Abstract
Egypt did not previously grow buckwheat, due to the belief that the environment does not meet the factors of growth, development, and productivity in an arid or semiarid region. The present study investigated two species of buckwheat, Fagopyrum tataricum (FT) and Fagopyrum esculentum (FE), which were planted in two different soil, weather, and water property sites, including the first in Belbies City and the second in Sadat City in the middle of January, November, and March for two successive seasons, 2018–2019 and 2019–2020. The study uniquely focuses on Egypt to investigate three interactions of location × species, location × sowing date, and species × sowing date on growth and productivity. The parameters measured included plant height (cm), number of branches, internodes, and leaves per plant, fresh weight (gm), number of grains per plant, grain weight of 1 m2, and yield (kg/Ha). Our results indicated significant differences in all measured interactions. For the location × species interaction, FT planted in Belbies City consistently outperformed all other combinations, with a plant height = 97.704 cm in the 1st season and productivity = 859.38 kg/ha in the 1st season, while FE in Sadat showed the lowest growth and productivity. For the interaction of location × sowing date, Belbies × mid-March sowing achieved the highest plant heights of 84.89 cm and 75.44 cm, and productivity of 702.88 kg/ha and 708.21 kg/ha in consecutive seasons. Conversely, Sadat City × Mid-March sowing resulted in the lowest plant heights of 57.500 cm, and 57.667 cm, and productivity of 490.67 kg/ha, and 444.55 kg/ha. The species × sowing date interaction further emphasized the superiority of FT sown in mid-March, which led to the best plant height growth of 95.78 cm in the 1st season and the highest productivity of 837.55 kg/ha in the 1st season. In contrast, FE sown in mid-March exhibited the poorest outcomes. The study provides an understanding of the two-way interactions affecting buckwheat cultivation in Egypt. Our results indicated its viability with appropriate species selection and sowing dates, contributing to agricultural diversity and sustainability.
1. Introduction
Agriculture, at the heart of global sustainability and food security, faces unprecedented challenges in the era of climate change [1]. Arid and semiarid regions, such as those predominant in Egypt, are particularly vulnerable, necessitating innovative agricultural practices and crop diversification. Among the various crops, buckwheat stands out for its exceptional adaptability, nutritional benefits, and potential to thrive under water-limited conditions, presenting an untapped resource for regions experiencing climatic adversity [2]. However, the exploration of underutilized crops such as buckwheat represents a frontier in agricultural research driven by the need to address food security and sustainable farming practices in arid environments. Recent studies have begun to underscore the resilience of crops to poor soil conditions, drought, and low water availability, making them attractive options for enhancing agricultural diversity in challenging landscapes in Egypt [3,4]. The agricultural history of Egypt is marked by a reliance on water-intensive crops, an approach that is increasingly unsustainable given the country’s water scarcity issues and the salinization of arable lands. The introduction of buckwheat, a crop previously overlooked due to misconceptions about its suitability, represents a paradigm shift toward sustainable agriculture, leveraging its minimal water requirement and adaptability [5]. However, this research challenges existing agricultural paradigms by demonstrating buckwheat’s viability in Egypt, thereby contributing to the diversification of crops—a cornerstone of food security and ecological sustainability. By dissecting the interaction between abiotic and biotic factors, this study aimed to identify new agricultural practices that boost productivity while ensuring resilience against climate change [6,7]. Nevertheless, the interaction of genetic, environmental, and management factors is crucial in understanding crop growth and productivity, an area of agricultural science that has become increasingly relevant with the advent of climate change and the push for sustainable practices. Buckwheat has emerged as a crop of interest due to its adaptability to diverse climatic and soil conditions, underscoring the importance of this study within Egypt’s unique agricultural patterns [8]. The variability in growth responses among buckwheat species to different environmental conditions highlights the significance of species selection, highlighting the complexity of genotype–environment interactions and their impact on crop performance across various settings [3,7,9,10]. Moreover, the influence of abiotic factors, such as soil conditions and external treatments, on buckwheat emphasizes the role of these factors in crop adaptability [6,11]. Environmental factors such as altitude and UV radiation also contribute to the complexity of buckwheat cultivation and have significant effects on growth and productivity [12,13]. Moreover, the impact of sowing date on buckwheat yield illustrates the significance of temporal factors in agricultural outcomes [5,14,15]. Challenges posed by seasonal transitions and specific soil conditions, such as salinity, necessitate a deeper understanding of optimal cultivation practices [4,16]. However, soil health and management practices play a critical role in determining crop productivity, highlighting the importance of soil conditions and agronomic practices in achieving sustainable yields [17,18,19]. The history of land use and previous cropping systems influences the success of current crops, revealing the intricate relationship between past and present agricultural practices [20,21].
Furthermore, the classification of Fagopyrum sp. involves distinguishing between F. esculentum and F. tataricum, which are species whose biological differences are emphasized. F. esculentum, commonly known as a common buckwheat species, is an annual Asian herb with small pinkish or white flowers and edible triangular seeds. In contrast, F. tataricum, which is also an erect annual herb, has a smaller seed size. Studies have shown that F. esculentum flowers earlier than F. tataricum and produces fewer nodes, branches, and inflorescences but more flowers per inflorescence [2,17]. Additionally, F. tataricum is more resistant to water stress and exhibits traits of drought tolerance, while F. esculentum has characteristics of drought avoidance [22]. Furthermore, there are differences in genome size between these species, with F. esculentum having a larger genome size than F. tataricum [7,18]. However, the influence of location, species choice, and sowing date on buckwheat growth and productivity, as well as the variability in certain buckwheat species in response to environmental conditions [3,9] and the role of genotype–environment interactions [7,10], and the effects of external treatments and soil conditions on buckwheat plants further expand our understanding of these interactions [6,11]. Additionally, the influence of altitude and UV radiation provides further context for understanding the environmental sensitivity of buckwheat [12,13], further to the impact of sowing date on buckwheat productivity [5,14,15]. Nevertheless, the transition between seasons [16] and the specific challenges of saline soils [4] further contribute to the understanding of the optimal conditions for buckwheat cultivation and the critical role of soil conditions in crop productivity. Previous crops and cultivation practices were influenced, along with insights into weed suppression and no-tillage systems [17,18,19,20,21,23,24,25].
