadows, M.; Sun, L.; Wu, T.; Bu, X.; Xu, Y. Differential Effects of Various Reclamation Treatments on Soil Characteristics: An Experimental Study of Newly Reclaimed Tidal Mudflats on the East China Coast. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, J.; Ding, N.; Fu, Q.; Guo, B.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Li, N. The Effect of Long-Term Reclamation on Enzyme Activities and Microbial Community Structure of Saline Soil at Shangyu, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, M. Response of Soil Physicochemical Properties and Enzyme Activities to Long-Term Reclamation of Coastal Saline Soil, Eastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, W.; Ren, W. Characterization of Soil Salinization and Its Driving Factors in a Typical Irrigation Area of Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Ting, W.; Haixia, W.; Min, W.; Xiangping, M.; Siwei, M.; Rui, Z.; Zhikuan, J.; Qingfang, H. Effects of Straw Mulch on Soil Water and Winter Wheat Production in Dryland Farming. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Zhu, M.; Wu, T.; Xu, Y. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Soil Salinity and Sodicity in Agricultural Reclaimed Coastal Wetlands, Eastern China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2020, 66, 1639–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Shangguan, Z. Response of Water Use Efficiency and Plant-Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry to Stand Quality in Robinia Pseudoacacia on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2021, 206, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, L.R.; Wardle, D.A.; Bardgett, R.D.; Clarkson, B.D. The Use of Chronosequences in Studies of Ecological Succession and Soil Development. J. Ecol. 2010, 98, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacosta, J.; Rosenberg, N.; Verma, S. Respiratory Release of CO2 in Alfalfa and Soybean under Field Conditions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1986, 37, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.L.; Mosier, A.R. Improved Soil Cover Method for Field Measurement of Nitrous Oxide Fluxes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapter 7: The Earth’s Energy Budget, Climate Feedbacks, and Climate Sensitivity. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/chapter/chapter-7/ (accessed on 19 May 2025).
