Effect of Caragana korshinskii Plantation Succession on Community Stability in Alpine Sandy Regions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experiment and Sampling Design
2.3. Plant Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Soil Sampling and Analysis
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
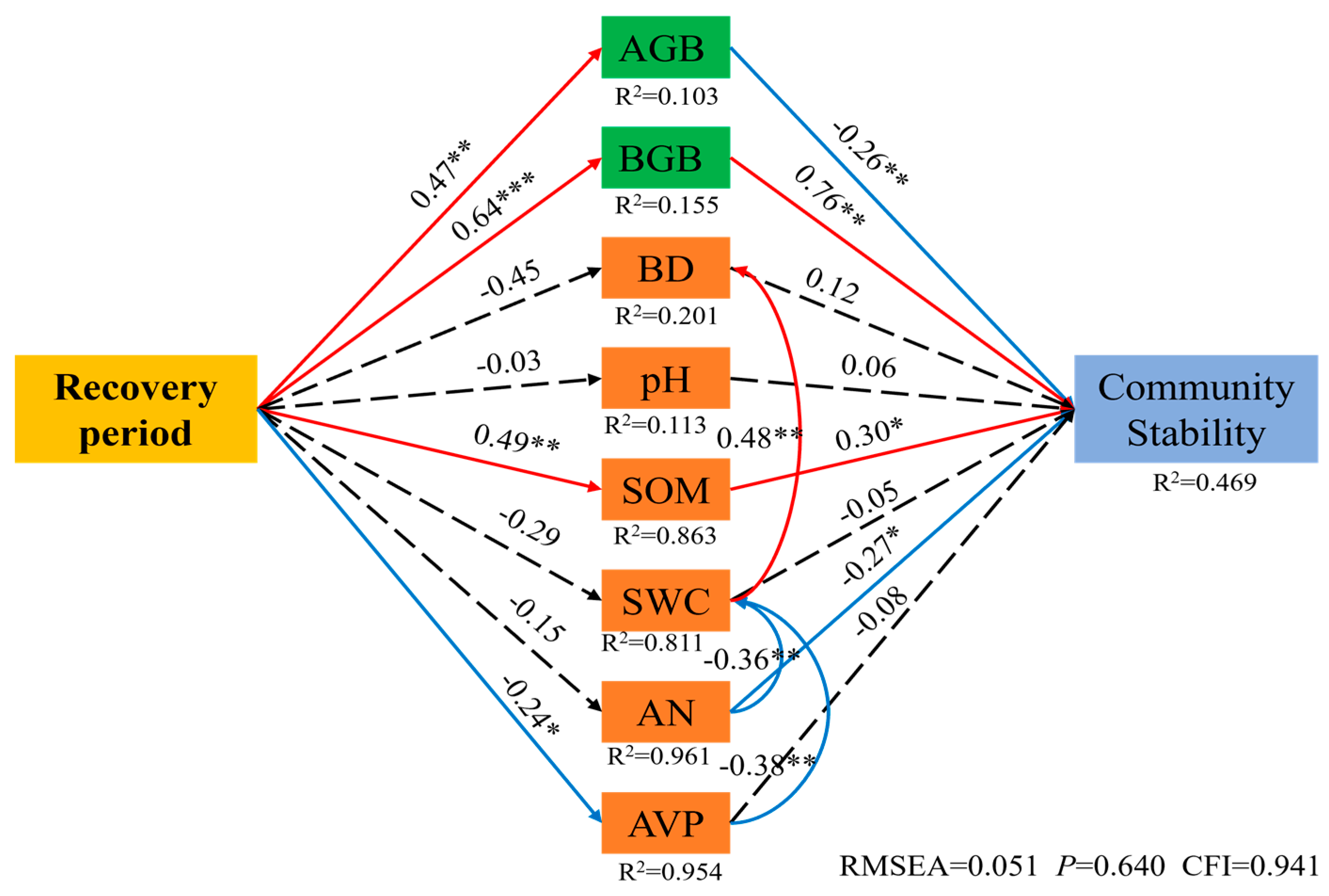
3. Results
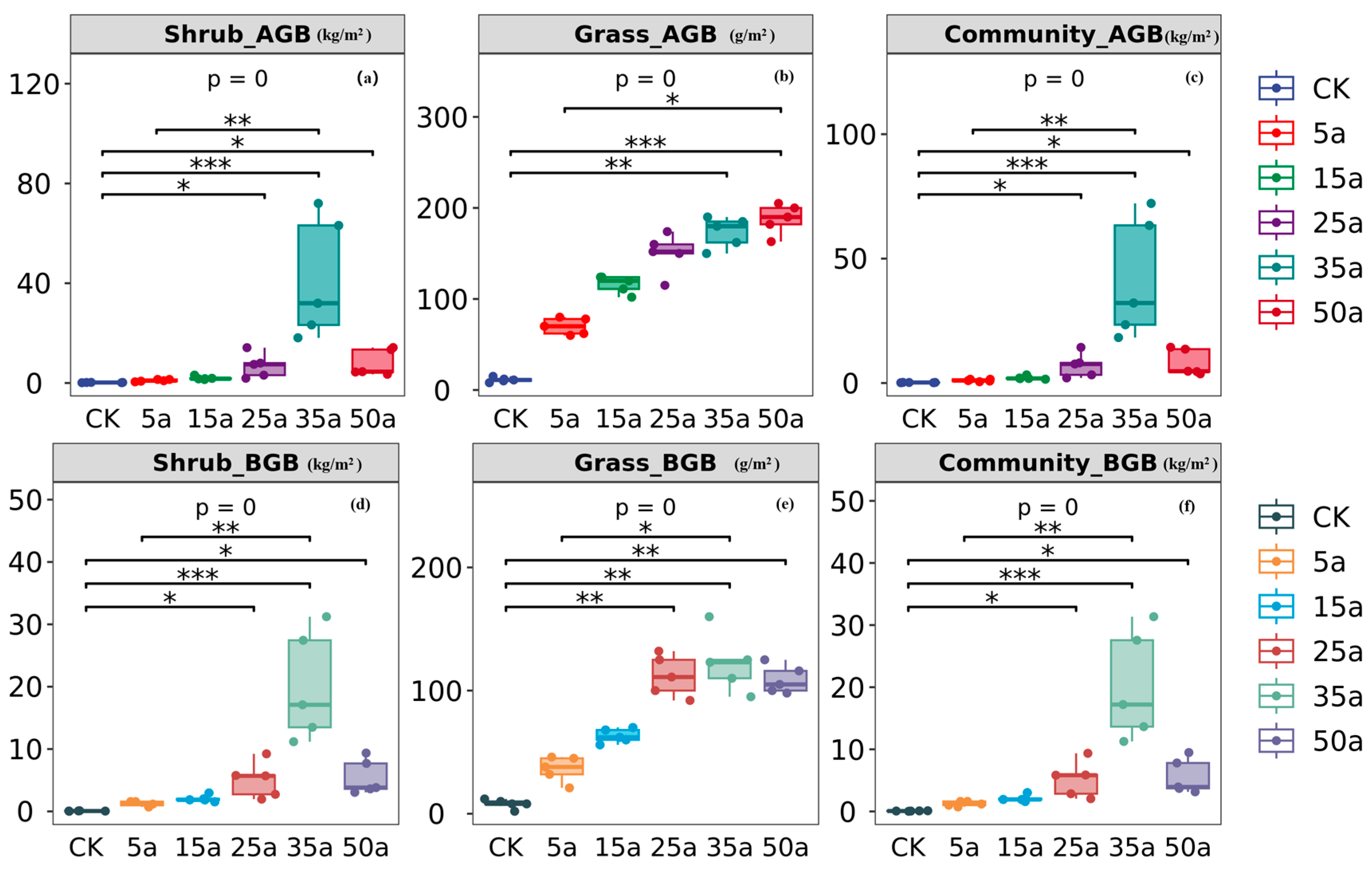
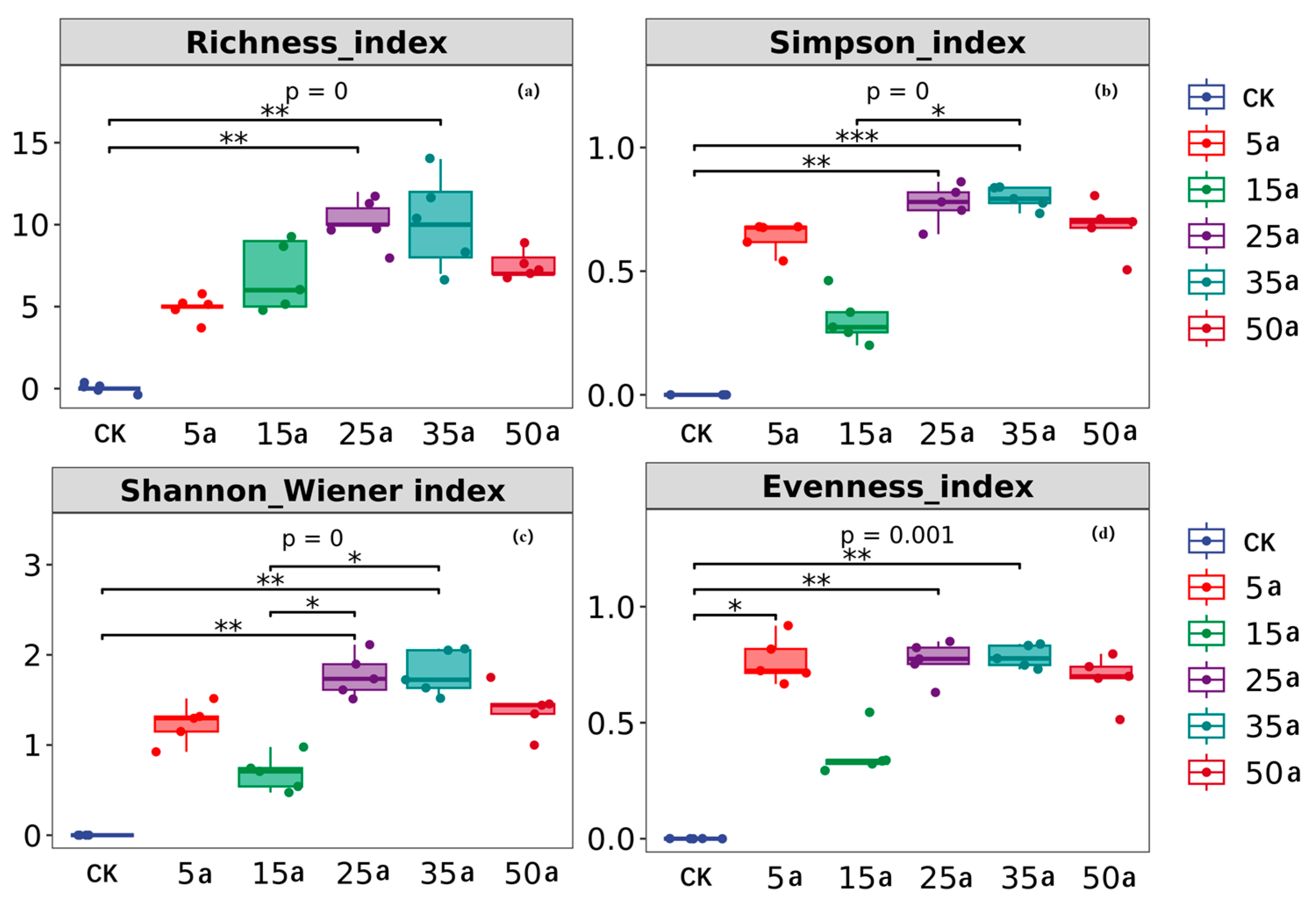
3.1. Change Characteristics in Artificial Caragana Microphylla Plant Communities
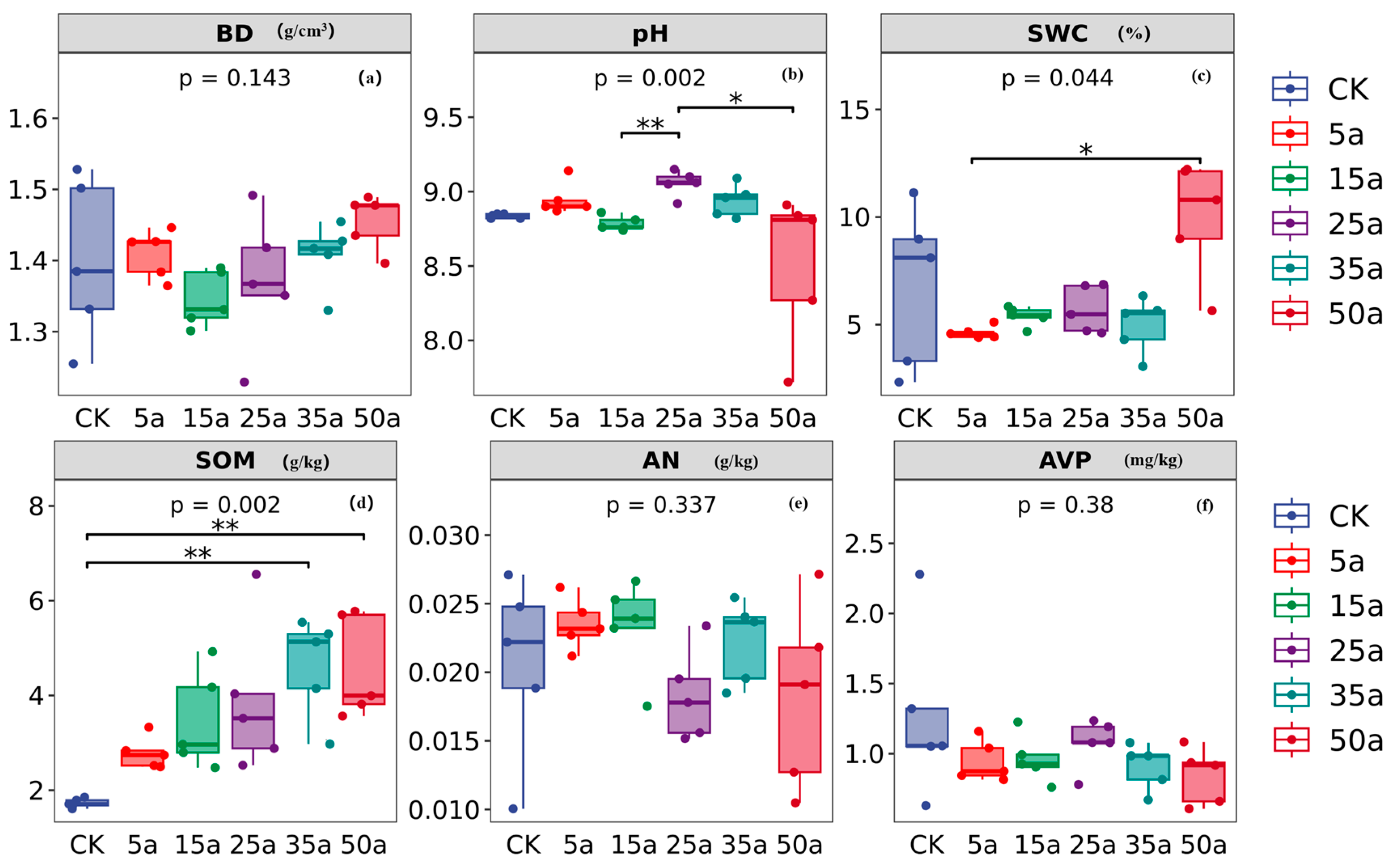
3.2. Change Characteristics of Soil Properties in Artificial Caragana Microphylla
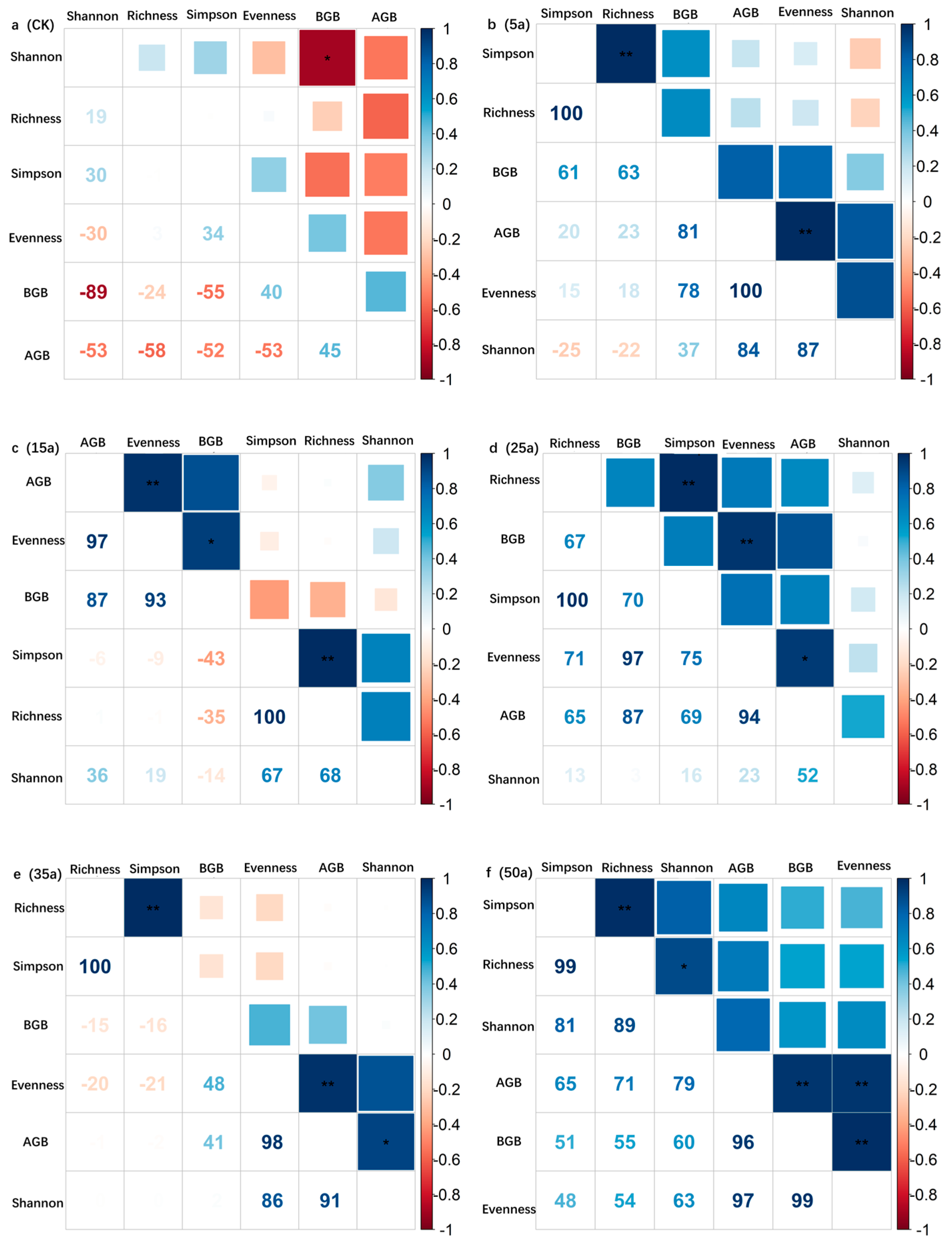
3.3. Change Characteristics of Community Stability in Artificial Caragana korshinskii
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation in Plant Community Diversity and Biomass
4.2. Variation in Soil Properties
4.3. Variation in Community Stability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garcia, F.N.; Wiesmeier, M.; Goberna, M.; Martínez, M.M.; Albaladejo, J. Carbon dynamics after afforestation of semiarid shrublands: Implications of site preparation techniques. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 319, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Hu, H.; Sun, W.; Zhu, J.; Liu, G.B.; Zhou, W.M.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, P.L.; Liu, X.P.; Wu, X.; et al. Effects of National Ecological Restoration Projects on Carbon Sequestration in China from 2001 to 2010. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saren, G.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Geng, X.Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, G.L. Sustainability of the Human Environment System in Inner Mongolia’s Sand Region from 2000 to 2020. China Deserts 2025, 45, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, G.M.; Liu, B.; Wang, G.; Zhang, B.L. The microbial biomass and activity in soil with shrub (Caragana korshinskii