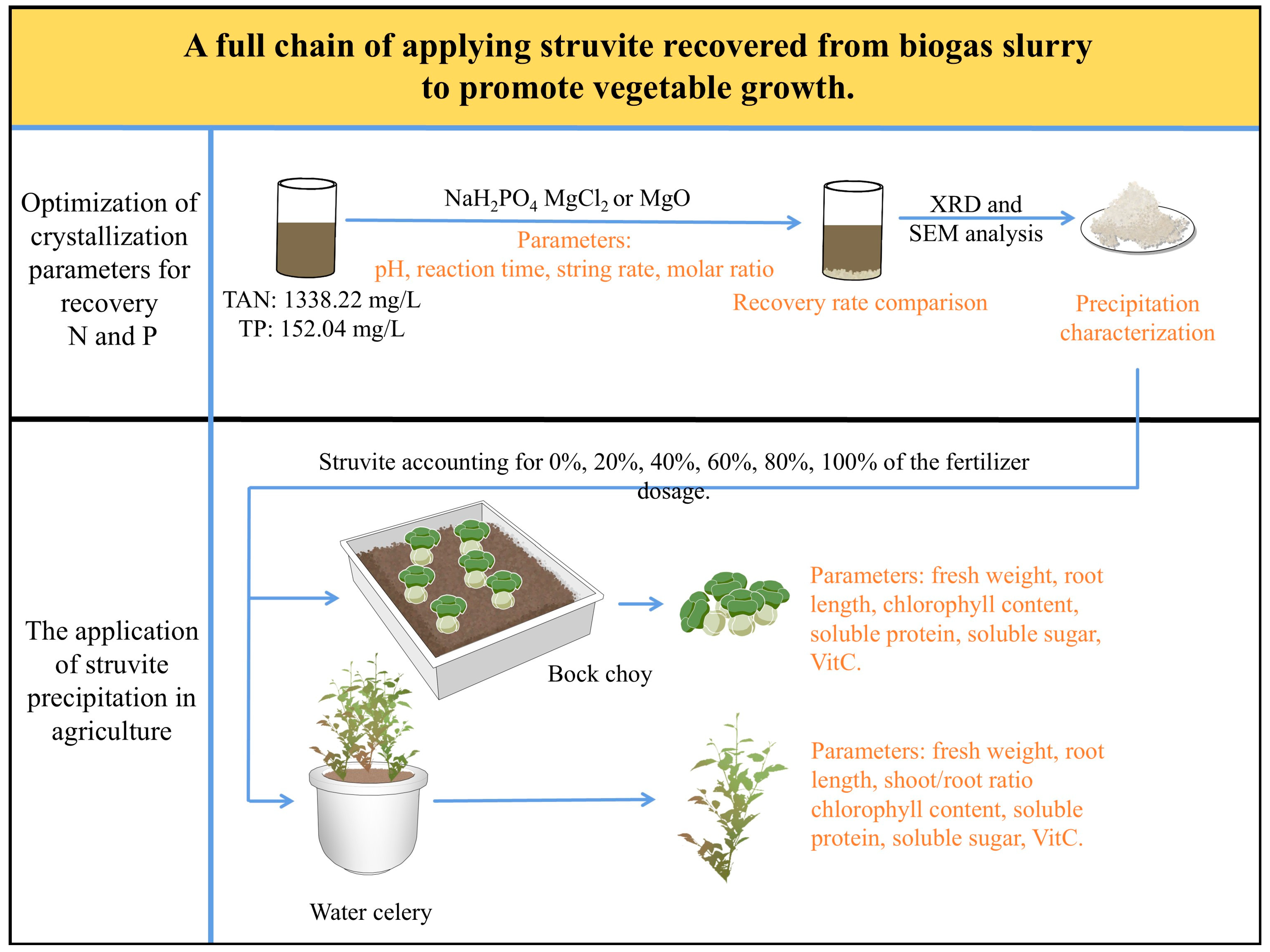
A Full Chain of Applying Struvite Recovered from Biogas Slurry to Promote Vegetable Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Collection
2.2. Crystallization Parameters
2.3. Characterization of Precipitations
2.4. Precipitations on Plant Growth
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
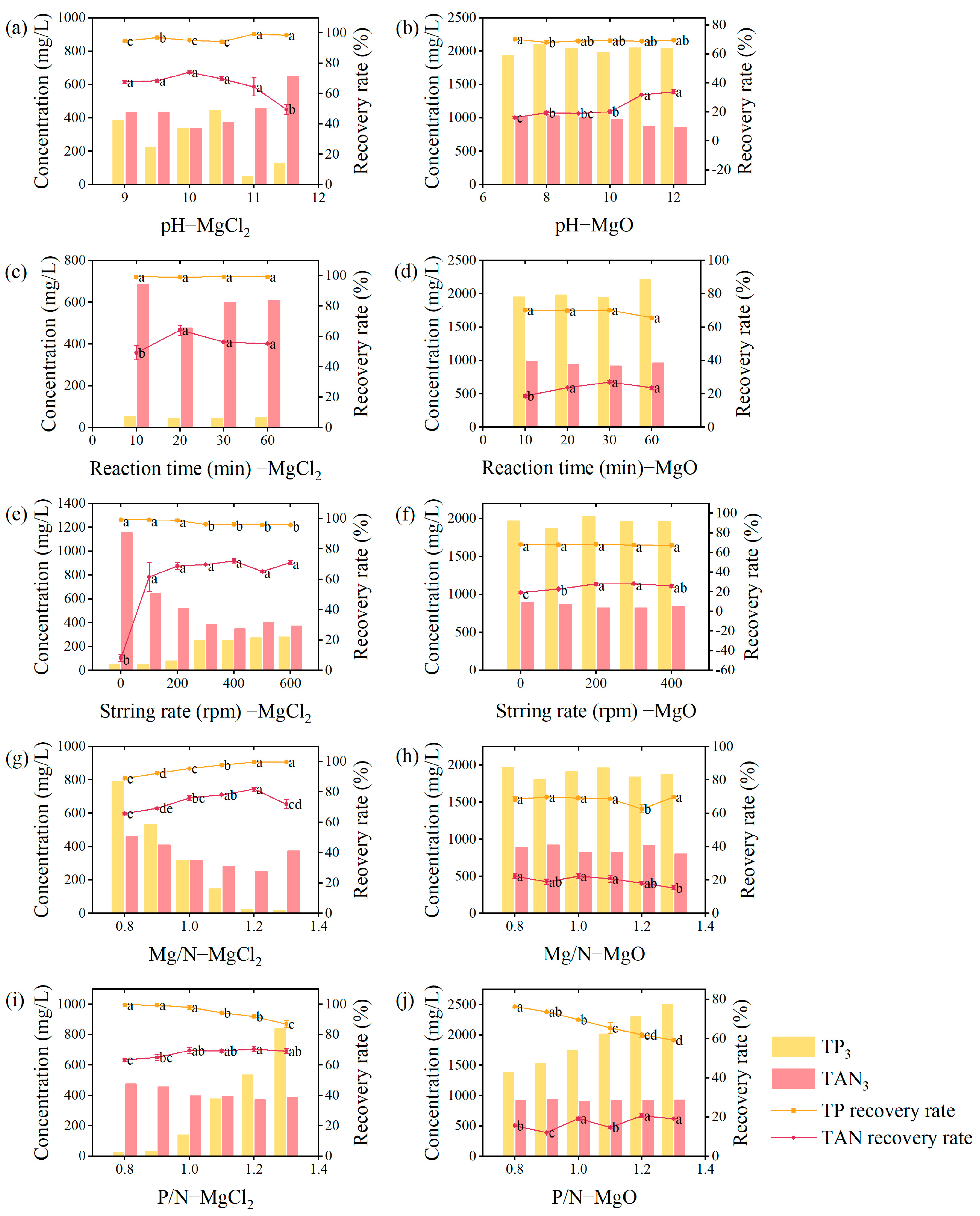
3.1. Optimization of Crystallization Parameters for Recovery of N and P
3.1.1. pH
3.1.2. Reaction Time
3.1.3. Stirring Rate
3.1.4. Molar Ratio
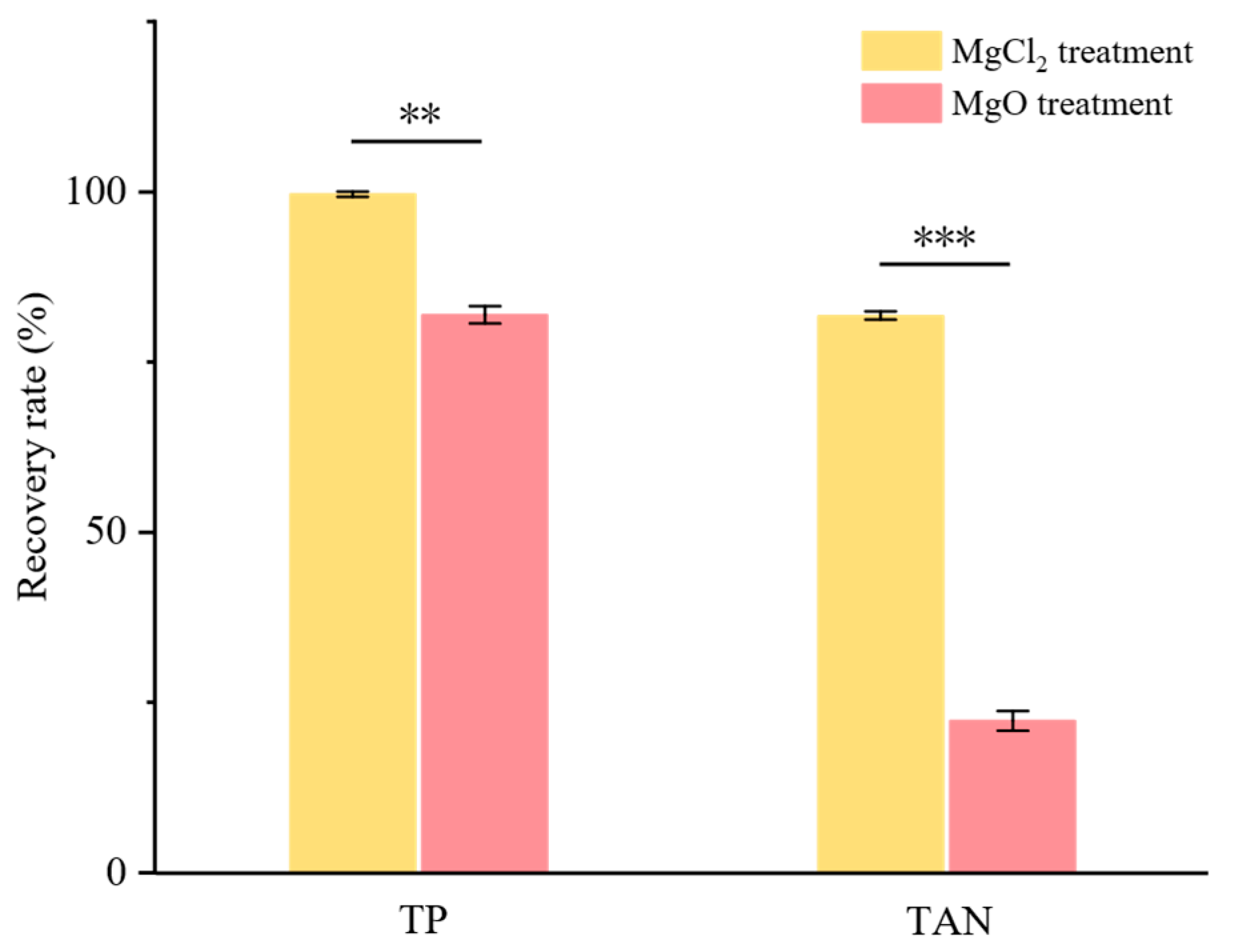
3.2. Comparison of Two Mg Sources
3.2.1. Recovery Rate
3.2.2. Characterization of Struvite
3.3. The Application of Struvite Precipitation in Agriculture
3.3.1. Terrestrial Vegetable Cultivation
3.3.2. Aquatic Vegetable Cultivation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, X.; Jin, M.; Feng, Q.; Sha, A.; Bai, S.; Zhao, X. Resource and Energy Utilization of Swine Wastewater Treatment: Recent Progress and Future Directions. Separations 2023, 10, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; He, T.; Zhang, Y. Treatment and utilization of swine wastewater—A review on technologies in full-scale application. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Hu, H. Surplus manure and barren croplands: Strategies for recycling livestock manure to rebuild crop-livestock linkages beyond the farm level. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2025; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Mao, K.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y. Crop livestock integration for sustainable agriculture in China: The history of state policy goals, reform opportunities and institutional constrains. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2023, 10, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Pal, P. Assessing the feasibility of N and P recovery by struvite precipitation from nutrient-rich wastewater: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17453–17464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barampouti, E.M.; Mai, S.; Malamis, D.; Moustakas, K.; Loizidou, M. Exploring technological alternatives of nutrient recovery from digestate as a secondary resource. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110379. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.; Yu, J.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S.; Direstiyani, L.C.; Lee, T. The effectiveness of step feeding strategies in sequencing batch reactor for a single-stage deammonification of high strength ammonia wastewater. Membr. Water Treat. 