- Kucera, C.L.; Kirkham, D.R. Soil Respiration Studies in Tallgrass Prairie in Missouri. Ecology 1971, 52, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armour, K.; Forster, P.; Storelvmo, T.; Collins, W.; Dufresne, J.L.; Frame, D.; Lunt, D.; Mauritsen, T.; Palmer, M.; Watanabe, M.; et al. The Earth’s Energy Budget, Climate Feedbacks and Climate Sensitivity. In Climate Change 2021—The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 923–1054. ISBN 978-1-009-15788-9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Castellano, M.J.; Ye, C.; Zhang, N.; Miao, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, J.; Ding, W. Oxygen Availability Regulates the Quality of Soil Dissolved Organic Matter by Mediating Microbial Metabolism and Iron Oxidation. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 7410–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; Hu, Y.; Weng, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, F.; Lin, W.; Wang, W.; Dong, G.; Yan, D. Drought–Flood Abrupt Alternation Events Increase Soil Nitrogen Loss via Surface Runoff in a Typical Grain Base in China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 60, 102543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Cui, J.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Li, B.; Chang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yao, D. Improving Earthworm Quality and Complex Metal Removal from Water by Adding Aquatic Plant Residues to Cattle Manure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Shi, J.; He, Y.; Wu, L.; Xu, J. Assembly of Root-Associated Bacterial Community in Cadmium Contaminated Soil Following Five-Year Consecutive Application of Soil Amendments: Evidences for Improved Soil Health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, version 2.7-1; 2025. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Munabi, S.K.; Aguti, J.; Nabushawo, H.M. Using the TAM Model to Predict Undergraduate Distance Learners Behavioural Intention to Use the Makerere University Learning Management System. OALib 2020, 07, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Ling, J.; Zhao, D.-Q.; Xu, Y.-P.; Liu, Z.-X.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, S.-L. Deep-Injected Straw Incorporation Improves Subsoil Fertility and Crop Productivity in a Wheat-Maize Rotation System in the North China Plain. Field Crop. Res. 2022, 286, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P.; Preece, C.; Peñuelas, J.; Giri, J. Soil carbon sequestration by root exudates. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglett, K.S.; Inglett, P.W.; Reddy, K.R.; Osborne, T.Z. Temperature Sensitivity of Greenhouse Gas Production in Wetland Soils of Different Vegetation. Biogeochemistry 2012, 108, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Nie, M.; Pendall, E. An Incubation Study of Temperature Sensitivity of Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Three Land-Cover Types near Sydney, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, P.; Lu, P.; Wang, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.-B.; Rao, X.-Q. Greenhouse Gas Fluxes from Soils of Different Land-Use Types in a Hilly Area of South China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 124, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaufler, G.; Kitzler, B.; Schindlbacher, A.; Skiba, U.; Sutton, M.A.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from European Soils under Different Land Use: Effects of Soil Moisture and Temperature. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, P.; Tong, C.; Yang, H.; Tan, L.; Lin, Y.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Tang, K.W. Seasonal Variations in Source-Sink Balance of CO2 in Subtropical Earthen Aquaculture Ponds: Implications for Carbon Emission Management. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Xu, X.; Duan, H.; Qi, T.; Qin, B.; Lee, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, W.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M. Eutrophic Lake Taihu as a significant CO2 source during 2000–2015. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Wen, X.; Yang, F.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Yu, G. Precipitation Frequency Controls Interannual Variation of Soil Respiration by Affecting Soil Moisture in a Subtropical Forest Plantation. Can. J. For. Res. 2011, 41, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, B.C. Soil Structure and Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Synthesis of 20 Years of Experimentation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2013, 64, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, X.