This research investigated the interaction between biotic and abiotic factors in buckwheat cultivation in arid regions of Egypt, aiming to optimize growth conditions and unlock the potential for resilience and nutrition in sustainable farming systems. By exploring buckwheat’s viability in these challenging climates, this study challenges traditional agricultural practices and offers insights into enhancing food security and sustainability amid environmental challenges. These findings suggest that selecting appropriate species and sowing dates, in addition to suitable farming practices, can significantly improve buckwheat productivity in Egypt, supporting the goals of agricultural diversification and sustainability in response to changing climate conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
Field experiments were conducted during the 2018–2019 and 2019–2020 seasons at two locations: the Belbies City site (BCS) and the experimental farm of the Environmental Studies & Research Institute (ESRI), University of Sadat City (SCS) in Sadat City, Monofiya. These experiments aimed to evaluate the growth and productivity of buckwheat plants under varying climatic conditions, focusing on the morphological characteristics and yield of grains from different buckwheat species and sowing dates.
The experimental treatments were as follows:
2.1. Materials
Locations of Cultivation: BCS Was Located at 30.4196° N, 31.5619° E, and SCS Was Located at 30.3594° N, 30.5327° E (Scheme 1).
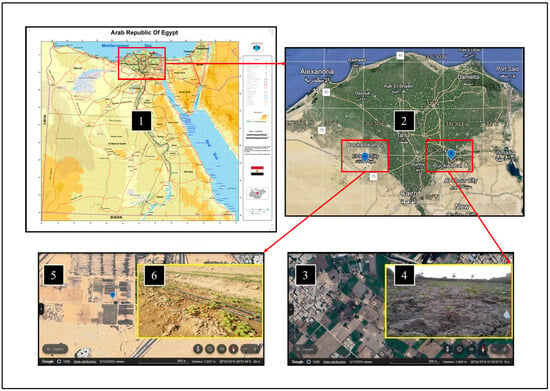
Scheme 1.
The study locations where the typography of each planting site showed, where: 1 = Map of Egypt (sourced by CAMPASS, 2023). 2 = A focused satellite image of the regions of both study locations (by Google Earth Web, 2023). 3 & 4 are satellite images of the planting sites of Belbies City and Sadat City, respectively (sourced by Google Earth Web, 2023). 5 & 6 are real images of the planting sites at the early stages of growth in Belbies City and Sadat City, respectively. Photos edited and compiled by the authors.
Species: Fagopyrum esculentum, Represented by “Japanese”; Fagopyrum tataricum, by “Madawaska”; Both Cultivars were Purchased Online from a Commercial Seed Company in California, United States, and Shipped to Egypt following the force Laws of the State Ministry of Agriculture for Quarantining and Importing Seeds.
Sowing Dates
Season 1: Second week of November 2018, January 2019, and March 2019
Season 2: Second weeks of November 2019, January 2020, and March 2020
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Seeds
The seeds were sealed in their original bags and then opened in the field for planting. The first batch was planted at the Belbies City site as afeer cultivation [14] (dry seeds in a dry land, a common planting method widespread in the cultivation of grain, e.g., wheat). The seeds were mixed with sand at a 1:2 v/v ratio to control the spread of the seeds on the designated plot and ensure that all the seeds were well sown with uniformity. The experiment used a rate of 160 seeds/m2 for all 3 sowing dates at both locations, and the first planting occurred at the Belbies City site in mid-November 2018. A total of 6 plots were planted in each patch. Three plots were randomly distributed for F. esculentum, and three were allocated for F. tataricum; each plot was an area of 4.5 m2 planted with ±720 seeds weighing approximately 21.800 g. In the second location, the seeds were sowed manually by clever farmers and then land scarfed via a handy fork to ensure the uniformity of the seeds and ensure that the soil was covered by a layer of soil at least 2 cm in length. However, due to the land structure, a raised bed is commonly used there, so the seeds were spread on the upper side of the raised bed where each plot was 6 m × 0.75 m = 4.5 m2, with the same rate of seed and sand mixture used in the first location. Irrigation was applied to both sites directly after sowing. However, at the location of Sadat City, the raised beds were covered by plastic sheets to avoid bird attacks.
2.2.2. Experimental Site Analysis
At the beginning of each experimental season, three soil samples from the top layer (0–30 cm) were randomly collected from the experimental sites. Then, the samples were air dried, ground, and sieved through a 2 mm sieve and then bulked together before being subjected to soil analysis for classifying soil texture through particle size distribution analysis (mechanical analysis) as well as determining some soil chemical characteristics [7]. The physical and chemical properties of the experimental soil during both seasons of the study are presented in Table 1, and the water properties, including physical, chemical, and biological parameters, were analysed at both sites, as shown in Table 2. However, weather data for both study sites, including temperature, total precipitation, relative humidity, wind gusts, sunshine duration, and soil temperature [0–7 cm down], were obtained by the weather model Nonhydrostatic Meso-Scale Modelling Technology (NMM) of Meteoblue based in Basil, Switzerland, as shown in Table 3.

Table 1.
Physical and chemical properties of the experimental soil samples.

Table 2.
Irrigation water properties of the experimental soil samples.

Table 3.
Weather data of the study locations.
2.2.3. Experimental Site Preparation
The experimental soil was prepared by land plowing in two perpendicular directions, and all the experimental plots received organic manure as compost at a rate of 16 tons/hectare, phosphorus fertilizer at 80 units P2O5/hectare as calcium superphosphate (15.5% P2O5), and agricultural sulfur as agricultural sorghum. Superfine 98% S at 180 kg/hectare full doses of compost, superphosphate, and agricultural sulfur were applied once during the final preparation of the experimental soil and thoroughly mixed with the soil before the ridges were constructed. However, nitrogen fertilizer was applied at 180 units N/hectare in the form of ammonium sulfate (20.6% N). The nitrogen dose was split into 3 portions. The first portion was added 15 days after the seeding date, and the remaining portions were subsequently added at a rate of one portion every 15 days until grain setting. Nitrogen fertilizer was applied manually at the Belbies site and through injection in a drip irrigation system as a plant fertigation application at the Sadat site.
