Coupling Coordination Development Between Cultivated Land and Agricultural Water Use Efficiency in Arid Regions: A Case Study of the Turpan–Hami Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
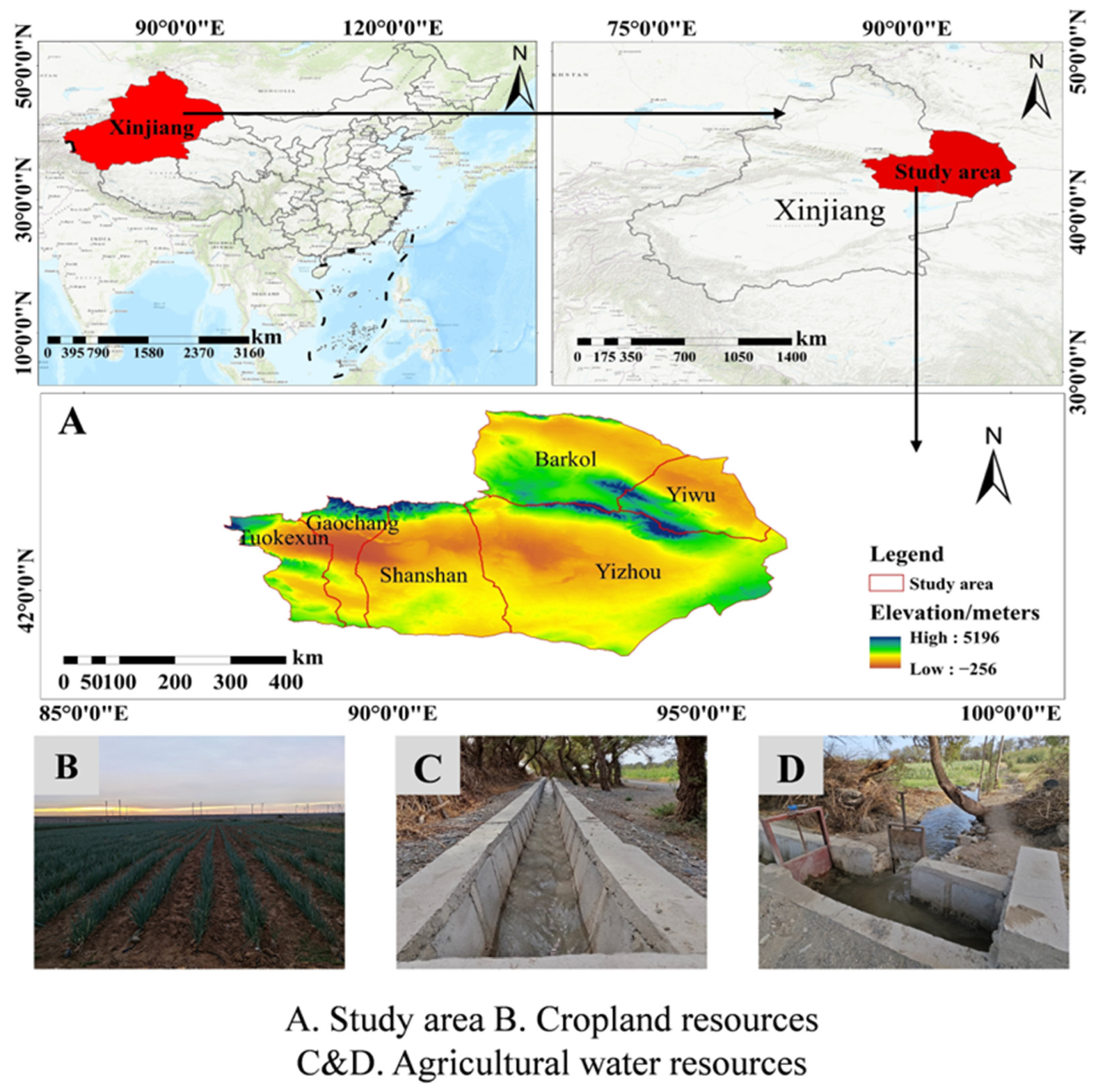
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Indicator System
2.2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Super-Efficiency SBM-DEA
2.3.2. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
2.3.3. Kernel Density Estimation Model
2.3.4. Dagum Gini Coefficient Decomposition Method
2.3.5. Moran’s I
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Cultivated Land and Agricultural Water Resource Utilization Efficiency
3.2. Coupling Coordination Degree Analysis of Cultivated Land and Agricultural Water Resource Utilization Efficiency
3.2.1. Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Coupling Coordination Degree
3.2.2. Spatial Evolution Characteristics of Coupling Coordination Degree
3.3. Analysis of Regional Differences in Coupling Coordination Degree
3.4. Spatial Aggregation Characteristics of Coupling Coordination Degree
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Differentiation Characteristics of Coupling Coordination Degree
4.2. Analysis of Regional Spatial Differences
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, H.; Fu, W.G. Agricultural water-soil resource matching and agricultural economic growth in China from a water footprint perspective: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2020, 41, 193–203. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J. Coupling coordinated development of water-energy-food-forest systems in the Yangtze River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 32, 1193–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Hu, B. Spatial evolution measurement of cultivated land and water resources in arid regions: A case study of Xinjiang. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2023, 23, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Lu, Q. Spatial correlation analysis of cultivated land and irrigation water resource utilization efficiency and their coupling coordination degree in China’s provinces. J. China Agric. Univ. 2022, 27, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Qiu, L.; Deng, M.; Dong, R. Study on vulnerability and coordination of Water-Energy-Food system in Northwest China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X. Analysis of production water use changes in Xinjiang based on LMDI method. Arid Land Geogr. 2016, 39, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Estimation of vegetation ecological water demand in the Turpan-Hami region over the past 30 years. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2024, 44, 8699–8715. [Google Scholar]
- Junran, D.; Desheng, W. An Evaluation of the Impact of Ecological Compensation on the Cross-Section Efficiency Using SFA and DEA: A Case Study of Xin’an River Basin. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7966. [Google Scholar]
