Abstract
Yellow stunt and root rot causes premature degradation of Astragalus adsurgens grasslands in China. However, the etiological factors underlying livestock poisoning following the ingestion of diseased plants remain elusive. The present study aimed to comprehensively characterize the alterations in toxic substances such as swainsonine and trace element profiles in A. adsurgens after infection with Alternaria gansuense, thereby elucidating the underlying mechanisms of livestock toxicity. Using ELISA and regression analyses, we found that diseased plants had higher selenium levels than the healthy ones, with varietal differences. Selenium in the Zahua variety was higher in healthy plants, while diseased plants of the Henan variety had the highest levels. Moreover, the diseased plants demonstrated decreased levels of iron, zinc, sodium, and magnesium, while manganese and calcium concentrations remained unchanged. Swainsonine was detected in both the healthy and infected specimens of Zhongsha No.1 and Henan varieties, with a marked post-infection increase. In conclusion, swainsonine is the primary toxin causing livestock poisoning, and it is unlikely that soil-accumulated selenium poisons animals. However, potential correlations might exist among the contents of selenium, sodium, and swainsonine. We recommend the cautious use of diseased A. adsurgens as livestock feed.
1. Introduction
Astragalus adsurgens(Pall) is an important perennial legume grass of the Astragalus genus in China. Due to its good yield, high protein content, and high nutritional value, it is used as feed in China [1,2]. It is widely grown in temperate regions of Russia, Mongolia, Japan, South Korea, and North America [1]. It also has excellent characteristics such as drought resistance and cold resistance, and is usually used as a windbreak and sandfixing plant, playing an important role in protecting the ecological environment. Other countries such as the United States believe that A. adsurgens is a poisonous herb, also known as locoweed, which can cause toxicity in livestock after consumption. However, research in China has found that it is a low-toxicity plant and safe for ruminant animals to consume [3,4,5].
Yellow stunt and root rot caused by Alternaria gansuense is a serious systemic disease found among A. adsurgens in China. It is also an important factor contributing to the premature degradation of A. adsurgens grasslands in northern China [6,7]. This fungus was initially named Embellisia astragali, but later, according to Woudenbergs new taxonomic system, the taxonomic status of this fungus was revised, and it was reclassified and named A. gansuense [8,9,10,11].
The symptoms of the disease include the discoloration of stems, wrinkling of leaves, dwarfing and proliferation of branches, decay of roots, and death in severe cases [12]. Previous studies have found that the main factor causing poisoning in livestock after consuming madder is the production of toxic coumarin by endophytic fungi in locoweed. The pathogenic bacterium of yellow stunt and root rot, A. gansuense, is closely related to endophytic fungi in locoweed. Using pellet feed made from healthy and infected A. adsurgens, mice fed with infected A. adsurgens exhibited less weight gain, the content of lactate dehydrogenase and alanine aminotransferase was higher, and the feed utilization rate was lower. Therefore, the toxicity of A. adsurgens was enhanced after infection [8,10,13]. Moreover, there exists a yeast amino acid reductase gene related to the production of coumarin in A. gansuense [8]. The pathogen can also synthesize swainsonine, which makes infected A. adsurgens toxic to animals that ingest it, causing serious effects on animal growth and development. Low doses of swainsonine (SW) may lead to weight loss and biochemical damage, while high doses may cause chronic diseases in livestock after prolonged consumption [14,15].
Current studies have found that SW is an indolizidine alkaloid first identified in Swainsona canescens [16]. In North America and China, this alkaloid is also present in various plants, which can cause locoism [17]. After being ingested by livestock, SW disrupts the synthesis of intracellular glycoproteins, leading to cell death [18]. Long-term intake of SW can cause chronic neurological diseases in livestock, manifesting as mania, infertility, abortion, growth defects, neuropathy, emaciation, etc. [19]. Based on its properties, related genes, or inhibitory effects on glycoprotein synthesis, swainsonine can be detected and studied by using techniques such as an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and chromatographic methods including gas chromatography (GC) and high–performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) [16,20,21]. Although plants with an SW content below 0.004% are safe for sheep, low doses may cause weight loss and biochemical damage, while high doses can lead to chronic diseases in livestock after weeks of consuming SW-containing A. adsurgens or Oxytropis plants [15]. It is currently known that β-ketoacyl synthase (KS) regulates SW synthesis, and the swnK-KS gene has been identified in A. gansuense, though the specific SW content remains undefined [22,23].
In addition to the effects of the secondary metabolite swainsonine in infected plants, A. adsurgens is also a selenium-accumulating plant belonging to the genus Astragalus. Studies have shown that when the content of selenium and selenium compounds in plants is too high, feeding them to animals can also cause poisoning [24]. At present, it is generally believed that seventeen elements are essential elements, including nine macronutrients and eight micronutrients [25]. Mineral elements play a crucial physiological role in plant growth. If a certain element is deficient, the plant cannot grow and develop normally, leading to corresponding physiological diseases. Moreover, an insufficient or imbalanced supply of elements in plants can also influence the occurrence of infectious diseases caused by fungi or bacteria [26,27]. The content of mineral elements can influence plant diseases, mainly reflected in two aspects. Firstly, as components of plants, mineral elements significantly affect the formation and changes in the morphological structure of plant cells, thereby influencing the infection process of pathogens on host plant cells. Secondly, mineral elements participate in and regulate various metabolic reactions in plants, which can affect their disease resistance [28,29,30].
The occurrence of many diseases is directly related to element deficiencies. Applying nitrogen fertilizer to Lolium perenne can accelerate the expansion of Rhizoctonia solani, leading to worsening of the disease [31]. Potassium, like other elements, has a certain effect on improving plant disease resistance. It can coordinate carbon and nitrogen metabolism processes, promote protein synthesis, and therefore increase potassium fertilizer to reduce the content of amino acids in plants, which is beneficial for promoting the synthesis of phenolic compounds in plants and hindering the growth and development of fungal hyphae [32]. A study has found that the application of potassium fertilizer can increase the content of polyphenolic compounds in rapeseed and inhibit the germination of A. brassicae spores, leading to a decrease in the incidence of rapeseed black spot disease [33]. When the ratio of potassium and nitrogen is balanced, the proportion of lemon infected with gummosis decreases [34].
Calcium is an important element in plants’ resistance to fungal or bacterial infections. When pathogens destroy the cell wall of host plants by producing pectinase, which then infects plant cells, Ca2+ can form calcium galacturonate, enhancing cell wall stability and reducing the impact of pectinase on the cell wall. It can also enhance the activity of various enzymes such as catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in plants, thereby improving plant resistance to pathogens [35,36]. Magnesium can inhibit plant diseases, such as Candidatus Liberibacter spp. and A. solani, and promote the occurrence of other plant diseases, such as alfalfa mosaic disease and cotton root rot disease (Phytotrichum omnivorum). Magnesium is also a component of plant cells involved in resistance to pathogens [37].