2.2.4. Data Recorded
Plant Vegetative Growth Parameters
After 70 days after sowing and after all the experimental treatments were carried out, a random and representative sample of 9 buckwheat plants from each experimental subplot was taken by cutting at ground level (at 2–3 cm above the ground surface) and subsequently transferred to the laboratory of the Environmental Studies and Research Institute to determine the following vegetative growth parameters.
Plant Height (cm)
The average plant height was recorded in centimeters (cm) from the point of contact of the plant stem with the soil up to the highest point of the inflorescence on the main stem of the buckwheat plant samples in each experimental subplot.
Number of Branches per Plant
The average number of lateral branches per plant was counted for the buckwheat plant samples in each experimental subplot, and the average number of branches per plant was calculated.
Whole-Plant Fresh Weight (gm)
The average fresh weight of the whole buckwheat plant (stem, lateral branches, and leaves) was recorded in grams (gm) by using a 3-decimal digital electronic balance directly after being taken from the fields of the study.
Harvesting of Buckwheat Grain Samples
At the harvesting stage, ±75 days after the sowing date, a representative sample of 9 individual buckwheat plants (group A plants), in addition to the plant samples harvested from one square meter from the middle of each experimental subplot (group B plants), was randomly taken by cutting at ground level (at 2–3 cm above the ground surface). Then, all the plant samples were left to air dry for at least 7–10 days for the plants planted in mid-November and January and for 3–5 days for the plants planted in mid-March. Afterward, each of the 10 dried plant samples was threshed by hand to obtain the grains from the dried main and lateral panicles per group of plants (group A plants) or per all plant samples harvested from each experimental subplot (group B plants). Moreover, the buckwheat grains were manually ground to clean and remove any impurities, foreign matter, or broken or immature grains. The cleaned grains of group B plants were used directly to determine the number of grains/plant, total grain yield per square meter (kg), and grain yield (kg/Ha), where Ha = 10,000 square meters.
Number of Seeds per Plant
The average number of seeds per plant in each experimental subplot was determined by manually counting the grains extracted from 9 plants in the dried main and lateral panicles of individual plants in group A. The total number of seeds was subsequently divided by 9 to obtain the grain count per plant.
Total Grain Weight per Square Meter (kg)
The average total grain yield per square meter was calculated by quantifying the number of harvested plants (group B) within one square meter. Then, the dried plants were threshed by hand to obtain the grains from the dried main and lateral panicles, and a 3-decimal-digit electronic balance was used to obtain the average grain yield/meter2 in kilograms (kg) units.
Total Grain Yield per Hectare (kg/ha)
The average total grain yield per hectare was calculated by multiplying the average grain yield/square meter (g) by the average number of buckwheat plants per hectare (a plant density of approximately 122 thousand plants per hectare) to obtain the average grain yield/hectare in kilograms per hectare (kg/ha).
2.3. The Statistical Analysis
A randomized complete block design incorporating three factors was used for the data analysis, with each parameter being replicated thrice. The treatment means were subjected to pairwise comparison using the least significant difference (LSD) test, as described by Snedecor and Cochran (1994) [26]. The data analysis was performed utilizing the Assistat software program, version 1.0.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the 2-Way Interaction Effect of Biotic and Abiotic Factors on the Growth of Buckwheat
3.1.1. Interaction between Location and Species
Through our results shown in Table 4 and Figure 1, we observed interaction effects between location (Belbies City vs. Sadat City) and species (Fagopyrum tataricum vs. Fagopyrum esculentum) on various growth characteristics of buckwheat over two seasons. For plant height, in both seasons, Fagopyrum tataricum plants grown in Belbies City had the highest average plant height, significantly surpassing those of all the other combinations. The least significant difference (LSD) at the 0.05 level highlights the statistical significance of these differences, clearly indicating the superior growth performance of Fagopyrum tataricum in Belbies City. For the branch number per plant, similar patterns were observed for the number of branches, with Fagopyrum tataricum in Belbies City producing the most branches compared to the other groups. The differences between the groups were statistically significant, as confirmed by the L.S.D., underscoring the combined influence of species and location on this growth characteristic. For the internode number per plant, the trend continues with the number of internodes, where Fagopyrum tataricum in Belbies City exhibited the highest count, significantly outperforming the buckwheat grown under other conditions. These results are consistent across both seasons, with the L.S.D. values affirming the significance of these findings. For the number of leaves per plant, Fagopyrum tataricum in Belbies City also had a significantly greater number of leaves than the other plants, indicating that a robust growth pattern was influenced by both the choice of species and the cultivation location. These differences were validated by the corresponding L.S.D. values. Finally, for the fresh weight per plant, to reflect the trends in the aforementioned parameters, Fagopyrum tataricum plants grown in Belbies City also had the highest fresh weight per plant, indicating that this combination was the most productive in terms of biomass accumulation. The statistical analysis, supported by the L.S.D. values, confirmed the impact of species and location on this critical growth metric.

Table 4.
Interaction between location and species and its effect on buckwheat growth characteristics.