K.) plantation in the semi-arid loess plateau in China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2010, 46, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.Q.; Guo, Y.; Huang, M.Z.; Feng, W.; Ye, Q.H.; Liu, J.X.; Li, X. Community structure characteristics and management strategies of red cone artificial forests with different restoration years. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 2022, 49, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Song, M. The role of plants and soil microorganisms in regulating nutrient cycling in ecosystems. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2010, 34, 979–988. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.Y.; Gao, C.J.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.H. Stability and evaluation methods of plant communities in southwest dry and hot river valleys. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2021, 27, 334–350. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, F.; Bai, Y. Multiple global changes drive grassland productivity and stability: A meta-analysis. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 2850–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.; Xiao, S.C.; Peng, X.; Ding, A.J.; Su, J. Radial growth of Korshinsk peashrub and its response to drought in different sub-arid climate regions of northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 326 Pt A, 116708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segrestin, J.; Gotzenberger, L.; Valencia, E.; De, B.F.; Leps, J. A unified framework for partitioning the drivers of stability of ecological communities. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2024, 33, e13828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polley, H.W.; Wilsey, B.J.; Derner, J.D. Dominant species constrain effects of species diversity on temporal variability in biomass production of tallgrass prairie. Oikos 2007, 116, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Lauenroth, W.K. Dominant species, rather than diversity, regulates temporal stability of plant communities. Oecologia 2011, 166, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.J.; Lu, Z.Y.; Wu, C.S.; Wen, H.D.