Trace elements can also be closely related to the occurrence and development of plant diseases by participating in metabolic reactions and affecting enzyme activity. Zinc is an essential element for plant sugar metabolism. The application of zinc fertilizer has no effect on stem rust and stripe rust in winter wheat but significantly reduces the occurrence of Puccinia reconditata. As a component of phenolase, copper can affect the synthesis of phytoalexin, and is also widely used as an effective ingredient in inorganic fungicides. It has been reported that the application of copper elements or the combined application of copper and iron elements will increase the incidence rate of onion white rot disease. On the other hand, the spraying of copper fertilizers can reduce leaf blight among cucurbitaceous crops (Alternaria cucumerina) [38,39]. Boron can regulate the synthesis of various phenolic compounds in plants. In addition, there are reports that applying calcium chloride can alleviate powdery mildew, and the proportion of chlorine in the fertilizer determines its effectiveness against powdery mildew [40,41]. Nevertheless, the potential synergistic effect of trace elements and swainsonine in chronic exposure has not been elucidated.
The objective of this study was to clarify the changes in mineral elements and the content of the toxic substance swainsonine in diseased and healthy plants of different A. adsurgens varieties, and to explore the correlation between mineral elements and swainsonine. These results will help us to gain a deeper understanding of the differences in toxic substance content between diseased plants with yellow stunt and root rot and healthy plants of different A. adsurgens varieties, providing data support for further understanding the disease and preventing its spread.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview and Management of Experimental Site
The tested plants of A. adsurgens were collected from the experimental site of Heping Campus of Gansu Agricultural Vocational and Technical College in Yuzhong County, Lanzhou City. The experimental site is located on the Loess Plateau, with an east longitude of 103.58°, a north latitude of 36.00°, and an altitude of 1750 meters (Figure 1A). It has a temperate continental climate with an average annual precipitation of about 300–400 mm and the soil is yellow loess [42]. The plants were grown in May 2012 using hole sowing, and the field management method comprised irrigation once a year, manual removal of weeds, and no chemical fertilizer [42].

Figure 1.
The location of the sampling sites: (A) The experimental field of A. adsurgens is located at the Heping Campus of Gansu Agricultural Vocational and Technical College in Yuzhong County, Lanzhou City, Gansu Province, China. (B) Plant material samples of A. adsurgens (left: healthy branches; right: diseased branches). (C) The experimental field of 4-year-old A. adsurgens.
2.2. Collection and Preservation of Plant Materials
In October 2015, mature branches of four-year-old A. adsurgens (yellow stunt and root rot high-resistance variety: Zahua; medium-resistance variety: Henan; and low-resistance variety: Zhongsha No.1 and Liaoning Fuxin) were collected. Whole plants were harvested using large flat-bladed shears, leaving a 5 cm basal stubble (Figure 1B,C). From each sampled community, 50 healthy branches and 50 branches with yellow stunt and root rot symptoms (characterized by complete reddish-brown discoloration and confirmed by microbiological testing) were randomly selected (to reduce the errors caused by subsequent measurements). All the branches were individually labeled, sealed in kraft paper envelopes, and transported to the laboratory for further analysis. Upon arrival, the samples were oven-dried at 60 °C for 48 h. The dried branches were pulverized using a mechanical grinder, and the resulting grass powder was transferred into sterile resealable plastic bags. Between samples, the grinder was thoroughly cleaned to prevent cross-contamination. The powdered samples were stored at −20 °C until subsequent analysis.
2.3. Digestion of Grass Samples
All glassware was pre-treated by immersion in 50% nitric acid for 48 h, followed by thorough rinsing with ultrapure water and oven-drying at 105 °C until use. For each sample, 1.0 g of herbal powder was accurately weighed into a digestion tube, and 10 mL of acid mixture (8 mL concentrated nitric acid, 1 mL perchloric acid, and 1 mL concentrated sulfuric acid) was sequentially added [43]. Blank controls containing only the acid mixture were prepared using the same procedure. The digestion system was preheated to 420 °C and equilibrated for at least 15 min before use. With the fume hood activated, the digestion tubes were placed in a heating block, capped, and digested at 420°C for 30 min. After digestion, the tubes were cooled to room temperature and rinsed with ultrapure water, and the contents were quantitatively transferred to a 50 mL volumetric flask, which was made up to volume with ultrapure water [44]. The digested solution was filtered through a 0.44 μm cellulose acetate membrane using a 50 mL syringe, and the filtrate was collected into pre-cleaned and dried amber glass vials. All the samples were stored at 4 °C pending analysis, and four technical replicates were performed for each sample.
2.4. Isolation and Cultivation of A. gansuense
Yellow stunt and root rot is a systemic disease of A. adsurgens characterized by the yellowing and necrosis of leaves, browning of petioles, stems turning from brown to black, overgrowth of tender branches, dwarfism of the entire plant, root rot, and plant death, especially in the age range of 2–8 years, causing serious harm [6]. Therefore, the 4-year-old A. adsurgens displayed symptomatic branches that were completely reddish-brown in color. A 4–5 cm segment of the rhizome was excised, rinsed under running tap water, and transferred to a sterile Petri dish on a clean bench (Suzhou Jinhua SJ-CJ-Bμ, Suzhou, China). Surface sterilization was performed via sequential immersion in 70% ethanol for 30 s (ethanol discarded into a designated waste container) followed by 1% sodium hypochlorite solution for 1 min, and triple rinsing with sterile deionized water [12]. Excess moisture was blotted using autoclaved filter paper, and these steps were all completed in the laminar flow hood. After longitudinally cutting the sterilized rhizome into several small pieces with a sterile surgical knife, we transferred the rhizome medulla tissue aseptically onto potato dextrose agar (PDA) plates. The plates were incubated in a low-temperature incubator (Panasonic MIR-554-PC, Osaka, Japan) at 22°C in darkness for 7 days [45]. Pure cultures (strain LYZ0001) were obtained via hyphal tip isolation from colony margins on fresh PDA plates.
For A. gansuense sporulation, the cultures were maintained on PDA for 4 weeks [8,12,45]. Single-spore isolation was performed under a stereomicroscope (Olympus SZ51, Tokyo, Japan) that had been disinfected, using flame-sterilized forceps, in a laminar flow hood to ensure a sterile environment. Fruiting bodies were located microscopically, transferred to fresh PDA plates, and gently streaked to release spores. Ten replicate plates were prepared. After 48 h of incubation, germinated spores were individually picked with a fine sterile inoculation needle and transferred to separate PDA plates (10 replicates) [9]. After 14 days of incubation at 22 °C in the dark, the highly active peripheral part of LYZ0001D mycelia was selected, transferred to 2 mL of sterile water, homogenized, and inoculated into a 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 100 mL of potato dextrose broth (PDB). The cultures were incubated in the dark at 22 °C on an orbital shaker (Shanghai Sukun NSKY-2102C, Shanghai, China) at 150 rpm for 20 days [8]. The harvested mycelia were filtered, blotted dry with autoclaved filter paper, and stored at −80 °C in sterile microcentrifuge tubes.
