Influence of Sludge and Feed Mixtures on Metal Retention, Pathogen Reduction, and Nutritional Value in Black Soldier Fly (BSF) (Hermetia illucens) Larval Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
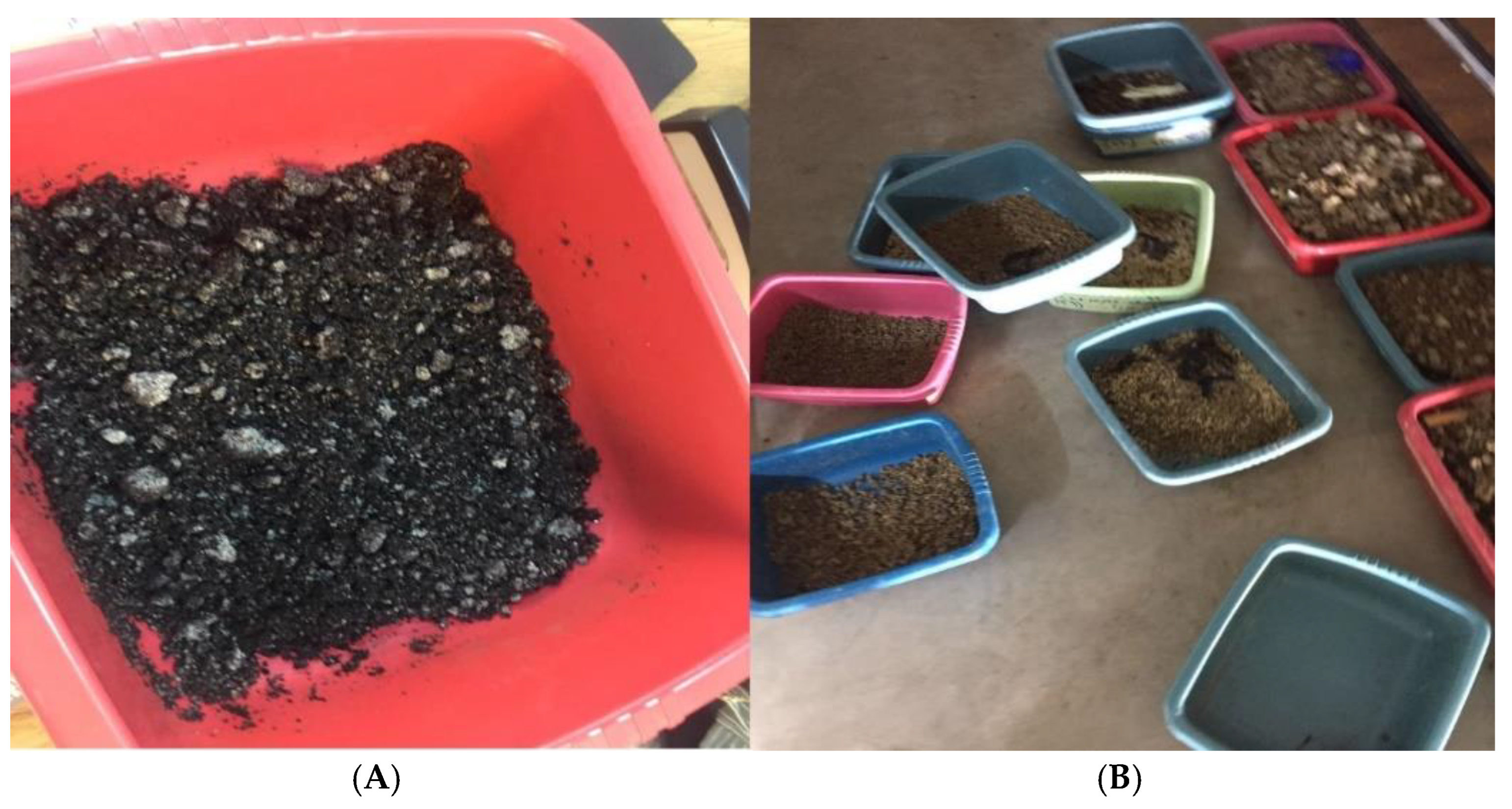
2.1. Experimental Design
- -
- TA: 100% sludge
- -
- TB: 75% sludge and 25% chicken feed
- -
- TC: 25% sludge and 75% chicken feed
- -
- TD: 100% chicken feed
2.2. Study Setting
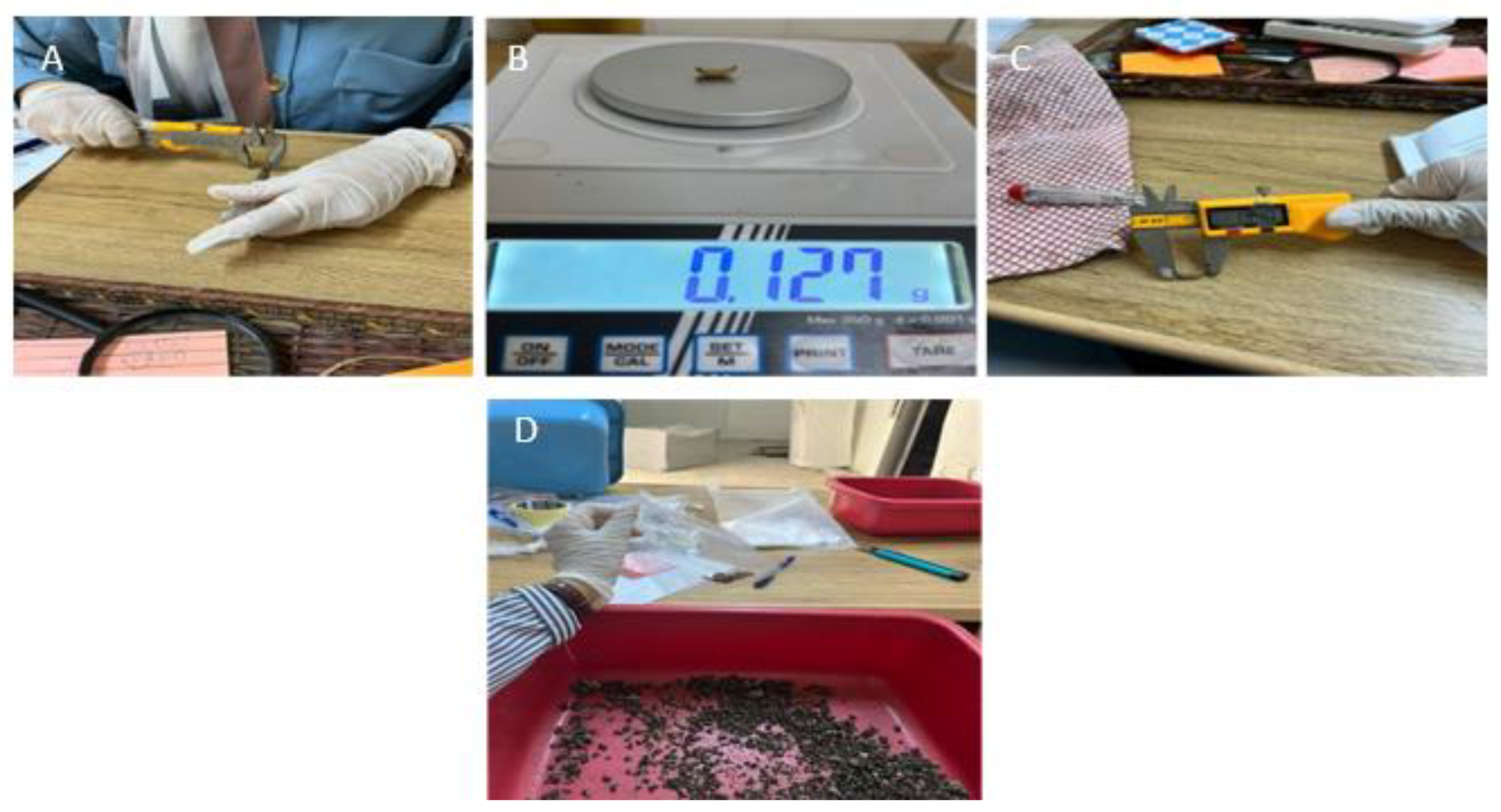
2.3. Feed Preparation and Measurement
2.4. Feeding Protocols and Early Larval Development
2.4.1. Feed Sample Preparation
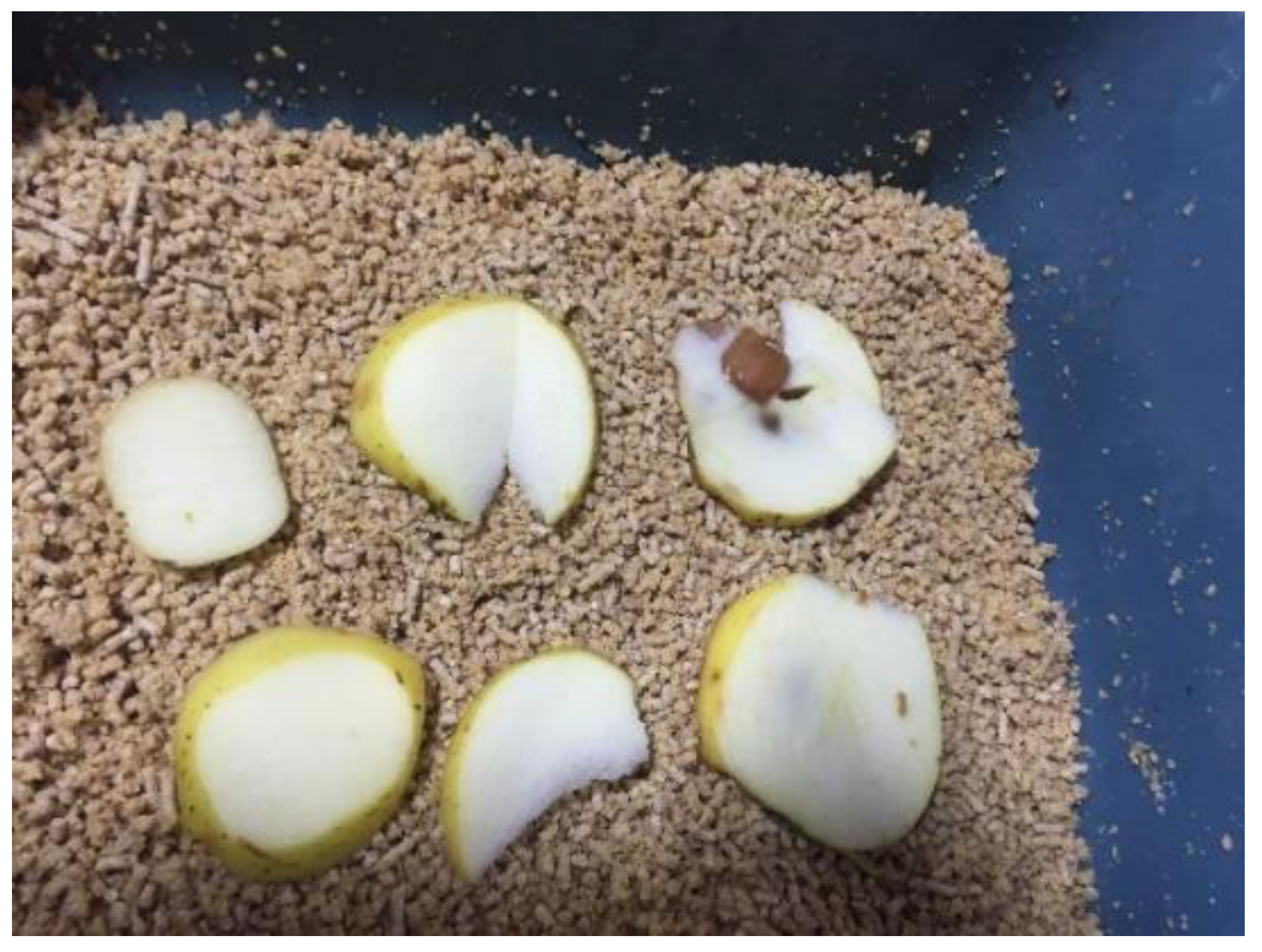
2.4.2. Larval Acclimation and Initial Measurements
2.4.3. Introduction of Larvae
2.5. Heavy Metal Concentrations
2.6. Microbial Analysis Procedure
2.7. Chemical Characterization of Frass Procedure
2.8. Monitoring and Data Collection
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Heavy Metals
3.2. Chemical Characterization Results
3.3. Microbial Analysis Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Heavy Metal Concentration
4.2. Microbial Analysis Discussion
4.3. Chemical Characterization Discussion
4.4. Implications for Sustainable Agriculture
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Surendra, K.; Tomberlin, J.K.; van Huis, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Heckmann, L.-H.L.; Khanal, S.K. Rethinking organic wastes bioconversion: Evaluating the potential of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens (L.))(Diptera: Stratiomyidae)(BSF). Waste Manag. 2020, 117, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Minor, M.; Morel, P.C.; Najar-Rodriguez, A.J. Bioconversion of three organic wastes by black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naser El Deen, S.; van Rozen, K.; Elissen, H.; van Wikselaar, P.; Fodor, I.; van der Weide, R.; Hoek-van den Hil, E.F.; Rezaei Far, A.; Veldkamp, T. Bioconversion of different waste streams of animal and vegetal origin and manure by black soldier fly larvae Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Insects 2023, 14, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Quan, J.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Relationship of black soldier fly larvae (BSFL) gut microbiota and bioconversion efficiency with properties of substrates. Waste Manag. 2024, 180, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.