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, Y.H.; Sha, L.Q. The impact of subtropical forest reverse succession on soil carbon storage. J. Yunnan Univ. 2016, 38, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Wang, S.L.; Chen, C.Y. Exploration of the decline mechanism of Chinese fir plantations. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2004, 1953–1957. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.L. Changes in plant biomass and soil nutrients of alpine shrub meadows with different degrees of degradation. Northwest Agric. J. 2014, 23, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Lal, R.; Chen, Y.; An, S. Soil, leaf and root ecological stoichiometry of Caragana korshinskii on the loess plateau of china in relation to plantation age. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.H.; Liu, G.B.; Wang, G. Effects of Caragana korshinskii Kom. cover on run off, sediment yield and nitrogen loss. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2010, 25, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Han, P.; Zhang, P.; Ding, F.; Ma, C. The impact of afforestation on soil organic carbon sequestration on the Qinghai Plateau, China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlton, B.Z.; Wang, Y.P.; Vitousek, P.M.; Field, C.B. A unifying framework for dinitrogen fixation in the terrestrial biosphere. Nature 2008, 454, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Xin, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, R.; Murray, P.J. Vegetation patches increase wind-blown litter accumulation in a semi-arid steppe of northern China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 124008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.X. The impact of artificial sand fixation vegetation restoration on soil microbial quantity in the Gonghe Basin, Qinghai Province. Resour. Environ. Arid. Reg. 2022, 36, 178–185. