Abstract
Ligusticum Chuanxiong, a perennial herb of considerable medicinal value commonly known as Chuanxiong, holds pivotal importance in sliced form for ensuring quality and regulating markets through geographical origin identification. This study introduces an integrated approach utilizing Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to establish an efficient method for rapidly determining the geographical origin of Chuanxiong slices. A dataset comprising 300 samples from 6 distinct origins was analyzed using a 1D-CNN model. In this study, we initially established a traditional classification model. By utilizing the Spectrum Outlier feature in TQ-Analyst 9 software to exclude outliers, we have enhanced the performance of the model. After evaluating various spectral preprocessing techniques, we selected Savitzky–Golay filtering combined with Multiplicative Scatter Correction (S-G + MSC) to process the raw spectral data. This approach significantly improved the predictive accuracy of the model. After 2000 iterations of training, the CNN model achieved a prediction accuracy of 92.22%, marking a 12.09% improvement over traditional methods. The application of the Class Activation Mapping algorithm not only visualized the feature extraction process but also enhanced the traditional model’s classification accuracy by an additional 7.41% when integrated with features extracted from the CNN model. This research provides a powerful tool for the quality control of Chuanxiong slices and presents a novel perspective on the quality inspection of other agricultural products.
1. Introduction
Chuanxiong [1], scientifically named Ligusticum Chuanxiong, belongs to the Apiaceae family and the Ligusticum genus and is a traditional Chinese medicinal material with a long-standing history, included in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. The underground rhizome of Ligusticum Chuanxiong is characterized by its pungent and warm nature, known for its ability to promote blood circulation, replenish energy, dispel wind, and alleviate pain [2], and is extensively used for the treatment of a variety of diseases. The original plant of Chuanxiong is Ligusticum, and it has various aliases due to its different geographical origins, such as Chuanxiong (Sichuan), Taixiong (Zhejiang), Fuxiong (Jiangxi), Guangxiong (Guangdong), and Xixiong (Gansu). The medicinal value of Chuanxiong is closely tied to its place of origin, particularly Chuanxiong from Pengzhou and Dujiangyan in Sichuan, which are renowned for their unique medicinal benefits and commercial potential [3], and thus considered high-quality Chuanxiong. However, the market is plagued with counterfeit and inferior products, and the practice of passing off inferior goods as superior is common, necessitating a rapid, reliable, and simple identification method.
Most Chuanxiong available on the market is in the form of sliced Chuanxiong. However, most quality control methods for Chuanxiong primarily target powdered forms, which have limitations in identifying Chuanxiong slices. Traditional quality control methods for Chuanxiong include morphological identification, moisture determination, microscopic identification, total ash determination, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS) [4,5,6]. Morphological identification, also known as empirical judgment [7,8], is simple and cost-effective, but its accuracy is greatly influenced by individual experience. Other methods, while accurate, have the disadvantages of being time-consuming, complex, and destructive to the sample. Therefore, developing a method for efficiently, accurately, and conveniently identifying the geographical origin of Chuanxiong slices is of significant importance.
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS), as a rapid, non-destructive, convenient, and accurate detection method, has been widely applied in the fields of food, agriculture, and medicine. The technology operates on the principle that molecules absorb near-infrared light in a manner that is unique to their chemical bonds, enabling the identification and quantification of various constituents within a sample. In agricultural applications, NIRS provides clear advantages, including the need for minimal sample preparation and the ability to perform rapid, large-scale analyses, which is especially beneficial for evaluating the quality of agricultural products. Some researchers have successfully utilized Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in combination with machine learning to authenticate adulteration in ground beef [9] and rice [10], the geographical origin of Eucommia ulmoides leaves [11] and green coffee beans [12], and the botanical origin of saffron [13] and turmeric [14]. To date, there has been no research on the rapid identification of the geographical origin of Chuanxiong slices using NIRS. Moreover, before NIRS data collection, samples usually need to be ground and sieved, but some studies have opted to omit this step [15]. Therefore, we explore the feasibility of measuring Chuanxiong slices directly without grinding, aligning with the purpose of non-destructive sampling.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), as excellent end-to-end models that integrate automatic feature extraction and automatic parameter optimization, have been widely applied in the field of spectral data analysis. Dong et al. employed near-infrared technology in conjunction with a CNN model to classify the varieties of mangoes [16]. Hao et al. used hyperspectral technology combined with a CNN model to classify the origin of goji berries [17]. Ren et al. used Raman spectroscopy technology combined with LIBS to classify 13 types of fish through the establishment of a CNN model [18]. Yang et al. used terahertz combined with a CNN model to authenticate the origin of coffee [19]. Li et al. used mid-infrared combined with a CNN model to detect sugar adulteration in honey [20]. These studies above demonstrate the widespread use of spectral technology combined with CNN models for qualitative or quantitative analysis of food or agricultural products. The constructed qualitative or quantitative CNN models have significantly improved prediction speed and accuracy for such analyses, offering a marked advantage over conventional methods.