-H.; Liu, S.; Deng, W.-K.; Wu, R.-T.; Cai, Y.-F.; Liao, X.-D.; Xing, S.-C. A sustainable and economic strategy to reduce risk antibiotic resistance genes during poultry manure bioconversion by black soldier fly Hermetia illucens larvae: Larval density adjustment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albalawneh, A.; Hasan, H.; Alarsan, S.F.; Diab, M.; Abu Znaimah, S.; Sweity, A.; Aladwan, M.M.; Sharman, B.; Alalwan, A.M.; AlBalawnah, Y.; et al. Evaluating the Influence of Nutrient-Rich Substrates on the Growth and Waste Reduction Efficiency of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, T.; van Rozen, K.; Elissen, H.; van Wikselaar, P.; van der Weide, R. Bioconversion of digestate, pig manure and vegetal residue-based waste operated by black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens L. (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Animals 2021, 11, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shumo, M.A.H.I.H. Use of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) in Bioconversion and Feed Production; Universitäts-und Landesbibliothek Bonn: Bonn, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, K.U.; Hollah, C.; Wiesotzki, K.; Rehman, R.U.; Rehman, A.U.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Nienaber, T.; Heinz, V.; Aganovic, K. Black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens as a potential innovative and environmentally friendly tool for organic waste management: A mini-review. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedalmoosavi, M.M.; Mielenz, M.; Veldkamp, T.; Daş, G.; Metges, C.C. Growth efficiency, intestinal biology, and nutrient utilization and requirements of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae compared to monogastric livestock species: A review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. An efficient strategy to promote food waste composting by adding black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae during the compost maturation phase. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2024, 18, 100180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Revealing the effects of fermented food waste on the growth and intestinal microorganisms of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. Waste Manag. 