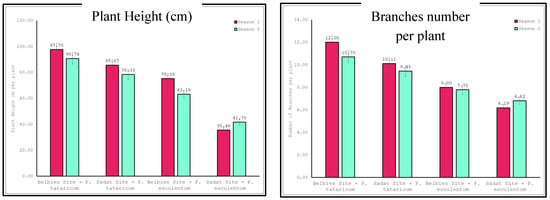
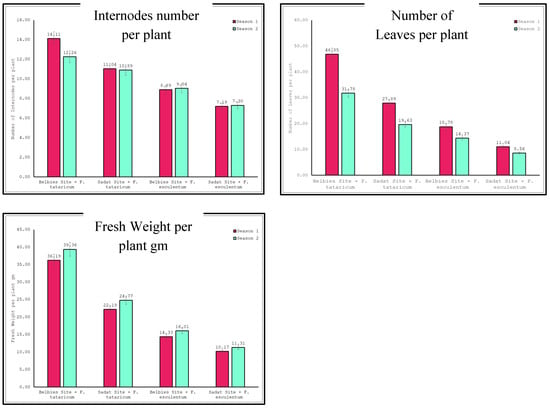
Figure 1.
Evaluation of location × species on the growth of buckwheat.
3.1.2. Interaction of Location × Planting Date
The results in Table 5 and Figure 2 show the interaction effects of location and sowing time on the growth of buckwheat plants across two parameters: physical growth characteristics and fresh weight per plant. The study differentiates results by location (Belbies City site vs. Sadat City site) and by sowing time (mid-January, mid-November, mid-March), presenting findings for two growing seasons. For plant height, in both the first and second seasons, plant height was consistently greater in Belbies City than in Sadat City across all sowing times. The least significant difference (L.S.D.) at the 0.05 level for plant height indicates significant differences between locations, with no significant variation among sowing times within the same location. For instance, in the first season, plant heights in Belbies City ranged from 84.889 cm to 88.222 cm, which was significantly greater than those in Sadat City, where heights ranged from 57.500 cm to 62.806 cm (p ≤ 0.05). For the branch and internode number, the number of branches and internodes per plant followed a similar pattern to that of plant height, with plants in Belbies City exhibiting more branches and internodes than those in Sadat City, regardless of sowing time. The L.S.D. values confirmed these differences as statistically significant (p ≤ 0.05), demonstrating the impact of location over sowing time on these growth parameters. The number of leaves per plant showed notable variability, with significant differences observed not only between locations but also among sowing times within the same location, especially in the first season. For example, in Belbies City, during the first season, sowing in mid-March resulted in the highest number of leaves (35.778), which was significantly greater than that of the other sowing times, indicating that both location and sowing time influence leaf production. In terms of fresh weight per plant, fresh weight per plant demonstrated significant variation influenced by both location and sowing time, with higher weights generally observed in Belbies City across all sowing times. In the second season, sowing in mid-March in Belbies City resulted in the highest fresh weight (28.857 g), which was significantly greater than that of all the measurements in Sadat City, where the maximum observed weight was 20.921 g for mid-March sowing.

Table 5.
Interaction effect of location × sowing time on the growth of buckwheat plants.
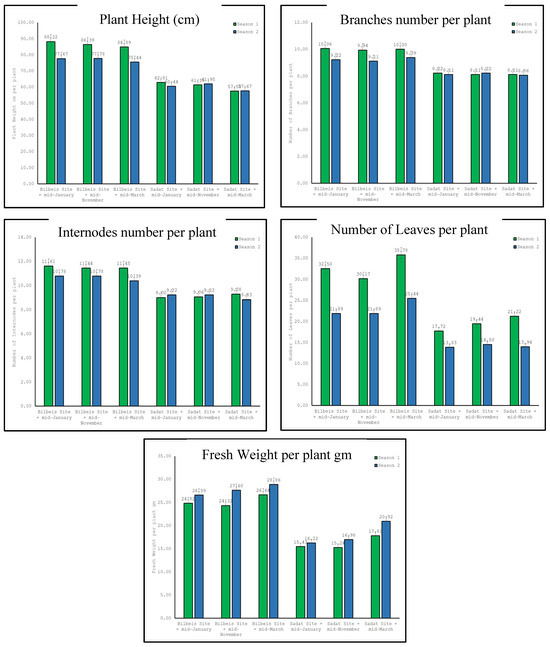
Figure 2.
Evaluation of location × sowing date on the growth of buckwheat.
3.1.3. Interaction Effect of Species × Sowing Time
Our results in Table 6 and Figure 3 detail the interaction effects of species (Fagopyrum tataricum × Fagopyrum esculentum) and planting time (mid-March, mid-January, mid-November) on the growth of buckwheat across various growth parameters over two growing seasons. For plant height, the data showed that, compared with Fagopyrum esculentum, Fagopyrum tataricum consistently achieved greater plant heights across all planting times, with significant differences noted (p ≤ 0.05). For instance, in the first season, the height reached 95.778 cm for Fagopyrum tataricum sown in mid-March, which was significantly taller than that of Fagopyrum esculentum in the same period, which reached only 46.611 cm. An L.S.D. of 0.05 validates the statistical significance of these differences. In terms of the number of branches, similar trends were observed for the number of branches, where Fagopyrum tataricum plants consistently had more branches than Fagopyrum esculentum plants across all planting times. The first season showed a significant difference with Fagopyrum tataricum sown in Mid-March having 11.722 branches, contrasting with 6.389 branches for Fagopyrum esculentum sown in the same period, supported by a statistically significant L.S.D. The number of internodes followed a pattern akin to plant height and branch number, with Fagopyrum tataricum exhibiting a higher number of internodes than Fagopyrum esculentum. This effect was consistent across all planting times and both seasons, demonstrating the influence of the species on this growth parameter. However, for the number of leaves, Fagopyrum tataricum plants also had a significantly greater number of leaves than Fagopyrum esculentum plants, with the greatest disparity observed in the first season. The difference in leaf count between the species was statistically significant, as indicated by the L.S.D. values. Finally, for fresh weight per plant, the fresh weight of Fagopyrum tataricum plants was significantly greater than that of Fagopyrum esculentum plants across all planting times and seasons. This parameter clearly illustrates the superior growth performance of Fagopyrum tataricum under the conditions tested.

Table 6.
Interaction effect of species × planting times on the growth of buckwheat.
