Analysis on Spatiotemporal Variation in Soil Drought and Its Influencing Factors in Hebei Province from 2001 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
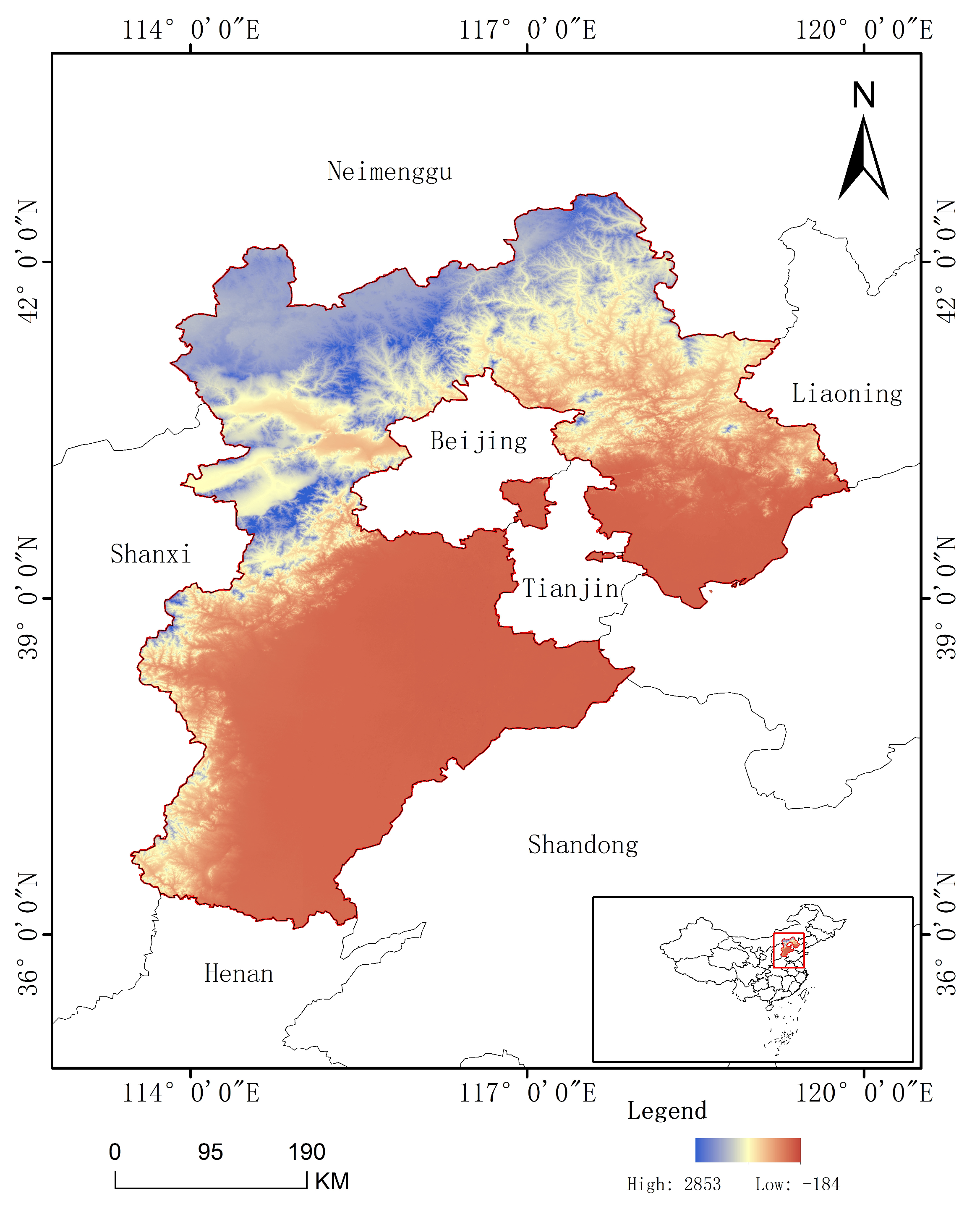
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
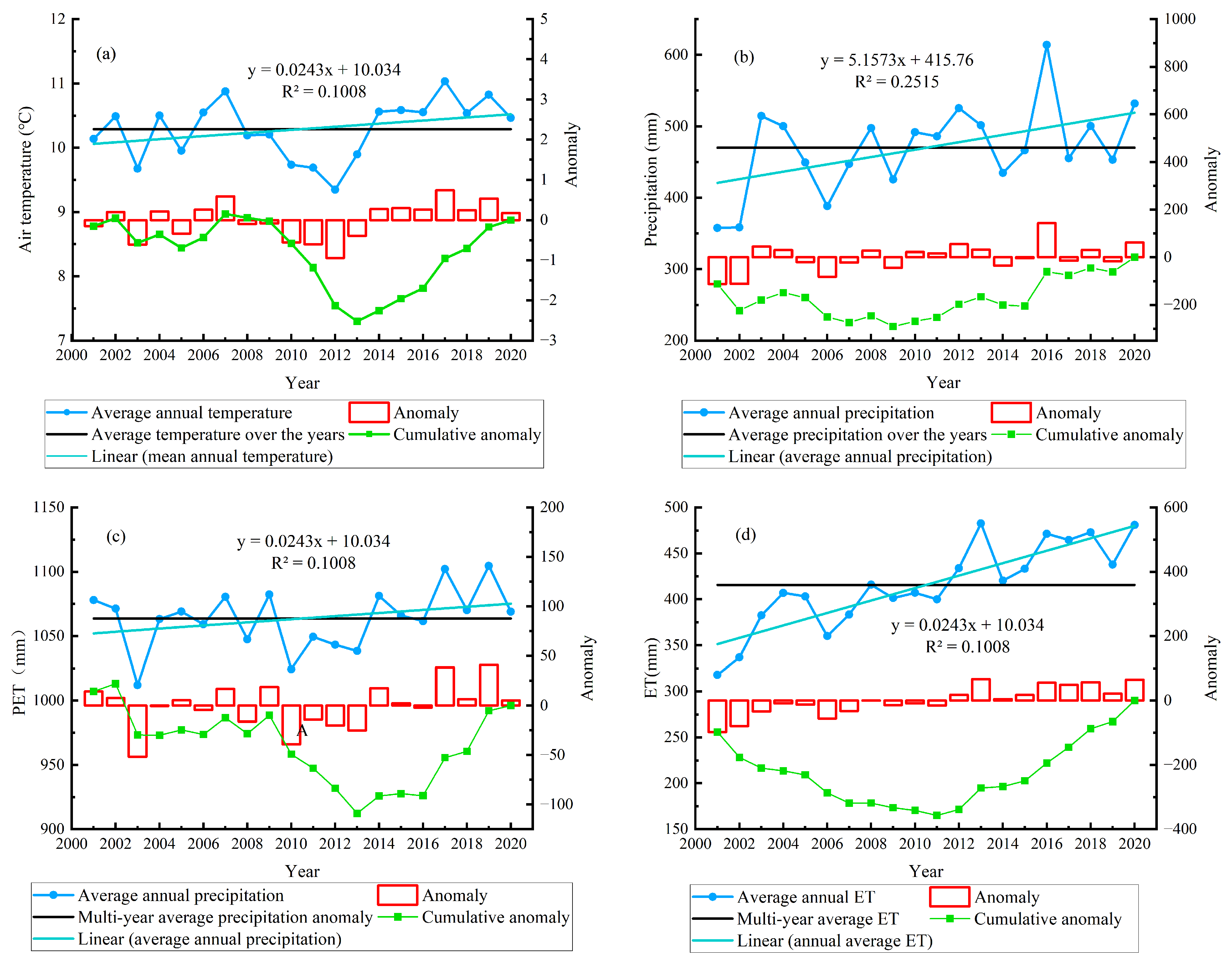
2.2. Data
2.3. Methodology
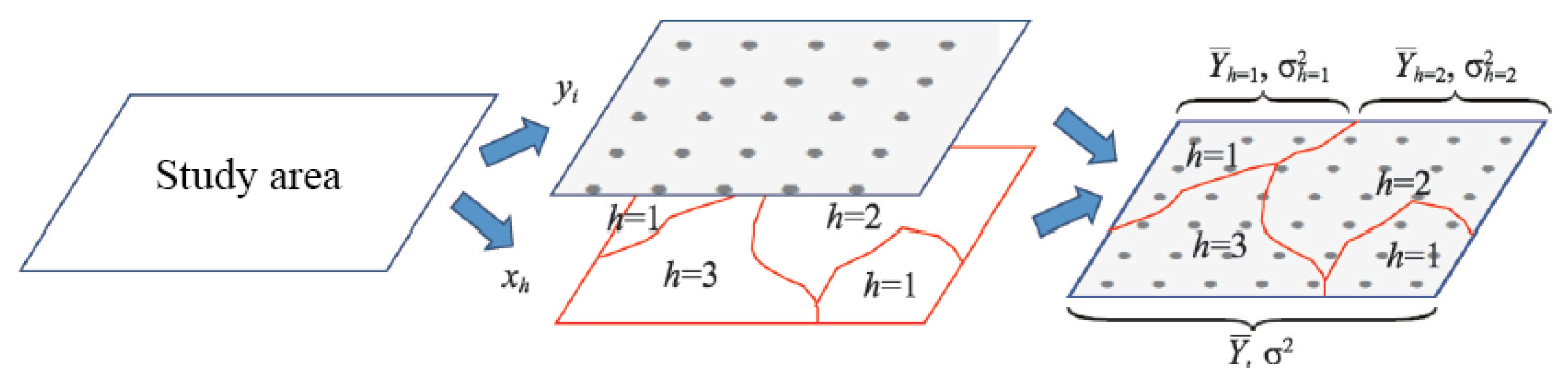
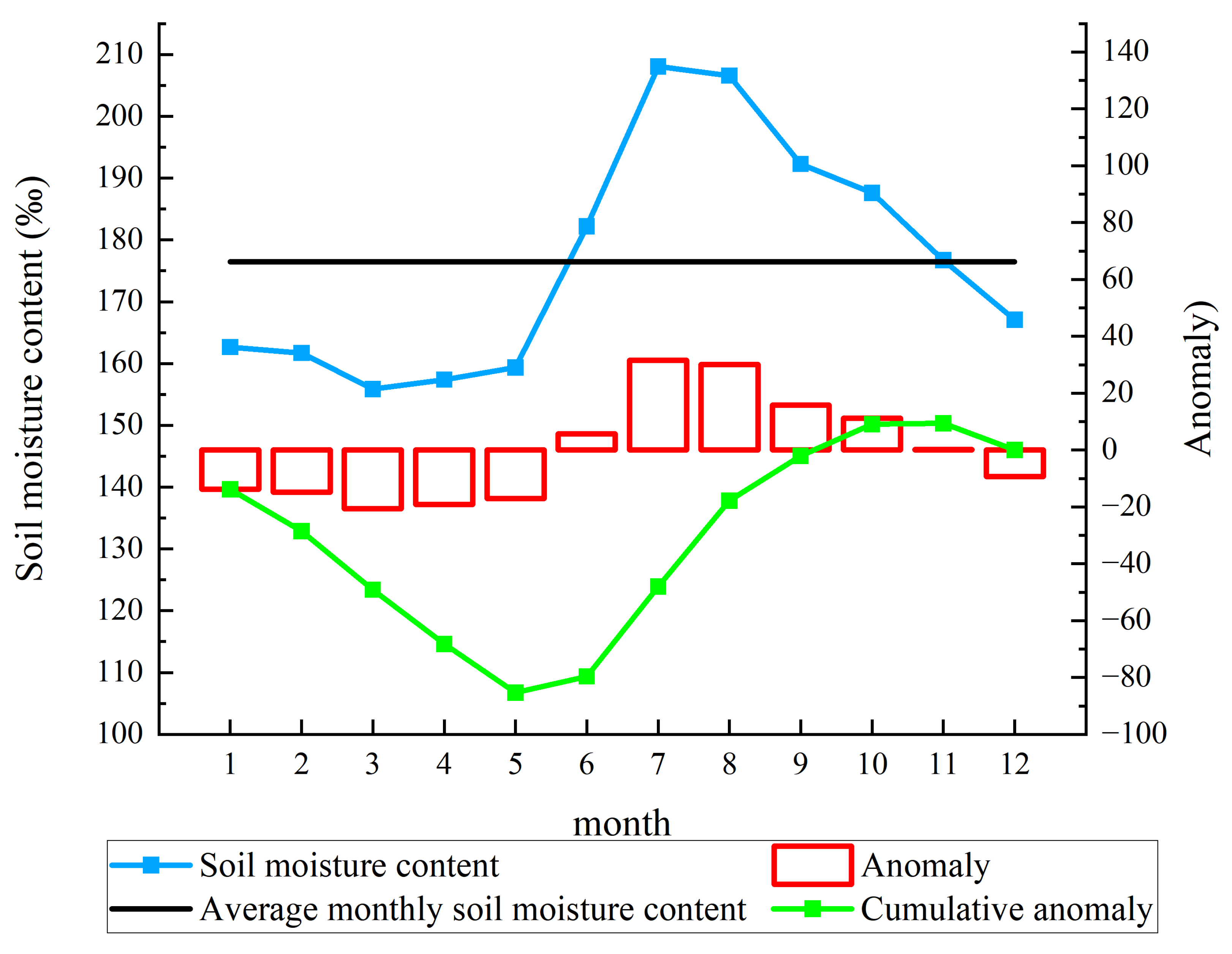
2.3.1. Cumulative Anomaly
2.3.2. Coefficient of Variation
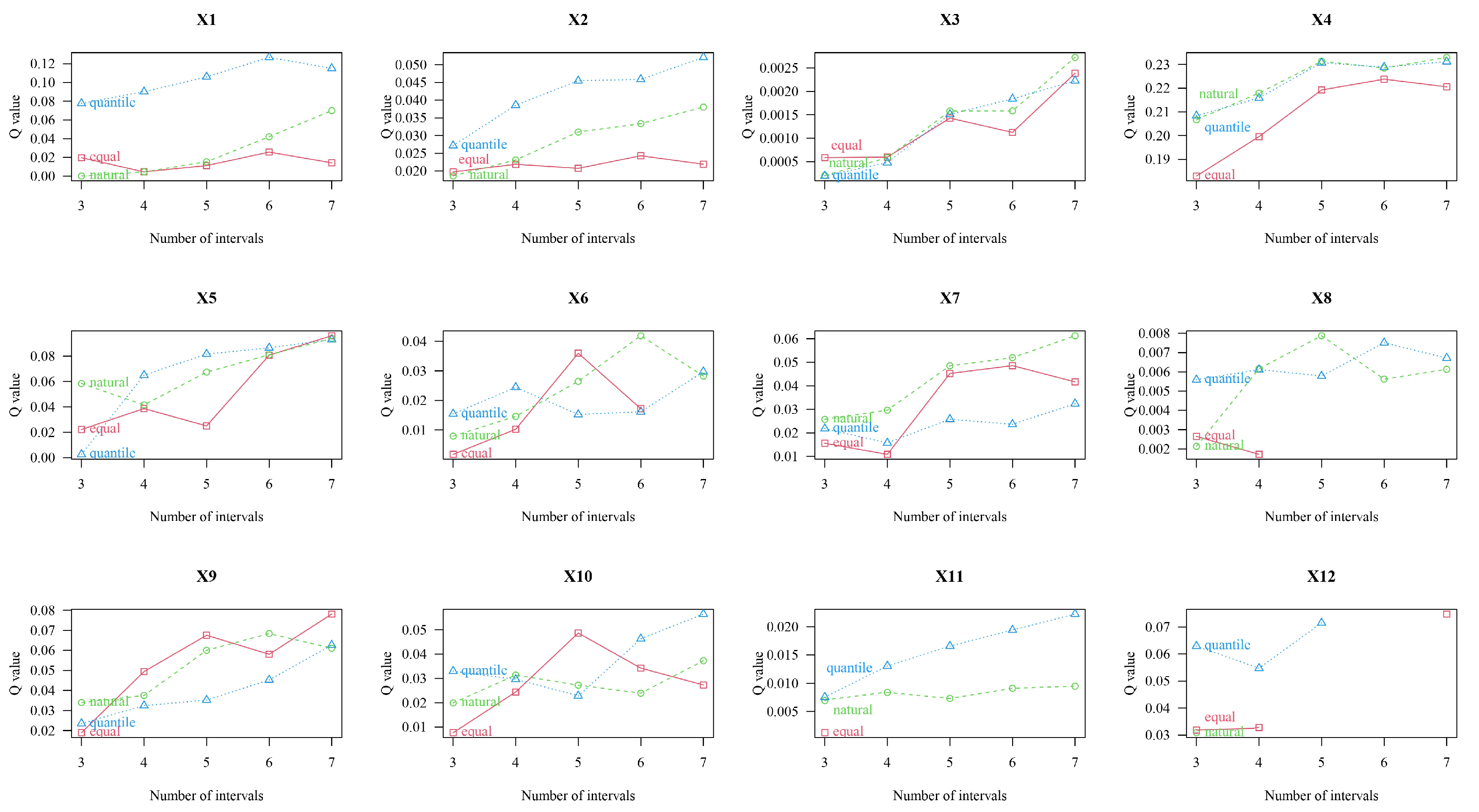
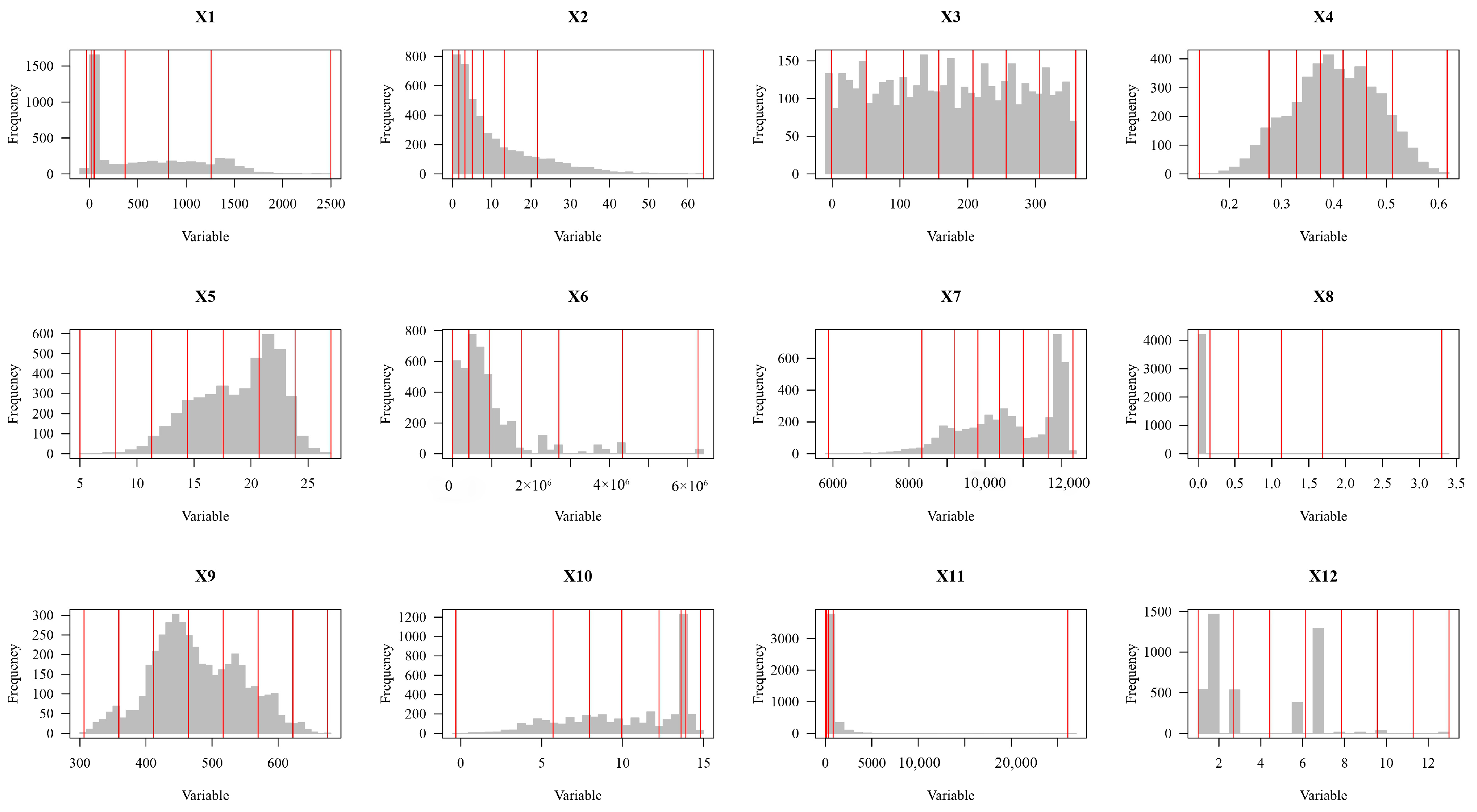
2.3.3. Natural Breakpoint Method
2.3.4. Center of Gravity Migration Model
2.3.5. Sen + Mann–Kendall Trend Analysis
2.3.6. Geographic Detector Model Based on Optimal Parameters
2.4. Classification of Drought Levels
3. Results
3.1. Interannual Spatial and Temporal Variation Characteristics of Soil Drought in Hebei Province
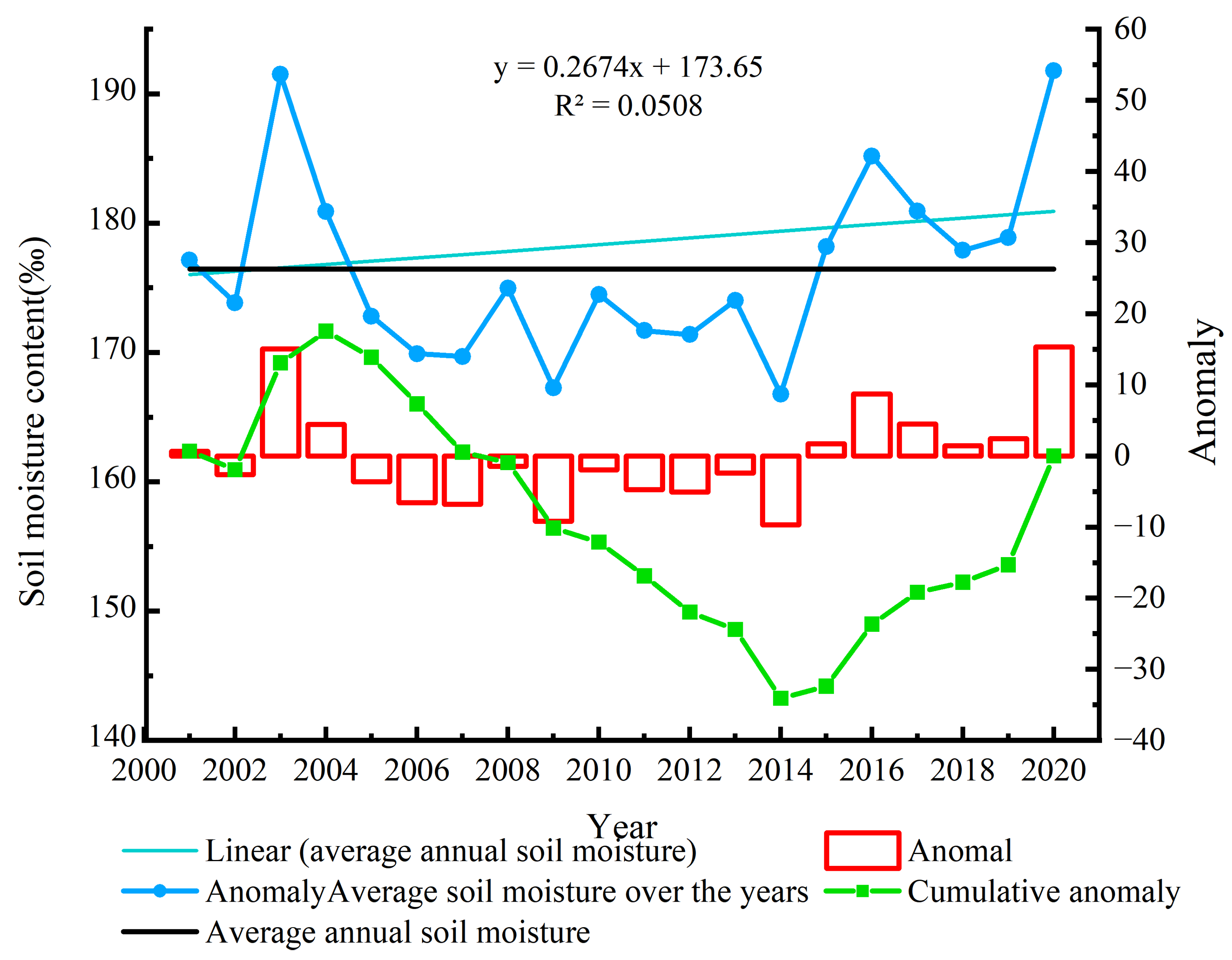
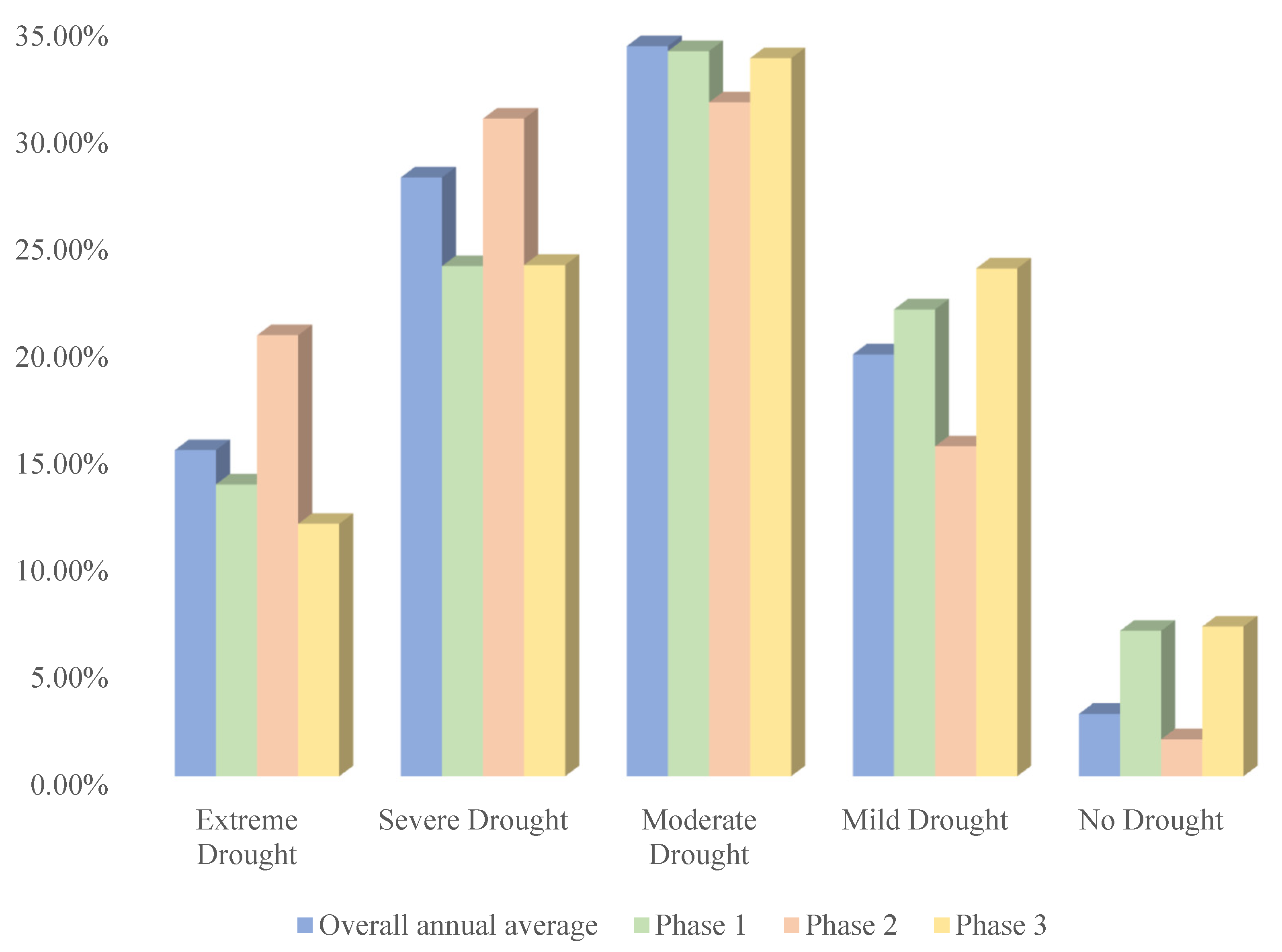
3.1.1. Interannual Temporal Variation Characteristics of Soil Drought
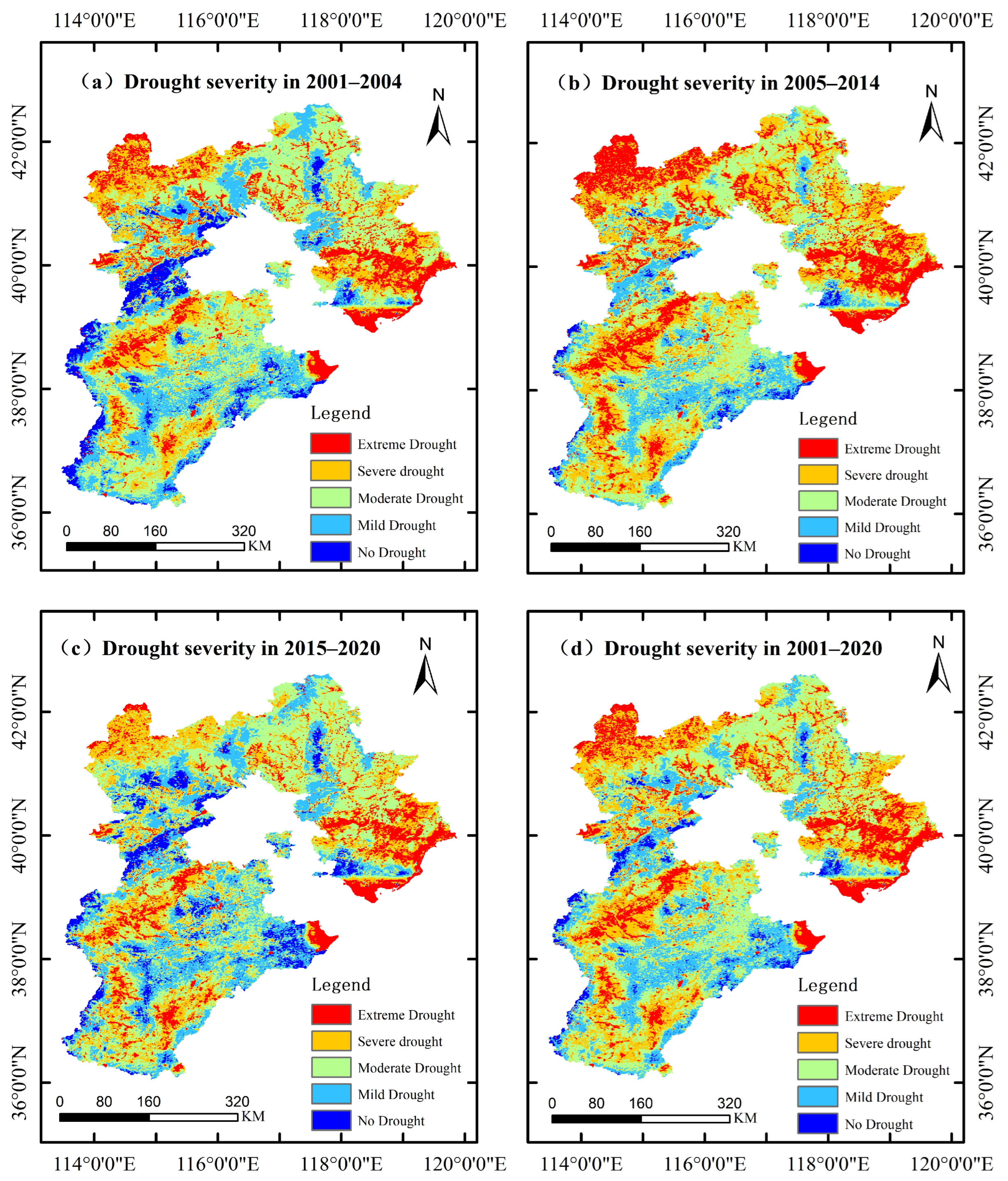
3.1.2. Interannual Spatial Variation Characteristics of Soil Drought
3.2. Intra-Annual Temporal and Spatial Variation in Soil Drought in Hebei Province
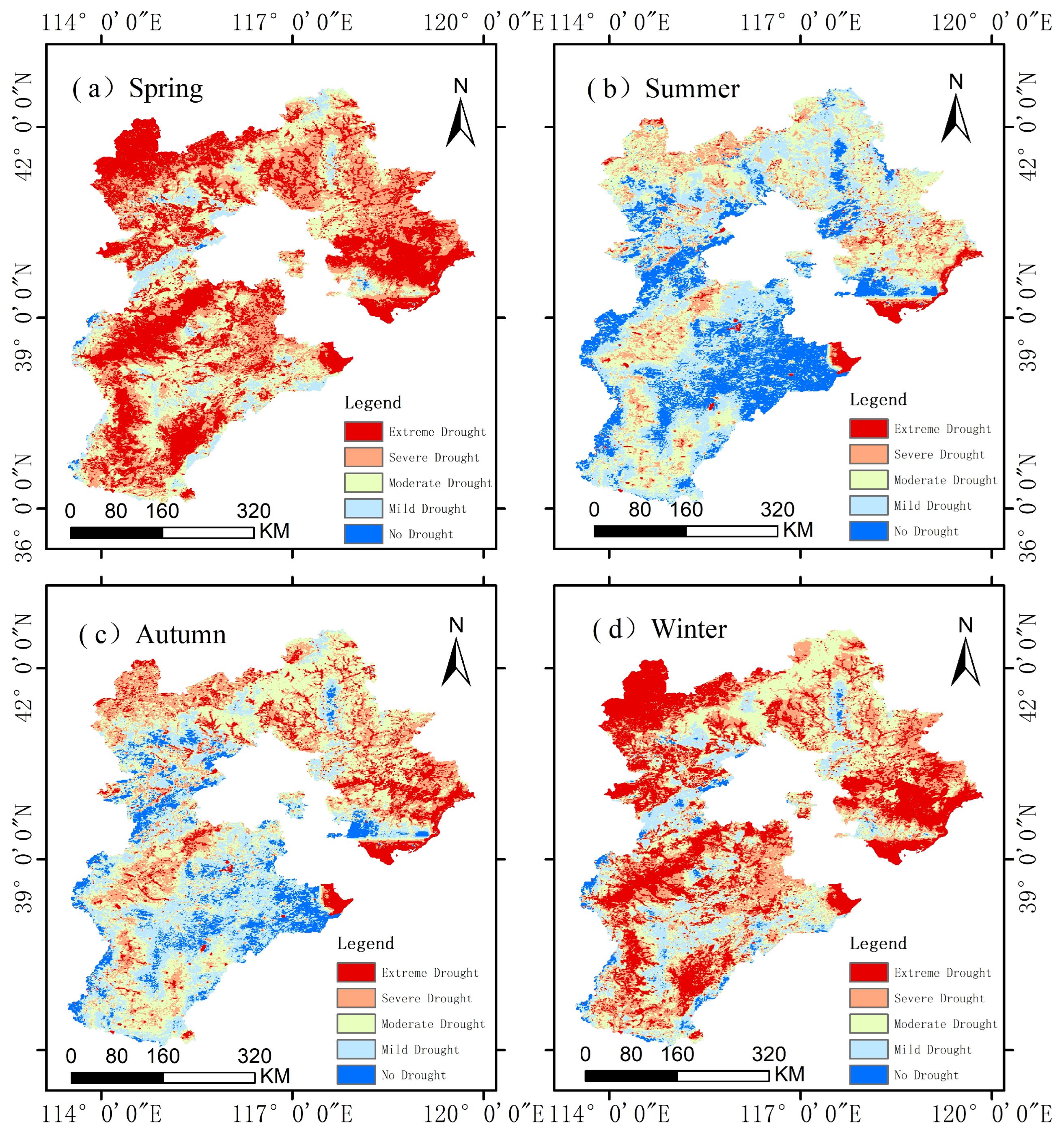
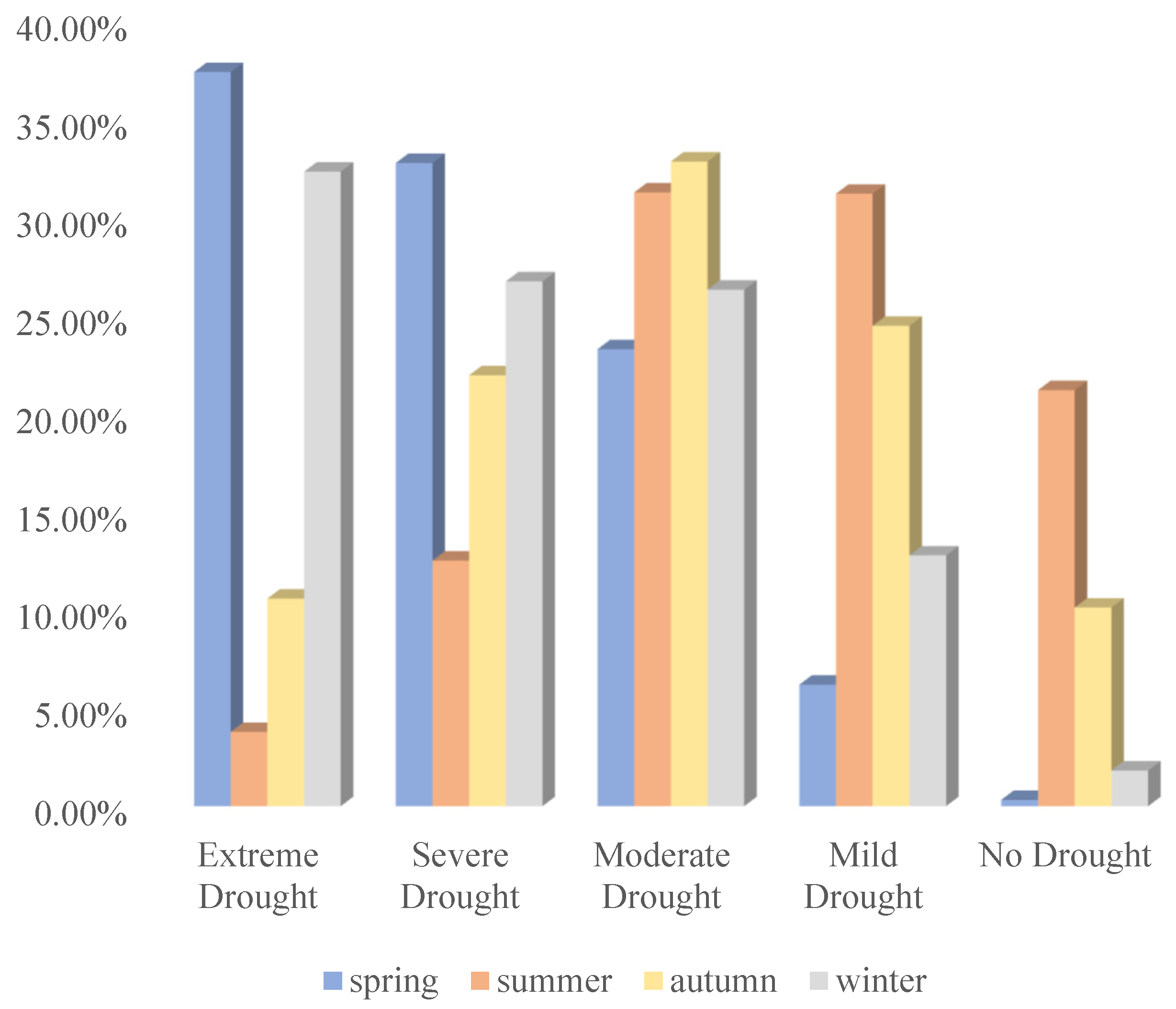
3.2.1. Annual Spatial Variation Characteristics of Soil Drought Characteristics of Intra-Year Temporal Variation of Soil Drought
3.2.2. Annual Spatial Variation Characteristics of Soil Drought
3.3. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Variation Characteristics of Soil Drought
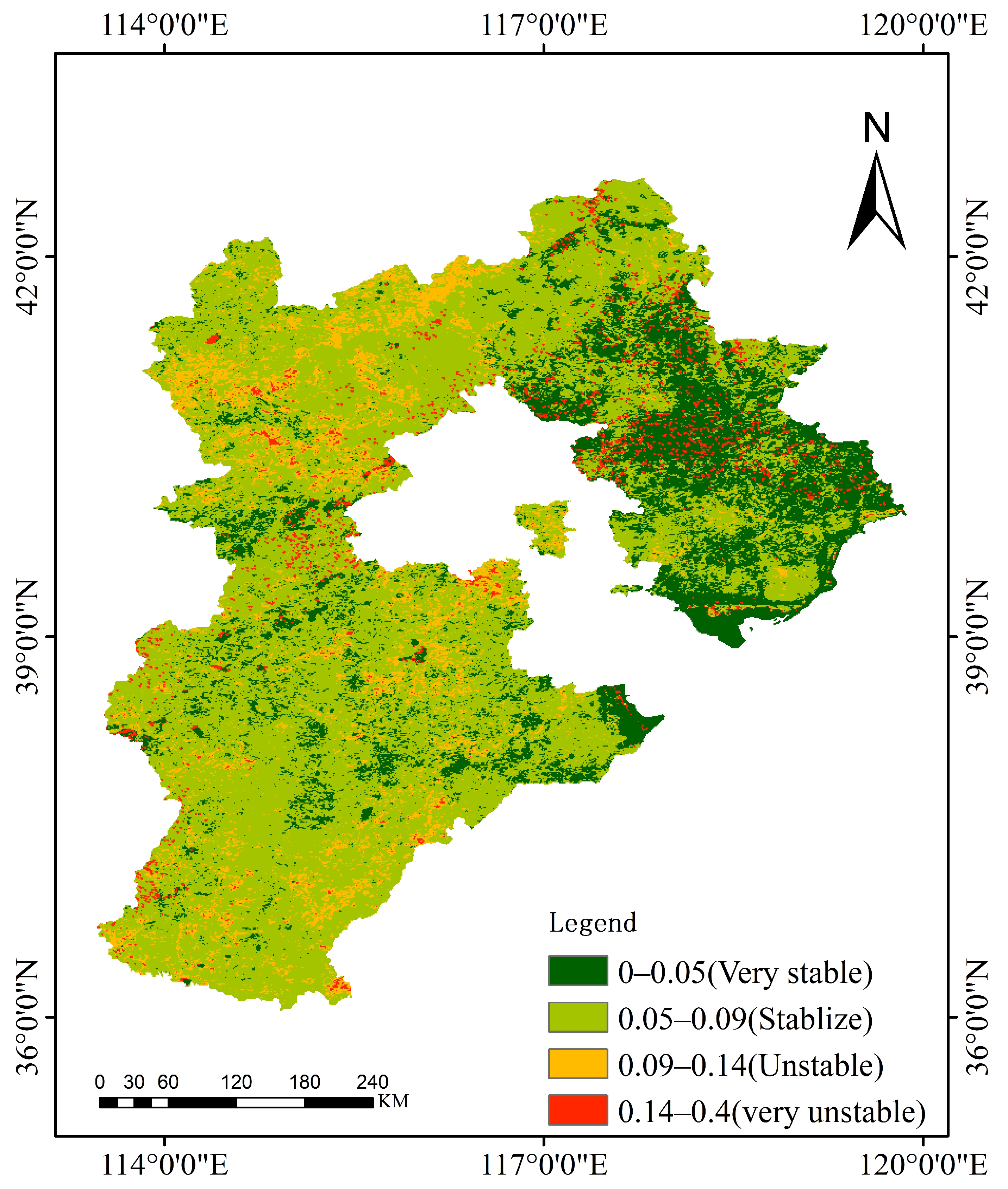
3.3.1. Stability of Soil Drought Changes
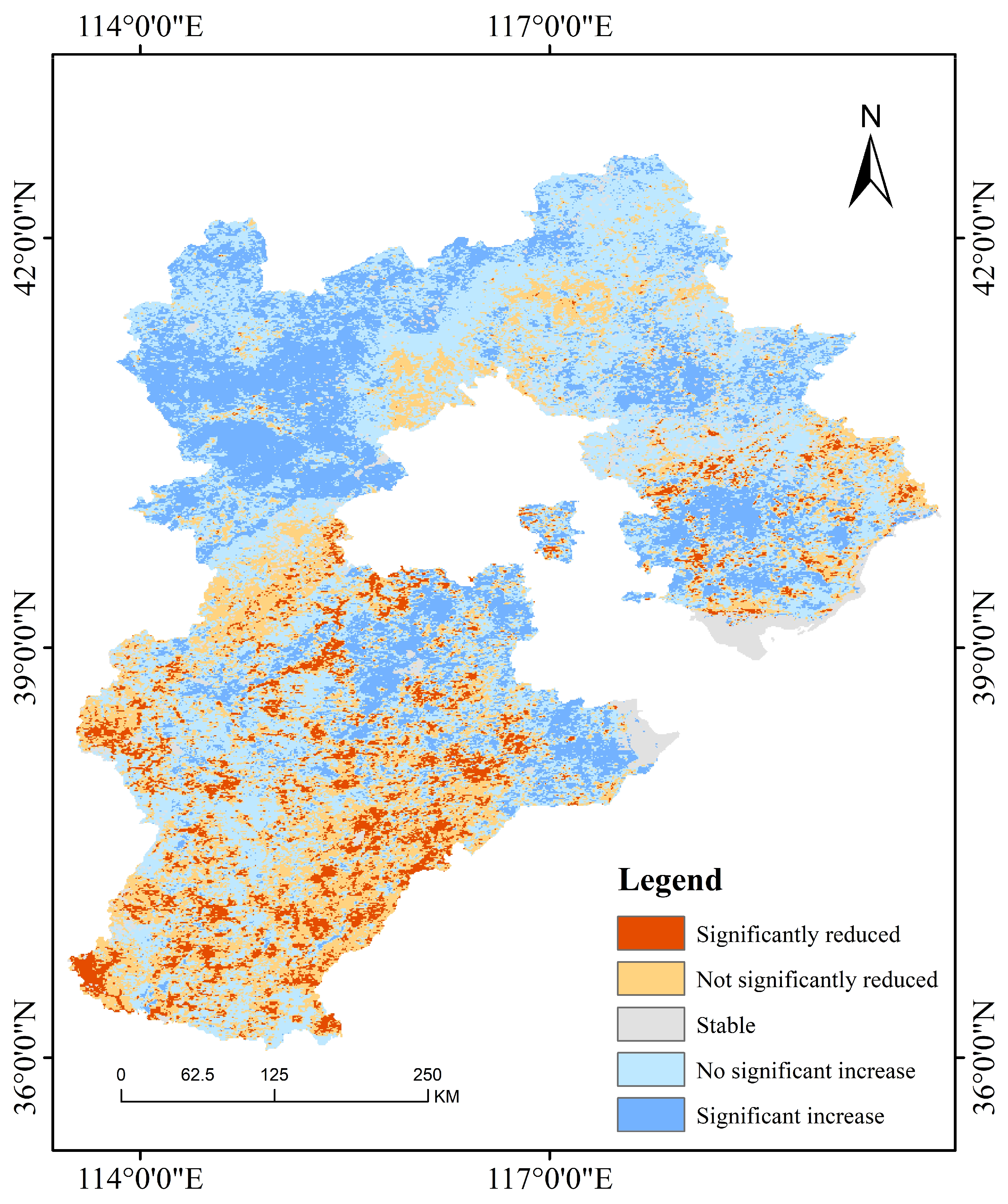
3.3.2. Trend Analysis of Soil Drought Changes
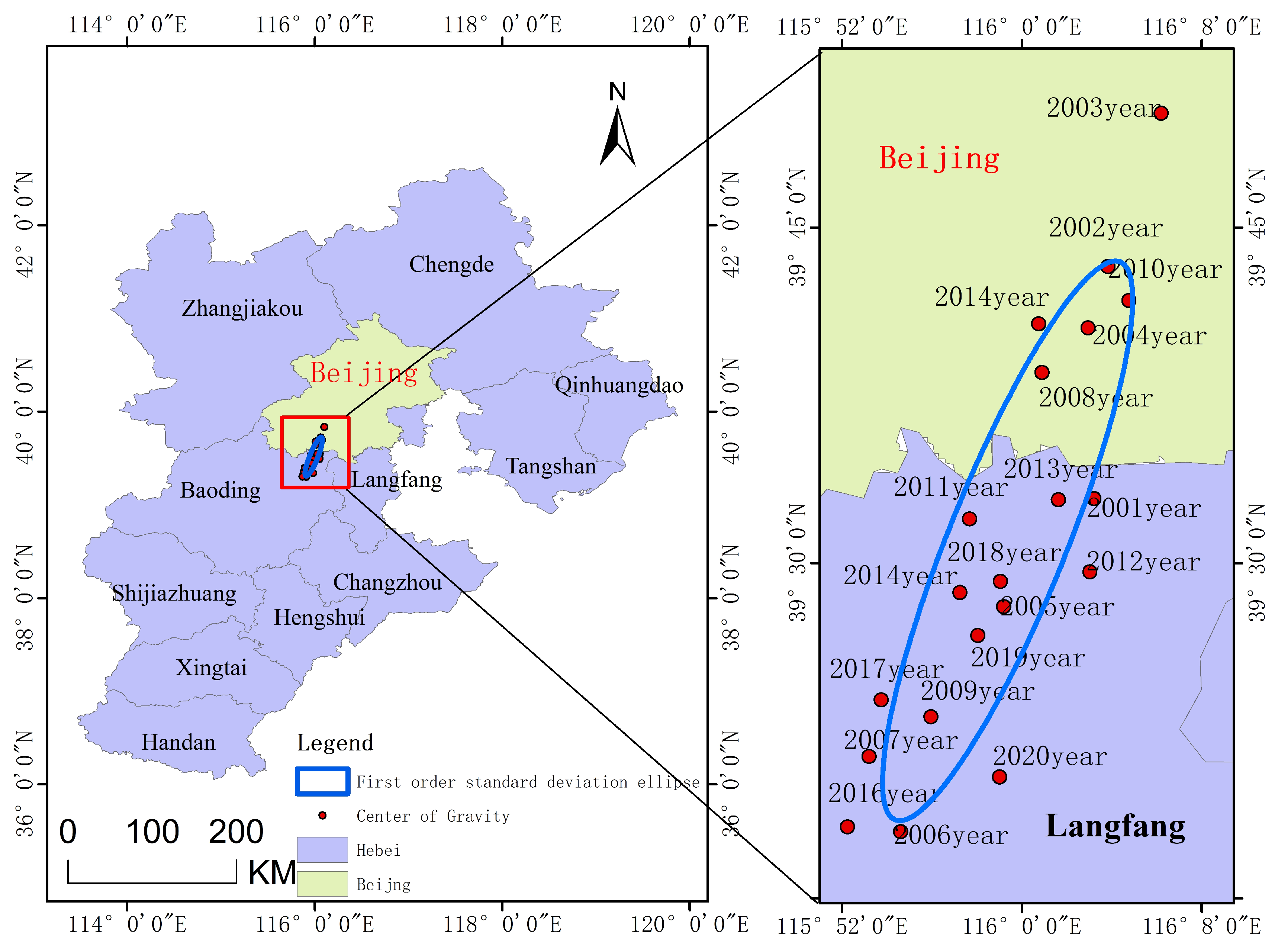
3.3.3. Analysis of the Change in Gravity Center in Drought-Prone Areas