2.5. Determination of Selenium Content
The digestion test solutions of the grass powder obtained above were transferred to 10 mL centrifuge tubes and arranged in sequence on a tube rack. Selenium standard solutions at concentrations of 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 μg/L were prepared using 8% nitric acid as the matrix-matched diluent. All the samples and standards were analyzed using a Thermo Scientific iCAP Q ICP-MS system (Shanghai, China). Instrumental parameters were optimized as follows: extraction voltage of 120 V, radio frequency (RF) power of 1400 W, carrier gas flow rate of 1.05 L/min, and nebulizer temperature of 2 °C. Each sample was measured in triplicate with automatic internal standardization. Prior to analysis, the instrument was calibrated using a multi-point standard curve (R2 ≥ 0.999), and daily performance verification was conducted with certified reference materials [46].
2.6. Determination of Mineral Elements
We diluted 2.5 mL of standard solutions for copper (Cu), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), and magnesium (Mg) elements, made up to volume in a 50 mL volumetric flask. Dilution was carried out step by step according to the concentration gradient; we injected the sample from low to high according to the measurement conditions of different elements, and obtained a qualified standard curve [47]. When preparing magnesium, we first prepared a 50 mg/mL strontium chloride solution, added 5 mL of strontium chloride solution to the magnesium element solution, and then made a series of concentration gradient standard solutions with a constant volume. When preparing the standard curve of magnesium, strontium chloride can reduce the interference effect of other elements [48]. We placed the prepared test solutions in the corresponding element determination conditions, as shown in Table S1 in order of numbering, and then directly injected them into the atomic absorption spectrophotometer (Thermo, S SERIES, Waltham, USA). We recorded the absorbance values of each sample and substituted them into the standard curve equation to calculate the content. Due to the high concentrations of calcium and magnesium in the sample solutions, they were diluted 25 and 100 times, respectively, before measurement.
2.7. Preparation for Determination of Swainsonine
The plant materials consisted of the aforementioned prepared grass powder, including the disease-resistant cultivar Henan, the low-resistance cultivar Zhongsha No.1, and plants of an undetermined cultivar collected from severely diseased specimens. The microbial material comprised the previously obtained A. gansuense mycelium. The prepared instruments include weighing bottles, mortars, beakers, volumetric flasks, pipettes, 96-well ELISA plates (Bunsen Health Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), precision air-drying ovens (Shanghai YiHeng Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd., DHG-9030, Shanghai, China), a Powerwave XS full-wavelength enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analyzer (Thermo, Scientific Multiskan SkyHigh, Waltham, USA), an ultrasonic cleaning machine (Ningbo Xinzhi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., SB-5200D, Ningbo, China), and a centrifuge (Thermo, Sorvall™ MTX-150, Waltham, USA). The reagents include acetic acid, methanol, boric acid (analytical pure), swainsonine standard solution (provided by the College of Veterinary Medicine, Northwest A&F University), α-mannosidase, and p-nitrophenyl-α-D-mannosidase (SUPELCO) [49]. The ELISA protocol for detecting α-mannosidase activity was adapted from standard ELISA procedures to ensure accurate quantification of enzyme activity in plant and microbial samples.
2.8. Sample Processing
First, we placed the grass powder in a sterilized centrifuge tube and freeze-dried it for 48 h to remove moisture. We weighed out 100 mg of dried grass powder, which was ground into a fine powder using a grinder machine, and transferred it to a dry and sterilized centrifuge tube. We added 5 mL of acetic acid and sonicated the mixture at 60 °C for 30 min [50,51]. Then, we performed centrifugation at 5000 r/min for 15 min before collecting the supernatant and placing it in a small, clean beaker. We added the same volume of acetic acid again and repeated the previous step: centrifugation at 5000 r/min for 15 min, collecting the supernatant, and repeating this process twice. We placed the supernatant in the same small beaker for all three replicates. Then, the extraction solution was evaporated to obtain a residue, which was dissolved via evaporation in an appropriate amount of methanol and underwent centrifugation at 12000 r/min for 10 min. We discarded any remaining solid residue, diluted it to 10 mL with chromatography pure methanol, and stored it in a refrigerator at 4 °C for subsequent analysis.
2.9. Drawing and Measurement of the Standard Curve for Swainsonine
The preparation of the swainsonine storage solution (1000 µg/mL) was as follows: We weighed 10 milligrams of swainsonine standard solution and dissolved it in 10 milliliters of chromatographically pure methanol. We prepared a series of swainsonine standard solutions with 9 concentration gradients using the stock solution. A total of 40 µL of each swainsonine standard solution at different concentrations was added into individual wells of a 96-well plate, ensuring three replicates for each concentration. Additionally, we employed a blank control and a negative control simultaneously. We added 50 µL of substrate solution (20 mmol/L p-nitrophenyl-α-D-mannoside solution) and 50 µL of buffer solution (pH = 4.5) to each well, gently shaking the plate to ensure thorough mixing, and incubated the wells in a 37 °C oven for 1 h. After incubation, we added 20 µL (0.025 μg/mL) of alphaglucosidase solution to each well, gently shaking each well, and incubating them again in a 37 °C oven for 1 h. Following this, we added 100 µL of reaction termination solution to each well, gently shaking them to ensure homogeneity. We immediately measured the absorbance values at a wavelength of 405 nm using a microplate reader. We calculated the inhibition rate and plotted a standard curve with the concentration of the swainsonine standard solution on the horizontal axis and the inhibition rate of swainsonine on α-mannosidase on the vertical axis. Finally, we obtained a regression equation for calculating sample content [52].
A total of 40 μL of the sample solutionswas usedfor testing and added to a 96-well plate. We performed 3 replicates for each sample at the same time. We added 50 μL of buffer solution and substrate solution to each well, gently shaking each well, and incubated them in a 37 °C oven for 1 h. We added 20 μL of alphamannosidase solution to each well, gently shook them, and incubated the wells at 37 °C for 1 h. We added 100 μL of termination solution to each well to complete the reaction, mixed them well, and measured the absorbance value of each well solution at a wavelength of 405 nm. According to the regression equation obtained in the previous step, we substituted the calculated inhibition rate of α-mannosidase for each sample into the equation, calculated the concentration of swainsonine in the sample solutions, and converted it to obtain the swainsonine content in the grass sample [49].