- Abudureheman, A.; Wang, Y.; Rao, F. Factors influencing cotton farmers’ water resource utilization efficiency under participatory irrigation management: A case study in Awat County, Xinjiang. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2018, 9, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. Research on agricultural water resource utilization efficiency in China based on DEA method. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2017, 38, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Adingo, S.; Yv, J.; Li, X. Spatiotemporal characteristics of agricultural resource utilization efficiency in Gansu Province, China based on DEA method. J. Resour. Ecol. 2024, 15, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Maimaitijiang, R.; Shi, J. Research on agricultural water resource utilization efficiency in Xinjiang based on three-stage DEA and Malmquist index. Guangdong Water Resour. Hydropower 2023, 2, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, G.; Li, L.; Song, Y. Provincial water use efficiency measurement and factor analysis in China: Based on SBM-DEA model. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, T.; Baohui, M. Evaluation of water resource use efficiency in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei based on three-dimensional water ecological footprint. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 113651. [Google Scholar]
- Muli, H.; Makau, J.; Mugure, L. Determinants of farmer empowerment in agriculture in Kenya: A Tobit approach. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11888. [Google Scholar]
- Maruf, M.; Kai, L. Decomposition analysis of natural gas consumption in Bangladesh using an LMDI approach. Energy Strategy Rev. 2022, 40, 100724. [Google Scholar]
- Youchen, S.; Kees, H.; Oliver, S. Europe-wide air pollution modeling from 2000 to 2019 using geographically weighted regression. Environ. Int. 2022, 168, 107485. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, J.; Ma, J.; Wang, S.; Qin, T.; Wang, Q. Agricultural water use efficiency in the Yangtze River Basin: Based on super-efficiency DEA and Tobit model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Jaime, V.; Manuel, M.; Juan, I. Disentangling the effect of climate and cropland changes on the water performance of agroecosystems (Spain, 1922–2016). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 130811. [Google Scholar]
- Lamy, M.; HAMED, M.; Latifa, D.; Zehri, F.; Sofien, T.; Houda, B. Examining the relationship between the economic growth, energy use, CO2 emissions, and water resources: Evidence from selected MENA countries. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2024, 23, 415–423. [Google Scholar]
- Westerlund, J. Testing for Error Correction in Panel Data. Ox. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2007, 69, 709–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Fan, X.; Xie, Q. Coupling coordination and driving factors of agricultural water resource ecological resilience and utilization efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Water Saving Irrig. 2024, 7, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Liting, X.; Shuang, S. Coupling coordination degree between social-economic development and water environment: A case study of Taihu lake basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 113651. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Duan, W.; Zou, S.; Chen, Y.; Philippe, D.; Tim, V.; Kaoru, T.; Mindje, K.; Alishir, K.; Peter, L. Coupling coordination analysis of the water-food-energy-carbon nexus for crop production in Central Asia. Appl. Energy 2024, 369, 123584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M.; Chandranath, C.; Rajendra, S. Examining the coupling and coordination of water-energy-food nexus at a sub-national scale in India–Insights from the perspective of Sustainable Development Goals. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 43, 140–154. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S. Prediction and regulation of coordinated development between urban environment and economy in Guangzhou. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 1994, 14, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wichelns, D. The water-energy-food: Is the increasing attention warranted, from either a research or policy perspective. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 69, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, Z.; Han, Y.; Milind, K.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of regional “water-soil-energy-carbon” coupling mechanism. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1613–1628. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, M.; Chen, S.; Ma, B.; Liu, Y. Analysis of grain water resource utilization efficiency and influencing factors: An empirical study based on provincial panel data in China. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2020, 36, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Zhang, Q. Analysis of coupling and coordinated development between water resources and socio-economy in Xinjiang. Mark. Res. 2020, 03, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Han, X.; Ma, B.; Li, D.; Wang, Z. Research on the Coupling Coordination Relationship and Spatial Equilibrium Measurement of the Water–Energy–Food Nexus System in China. Water 2025, 17, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Guo, J.; Huang, X.; Shang, Z.; Jin, B. Spatio-temporal characteristics and coupling coordination relationship between industrial green water efficiency and science and technology innovation: A case study in China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. An Evaluation Scheme Driven by Science and Technological Innovation—A Study on the Coupling and Coordination of the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation-Economy-Ecology Complex System in the Yangtze River Basin of China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Du, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H. Exploring the coupling coordination relationship of water resources, socio-economy and eco-environment in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, M.; Shi, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Cai, W. Coupling coordination degree of land, ecology, and food and its influencing factors in Henan Province. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Aihemaitijiang, G.; Wan, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, J. Exploring Spatio-Temporal Variations in Water and Land Resources and Their Driving Mechanism Based on the Coupling Coordination Model: A Case Study in Western Jilin Province, China. Agriculture 2025, 15, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J. Spatiotemporal characteristics of coupling coordination of urban water-soil resource utilization efficiency in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 40, 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, F. Spatio-temporal evolution pattern and obstacle factors of water-energy-food nexus coupling coordination in the Yangtze River economic belt. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 444, 141229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Peng, J.; Deng, Z.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal differentiation of cultivated land use efficiency in China under dual perspectives of non-point source pollution and carbon emissions. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2015, 25, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Bai, L.; Zhou, K.; Kou, Y.; Yuan, W. Study on the Coupling Coordination Degree and Driving Mechanism of “Production-Living-Ecological” Space in Ecologically Fragile Areas: A Case Study of the Turpan–Hami Basin. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Abulizi, A.; Mamitimin, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, L. Coordination analysis and evaluation of population, water resources, economy, and ecosystem coupling in the Tuha region of China. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Zheng, X. Measurement and Improvement Potential of Agricultural Water Use Efficiency Based on a Meta-Frontier SBM Model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2018, 27, 2293–2304. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, L. Research on Green Efficiency Changes of Water Resources in China Based on SBM-Malmquist Productivity Index Model. Resour. Sci. 2018, 40, 993–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, A.; Xiong, Y. Spatial Differences and Interactive Spillover Effects between Urban Land Use Ecological Efficiency and Industrial Structure Upgrading in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 125–139. [Google Scholar]
- Tone, K. A Slacks-Based Measure of Efficiency in Data Envelopment Analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A Slacks-Based Measure of Super-Efficiency in Data Envelopment Analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Luo, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, W. Coupling Coordination between New Urbanization and Food Security in Key Agricultural Regions of Central China: A Case Study of Henan Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, J.; Li, F.; Zheng, S.; Deng, Y. Assessment of county level urbanization with the consideration of coupling coordination among population–economy–space–society–green in the Lower Yellow River basin of China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Yang, H. Collaborative models and uncertain water quality in payments for watershed services: China’s Jiuzhou River eco-compensation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 70, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Guo, W.; Yang, S. Coupling Dynamics of Resilience and Efficiency in Sustainable Tourism Economies: A Case Study of the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Zhuo, N.; Yang, H. Embodied CO2 in China’s trade of harvested wood products based on an MRIO model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z. Measurement and Spatiotemporal Evolution of Urban Land Green Use Efficiency in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 30, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Dagum, C. Decomposition and Interpretation of Gini and the Generalized Entropy Inequality Measures. Statistica 1997, 57, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Dagum, C. A New Approach to the Decomposition of the Gini Income Inequality Ratio. Empir. Econ. 1997, 22, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirgol, B.; Dieppois, B.; Northey, J. Future changes in agrometeorological extremes in the southern Mediterranean region: When and where will they affect croplands and wheatlands? Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 358, 110232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Yipar, A.; Zulikatiayi, A.; Dong, X.; Wang, X. Evaluation of the Implementation Effect of the “13th Five-Year Plan” for Tuberculosis Prevention and Control in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. J. Trop. Med. 2024, 24, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Shen, L.; Ye, P. The Conference on “Water Resources Forum—Coordinated Development of Water Resources, Ecology and Environment” Held in Xinjiang. Resour. Sci. 2005, 6, 194–195. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.; Lu, Q.; Yang, X. Spatiotemporal Assessment of Recreation Ecosystem Service Flow from Green Spaces in Zheng-zhou’s Main Urban Area. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, G.; Huang, X. Coupling Coordination Analysis of Urban Social Vulnerability and Human Activity Intensity. Environ. Res. Commun. 2025, 7, 035009. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Pu, C.; Dong, L.; Yan, Z. Study on water resource pressure and cultivated land use efficiency changes and their coupling relationship in Xinjiang. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2022, 61, 165–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, R.; Chen, Z.; Yin, Z.; Lu, R. Coupling coordination characteristics of water and soil resources in Hexi region, Gansu Province from 2000 to 2019. J. Desert Res. 2022, 42, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- He, G.; Zhang, S.; Bao, K.; Yang, X.; Hou, X. Coupling coordination and spatiotemporal differentiation of land and water resource utilization efficiency in the Huai River Basin. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, S.; Huang, X.; Lin, N.; Yi, Z. Synergistic reduction of air pollutants and carbon emissions in Chengdu-Chongqing urban agglomeration, China: Spatial-temporal characteristics, regional differences, and dynamic evolution. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 493, 144929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Spatial differentiation and influencing factors of eco-economic system coordination degree at county level in Jiangsu Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2017, 24, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, W.; Kuang, X. Radiation effect or siphon effect? Coupled coordination and spatial effects of digital economy and green manufacturing efficiency—Evidence from spatial Durbin modelling. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0313654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Indicator Category | Data Types | Cultivated Land Indicators | Agricultural Water Resource Indicators |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Indicators | Cropping System | Crop sown area, mu | Effective irrigated area, mu |
| Capital Input | Total agricultural machinery power, kW | Total fixed asset investment, 10,000 CNY | |
| Labor Input | Employment in primary industry, persons | Employment in primary industry, persons | |
| Resource Endowment | Pesticide usage, kg | Total agricultural water use, 10,000 m3 | |
| Means of Production | Plastic film coverage area, mu | Total grain production, tons | |
| Chemical fertilizer application, tons | Chemical fertilizer application, tons | ||
| Output Indicators | Gross agricultural output value, 10,000 CNY | Gross agricultural output value, 10,000 CNY |
| CCD | Classification Criteria |
|---|---|
| 0 < D ≤ 0.2 | Severe Imbalance |
| 0.2 < D ≤ 0.4 | Mild Imbalance |
| 0.4 < D ≤ 0.6 | Moderate Coordination |
| 0.6 < D ≤ 0.8 | Good Coordination |
| 0.8 < D ≤ 1 | High-quality Coordination |