2020, 11, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhi, M.; Guo, J.; Gaballah, M.S.; Li, B.; Zheng, J. Selecting the optimal nutrients recovery application for a biogas slurry based on its characteristics and the local environmental conditions: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonni, A.K.; Wai-hung, L.; Gilbert, Y.S.C. Physico-chemical treatments for removal of recalcitrant contaminants from landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Liu, X.; Du, B.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Q. Component analysis and risk assessment of biogas slurry from biogas plants. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 44, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Tsang, D.; Wang, H.; Chen Hm Gao, B. Recovery of phosphorus from wastewater: A review based on current phosphorous removal technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 53, 1148–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilleos, P.; Roberts, K.R.; Williams, I.D. Struvite precipitation within wastewater treatment: A problem or a circular economy opportunity? Heliyon 2022, 8, e09862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, N.; Dey, B.; Unpaprom, Y.; Ramaraj, R.; Maniam, G.P.; Govindan, N.; Jayaraman, S.; Arunachalam, T.; Paramasivan, B. Engineering principles and process designs for phosphorus recovery as struvite: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Shen, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Shi, J. Phosphorus recovery from wastewater by struvite crystallization: Property of aggregates. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astals, S.; Martínez-Martorell, M.; Huete-Hernández, S.; Aguilar-Pozo, V.B.; Dosta, J.; Chimenos, J.M. Nitrogen recovery from pig slurry by struvite precipitation using a low-cost magnesium oxide. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, T.H.; Mahasti, N.; Lu, M.C.; Huang, Y.H. Ammonium-nitrogen recovery as struvite from swine wastewater using various magnesium sources. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 308, 122870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabdasli, I.; Safak, A.; Tunay, O. Bench-scale evaluation of treatment schemes incorporating struvite precipitation for young landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Liang, X.; Goh, H.H.; Chew, K.W. From liquid waste to mineral fertilizer: Recovery, recycle and reuse of high-value macro-nutrients from landfill leachate to contribute to circular economy, food security, and carbon neutrality. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 170, 791–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Tait, S.; Astals, S.; Del Valle-Zermeño, R.; Martínez MMata-Alvarez, J.; Chimenos, J. Reagent use efficiency with removal of nitrogen from pig slurry via struvite: A study on magnesium oxide and related by-products. Water Res. 2015, 84, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.J.