2.10. Statistical Analysis
A t-test was used to evaluate the mineral elements in the healthy and diseased plants. Two-way ANOVA was employed to assess the impacts of variety and healthy/diseased status on mineral elements. A regression analysis was conducted to explore the relationship between mineral elements and swainsonine. All the statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 26.0 for Windows, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05. Data plotting was carried out using Origin version 24, and spatial distribution maps were drawn with ArcGIS 10.7.
3. Results
3.1. Determination Results of Selenium Content
After the occurrence of yellow stunt and root rot, the selenium content in the plants of A. adsurgens significantly increased compared to healthy plants (p < 0.01) (Figure 2). The selenium content in the healthy A. adsurgens plants ranged from 0.192 to 0.367 mg/kg, while the selenium content in the diseased plants ranged from 0.748 to 1.109 mg/kg. The selenium content in different varieties of A. adsurgens also varied. Before disease onset, the selenium content in the mixed flowers was significantly higher than that in Zhongsha No.1 (p < 0.05). Following disease onset, the selenium content in Henan was significantly higher than that in Zahua and Zhongsha No.1 varieties (p < 0.05) (Table 1). The analysis shows that there was an extremely significant effect of healthy and diseased status on selenium content in the same variety of plant (p < 0.001), and that the variety also had a significant effect on selenium content (p < 0.05). The interaction between the two had an effect on selenium content, slightly stronger than the effect of plant variety (p < 0.01).

Figure 2.
The differences in selenium content between healthy and diseased plants of different varieties of A. adsurgens. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences between the diseased and healthy plants. “HD” represents healthy or diseased; “V” represents variety; “HD × V” represents the interaction between the two.

Table 1.
Selenium content in various varieties of A. adsurgens (mg/kg).
3.2. Standard Curves for Other Mineral Elements
The standard curve regression equations for the seven tested mineral elements are shown in Table 2, and the linear correlation coefficients of all the regression equations are greater than 0.995. We measured the absorbance values (Abs) of each element in the samples, input them into the regression equation of the standard curve, and obtained the concentrations of each mineral element in the sample solutions. Based on the total volume of the solutions and the mass of each grass sample taken during the experiment, we calculated the content of various mineral elements in each sample of A. adsurgens.

Table 2.
Regression equation for concentration gradient and standard curve of each element standard solution.
3.3. Element Content
Six mineral elements were measured in diseased and healthy plants of different varieties of A. adsurgens, but no copper was detected. The copper content in A. adsurgens did not reach the minimum detection limit of the atomic absorption spectrophotometer. The following details the specific results (Table 2).
The calcium content in the plants that were not infected with yellow stunt and root rot was 3366.83–4925.83 mg/kg, while the content in the diseased plants ranged from 3363.16 to 4213.55 mg/kg. The calcium content increased after disease onset in the Liaoning Fuxin and Henan varieties, while the content decreased after disease onset in the Zahua and Zhongsha No.1 varieties. Moreover, when comparing calcium content in healthy and diseased plants of the same variety, plants of the Henan variety showed a significant increase in calcium content (p < 0.05) (Figure 3A). There was no statistically significant difference in calcium content between healthy and diseased plants of the remaining varieties (Table 3).

Figure 3.
Comparison of mineral element contents between healthy and diseased plants of different A. adsurgens varieties: (A) differences in calcium content, (B) iron content, (C) magnesium content, (D) manganese content, (E) sodium content, and (F) zinc content between healthy and diseased plants of same variety. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences in elemental contents between healthy and diseased plants. “HD” represents healthy or diseased status; “V” represents variety; “HD × V” represents interaction between two factors.

Table 3.
Mineral element content in healthy and diseased plants of different varieties of A. adsurgens (mg/kg).
The iron content in the healthy plants ranged from 63.57 to 198.88 mg/kg, while the content in the diseased plants ranged from 53.75 to 135.26 mg/kg, showing an overall downward trend. However, the content in the Liaoning Fuxin varieties increased after disease onset. The comparison within the same variety shows that the iron content significantly decreased in the diseased plants of Zahua and Zhongsha No.1 (p < 0.05) (Figure 3B). The comparison between varieties shows that the iron content in the plants of A. adsurgens without yellow stunt and root rot was significantly higher in Zhongsha No.1 than in the Henan and Liaoning Fuxin varieties. In the case of disease onset, the iron content in Liaoning Fuxin was significantly higher than that in the other three varieties (p < 0.05) (Table 3).
The magnesium content in the healthy A. adsurgens plants ranged from 1902.82 to 2601.19 mg/kg, while the magnesium content in the diseased plants ranged from 1523.38 to 2288.30 mg/kg. After being infected with yellow stunt and root rot, the magnesium content in all four varieties of A. adsurgens decreased. The comparison within the same variety shows that the magnesium content in Zahua decreased significantly after disease onset (p < 0.05) (Figure 3C). There was no significant difference in magnesium content among different varieties when healthy. In the case of diseased plants, there was a significant difference in magnesium content among different varieties (p < 0.05), with Henan having the highest content and Zhongsha No.1 having the lowest (Table 3).
The content of manganese in the healthy plants was 17.24–23.73 mg/kg, and the content in the diseased plants was in the range of 15.00–24.51 mg/kg. The comparison within the same variety shows that the manganese content in both Zahua and Zhongsha No.1 decreased significantly after disease onset (p < 0.05) (Figure 3D). In terms of varieties, there was no significant difference in the manganese content among different varieties when healthy. In the case of the occurrence of yellow stunt and root rot, the manganese content in the plants of the Henan and Liaoning Fuxin varieties was significantly higher than that in the mixed-flower variety and Zhongsha No. 1 varieties (p < 0.05) (Table 3).
The sodium content in the plants that were not infected with yellow stunt and root rot was 624.14–846.43 mg/kg, while the sodium content in the affected plants ranged from 397.72 to 741.06 mg/kg. Except for Henan, the sodium content of the other three varieties sharply decreased after the occurrence of yellow stunt and root rot (p < 0.05) (Figure 3E). In terms of variety, the sodium content of the healthy plantsof Liaoning Fuxin was significantly higher than that of Zhongsha No.1 (p < 0.05). In the case of diseased plants, the content in the Henan plants was significantly higher than that in the other three varieties (p < 0.05) (Table 3).
The zinc content in the plants that were not infected with yellow stunt and root rot was 7.58–13.60 mg/kg, while the zinc content in the diseased plants ranged from 8.16 to 11.41 mg/kg. The comparison within the same variety shows that the zinc content in both Henan and Zahua decreased significantly when diseased (p < 0.05) (Figure 3F). In terms of variety, the zinc content in both the healthy and diseased plants was significantly lower in Henan and Zahua (p < 0.05) (Table 3).