| Year | Farmland Resources | Agricultural Water Resource Utilization Efficiency | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaochang | Shanshan | Tuokexun | Yizhou | Barkol | Yiwu | Gaochang | Shanshan | Tuokexun | Yizhou | Barkol | Yiwu | |
| 2000 | 0.122 | 0.072 | 0.069 | 0.115 | 2.830 | 0.142 | 0.205 | 0.102 | 0.377 | 0.208 | 1.050 | 1.330 |
| 2001 | 0.179 | 0.108 | 0.137 | 0.114 | 0.803 | 0.151 | 0.286 | 0.166 | 0.412 | 0.165 | 0.745 | 0.448 |
| 2002 | 0.158 | 0.152 | 0.221 | 0.125 | 0.706 | 0.168 | 0.427 | 0.188 | 1.013 | 0.163 | 1.016 | 0.357 |
| 2003 | 0.196 | 0.143 | 0.263 | 0.144 | 0.714 | 0.243 | 0.529 | 0.201 | 0.543 | 0.179 | 1.040 | 0.841 |
| 2004 | 0.176 | 0.179 | 0.162 | 0.157 | 1.011 | 0.279 | 0.536 | 0.241 | 0.231 | 0.234 | 1.024 | 1.010 |
| 2005 | 0.204 | 0.177 | 0.268 | 0.164 | 0.265 | 0.322 | 1.052 | 0.238 | 0.355 | 0.274 | 1.029 | 1.024 |
| 2006 | 0.236 | 0.252 | 0.237 | 0.175 | 0.219 | 0.382 | 1.026 | 0.251 | 0.343 | 0.226 | 0.673 | 0.547 |
| 2007 | 0.269 | 0.326 | 0.340 | 0.188 | 0.276 | 0.526 | 1.024 | 0.302 | 0.399 | 0.234 | 0.702 | 0.775 |
| 2008 | 0.276 | 0.343 | 0.281 | 0.205 | 0.397 | 1.007 | 0.525 | 0.310 | 0.383 | 0.228 | 1.049 | 1.043 |
| 2009 | 0.282 | 0.369 | 0.397 | 0.234 | 0.392 | 0.524 | 0.407 | 0.346 | 0.323 | 0.235 | 0.499 | 0.661 |
| 2010 | 0.300 | 0.370 | 0.369 | 0.256 | 0.461 | 0.627 | 0.394 | 0.423 | 0.344 | 0.256 | 0.459 | 0.632 |
| 2011 | 0.342 | 0.374 | 0.315 | 0.300 | 0.466 | 1.021 | 0.397 | 0.384 | 0.272 | 0.307 | 0.480 | 1.015 |
| 2012 | 0.444 | 0.437 | 0.398 | 0.329 | 0.487 | 0.626 | 0.505 | 1.011 | 0.275 | 0.340 | 0.504 | 0.528 |
| 2013 | 0.588 | 0.525 | 0.382 | 0.363 | 0.565 | 0.701 | 0.754 | 0.507 | 0.306 | 0.298 | 0.494 | 0.649 |
| 2014 | 0.612 | 0.442 | 0.390 | 0.332 | 0.565 | 0.701 | 1.011 | 0.443 | 0.335 | 0.297 | 0.511 | 0.538 |
| 2015 | 0.659 | 0.495 | 0.427 | 0.349 | 1.020 | 0.841 | 1.014 | 0.563 | 0.344 | 0.312 | 0.583 | 0.849 |
| 2016 | 0.689 | 0.541 | 0.475 | 0.371 | 1.022 | 1.025 | 0.561 | 0.528 | 0.368 | 0.346 | 0.853 | 1.109 |
| 2017 | 0.644 | 0.480 | 0.465 | 0.335 | 0.790 | 0.696 | 0.469 | 0.476 | 0.355 | 0.328 | 0.714 | 0.882 |
| 2018 | 0.729 | 0.521 | 0.437 | 0.317 | 0.704 | 0.609 | 0.595 | 0.634 | 0.347 | 0.338 | 0.629 | 0.587 |
| 2019 | 0.729 | 0.546 | 0.481 | 0.357 | 0.675 | 0.653 | 0.633 | 1.208 | 0.363 | 0.358 | 0.812 | 0.695 |
| 2020 | 0.765 | 0.832 | 0.595 | 0.428 | 0.736 | 0.868 | 0.870 | 0.978 | 0.450 | 0.422 | 1.048 | 0.837 |
| 2021 | 0.917 | 1.042 | 0.756 | 0.455 | 0.723 | 1.028 | 1.052 | 1.016 | 0.564 | 0.493 | 0.810 | 1.031 |
| 2022 | 1.091 | 1.063 | 1.012 | 0.477 | 1.085 | 0.959 | 1.144 | 0.796 | 1.026 | 0.775 | 1.040 | 1.045 |
| 2023 | 1.008 | 1.002 | 1.175 | 0.375 | 0.892 | 0.679 | 1.026 | 1.052 | 0.981 | 1.036 | 1.021 | 1.069 |
| Mean | 0.484 | 0.450 | 0.419 | 0.278 | 0.746 | 0.616 | 0.685 | 0.515 | 0.446 | 0.335 | 0.783 | 0.812 |
| County/District | Regression Equation | R2 | Trend Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gaochang | = −35.09098 + | 0.81949 | Moderate-to-strong upward trend |
| Shanshan | = −46.38997 + | 0.93279 | Strong and steady upward trend |
| Tuokexun | = −23.96546 + | 0.54497 | Moderate upward trend |
| Yizhou | = −25.57487 + | 0.91584 | Significant upward trend |
| Barkol | = 0.5828 + | 0.0004 | No meaningful linear trend |
| Yiwu | = −23.78798 + | 0.54231 | Moderate upward trend |
| Year | Gini Coefficient | Intra-Regional Disparity | Inter-Regional Disparity | Contribution Rate (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turpan | Hami | Turpan–Hami | Intra-Regional | Inter-Regional | Hypervariation Density | ||