The study rapidly identified the geographical origin of Chuanxiong slices using a method combining Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and a CNN model. The modeling effects of CNN, preprocessing, and parameter optimization methods were comprehensively compared and discussed, laying the groundwork for enhancing the quality evaluation system for Chuanxiong slices.
The study initially introduces a qualitative analysis model established using traditional near-infrared technology. Subsequently, it elaborates on the development process of a model based on one-dimensional 1D-CNN and compares it with conventional methods. The paper also discusses the application of the Class Activation Mapping (CAM) algorithm for feature visualization and validates the effectiveness of features extracted by CNNs in traditional models. Finally, the process of feature extraction by the CNN is discussed.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Spectral Acquisition
Chuanxiong samples were purchased from six different production bases, namely Sichuan (XF, PZA, and PZB), Yunnan (XS), Shaanxi (SL), and Hebei (BD) (Figure 1). Among these, three different production areas of Chuanxiong were used from Sichuan, including one batch from Shifang and two from Pengzhou. The Chuanxiong samples were processed into slices with a thickness of 3 mm, and after removing surface impurities, they were stored in a dry, low-temperature environment.
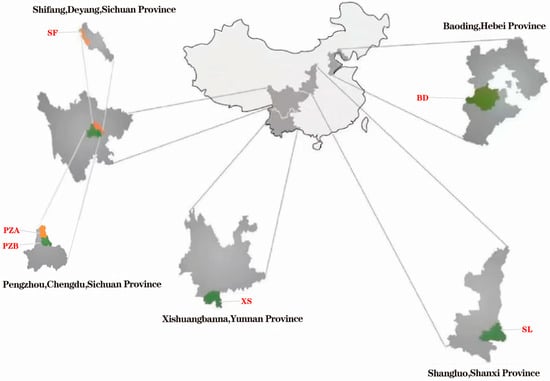
Figure 1.
Chuanxiong origin locations.
For each production area, 50 Chuanxiong slices were randomly selected for spectral data collection (Figure 2), ensuring that the selected samples covered the integrating sphere window. The collection was performed in the diffuse reflectance mode on an Antaris™II FT-NIR spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific Co., Carlsbad, CA, USA). Before collecting the spectral data, the instrument was turned on and preheated for 30 min with the laboratory temperature maintained at approximately 24 °C. The scan count for the collection procedure was set to 32, and the resolution was set to 8 cm−1, generating a total of 1557 wavenumbers from 4000 to 10,000 cm−1. Each sample was scanned three times, and the average value was taken. A total of 50 spectral datasets were collected for each of BD, PZA, PZB, XS, SL, and BD (Figure 3).
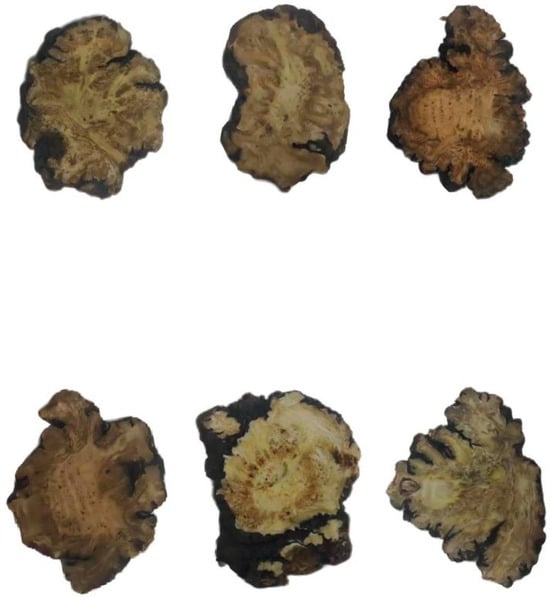

Figure 2.
Samples of BD (Upper Left), PZA (Upper Middle), XS (Upper Right), SL (Lower Left), SF (Lower Middle), and PZB (Lower Right).
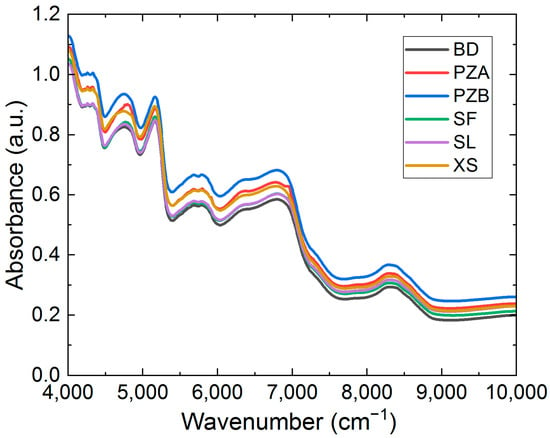
Figure 3.
Original mean spectra of the six samples.
2.2. Sample Set Division and Spectral Pretreatment
The dataset was randomly divided into a training set and a prediction set in a ratio of 4:1. Each production area contributed 40 spectral lines to the training set, totaling 240 spectral lines, and 10 spectral lines to the prediction set, totaling 60 spectral lines.