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.; Park, K.Y. Characteristics of vegetable crop cultivation and nutrient releasing with struvite as a slow-release fertilizer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34332–34344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzberger, A.J.; Cusick, R.D.; Margenot, A.J. A review and meta-analysis of the agricultural potential of struvite as a phosphorus fertilizer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Li, Y.P.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.J.; Yu, X.; Ou, R.W.; Zeng, G.S. A review of struvite crystallization for nutrient source recovery from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corre, K.S.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Hobbs, P.; Parsons, S.A. Phosphorus recovery from wastewater by struvite crystallization: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 433–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifian, M.; Liu, J.; Mattisaaon, B. Struvite-based fertilizer and its physical and chemical properties. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Shim, S.; Won, S.; Ra, C. Struvite recovered from various types of wastewaters: Characteristics, soil leaching behaviour, and plant growth. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2864–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.T.; Deng, R.; Zou, X.H.; Ma, X.; Xie, Z.P.; Wang, C.A. The transformation processes of struvite slow–release fertilizer in vegetable by isotopic tracing. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2020, 29, 3517–3523. [Google Scholar]
- Achat, D.L.; Sperandio, M.; Daumer, M.L.; Santellani, A.C.; Prud’Homme, L.; Akhtar, M.; Morel, C. Plant-Availability of Phosphorus Recycled from Pig Manures and Dairy Effluents as Assessed by Isotopic Labeling Techniques. Geoderma 2014, 232, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astals Ryu, H.D.; Lee, S.I. Struvite recovery from swine wastewater and its assessment as a fertilizer. Environ. Eng. Res. 2015, 21, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, A.; Kuru, B. The fertilizer effect of struvite recovered from daily industry wastewater on the growth and nutrition of maize plant. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 3155–3162. [Google Scholar]