2023, 171, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzepe, D.; Nana, P.; Kuietche, H.M.; Kimpara, J.M.; Magatsing, O.; Tchuinkam, T.; Djouaka, R. Feeding strategies for small-scale rearing black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) as organic waste recycler. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguz, M.; Gasco, L.; Tomberlin, J.K. Impact of pH and feeding system on black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens, L.; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larval development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyakeri, E.; Ayieko, M.; Amimo, F.; Salum, H.; Ogola, H. An optimal feeding strategy for black soldier fly larvae biomass production and faecal sludge reduction. J. Insects Food Feed. 2019, 5, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N.; Costa, R.; Ameixa, O.M. The influence of non-optimal rearing conditions and substrates on the performance of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). Insects 2022, 13, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gligorescu, A.; Toft, S.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Axelsen, J.A.; Nielsen, S.A. Development, metabolism and nutrient composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens; Diptera: Stratiomyidae) in relation to temperature and diet. J. Insects Food Feed. 2018, 4, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobbi, P.; Martinez-Sanchez, A.; Rojo, S. The effects of larval diet on adult life-history traits of the black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 110, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, S.Y.; Tanga, C.M.; Osuga, I.M.; Cheseto, X.; Ekesi, S.; Dicke, M.; van Loon, J.J.A. Nutritional composition of black soldier fly larvae feeding on agro-industrial by-products. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2020, 168, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros-Rodríguez, A.; Rangseekaew, P.; Lasudee, K.; Pathom-aree, W.; Manzanera, M. Regulatory risks associated with bacteria as biostimulants and biofertilizers in the frame of the European Regulation (EU) 2019/1009. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Taethaisong, N.; Meethip, W.; Surakhunthod, J.; Sinpru, B.; Sroichak, T.; Archa, P.; Thongpea, S.; Paengkoum, S.; Purba, R.A.P.; et al. Nutritional composition of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) and its potential uses as alternative protein sources in animal diets: A review. Insects 2022, 13, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navajas-Porras, B.; Delgado-Osorio, A.; Hinojosa-Nogueira, D.; Pastoriza, S.; Almécija-Rodríguez, M.d.C.; Rufián-Henares, J.Á.; Fernandez-Bayo, J.D. Improved nutritional and antioxidant properties of black soldier fly larvae reared on spent coffee grounds and blood meal by-products. Food Res. Int. 2024, 196, 115151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmiera, N.; Al-Talib, H.; Sahlan, N.; Krasilnikova, A.; Sahudin, S.; Heo, C.C. Antimicrobial Activity of Black Soldier Fly, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) Larval Hemolymph against Various Pathogenic Bacteria. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 17, 8887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalander, C.H.; Fidjeland, J.; Diener, S.; Eriksson, S.; Vinnerås, B. High waste-to-biomass conversion and efficient Salmonella spp. reduction using black soldier fly for waste recycling. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 261–271. [Google Scholar]
- Widyastuti, R.; Rahmat, A.; Warganegara, H.A.; Ramadhani, W.; Prasetyo, B.; Riantini, M. (Eds.) Chemical content of waste composting by black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Alegbeleye, O.O.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Manure-borne pathogens as an important source of water contamination: An update on the dynamics of pathogen survival/transport as well as practical risk mitigation strategies. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 227, 113524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belperio, S.; Cattaneo, A.; Nannoni, E.; Sardi, L.; Martelli, G.; Dabbou, S.; Meneguz, M. Assessing Substrate Utilization and Bioconversion Efficiency of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae: Effect of Diet Composition on Growth and Development Temperature. Animals 2024, 14, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasato, I.; Oddon, S.B.; Loiotine, Z.; Resconi, A.; Gasco, L. Wheat starch processing by-products as rearing substrate for black soldier fly: Does the rearing scale matter? Animal 2024, 18, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneguz, M.