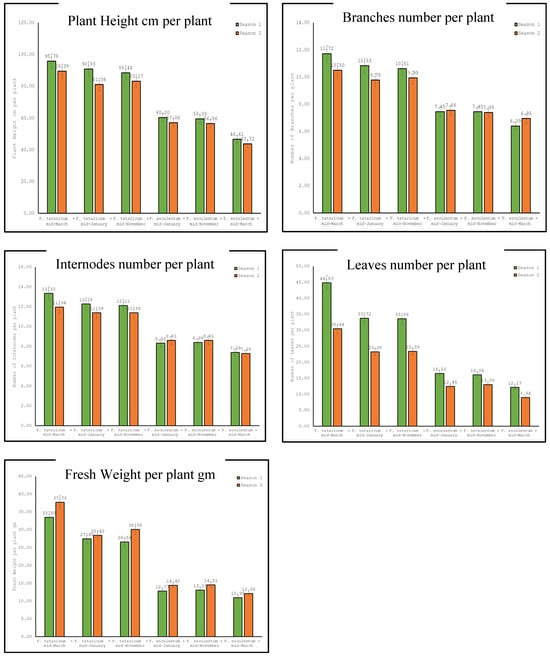
Figure 3.
Evaluation of species × sowing date on the growth of buckwheat.
3.2. Evaluation of the 2-Way Interaction between Biotic and Abiotic Factors on the Productivity of Buckwheat
3.2.1. Interaction between Location and Species
The obtained results in Table 7 and Figure 4 show the interaction effects of location (belbies vs. Sadat) and species (Fagopyrum tataricum vs. Fagopyrum esculentum) on the productivity of buckwheat plants, examining parameters such as the number of seeds per plant, grains per square meter, and productivity rate per hectare over two growing seasons. For the number of seeds per plant, Fagopyrum tataricum in Belbies City exhibited the highest number of seeds per plant in both seasons (48.07 and 49.63, respectively), significantly outperforming all the other treatment combinations. Fagopyrum esculentum in Sadat City had the lowest seed count (13.67 and 14.63, respectively). A least significant difference (LSD) of 0.05 was used to confirm these differences as statistically significant. Similarly, Fagopyrum tataricum grown in Belbies City achieved the highest grain yield per square meter (0.0886 kg and 0.0867 kg, respectively, in the first and second seasons), markedly higher than the lowest yields observed for Fagopyrum esculentum in Sadat City (0.0314 kg and 0.032 kg, respectively). The LSD test results validated the significant impact of both location and species on grain yield. Additionally, for the kg/Hectare productivity rate, which reflects trends in the other parameters, Fagopyrum tataricum in Belbies City also led in terms of productivity per hectare, with 859.38 kg and 832.27 kg in the first and second seasons, respectively. In contrast, Fagopyrum esculentum in Sadat City had the lowest productivity (316.32 kg and 319.12 kg, respectively). The statistical significance of these differences was confirmed by the LSD test at 0.05.

Table 7.
Interaction effect of location × species on the productivity of buckwheat.
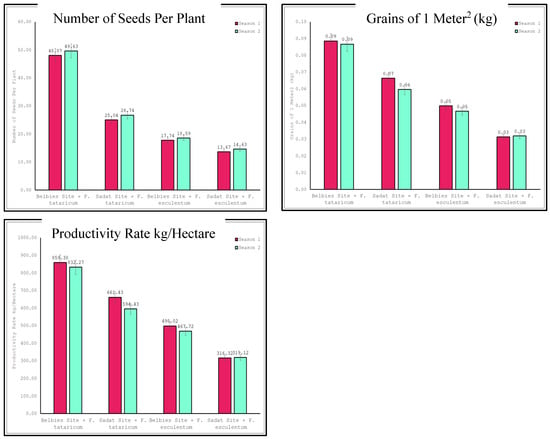
Figure 4.
Evaluation of location × species on the productivity of buckwheat.
These results delineate a clear pattern of superior performance by Fagopyrum tataricum, especially when cultivated in Belbies City, across all the measured productivity parameters. Conversely, Fagopyrum esculentum in Sadat City consistently exhibited the lowest productivity. The statistically significant differences, as indicated by the LSD tests, affirm that both the choice of species and the cultivation location critically influence buckwheat productivity.
3.2.2. Interaction of Location × Sowing Time
Our findings in Table 8 and Figure 5 explore the interaction effect of location (Belbies City site vs. Sadat City site) and sowing time (mid-January, mid-November, and mid-March) on the productivity of buckwheat, focusing on the number of seeds per plant, grains per square meter, and the productivity rate per hectare across two growing seasons. For the number of seeds per plant, the data clearly illustrate the influence of both sowing time and location on the number of seeds per plant. In both seasons, sowing at the Belbies City site in mid-March resulted in the highest number of seeds (37.72 and 37.83, respectively), significantly surpassing the counts in Sadat city at any sowing time. A least significant difference (LSD) of 0.05 was used to confirm the statistical significance of these observations. Similarly, the highest grain yield per square meter was observed for buckwheat sown in mid-March at the Belbies City site (0.0723 kg and 0.073 kg in the first and second seasons, respectively), indicating optimal productivity when sown during this period. Again, the yields were significantly lower in Sadat City, regardless of the sowing time, with the LSD values substantiating the significance of the interaction between location and sowing time. However, for the kg/Hectare productivity rate, which reflects the trends in number of seeds per plant and grains per square meter, the highest productivity rates per hectare were achieved with mid-March sowing at the Belbies City site (702.88 kg and 708.21 kg in the first and second seasons, respectively). In contrast, all the productivity metrics in Sadat City were significantly lower, underscoring the influence of both sowing date and location on overall productivity. The differences across these groups were statistically significant, as indicated by the LSD at 0.05.

Table 8.
Interaction effect of location × sowing time on the productivity of buckwheat.