- Ponce, R.; De, S.M. Efficacy of magnesium ammonium phosphate recovered from wastewater on white lupin plant. A greenhouse experiment. Agrochimica 2008, 52, 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo, V.; Pérez, R.; González, F.; Santander, C.; Ruiz, A.; Holzapfel, E.; Cornejo, P.; Vidal, G. Improved Phosphorus Bioavailability in Lettuce Crop via Naganishia albida Inoculation of Wastewater-Derived Struvite. Agronomy 2025, 15, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.D.; Fattah, K.P.; Huchzermeier, M.P. Struvite recovery from anaerobically digested dairy manure: A review of application potential and hindrances. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonne, C.; Ok, Y.S.; Dietz, R.; Alstrup, A.K.O. Pig slurry needs modifications to be a sustainable fertilizer in crop production. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansel, B.; Lunn, G.; Monje, O. Struvite formation and decomposition characteristics for ammonia and phosphorus recovery: A review of magnesium-ammonia-phosphate interactions. Chemosphere 2018, 194, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Liu, X. A Review of Oenanthe javanica (Blume) DC. as Traditional Medicinal Plant and Its Therapeutic Potential. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 6495819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Chang, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, W. The Safety of Consuming Water Dropwort Used to Purify Livestock Wastewater Considering Accumulated Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Yadav, P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Rai, P. Brassica juncea: A Crop for Food and Health. In The Brassica juncea Genome; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Medhi, D.; DeDatta, S. Residual effect of fertilizer phosphorus in lowland rice. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1996, 46, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.L.; Engeseth, N.J. Comparison of growth characteristics, functional qualities, and texture of hydroponically grown and soil–grown lettuce. LWT 2021, 150, 111931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viña, S.Z.; Chaves, A.R. Texture changes in fresh cut celery during refrigerated storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 1308–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Sun, X.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Xiong, A. Integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic revealed the effect of salicylic acid treatment on improving the storability of ‘Ventura’ celery. Postharvest Biol. Tec. 2025, 228, 113656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, T.; Yan, J.; Zhao, X.; Touheti, T.; Xu, Y.; Gan, T.; Zhao, X.; He, L.; Gustave, W.; Zhang, X.; et al. Combined effects of biochar and silkworm excrement compost applications on soil properties and vegetable growth. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 210, 106067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Anunonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Wellburn, A.R. Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1983, 11, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.K.; Jiang, W.B.; Zhao, Y.M. Experiment Guidance of Postharvest Physiology and Biochemistry of Fruits and Vegetables; China Light Industry Press Ltd.: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, S.; Ackermann, G.; Linder, P. Application of reactions in spectrophotometry.2. detection and spectrophotometric detection of phenolic-compounds with the iron(III)/1,10–phenanthroline complex. Talanta 1992, 39, 693–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Morales, C.; Fernández, B.; Molina, F.J.; Naranjo-Fernández, D.; Matamoros-Veloza, A.; Camargo-Valero, M.A. Influence of pH and Temperature on Struvite Purity and Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; He, X.; Deng, Y.; Tsang, D.; Jiang, R.; Becker, G.; Kruse, A. Phosphorus recovered from digestate by hydrothermal processes with struvite crystallization and its potential as a fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.D.; Philp, R.; Churchley, J.; Parsons, S.A. Analysis of struvite precipitation in real and synthetic liquors. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2000, 78, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.M.; Kiselev, A. Stirring speeds up chemical reaction. Nonlinearity 2022, 35, 4599–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Q.; Li, Y.M.; Wu, X.H.; Yang, L.; Wang, L. Characterization of morphology and component of struvite pellets crystallized from sludge dewatering liquor: Effects of total suspended solid and phosphate concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 310, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukic, E.; van Maldegem, K.A.; Shaikh, K.M.; Fukuda, K.; Toepel, M.; Solymosi, K.; Hellsten, J.; Hansen, T.H.; Husted, S.; Higgins, J.; et al. Chloroplast magnesium transporters play essential but differential roles in maintaining magnesium homeostasis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 14, 1221436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donten, M.; VandeVondele, J.; Hamm, P. Speed Limits for Acid Base Chemistry in Aqueous Solutions. Chimia 2012, 66, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.J.; Park, K.Y. Economic feasibility of phosphorus recovery through struvite from liquid anaerobic digestate of animal waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 40703–40714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corre, K.S.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Hobbs, P.; Parsons, S.A. Impact of reactor operation on success of struvite precipitation from synthetic liquors. Environ. Technol. 