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Liang, A.; Jia, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, X. Effect of Soil Temperature and Soil Moisture on CO2 Flux from Eroded Landscape Positions on Black Soil in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2014, 144, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Joshi, A.P.; Ghoshal, P.K.; Ghosh, J.; Akhand, A.; Bhattacharya, T.; Sreeush, M.G.; Valsala, V. Mechanisms and Drivers Controlling Spatio-Temporal Evolution of pCO2 and Air-Sea CO2 Fluxes in the Southern Java Coastal Upwelling System. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2023, 293, 108509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, P.; Tong, C.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Yang, H.; Hong, Y.; Tian, Y.; Tang, C.; Ruan, M.; et al. Effects of Conversion of Coastal Marshes to Aquaculture Ponds on Sediment Anaerobic CO2 Production and Emission in a Subtropical Estuary of China. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 338, 117813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, M.; Tan, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Tan, Y.; Xiao, L.; Xu, Z. Salt-Tolerant Plant Moderates the Effect of Salinity on Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization in a Subtropical Tidal Wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-L.; Ge, Z.-M.; Xie, L.-N.; Li, S.-H.; Tan, L.-S. Effects of Waterlogging and Salinity Increase on CO2 Efflux in Soil from Coastal Marshes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Ball, T.; Conen, F.; Dobbie, K.E.; Massheder, J.; Rey, A. Exchange of Greenhouse Gases between Soil and Atmosphere: Interactions of Soil Physical Factors and Biological Processes. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2003, 54, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Riddle, C.; Congreves, K.A.; Abalos, D.; Berg, A.A.; Brown, S.E.; Ambadan, J.T.; Gao, X.; Tenuta, M. Globally Important Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Croplands Induced by Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.-Z.; Xu, C.; Wu, J.-W.; Huang, J.-S.; Ma, T. Effect of Salinity on Soil Respiration and Nitrogen Dynamics. Ecol. Chem. Eng. S 2013, 20, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, W.; Ma, L.; Guo, H.; Min, W.; Li, Q.; Liao, N.; Hou, Z. Effects of Saline Water Irrigation and N Application Rate on NH3 Volatilization and N Use Efficiency in a Drip-Irrigated Cotton Field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossio, D.A.; Cook-Patton, S.C.; Ellis, P.W.; Fargione, J.; Sanderman, J.; Smith, P.; Wood, S.; Zomer, R.J.; Von Unger, M.; Emmer, I.M.; et al. The Role of Soil Carbon in Natural Climate Solutions. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, H.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, F.; Li, X.; et al. Biochar as a Sustainable Tool for Improving the Health of Salt-Affected Soils. Soil Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, L.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Yang, H.; Tan, L.; Luo, L.; Tong, C.; Hong, Y.; Zhu, W.; Tang, K.W. Landscape Change Affects Soil Organic Carbon Mineralization and Greenhouse Gas Production in Coastal Wetlands. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2022, 36, e2022GB007469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Tong, C.; Yang, H.; Zhu, W.; Sun, D.; Tan, L.; Hong, Y.; Tang, K.W. Variable Responses of Mineral-Bound Soil Organic Carbon to Land Cover Change in Southern China’s Coastal Wetlands. Catena 2024, 242, 108129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Du, Y.; Xu, L.; Hu, J.; Zhu, C. Coastal Reclamation Alters Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics: A Meta-Analysis in China. Catena 2024, 240, 107975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Qian, L.; Dong, H.; Mei, W.; Fu, X.; Hu, Y.; Yan, J.; Sun, Y.; Wu, P.; Chen, X.; et al. The High Organic Carbon Accumulation in Estuarine Wetlands Necessarily Does Not Represent a High CO2 Sequestration Capacity. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Ge, Y.; Sun, L. Effects of Soil Reclamation on the Oat Cultivation in the Newly Reclaimed Coastal Land, Eastern China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 129, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruis, S.J.; Blanco-Canqui, H.; Jasa, P.J.; Jin, V.L. No-till Farming and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes: Insights from Literature and Experimental Data. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.V.; Evers, S.; Aplin, P.; Crout, N.; Dahalan, M.P.B.; Sjogersten, S. Greenhouse Gas Emissions Resulting from Conversion of Peat Swamp Forest to Oil Palm Plantation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, R. Impacts of Changes in Peat Soils Due to Agricultural Activities on Greenhouse Gases (Especially N2O) Emissions and Their Mitigations. Pedosphere 2023, 35, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A. The Contribution of Manure and Fertilizer Nitrogen to Atmospheric Nitrous Oxide since 1860. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zou, J.; Guo, Y.; Gao, Z. Annual nitrous oxide emissions from open-air and greenhouse vegetable cropping systems in China. Plant Soil 2013, 370, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, R.D.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Canary, J.D.; Kaye, J.P. Roots Exert a Strong Influence on the Temperature Sensitivityof Soil Respiration. Nature 1998, 396, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, W.; Peng, K.; Wu, Z.; Ling, Z.; Li, Z. Assessment of the Impact of Wetland Changes on Carbon Storage in Coastal Urban Agglomerations from 1990 to 2035 in Support of SDG15.1. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Song, Z.; Van Zwieten, L.; Guo, L.; Yu, C.; Wang, W.; Li, Q.; Hartley, I.P.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Storage, Patterns and Influencing Factors for Soil Organic Carbon in Coastal Wetlands of China. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 6065–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.W.; Rhymes, J.M.; Jones, D.L. Saltwater Intrusion Induces Shifts in Soil Microbial Diversity and Carbon Use Efficiency in a Coastal Grassland Ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 170, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xia, L.; Zhu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, X.; An, S. Shift in Soil Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Pools in Different Reclaimed Lands Following Intensive Coastal Reclamation on the Coasts of Eastern China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Xu, M. A novel ecological risk assessment approach applied to jiangsu coastal zone, china. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 244, 106815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Zeng, C.; Tong, C.; Chen, G.; Huang, J.; Pan, H.; Peguero, G.; Vallicrosa, H.; et al. The Response of Stocks of C, N, and P to Plant Invasion in the Coastal Wetlands of China. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.-C.; Li, B.-H.; Hu, J.-W.; Ding, X.-J.; Liu, C.-Y.; Yang, G.-P. Tidal Effects on Carbon Dioxide Emission Dynamics in Intertidal Wetland Sediments. Environ. Res. 2023, 238, 117110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Ning, J.; Bi, X. Dynamics of Wetlands and Their Effects on Carbon Emissions in China Coastal Region—Case Study in Bohai Economic Rim. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 87, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Su, J. Development and Management of Land Reclamation in China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2014, 102, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kiran, B.R.; Mohan, S.V. Carbon Farming: A Circular Framework to Augment CO2 Sinks and to Combat Climate Change. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2024, 3, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, F.; Gao, Q.; Tian, X. Carbon Dioxide and Methane Fluxes from Feeding and No-Feeding Mariculture Ponds. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Gao, Q.; Tian, X.; Xiong, Y. Variations in CO2 Fluxes from Grass Carp Ctenopharyngodon Idella Aquaculture Polyculture Ponds. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2015, 8, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Che, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, X.; Shi, X. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Comprehensive Greenhouse Effect Potential of Megalobrama Amblycephala Culture Pond Ecosystems in a 3-Month Growing Season. Aquacult. Int. 2016, 24, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Yang, J.; Gao, P.; Zhang, J.; Jin, W. Determining Minimum Data Set for Soil Quality Assessment of Typical Salt-Affected Farmland in the Coastal Reclamation Area. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 128, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Niu, X. The Yield Increase and Land Improvement Effects of Different Sorghum/Wild Soybean Intercropping Patterns on Reclaimed Coastal Salt Pans. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, X. Warming-Induced Greenhouse Gas Fluxes from Global Croplands Modified by Agricultural Practices: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Abdalla, M.; Xia, L.; Zhou, F.; Sun, W.; Smith, P. Can Cropland Management Practices Lower Net Greenhouse Emissions without Compromising Yield? Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 4657–4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
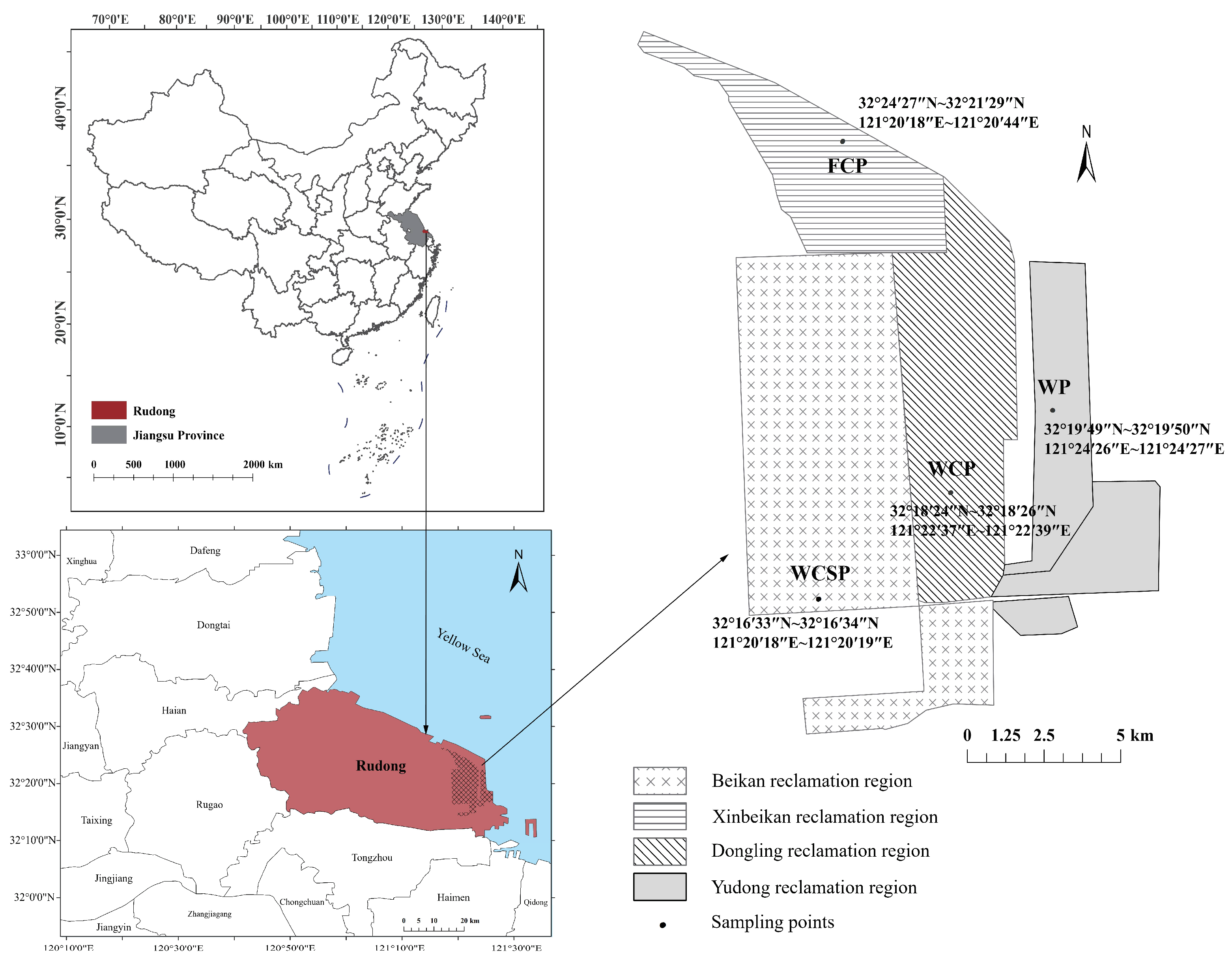
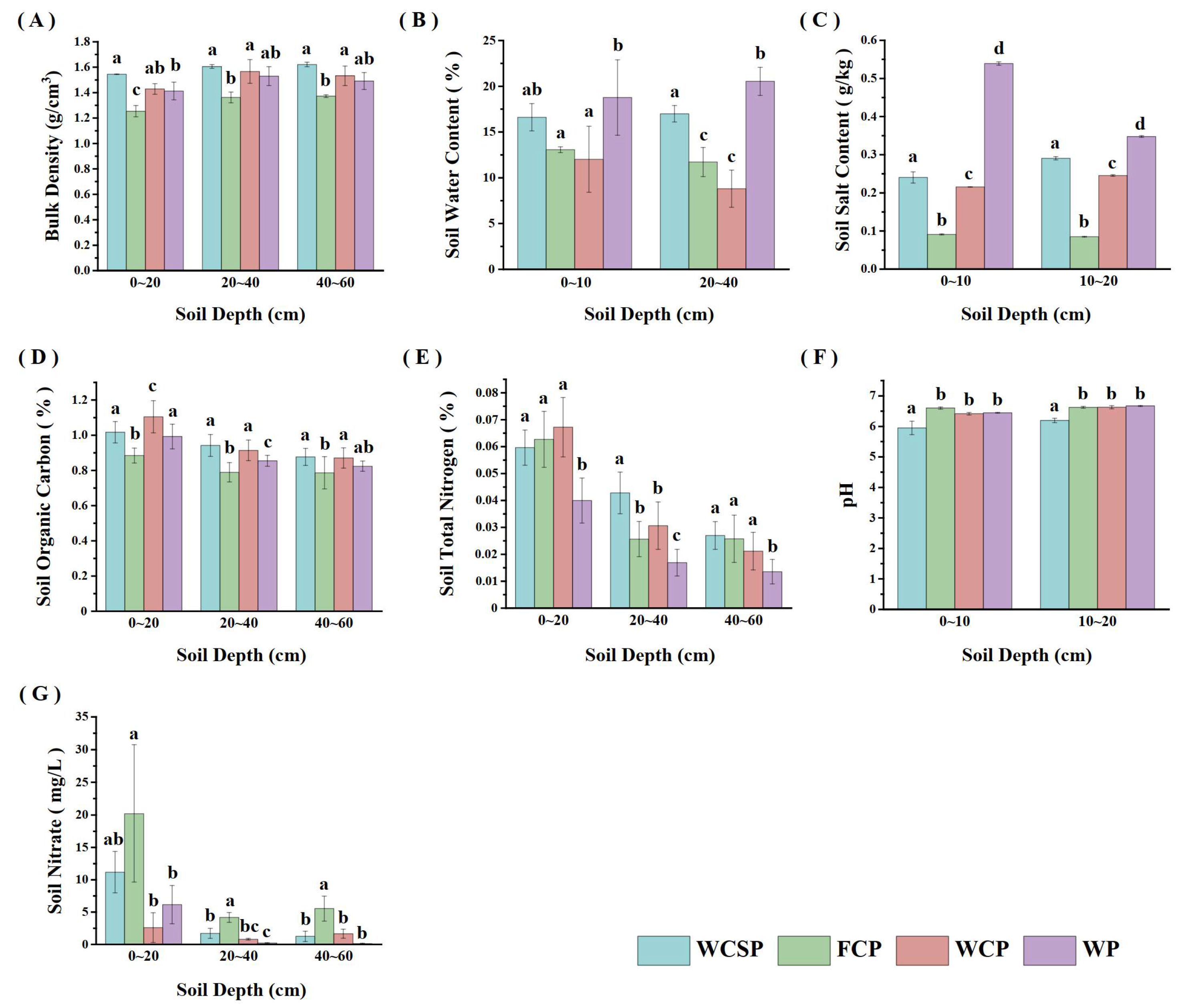
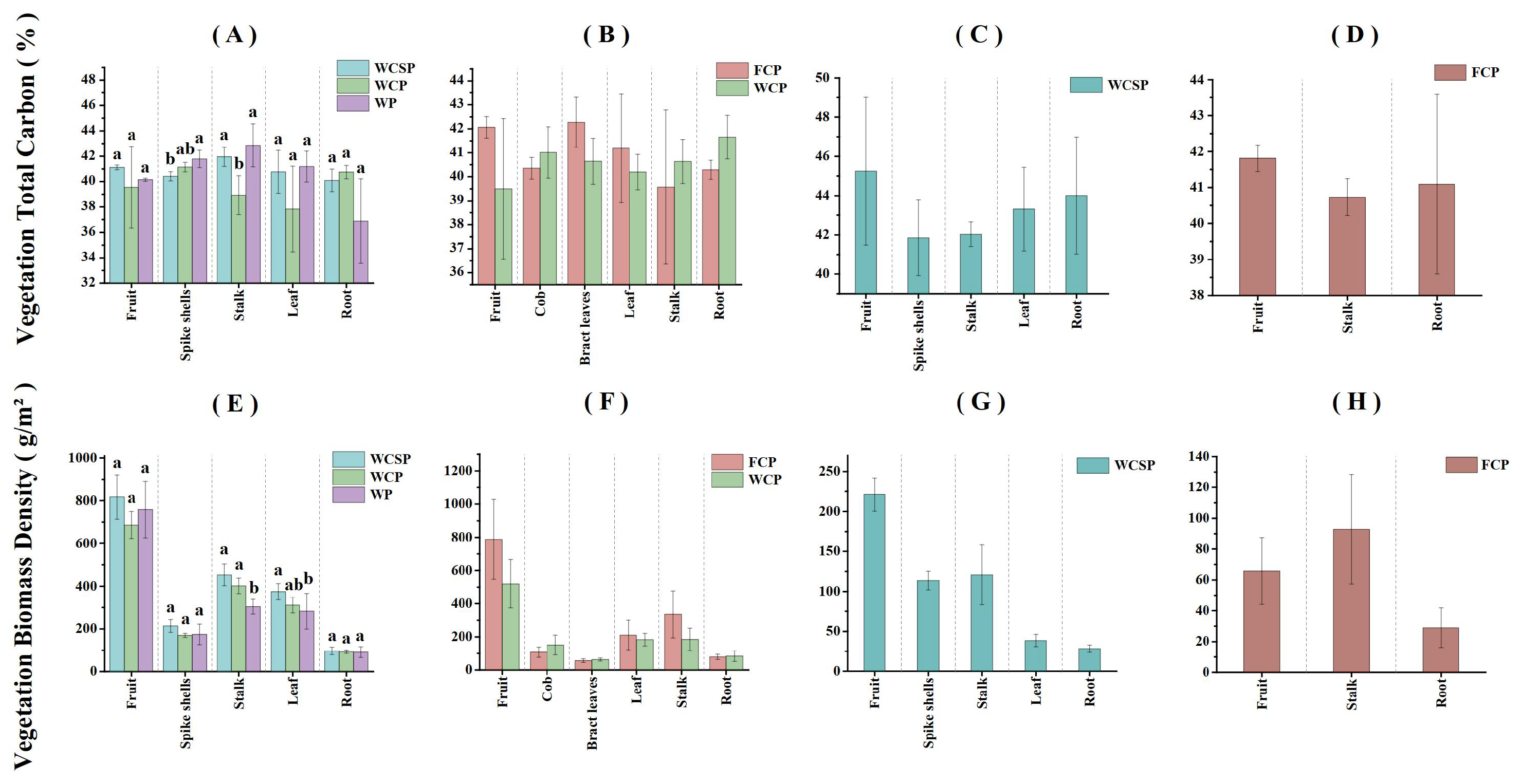
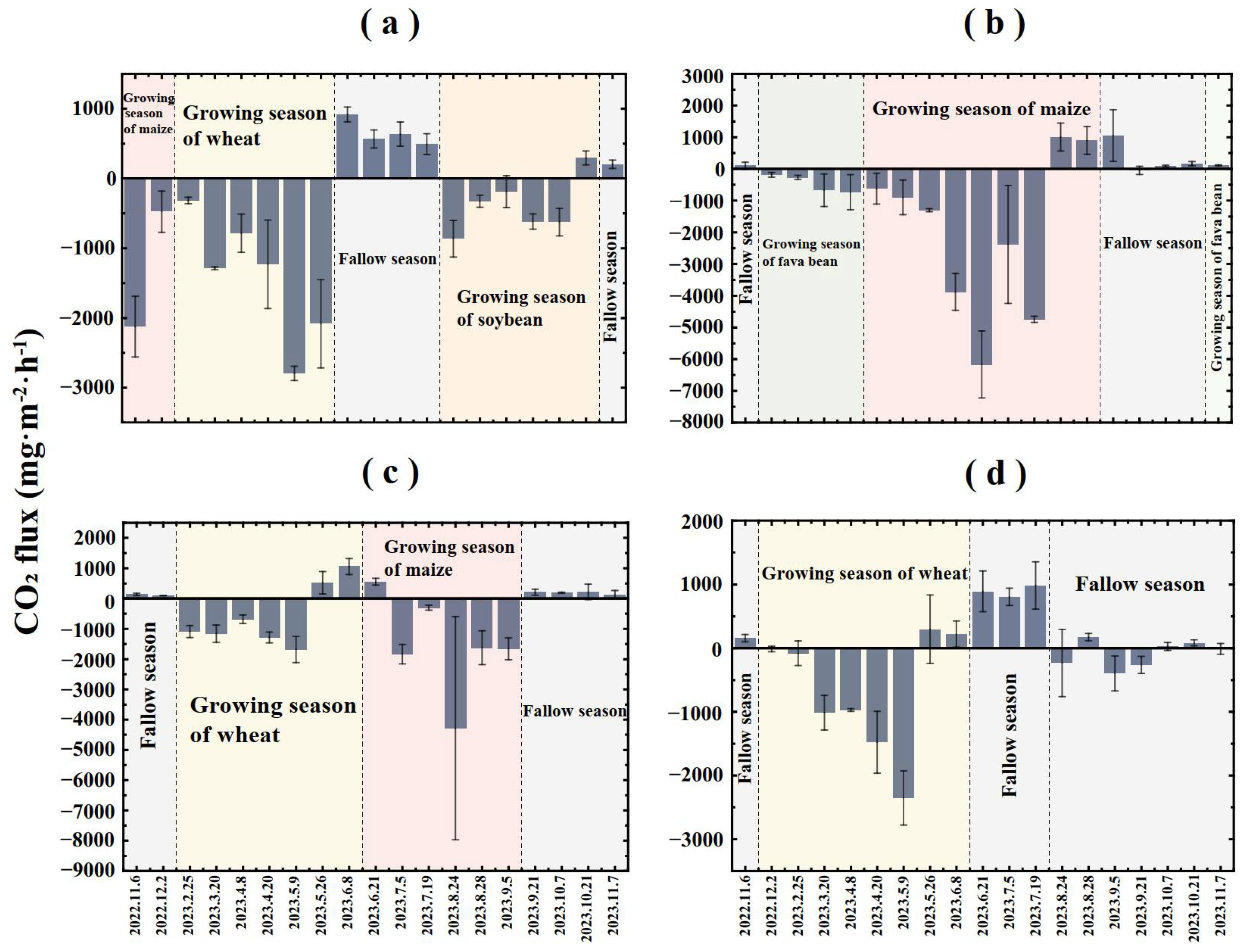

| Site | Reclamation Years | Land Use Planting System |
|---|---|---|
| WCSP | 65 | Wheat–corn–soybean rotational cropping arable land system |
| FCP | 49 | Fava bean–corn rotational cropping arable land system |
| WCP | 41 | Wheat–corn rotational cropping arable land system |