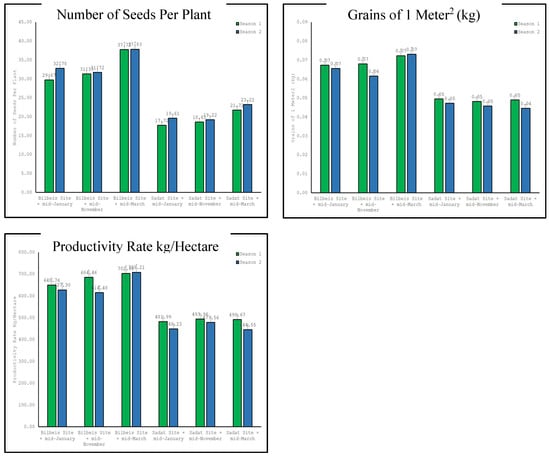
Figure 5.
Evaluation of location × sowing date on the productivity of buckwheat.
These results demonstrated the significant effects of sowing time and location on the productivity of buckwheat, with mid-March sowing occurring at the Belbies City site consistently yielding the highest number of seeds, highest grain weight per square meter, and greatest productivity per hectare. Conversely, the Sadat City site had the lowest productivity across all sowing times, and the statistical analysis confirmed the robustness of these findings.
3.2.3. Interaction of Species × Sowing Date
Our obtained results in Table 9 and Figure 6 present the interaction effects of species (Fagopyrum tataricum vs. Fagopyrum esculentum) and sowing time (mid-March, mid-January, mid-November) on the productivity of buckwheat, with a focus on the number of seeds per plant, grains per square meter, and the productivity rate per hectare across two growing seasons. This analysis is structured to highlight the significant differences and trends in buckwheat productivity, providing insights into how these factors influence buckwheat productivity. For the number of seeds per plant, Fagopyrum tataricum produced significantly greater numbers of seeds per plant across all sowing times than did Fagopyrum esculentum, with the highest counts observed for mid-March sowing in both seasons (45.17 and 45.72, respectively). This indicates a clear advantage of Fagopyrum tataricum in terms of seed production, especially when sown in mid-March. A least significant difference (LSD) of 0.05 underscores the statistical significance of these differences. However, for grains per square meter, Fagopyrum tataricum sown in mid-March also yielded the highest grain weight per square meter (0.0858 kg and 0.084 kg in the first and second seasons, respectively), significantly outperforming Fagopyrum esculentum sown during the same period. This finding suggested that not only the choice of species but also the timing of sowing significantly affect grain production. The LSD test results confirmed the statistical significance of these observations. However, according to the results in seeds per plant and grains per square meter, Fagopyrum tataricum sown in mid-March achieved the highest productivity rates per hectare (837.55 kg and 818.36 kg in the first and second seasons, respectively). In contrast, Fagopyrum esculentum, especially when sown in mid-March, had the lowest productivity, highlighting the substantial impact of both species and sowing time on overall productivity. The differences across these groups were statistically significant, as indicated by the LSD at 0.05. These results demonstrate the superior performance of Fagopyrum tataricum over Fagopyrum esculentum in terms of productivity, as sowing in mid-March further enhanced its productivity.

Table 9.
Interaction effect of species × sowing time on the productivity of buckwheat.
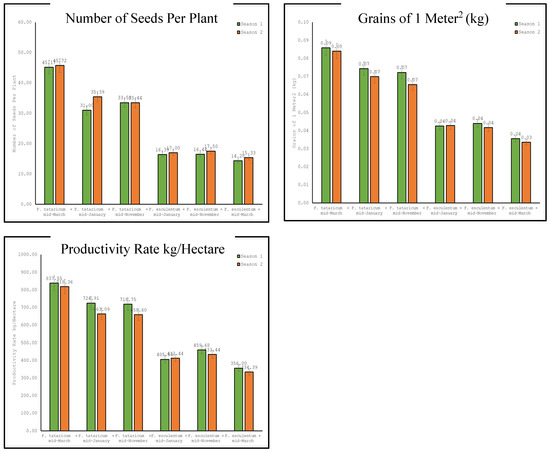
Figure 6.
Evaluation of species × sowing date on the productivity of buckwheat.
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation of the 2-Way Interaction Effect of Biotic and Abiotic Factors on the Growth of Buckwheat
The observed variations in buckwheat growth and productivity across different locations, species, and sowing dates, as indicated in the experimental outcomes, can be attributed to complex interactions among genetic, environmental, and management factors [1,6,23]. The superior vegetative growth characteristics exhibited by Fagopyrum tataricum (FT) in Belbies (BCS) compared to those of the Sadat City site (SCS) and Fagopyrum esculentum (FE) underscore the influence of both location and species on buckwheat growth. This advantage is likely due to the genetic predisposition of FT to adapt better to the environmental conditions present in Belbies, such as soil type, pH, and microclimate, which may be more conducive to its growth than the conditions in Sadat city. Furthermore, the soil and water analyses (Table 1 and Table 2) provide insights into these environmental conditions, revealing differences in pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and nutrient availability between the two sites, which could significantly affect plant growth [15]. The variations in temperature, precipitation, and relative humidity (Table 3) between the locations across the seasons also influenced these outcomes. Moreover, the impact of sowing time on growth parameters highlights the significance of temporal factors on agricultural outcomes, as demonstrated by the optimal performance of Belbies plants sown in mid-March, which could be attributed to more favorable weather conditions during critical growth stages. These findings are supported by weather data, indicating that seasonal transitions and specific climatic conditions during the growth period significantly influence vegetative development [17,24]. Additionally, the interaction effect between species and sowing time, particularly the superior performance of FT over FE across all sowing times, can be explained by the inherent genetic differences between the two species. The better adaptation of FT to water stress and its drought tolerance [10] may have contributed to its greater resilience and superior growth under varying environmental conditions. The differences in genome size between these species [21,22] may also play a role in their adaptability, with FT possibly possessing genetic traits that confer an advantage under the specific conditions experienced during the experimental periods. The methodologies employed in this study, including detailed site preparation, soil and water analysis, and careful selection of sowing times and species, provided a robust framework for evaluating the interactions between genetic, environmental, and management factors in buckwheat cultivation. The use of organic manure, phosphorus fertilizer, and split applications of nitrogen fertilizer reflects contemporary agricultural practices aimed at enhancing crop productivity while considering sustainability [8,15]. The differential performance of buckwheat species across locations and sowing times is a clear indication of the complexity of genotype–environment interactions. The adaptability of Fagopyrum tataricum (FT) to conditions at the Belbies City site, compared to that of Fagopyrum esculentum (FE), whose disparity in performance at the Sadat City site mirrors previous