Typically, the spectra collected contain interfering information, such as baseline drift, noise, and scattered light caused by instruments and detection conditions. The most appropriate preprocessing method should be selected based on the specific characteristics of the data [21]. Common preprocessing techniques encompass smoothing, differentiation, standard normal variate transformation (SNV), and multiple scatter correction (MSC).
Common methods for noise reduction in spectral analysis include moving average smoothing and Savitzky–Golay (S-G) convolution smoothing. This study employs S-G convolution smoothing for spectral data preprocessing. Derivative methods, such as first-order (1st D) and second-order derivatives (2nd D), are commonly used for baseline correction. SNV and MSC are widely applied in solid diffuse reflectance spectroscopy to effectively mitigate the effects of sample surface scattering [22]. By applying these preprocessing techniques and their combinations, this study aims to identify the optimal method to enhance the predictive accuracy and stability of the model.
2.3. Discriminant Analysis
We conducted Discriminant analysis (DA) and partial least squares (PLS) analysis on spectral preprocessing and raw spectra using the commercial software package TQ Analyst 9 (Thermo Nicolet Corporation, Madison, WI, USA).
We employed the DA method to identify Chuanxiong from different origins. DA is a supervised pattern recognition technique that builds a classifier model from a data matrix and known class information. The class membership of an unknown sample is determined by calculating the Mahalanobis distance from the sample to the center of each class. The greater the Mahalanobis distance between two groups, the larger the spectral differences. If an unknown sample is close to its class center, it is “correctly classified”. If not, it is assigned to another class and labeled as “incorrectly classified” [23].
The outlier spectrum removal feature in TQ Analyst 9 software is also based on the calculation of the Mahalanobis distance. We considered spectra with a Mahalanobis distance greater than 2 as outliers, and thus, we excluded three spectra with Mahalanobis distances exceeding 2 [24].
2.4. The Construction and Evaluation of the CNN Model
To identify Chuanxiong from various origins, a supervised classification model needs to be established. CNN is a tool that integrates feature extraction and the modeling process. It can preprocess raw data without prior knowledge or manual intervention, making it widely used in the field of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy analysis [25]. This study develops a Near-Infrared Spectroscopy analysis model based on a 1D-CNN to analyze the near-infrared spectra of Chuanxiong slices from different production areas.
The 1D-CNN model, suitable for spectral data, consists of multiple convolutional and fully connected layers interconnected through specific activation functions, as shown in Figure 4. The input layer of the model receives one-dimensional spectral data with 1557 features and gradually extracts features through several convolutional layers, utilizing the Swish activation function, an emerging activation function considered superior to the traditional ReLU activation function in certain tasks [26].
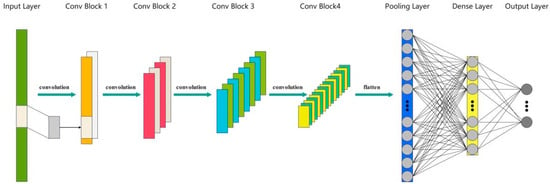
Figure 4.
Schematic diagram of a CNN architecture.
The configuration of each convolutional layer in the model is as follows: The first convolutional layer (conv1) uses 64 filters with a size of 3 and a stride of 2. The next three convolutional layers use 128, 256, and 512 filters, respectively, with the same size of 3 and a stride of 2. The last convolutional layer (conv2) also uses 512 filters with a stride of 2 and serves as the input to the global max pooling layer [27,28,29]. After the convolutional layers, the model includes a max pooling layer to reduce the spatial dimensions of the features while retaining the most important ones. Subsequently, the data are flattened and passed through a fully connected layer with 512 units, which also uses the Swish activation function. To enhance the generalization ability of the model, a Dropout layer with a dropout rate of 0.1 follows the fully connected layer. Finally, the output layer contains 6 neurons corresponding to 6 categories and uses the softmax activation function for multi-class classification [28].
After the model construction is complete, the model is compiled and the loss function, optimizer, and evaluation metrics are set. The categorical cross-entropy is used as the loss function, the Adam optimizer is used for parameter updates, and accuracy is used as the evaluation metric [29]. The training and validation sets for model training are obtained through random division of the dataset. During the training process, the changes in loss and accuracy are recorded and visualized to assess the model’s performance. Additionally, the predictive results of the model are evaluated using a confusion matrix to visually display the performance across various categories.
2.5. Feature Extraction in CNN Models
To further understand the decision-making process of the model, the feature maps of the convolutional layers are visualized to intuitively see how each layer extracts increasingly abstract features from the raw data. By comparing feature maps from different layers, one can observe how the characteristics of the input raw data change as the network depth increases. CAM is utilized for the localization of feature positions in image-processing models by generating visual heatmaps. It accomplishes this by weighting the feature maps of the last convolutional layer and subsequently upsampling them. The resulting heatmaps reveal the spatial distribution of features upon which the model’s decisions are based, thereby facilitating the assessment of potential model misguidance [30]. Finally, through the Class Activation Mapping algorithm, the response of the model to specific categories can be visualized, providing an intuitive explanation for the predictions.