| WP | 16 | Wheat continuous cropping arable land system |
| Plot | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WCSP | FCP | WCP | WP | |
| CO2 | −51,273.55 ± 4746.99 bc | −81,181.77 ± 18,715.87 b | −35,678.02 ± 1086.91 ac | −7446.77 ± 6497.05 a |
| N2O | 1.674 ± 0.598 b | 5.016 ± 0.862 a | 7.329 ± 0.260 a | 0.701 ± 1.032 b |
| GWP | −187,305 ± 17,598.45 cb | −295,577 ± 68,741.63 cb | −127,767.24 ± 4064.92 ab | −27,012.72 ± 33,412.39 a |
| Greenhouse Gas Emission | Period | Plot | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WCSP | FCP | WCP | WP | ||
| CO2 | Fallow period | 180.74 ± 16.43 a | 106.86 ± 35.13 ab | 70.17 ± 83.72 b | 79.00 ± 29.85 b |
| Crop growth period | −424.19 ± 57.21 ab | −542.93 ± 94.27 b | −438.46 ± 97.40 ab | −257.63 ± 64.85 a | |
| N2O | Fallow period | 0.0013 ± 0.0057 b | 0.0120 ± 0.0028 b | 0.0491 ± 0.0201 a | −0.0015 ± 0.0019 b |
| Crop growth period | 0.0147 ± 0.0058 b | 0.0283 ± 0.0075 c | 0.0325 ± 0.0052 abc | 0.0142 ± 0.0042 abc | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, R.; Zhai, J.; Lu, Y.; Tao, J.; Pu, L.; Huang, S. Impact of Coastal Beach Reclamation on Seasonal Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Study of Diversified Saline–Alkaline Land Use Patterns. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131403
Xie J, Yuan Y, Wang X, Zhang R, Zhong R, Zhai J, Lu Y, Tao J, Pu L, Huang S. Impact of Coastal Beach Reclamation on Seasonal Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Study of Diversified Saline–Alkaline Land Use Patterns. Agriculture. 2025; 15(13):1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131403
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Jiayi, Ye Yuan, Xiaoqing Wang, Rui Zhang, Rui Zhong, Jiahao Zhai, Yumeng Lu, Jiawei Tao, Lijie Pu, and Sihua Huang. 2025. "Impact of Coastal Beach Reclamation on Seasonal Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Study of Diversified Saline–Alkaline Land Use Patterns" Agriculture 15, no. 13: 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131403
APA StyleXie, J., Yuan, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, R., Zhong, R., Zhai, J., Lu, Y., Tao, J., Pu, L., & Huang, S. (2025). Impact of Coastal Beach Reclamation on Seasonal Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Study of Diversified Saline–Alkaline Land Use Patterns. Agriculture, 15(13), 1403. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131403