To sum up, the disease condition had an effect on calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, and sodium content, among which the effects on iron and magnesium were the most significant (p < 0.001), and the effects on the others were relatively weak. The analysis shows that variety had a significant effect on iron and zinc content, especially iron (p < 0.001), with little effect on the other elements. The interaction between the two had an effect on calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, and sodium content, among which the effects on iron and magnesium were the most significant (p < 0.001), and the effect on zinc was minimal (Figure 3).
3.4. Results of Swainsonine Test
The regression equation of the standard curve fitted based on nine concentrations of standard solutions was y = 0.3243x − 0.2276, with a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.9984 (Figure S1). Using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, swainsonine was detected in both the infected and uninfected A. adsurgens, with a concentration ranging from 22.13 to 128 mg/kg. The content of swainsonine in the healthy plants ranged from 22.13 to 27.91 mg/kg, while in the diseased plants it ranged from 81.86 to 128.00 mg/kg. After infection with yellow stunt and root rot, the content of swainsonine in Zhongsha No.1 increased by 193%, and the swainsonine content in Henan increased by 329% (Figure 4). Furthermore, we observed that A. gansuense can also produce swainsonine, with a content of 55.02 mg/kg. In summary, the effect of disease on swainsonine content in A. adsurgens was extremely significant (p < 0.001), while the effects of variety and the interaction between disease and variety were minimal.

Figure 4.
A comparison of the swainsonine content in healthy plants and diseased plants of different varieties of A. adsurgens. In the figure, plants labeled with different letters show significant differences (p < 0.05). “HD” represents healthy or diseased status; “V” represents variety; “HD × V” represents the interaction between the two.
3.5. The Correlation Between Swainsonineand Elements
As shown in Figure 5E,F, there was a significant negative correlation between swainsonine content and sodium content (p < 0.05), while there was an extremely significant positive correlation between swainsonine content and selenium content (p < 0.001). In addition, there was no significant correlation between swainsonine and the other elements.
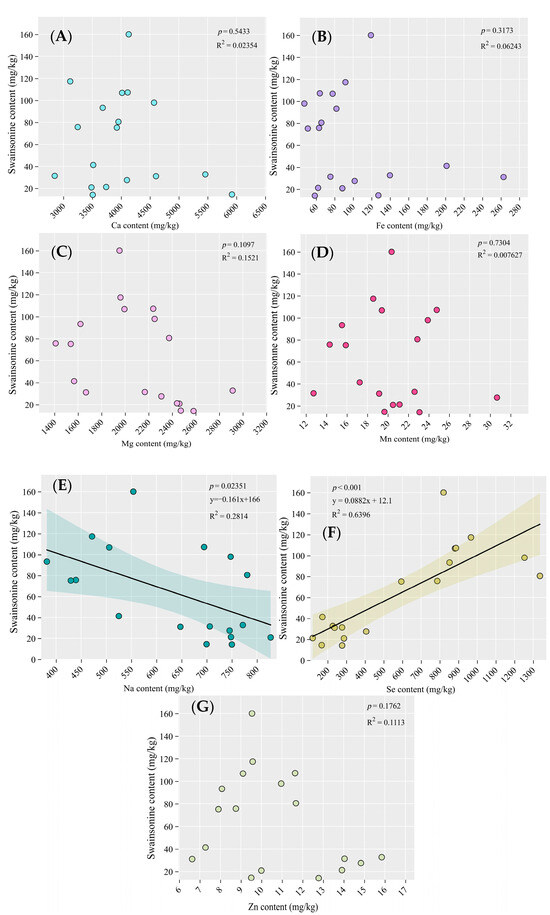
Figure 5.
The correlation between swainsonine and mineral elements: (A) the correlation between Ca (B) Fe, (C) Mg, (D) Mn, (E) Na, (F) Se, and (G) Zn content and swainsonine. Significance level: p < 0.001 indicates an extremely significant difference; p < 0.05 indicates significance.
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in Selenium Content of Diseased Plants and Its Impact on Livestock Feeding
Selenium is an essential trace element for humans and animals, significantly influencing the activity of over thirty enzymes in organisms [53]. However, selenium exhibits a dualistic nature. When selenium is deficient, it can lead to decreased human immunity and malnutrition and trigger diseases such as hepatic necrosis, Keshan disease, and Kaschh-Beck disease [54,55]. In animals, selenium deficiency may cause white muscle disease, reduced immunity, and stunted growth [56]. Conversely, excessive selenium intake can also lead to poisoning in both humans and animals. The risk level for acute selenium poisoning in animals is 2–5 mg/kg bodyweight via a single ingestion [57,58]. Selenium in natural plants is usually divided into two types: organic selenium and inorganic selenium. Notably, organic selenium constitutes the predominant proportion, accounting for approximately 80% of the total selenium content. This organic fraction encompasses various bioactive compounds, including selenoproteins, selenium-containing nucleic acids, and selenium polysaccharides, which exhibit superior bioavailability and are more readily assimilated by the animal digestive system compared to their inorganic counterparts. Organic selenium constitutes approximately 80% of the total selenium content and is more readily absorbed by animal digestive systems [59]. In general plant species, the selenium concentration typically ranges from 0.05 to 1.50 ppm. However, selenium hyperaccumulator plants exhibit remarkably elevated selenium concentrations, reaching several thousand ppm. Notably, certain species within the Astragalus genus demonstrate exceptional selenium accumulation capacity, with concentrations ranging from 1000 to 10000 ppm [60,61]. These hyperaccumulators efficiently absorb selenium from soil and tolerate high selenium levels. However, excessive selenium accumulation in plants may produce foul odors, rendering forage unpalatable. The direct consumption of such plants by animals can cause acute selenium poisoning. In regions with declining soil selenium, plants may convert selenium into bioavailable forms, leading to chronic selenium toxicity in animals through the food chain [62]. As early as 1295, it was recorded in the book of Marco Polo that in the ancient Suzhou (now Hexi Corridor) area in China, horses were found to have symptoms of hair loss and muscle loss, which is generally believed in the academic community to be the earliest recorded instance of selenium poisoning in animals [56]. Some researchers have hypothesized that the toxicity observed in certain Oxytropis species within China’s Hexi Corridor region may be attributed to excessive selenium accumulation. However, analytical data show that selenium content in Oxytropis glabra ranges from 0.052 to 0.174 ppm, and Oxytropis ochrocephala contains 0.058–0.078 ppm, both below the risk threshold for selenium poisoning among animals [63,64]. Thus, the toxicity of Astragalus and Oxytropis species is unlikely attributable to high selenium levels.
