Effective Biotic Elicitors for Augmentation of Secondary Metabolite Production in Medicinal Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
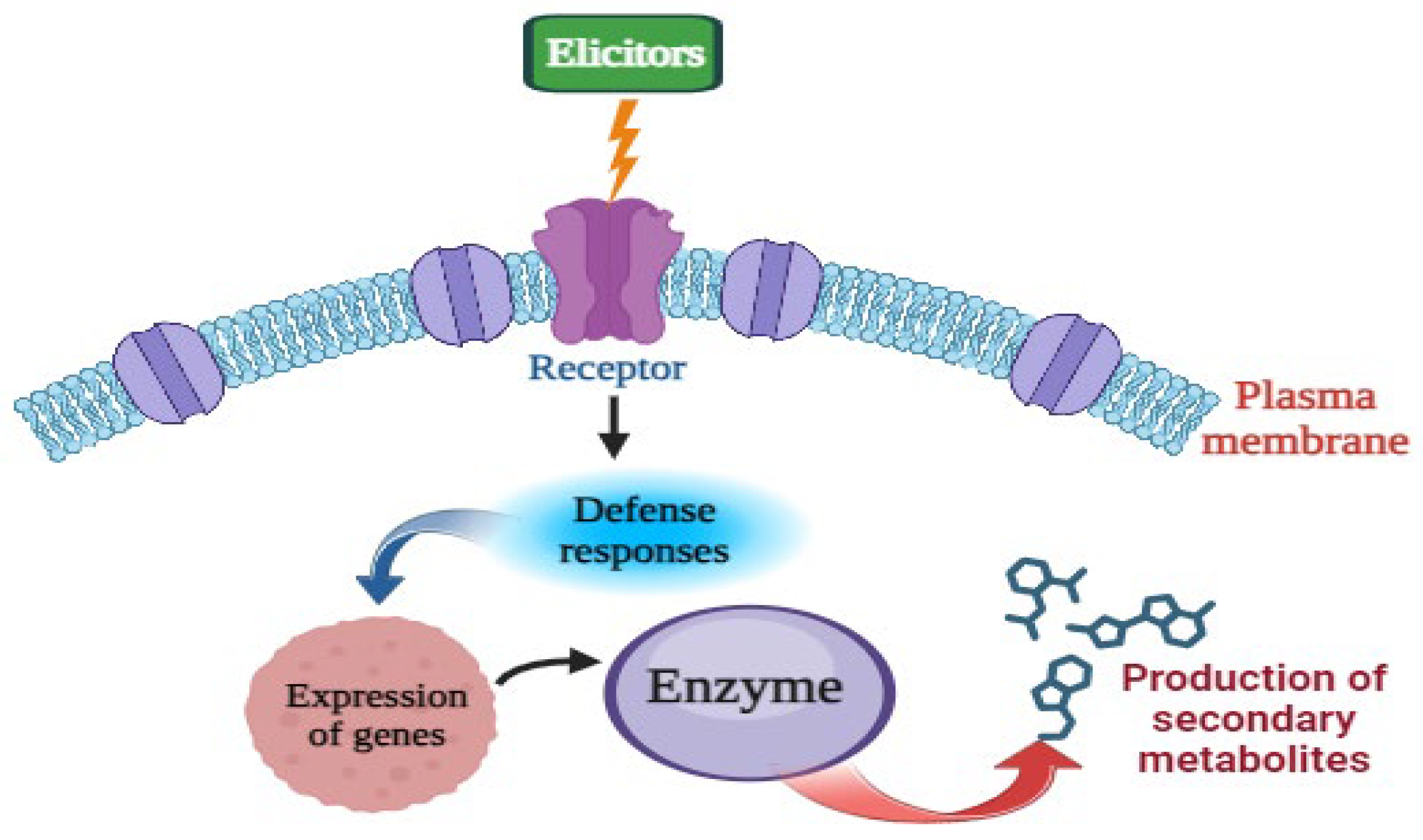
2. Mode of Action of Elicitors
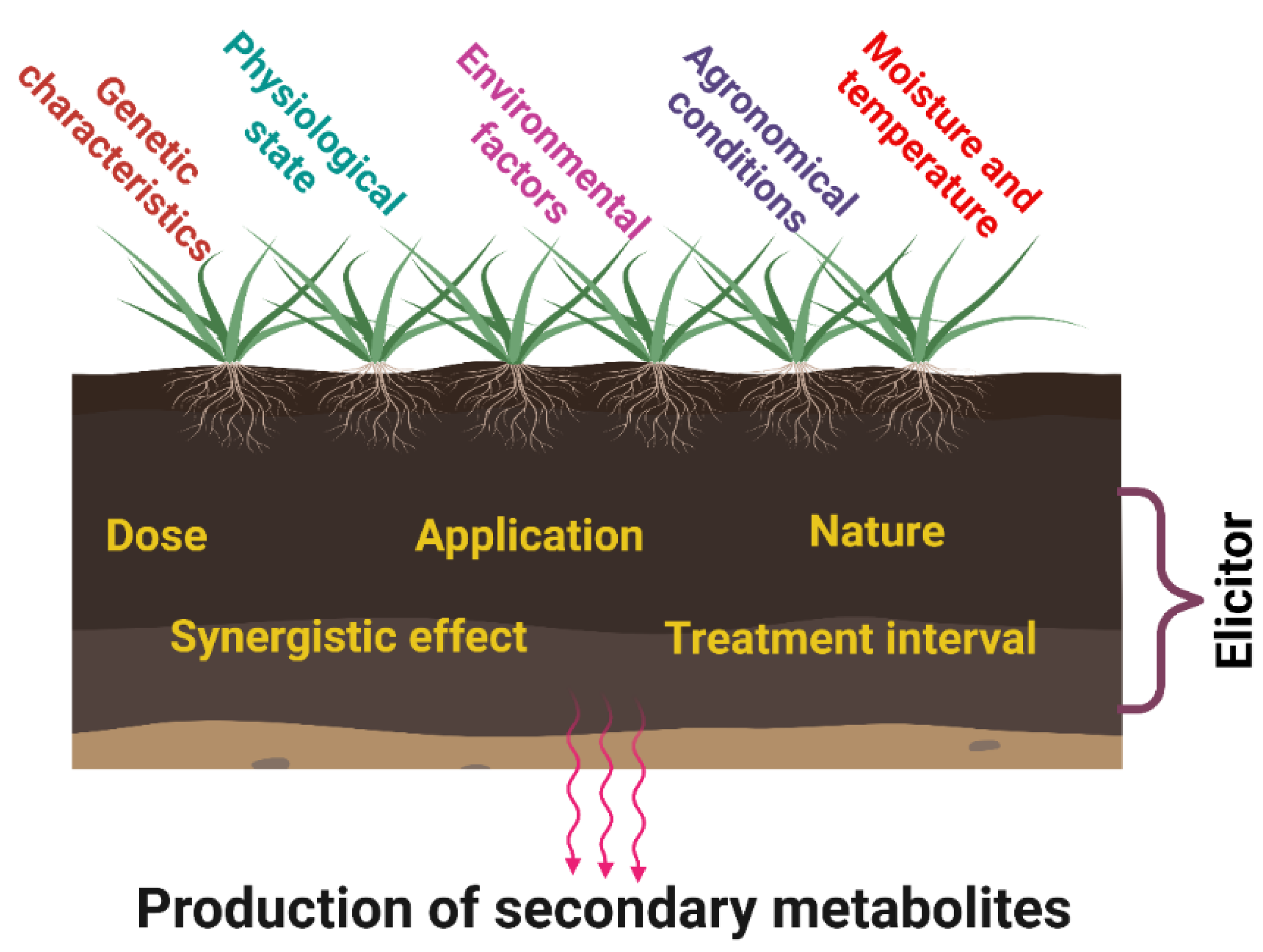
3. Parameters Affecting Elicitors
4. Biotic Elicitors and Their Classification
4.1. Proteins
4.2. Carbohydrates
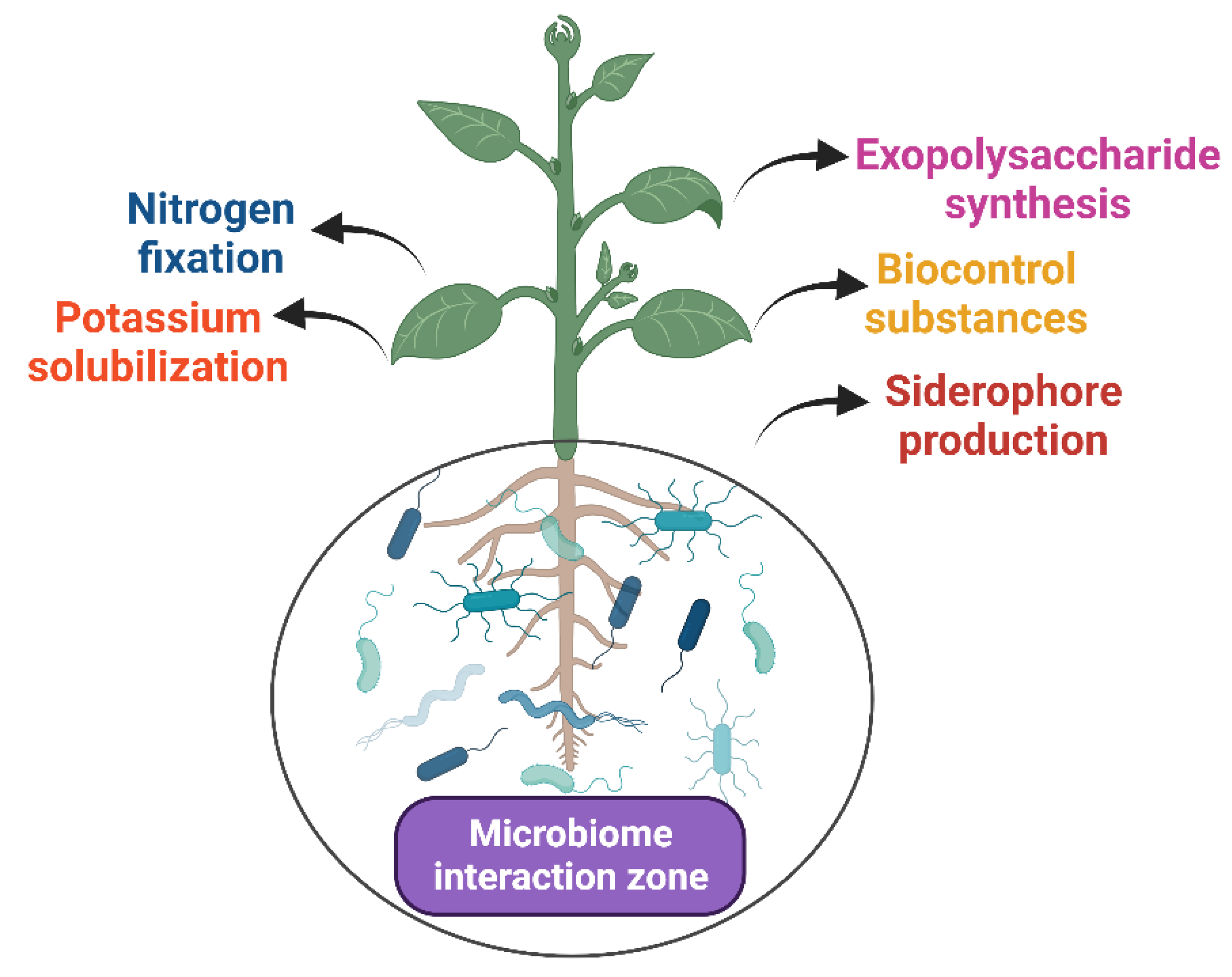
4.3. Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR)
4.4. Parasites
4.5. Virus
4.6. Bacteria
4.7. Fungal Elicitation
| Fungi Elicitor | Plant Species | Secondary Metabolites | Biological Activity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phytophthora megasperma | Soyabeans and capsicum annum | Glyceollin | Antiestrogen effect in breast cancers, anti-vasculogenesis, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, anti-septic, and osteoinductive activity | Akutagawa et al., 2019; Chamkhi et al., 2021 [93,94] |
| Alternaria carthami | Catharanthus Tinctorius L. | Polyacetylenes | Antiproliferative, anti-inflammatory, antifungal antimicrobial, insecticidal, and repellent activity | |
| Alternaria tenuis | Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don | Diosgenin | Anti-diabetic, apoptotic, necrotic, and anti-proliferative, anti-Alzheimer, genotoxic, mutagenic, autoimmune encephalitis activity, and cardiovascular disorders | Banchio et al., 2008; Iman et al., 2016 [54,95] |
| Fungal mycelia | Panax Ginseng C.A. | Anti-tumor and immunomodulating activity | Rokem et al., 1984 [96] | |
| Rhizopus arrhizus | Morinda citrifolia L. | Akutagawa et al., 2019 [93] | ||
| Aspergillus flavus | Zea mays L. | Anthocyanin | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer and anti-allergic activity | Bahadur et al., 2007 [56] |
| Penicillium chrysogenum | Arabidopsis thaliana | Artemisinin | Anti-angiogenic, anti-tumoral, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, osteoprotective, antiviral, antimalarial, antiparasitic, and antifungal activity | Bahadur et al., 2007; Banchio et al., 2008 [54,56] |
| Phytophthora parasitica | Nicotiana tabacum | Coumarin | Antioxidant, antibacterial, antiproliferative, aminudin α-glucosidase inhibitory activity | Akutagawa et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2003 [93,97] |
| Protomyces gravidus | Ambrosia artemisiifolia | Thiarubrine A | Antibiotic, antiviral, and anti-HIV activity | Chen et al., 2003 [97] |
| Rhizoctonia solani | Abrus precatorius L. | Sesquiterpenes | Anti-Alzheimer, anti-influenza A (H1N1), Cytotoxic, allelopathic, and antibacterial activity | Banchio et al., 2008 [54] |
| Pythium aphanidermatum | Nicotiana Tabaccum, Lycopersicon esculentum | p-Hydroxy benzoic acid, rosmarinic acid | Anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, anti-diabetic, antioxidant, anticancer, genotoxic, antimicrobial, hepatoprotective, allelochemical, immunotherapeutic, antifeedant, antibacterial, antifungal, molluscicide activity, and anti-convulsant activity | Bahadur et al., 2007; Banchio et al., 2008; Iman et al., 2016 [54,56,95] |
| Aspergillus niger | Abrus precatorius L., Gymnema sylvestre, Taxuschinensis | |||
| Rhizoctonia solani | Phaseolus vulgaris L. | Sesquiterpenes | Anti-Alzheimer, anti-influenza A (H1N1), Cytotoxic, allelopathic, and antibacterial activity | Banchio et al., 2008 [54] |
| Verticillium alboatrum | Withania somnifera | Phytoalexins | Antimicrobial and anticancer activity | Chamkhi et al., 2021 [94] |
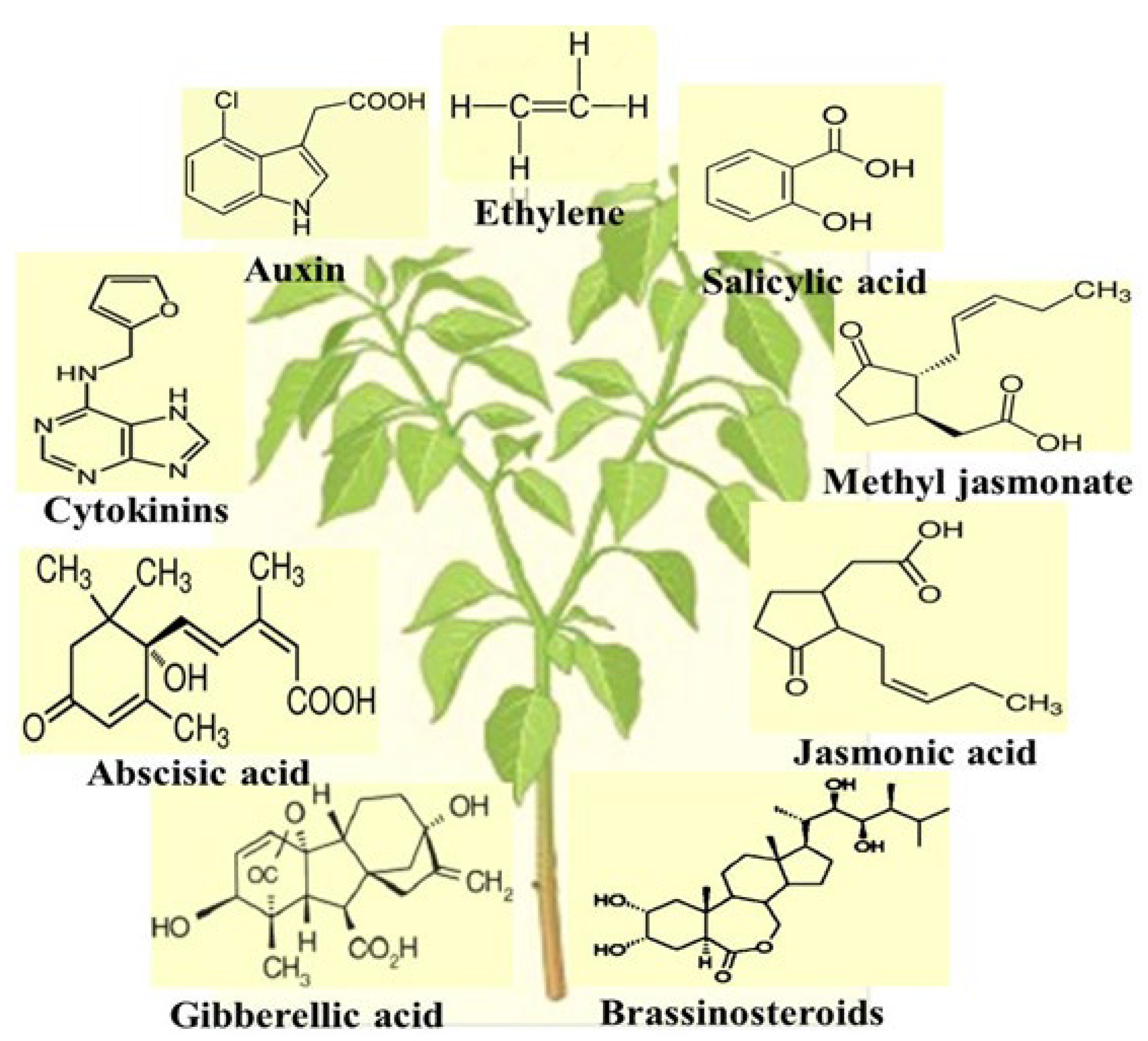
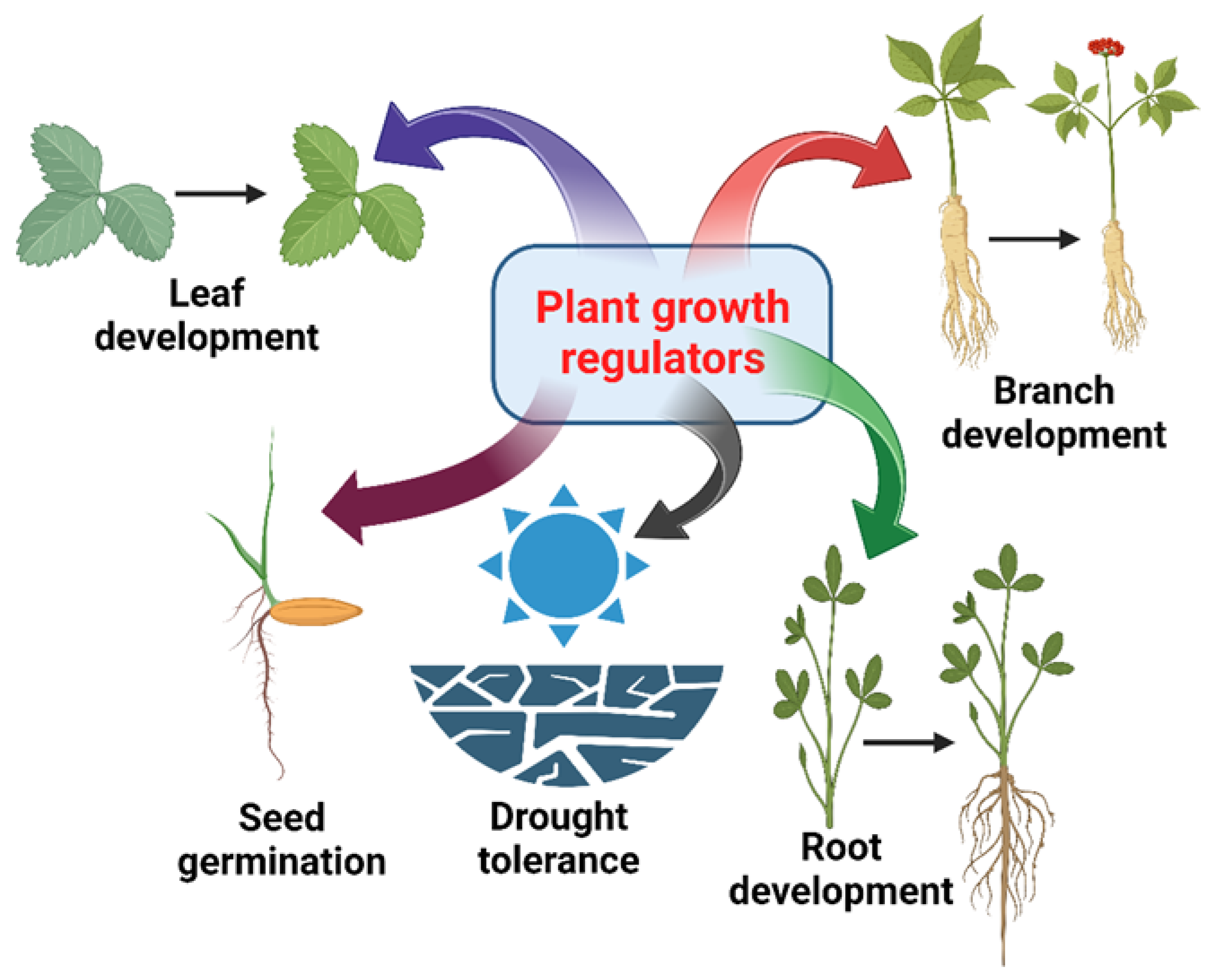
4.8. Plant Growth Regulators
4.8.1. Ethylene
4.8.2. Auxin
4.8.3. Cytokinins
4.8.4. Abscisic Acid
4.8.5. Gibberellic Acid
4.8.6. Brassinosteroids
| Plant Species | Compounds | References |
|---|---|---|
| Gibberellic acid | ||
| Salvia miltiorrhiza | Tanshinones | Yuan et al., 2018 [143] |
| Echinacea pupurea | Caffeic acid derivatives | Abbasi, 2012 [144] |
| Caftaric and cichoric acid | Jones et al., 2009 [145] | |
| Artemisia annua | Artemisinin | Banyai et al., 2011 [146] |
| Brassinosteroids | ||
| Aegle marmelos | 24-Epibrassinolide | Sondhi et al., 2008 [147] |
| Brassica napus | Nolan et al., 2020 [148] | |
| Helianthus annuus | Filová et al., 2013 [149] | |
| Pisum sativum | Fedina et al., 2017 [150] | |
| Raphanus sativus | Chaudhary et al., 2012 [151] | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | GSK-3/Shaggy, BKI1 | Rozhon et al., 2014 [152] |
| Brassica campestris | 24-Epibrassinolide, brassinolide | Ferrie et al., 2005 [153] |
| Solanum lycopersicum | 28-Homobrassinolide, 24-epibrassinolide | Hayat et al., 2012 [154] |
| Cupressus arizonica | Teasterone, 28-homocastasterone, 3-dehydroteasterone, brassinolide, and dolichosterone | Griffiths et al., 1995 [155] |
| Equisetum arvense | Brassinolide, 24-epibrassinolide, and 28- homobrassinolide | Vardhini et al., 2006 [156] |
| Thea sinensis | Brassinolide, castasterone, 28-norbrassinolide, brassinone, 24-ethylbrassinone, and dolichosterone | Ikekawa et al., 1984 [157] |
| Citrus sinensis | Castasterone | Motegi et al., 1994 [158] |
| Zea mays | 28-Norbrassinolide, 28-norcastasterone, 28-homocastasterone, and 28-homodolichosterone | Tumova et al., 2018 [159] |
| Lilium elegans | Brassinolide, castasterone, typhasterol, and teasterone | Suzuki et al., 1994 [160] |
4.8.7. Jasmonic Acid (JA)
| Plant Species | Compounds | References |
|---|---|---|
| Celastrus paniculatus | Phenolics | Anusha et al., 2016 [166] |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | Soyasaponin | Hayashi et al., 2003 [167] |
| Hypericum perforatum | Phenyl propanoids | Gadzovska et al., 2007 [168] |
| Mentha piperita | Rosmarinic acid | Krzyzanowska et al., 2012; Almagro et al., 2014 [162,169] |
| Psoralea corylifolia L. | Psoralen | Siva et al., 2015 [170] |
| Vitis rotundifolia | Stilbene | Nopo-olazabal et al., 2014 [171] |
| Vitis vinifera | Anthocyanin, stilbene, trans-resveratrol | Curtin et al., 2003; Xu et al., 2015 [172,173] |
| Plumbago indica | Plumbagin | Gangopadhyay, 2011 [174] |
| Plumbago rosea | Silja, 2014 [175] |
4.8.8. Methyl Jasmonate
4.8.9. Salicylic Acid (SA)
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samtiya, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Dhewa, T.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M. Potential Health Benefits of Plant Food-Derived Bioactive Components: An Overview. Foods 2021, 10, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, N.; Jain, D.; Janmeda, P.; Mitra, D. Role of Medicinal plants in Pharmaceutical Sector: An Overview. Glob. J. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2021, 10, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, D.; Janmeda, P. Pharmacognostic standardization and qualitative analysis of Gymnosporia senegalensis. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 3, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, A.; Ravishankar, G.A. Influence of abiotic stress signals on secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Signal Behav. 2011, 6, 1720–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A. Natural products and plant disease resistance. Nature 2001, 411, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksman-Caldentey, K.M.; Inzé, D. Plant cell factories in the post-genomic era: New ways to produce designer secondary metabolites. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, P.M.; Al-Khayri, J.M. Abiotic and biotic elicitors-role in secondary metabolites production through in vitro culture of medicinal plants. In Abiotic and Biotic Stress in Plants-Recent Advances and Future Perspectives; In Tech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2016; pp. 247–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.A.; Balick, M.J. The Ethnobotanical Approach to Drug Discovery. Sci. Am. 1994, 270, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, N.R.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolic changes of salicylic acid-elicited Catharanthus roseus cell suspension cultures monitored by NMR-based metabolomics. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawauchi, M.; Toshi-Hide, A.; Masanori, K. Molecular cloning and transcriptional analysis of WRKY and solavetivone biosynthetic genes in the hairy roots of Hyoscyamus albus. Plant Gene 2016, 5, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Sandhu, K.S.; Kamal, R.; Kaur, K.; Singh, J.; Röder, M.S.; Muqaddasi, Q.H. Omics for the Improvement of Abiotic, Biotic, and Agronomic Traits in Major Cereal Crops: Applications, Challenges, and Prospects. Plants 2021, 23, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnenburg, H.; Knorr, D. Strategies for the improvement of secondary metabolite production in plant cell cultures. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1995, 17, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdeo, A.G. Plant cell elicitation for production of secondary metabolites: A review. Pharmacog. Rev. 2007, 1, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Montesano, M.; Brader, G.; Palva, E.T. Pathogen derived elicitors: Searching for receptors in plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2003, 4, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Brugger, A.; Lamotte, O.; Vandelle, E.; Bourque, S.; Lecourieux, D.; Poinssot, B.; Wendehenne, D.; Pugin, A. Early signaling events induced by elicitors of plant defenses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S. Biological elicitors of plant secondary metabolites: Mode of action and use in the production of nutraceutics. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 698, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdeo, A.G. Investigation on Pilot Scale Bioreactor with Reference to the Synthesis of Bioactive Compounds from Cell Suspension Cultures of Catharanthus roseus Linn. Ph.D. Thesis, Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore, India, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, D.; Chaudhary, P.; Tripathi, R.; Janmeda, P. The impact of various environmental factors on secondary metabolites in plants. In The Life of Plants in a Changing Environment; Cambridge Scholars Publishing: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2021; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Vásquez, R.; Day, R.; Buschmann, H.; Randles, S.; Beeching, J.R.; Cooper, R.M. Phenylpropanoids, phenylalanine ammonia lyase and peroxidases in elicitor-challenged cassava (Manihot esculenta) suspension cells and leaves. Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamiołkowska, A. Natural Compounds as Elicitors of Plant Resistance against Diseases and New Biocontrol Strategies. Agronomy 2020, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Kastell, A.; Speiser, C.; Smetanska, I. Enhanced resveratrol production in Vitis vinifera cell suspension cultures by heavy metals without loss of cell viability. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.; Krishnamurthy, R. Elicitors in plant tissue culture. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2013, 2, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall, D.R.; Whitehead, I.M. The use of biotic and abiotic elicitors to induce the formation of secondary plant products in cell suspension cultures of Solanaceous plants. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1988, 16, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alami, I.; Mari, S.; Clérivet, A. A glycoprotein from Ceratocystis fimbriata f. sp.platani triggers phytoalexin synthesis in Platanus × acerifolia cell-suspension cultures. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färber, K.; Schumann, B.; Miersch, O.; Roos, W. Selective desensitization of jasmonate- and pH-dependent signaling in the induction of benzophenanthridine biosynthesis in cells of Eschscholzia californica. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.K.; McNeil, M.; Albersheim, P. The primary structures of one elicitoractive and seven elicitor-inactive hexa (beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-D-glucitols isolated from the mycelial walls of Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glycinea. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 11321–11336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Yoshikawa, N.; Tabata, M. Induction of shikonin formation by agar in Lithospermum erythrorhizon cell suspension cultures. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 2451–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Neill, S.; Cai, W.; Tang, Z. Hydrogen peroxide and jasmonic acid mediate oligo- galacturonic acid induced saponin accumulation in suspension–cultured cells of Panax ginseng. Physiol. Plant. 2003, 118, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaraiah, P.; Ramakrishna, S.V.; Reddanna, P.; Kavi Kishor, P.B. Enhanced production of plumbagin in immobilized cells of Plumbago rosea by elicitation and in situ adsorption. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 101, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlita, A.; Sidwa-Gorycka, M.; Paszkiewicz, M.; Malinski, E.; Kumirska, J.; Siedlecka, E.M.; Łojkowska, E.; Stepnowski, P. Application of chitin and chitosan as elicitors of coumarins and fluoroquinolone alkaloids in Ruta graveolens L. (common rue). Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2008, 51, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taurino, M.; Ingrosso, I.; D’amico, L.; De Domenico, S.; Nicoletti, I.; Corradini, D.; Santino, A.; Giovinazzo, G. Jasmonates elicit different sets of stilbenes in Vitis vinifera cv. Negramaro cell cultures. Springer Plus 2015, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, Y.; Bengi, E. Effects of sucrose and polyethylene glycol on hypericins content in Hypericum adenotrichum. Eurasia J. Biosci. 2013, 7, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Brodelius, P.; Funk, C.; Häner, A.; Villegas, M. A procedure for the determination of optimal chitosan concentrations for elicitation of cultured plant cells. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 2651–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radman, R.; Saez, T.; Bucke, C.; Keshavarz, T. Elicitation of plants and microbial cell systems. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2003, 37, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyabama, M.; Bernstein, N.; Anusuya, S. Chitosan elicitation for increased curcumin production and stimulation of defence response in turmeric (Curcuma longa L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 89, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, J.; Rosenberg, R.; Smotrich, A.; Hanuš, L.; Bernstein, N. Hypoglycemic activity of withanolides and elicited Withania somnifera. Phytochemistry 2015, 116, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.M.; Manohar, S.H.; Praveen, N.; Murthy, H.N. Effects of sucrose and pH levels on in vitro shoot regeneration from leaf explants of Bacopa monnieri and accumulation of bacoside A in regenerated shoots. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2010, 100, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.L.R.; Oliveira, C.F.R.; Oliveira, C.T. Insecticidal Activity of Plant Lectins and Potential Application in Crop Protection. Molecules 2015, 20, 2014–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet, J.C.; Nespoulous, C.; Pernollet, J.C. Structures of elicitin isoforms secreted by Phytophthora drechsleri. Phytochemistry 1992, 31, 1471–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Frachisse, J.M.; Thomine, S.; Barbier-Brygoo, H.; Guern, J. Elicitor-induced chloride efflux and anion channels in tobacco cell suspensions. Int. J. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 1998, 36, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Dong, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, L.; Jing, M.; Dou, D. Type 2 Nep1-Like Proteins from the Biocontrol Oomycete Pythium oligandrum Suppress Phytophthora capsici Infection in Solanaceous Plants. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, N.; Minami, E. Oligosaccharide signaling for defence responses in plant. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2001, 59, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, J.; Grisebach, H.; Bonhoff, A.; Grab, D.; Hoffmann, C.; Kochs, G.; Mieth, H.; Schmidt, W.; Stäb, M. Phytoalexin synthesis in soybean following infection of roots with Phytophthora megasperma or treatment of cell cultures with fungal elicitor. In Recognition in Microbe-Plant Symbiotic and Pathogenic Interactions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; Volume 4, pp. 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.N.; Jha, D.K. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): Emergence in agriculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 1327–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Andelkovic, S.; Panneerselvam, P.; Manisha; Senapati, A.; Vasić, T.; Ganeshamurthy, A.N.; Devvret, V.; Poonam; Radha, T.K.; et al. Plant growth promoting microorganisms (PGPMs) helping in sustainable agriculture: Current perspective. Int. J. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. 2019, 7, 50–74. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Viveros, O.; Jorquera, M.A.; Crowley, D.E.; Gajardo, G.; Mora, M.L. Mechanisms and practical considerations involved in plant growth promotion by rhizobacteria. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2010, 10, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousar, B.; Bano, A.; Khan, N. PGPR Modulation of Secondary Metabolites in Tomato Infested with Spodoptera litura. Agronomy 2020, 10, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Bélanger, R.R.; Benhamou, N.; Paulitz, T.C. Defense enzymes induced in cucumber roots by treatment with plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and Pythioum aphanidermatum. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2000, 56, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Mondal, R.; Jain, D.; Vasić, T.; Sharma, K.; Khoshru, B.; Panneerselvam, P.; Ganeshamurthy, A.N.; Mon, M.E.; Mahakur, B.; et al. Influence of arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on plant growth promotion and nutrient managnment. In Research Advancements and Beneficial Effects of Plant Growth Promoting Microorganism in Agriculture; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrucken, Germany, 2019; pp. 41–57. [Google Scholar]