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; Feng, W.; Wang, X.J. Soil fungal community composition and diversity of different sand fixing plants in Hulunbuir Sandy Land. Chin. Soil Water Conserv. Sci. 2021, 19, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X.W.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.P.; Cheng, B.; Shi, Q.L.; Liu, P.; Li, L. Study on the effects of caragana twig artificial forest on soil physical and chemical properties changes in Northwest Shanxi Province. J. Northwest Bot. 2003, 23, 628–632. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.K.; Zheng, X.X.; Lin, H.Z.; Lin, X.; Huang, L.J. Changes in functional traits and environmental factors of island plants at different stages of succession. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 39, 3749–3758. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.N.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.X.; Xu, Y.D.; Wu, X.H.; Dan, X.K.; Liu, S.L.; Dong, Q.M.; Dong, S.K.; Wen, L. The succession dynamics of artificially restored plant communities in the degraded grassland of the “black soil beach” type in the Sanjiangyuan area. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 39, 2444–2453. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, Y.M.; Luo, Y.J.; Zhou, J.F.; Zhang, J.H. The impact of the ecological restoration project of desertification grassland in northwest Sichuan on the vegetation community of sandy land. Grassl. Sci. 2009, 26, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.S.; Jin, W.Z.; Liu, Y.H. Comprehensive management technology for desertification land sealing and protection area in Gonghe County. Qinghai Agric. For. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 8–12+72. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.L.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z.H.; Sun, Z.; Liu, L.X.; Mi, H.Y.; Fan, Y.J. Estimation Model for the Biomass of Jinjia in the Middle of Maowusu Sandy Land. Resour. Environ. Arid. Reg. 2015, 29, 128–133. [Google Scholar]