This study elucidates the feature extraction process of a Convolutional Neural Network model and examines the changes in spectral data within the model by visualizing the feature maps of three convolutional layers. In the first convolutional layer Conv1, the one-dimensional raw input spectrum is transformed by 64 convolutional kernels into 64 feature maps, that is, 64 one-dimensional vectors. These 64 feature maps represent the output after the model has learned 64 types of features. In the second convolutional layer Conv2, the 64 feature maps are transformed into 128 feature maps, which are then transformed into 256 feature maps in the third convolutional layer through 256 convolutional kernels, and finally, into 512 feature maps in the fourth convolutional layer through 512 convolutional kernels. Through four rounds of convolution, the length of the feature maps continuously decreases while their number increases. A softmax activation function was applied in all four convolutional layers, setting the negative values after convolution to zero.
Using layer-by-layer convolution, important bands are continuously enhanced while unimportant bands are gradually weakened. The visualization of feature maps can demonstrate the process of feature extraction by Convolutional Neural Networks. In this study, the visualization of feature maps was obtained by using the average spectrum as input.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. NIR Spectral Features Analysis
Chuanxiong primarily contains volatile oils, alkaloids, polysaccharides, and other compounds. Among these, ligustilide and ferulic acid are key characteristic substances used for origin identification and quality analysis. These compounds feature hydrogen-containing groups, thus exhibiting characteristic absorption in infrared spectra. Figure 3 shows the mean spectra of Chuanxiong slices collected from six different production areas. These spectra exhibit a high degree of similarity in shape and peak positions, indicating similar compositional information. The absorption band at 4750 cm−1 was attributed to the combination of O-H bending and C-O stretching [31]. The absorption band at 5164 cm−1 was mainly induced by the combination of O-H and C-O stretching [32]. The absorption bands at 5696 cm−1 and 5773 cm−1 belong to the first overtone of C-H stretching vibrations [33]. The absorption bands at 6352 cm−1 and 6822 cm−1 belong to the first overtone of the O-H and N-H stretching [34]. The absorption peak at around 8311 cm−1 was induced by the second overtone of C-H stretching.
3.2. Traditional Classification Model Analysis
In this study, a traditional qualitative model was established using the DA function of TQ Analyst 9 software. As described in Section 3.1 and depicted in Figure 3, the main absorption peaks in the average spectrum of Chuanxiong slices were manually selected for the model’s characteristic spectral regions, specifically, 4035–5348 cm−1, 8043–8975 cm−1, and 6900–7410 cm−1. As shown in Table 1, after applying various spectral preprocessing methods to the spectral data, it was found that the model established using the combination of S-G and MSC was the most outstanding. However, the overall accuracy rate of the best traditional qualitative model established was only 80.13%, which is relatively low and largely dependent on the researcher’s experience. There is, therefore, a significant need for a more reliable, effective, and stable modeling technique.

Table 1.
Classification results of traditional qualitative models combined with different spectral preprocessing methods and feature spectra extracted by traditional methods.
3.3. Classification Model Based on CNN
In this section, a total of six production areas were selected, comprising 300 samples, without any processing such as the exclusion of outlier spectra. The 300 samples were divided into a training set containing 210 samples and a test set containing 90 samples, in a ratio of 7:3. To ensure the representativeness of the samples in both the training and test sets, all samples were randomly selected by a specific code. Figure 5 represents the confusion matrix, where the model randomly selected 30% of the spectra, i.e., 90 spectra for validation. The y-axis represents the true origin of the samples and the x-axis represents the predicted origin by the model. The numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 represent BD, PZA, PZB, SF, SL, and XS, respectively. The numbers on the diagonal represent the number of samples where the true and predicted origins match, indicating successful model predictions. For example, out of 16 randomly selected BD spectra, 13 were correctly identified, with 1 misidentified as SF, 1 as SL, and 1 as XS. Out of 19 PZA spectra, 16 were correctly identified, with 3 misidentified as XS. Out of 13 PZB spectra, 12 were correctly identified, with 1 misidentified as XS. Fifteen SF spectra were all correctly identified. Sixteen SL spectra were all correctly identified. Eleven XS spectra were all correctly identified. In total, out of 90 randomly selected spectra for validation, 83 were correctly predicted, resulting in an overall accuracy rate of 92.22% for the prediction set. As shown in Figure 6, the accuracy after 100 epochs was 34.44%, after 500 epochs it was 82.22%, after 1000 epochs it was 87.78%, after 1500 epochs it was 88.89%, and after 2000 epochs it was 92.22%.
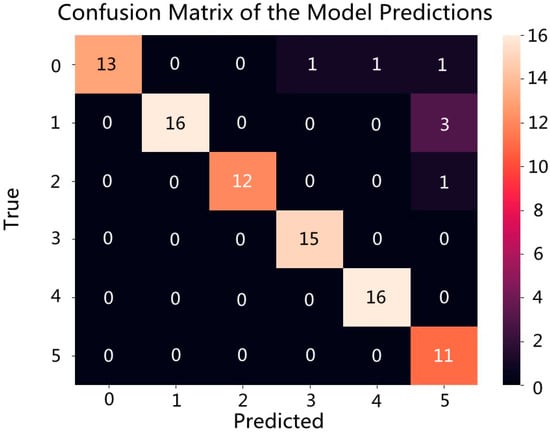
Figure 5.