| 2000 | 0.374 | 0.152 | 0.298 | 0.488 | 34.78 | 65.05 | 0.17 |
| 2001 | 0.213 | 0.092 | 0.243 | 0.246 | 42.37 | 41.16 | 16.46 |
| 2002 | 0.221 | 0.149 | 0.253 | 0.238 | 46.15 | 14.22 | 39.63 |
| 2003 | 0.200 | 0.113 | 0.213 | 0.229 | 42.50 | 33.10 | 24.41 |
| 2004 | 0.213 | 0.072 | 0.204 | 0.273 | 36.05 | 56.25 | 7.70 |
| 2005 | 0.137 | 0.112 | 0.123 | 0.156 | 43.05 | 30.99 | 25.95 |
| 2006 | 0.114 | 0.096 | 0.111 | 0.123 | 45.68 | 1.16 | 53.16 |
| 2007 | 0.120 | 0.071 | 0.144 | 0.132 | 44.83 | 3.44 | 51.72 |
| 2008 | 0.169 | 0.024 | 0.185 | 0.222 | 34.36 | 43.26 | 22.38 |
| 2009 | 0.092 | 0.005 | 0.120 | 0.118 | 35.51 | 24.07 | 40.42 |
| 2010 | 0.092 | 0.018 | 0.116 | 0.115 | 37.82 | 26.65 | 35.53 |
| 2011 | 0.135 | 0.036 | 0.155 | 0.165 | 38.64 | 52.16 | 9.20 |
| 2012 | 0.085 | 0.094 | 0.068 | 0.089 | 47.61 | 5.92 | 46.48 |
| 2013 | 0.090 | 0.087 | 0.092 | 0.091 | 49.45 | 0.19 | 50.35 |
| 2014 | 0.103 | 0.103 | 0.084 | 0.113 | 45.27 | 10.81 | 43.92 |
| 2015 | 0.113 | 0.097 | 0.111 | 0.121 | 46.33 | 11.91 | 41.76 |
| 2016 | 0.126 | 0.051 | 0.125 | 0.160 | 36.35 | 39.98 | 23.67 |
| 2017 | 0.100 | 0.039 | 0.101 | 0.127 | 36.27 | 33.82 | 29.91 |
| 2018 | 0.079 | 0.066 | 0.087 | 0.082 | 48.12 | 5.32 | 46.56 |
| 2019 | 0.089 | 0.082 | 0.088 | 0.092 | 47.94 | 12.34 | 39.72 |
| 2020 | 0.079 | 0.067 | 0.085 | 0.083 | 47.80 | 8.20 | 44.00 |
| 2021 | 0.080 | 0.054 | 0.093 | 0.088 | 45.07 | 29.59 | 25.34 |
| 2022 | 0.049 | 0.023 | 0.064 | 0.056 | 43.39 | 39.69 | 16.93 |
| 2023 | 0.046 | 0.006 | 0.057 | 0.062 | 32.53 | 67.47 | 0.00 |
| Mean | 0.130 | 0.071 | 0.134 | 0.153 | 42.00 | 27.36 | 30.64 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Z | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 0.13 | 1.003 | 0.158 |
| 2004 | 0.061 | 0.793 | 0.214 |
| 2013 | −0.562 | −1.1 | 0.136 |
| 2023 | −0.054 | 0.443 | 0.329 |
| Types | 2000 | 2010 | 2016 | 2020 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-High (HH) Cluster | Barkol | Shanshan | Gaochang | ||
| High-Low (HL) Cluster | Shanshan Barkol | ||||
| Low-High (LH) Cluster | Yizhou | Yizhou | Yizhou | Yizhou | Yizhou |
| Low-Low (LL) Cluster | Shanshan | Gaochang Shanshan | Yiwu |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, Y.; Abliz, A.; Guo, D.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Nurahmat, B. Coupling Coordination Development Between Cultivated Land and Agricultural Water Use Efficiency in Arid Regions: A Case Study of the Turpan–Hami Basin. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111153
Kong Y, Abliz A, Guo D, Liu X, Li J, Nurahmat B. Coupling Coordination Development Between Cultivated Land and Agricultural Water Use Efficiency in Arid Regions: A Case Study of the Turpan–Hami Basin. Agriculture. 2025; 15(11):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111153
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Yue, Abdugheni Abliz, Dongping Guo, Xianhe Liu, Jialin Li, and Buasi Nurahmat. 2025. "Coupling Coordination Development Between Cultivated Land and Agricultural Water Use Efficiency in Arid Regions: A Case Study of the Turpan–Hami Basin" Agriculture 15, no. 11: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111153
APA StyleKong, Y., Abliz, A., Guo, D., Liu, X., Li, J., & Nurahmat, B. (2025). Coupling Coordination Development Between Cultivated Land and Agricultural Water Use Efficiency in Arid Regions: A Case Study of the Turpan–Hami Basin. Agriculture, 15(11), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111153