In this study, the selenium content in plants was determined by ICP-MS. The selenium content in healthy A. adsurgens ranged from 0.192 to 0.367mg/kg, whereas that in the plants affected by yellow stunt and root rot ranged from 0.748 to 1.109 mg/kg. Therefore, the occurrence of disease can lead to an increase in selenium content in A. adsurgens. The total selenium content in the surface soil of Lanzhou City is 0.179 ± 0.066 mg/kg, which is at a moderate level compared to the national soil selenium content. Meanwhile, the soil selenium content in Yuzhong County is relatively high. In Heping Town, where the experimental site is located, the soil selenium content is 0.157 ± 0.021 mg/kg [65,66]. According to the comparison between the selenium content in soil and that in A. adsurgens, plants have a certain enrichment effect on selenium, and the enrichment effect is more pronounced after infection with yellow stunt and root rot. However, the mechanism by which diseases increase the content of mineral elements in plants is still unclear.
We found that the reason for the increase in selenium content in the diseased plants may be related to the decrease in the dry weight of the plants after disease onset. The dry weight of the healthy plants was approximately 67.20 g per plant, while the average dry weight of all the diseased plants was 51.24 g per plant, a decrease of 23.75%. The single weight of the plants with partially stunted branches was 46.30 g, a decrease of 31.10% compared to before [12]. The decrease in dry weight per plant led to an increase in the proportion of selenium, but this conclusion still needs further verification.
When the selenium content in feed exceeds 5 ppm, long-term consumption can cause chronic poisoning. At 10–25 ppm, it can cause acute poisoning in most animals [62]. The selenium content in the healthy plants did not reach the level of animal poisoning. After infection with yellow stunt and root rot, the selenium content in A. adsurgens increased, with the highest exceeding 1 ppm. However, this level of selenium content in A. adsurgens will not cause poisoning in animals after consumption.
4.2. Alterations in the Concentrations of Other Mineral Elements in Diseased A. adsurgens
After infection with yellow stunt and root rot, other elements in A. adsurgens showed little change, such as manganese. The calcium content decreased, but the difference was not significant. The contents of iron, zinc, sodium, and magnesium all decreased significantly (p < 0.05). After studying the nutritional substances of infected and healthy plants, it was found that the content of soluble sugars and calcium in plants significantly decreased (p < 0.05) after infection [12]. The decrease in the content of most mineral elements may be related to the root rot of A. adsurgens. After disease onset, the ability of plants to absorb mineral nutrients from the soil through their roots decreases, and the mineral element content in the aboveground part also decreases as a result.
4.3. The Influence of Changes in Swainsonine Content of Diseased Astragalus adsurgens on Livestock and Its Correlation with Mineral Elements
Swainsonine was detected in A. adsurgens and A. gansuense infected with yellow stunt and root rot. The content of swainsonine in healthy A. adsurgens was 0.002–0.003%, while that in the diseased plants was 0.008–0.013%, and the content in A. gansuense was approximately 0.006% [67]. This is consistent with the results of previous studies that proved the existence of the β-ketoacyl synthase (KS) gene in A. adsurgens and detected the production of swainsonine [22].
The content of swainsonine in locoweed varies from less than the detection limit (0.001%) to more than 0.2%. The difference in content is related to a variety of factors. The content of swainsonine varies greatly between different locoweed species; for example, the average content of swainsonine in A. adsurgens is less than 0.001%, while the content in A. mollissimus is higher than 0.1%. There are differences in swainsonine content between different populations of the same locoweed species due to environmental factors [68,69]. The swainsonine content in the same locoweed species in the same habitat is different in different plants and in different parts of the same plant. The root contains less swainsonine than the stem and leaf. For example, the content of swainsonine in the aboveground part of Oxytropis sericea is nearly 10 times higher than that in the underground part. The content of swainsonine in different parts of plants at different growth stages also varies [70]. These distribution changes provide an important basis for further study of swainsonine in A. adsurgens.
A. adsurgens containing swainsonine is similar to locoweed and can cause animal poisoning. Locoweed feeding trials have shown that when sheep were fed with O. kansuensis powder at a daily dose of 8–10 g per kilogram of bodyweight, they showed poisoning symptoms within 20–25 days and died after 56 days [71]. However, when the same O. kansuensis powder and dose were used but administered once every two weeks, the sheep did not show poisoning symptoms [72]. The swainsonine content in these O. kansuensis plants was approximately 0.021%. The swainsonine content in O. ochrocephala is slightly lower, at 0.012%, and the symptoms of poisoning in sheep during feeding trials were milder [71,73,74]. When the swainsonine content in locoweed reaches 0.001% or higher, livestock consuming 2% of their bodyweight in locoweed daily will be poisoned. Low swainsonine content or reduced intake may lead to weight loss but will not cause neurological poisoning [15,70]. Moreover, previous studies have proven that A. adsurgens infected by A. gansuense is toxic to mice, and the infection can increase in toxicity [75]. A. adsurgens severely affected by yellow stunt and root rot may contain 0.001% swainsonine. However, diseased A. adsurgens are stunted, with reduced biomass and poor palatability. Therefore, under natural conditions, it is unlikely that livestock will consume only diseased A. adsurgens. The likelihood of severe poisoning in livestock is relatively low. Additionally, when feeding livestock with healthy A. adsurgens, the amount should also be appropriate.
In this study, it was found that there is a significant negative correlation between swainsonine content and sodium content (Figure 5E), while there is an extremely significant positive correlation between swainsonine content and selenium content (Figure 5F). Therefore, we believe that the increase in the content of swainsonine may be related to the decrease in sodium in A. adsurgens, and it is closely associated with the increase in selenium. Whether the causes of the disease and the increase in toxins are directly related to the amounts of these two elements still requires further exploration.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we investigated the toxic substances (selenium and swainsonine) in A. adsurgens infected by A. gansuense for the first time and preliminarily concluded that the selenium enriched in infected A. adsurgens cannot cause animal poisoning. However, in the case of continuous feeding for multiple days, swainsonine in A. adsurgens can easily cause animal poisoning. Therefore, the main reason for the pathological changes in mice during the feeding experiment may be swainsonine. A. adsurgens with yellow stunt and root rot may contain more than 0.001% swainsonine, which can easily lead to poisoning when animals feed on it for a long time. Therefore, caution should be exercised when using infected A. adsurgens to feed livestock in animal husbandry production. Our paper provides guidance for the subsequent feeding of livestock with A. adsurgens. In addition, the contents of the mineral elements sodium and selenium identified in our study are closely related to the amount of swainsonine, which may also provide reference value for the subsequent prevention and control of yellow stunt and root rot.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agriculture15131401/s1, Figure S1: Standard curve for the determination of swainsonine content; Table S1: Mineral element determination conditions.