Confusion matrix of the classification model established based on CNN (0 = BD, 1 = PZA, 2 = PZB, 3 = SF, 4 = SL, 5 = XS).
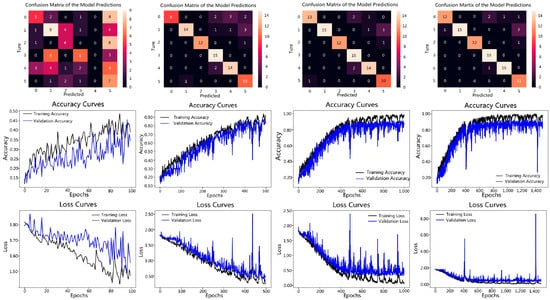
Figure 6.
Confusion Matrices (top), Accuracy Rates (middle), and Loss Functions (bottom) Represented by Different Learning Epochs (from left to right, the learning epochs are 100, 500, 1000 and 1500).
The accuracy of the model established by the Convolutional Neural Network increased with the number of learning epochs (Figure 6 and Figure 7). The Loss curves typically refer to graphs in the field of machine learning and deep learning that display how the loss function value changes over time (usually the number of iterations or training cycles). The lower the loss function value, the more accurate the predictions of the model. As can be seen from Figure 8, the loss value decreases as the number of learning epochs increases. Before reaching 750 epochs, the loss value drops rapidly, indicating that the model structure is well-suited for the current classification task and the learning rate is properly set, allowing the model to learn quickly. Upon reaching 750 epochs, the loss value is low and fluctuates, basically remaining unchanged, indicating that the predictions of the model are very close to the true values, and the model performs well. Figure 9 visualizes the importance of Chuanxiong from each production area in the classification decision-making process, based on the extracted feature spectra using the Class Activation Mapping algorithm for this section of the spectrum. The red shaded area indicates the standard deviation of the Class Activation Mapping values, i.e., the contribution rate of this section of the spectrum to the classification decision, with higher values indicating greater contributions, which can be interpreted as characteristic spectra. The blue solid line represents the average spectrum, while the blue shaded area represents the standard deviation of the spectrum. Three spectral intervals of 4000–4100 cm−1, 4300–4400 cm−1, and 5150–5410 cm−1, which significantly contribute to the classification decision, were selected.
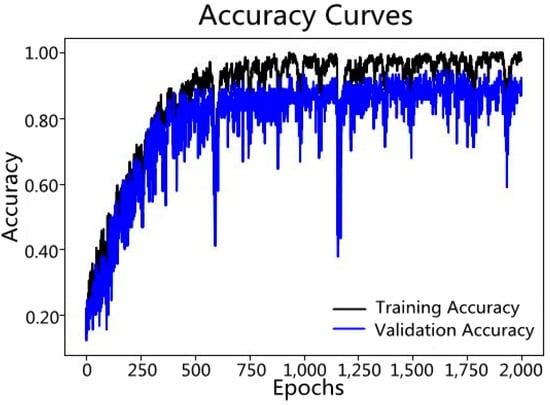
Figure 7.
Variation in accuracy of the CNN model over 2000 learning epochs.
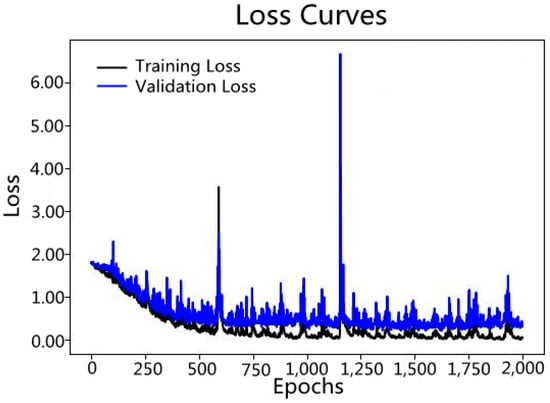
Figure 8.
Variation in Loss curves of the CNN model over 2000 learning epochs.
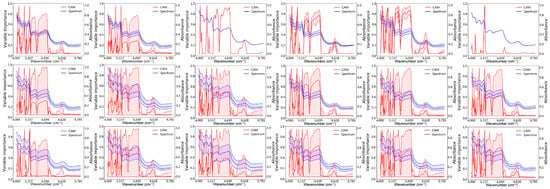
Figure 9.
Important spectral distribution map of near-infrared spectra for correctly classified groups of Chuanxiong slices after 2000 learning epochs. (from top to bottom is the group of error, test and train, respectively, and from left to right is the BD, PZA, PZB, SF, SL, and XS).