3.4. Analysis of Influencing Factors of Spatial Variation of Soil Moisture in Hebei Province Based on OPGD Model
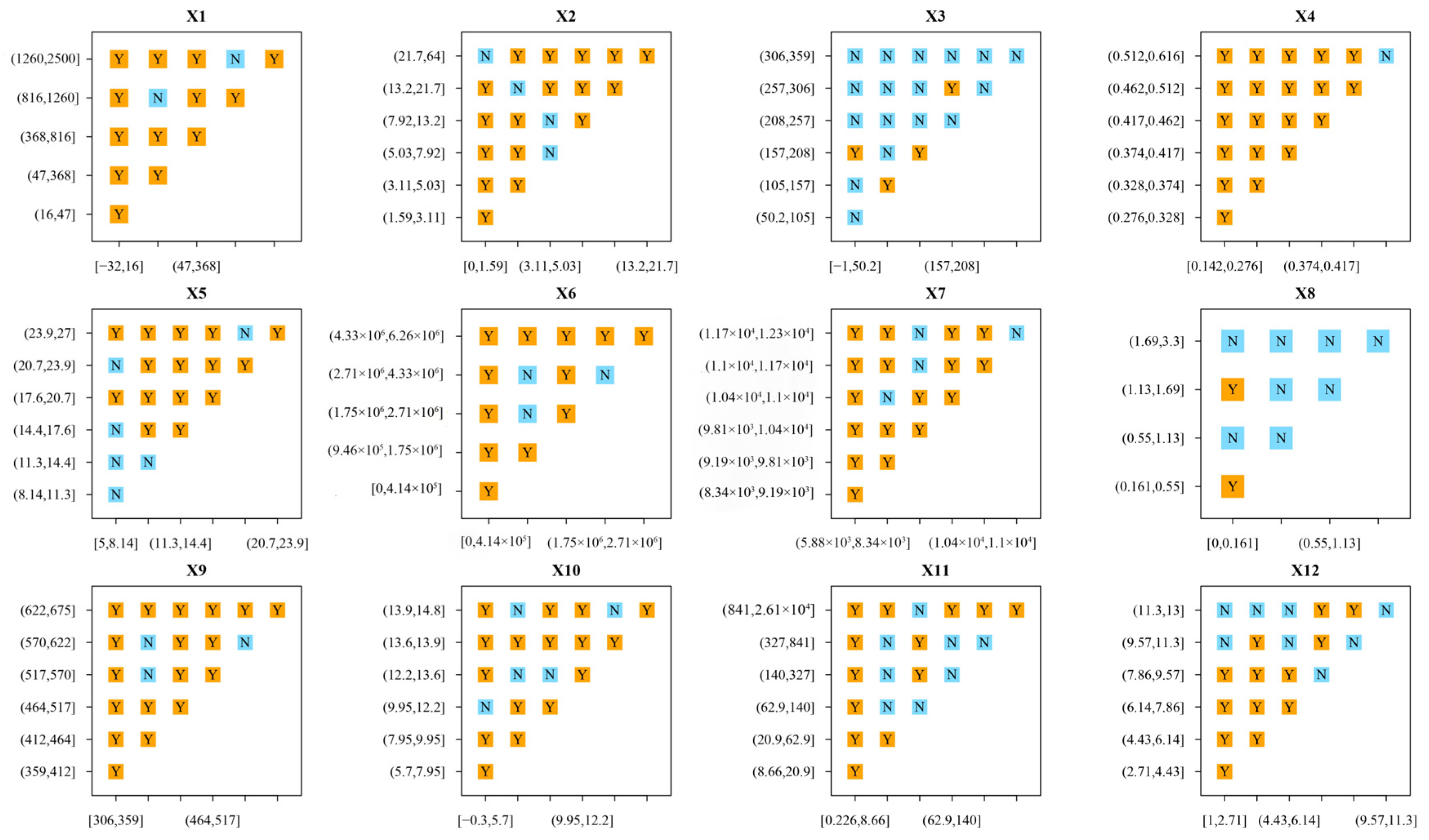
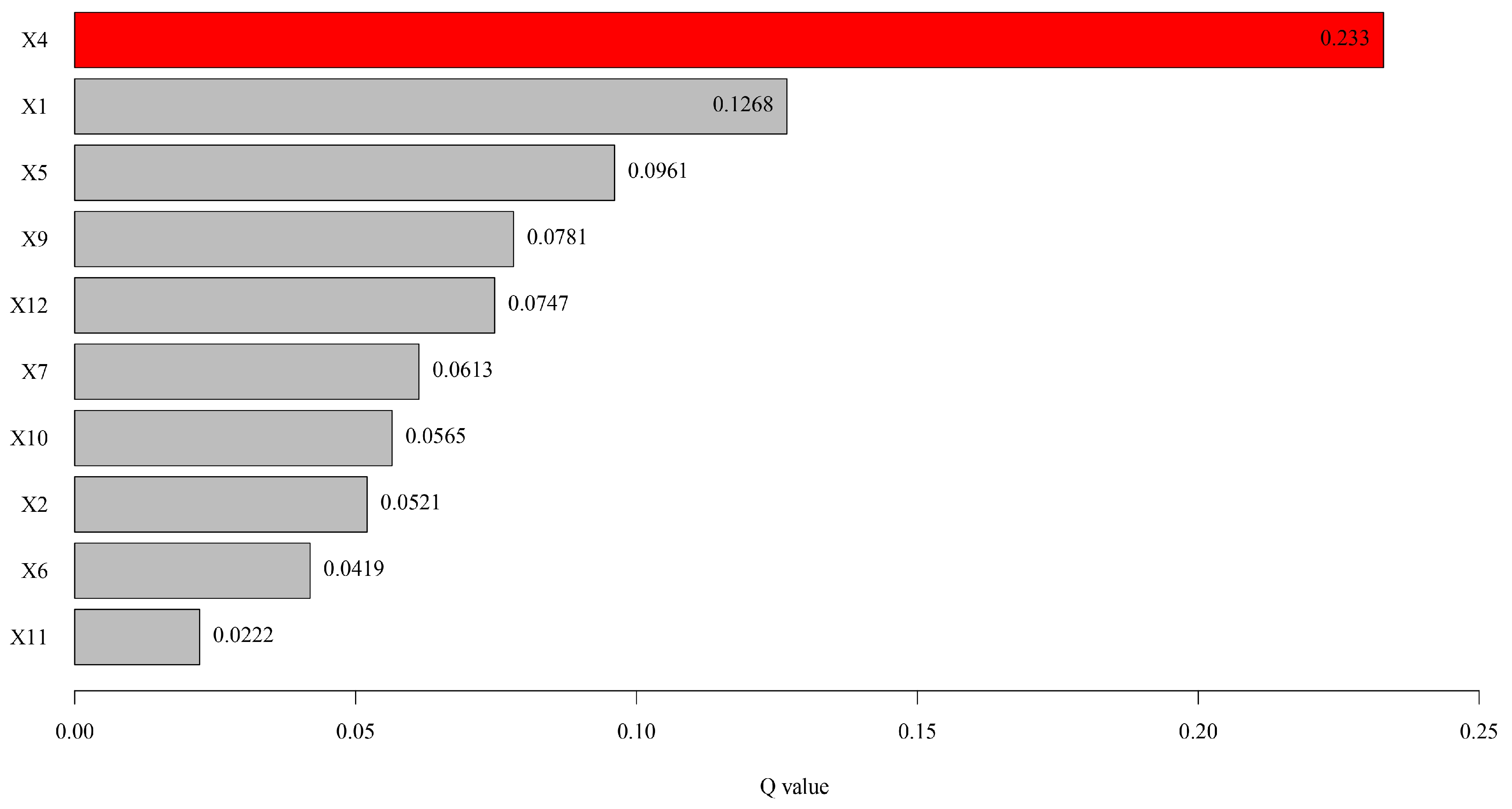
3.4.1. Factor Detector Analysis
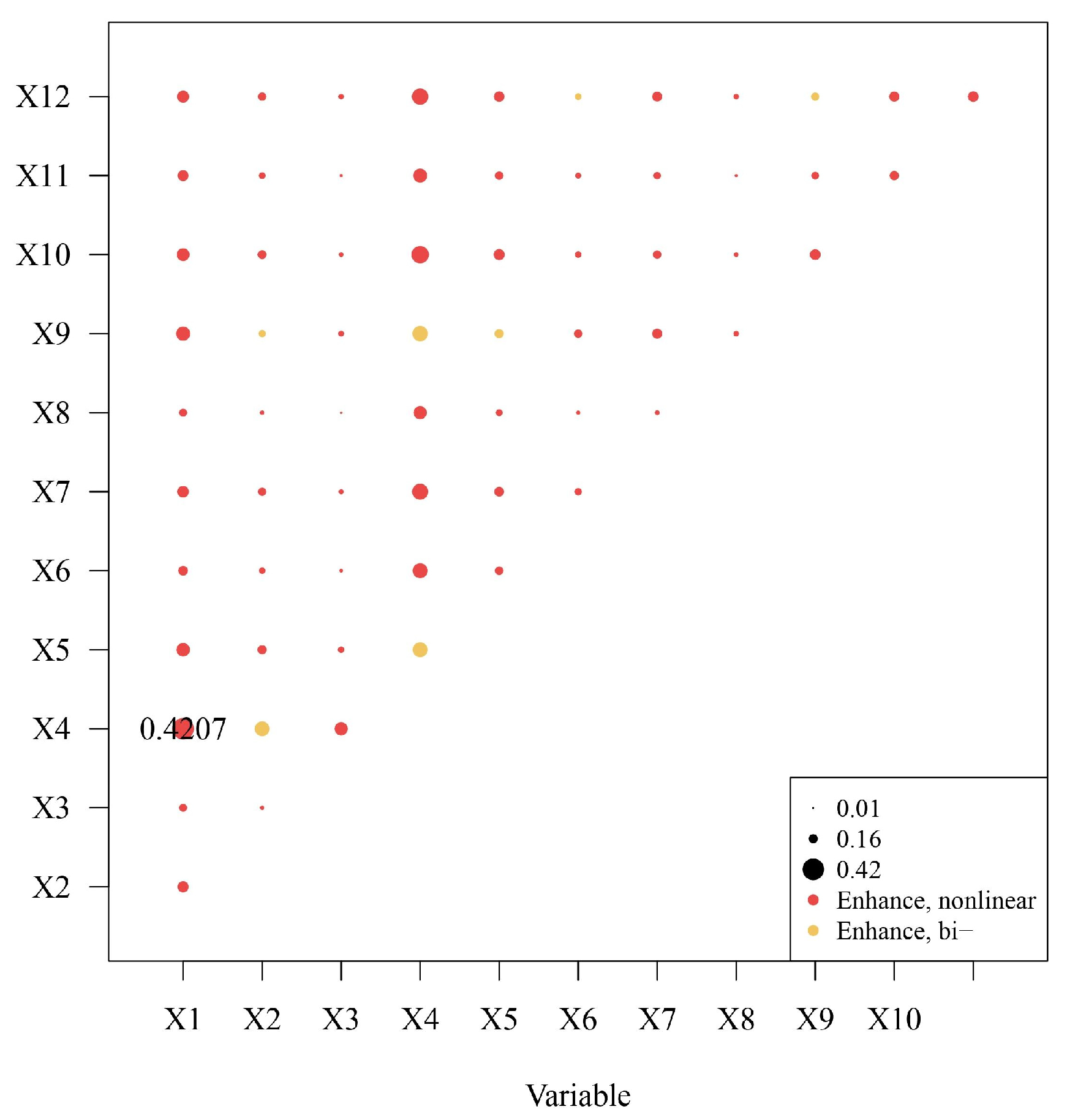
3.4.2. Interaction Detection Analysis
3.4.3. Risk Detection Analysis
3.4.4. Ecological Detection and Analysis
4. Discussion
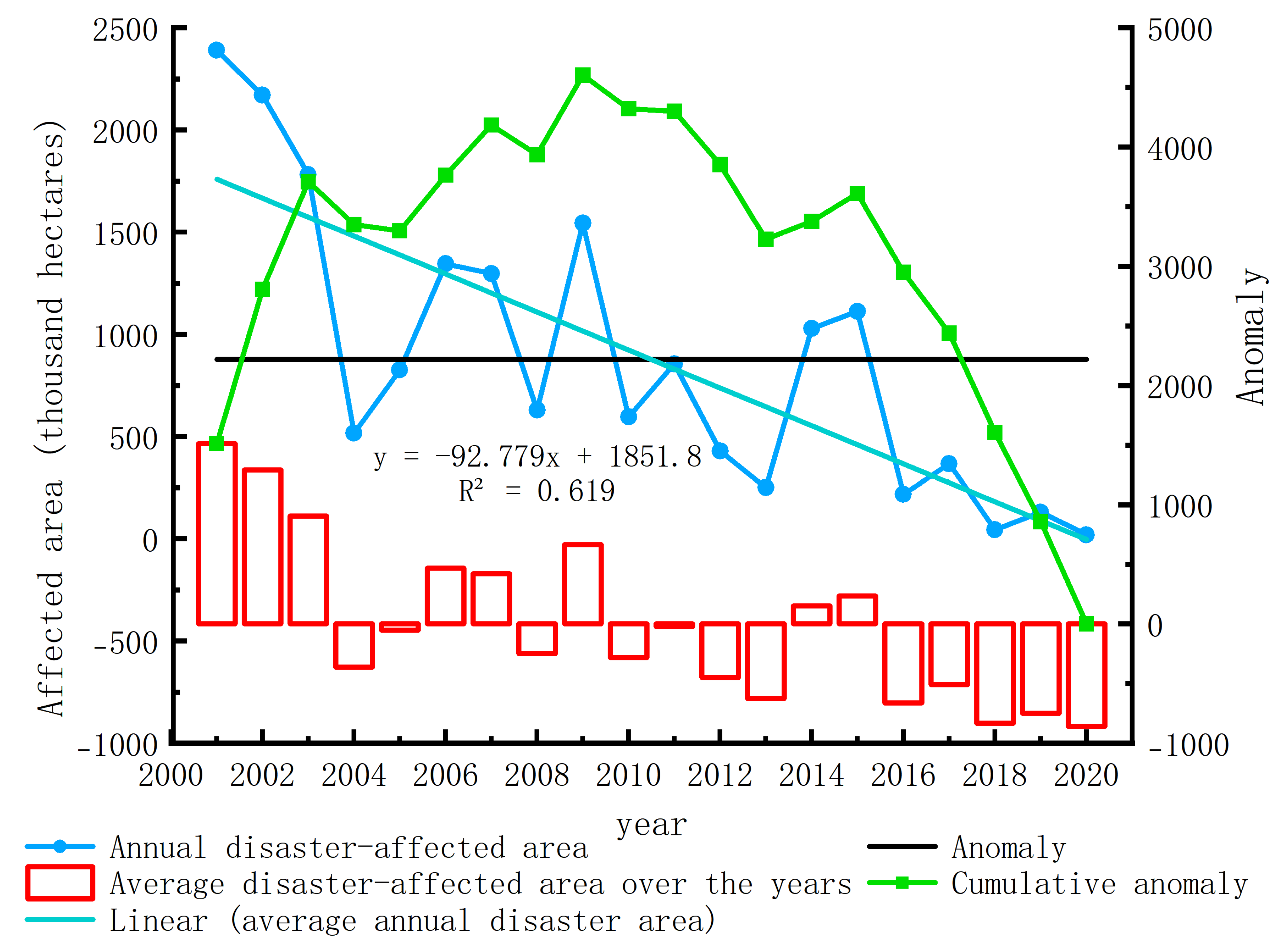
4.1. Spatio-Temporal Differentiation Analysis of Soil Drought
4.2. Nonlinear Driving Mechanism of Multi-Factor Interaction
4.3. Implications for Regional Ecological Management
4.4. Research Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, B.; Xie, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, S.; Li, R.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Impact of groundwater extraction on hydrological process over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. J. Hydrol. 2022, 609, 127689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, B.; Nasseri, M.; Zahraie, B. Identification of long-term annual pattern of meteorological drought based on spatiotemporal methods: Evaluation of different geostatistical approaches. Nat. Hazards 2015, 76, 515–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuquan, T.; Ting, M.; Jingya, T.; Qian, Y.; Junlei, X.; Chao, Z.; Cong, W. Space-time dynamics and potential drivers of soil moisture and soil nutrients variation in a coal mining area of semi-arid, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111242. [Google Scholar]
- Mengistu, A.G.; Woyessa, Y.E.; van Rensburg, L.D.; Tesfuhuney, W.A. Analysis of the spatio-temporal variability of soil water dynamics in an arid catchment in South Africa. Geoderma Reg. 2021, 25, e00395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Liu, F. The evolution and configuration mechanism of spatial correlation network in China’s innovation ecosystem. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 38, 104157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, J.; Liang, E.; Wang, X. Exploring the natural-socioeconomic driving and response mechanisms of ecosystem services interactions to optimize ecosystem management: A case study in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitituersun, A.; Yang, H.; Aobuliaisan, N.; Maimaitiaili, K.; Chenyu, O. Assessing subtle changes in arid land river basin ecological quality: A study utilizing the PIE engine platform and RSEI. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthof, I.; Rainville, T. Dynamic surface water maps of Canada from 1984 to 2019 Landsat satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 279, 113121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Liqiang, Y.; Longling, Z.; Jiqiong, L. Analysis on variation characteristics of the minimum flow at Datong Station under the influence of the Three Gorges Reservoir. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 787, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasempour, R.; Aalami, M.T.; Saghebian, S.M.; Kirca, V.S.O. Analysis of spatiotemporal variations of drought and soil salinity via integrated multiscale and remote sensing-based techniques (Case study: Urmia Lake basin). Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Bi, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Song, W. Topography Dominates the Spatial and Temporal Variability of Soil Bulk Density in Typical Arid Zones. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Huang, Q.; Huang, S.; Leng, G.; Bai, Q.; Liang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Fang, W. Spatial-temporal dynamics of agricultural drought in the Loess Plateau under a changing environment: Characteristics and potential influencing factors. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, F.; Ruhollah, T.; Ali, H.A.M.; Mojtaba, Z.; Brandon, H.; Thomas, S. Spatiotemporal Assessment of Soil Organic Carbon Change Using Machine-Learning in Arid Regions. Agronomy 2022, 12, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Corti, T.; Davin, E.L.; Hirschi, M.; Jaeger, E.B.; Lehner, I.; Orlowsky, B.; Teuling, A.J. Investigating soil moisture–climate interactions in a changing climate: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 125–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, N.Q.; Govind, A.; Ha, T.V. Spatial and temporal variability of soil moisture active and passive (SMAP) droughts and their impacts on vegetation in the Central Highlands of Vietnam. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.W.; Chadwick, D.R.; Zang, H.; Jones, D.L. Use of metabolomics to quantify changes in soil microbial function in response to fertiliser nitrogen supply and extreme drought. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, W.; Qianlai, Z.; Mingyi, Z.; Xinxin, J.; Na, Y.; Ting, Y. Temporal and spatial changes in soil organic carbon and soil inorganic carbon stocks in the semi-arid area of northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.N.; Tsheko, R. Spatial and temporal variation of soil properties and soil organic carbon in semi-arid areas of Sub-Sahara Africa. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 36, e00770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuting, Y.; Xiao, B.; Wanqiang, Y.; Pengfei, L.; Jinfei, H.; Li, K. Spatioemporal dynamics and driving forces of soil organic carbon changes in an arid coal mining area of China investigated based on remote sensing techniques. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yao, F.