findings [6,27], highlighted species-specific responses to environmental conditions. This suggests that species selection cannot be universal but rather should be tailored to the specific environmental conditions of the cultivation site, taking into account the local soil, water, and climatic characteristics. The disparities in soil pH, EC, and nutrient availability between the two sites likely played a significant role in influencing plant growth and development. For instance, the relatively higher pH and EC values at the Sadat City site might have imposed additional stress on FE, which, coupled with its inherent drought avoidance characteristics, could explain its underperformance compared to that of FT, which exhibits traits of drought tolerance. These findings align with the physiological and genetic makeup of buckwheat species, which significantly influences their response to abiotic stresses [10]. The experimental design, which meticulously accounted for the variations in planting times and employed rigorous soil preparation and fertilization regimes, underscores the importance of management practices in optimizing crop yields. The application of organic manure, phosphorus, and nitrogen fertilizers, as described, likely enhanced the soil’s fertility, thereby supporting the vegetative and reproductive growth of buckwheat. However, the critical role of soil health and management practices in sustainable crop production has been noted [8,15]. Furthermore, weather data analysis, which offers insights into temperature, precipitation, and relative humidity variations, provides a contextual background for interpreting the experimental results. The optimal growth and productivity observed for buckwheat sown in mid-March at the Belbies site could be attributed to the alignment of critical growth stages with favorable weather conditions, highlighting the temporal dimension of environmental suitability for crop cultivation. In summary, the findings of this study contribute to a deeper understanding of how genetic, environmental, and management factors converge to influence crop growth and productivity.
4.2. Evaluation of the 2-Way Interaction between Biotic and Abiotic Factors on the Productivity of Buckwheat
The differences in buckwheat productivity observed across various experimental conditions, including location, species selection, and sowing time, can be attributed primarily to the complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and agronomic factors. However, the significant impact of the location × species interaction particularly underscores the importance of selecting the appropriate species for specific environmental conditions, as Fagopyrum tataricum exhibited greater productivity in Belbies than in Sadat due to its genetic adaptability to local environmental and soil conditions [5]. Moreover, its inherent genetic traits, such as increased tolerance to local abiotic stresses indicated by soil pH, EC, and soil texture characteristics, further contributed to its superior performance in Belbies. Conversely, Fagopyrum esculentum showed reduced productivity across both locations, indicating its possibly lesser adaptability to the given environmental conditions or its specific genetic makeup, rendering it less efficient under the tested conditions [6,27]. Furthermore, the interaction between location and sowing date highlights the critical role of sowing timing in optimizing buckwheat productivity, with mid-March sowing in Belbies achieving the highest productivity due to the optimal alignment of the sowing date with favorable environmental conditions, such as temperature and humidity, conducive to buckwheat growth. This is supported by weather data analysis, where temperature and precipitation patterns likely favored the mid-March sowing period, resulting in enhanced growth and productivity [12,20]. Additionally, the interaction between species and sowing date provides insights into how genetic factors combined with agronomic practices influence crop outcomes, with Fagopyrum tataricum exhibiting superior performance after mid-March sowing, emphasizing its adaptability to the climatic conditions that prevailed during this period. This adaptability, possibly due to its genetic traits favouring growth under specific environmental conditions experienced in the spring season in Egypt, further accentuates the need for species-specific management practices to optimize productivity. The observed variances in productivity related to sowing time and species selection underscore the complex genotype-by-environment interactions that influence crop performance [8]. Moreover, comprehensive soil and water analyses were conducted at the beginning of each experimental season, and the physical and chemical properties of the soil and irrigation water quality were recorded; these analyses directly impacted plant growth, development, and ultimately productivity. The suitability of the soil and water properties in Belbies for buckwheat cultivation, especially for F. tataricum, may have contributed to the higher productivity observed at this location. Additionally, the methodological approach, including the use of organic manure, phosphorus fertilizer, and nitrogen fertilizer, likely provided an optimal nutrient regime that supported the growth and productivity of buckwheat plants under the tested conditions. The strategic application of fertilizers, based on the specific growth stages of buckwheat, enhances nutrient availability during critical periods of growth and development, contributing to the observed differences in productivity across different sowing times and species. In conclusion, the results of this study elucidate the intricate relationships among genetic, environmental, and management factors in determining crop productivity. The adaptability of Fagopyrum tataricum to the specific conditions in Belbies, especially when sown in mid-March, highlights the potential for optimizing buckwheat cultivation through careful selection of species and sowing times that align with local environmental conditions. These findings contribute to the broader understanding of sustainable agricultural practices that can enhance crop resilience and productivity in the face of changing climatic conditions, providing valuable insights into the development of sustainable agricultural practices that leverage genetic diversity and environmental management to optimize crop productivity [22,25,28].
