Synergistic Effects of Fertilization on Maize Yield and Quality in Northeast China: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.1.1. Data Sources
2.1.2. Data Organization and Supplementation
2.1.3. Data Classification
- (1)
- Natural factors: mean annual precipitation (MAP), mean annual temperature (MAT), soil type, soil pH, soil organic matter content (SOM), soil total nitrogen content (TN), soil available nutrient content (soil alkaline nitrogen (Alk-N), soil available phosphorus (P), and soil available potassium (K)).
- (2)
- Human management practices: planting density and nutrient inputs (N rate, P2O5 rate, K2O rate).
2.2. Data Calculation
3. Results
3.1. Natural Factors
3.1.1. Climatic Conditions
3.1.2. Soil Properties
3.2. Human Management Practices
3.2.1. Nutrient Inputs
3.2.2. Planting Density
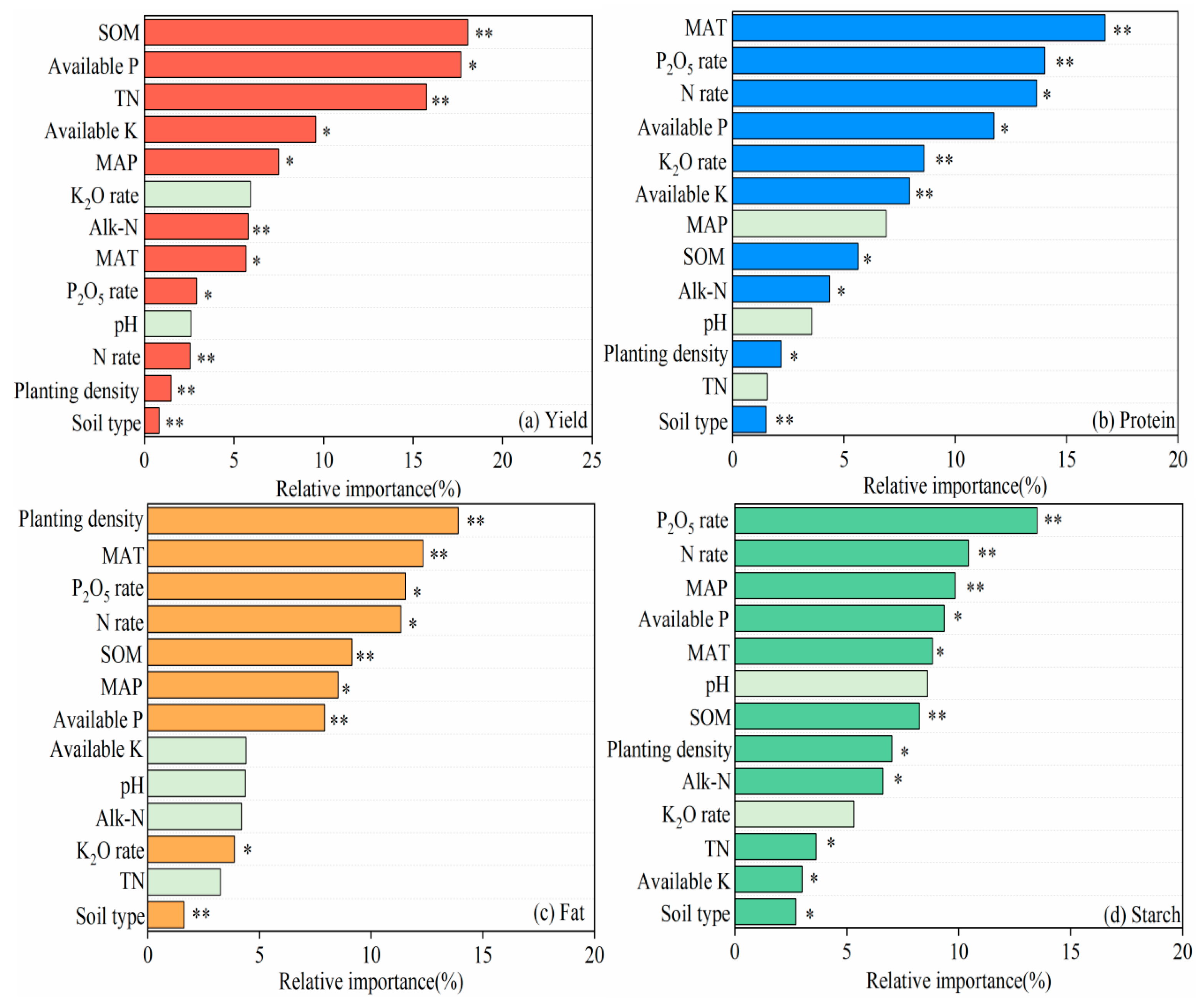
3.3. Relative Importance of Explanatory Variables
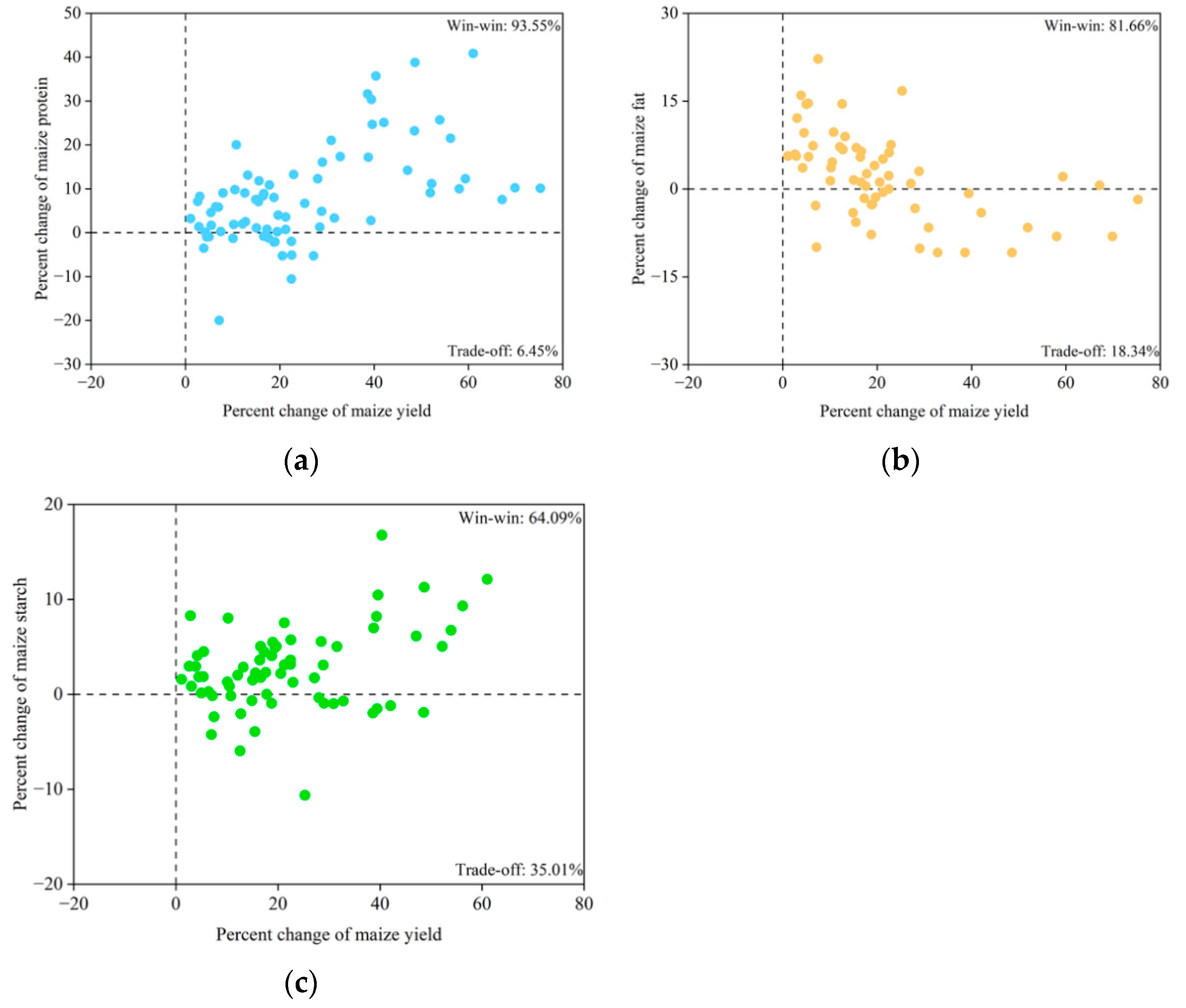
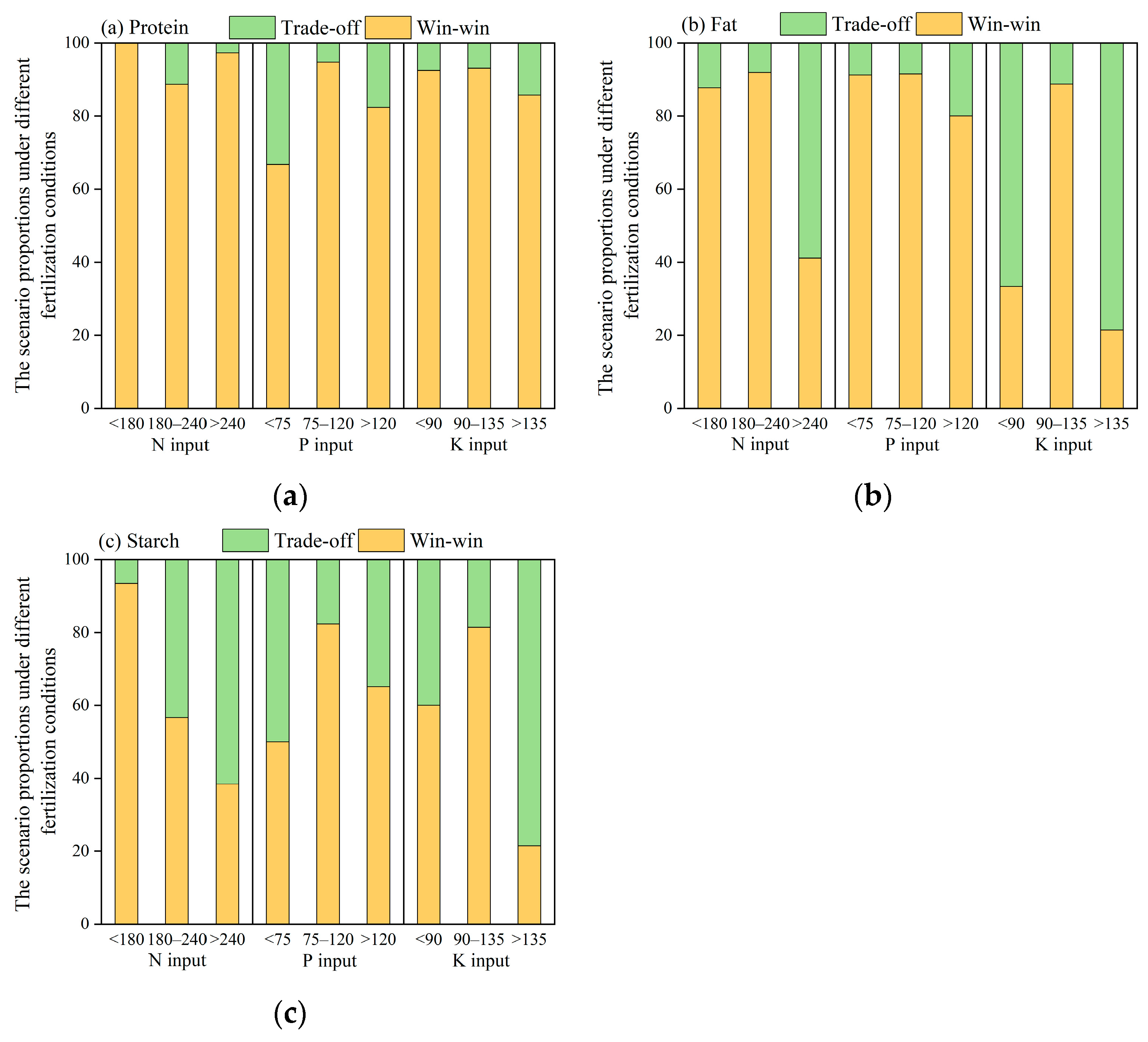
3.4. Synergistic Effects of Fertilization on Maize Yield and Quality in Northeast China
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Environmental Factors on Yield and Quality Improvement Under Fertilization in Northeast China
4.2. Effects of Management Practices on Maize Yield and Quality Improvement
4.3. Synergistic Relationship Between Yield and Quality in the Major Maize-Producing Region of Northeast China