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.; Liu, Q. Evaluating the performance of eight drought indices for capturing soil moisture dynamics in various vegetation regions over China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhuang, Q.; Miralles, D.G.; Teuling, A.J.; Zhang, T.; An, P.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, D.; et al. Agriculture intensifies soil moisture decline in Northern China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayidjakhon, K.; Fadong, L.; Rashid, K.; Qiuying, Z.; Yunfeng, Q.; Sarvar, O.; Peng, Y.; Peifang, L.; Hubert, H.; Chao, T.; et al. Evaluation of the perennial spatio-temporal changes in the groundwater level and mineralization, and soil salinity in irrigated lands of arid zone: As an example of Syrdarya Province, Uzbekistan. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 263, 107444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Kong, L.; Zhang, J.; Abuduwaili, J. Unveiling Latent interaction mechanisms influencing the spatial pattern of soil salinity in arid Oases: Insights from integrated modeling. Catena 2025, 250, 108769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Qi, L.; Zhang, P. Spatiotemporal variation and controlling factors of dried soil layers in a semi-humid catchment and relevant land use management implications. Catena 2024, 240, 107973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Quan, W.; Tian, J.; Li, J.; Feng, P. Spatial and temporal variations of ecosystem water use efficiency and its response to soil moisture drought in a water-limited watershed of northern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 355, 120251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, K.; Gao, J.; Wu, S. Climatic determinants impacting the distribution of greenness in China: Regional differentiation and spatial variability. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, F.; Jamali, S.; Ghorbanian, A.; Mokhtarzade, M. Global soil moisture trend analysis using microwave remote sensing data and an automated polynomial-based algorithm. Glob. Planet. Change 2023, 231, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irina, O.; Anisoara, I.; George, B.; Denis, M.; ClaudiuValeriu, A.; Argentina, N.; Vasile, C.; Stefan, N. Assessment of Soil Moisture Anomaly Sensitivity to Detect Drought Spatio-Temporal Variability in Romania. Sensors 2021, 21, 8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapkwang, C.C.; Onyando, J.O.; Kundu, P.M.; Hoedjes, J. Evaluation of Spatio-Temporal Soil Moisture Variability in Semi-Arid Rangeland Ecosystem, Maasai Mara National Reserve, Kenya. J. Eng. Res. Rep. 2021, 20, 64–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakkappa, R.N.; Koluru, N.R.; Bheemsain, R.K.D.; Umapathi, S.; Kasareddy, B.; Verappa, R.H.; Vijay, B.W.; Rangappa, U.M. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Soil Properties and Nutrient Uptake for Sustainable Intensification of Rainfed Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajana) in Semi-Arid Tropics of India. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, X.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Z. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Soil Organic Carbon in a Semi-Arid Area of Aohan County, Chifeng City, China. Water 2023, 15, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, P.; Song, N.; Li, C.; Wang, J. Regional Soil Moisture Estimation Leveraging Multi-Source Data Fusion and Automated Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zongyu, L.; Zhilin, S.; Lixia, S.; Jing, L.; Wenhua, X.; Haiyang, D.; Haolei, Z. Hydrological variation and hydro-sediment interrelation of the Luozha River in the Lancang River Basin. Water Supply 2022, 22, 4839–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geographic detectors: Principles and prospects. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chu, D.; Tian, D. A Preliminary Study on the Occurrence and Classification of Lignite Calcareous Soil in the Baishan Plateau of Hebei Province. J. Hebei Agric. Univ. 1987, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, B.; Wang, C. Soil texture classification of the Hebei Plain based on regional soil elemental geochemistry. Quat. Res. 2017, 37, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Li, C.; Cai, J.; Wang, S. Bibliometric analysis and visualization of the relationship between climate change and soil moisture from 1988 to 2023. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2024, 42, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng Chaolei, J.I.A.L.Z.T. Global daily surface soil moisture dataset at 1-km resolution (2000–2020). Sci. Data 2023, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, T.; Tang, X. Estimation of Actual Evapotranspiration and Water Stress in Typical Irrigation Areas in Xinjiang, Northwest China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Potential Evapotranspiration Dataset for China (1901–2023). 2024. Available online: https://loess.geodata.cn/data/datadetails.html?dataguid=34595274939620&docid=74 (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Peng, S. 1-km Monthly Mean Temperature Dataset for China (1901–2023). 2024. Available online: https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/en/data/71ab4677-b66c-4fd1-a004-b2a541c4d5bf/ (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Peng, S. High-Spatial-Resolution Monthly Precipitation Dataset Over China During 1901–2017. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/3114194 (accessed on 2 March 2025).