2007, 28, 1245–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, N.; Bouzas, A.; Seco, A.; Ferrer, J. Struvite precipitation assessment in anaerobic digestion processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 141, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadekar, S.; Pullammanappallil, P. Validation and Applications of a Chemical Equilibrium Model for Struvite Precipitation. Environ. Model. Assess 2010, 15, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenburg, P.; Capdevielle, A.; Teychené, S.; Biscans, B. Struvite precipitation with MgO as a precursor: Application to wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 133, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, A.; Karadag, D.; Tosun, I.; Ozturk, M. Use of magnesite as a magnesium source for ammonium removal from leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Chen, S. Selection of cost-effective magnesium sources for fluidized struvite crystallization. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 70, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Zeng, G.; Song, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Wu, S. Ultrasonic power combined with seed materials for recovery of phosphorus from swine wastewater via struvite crystallization process. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Pozo, V.B.; Chimenos, J.M.; Elduayen-Echave, B.; Olaciregui-Arizmendi, K.; Lópeze, A.; Gómez, J.; Guembe, M.; García, I.; Ayesa, E.; Astals, S. Struvite precipitation in wastewater treatment plants anaerobic digestion supernatants using a magnesium oxide by-product. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, G.; Huang, B.; Dai, M.; Wen, Z. Effects of seed crystal concentration, pH, and stirring rate on ammonium sulfate crystallization under the action of ammonium nitrate. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2023, 198, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarragó, E.; Sciarria, T.P.; Ruscalleda, M.; Colprim, J.; Balaguer, M.D.; Adani, F.; Puig, F. Effect of suspended solids and its role on struvite formation from digested manure. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Tang, R.; Wu, G.; Wang, W.; Yuan, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhan, X.; Hu, Z.-H. Co-precipitation of heavy metals with struvite from digested swine wastewater: Role of suspended solids. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 131633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elduayen-Echave, B.; Azcona, M.; Grau, P.; Schneider, P.A. Effect of the shear rate and supersaturation on the nucleation and growth of struvite in batch stirred tank reactors. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 38, 101657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Chen, H.; Song, X.F.; Yu, J.G. Metastable Zone Width and the Primary Nucleation Kinetics for Cooling Crystallization of NaNO3 from NaCl-NaNO3-H2O System. J. Cryst. Growth 2019, 518, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Wang, L.; Wei, J.; Cen, Z.; Wei, X. Effects of organic pollutants on struvite crystallization kinetics and the molecular mechanism of inhibition on crystal growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 164882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhele, B.; Zhan, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, X. Review: Nitrogen assimilation in crop plants and its affecting factors. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerendás, J.; Führs, H. The significance of magnesium for crop quality. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, C.; Dong, Q.; Cheng, C.; Ji, L.; Zhuang, C. Effect of fertilizer with different ammonia-nitrate ratio on rice seedling quality and soil nutrient. S. China J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 36, 2183–2190. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Shahrajabian, M.; Cheng, Q. The roles of a light-dependent protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (LPOR), and ATP-dependent dark operative protochlorophyllide oxidoreductase (DPOR) in chlorophyll biosynthesis. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2021, 49, 12456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Z.; Zhao, Q.L. Recovery of ammonium-nitrogen from landfill leachate as a multi-nutrient fertilizer. Ecol. Eng. 2003, 20, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troelstra, S.R.; van Dijk, K.; Blacquiire, T. Effects of N source on proton excretion, ionic balance and growth of Alnus glutinosa (L.) Gaertner: Comparison of N2 fixation with single and mixed sources of NO3 and NH4. Plant Soil 1985, 84, 361–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Que, F.; Xu, Z.S.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.S. Exogenous gibberellin enhances secondary xylem development and lignification in carrot taproot. Protoplasma 2017, 254, 830–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.Y.; Wang, N.; Si, C.C. The Application of Nitrogen Source in Regulating Lignin Biosynthesis, Storage Root Development and Yield of Sweet Potato. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, X.Y.; Gu, J.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Fan, C.Z.; Gu, W.W. The status of research on the root exudates of submerged plants and their effects on aquatic organisms. Water 2024, 16, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhanga, M.; Zhoua, T.; Ding, Z.; Tang, H.; Ji, Y.; Wang, C. Influences of changes in pH, temperature, and particle size on surface reaction resistance and diffusion resistance in the struvite dissolution process. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 200, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, E.; Sarkar, S.; Maji, P.K. A review on slow-release fertilizer: Nutrient release mechanism and agricultural sustainability. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
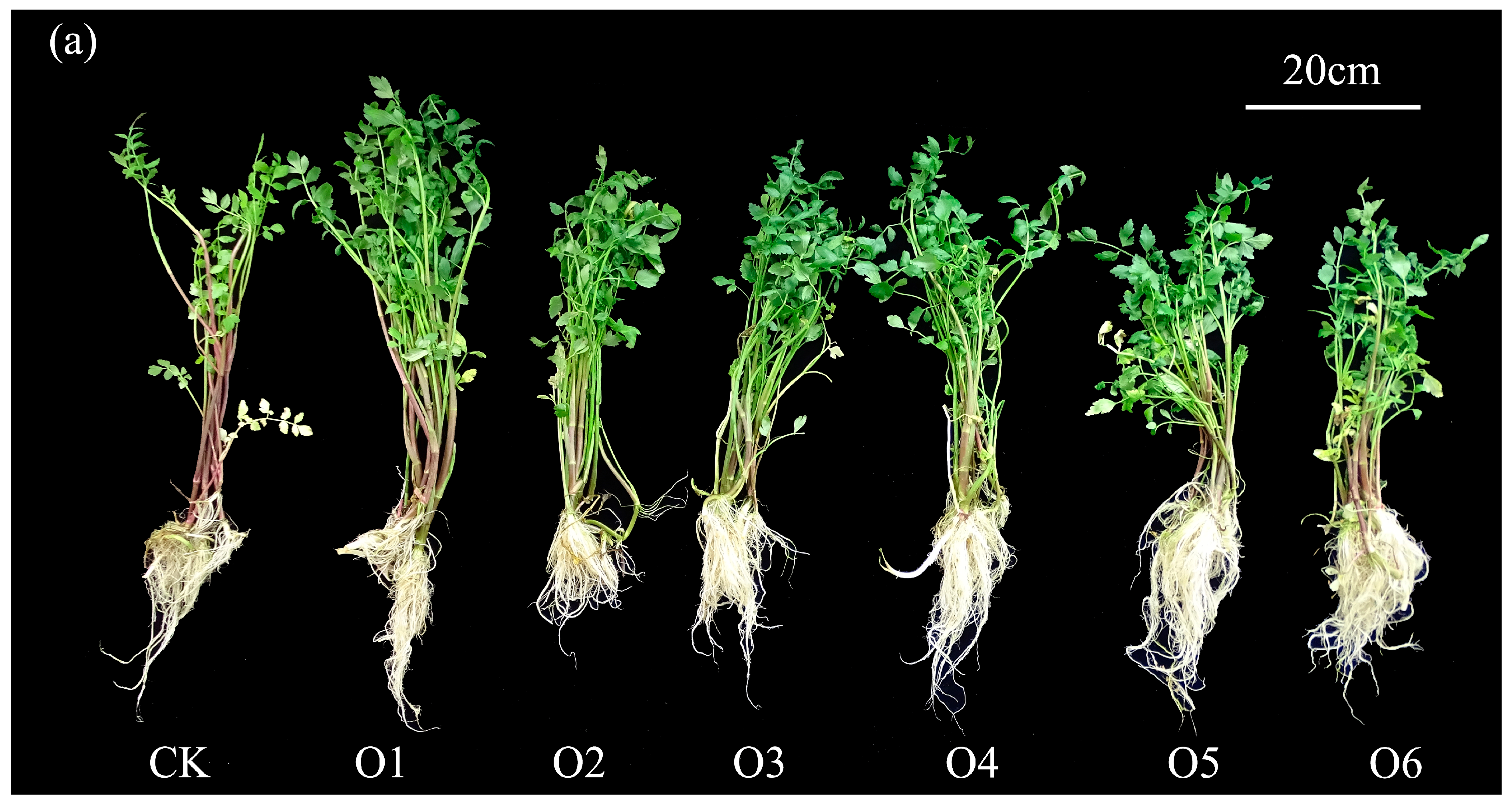




| Parameter | Values | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Mg2+ | 11.08 | mg·L−1 |
| TP | 152.04 | mg·L−1 |
| TAN | 1338.22 | mg·L−1 |
| pH | 8.0–8.2 | – |
| Parameter | Groups | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH value | 9.0, 9.5, 10.0, 10.5, 11.0, 11.5 (treatment of MgCl2) 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10.0, 11.0, 12.0 (treatment of MgO) | – |
| Reaction time | 10, 20, 30, 60 | min |
| Stirring rate | 0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 (treatment of MgCl2) 0, 100, 200, 300, 400 (treatment of MgO) | rpm |
| P/N | 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 | – |
| Mg/N | 0.8, 0.9, 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 | – |
| Vegetable | Fertilizer Ratio | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Struvite | - | 0% | 20% | 40% | 60% | 80% | 100% | |
| Commercial fertilizer | - | 100% | 80% | 60% | 40% | 20% | 0% | |
| Water celery | CK | O1 | O2 | O3 | O4 | O5 | O6 | |
| Bock choy | CK | B1 | B2 | B3 | B4 | B5 | B6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Sun, L.; Cui, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Chang, Y.; Yao, D. A Full Chain of Applying Struvite Recovered from Biogas Slurry to Promote Vegetable Growth. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131352
Li Y, Wang W, Sun L, Cui J, Liu X, Liu J, Chang Y, Yao D. A Full Chain of Applying Struvite Recovered from Biogas Slurry to Promote Vegetable Growth. Agriculture. 2025; 15(13):1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131352
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yunhan, Wei Wang, Linhe Sun, Jian Cui, Xiaojing Liu, Jixiang Liu, Yajun Chang, and Dongrui Yao. 2025. "A Full Chain of Applying Struvite Recovered from Biogas Slurry to Promote Vegetable Growth" Agriculture 15, no. 13: 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131352
APA StyleLi, Y., Wang, W., Sun, L., Cui, J., Liu, X., Liu, J., Chang, Y., & Yao, D. (2025). A Full Chain of Applying Struvite Recovered from Biogas Slurry to Promote Vegetable Growth. Agriculture, 15(13), 1352. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15131352