- Jaleel, C.A.; Gopi, R.; Gomathinayagam, M.; Panneerselvam, R. Traditional and nontraditional plant growth regulators alter phytochemical constituents in Catharanthus roseus. Process Biochem. 2009, 44, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaleel, C.A.; Manivannan, P.; Sankar, B.; Kishorekumar, A.; Gopi, R.; Somasundaram, R.; Panneerselvam, R. Pseudomonas fluorescens enhances biomass yield and ajmalicine production in Catharanthus roseus under water deficit stress. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 60, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namdeo, A.G.; Patil, S.; Fulzele, D.P. Influence of fungal elicitors on production of ajmalicine by cell cultures of Catharanthus roseus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbanpour, M.; Hatami, M.; Khavazi, K. Role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on antioxidant enzyme activities and tropane alkaloid production of Hyoscyamus niger under water deficit stress. Turk. J. Biol. 2013, 37, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchio, E.; Bogino, P.C.; Zygadlo, J.; Giordano, W. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria improve growth and essential oil yield in Origanum majorana L. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2008, 36, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchio, E.; Xie, X.; Zhang, H.; Paré, P.W. Soil bacteria elevate essential oil accumulation and emissions in sweet basil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, A.; Singh, U.P.; Sarma, B.K.; Singh, D.P.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, A. Foliar application of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria increases antifungal compounds in pea (Pisum sativum) against Erysiphe pisi. Mycobiology 2007, 35, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, L.; Wu, J. Promotion of Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root growth and tanshinone production by polysaccharide-protein fractions of plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Bacillus cereus. Process. Biochem. 2010, 45, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanpour, M.; Hatami, M. Biopriming of Salvia officinalis Seed with Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Affects Invigoration and Germination Indices. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 8, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hemashenpagam, N.; Selvaraj, T. Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungus and plant growth promoting rhizo microorganisms (PGPR’s) on medicinal plant Solanum viarum seedlings. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vafadar, F.; Amooaghaie, R.; Otroshy, M. Effects of plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on plant growth, stevioside, NPK, and chlorophyll content of Stevia rebaudiana. J. Plant Interact. 2014, 9, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellari, L.D.R.; Santoro, M.V.; Nievas, F.; Giordano, W.; Banchio, E. Increase of secondary metabolite content in marigold by inoculation with plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2013, 70, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Malik, N.A.; Kumar, I.S.; Nadarajah, K. Elicitor and Receptor Molecules: Orchestrators of Plant Defense and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Han, X.; Feng, D.; Yuan, D.; Huang, L.-J. Signaling Crosstalk between Salicylic Acid and Ethylene/Jasmonate in Plant Defense: Do We Understand What They Are Whispering? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Gui, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Guo, J.; Niu, D. Induced Systemic Resistance for Improving Plant Immunity by Beneficial Microbes. Plants 2022, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Sohal, B.S. Role of elicitors in inducing resistance in plants against pathogen infection: A review. ISRN Biochem. 2013, 2013, 762412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, A.; Raytekar, N.A.; Meena, M.; Swapnil, P. Current research in microbial sciences efficiency of microbial bio-agents as elicitors in plant defense mechanism under biotic stress: A review. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2021, 2, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, M.; Ma, H.; Li, H.; Guo, B.; Zhang, X.; Ye, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y. Differential regulation of defense-related proteins in soybean during compatible and incompatible interactions between Phytophthora sojae and soybean by comparative proteomic analysis. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 1263–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alazem, M.; Lin, N.S. Roles of plant hormones in the regulation of host-virus interactions. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boya, P.; Codogno, P.; Rodriguez-Muela, N. Autophagy in stem cells: Repair, remodelling and metabolic reprogramming. Development 2018, 145, dev146506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, T.; Pandey, S.S.; Maji, D.; Gupta, V.; Kalra, A.; Singh, M.; Mathur, A.; Mathur, A.K. Enhanced expression of ginsenoside biosynthetic genes and in vitro ginsenoside production in elicited Panax sikkimensis (Ban) cell suspensions. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, R.; Xavier, L.S.E.; Udayakumaran, G.; Kumar, D.S.; Venkatesh, R.; Nagella, P. Biotic elicitors: A boon for the in-vitro production of plant secondary metabolites. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2022, 149, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayani, M.; Srivastava, S. Elicitation: A stimulation of stress in in vitro plant cell/tissue cultures for enhancement of secondary metabolite production. Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 1227–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsa, P.; Chiltz, A.; Luini, E.; Vandelle, E.; Pugin, A.; Roblin, G. Cytosolic calcium rises and related events in ergosterol-treated nicotiana cells. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 49, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Monaim, M.F.; Ismail, M.E.; Morsy, K.M. Induction of systemic resistance of benzothiadiazole and humic acid in soybean plants against fusarium wilt disease. Mycobiology 2011, 39, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, W.; Chen, F.; Mao, B.L.Q.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Z.; He, Z. N-Acetylchito oligosaccharides elicit rice defence responses including hypersensitive response-like cell death, oxidative burst and defence gene expression. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2004, 64, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, E.; Kuchitsu, K.; He, D.Y.; Kouchi, H.; Midoh, H.; Ohtsuki, Y.; Shibuya, N. Two novel genes rapidly and transiently activated in suspension-cultured rice cells by treatment with N-actylchitoheptaose, a biotic elicitor for phytoalexin production. Plant Cell Physiol. 1996, 37, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanabria, N.M.; Huang, J.C.; Dubery, I.A. Self/non-self perception in plants in innate immunity and defense. Self/Nonself 2010, 1, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander, P.; Vårum, K.M.; Domard, A.; Eddine, N.; Moerschbacher, B.M.; Moerschbacher, B.M. Comparison of the ability of partially N-acetylated chitosans and chito oligosaccharides to elicit resistance reactions in wheat leaves. Plant Physiol. 1998, 118, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, R.B.; Okada, M.; Ito, Y.; Tsukada, K.; Zaghouani, H.; Shibuya, N.; Stacey, G. Binding site for chitin oligosaccharides in the soybean plasma membrane. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhegger, R.; Ihring, A.; Gantner, S.; Bahnweg, G.; Knappe, C.; Vogg, G.; Hutzler, P.; Schmid, M.; Van Breusegem, F.; Eberl, L.; et al. Serratia Mg, and pseudomonas Isof. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagyaraj, D.J. Mycorrhiza. In Biological Interactions with VAM Fungi; Powell, C.L., Bagyaraj, D.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984; pp. 131–153. [Google Scholar]
- Pusztahelyi, T.; Holb, I.J.; Pócsi, I. Secondary metabolites in fungus-plant interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ola, A.R.B.; Metboki, G.; Lay, C.S.; Sugi, Y.; Rozari, P.; Darmakusuma, D.; Hakim, E.H. Single Production of Kojic Acid by Aspergillus flavus and the Revision of Flufuran. Molecules 2019, 24, 4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, T.; Ravishanakar, G.A.; Reddy, B.O. Production of thiophenes from callus cultures of Tagetes patula L. and its mosquito larvicidal activity. Indian. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 41, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Stimulation of methanol production in Mentha piperita cell culture. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2008, 44, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, C.S.; Murugesh, S.; Srinivasan, V.M. Gymnemic acid production in suspension calli culture of Gymnema sylvestre. J. Appl. Sci. 2006, 6, 2263–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karwasara, V.S.; Tomar, P.; Dixit, V.K. Influence of fungal elicitation on glycyrrhizin production in transformed cell cultures of Abrus precatorius Linn. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2011, 7, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranya, S.P.; Velayutham, K.C.; Preethi, B. Rapid and mass multiplication of Oldenlandia umbellata L. from the leaf explants through callus culture. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 3779–3783. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, D.; Djebaili, R.; Pellegrini, M.; Mahakur, B.; Sarker, A.; Chaudhary, P.; Khoshru, B.; Gallo, M.D.; Kitouni, M.; Barik, D.P.; et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis: Plant growth improvement and induction of resistance under stressful conditions. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 44, 1993–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Mathur, A.; Kalra, A.; Gupta, M.M.; Lal, R.K.; Mathur, A.K. Fungal elicitor-mediated enhancement in growth and asiaticoside content of Centella asiatica L. shoot cultures. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 69, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Téllez, V.I.; Cruz-Olmedo, A.K.; Plasencia, J.; Gavilanes-Ruíz, M.; Arce-Cervantes, O.; Hernández-León, S.; Saucedo-García, M. The Protective Effect of Trichoderma asperellum on Tomato Plants against Fusarium oxysporum and Botrytis cinerea Diseases Involves Inhibition of reactive oxygen species Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Moieni, A.; Safaie, N.; Farhadi, S. Elicitors derived from endophytic fungi Chaetomium globosum and Paraconiothyrium brasiliense enhance pacilitaxel production in Corylus avellana cell suspension culture. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 36, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutagawa, K.; Fujita, T.; Ouhara, K.; Takemura, T.; Tari, M. International immunopharmacology glycyrrhizic acid suppresses in FL Ammation and reduces the increased glucose levels induced by the combination of Porphyromonas gulae and ligature placement in diabetic model mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 68, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamkhi, I.; Benali, T.; Aanniz, T.; El, M.N.; Guaouguaou, F.E.; El, O.N.; El-Shazly, M.; Zengin, G.; Bouyahya, A. Plant-microbial interaction: The mechanism and the application of microbial elicitor induced secondary metabolites biosynthesis in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 167, 269–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman, N.A.; Ahmad, F.; Taher, M. Phytochemistry letters Incrassamarin A-D: Four new 4-substituted coumarins from Calophyllum incrassatum and Their biological activities. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 16, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokem, J.S.; Schwarzberg, J.; Goldberg, I. Autoclaved fungal mycelia increase diosgenin production in cell suspension cultures of Dioscorea deltoidea. Plant Cell Rep. 1984, 3, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.H.; Zhou, H.J.Z.; Fang, X. Inhibition of human cancer cell line growth and human umbilical vein endothelial cell angiogenesis by artemisinin derivatives in vitro. Pharmacol. Res. 2003, 48, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Brouard, E.; Hilbert, G.; Renaud, C.; Petit, J.P.; Edwards, E.; Betts, A.; Delrot, S.; Ollat, N.; Guillaumie, S.; et al. Differential response of the accumulation of primary and secondary metabolites to leaf-to-fruit ratio and exogenous abscisic acid. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2021, 27, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Sun, P.; Wu, L.; Zheng, H. Progress of ethylene action mechanism and its application on plant type formation in crops. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekgaarden, C.; Caarls, L.; Vos, I.A.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; Van Wees, S.C.M. Ethylene: Traffic controller on hormonal crossroads to defense. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, N.; Khan, N.A.; Ferrante, A.; Trivellini, A.; Francini, A.; Khan, M.I.R. Ethylene role in plant growth, development and senescence: Interaction with other phytohormones. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 235913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazar, R.; Khan, M.I.; Iqbal, N.; Masood, A.; Khan, N.A. Involvement of ethylene in reversal of salt-inhibited photosynthesis by sulfur in mustard. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSteen, P.; Zhao, Y. Plant hormones and signaling: Common themes and new developments. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, J.B.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L. The effect of exogenous ethylene and methyl jasmonate on pal activity, phenolic profiles and antioxidant capacity of carrots (Daucus carota) under different wounding intensities. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2009, 51, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, S.W.; Chen, G.H.; Chen, C.T.; Tzen, J.T.C.; Yang, C.Y. Ethylene signaling modulates contents of catechin and ability of antioxidant in Camellia sinensis. Bot. Stud. 2018, 59, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Xu, T.; Cui, B.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yang, D. Effects of abscisic acid, gibberellin, ethylene and their interactions on production of phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zu, Y.G.; Efferth, T.; Tang, Z.H. The combined effects of ethylene and MeJA on metabolic profiling of phenolic compounds in Catharanthus roseus revealed by metabolomics analysis. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xu, L.; Gao, S.; Lyu, X.; Cao, X.; Yao, Y. Melatonin alters the secondary metabolite profile of grape berry skin by promoting VvMYB14-mediated ethylene biosynthesis. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharudin, N.F.; Osman, N.I. Plant development, stress responses, and secondary metabolism under ethylene regulation. Plant Stress 2023, 7, 100146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-García, D.; Nair, V.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Jacobo-Velázquez, D.A. Plants as biofactories: Postharvest stress-induced accumulation of phenolic compounds and glucosinolates in broccoli subjected to wounding stress and exogenous phytohormones. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 171378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninkuu, V.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Fu, Z.; Yang, T.; Zeng, H. Biochemistry of terpenes and recent advances in plant protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taya, M.; Mine, K.; Kino-Oka, M.; Tone, S.; Ichi, T. Production and release of pigments by culture of transformed hairy root of red beet. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1992, 73, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, P.R.H.; van der Heijden, R.; Verpoorte, R. Effect of terpenoid precursor feeding and elicitation on formation of indole alkaloids in cell suspension cultures of Catharanthus roseus. Plant Cell Rep. 1993, 12, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çakmakç, R.; Mosber, G.; Milton, A.H.; Alatürk, F.; Ali, B. The effect of auxin and auxin-producing bacteria on the growth, essential oil yield, and composition in medicinal and aromatic plants. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.D.; Sato, A.; Salgueiro Lage, C.L.S.; Aguiar, D.S.S.G.R.; De Almeida, A.D.; Esquibel, M.A. Essential oil composition of Melissa officinalis L. in vitro produced under the influence of growth regulators. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2005, 16, 1387–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Puri, S. Plant growth regulator mediated consequences of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2018, 9, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.S.; Khattak, A.M.; Basit, A.; Alam, M.; Shah, S.T.; Ahmad, N.; Gilani, S.A.Q.; Ullah, I.; Anwar, S.; Mohamed, H.I. Callus induction, proliferation, enhanced secondary metabolites production and antioxidants activity of Salvia moorcroftiana L. as influenced by combinations of auxin, cytokinin and melatonin. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2022, 65, e22210200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Yong, J.W.H.; Tan, S.N.; Yang, X.H.; Ong, E.S. Analysis of cytokinin nucleotides in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) water using capillary zone electrophoresis-tandem mass spectrometry after solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1133, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vylíčilová, H.; Bryksová, M.; Matušková, V.; Doležal, K.; Plíhalová, L.; Strnad, M. Naturally occurring and artificial N9-cytokinin conjugates: From synthesis to biological activity and back. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babosha, A.V.; Ryabchenko, A.S.; Avetisyan, T.V. Effect of exogenous cytokinins on dynamics of development and differentiation of infectious structures of the pathogen of wheat powdery mildew. Cell Tissue Biol. 2009, 3, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, A.; Fukushima, S.; Okada, K.; Jiang, C.J.; Yoshida, R.; Nakayama, A.; Shimono, M.; Sugano, S.; Yamane, H.; Takatsuji, H. WRKY45-dependent priming of diterpenoid phytoalexin biosynthesis in rice and the role of cytokinin in triggering the reaction. Plant Mol. Biol. 2014, 86, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrandino, A.; Lovisolo, C. Abiotic stress effects on grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.): Focus on abscisic acid-mediated consequences on secondary metabolism and berry quality. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 103, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Villagra, J.; Rodrigues-Salvador, A.; Nunes-Nesi, A.; Cohen, J.D.; Reyes-Díaz, M.M. Age-related mechanism and its relationship with secondary metabolism and abscisic acid in Aristotelia chilensis Plants subjected to drought stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.Y.; Sun, W.J.; Jiang, R.; Chen, J.F.; Ying, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.S. Phytohormones jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, gibberellins, and abscisic acid are key mediators of plant secondary metabolites. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 7, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Khosla, P.K.; Puri, S. Improving production of plant secondary metabolites through biotic and abiotic elicitation. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2019, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.H.; Jaafar, H.Z. Abscisic acid induced changes in production of primary and secondary metabolites, photosynthetic capacity, antioxidant capability, antioxidant enzymes and lipoxygenase inhibitory activity of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth. Molecules 2013, 18, 7957–7976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Yang, B.; Ren, C.G.; Wang, H.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Dai, C.C. Involvement of abscisic acid and salicylic acid in signal cascade regulating bacterial endophyte-induced volatile oil biosynthesis in plantlets of Atractylodes lancea. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 153, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreher, K.; Callis, J. Ubiquitin, hormones and biotic stress in plants. Ann. Bot. 2007, 99, 787–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciorek, T.; Friml, J. Auxin signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 1199–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parray, J.A.; Jan, S.; Kamili, A.N.; Qadri, R.A.; Egamberdieva, D.; Ahmad, P. Current perspectives on plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 35, 877–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomster, T.; Salojärvi, J.; Sipari, N.; Brosché, M.; Ahlfors, R.; Keinänen, M.; Overmyer, K.; Kangasjärvi, J. Apoplastic reactive oxygen species transiently decrease auxin signaling and cause stress-induced morphogenic response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 157, 1866–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, A.; Bertoletti, C. Urea derivatives on the move: Cytokinin-like activity and adventitious rooting enhancement depend on chemical structure. Plant Biol. 2009, 11, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chauhan, N.S.; Singh, M.; Idris, A.; Madanala, R.; Pande, V.; Mohanty, C.S. Establishment of an efficient and rapid method of multiple shoot regeneration and a comparative phenolics profile in in vitro and greenhouse-grown plants of Psophocarpus tetragonolobus (L.) DC. Plant Signal Behav. 2014, 9, e970443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharath, P.P.; Shashibhushan, G.; Agepati, S.R. Abscisic Acid-Induced Stomatal Closure: An Important Component of Plant Defense against Abiotic and Biotic Stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 615114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, F.; Hong, Y.; Yao, J.; Ren, Z.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J.K. The flowering repressor SVP confers drought resistance in Arabidopsis by regulating abscisic acid catabolism. Mol. Plant. 2018, 11, 1184–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Gao, J.; Zhu, X.; Song, Y.; Li, Z.; Ren, G.; Zhou, X.; Kuai, B. ABF2, ABF3, and ABF4 promote ABA-mediated chlorophyll degradation and leaf senescence by transcriptional activation of chlorophyll catabolic genes and senescence-associated genes in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 1272–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chan, Z.; Gao, J.; Xing, L.; Cao, M.; Yu, C.; Hu, Y.; You, J.; Shi, H.; Zhu, Y.; et al. ABA receptor PYL9 promotes drought resistance and leaf senescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1949–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedden, P. The Current Status of Research on Gibberellin Biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 1832–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Cui, H.; Zhang, J.; Kang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Yi, F.; Yang, Q.; Long, R. Gibberellins Inhibit Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Promote Nitrogen Metabolism in Medicago truncatula. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, S. Gibberellin metabolism and its regulation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manghwar, H.; Hussain, A.; Ali, Q.; Liu, F. Brassinosteroids (BRs) role in plant development and coping with different stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Yadav, S.; Srivastava, A.; Shrivastava, N. Methyl jasmonate mediates upregulation of bacoside A production in shoot cultures of Bacopa monnieri. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Cui, G.H.; Mao, Y.; He, X. Effect of Gibberellins and its synthetic inhibitor on metabolism of tanshinones. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Form. 2008, 14, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasi, B.H.; Stiles, A.R.; Saxena, P.K.; Liu, C.Z. Gibberellic acid increases secondary metabolite production in Echinacea purpurea hairy roots. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 168, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M.P.; Saxena, P.K.; Murch, S.J. Elicitation of secondary metabolism in Echinacea purpurea L. by gibberellic acid and triazoles. Eng. Life Sci. 2009, 9, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banyai, W.; Mii, M.; Supaibulwatana, K. Enhancement of artemisinin content and biomass in Artemisia annua by exogenous GA 3 treatment. Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 63, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondhi, N.; Bhardwaj, R.; Kaur, S.; Kumar, N.; Singh, B. Isolation of 24-epibrassinolide from leaves of Aegle marmelos and evaluation of its anti-genotoxicity employing Allium cepa chromosomal aberration assay. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 54, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.M.; Vukašinović, N.; Liu, D.; Russinova, E.; Yin, Y. Brassinosteroids: Multidimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 295–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filová, A.; Sytar, O.; Krivosudská, E. Effects of brassinosteroid on the induction of physiological changes in Helianthus annuus L. under copper stress. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. 2013, 61, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedina, E.; Yarin, A.; Mukhitova, F.; Blufard, A.; Chechetkin, I. Brassinosteroid-induced changes of lipid composition in leaves of Pisum sativum L. during senescence. Steroids 2017, 117, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.P.; Oral, H.V.; Bhardwaj, R.; Yu, J.Q.; Tran, L.S. Interaction of brassinosteroids and polyamines enhances copper stress tolerance in Raphanus sativus. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5659–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozhon, W.; Wang, W.; Berthiller, F.; Mayerhofer, J.; Chen, T.; Petutschnig, E.; Sieberer, T.; Poppenberger, B.; Jonak, C. Bikinin-like inhibitors targeting GSK3/Shaggy-like kinases: Characterisation of novel compounds and elucidation of their catabolism in planta. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrie, A.M.R.; Dirpaul, J.; Krishna, P.; Krochko, K.W.A.; Keller, W.A. Effects of brassinosteroids on microspore embryogenesis in Brassica species. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2005, 41, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, S.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Hasan, S.A. Foliar spray of brassinosteroid enhances yield and quality of Solanum lycopersicum under cadmium stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 19, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, G.P.; Sasse, J.M.; Yokota, T.; Cameron, W.D. 6-Deoxotyphasterol and 3-Dehydro-6-deoxoteasterone, Possible Precursors to Brassinosteroidsin the Pollen of Cupressus arizonica. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhini, B.V.; Anuradha, S.; Rao, S.S.R. Brassinosteroids-New class of plant hormone with potential to improve crop productivity. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ikekawa, N.; Takatsuto, S.; Kitsuwa, T.; Saito, H.; Morishita, T.; Abe, H. Analysis of natural brassinosteroids by gas chromatography and gas chromatography-Mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1984, 290, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motegi, C.; Takatsuto, S.; Gamoh, K. Identification of brassinolide and castasterone in the pollen of orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck) by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 658, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tůmová, L.; Tarkowská, D.; Řehořová, K.; Marková, H.; Kočová, M.; Rothová, O.; Čečetka, P.; Holá, D. Drought-tolerant and drought-sensitive genotypes of maize (Zea mays L.) differ in contents of endogenous brassinosteroids and their drought-induced changes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Fujioka, S.; Yokota, T.; Murofushi, N.; Sakurai, A. Identification of brassinolide, castasterone, typhasterol, and teasterone from the pollen of Lilium elegans. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 2075–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creelman, R.A.; Mullet, J.E. Biosynthesis and action of jasmonates in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 1997, 48, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro, L.; Gutierrez, J.; Pedreño, M.A.; Sottomayor, M. Synergistic and additive influence of cyclodextrins and methyl jasmonate on the expression of the terpenoid indole alkaloid pathway genes and metabolites in Catharanthus roseus cell cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2014, 119, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Hisano, H.; Hojo, Y.; Matsuura, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Mori, I.C.; Senthil-Kumar, M.S. Global profiling of phytohormone dynamics during combined drought and pathogen stress in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals ABA and JA as major regulators. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, L.; Inzé, D.; Goossens, A. Jasmonate–inducible gene: What does it mean? Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Rekha, K.; Rajakumar, G. Elicitation Enhanced the Production of Phenolic Compounds and Biological Activities in Hairy Root Cultures of Bitter melon (Momordica charantia L.). Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2016, 59, e160393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusha, T.S.; Joseph, M.V.; Elyas, K.K. Callus induction and elicitation of total phenolics in callus cell suspension culture of Celastrus paniculatus–wild, an endangered medicinal plant in India. Pharmacogn. J. 2016, 8, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Huang, P.; Inoue, K. Up-regulation of soyasaponin biosynthesis by methyl jasmonate in cultured cells of Glycyrrhiza glabra. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadzovska, S.; Maury, S.; Delaunay, A.; Spasenoski, M.; Joseph, C.; Hagège, D. Jasmonic acid elicitation of Hypericum perforatum L. cell suspensions and effects on the production of phenylpropanoids and naphtodianthrones. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2007, 89, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzanowska, J.; Czubacka, A.; Pecio, L.; Przybys, M.; Doroszewska, T.; Stochmal, A.; Oleszek, W. The effects of jasmonic acid and methyl jasmonate on rosmarinic acid production in Mentha × piperita cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2012, 108, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, G.; Sivakumar, S.; Premkumar, G.; Senthil, K.T.; Jayabalan, N. Enhanced production of psoralen through elicitors treatment in adventitious root culture of Psoralea corylifolia (L). Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Nopo-Olazabal, C.; Condori, J.; Nopo-Olazabal, L.; Medina-Bolivar, F. Differential induction of antioxidant stilbenoids in hairy roots of Vitis rotundifolia treated with methyl jasmonate and hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 74, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, C.; Zhang, W.; Franco, C. Manipulating anthocyanin composition in Vitis vinifera suspension cultures by elicitation with jasmonic acid and light irradiation. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Zhan, J.C.; Huang, W.D. Effects of ultraviolet C, methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid, alone or in combination, on stilbene biosynthesis in cell suspension cultures of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Cabernet Sauvignon. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 122, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangopadhyay, M.; Dewanjee, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Enhanced plumbagin production in elicited Plumbago indica hairy root cultures. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silja, P.K.; Gisha, G.P.; Satheeshkumar, K. Enhanced plumbagin accumulation in embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Plumbago rosea L. following elicitation. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2014, 119, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyasri, R.; Muthuramalingam, P.; Karthick, K.; Shin, H.; Choi, S.; Ramesh, M. Methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid as powerful elicitors for enhancing the production of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants: An updated review. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2023, 153, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-May, E.; Galaz-Avalos, R.M.; Loyola-Vargas, V.M. Differential secretion and accumulation of terpene indole alkaloids in hairy roots of Catharanthus roseus treated with methyl jasmonate. Mol. Biotechnol. 2009, 41, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.T.; Kim, M.Y.; Hong, M.H.; Ahn, J.C.; Hwang, B. Stimulation of asiaticoside accumulation in the whole plant culture of Centella asiatica (L.) urban by elicitors. Plant Cell Rep. 2004, 23, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corchete, P.; Bru, R. Proteome alterations monitored by DIGE analysis in Silybum marianum cell cultures elicited with methyl jasmonate and methyl B cyclodextrin. J. Proteom. 2013, 85, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.B.; Yu, K.W.; Hahn, E.J.; Paek, K.Y. Differential responses of antioxidants enzymes, lipoxygenase activity, ascorbate content and the production of saponins in tissue cultured root of mountain Panax ginseng C.A. Mayer and Panax quinquefolium L. in bioreactor subjected to methyl jasmonate stress. Plant Sci. 2005, 169, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.; Ali, H.; Khan, T.; Kayani, W.; Khan, M.A. Impacts of methyl jasmonate and phenyl acetic acid on biomass accumulation and antioxidant potential in adventitious roots of Ajuga bracteosa Wall ex Benth., a high valued endangered medicinal plant. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants. 2017, 23, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Largia, M.J.V.; Pothiraj, G.; Shilpha, J.; Ramesh, M. Methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid synergism enhances bacoside A content in shoot cultures of Bacopa monnieri (L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2015, 122, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, D.; Cuaspud, O.; Arias, J.P.; Ruiz, O.; Arias, M. Effect of salicylic acid and methyl jasmonate in the production of phenolic compounds in plant cell suspension cultures of Thevetia peruviana. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 19, e00273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellapan, P.; Rohani, E.R.; Mohd Noor, N.M. Sesquiterpene production in methyl jasmonate-induced Persicaria minor cell suspension culture. Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 3051–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajungla, L.; Patil, P.P.; Barmukh, R.B.; Nikam, T.D. Influence of biotic and abiotic on accumulation of hyoscyamine and scopolamine in root cultures of Datura metel L. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2009, 8, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Chodisetti, B.; Rao, K.; Gandi, S.; Giri, A. Gymnemic acid enhancement in the suspension cultures of Gymnema sylvestre by using the signaling molecules-Methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 2015, 51, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Shi, M.; Cui, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kai, G. Effects of methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid on tanshinone production and biosynthetic gene expression in transgenic Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2015, 62, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, Y.; Moghadam, K.P.; Bahramnejad, B.; Habibi, P. Methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid effects on the dopamine production in hairy cultures of Portulaca oleracea (Purslan). Bull. Environ. Pharmacol. Life Sci. 2013, 2, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Pirian, K.; Piri, K. Effect of methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid on noradrenalin accumulation in hairy roots of Portulaca oleracea (L.). Int. Res. J. Appl. Basic Sci. 2012, 3, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Izabela, G.; Halina, W. The effect of methyl jasmonate on production of antioxidant compounds in shoot cultures of Salvia officinalis L. Herba Pol. 2009, 55, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Firouzi, A.; Mohammadi, S.A.; Khosrowchahli, M.; Movafeghi, A.; Hasanloo, T. Enhancement of silymarin production in cell culture of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn by elicitation and precursor feeding. J. Herbs Spices Med. Plants 2013, 19, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, V.; Kuvalekar, A.; Harsulkar, A. Microbial elicitation in root cultures of Taverniera cuneifolia (Roth) Arn. for elevated glycyrrhizic acid production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 54, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivanandhan, G.; Dev, G.K.; Jeyaraj, M.; Rajesh, M.; Arjunan, A.; Muthuselvam, M.; Manickavasagam, M.; Selvaraj, N.; Ganapathi, A. Increased production of withanolide A, withanone, and withaferin A in hairy root cultures of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal elicited with methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2013, 114, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khojasteh, A.; Mirjalili, P.J.; Eibl, R.; Rosa, M. Cusido Methy-Jasmonate enhanced production of rosamarinic acid in cell cultures of Satureja khuzistanica in a bioreactor. Eng. Life Sci. 2016, 16, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedapudi, S.; Chin, C.K.; Pedersen, H. Production and elicitation of benzalacetone and the raspberry ketone in cell suspension cultures of Rubus idaeus. Biotechnol. Prog. 2000, 16, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, M.; Arakawa, T.; Mikami, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Kawahar, N.; Hayashi, T.; Ishimaru, H. Phytoalexins from hairy root culture of Hyoscyamus albus treated with methyl jasmonate. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, L.F.; Gao, L.L.; Singh, K.B. Jasmonate Signalling and Defence Responses in the Model Legume Medicago truncatula-A Focus on Responses to Fusarium Wilt Disease. Plants 2016, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perassolo, M.; Quevedo, C.V.; Giulietti, A.M.; Rodríguez, T.J.R. Stimulation of the proline cycle and anthraquinone accumulation in Rubia tinctorum cell suspension cultures in the presence of glutamate and two proline analogs. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2011, 106, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.Y.; Son, S.Y.; Rhee, H.S.; Yoon, S.Y.H.; Lee-Parsons, C.W.; Park, J.M. Synergistic effects of sequential treatment with methyl jasmonate, salicylic acid and yeast extract on benzophenanthridine alkaloid accumulation and protein expression in Eschscholtzia californica suspension cultures. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 135, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Sankar, P.D. Effect of methyl jasmonate and chitosan on growth characteristics of Ocimum basilicum L., Ocimum sanctum L. and Ocimum gratissimum L. cell suspension cultures. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 4759–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suan, S.K.; Bhatt, A.; Lai, K.C. Effect of sucrose and methyl jasmonate on biomass and anthocyanin production in cell suspension culture of Melastoma malabathricum (Melastomaceae). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2011, 59, 597–606. [Google Scholar]
- Shabani, L.; Ehsanpour, A.A.; Asghari, G.; Emami, J. Glycyrrhizin production by in vitro cultured Glycyrrhiza glabra elicited by methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 56, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaweesak, J.; Seiichi, S.; Hiroyuki, T.; Waraporn, P. Elicitation effect on production of plumbagin in in vitro culture of Drosera indica (L.). J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 4949–4953. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z.; Han, C.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, K.; Huang, H.; Ren, C. Brassinosteroid enhances jasmonate-induced anthocyanin accumulation in Arabidopsis seedlings. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.G.; Sanz, C.; Olías, R.; Olías, J.M. Effect of methyl jasmonate on in vitro strawberry ripening. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3733–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Smith, M.A.L.; Pépin, M.F. Effects of exogenous methyl jasmonate in elicited anthocyanin-producing cell cultures of ohelo (Vaccinium pahalae). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Plant 1999, 35, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniewski, M.; Horbowicz, M.; Puchalski, J.; Ueda, J. Methyl jasmonate stimulates the formation and the accumulation of anthocyanin in Kalanchoe blossfeldiana. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2003, 25, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, E.; Thelen, A.; Petersen, M. Fungal elicitor preparation and methyl jasmonate enhance rosmarinic acid accumulation in suspension cultures of Coleus blumei. Plant Cell Rep. 1999, 18, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, Q.; Hayat, S.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, A. Effect of exogenous salicylic acid under changing environment: A review. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2010, 68, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryals, J.A.; Neuenschwander, U.H.; Willits, M.G.; Molina, A.; Steiner, H.Y.; Hunt, M.D. Systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, E.E.; Johnson, R.R.; Ryan, C.A. Regulation of expression of proteinase inhibitor genes by methyl jasmonate and jasmonic acid. Plant Physiol. 1992, 98, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.W.; Lv, S.S.; Zhao, D.; Chen, J.W.; Yang, W.T.; Wu, W. Effects of salicylic acid on monoterpene production and antioxidant systems in Houttuynia cordata. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, L.L. The myriad plant responses to herbivores. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2000, 19, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, S.S.; Kurosaki, F.; Nishi, A. Role of salicylic acid and intrercelluar Ca2+ in the induction of chitinase activity in carrot suspension culture. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1994, 45, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, J.G.; Ahire, M.L.; Nitnaware, K.M.; Panda, S.; Bhatt, V.P.; Kishor, P.B.; Nikam, T.D. In vitro propagation and production of cardiotonic glycosides in shoot cultures of Digitalis purpurea L. by elicitation and precursor feeding. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 2379–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avancini, G.; Abreu, I.N.; Saldaña, M.D.; Mohamed, R.S.; Mazzafera, P. Induction of pilocarpine formation in jaborandi leaves by salicylic acid and methyl jasmonate. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitta-Alvarez, S.I.; Spollansky, T.C.; Giulietti, A.M. The influence of different biotic and abiotic elicitors on the production and profile of tropane alkaloids in hairy root cultures of Brugmansia candida. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2000, 26, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgakov, V.P.; Tchernoded, G.K.; Mischenko, N.P.; Khodakovskaya, M.V.; Glazunov, V.P.; Radchenko, S.V.; Zvereva, E.V.; Fedoreyev, S.A.; Zhuravlev, Y.N. Effect of salicylic acid, methyl jasmonate, ethephon and cantharidin on anthraquinone production by Rubia cordifolia callus cultures transformed with the rolB and rolC genes. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 97, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chodisetti, B.; Rao, K.; Gandi, S.; Giri, A. Improved gymnemic acid production in the suspension cultures of Gymnema sylvestre through biotic elicitation. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2013, 7, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, A.; Vlase, L.; Halmagyi, A.; Deliu, C.; Coldea, G. Effects of plant growth regulators and elicitors on production of secondary metabolites in shoot cultures of Hypericum hirsutum and Hypericum maculatum. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2011, 106, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, N.; Kiridena, S. A fuzzy rough sets-based multi-agent analytics framework for dynamic supply chain configuration. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 6984–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kitisripanya, T.; Komaikul, J.; Tawinkan, N.; Atsawinkowit, C.; Putalun, W. Dicentrine production in callus and cell suspension cultures of Stephania venosa. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 443–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Plant Species | Elicitor | Compound | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | |||
| Nicotiana tabacum | Cellulose | Phytoalexins | Threlfal and Whithead, 1988 [23] |
| Plantanus acerifolia | Glycoprotein | Coumarin | Alami et al., 1998 [24] |
| Eschscholzia californica | Yeast cell | Benzophenanthridine | Farber et al., 2003 [25] |
| Carbohydrates | |||
| Glycine max | Carbohydrates | Phytoalein | Sharp et al., 1984 [26] |
| Lithospermum erythrorhizon | Oligogalacturonic acid | Naphthoquinone hikonin | Fukui et al., 1983 [27] |
| Panax ginseng | Saponin | Hu et al., 2003 [28] | |
| Plumbago rosea | Plumbagin | Komaraiah et al., 2003 [29] | |
| Ruta graveolens | Fluoroquinolone alkaloids | Orlita et al., 2008 [30] | |
| Vitis vinifera | Trans-resveratrol, viniferins | Taurino et al., 2015 [31] | |
| Hypericum adenotrichum | Oligogalacturonic acid and sucrose | Hypericin | Omer and Bengi, 2013 [32] |
| Nicotiana tabacum | Chitosan | Phytoalexins | Brodelius et al., 1989 [33] |
| Eschscholzia californica | |||
| Curcuma longa L. | Indirubin | Radman et al., 2003 [34] | |
| Lupines albus | Isoflavonoids, Genistein | ||
| Polygonum tinctorium | Anthracene | ||
| Rheum palmatun | Curcumin | Sathiyabama et al., 2016 [35] | |
| Withania somnifera | Sucrose and Chitson | Withania A | Gorelick et al., 2015 [36] |
| Bacopa monnieri | Sucrose | Bacoside A | Naik et al., 2010 [37] |
| Plant Species | Compound | References |
|---|---|---|
| Catharanthus roseus | Ajmalicine and serpentine | Jaleel et al., 2007, 2009; Namdeo et al., 2002 [50,51,52] |