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Richel, A. The effect of corn straw return on corn production in Northeast China: An integrated regional evaluation with meta-analysis and system dynamics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, M.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Hassan, M.; Yuan, H.; Liu, L.; He, B.; Ejaz, I.; White, P.; Cakmak, I.; et al. Improvement of nutritional quality of food crops with fertilizer: A global meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Shao, C.; Shi, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, R. Development trend and driving factors of agricultural chemical fertilizer efficiency in China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Jin, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Kanter, D.; Wu, B.; Xi, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; et al. Fertilizer overuse in Chinese smallholders due to lack of fixed inputs. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, W.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Xia, Q.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z. Rhizosphere soil properties, microbial community, and enzyme activities: Short-term responses to partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.; Guo, A.; Yang, X.; Li, W.; Xia, Q.; Gao, Z.; Yang, Z. Combined foliar and soil selenium fertilizer increased the grain yield, quality, total Se, and organic Se content in naked oats. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 100, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; Yang, J.; Han, X. Long-term rotation fertilisation has differential effects on soil phosphorus. Plant Soil Environ. 2020, 66, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cui, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Mi, G.; Gao, Q. Synergistic regulation of nitrogen and sulfur on redox balance of maize leaves and amino acids balance of grains. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 576718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, P.E.; Schneider, J.; Müller, F.; Wiedmaier-Czerny, N.; Vetter, W.; Weiß, T.M.; Würschum, T.; Frank, J. Location and variety but not phosphate starter fertilization influence the profiles of fatty acids, carotenoids, and tocochromanols in kernels of modern corn (Zea mays L.) hybrids cultivated in Germany. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2845–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, P.; Malzer, G.; Sparrow, S.; Zhang, M. Soybean yield and quality in relation to soil properties. Agron. J. 2012, 104, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Improved Crop Quality by Nutrient Management; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007.