5. Conclusions
This research highlights critical findings on buckwheat cultivation in Egypt from three interactions: location × species, location × sowing date, and species × sowing date. The study demonstrated that Fagopyrum tataricum significantly outperformed Fagopyrum esculentum, particularly when sown in mid-March. It also showed a significant increase by planting it in the Belbies City site, with productivity reaching up to 859 kg/ha. This underscores the adaptability of this species and the importance of choosing the right sowing dates. Additionally, the interaction between location and sowing date revealed that mid-March sowing in Belbies yielded the highest productivity, emphasizing the impact of environmental conditions on crop growth. The study’s insights into these interactions offer valuable guidance for optimizing buckwheat cultivation in Egypt, contributing to the development of sustainable agricultural practices in arid and semiarid regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M.H. and H.A.A.E.-A.; methodology, M.M.H.; software, N.M.M.; validation, M.M.H., H.A.A.E.-A. and A.M.S.H.; formal analysis, N.M.M.; investigation, A.M.S.H.; resources, H.A.A.E.-A.; data curation, N.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.H.; writing—review and editing, H.A.A.E.-A. and M.M.H.; visualization, N.M.M.; supervision, H.A.A.E.-A.; project administration, H.A.A.E.-A. and N.M.M.; funding acquisition, M.M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded in part by Open Access funding provided by the Qatar National Library (QNL).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author, Hassona, M, M.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barrett, C.B. Overcoming global food security challenges through science and solidarity. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2021, 103, 422–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keler, V.V.; Demeneva, A.A.; Martynova, O.V. Influence of various elements from cultivation technology on the buckwheat yield. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 659, 12061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusa, L.; Gresta, F.; Sperlinga, E.; Ruberto, G. Effect of sowing time and soil water content on grain yield and phenolic profile of four buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench.) varieties in a Mediterranean environment. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 62, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.N.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Yang, H.B. Transcriptome analysis reveals salinity responses in four Tartary buckwheat cultivars. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowmya, S.A.; Vijayakumar, B.; Vishwanath, Y.C.; Ganiger, V.M.; Hegde, L.; Lokesh, M.S. Evaluation of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench.) genotypes under northern dry zone of Karnataka. Pharma Innov. J. 2021, 10, 1974–1979. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; He, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, H.; Gao, B.; Yang, K.; Zhou, M. Resequencing of global Tartary buckwheat accessions reveals multiple domestication events and key loci associated with agronomic traits. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, H.L.S. Methods of Analysis of Soils, Plants, Waters, Fertilisers & Organic Manures; Fertiliser Development and Consultation Organisation: New Delhi, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Calegari, A.; Tiecher, T.; Wutke, E.B.; Canalli, L.D.S.; Bunch, R.; Rheinheimer, D.D.S. The role and management of soil mulch and cover crops in Conservation Agriculture systems. In Advances in Conservation Agriculture; Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2020; pp. 179–248. [Google Scholar]
- Germ, M.; Gaberščik, A. The effect of environmental factors on buckwheat. In Molecular Breeding and Nutritional Aspects of Buckwheat; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Fesenko, N.N.; Glazova, Z.I.; Fesenko, I.N. Cold stress at seedlings stage of buckwheat optimizes development of both roots and aboveground biomass and limits the excessive vegetative growth interfering with seed formation (an analytical review). Acta Agric. Slov. 2020, 116, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassona, M.M.; Hussein, A.S.; Morsy, N.; AAbd El-Aal, H. Chemical, rheological, sensorial and functional properties buckwheat semolina flour composite pasta. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 66, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Macchia, M.; Cerri, D.; Gatta, D.; Arduini, I.; Saccomanni, G. Rutin content in the forage and grain of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) as affected by sowing time and irrigation in a Mediterranean environment. Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, A.; Fallah, S.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Mehdi, B.; Kaul, H.P. Growth analysis and land equivalent ratio of fenugreek-buckwheat intercrops at different fertilizer types. Die Bodenkult. J. Land Manag. Food Environ. 2018, 69, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, H.; Link, W.; Street, K.; Stoddard, F.L. ILB 938, a valuable faba bean (Vicia faba L.) accession. Plant Genet. Resour. 2018, 16, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oomah, B.D.; Mazza, G. Flavonoids and antioxidative activities in buckwheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 1746–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, G.H.; Kim, S.L.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.K.; Park, J.H.; Kim, C.G.; Heu, S. Effect of sowing time on buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) growth and yield in central Korea. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 18, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maletić, R.O.; Jevđović, R. The influence of meteorological conditions on major quantitative and qualitative traits of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). J. Agric. Sci. 2003, 48, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Facho, Z.H.; Khan, F.; Tao, W.; Ali, S. Species divergence and diversity in buckwheat landraces collected from the western himalayan region of pakistan. Pak. J. Bot 2019, 51, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunori, A.; Végvári, G. Rutin content of the grain of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench. and Fagopyrum tataricum Gaertn.) varieties growtn in southern Italy. Acta Agron. Hung. 2007, 55, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larney, F.J.; Blackshaw, R.E. Weed seed viability in composted beef cattle feedlot manure. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1105–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.D.; Ma, Y.J.; Parry, J.; Gao, J.M.; Yu, L.L.; Wang, M. Phenolics content and antioxidant activity of tartary buckwheat from different locations. Molecules 2011, 16, 9850–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JoJohansson, E.; Kuktaite, R.; Labuschagne, M.; Lama, S.; Lan, Y.; Nakimbugwe, D.; Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R.; Tafesse, F.; Tesfaye, K.; Vazquez, D. Adaptation to abiotic stress factors and their effects on cereal and pseudocereal grain quality. In Developing Sustainable and Health Promoting Cereals and Pseudocereals; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 339–358. [Google Scholar]
- Boglaienko, D.; Soti, P.; Shetty, K.G.; Jayachandran, K. Buckwheat as a cover crop in Florida: Mycorrhizal Status and soil analysis. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2014, 38, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidbaigi, R.; Mastro, G.D.E. Influence of sowing time on the biological behaviour, biomass production, and rutin content of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). Ital. J. Agron. 2004, 8, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Björkman, T.; Shail, J.W. Using a buckwheat cover crop for maximum weed suppression after early vegetables. HortTechnology 2013, 23, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snedecor, G.W.; Cochran, W.G. Statistical Methods, 8th ed.; Iowa State University Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bulan, M.T.S.; Stoltenberg, D.E.; Posner, J.L. Buckwheat species as summer cover crops for weed suppression in no-tillage vegetable cropping systems. Weed Sci. 2015, 63, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Masoni, A.; Arduini, I. Forage and grain yield of common buckwheat in Mediterranean conditions: Response to sowing time and irrigation. Crop Pasture Sci. 2016, 67, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).