Author Contributions
H.L. conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, resources, software, supervision, validation, visualization, writing—original draft, and writing—review and editing. Y.L. conceptualization, data curation, software, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, validation, and writing—original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Forestry and Grassland Administration (20220104) and the Earmarked Fund for CARS (CARS-34).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the Heping Farm of Gansu Vocational College of Agriculture for providing the experimental plots. In addition, we also appreciate the assistance of the Testing Center of North Minzu University and Gansu University of Chinese Medicine in the determination of swainsonine content and the measurement of mineral elements.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sun, Q.Z.; Gui, R.; Na, R.S.; Nada, M.D.; Zhai, Z.H. Study on productivity of Astragalus adsurgens Pall. with different growth periods. Grassl. China 1999, 5, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lei, Z.Y.; Feng, X.Q. Gas Chromatographic Determination of Trace 3-Nitropropionic Acid in Astragalus adsurgens. Grassl. China 1992, 3, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Su, S.F. Revisiting the Forage Utilization Issues of Astragalus adsurgens. Pratacultural Sci. 1987, 2, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, D.; Ralphs, M.; Welch, K.; Stegelmeier, B. Locoweed poisoning in livestock. Rangelands 2009, 31, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.G.; Dong, S.T.; Yang, Z.B.; Yang, W.R.; Jiang, S.Z. Experiment on Feeding Small-tailed Han Sheep with Astragalus adsurgens. Pratacultural Sci. 2008, 3, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Z.; Nan, Z.B. Symptomology and etiology of a new disease, yellow stunt, and root rot of standing milkvetch caused by Embellisia sp. in Northern China. Mycopathologia 2007, 163, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Nan, Z.B.; Hou, F.J. The roles of an Embellisia sp. causing yellow stunt and root rot of Astragalus adsurgens and other fungi in the decline of legume pastures in northern China. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2007, 36, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L. Study on Molecular Biology of Embellisia astragali. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Z.; Nan, Z.B. A new species, Embellisia astragali sp. nov., causing standing milk-vetch disease in China. Mycologia 2007, 99, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woudenberg, J.H.C.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Binder, M.; Crous, P.W. Alternaria redefined. Stud. Mycol. 2013, 75, 171–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Li, Y.Z.; Creamer, R. A re-examination of the taxonomic status of Embellisia astragali. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z. Study of yellow stunt and root rot (Embellisia astragali sp. nov. Li & Nan) of Astragalus adsurgens. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Z.; Creamer, R.; Baucom, D.; Nan, Z.B. Pathogenic Embellisia astragali on Astragalus adsurgens is very closely related to locoweed endophyte. Phytopathology 2011, 101, S102–S103. [Google Scholar]
- James, L.F.; Hartley, W.J.; Kampen, K.R.V. Syndromes of astragalus poisoning in livestock. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1981, 178, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegelmeier, B.L.; James, L.F.; Panter, K.E.; Gardner, D.R.; Pfister, J.A.; Ralphs, M.H.; Molyneux, R.J. Dose response of sheep poisoned with locoweed (Oxytropis sericea). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1999, 11, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, D.; Molyneux, R.; Ralphs, M. Analysis of swainsonine: Extraction methods, detection, and measurement in populations of locoweeds (Oxytropis spp.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4573–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molyneux, R.; James, L. Loco intoxication: Indolizidine alkaloids of spotted locoweed (Astragalus lentiginosus). Science 1982, 216, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, J.; Nakagawa, H.; Takahashi, M.; Kudo, T.; Kamiyama, N.; Sun, B.; Oshima, T.; Sato, Y.; Deguchi, K.; Todo, S. Swainsonine reduces 5-fluorouracil tolerance in the multistage resistance of colorectal cancer cell lines. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Donzelli, B.G.G.; Creamer, R.; Baucom, D.L.; Gardner, D.R.; Pan, J.; Moore, N.; Jaromczyk, J.W.; Schardl, C.L. Swainsonine Biosynthesis Genes in Diverse Symbiotic and Pathogenic Fungi. G3-Genes Genomes Genet. 2017, 7, 1791–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.S.; Allred, K.W.; Kiehl, D.E. Swainsonine content of New Mexican locoweeds. J. Anim. Sci. 1992, 70, 405–407. [Google Scholar]
- O”Donnell, J.; Dickinson, C.H. Pathogenicity of Alternaria and Cladosporium isolates on Phaseolus. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1980, 74, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.H.; Zhai, X.H.; Li, Q.F.; Wang, J.H.; Geng, G.X. Determination of Swainsonine in Astragalus locoweed by internal standard gas chromatography. J. Northwest Sci-Tech Univ. Agric. For. 2008, 36, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, A.I.; Neyaz, M.; Cook, D.; Creamer, R. Molecular Characterization of a Fungal Ketide Synthase Gene Among Swainsonine-Producing Alternaria Species in the USA. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 2554–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.C.; James, L.F. Toxicity of nitro-containing Astragalus to sheep and chicks. J. Range Manag. 1975, 28, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H. Plant Biology, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Zamioudis, C.; Berendsen, R.L.; Weller, D.M.; Van Wees, S.C.M.; Bakker, P.A.H.M. Induced Systemic Resistance by Beneficial Microbes. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2014, 52, 347–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, T.; Zeiger, E. Plant Physiology, 5th ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Xu, K.; Wang, X.F.; Zhu, Y.H. Research progress on mineral nutrition and plant disease mechanism. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2003, 4, 385–393. [Google Scholar]
- Marschner, H. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.Q.; Huang, L.P.; Zhang, Z. Research Progress of the Relationship Between Mineral Nutrients Deficiency or Imbalance and Plant Disease. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2016, 32, 174–176. [Google Scholar]
- Fidanza, M.A.; Dernoeden, P.H. Interaction of nitrogen source, application timing, and fungicide on Rhizoctonia blight in ryegrass. HortScience 1996, 31, 389–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, C.V.; Rao, G.R.; Reddy, K.B. Effect of nitrogen and potassium nutrition on sheath rot incidence and phenol content in rice (Oryz asativa L.). Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2001, 16, 254–257. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.R.; Kolte, S.J. Effect of soil-applied NPK fertilizers on severity of black spot disease (Alternaria brassicae) and yield of oilseed rape. Plant Soil 1994, 167, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; He, P.; Jin, J.Y. Advances in effect of potassium nutrition on plant disease resistance and its mechanism. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2006, 12, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, K.G.; Zhao, X.Q.; Li, J.Q.; Liu, X.L. Progressing on the Relation between Mineral Nutrients and Plant Disease. J. China Agric. Univ. 2000, 5, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, W.S.; Sams, C.E.; Kelman, A. Enhancing the natural resistance of plant tissues to postharvest diseases through calcium applications. HortScience 1994, 29, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.M.; Jones, J.B. The role of magnesium in plant disease. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A.K.; Singh, R.D. Effect of Nitrogenous Fertilizers and Trace Elements on the Severity of Alternaria Blight of Bottle Gound. Ann. Arid. Zone 1992, 31, 63–64. [Google Scholar]