- Kushwah, N.; Billore, V.; Sharma, O.P.; Singh, D.; Chauhan, A.P.S. Integrated Nutrient management for optimal plant health and crop yield. Plant Sci. Archit. 2024, 8, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, X. Rhizosphere processes and management for improving nutrient use efficiency and crop productivity: Implications for China. Adv. Agron. 2010, 107, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, T.S.; Collins, S.L.; Yu, K.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Li, H.; Ye, J.S. A global meta-analysis on the effects of organic and inorganic fertilization on grasslands and croplands. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3411. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M.D.; Ros, G.H.; de Vries, W. Impacts of agronomic measures on crop, soil, and environmental indicators: A review and synthesis of meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Makowski, D.; Piraux, F.; Brun, F. From Experimental Network to Meta-Analysis; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Liu, X.; He, X. A global meta-analysis of crop yield and agricultural greenhouse gas emissions under nitrogen fertilizer application. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, F.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Q.; Yan, L. Optimum management strategy for improving maize water productivity and partial factor productivity for nitrogen in China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 303, 109043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.M.; Rajput, D.S.; Somula, R.S.; Ram, S. Principles and practices of making agriculture sustainable: Crop yield prediction using Random Forest. Scalable Comput-Prac. 2020, 21, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Drury, C.F.; Liebig, M.; Johnson, J.M.; Wang, Z.; Feng, H.; Abalos, D. The role of conservation agriculture practices in mitigating N2O emissions: A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Fu, Y.; Hao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Jin, X.; Bryant, C.R.; Senthilnath, J. Integrated phenology and climate in rice yields prediction using machine learning methods. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Mei, F.; Ling, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, C.; Leghari, S.J.; Guang, X.; Wang, T. Does continuous straw returning keep China farmland soil organic carbon continued increase? A meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The meta-analysis of response ratios in experimental ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Impacts of crop type and climate changes on agricultural water dynamics in Northeast China from 2000 to 2020. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikeh, S.O.; Kling, J.G.; Horst, W.J.; Chude, V.O.; Carsky, R.J. Growth and distribution of maize roots under nitrogen fertilization in plinthite soil. Field Crops Res. 1999, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Li, L.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Anwar, S.; Fudjoe, S.K. Nitrogen supply affects yield and grain filling of maize by regulating starch metabolizing enzyme activities and endogenous hormone contents. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 798119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wu, S.; Yan, Z. Effects of climate change on corn yields: Spatiotemporal evidence from geographically and temporally weighted regression model. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Gao, J.; Ma, D.; Guo, H.; Hu, S. Patterns of influence of meteorological elements on maize grain weight and nutritional quality. Agronomy 2023, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Gu, X.; Ding, M.; Lu, W.; Lu, D. Heat stress during grain filling affects activities of enzymes involved in grain protein and starch synthesis in waxy maize. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Sun, X.; Yan, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, R.; Lu, W. Effects of high temperature during grain filling under control conditions on the physicochemical properties of waxy maize flour. Carbohyd. Polym. 2013, 98, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, P.; Xie, R.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Ming, B.; Ma, D.; Liang, S. Spatial adaptabilities of spring maize to variation of climatic conditions. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Liu, Y.; Xie, R.; Ming, B.; Ma, D.; Li, S.; Mei, X. Temporal and spatial variation in accumulated temperature requirements of maize. Field Crops Res. 2014, 158, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.V.; Assefa, Y.; Schwalbert, R.; Ciampitti, I.A. Maize yield and planting date relationship: A synthesis-analysis for US high-yielding contest-winner and field research data. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Yue, W.; Bi, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, D.; Peng, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, S. Influence of climatic variables on maize grain yield and its components by adjusting the sowing date. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1411009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; An, F.; Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Variations on soil salinity and sodicity and its driving factors analysis under microtopography in different hydrological conditions. Water 2016, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yaa, O.K.; Wu, J. Effects of different organic materials application on soil physicochemical properties in a primary saline-alkali soil. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2020, 53, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Guo, Z.; Peng, C. Distribution and storage of soil organic carbon in China. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, X.; Bao, Z.; Gao, J.; Meng, J.; Han, X.; Liu, Z.; Lan, Y.; Chen, W. Responses of microbial necromass carbon and microbial community structure to straw-and straw-derived biochar in brown earth soil of Northeast China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 967746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliani, L.M.; Hallett, P.D.; Loades, K.W. Effects of soil structure complexity to root growth of plants with contrasting root architecture. Soil Till. Res. 2024, 238, 106023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X. Effects of soil pH and texture on soil carbon and nitrogen in soil profiles under different land uses in Mun River Basin, Northeast Thailand. Peer. J. 2019, 7, e7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangisoni, J.H.; Jayne, T.S.; Chigowo, M. Effects of Nitrogen and Carbon Application on Maize Output in Ntcheu and Dedza Districts of Central Malawi. J. Econ. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T.; Lu, Z.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Han, X.; Wang, Y. Long-term application of manure increased soil amino acid pool under maize-maize-soybean rotation system. J. Soil. Sediment. 2024, 24, 3572–3584. [Google Scholar]
- D’Hose, T.; Cougnon, M.; De Vliegher, A.; Vandecasteele, B.; Viaene, N.; Cornelis, W.; Bockstaele, E.; Reheul, D. The positive relationship between soil quality and crop production: A case study on the effect of farm compost application. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2014, 75, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, J.M.; Baltensperger, D.D.; Cassman, K.G.; Mason, S.C.; Pavlista, A.D. Importance and effect of nitrogen on crop quality and health. In Nitrogen in the Environment; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 51–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Maqsood, M.; Ijaz, M.; Ul-Allah, S.; Sattar, A.; Sher, A.; Nawaz, A. Combined application of potassium and zinc improves water relations, stay green, irrigation water use efficiency, and grain quality of maize under drought stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 2214–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Lei, B.; Xing, G. Effects of Phosphorus Application Levels on Its Uptake and Utilization in Foxtail Millet. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, D.; Ren, K.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Duan, Y.; Lu, C. Response of maize yield and nitrogen recovery efficiency to nitrogen fertilizer application in field with various soil fertility. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1349180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Xue, W.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, Z.; Wang, W.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H.; Qiu, P.; Xue, J.; Chen, B. Nitrogen fertilizer application rate affects the dynamic metabolism of nitrogen and carbohydrates in kernels of waxy maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1416397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, X.U.E.; Xie, R.Z.; Zhang, W.F.; Wang, K.R.; Hou, P.; Ming, B.; Gou, L.; Shaokun, L.I. Research progress on reduced lodging of high-yield and-density maize. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 2717–2725. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Brooker, R.W.; Zhang, F.; Davies, W.J.; Shen, J. Root competition resulting from spatial variation in nutrient distribution elicits decreasing maize yield at high planting density. Plant Soil 2019, 439, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, R. Optimum planting density improves resource use efficiency and yield stability of rainfed maize in semiarid climate. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 752606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Wang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Du, F.; Chen, J.; Xiao, C. Effects of planting density and nitrogen (n) application rate on light energy utilization and yield of maize. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Gao, J.; Ma, D.; Guo, H.; Zhao, H. Effect of planting density on the nutritional quality of grain in representative high-yielding maize varieties from different eras. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Zheng, X.; Xue, J.; Li, S. Response of grain yield to planting density and maize hybrid selection in high latitude China—A multisource data analysis. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Dou, Z.X.; Ying, H.; Zhang, F. Producing more with less: Reducing environmental impacts through an integrated soil-crop system management approach. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.; Huang, Q. Effects of long-term fertilization on corn productivity and its sustainability in an Ultisol of southern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouf Shah, T.; Prasad, K.; Kumar, P. Maize—A potential source of human nutrition and health: A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1166995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsenios, N.; Sparangis, P.; Chanioti, S.; Giannoglou, M.; Leonidakis, D.; Christopoulos, M.V.; Katsaros, G.; Efthimiadou, A. Genotype × environment interaction of yield and grain quality traits of maize hybrids in Greece. Agronomy 2021, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