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F.; Dama, A.; Lussiana, C.; Renna, M.; Gasco, L. Effect of rearing substrate on growth performance, waste reduction efficiency and chemical composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5776–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, H.M.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Lambert, B.D.; Kattes, D. Development of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae fed dairy manure. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 37, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment | Cd (mg/kg) | Co (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | Ni (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | |
| TA | 0.000 | 0.0000 | 7.3400 | 7.1518 | 25.0400 | 40.9500 | 23.3000 | 23.7850 | 15.99 | 9.0782 |
| TB | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 7.2900 | 5.3227 | 30.6600 | 40.8300 | 18.4100 | 21.4180 | 6.4900 | 3.5723 |
| TC | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 5.9600 | 3.2536 | 0.7000 | 8.5060 | 6.0900 | 8.8416 | 3.8600 | 0.1743 |
| TD | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 5.5200 | 1.9410 | 0.0000 | 4.5100 | 1.9600 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| p-value | - | 0.0390 | 0.0070 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0009 | 0.0004 | 0.000 | |
| Treatment | % Moisture | Ash Content (%) | pH | Ec (dS/m) | N (%) | P (%) | Ca (%) | Mg (%) | Na (%) | K (%) | Cl (%) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | |
| TA | 6.76 | 18.64 | 21.46 | 24.65 | 5.93 | 5.81 | 1.54 | 3.39 | 7.00 | 5.96 | 0.53 | 0.74 | 3.76 | 4.72 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.20 | 0.47 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.15 | 0.33 |
| TB | 7.71 | 11.80 | 17.88 | 24.97 | 5.86 | 6.26 | 1.57 | 3.50 | 5.81 | 5.72 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 3.20 | 2.68 | 0.70 | 1.04 | 0.25 | 0.49 | 0.43 | 0.64 | 0.23 | 0.34 |
| TC | 9.70 | 10.89 | 9.56 | 15.24 | 6.05 | 6.32 | 1.51 | 3.57 | 3.58 | 5.56 | 0.34 | 0.35 | 1.74 | 0.78 | 0.44 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.51 | 0.50 | 1.32 | 0.23 | 0.58 |
| TD | 10.70 | 10.82 | 5.52 | 6.58 | 5.99 | 6.73 | 1.63 | 2.81 | 2.47 | 4.03 | 0.19 | 0.20 | 1.1 | 0.13 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.38 | 0.73 | 1.23 | 0.28 | 0.53 |