Under the same conditions, these three characteristic spectra were utilized in the modeling of the traditional classification model, as shown in Table 2. As shown in Table 3, the best accuracy of the newly established model is still achieved using the S-G + MNC preprocessing method, with the best accuracy being 87.54%. Compared to the accuracy of the traditional model, the model using the characteristic spectra extracted by the CNN model showed a 7.41% improvement in accuracy.

Table 2.
Classification results from traditional qualitative models combined with different spectral preprocessing methods and CNN models combined with Class Activation Mapping (CAM) algorithm for feature spectral extraction.

Table 3.
New model and traditional model accuracy changes.
3.4. Comparative Performance Analysis of New and Traditional Models
In this study, we meticulously compared the performance of the new model, which utilized feature spectra selected by a CNN model, with that of the traditional model, which relied on conventional feature spectra selection methods. As depicted in Table 3, the new model achieved an accuracy of 87.54% when employing optimal preprocessing methods such as S-G + MSC, representing a significant increase of 7.41% compared to the traditional model’s 80.13%. Additionally, when the S-G + SNV preprocessing method was applied, the new model’s accuracy saw an increase of up to 9.87%. Among 17 preprocessing methods, 13 resulted in improved accuracy for the new model, further underlining the superiority of CNN in feature selection.
However, we also noted that not all preprocessing methods improved the performance of the new model. For example, under the combination of S-G + 2nd D, the new model’s accuracy dropped to 55.22%, which is 4.04% lower than the traditional model’s 59.26%. Particularly in the S-G + MSC + 2nd D combination, the new model’s performance decline was the most pronounced, suggesting potential incompatibilities between the preprocessing methods and the feature spectra selected by CNN.
The overall analysis indicates that when combined with appropriate preprocessing methods and feature selection strategies, the new model has the potential to outperform the traditional model.
3.5. Analysis of the Feature Extraction Process in CNN Models
This section primarily discusses the changes in the feature maps of the four convolutional layers after 2000 epochs of deep learning when using the near-infrared spectrum of Chuanxiong as the model input, without altering other parameters. This analysis elucidates the feature extraction process of the Convolutional Neural Network model: The first layer extracts 64 feature maps, the second layer extracts 128 feature maps, the third layer extracts 256 feature maps, and the fourth layer extracts 512 feature maps. The first six feature maps from each of the four convolutional layers are selectively discussed (Figure 10).
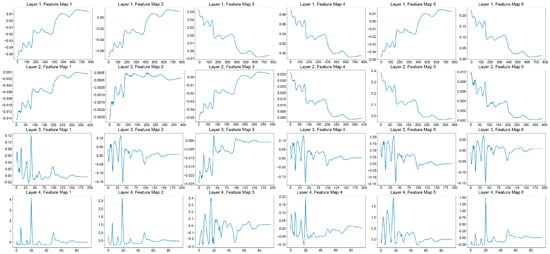
Figure 10.
Visualization of feature maps from four convolutional layers for Chuanxiong slices’ input spectra. (from top to bottom is the first, second, third and fourth convolutional layer, respectively, and from left to right are six feature maps from 1 to 6).
The Convolutional Neural Network acquires overall spectral shape information through layer-by-layer feature extraction while eliminating irrelevant noise information. As the number of convolutional model layers increases, the dimensions of the feature maps continuously decrease. Due to the spatial invariance of the Convolutional Neural Network model, the visualization of feature maps can reflect the changes in the original input spectrum across different convolutional layers. Regarding the first convolutional layer, feature maps 4 and 6 show a higher response within specific frequency ranges, indicating that the first convolutional layer may be extracting local spectral features, such as characteristics of certain chemical bonds or molecular structures. Feature map 5 responds with a lower intensity across most frequency ranges, which may imply that these convolutional kernels play a role in smoothing noise or baseline correction [35,36]. Regarding the second convolutional layer, feature maps 3, 2, and 1 display responses across different frequency ranges, suggesting that the second convolutional layer is extracting more complex spectral features, possibly including combined characteristics of multiple chemical bonds of Chuanxiong. Feature map 5 shows a higher response across a broader frequency range, which may indicate that it is extracting overall spectral features or a wider range of chemical information. In the third convolutional layer, feature maps 1, 4, and 6 exhibit strong responses within specific frequency ranges, which may indicate that the third convolutional layer is further refining the feature extraction, focusing on features closely related to the classification of Chuanxiong origin. Feature maps 5 and 3 have more complex responses, potentially extracting higher-level features that are crucial for distinguishing Chuanxiong from different origins. Concerning the fourth convolutional layer, feature maps 1, 2, and 3 show strong responses within narrower frequency ranges, indicating that the fourth convolutional layer may be extracting very specific spectral features that are crucial for the final origin classification decision. Feature maps 3, 5, and 6 have broader response ranges, which may imply that they are integrating information from the first three layers to provide comprehensive features for the final classification.