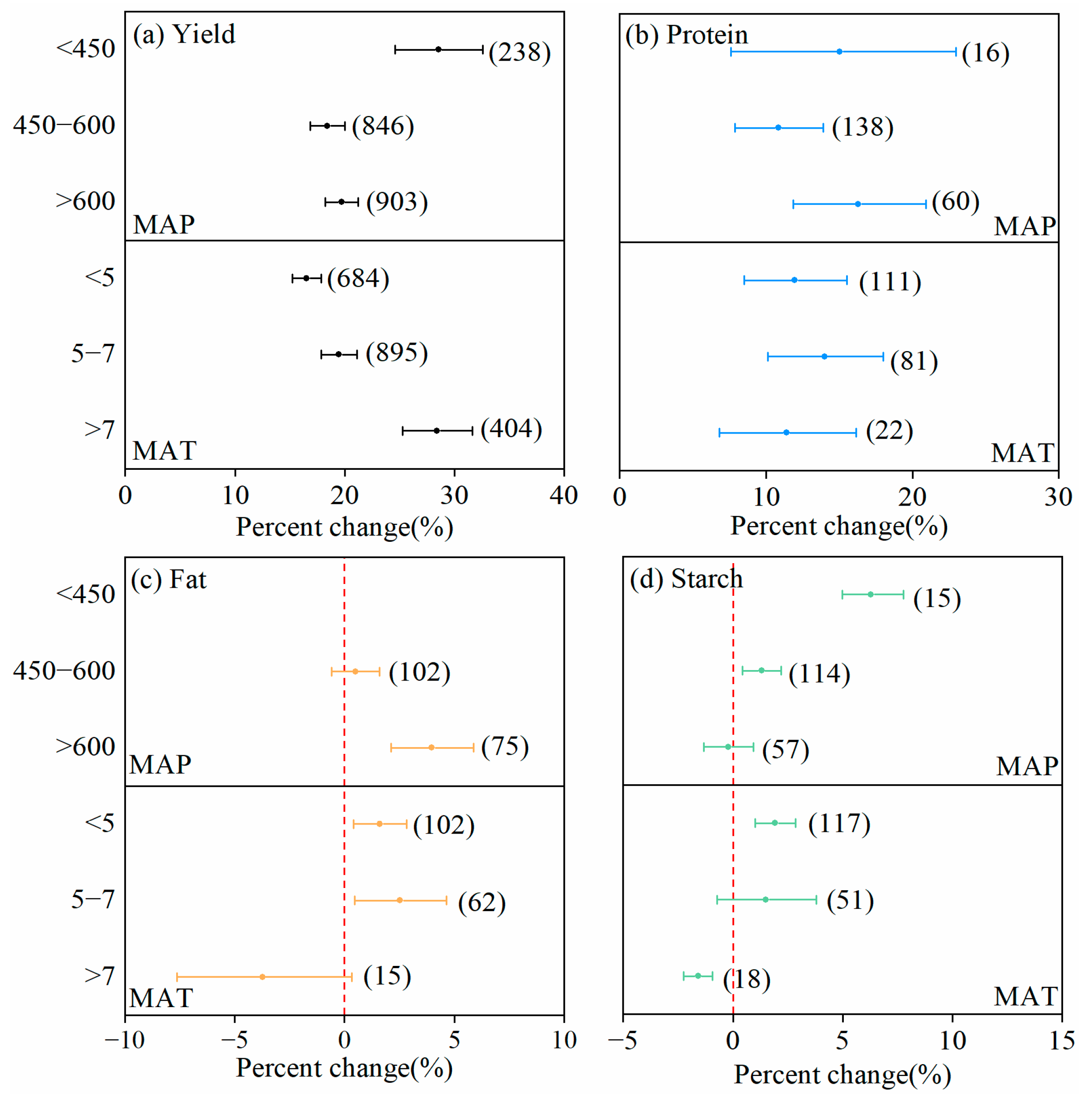
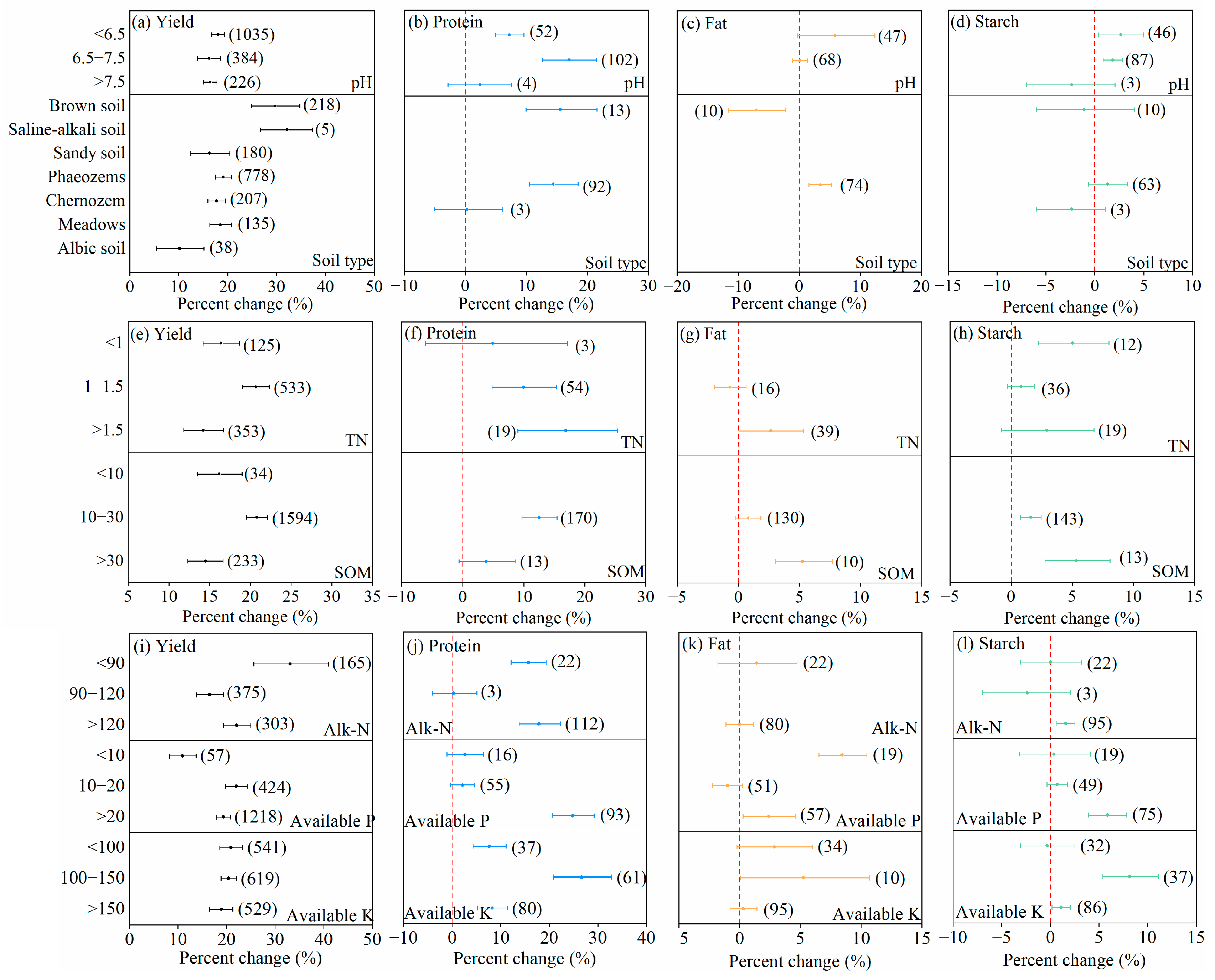
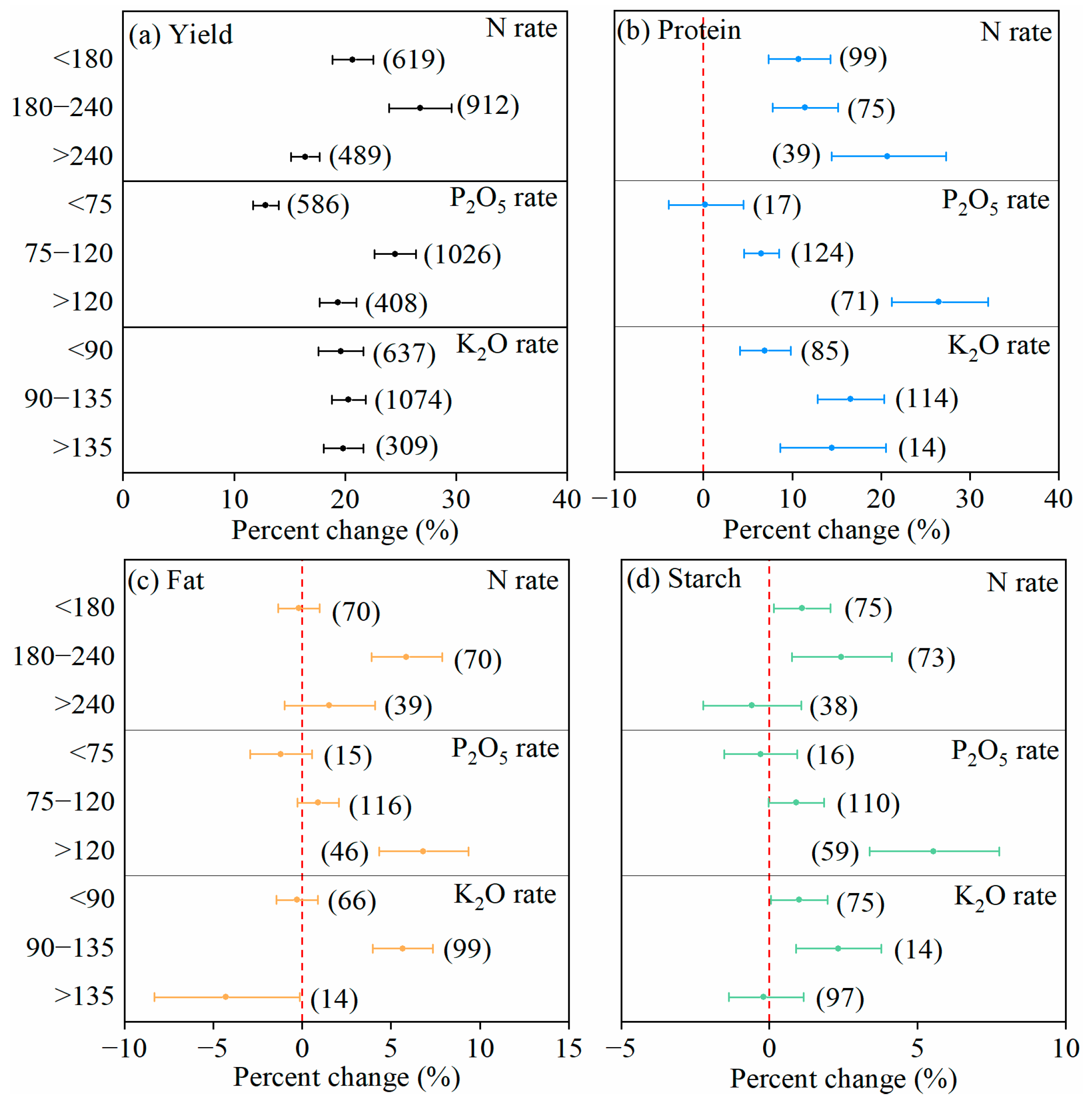
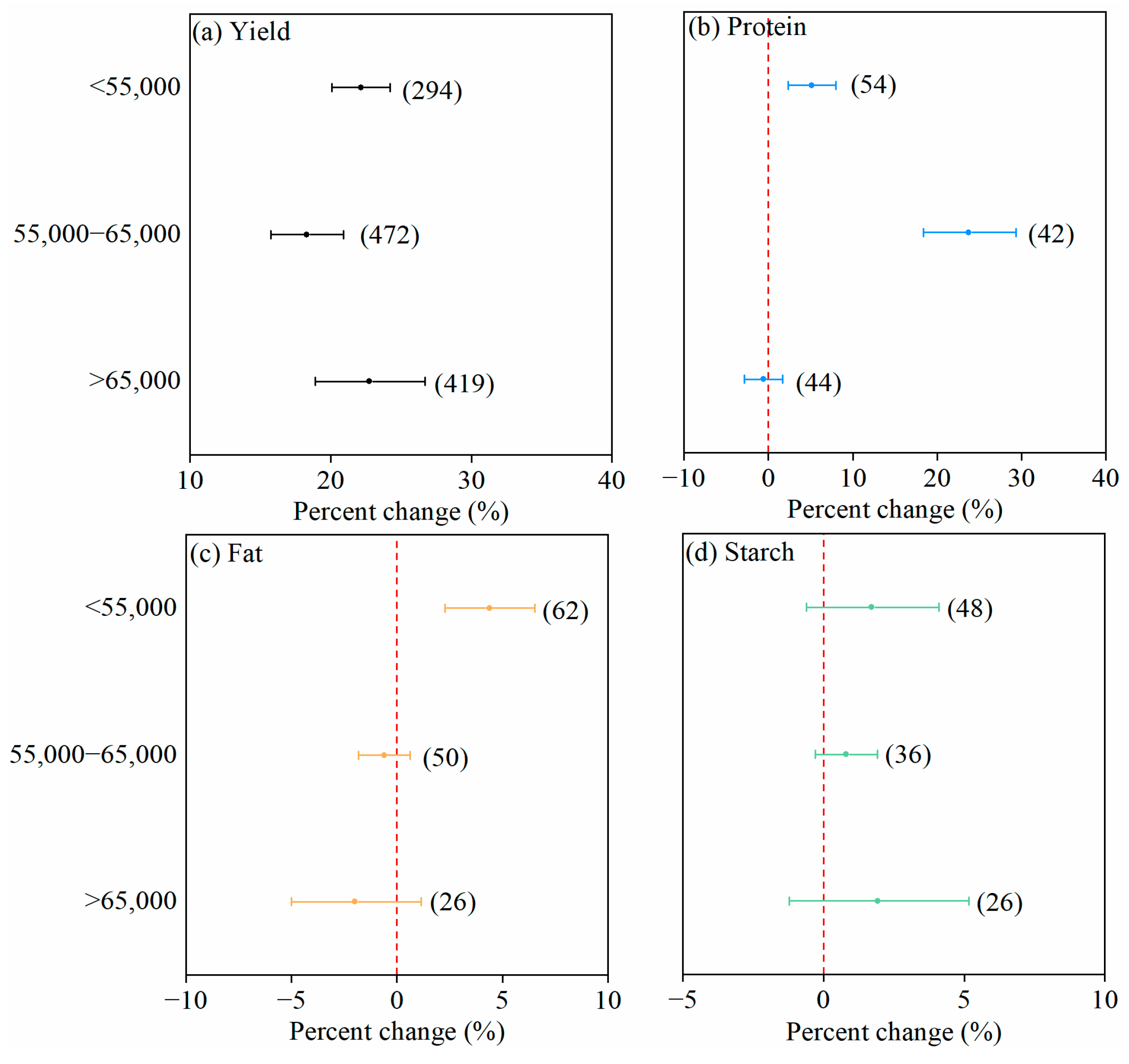
| Factors | Subgroup |
|---|---|
| Mean annual precipitation (℃) | <450; 450–600; >600 |
| Mean annual temperature (mm) | <5; 5–7; >7 |
| Soil type | Saline–alkali soil > Brown soil > Phaeozems > Meadows > Chernozem > Sandy soil > Albic soil |
| Soil pH | <6.5; 6.5–7.5; >7.5 |
| Soil organic matter (g kg−1) | <10; 10–30; >30 |
| Soil total nitrogen (g kg−1) | <1; 1–1.5; >1.5 |
| Soil alkaline nitrogen (mg kg−1) | <90; 90–120; >120 |
| Soil available phosphorus (mg kg−1) | <10; 10–20; >20 |
| Soil available potassium (mg kg−1) | <100; 100–150; >150 |
| Planting density (plants ha−1) | <55,000; 55,000–65,000; >65,000 |
| N rate (kg ha−1) | <180; 180–240; >240 |
| P2O5 rate (kg ha−1) | <75; 75–120; >120 |
| K2O rate (kg ha−1) | <90; 90–135; >135 |
| Indicator | n | E | Q-val | df | PQ-val | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield | 2020 | 20.0% | 69,800 | 2019 | <0.001 | 98.8 |
| Protein | 213 | 12.6% | 1888.3 | 212 | <0.001 | 88.0 |
| Fat | 179 | 1.4% | 243.64 | 178 | <0.01 | 80.7 |
| Starch | 186 | 1.2% | 205.49 | 185 | <0.01 | 90.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; An, Y.; Wang, S.; Feng, G.; Lv, J.; Li, X.; Gao, Q. Synergistic Effects of Fertilization on Maize Yield and Quality in Northeast China: A Meta-Analysis. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131371
Gao X, Zhang L, An Y, Wang S, Feng G, Lv J, Li X, Gao Q. Synergistic Effects of Fertilization on Maize Yield and Quality in Northeast China: A Meta-Analysis. Agriculture. 2025; 15(13):1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131371
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xiaoqi, Lingchun Zhang, Yulin An, Shaojie Wang, Guozhong Feng, Jiayi Lv, Xiaoyu Li, and Qiang Gao. 2025. "Synergistic Effects of Fertilization on Maize Yield and Quality in Northeast China: A Meta-Analysis" Agriculture 15, no. 13: 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131371
APA StyleGao, X., Zhang, L., An, Y., Wang, S., Feng, G., Lv, J., Li, X., & Gao, Q. (2025). Synergistic Effects of Fertilization on Maize Yield and Quality in Northeast China: A Meta-Analysis. Agriculture, 15(13), 1371. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131371