| p-value | 0.0410 | 0.0390 | 0.0000 | 0.00 | 0.4160 | 0.2690 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0268 | 0.0410 | 0.3810 | 0.1150 | 0.0000 | 0.00 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | NS | NS | 0.0000 | 0.000 | NS | NS |
| Treatment | Total Coliform (MPN/g Sample) | Fecal Coliform (MPN/g Sample) | E-coli (MPN/g Sample) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | Substrate | Frass | |
| TA | >16 × 103 | 7.8 × 103 | >16 × 103 | 2.8 × 103 | 5.4 × 103 | 6.1 × 102 |
| TB | >16 × 103 | >16 × 103 | >16 × 103 | >16 × 103 | >16 × 103 | >16 × 103 |
| TC | >16 × 103 | >16 × 103 | >16 × 103 | >16 × 103 | 3.5 × 103 | >16 × 103 |
| TD | 0 | >16 × 103 | 0 | >16 × 103 | 0 | >16 × 103 |
| p-value | 0.008 | 0.018 | 0.027 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albalawneh, A.; Hasan, H.; Alarsan, S.F.; Abu Znaimah, S.; Diab, M.; Alalwan, A.M.; AlBalawnah, Y.; Alnaimat, E.; Sharman, B.; Dayyeh, M.A. Influence of Sludge and Feed Mixtures on Metal Retention, Pathogen Reduction, and Nutritional Value in Black Soldier Fly (BSF) (Hermetia illucens) Larval Substrates. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101080
Albalawneh A, Hasan H, Alarsan SF, Abu Znaimah S, Diab M, Alalwan AM, AlBalawnah Y, Alnaimat E, Sharman B, Dayyeh MA. Influence of Sludge and Feed Mixtures on Metal Retention, Pathogen Reduction, and Nutritional Value in Black Soldier Fly (BSF) (Hermetia illucens) Larval Substrates. Agriculture. 2025; 15(10):1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101080
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbalawneh, Abeer, Heba Hasan, Sami Faisal Alarsan, Saja Abu Znaimah, Mai Diab, Ahmad Mohammed Alalwan, Yazan AlBalawnah, Ehab Alnaimat, Bilal Sharman, and Musa Abu Dayyeh. 2025. "Influence of Sludge and Feed Mixtures on Metal Retention, Pathogen Reduction, and Nutritional Value in Black Soldier Fly (BSF) (Hermetia illucens) Larval Substrates" Agriculture 15, no. 10: 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101080
APA StyleAlbalawneh, A., Hasan, H., Alarsan, S. F., Abu Znaimah, S., Diab, M., Alalwan, A. M., AlBalawnah, Y., Alnaimat, E., Sharman, B., & Dayyeh, M. A. (2025). Influence of Sludge and Feed Mixtures on Metal Retention, Pathogen Reduction, and Nutritional Value in Black Soldier Fly (BSF) (Hermetia illucens) Larval Substrates. Agriculture, 15(10), 1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture15101080