| Hyoscyamus niger | Scopolamine, hyoscyamine | Ghorbanpour et al., 2013 [53] |
| Ocimum basilicum | α-terpineol, eugenol | Banchio et al., 2008, 2009 [54,55] |
| Origanum majorana L. | α-terpineol | |
| Pisum sativum | Gallic acid, ferulic acid, cinnamic | Bahadur et al., 2007 [56] |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza | Tanshinone | Zhao et al., 2010 [57] |
| Salvia officinalis | Cis-thujone. Camphor | Ghorbanpour et al., 2014 [58] |
| Solanum viarum | Orthodihydroxy, tannins, flavonoids, Saponins, alkaloids | Hemashenpagam and selvaraj, 2011 [59] |
| Stevia rebaudiana | Stevioside | Vafadar et al., 2014 [60] |
| Targetes minuta | Monoterpenes, phenolic compounds | Cappellari et al., 2013 [61] |
| Bacterial Elicitor | Plant Species | Types of Elicitors | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacillus subtilis | Gymncma sylvestre | Acetoin, Surfactin, mycosubtilin, fengycin, iturines, 2,3-butanediol, StPep1 | Vatsa et al., 2011 [73] |
| Helminthosporium victoria | Solanum tuberosum | Victorin | Abdel-monaim et al., 2011 [74] |
| Magnaporthe grisea | Oryza sativa L. | PemG1 | Ning et al., 2004 [75] |
| Phytophthora and Pythium | Nicotiana tabacum | β-Glucans and chitin oligomers | Abdel-monaim et al., 2011 [74] |
| Phytophthora infestans | Glucans and eicosapentaenoic acid | Ning et al., 2004; Vatsa et al., 2011 [73,75] | |
| Phytophthora sojae | Glycoprotein | Minami et al.1996 [76] | |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS374r | Hypericum perforatum L. | Pseudobactin | Minami et al. 1996; Sanabria et al., 2010; Vander et al., 1998 [76,77,78] |
| Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato (Pst) DC3000 | Pinellia ternate | Coronatine | Vander et al., 1998 [78] |
| Trichoderma harzianum | Triticum aestivum | C6 Zinc finger protein-like elicitor (Thc6) | Day et al., 2014; Vander et al., 1998 [78,79] |
| Arthrobacter spp. | Oryza sativa L. | N, N-Dimethyl hexadecyl amine | Sanabria et al., 2010 [77] |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | Hypericum perforatum L. | ||
| Sinorhizobium meliloti | Medicago sativa | ||
| Burkholderia gladioli | Panicum virgatum | Lipopolysaccharides | Schuhegger et al., 2006 [80] |
| Plant Species | Compounds | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Ethylene | ||
| Fragaria ananassa | Anthocyanin | McSteen et al., 2008 [103] |
| Daucus carota | Phenolic compounds | Heredia et al., 2009; Ke et al., 2018; Liang et al., 2013; Liu et al., 2016 [104,105,106,107] |
| Camellia sinensis L. | ||
| Salvia miltiorrhiza | ||
| Catharanthus roseus | ||
| Vitis vinifera | Flavonoids, Phenolic acids, Stilbenes, and Flavonols | Ma et al., 2021 [108] |
| Rauwolfia serpentina | Alkaloids | Baharudin et al., 2023 [109] |
| Catharanthus roseus | ||
| Arabidopsis sp. | Glucosinolate | Villarreal-García et al., 2016 [110] |
| Pinophyta sp. | Terpenoids | Ninkuu et al., 2021 [111] |
| Auxin | ||
| Beeta vulgaris | Betalain | Taya et al., 1992 [112] |
| Catharanthus roseus | Indole alkaloids | Moreno et al., 1993 [113] |
| Chamomile recutita | α-Bisabolol oxide | Çakmakçı et al., 2020 [114] |
| Melissa officinalis Lam | Nerol and Geraniol | Da Silva et al. 2005 [115] |
| Papaver somniferum | Thebaine | Jamwal et al., 2018 [116] |
| Rauvolfia serpentine | Reserpine | |
| Corydalis ambigua | Corydaline | |
| Salvia moorcroftiana L. | Phenolic compound, and Flavonoid | Bano et al., 2022 [117] |
| Cytokinin | ||
| Cocos nucifera | 1,3-Diphenylurea | GE, 2006 [118] |
| Nicotiana tabacum | Cytokinin 7 and 9-glucosides | Vylicilova, 2020 [119] |
| Triticum aestivum | trans-Zeatin | Babosha et al., 2009 [120] |
| Oryza sativa | Isopentenyladenine | Akagi et al., 2014 [121] |
| Abscisic acid | ||
| Vitis vinifera L. | Polyphenols | Ferrandino et al., 2014 [122] |
| Anthocyanins | Wang et al., 2021 [98] | |
| Aristotelia chilensis | González-Villagra et al., 2018 [123] | |
| Malus hupehensis | Lv et al., 2021 [124] | |
| Artemisia annua | Artemisinin | |
| Orthosiphon stamineus Benth | Phenolics, Flavonoids and Soluble sugars | Thakur et al., 2019 Ibrahim et al., 2013 [125,126] |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza | ||
| Atractylodes lancea | Atractylone, β-Eudesmol and Hinesol, Atractylodin, Volatile oil | Wang et al., 2015 [127] |
| Plant Species | Compounds | References |
|---|---|---|
| Catharanthus roseus | Ajmalicine, serpentine, catharanthine, ajmaline | Ruiz-May et al., 2009 [177] |
| Centella asiatica | Asiaticoside and centelloside | Kim et al., 2004; Gangopadhayay et al., 2011 [174,178] |
| Hypericum perforatum | Flavonoids | Wang et al., 2015 [127] |
| Panax ginseng | Ginsenosides | Kim et al., 2004; Corchete and Bru, 2013 [178,179] |
| Ginsenosidea (Rg3) | Ali et al., 2005 [180] | |
| Ajuga bracteosa | Phenols, flavonoids, Phytoecydysteroids | Saeed et al., 2017 [181] |
| Andrographis paniculata | Andrographolide | Sharma, 2015 [142] |
| Artemesia absinthium | Phenols and flavonoids | Ali et al., 2015 [180] |
| Bacopa monnieri | Bacoside A | Largia et al., 2015 [182] |
| Thevetia perwiana | Phenolic compounds | Mendoza et al., 2018 [183] |
| Persicaria minor | Sesquiterpenes | Sellapan et al., 2018 [184] |
| Gymnema sylvestre | Gymnemic acid | Ajungla, 2009; Chodisetti et al., 2015 [185,186] |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza | Tanshinone | Hao et al., 2015 [187] |
| Portulaca oleracea | Dopamine, Non-adrenaline | Ahmadi et al., 2013, Pirian and Piri, 2012 [188,189] |
| Salvia officinalis | Diterpenoid | Izabela and Halina, 2009 [190] |
| Silybum marianum | Silymarin, tanshinone | Firouzi et al., 2003; Hao et al., 2015 [187,191] |
| Taverniera cuneifolia | Glycyrrhizic acid | Awad, 2014 [192] |
| Vitis vinifera | Stilbene, trans-resveratrol, anthocyanin | Xu et al., 2015; Taurino, 2015 [31,173] |
| Withania somnifera | Withanolide A, withanone, withaferin A | Sivanandhan et al., 2013 [193] |
| Satureja khuzistanica | Rosmarinic acid | Khojasteh et al., 2016 [194] |
| Taxus baccata | Phenolic content | Ghobanpour et al., 2014 [60] |
| Taxus cuspidate | Paclitaxel | Pedapudi et al., 2000 [195] |
| Taxus canadensis | ||
| Hyoscyamus albus | Phytoalexins | Kuroyanagi et al., 1998 [196] |
| Medicago truncatula | Protein content | Thatcher et al., [197] |
| Rubia tinctorum | Anthraquinone | Perassolo et al., 2011 [198] |
| Eschscholtzia californica | Benzophenanthridine alkaloid | Cho et al., 2008 [199] |
| Origanum basilicum | Hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives | Mathew and Sankar, 2012 [200] |
| O. sanctum | ||
| O. gratissimum | ||
| Melastoma malabathricum | Anthocyanin | Suan et al., 2011 [201] |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | Glycyrrhizin | Shabani et al., 2009 [202] |
| Drosera indica | Plumagin | Thaweesak et al., 2011 [203] |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | Anthocyanin | Peng et al., 2011 [204] |
| Fragaria ananassa | Perez et al., 1977 [205] | |
| Vaccinium pahalae | Fang et al., 1999 [206] | |
| Tulipa Gesneriana | Saniewski et al., 2003 [207] | |
| Rubus idaeus | Rubusidaeus ketone benzal acetone | Pedapudi et al., 2000 [195] |
| Coleus blumei | Rosmarinic acid | Szabo et al., 1999 [208] |
| Plant Species | Compounds | References |
|---|---|---|
| Datura metel | Hyoscyamine and scopolamine | Ajungla, 2009 [185] |
| Daucus carota | Chitinase | Muller et al., 1994 [214] |
| Digitalis purpurea | Digitoxin | Patil et al., 2013 [215] |
| Brumansia candida | Scopolamine (alkaloid) | Avancini et al., 2003 [216] |
| Pitta-alvarez et al., 2000 [217] | ||
| Rubia cordifolia | Anthraquinone | Bulgakov et al., 2002 [218] |
| Gymnema sylvestre | Gymnemic acid | Chodisetti et al., 2013 [219] |
| Hypericum hirsutum | Hypericin and pseudohypericin | Coste et al., 2011 [220] |
| Vitis vinifera | Stilbene, vinblastine and vincristine | Xu et al., 2015 [173] |
| Withania somnifera | Withanolide A, withanone, and withaferin A | Sivanandhan et al., 2013 [193] |
| Aloe vera | Polysaccharides and phenolics | Shukla and kiridena, 2016 [221] |
| Stephania venosa | Dicentrine | Kitisripanya et al., 2013 [222] |
| Pilocarpus pennatifolius | pilocarpine | Avancini et al., 2003 [216] |
| Glycyrrhiza glabra | Glycyrrhizin | Shabani et al., 2009 [202] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jain, D.; Bisht, S.; Parvez, A.; Singh, K.; Bhaskar, P.; Koubouris, G. Effective Biotic Elicitors for Augmentation of Secondary Metabolite Production in Medicinal Plants. Agriculture 2024, 14, 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060796
Jain D, Bisht S, Parvez A, Singh K, Bhaskar P, Koubouris G. Effective Biotic Elicitors for Augmentation of Secondary Metabolite Production in Medicinal Plants. Agriculture. 2024; 14(6):796. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060796
Chicago/Turabian StyleJain, Divya, Shiwali Bisht, Anwar Parvez, Kuldeep Singh, Pranav Bhaskar, and Georgios Koubouris. 2024. "Effective Biotic Elicitors for Augmentation of Secondary Metabolite Production in Medicinal Plants" Agriculture 14, no. 6: 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060796
APA StyleJain, D., Bisht, S., Parvez, A., Singh, K., Bhaskar, P., & Koubouris, G. (2024). Effective Biotic Elicitors for Augmentation of Secondary Metabolite Production in Medicinal Plants. Agriculture, 14(6), 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14060796