- Valencia, E.; de Bello, F.; Galland, T.; Adler, P.B.; Leps, J.; E-Vojtko, A.; van Klink, R.; Carmona, C.P.; Danihelka, J.; Dengler, J.; et al. Synchrony matters more than species richness in plant community stability at a global scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24345–24351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. (Ed.) Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gweon, H.S.; Bowes, M.J.; Moorhouse, H.L.; Oliver, A.E.; Bailey, M.J.; Acreman, M.; Read, D.S. Contrasting community assembly processes structure lotic bacteria metacommunities along the river continuum. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.F.; Chai, Q.L.; Ma, Z.Y.; An, Q.Q.; Wu, G.L.; Chang, X.F.; Zheng, J.Y.; Wang, G. Does artificial Caragana korshinskii plantation increase soil carbon continuously in a water-limited landscape on the Loess Plateau? Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar]
- Berthrong, S.T.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. A global meta-analysis of soil exchangeable cations, pH, carbon, and nitrogen with afforestation. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 2228–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Willis, C.G.; Klein, J.A.; Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.K.; Zhao, X. Recovery of plant species diversity during long-term experimental warming of a species-rich alpine meadow community on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 213, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimm, S.L. The complexity and stability of ecosystems. Nature 1984, 307, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Duan, P.; Yung, J.C.; Weng, C.N.