- Rijtema, P.E. An Analysis of Actual Evapotranspiration; Wageningen University and Research: Gelderland, The Netherlands, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Milly, P.C.; Dunne, K.A. Potential evapotranspiration and continental drying. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Xv, W.; Yang, F.; Jiang, L.; Shi, Y. Deep learning-based study of strength variance coefficient for large diameter thin-walled structures. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 211, 113059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, H. Understanding the Grain Production Growth Pathways Transition and Its Implications for Sustainable Grain Production in China. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 1993–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.W.; Li, J.B. Runoff Variation Trend of Three Diversions in Recent 60 Years and the Analysis of Influencing Factors. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 3248, 3032–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, H. Activity clustering for anomaly detection. Int. J. Intell. Inf. Database Syst. 2013, 7, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weixiong, W.; Ronghui, L.; Jinhua, S. Assessment of Regional Spatiotemporal Variations in Drought from the Perspective of Soil Moisture in Guangxi, China. Water 2022, 14, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xu, Y.-P.; Wang, Y.; Gu, H.; Wang, F.; Pan, S. Influences of climatic variability and human activities on terrestrial water storage variations across the Yellow River basin in the recent decade. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wu, Y.; Wei, J.; Yao, L.; Chu, Z.; Wang, C.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Z. Study on the Response of Habitat Quality to Land Use Change in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Based on the InVEST-GWR Model. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Luo, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, X.; Deng, Y.; Du, T.; Wang, H.; Jiao, C.; Yuan, G.; Shao, M. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Soil Moisture for a Tamarisk Stand under Groundwater Control in a Hyper-Arid Region. Water 2023, 15, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, M.; Knudsen, M.T.; Hermansen, J.E. A comparison of Land Use Change models: Challenges and future developments. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, A.; Xu, X. The Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Sustainable Development Strategy of Huizhou’s Traditional Villages in the Xin’an River Basin. Land. 2025, 14, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of changes in meteorological variables using Mann-Kendall and Sen’s slope estimator statistical tests in Serbia. Glob. Planet. Change 2013, 100, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H. Trend detection in hydrologic data: The Mann–Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H.; Rao, A.R. A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J. Hydrol. 1998, 204, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Mahmud, I. pyMannKendall: A python package for non parametric Mann Kendall family of trend tests. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, A.I. Kendall rank correlation and Mann-Kendall trend test. R. Package Kendall 2005, 602, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cen, Q.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, H. Exploration of urban neighborhood blue-green space quality patterns and influencing factors in waterfront cities based on MGWR and OPGD models. Urban. Clim. 2024, 55, 101942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Feng, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Hao, C. Analysis of the Influence of Driving Factors on Vegetation Changes Based on the Optimal-Parameter-Based Geographical Detector Model in the Yima Mining Area. Forests 2024, 15, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan-dan, L.; Yong-liang, L. Expansion and Quantitative Attribution of China’s Built-up Areas Based on Parameter Optimal Geodetector. J. Hebei Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Eng. 2023, 33, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Haochuan, L.; Haiyan, S.; Wang, Y. Analysis of soil organic matter influencing factors in the Huangshui River Basin by using the optimal parameter-based geographical detector model. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2246935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, C.; Mao, F.; Du, H.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Z. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Forest Carbon Storage Based on BIOME-BGC Model and Geographical Detector in Eight Basins of Zhejiang Province in China. Forests 2025, 16, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jinfeng, W.; Yong, G.; Xu, C. An optimal parameters-based geographical detector model enhances geographic characteristics of explanatory variables for spatial heterogeneity analysis: Cases with different types of spatial data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tan, S.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Wu, R. Quantitative analysis of fractional vegetation cover in southern Sichuan urban agglomeration using optimal parameter geographic detector model, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Attributing spatially stratified heterogeneity in biodiversity of urban–rural interlaced zones based on the OPGD model. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 83, 102789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yin, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Han, J.; Yu, B.; Xue, J. Spatial Heterogeneity and Driving Factors of Soil Moisture in Alpine Desert Using the Geographical Detector Method. Water 2021, 13, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wu, P.; Li, X.; Wei, X. Identifying driving factors and their interacting effects on accumulation of heavy metals in cultivated soils based on optimal parameter geographic detector model. J. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 266, 107573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhan, X.; Liu, D.; Zhu, H. Spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of milk tea stores in Wuhan based on sDNA and OPGD models. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0319075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Kafy, A.-A.; Ren, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, S.; Li, J. Application of the Optimal Parameter Geographic Detector Model in the Identification of Influencing Factors of Ecological Quality in Guangzhou, China. Land 2022, 11, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Song, R.; Guo, Z. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Various Landscape Processes and Their Driving Factors Based on the OPGD Model for the Jiaozhou Bay Coast Zone, China. Land 2022, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. NDVI dynamic changes and their relationship with meteorological factors and soil moisture. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Sun, G.; Zhi, L.; Zhao, J. Negative soil moisture-precipitation feedback in dry and wet regions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number | Driving Factors | Resolution | Source | Time Periods (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | Elevation | 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud https://www.gscloud.cn/#page1/2 (accessed on 2 March 2025) | / |
| X2 | Slope | 30 m | ||
| X3 | Aspect | 30 m | ||
| X4 | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVl) | 1 km | Google Earth Engine https://earthengine.google.com/ (accessed on 2 March 2025) | 2001–2020 |
| X5 | Land Surface Temperature (LST) | 1 km | ||
| X6 | GDP per unit area | 1 km | CAS Resources and Environmental Science Data Center https://www.resdc.cn/Introduction.aspx (accessed on 2 March 2025) | 2001–2020 |
| X7 | Potentialapot Evranspiration (PET)_ | 1 km | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center [41] https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home (accessed on 2 March 2025) | 2001–2020 |
| X8 | River density | 1 km | CAS Resources and Environmental Science Data Center https://www.resdc.cn/Introduction.aspx (accessed on 2 March 2025) | 2020 |
| X9 | Precipitation | 1 km | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home (accessed on 2 March 2025) | 2001–2020 |
| X10 | Temperature | 1 km | National Tibetan Plateau Data Center [42] https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/home (accessed on 2 March 2025) | 2001–2020 |
| X11 | Population density | 1 km | CAS Resources and Environmental Science Data Center [43] https://www.resdc.cn/Introduction.aspx (accessed on 2 March 2025) | 2001–2020 |
| X12 | Soil type | 1 km | Chinese Soil Database http://vdb3.soil.csdb.cn (accessed on 2 March 2025) | 1995 |
| Grade | Soil Moisture Content | Drought Level |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [0, 150) | Extreme Drought |
| 2 | [150, 175) | Severe Drought |
| 3 | [175, 200) | Moderate Drought |
| 4 | [200, 225) | Mild Drought |
| 5 | [225, 1] | No Drought |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, B.; Wen, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, S.; Shang, G.; An, S.; Li, Z. Analysis on Spatiotemporal Variation in Soil Drought and Its Influencing Factors in Hebei Province from 2001 to 2020. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101109
Zeng B, Wen B, Zhang X, Zhao S, Shang G, An S, Li Z. Analysis on Spatiotemporal Variation in Soil Drought and Its Influencing Factors in Hebei Province from 2001 to 2020. Agriculture. 2025; 15(10):1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101109
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Biao, Bo Wen, Xia Zhang, Suya Zhao, Guofei Shang, Shixin An, and Zhe Li. 2025. "Analysis on Spatiotemporal Variation in Soil Drought and Its Influencing Factors in Hebei Province from 2001 to 2020" Agriculture 15, no. 10: 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101109
APA StyleZeng, B., Wen, B., Zhang, X., Zhao, S., Shang, G., An, S., & Li, Z. (2025). Analysis on Spatiotemporal Variation in Soil Drought and Its Influencing Factors in Hebei Province from 2001 to 2020. Agriculture, 15(10), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101109