4. Conclusions
To address the need for rapid, non-destructive, and convenient identification of the geographical origin of Chuanxiong slices, a method was developed that combines Near-Infrared Spectroscopy with Convolutional Neural Networks. This innovative approach allows for the efficient and accurate determination of the source of Chuanxiong slices. Initially, a qualitative analysis model was established using traditional near-infrared identification methods. This process involved steps such as excluding outlier spectra and selecting the optimal spectral pretreatment, aiming to achieve the best traditional model for identifying the origin of Chuanxiong slices. Subsequently, a model based on 1D-CNN was established by integrating Convolutional Neural Networks. The experimental results indicate that the CNN model can effectively extract features from near-infrared spectral data and accurately classify Chuanxiong slices from different origins. During the model training process, the predictive accuracy gradually improved with the increase in the number of learning iterations, ultimately reaching an accuracy rate of 92.22%. Compared to the traditional analysis model, the model accuracy improved by 12.09% using Convolutional Neural Networks for identification. Moreover, by integrating the Class Activation Mapping algorithm, the features and their extraction process were also visualized based on the Convolutional Neural Network model, thereby providing an intuitive interpretation of the predictions. Further analysis revealed that as the number of Convolutional Neural Network layers increased, the model was able to extract increasingly abstract features layer by layer, progressively enhancing important bands and suppressing irrelevant noise. By visualizing the feature maps of the convolutional layers, the researchers observed the evolution of the input spectral data within the network and how the model distinguished Chuanxiong from different origins through feature extraction. Finally, three spectral intervals that significantly contributed to the classification decision were selected and applied to the traditional classification model to verify the effectiveness of the extracted features. This demonstrates that features extracted by deep learning can complement traditional methods, enhancing classification accuracy.
In summary, this study demonstrates that the deep learning approach combining Near-Infrared Spectroscopy technology and Convolutional Neural Networks can effectively identify Chuanxiong slices from different origins. This provides a new method for Chuanxiong quality monitoring and has the potential to be extended to the quality inspection of other agricultural products.
This study is focused on developing a qualitative model for Chuanxiong slices, but it has not yet delved into the chemical substances behind the characteristic spectra using a CNN model, nor has it undergone corresponding chemical experimental verification. Looking forward, we plan to integrate chemical experiments with the CNN model, aiming not only to establish a qualitative model for Chuanxiong slices but also to quantitatively analyze the chemical components indicated by the characteristic spectra, particularly the representative trace active components in Chuanxiong, such as ferulic acid and imperatorin.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.H. and Y.P.; Methodology, C.L.; Validation, L.Z.; Formal analysis, H.W.; Resources, A.W.; Data curation, L.T. and K.F.; Project administration, Y.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is sponsored by the Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine Traditional Chinese Medicine Research Special General Project (2023MS093), the National Natural Science Foundation Youth Program (32201667), and the Sichuan Provincial Natural Science Foundation Youth Fund (24NSFSC5338). The authors wish to thank the instrumental support provided by Thermo Fisher Scientific—CN, specifically from the engineers Deng Hong, Zhou Xueqiu, and Sun Xianbing.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Shan, F.; Hao, J. Herbal textual research on origin and development of chuanxiong. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2011, 36, 2306–2310. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22097351/ (accessed on 27 June 2024). [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zeng, J.-X.; Lin, J.-X.; Xia, Y.-F.; He, G.-H. Herbal textual research on Chuanxiong Rhizoma in Chinese classical prescriptions. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021, 46, 4293–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Peng, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Xiang, C. Discussion on forming pattern of dao-di herbs Ligusticum chuanxiong. China J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2011, 36, 2303–2305. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22097350/ (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Yang, J.; Feng, X.-L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zou, J.; Wang, C.-X.; Mu, Z.-Q.; Yao, X.-S.; Gao, H. Novel phthalide derivatives identified from Ligusticum chuanxiong (Chuanxiong). Chin. Med. 2016, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Jia, X.; Fang, X.; Li, P.; He, C.; Chen, M. Ultrasonic extraction, antioxidant and anticancer activities of novel polysaccharides from Chuanxiong rhizome. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, W.; Wu, T. Unveiling differential mechanisms of chuanxiong cortex and pith in the treatment of coronary heart disease using SPME-GC×GC-MS and network pharmacology. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2023, 234, 115540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, D.C.; DeVries, J.W.; Spink, J. The economics of a food fraud incident—Case studies and examples including Melamine in Wheat Gluten. Food Control 2017, 71, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, J.; Washmin, N.; Borah, T.; Sarmah, P.; Konwar, P.; Siga, A.; Haldar, S.; Banik, D. Physicochemical properties, chemical composition and sensory attributes of Alpinia nigra (Gaertn.) B.L. Burtt rhizome: An underutilized spice source. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, S.; Guo, B.; Tang, P.; Yin, X.; Pan, F.; Zhao, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D. Rapid detection of adulteration of minced beef using Vis/NIR reflectance spectroscopy with multivariate methods. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 230, 118005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Li, P. Rapid identification of adulterated rice based on data fusion of near-infrared spectroscopy and machine vision. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 3881–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y. Development of machine learning models using multi-source data for geographical traceability and content prediction of Eucommia ulmoides leaves. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 313, 124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudo, A.; Grassi, S.; Savorani, F.; Gavoci, G.; Casiraghi, E.; Geobaldo, F. Determination of the geographical origin of green coffee beans using NIR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis. Food Control 2019, 99, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirvaresi, A.; Nikounezhad, N.; Amirahmadi, M.; Daraei, B.; Parastar, H. Comparison of near-infrared (NIR) and mid-infrared (MIR) spectroscopy based on chemometrics for saffron authentication and adulteration detection. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Dong, Y.; Song, R.; Ma, J.; Fan, Q.; Wei, J.; et al. Fast discrimination and quantification analysis of Curcumae Radix from four botanical origins using NIR spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics tools. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 254, 119626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Jin, K.; Zhong, L.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, A. Near-infrared spectroscopy combined with machine learning for rapid identification of Atractylodis rhizoma decoction pieces. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, J.; Sun, P.; Ran, W.; Li, Y. Mango variety classification based on convolutional neural network with attention mechanism and near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 2237–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Dong, F.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Cui, J.; Men, J.; Liu, S. Combined hyperspectral imaging technology with 2D convolutional neural network for near geographical origins identification of wolfberry. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 4923–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Tian, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Geng, X.; Wang, K.; Du, Z.; Li, Y.; Lin, H. Rapid identification of fish species by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy coupled with machine learning methods. Food Chem. 2023, 400, 134043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, C.; Mei, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, W.; Han, D.; Xu, K. Determination of the Geographical Origin of Coffee Beans Using Terahertz Spectroscopy Combined With Machine Learning Methods. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 680627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zeng, J.; Lin, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Yao, L.; Wang, S.; Du, J.; Wu, Z. Mid-infrared spectra feature extraction and visualization by convolutional neural network for sugar adulteration identification of honey and real-world application. LWT 2021, 140, 110856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Lin, T.; Ying, Y. Deep learning for vibrational spectral analysis: Recent progress and a practical guide. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1081, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; He, M.; Wang, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W. Fast Discrimination and Quantification Analysis of Atractylodis rhizoma Using NIR Spectroscopy Coupled with Chemometrics Tools. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 7707–7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.A.; Conceição, D.G.; Viana, M.B.; Silva, G.d.J.; Santos, L.S.; Ferrão, S.P.B. NIR and MIR spectroscopy for quick detection of the adulteration of cocoa content in chocolates. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Zhu, M.; Shi, T.; Luo, X.; Gan, B.; Tang, L.; Chen, Y. Adulteration detection of corn oil, rapeseed oil and sunflower oil in camellia oil by in situ diffuse reflectance near-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Control 2021, 121, 107577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.Q.; Ming, W.; Zeng, H.T.; Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, H.M. Deep learning-based component identification for the Raman spectra of mixtures. Analyst 2019, 144, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Pan, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, G. Development of analytical method associating near-infrared spectroscopy with one-dimensional convolution neural network: A case study. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 2963–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Garg, N.M.; Iyengar, S.R.S.; Singh, V. Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging for determination of protein content in barley samples using convolutional neural network. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 3548–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.; Yu, J.; Sun, D.-W.; Wei, Q.; Li, Q. Distinguishing pericarpium citri reticulatae of different origins using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy combined with convolutional neural networks. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 299, 122771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, C.A.; Wang, C.J.; Savic, L.J.; Ferrante, M.; Schobert, I.; Schlachter, T.; Lin, M.; Duncan, J.S.; Weinreb, J.C.; Chapiro, J.; et al. Deep learning for liver tumor diagnosis part I: Development of a convolutional neural network classifier for multi-phasic MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 3338–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning Deep Features for Discriminative Localization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Yan, H.; Chang, X.W.; Zhou, G.S.; Zhu, L.; Liu, P.; Guo, S.; Dong, T.T.X.; Duan, J.A. Rapid Geographical Origin Identification and Quality Assessment of Angelicae Sinensis Radix by FT-NIR Spectroscopy. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2021, 2021, 8875876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Li, B.Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.H.; Pan, X.B.; Wang, Y.L. Characterization of Radix Angelicae sinensis by Fluorescence and Near-Infrared Spectroscopies. Anal. Lett. 2024, 57, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wei, D.; Su, S.; Guo, S.; Qian, S.; Yan, H.; Zhao, M.; Shang, E.; Qian, D.; Sun, X.; et al. An integrated strategy for rapid discovery and prediction of nucleobases, nucleosides and amino acids as quality markers in different flowering stages of Flos Chrysanthemi using UPLC–MS/MS and FT-NIR coupled with multivariate statistical analysis. Microchem. J. 2020, 153, 104500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.Z.; Fu, X.S.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, X.P.; Ye, Z.H. Tracing geographical origins of teas based on FT-NIR spectroscopy: Introduction of model updating and imbalanced data handling approaches. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 1537568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acquarelli, J.; van Laarhoven, T.; Gerretzen, J.; Tran, T.N.; Buydens, L.M.C.; Marchiori, E. Convolutional neural networks for vibrational spectroscopic data analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 954, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.; Fearn, T. Modern practical convolutional neural networks for multivariate regression: Applications to NIR calibration. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 182, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).