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Bahtebay, J.; Ma, X. Vegetation cover changes in China induced by ecological restoration-protection projects and land-use changes from 2000 to 2020. Catena 2022, 217, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enquist, B.J. Universal scaling in tree and vascular plant allometry: Toward a general quantitative theory linking plant form and function from cells to ecosystems. Tree Physiol. 2002, 22, 1045–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y.B. Soil moisture decline due to afforestation across the Loess Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 546, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.Q.; Zhao, C.; Fang, S.; Yu, K. Effects of different vegetation restoration on soil water storage and water balance in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 206, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyburn, J.; Mckenzie, P.; Crawley, M.J.; Fornara, D.A. Effects of grassland management on plant C:N:P stoichiometry: Implications for soil element cycling and storage. Ecosphere 2017, 8, e01963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Pei, H.K. Study on the composition and properties of soil humus in alpine meadow vegetation. Soil Bull. 2004, 35, 562–565. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.S.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, M.C. Spatial and temporal variability of soil properties under Caragana microphylla shrubs in the northwestern Shanxi Loess Plateau, China. J. Arid Environ. 2011, 75, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.J.; Yan, J. Accumulation of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in Pinus yunnanensis forests at different age stages. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 253, 625–631. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Wang, C.T.; Wang, G.X.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Xiang, Z.Y. Changes in soil enzyme activity and microbial community structure of alpine meadows at different degradation and succession stages in the three rivers source region. J. Grassl. Ind. 2014, 23, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.Y.; Jiang, D.M.; Zhu, L.H.; Nan, Y.H. Causes of grassland degradation and changes in plant diversity in horqin sandy land. J. Grassl. Ind. 2006, 15, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.M.; Liu, X.P.; He, Y.H.; Zhang, T.H.; Wei, J.; Che, L.; Sun, S.S. Changes of plant community characteristics and influencing factors during closure and restoration of Horqin Sandy Land. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 43, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.L.; Cui, J.H.; Su, Y.Z. Comparison of leaf area and leaf dry matter content of major plants in different dune habitats. Chin. J. Ecol. 2005, 25, 304–311. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Cheng, X.; Huang, M.; Shao, M.; Warrington, D.N. A comparison of fine root distribution and water consumption of mature Caragana korshinkii Kom grown in two soils in a semiarid region, China. Plant Soil 2009, 315, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Loreau, M. The causes and consequences of compensatory dynamics in ecological communities. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 393–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hector, A.; Hautier, Y.; Saner, P.; Wacker, L.; Bagchi, R.; Joshi, J.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Spehn, E.M.; Bazeley-White, E.; Weilenmann, M.; et al. General stabilizing effects of plant diversity on grassland productivity through population asynchrony and overyielding. Ecology 2010, 918, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, L.; Valencia, E.; Galland, T.; Gotzenberger, L.; Leps, J.; Evojtko, A.; Carmona, C.P.; Majekova, M.; Danihelka, J.; Dengler, J.; et al. Functional trait trade-offs define plant population stability across different biomes. Proc. R. Soc. B 2023, 290, 20230344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majekova, M.; Bello, F.D.; Dolezal, J.; Leps, J. Plant functional traits as determinants of population stability. Ecology 2014, 95, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bello, F.; Lavorel, S.; Hallett, L.M.; Valencia, E.; Garnier, E.; Roscher, C.; Conti, L.; Galland, T.; Goberna, M.; Májekova, M.; et al. Functional trait effects on ecosystem stability: Assembling the jigsaw puzzle. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2021, 36, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loreau, M.; De Mazancourt, C. Species synchrony and its drivers: Neutral and nonneutral community dynamics in fluctuating environments. Am. Nat. 2008, 172, E48–E66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, S.; Shen, R.; Gong, Y.; Wang, C.; Hong, P.; Reuman, D.C. Biodiversity stabilizes plant communities through statistical-averaging effects rather than compensatory dynamics. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, D.; Zhao, X.; Qin, R.; Su, H.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; et al. Effect of Caragana korshinskii Plantation Succession on Community Stability in Alpine Sandy Regions. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111143
Shi Z, Ma L, Zhang Z, Li H, Wei D, Zhao X, Qin R, Su H, Li S, Hu X, et al. Effect of Caragana korshinskii Plantation Succession on Community Stability in Alpine Sandy Regions. Agriculture. 2025; 15(11):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111143
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhengchen, Li Ma, Zhonghua Zhang, Honglin Li, Dengxian Wei, Xuebin Zhao, Ruimin Qin, Hongye Su, Shan Li, Xue Hu, and et al. 2025. "Effect of Caragana korshinskii Plantation Succession on Community Stability in Alpine Sandy Regions" Agriculture 15, no. 11: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111143
APA StyleShi, Z., Ma, L., Zhang, Z., Li, H., Wei, D., Zhao, X., Qin, R., Su, H., Li, S., Hu, X., Ade, H., & Zhou, H. (2025). Effect of Caragana korshinskii Plantation Succession on Community Stability in Alpine Sandy Regions. Agriculture, 15(11), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15111143