- Gadi, B.; Jeffrey, G. Copper as a biocidal tool. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sawant, I.S.; Sawant, S.D.; Saha, S.; Kadam, P.; Somkuwar, R.G. Aqueous chlorine dioxide for the management of powdery mildew vis-a-vis maintaining quality of grapes and raisins. J. Eco-Friendly Agric. 2017, 12, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ehret, D.L.; Utkhede, R.S.; Frey, B.; Menzies, J.G.; Bogdanoff, C. Foliar applications of fertilizer salts inhibit powdery mildew on tomato. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2002, 24, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.Y. Study on the Resistance Mechanism of Nine Astragalus adsurgens Varieties to Yellow Stunt Root and Rot and Comprehensive Evaluation for Germplasm Characteristics. Ph.D. Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sa, F.; Vong, W.T.; Chan, T.M.; Lam, C.W.K. Determination of heavy metals in proprietary Chinese medicines by inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkouri, N.; Torabpour, M. Microwave assisted digestion coupled with inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry for determining element concentrations in halophytes. J. Basic Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 2, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M. The Effects of Yellow Stunt and Root Rot of Astragalus adsurgens on Swainsonine Content in Plants and Evaluation on New Disease Resistant Germplasms. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.L. Determination of Trace Heavy Metals in Porphyra by Microwave Digestion-ICP-MS Method. Zhejiang Chem. Ind. 2013, 44, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Leite, C.C.; De, J.A.; Potes, M.L.; Vieira, M.A.; Samios, D.; Silva, M.M. Direct Determination of Cd, Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, Na, Ni, Pb, and Zn in Ethanol Fuel by High-Resolution Continuum Source Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 7358–7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stendig, L.G.; Penciner, J.; Rudy, N.; Wacker, W.E. Comparison of diluents for serum magnesium estimation by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Magnesium 1984, 3, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.H. The study of Enzymatic Method and Gas chromatography for Determination of Swainsonine. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xi’an, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Krasnodêbska, O.B.; Kowalska, J. Ultrasound-assisted acetic acid extraction of metals from soils. Chem. Anal. 2003, 48, 967–974. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.H.; Han, Q.; Guo, D.S. Extraction and Content Determination of Crude Polysaccharides from Wild Portulaca oleracea Grass Powder. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, S.Q.; Chen, G.Y.; Hu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Ma, C.H. Determination of Swainsonine Content in Rabbit Serum by α-Mannosidase Method. China Herbiv. Sci. 2012, 32, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Panigati, M.; Falciola, L.; Mussini, P.; Beretta, G.; Facino, R.M. Determination of selenium in Italian rices by differential pulse cathodic stripping voltammetry. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, K.; Bieri, J.G.; Briggs, G.M.; Scott, M.L. Prevention of Exudative Diathesis in Chicks by Factor 3 and Selenium. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1957, 95, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.Q.; Yin, Z.F.; Wei, L.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Yang, X.Y. The duality of selenium and its related health issues. J. Chengde Med. Coll. 1999, 1, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Peng, Z.K.; Luo, Z.M. The multiple biological functions of selenium and its impact on human and animal health. J. Hunan Agric. Univ. 1997, 23, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P.; Margaret, P. Selenium and human health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, D.; Raisbeck, M.F. Pathology of experimentally induced chronic selenosis (alkali disease) in yearling cattle. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1995, 7, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.X.; Zhou, W.S.; Guo, S.H. Advances of Studies on Microelement Selenium in Plants. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2009, 37, 5844–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.A.; Shrift, A. Selenium: Toxicity and tolerance in higher plants. Biol. Rev. 1982, 57, 59–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, X.F.; Xu, H.S. Functions of Selenium in Plants. Plant Physiol. J. 1999, 35, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H. Selenosis. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 1993, 13, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.X.; Zheng, B.S.; Zhao, C.Z.; Yin, C.Q.; Lang, Y.B.; Zhang, A.L. Study on Selenium in Poisonous Oxytropis Plants (Locoweed) from the Hexi Corridor and Its Association with Livestock Poisoning. Adv. Earth Sci. 2004, 19, 502–505. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.X.; Zheng, B.S.; Wang, M.S.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, X.J.; Ling, H.W.; Luo, C. Environmental Geochemistry of Selenium in the Hexi Corridor Region and Investigation into the Causes of Livestock Poisoning by Toxic Plants. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2006, 26, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, F.; Bi, D.; Wang, H.K.; Li, H.Y.; Zhou, S.B.; Zhao, Q.G.; Yin, X.B. Distribution and Speciation of Selenium in Alkaline Soils and Agricultural Products of Lanzhou. Soils 2012, 44, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.J.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, G.Y.; Wang, P. Analysis of Selenium Speciation in Soils and Key Agricultural Products from Lanzhou City. Gansu Sci. Technol. Inf. 2016, 45, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Li, Y.Z. Alternaria gansuense, a Plant Systematic Fungal Pathogen Producing Swainsonine in Vivo and in Vitro. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Gardner, D.R.; Pfister, J.A. Swainsonine-containing plants and their relationship to endophytic fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 7326–7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Gardner, D.R.; Lee, S.T.; Pfister, J.A.; Stonecipher, C.A.; Welsh, S.L. A swainsonine survey of North American Astragalus and Oxytropis taxa implicated as locoweeds. Toxicon 2016, 118, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.; Gardner, D.R.; Ralphs, M.H.; Pfister, J.A.; Welch, K.D.; Green, B.T. Swainsoninine concentrations and endophyte amounts of Undifilum oxytropis in different plant parts of Oxytropis sericea. J. Chem. Ecol. 2009, 35, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; He, B.X. A study on the toxicity of Oxytropis kansuonisis in sheep. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 1995, 21, 5–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Mo, C.H.; Zhao, B.Y.; Cao, G.R. Study on the Toxicity of Intermittent Feeding of Oxytropis kansuensis to Sheep. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 1998, 30, 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.Q.; Xue, D.M.; Cao, G.R.; Duan, D.X. Pathological Observations of Oxytropis kansuensis Poisoning in Goats. J. Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 1991, 3, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.F.; Wang, J.H.; Yuan, Y.; Qi, X.R.; Zhao, Y. Pathology of Oxytropis glacialis Poisoning in Goats. Chin. J. Vet. Sci. 2001, 21, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Nan, Z.B.; Li, Y.Z. Toxicity of standing milkvetch infected with Alternaria gansuense in white mice. Front. Vet. Sci. 2025, 11, 1477970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).