Crushing Force Prediction Method of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Based on Particle Phenotype
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
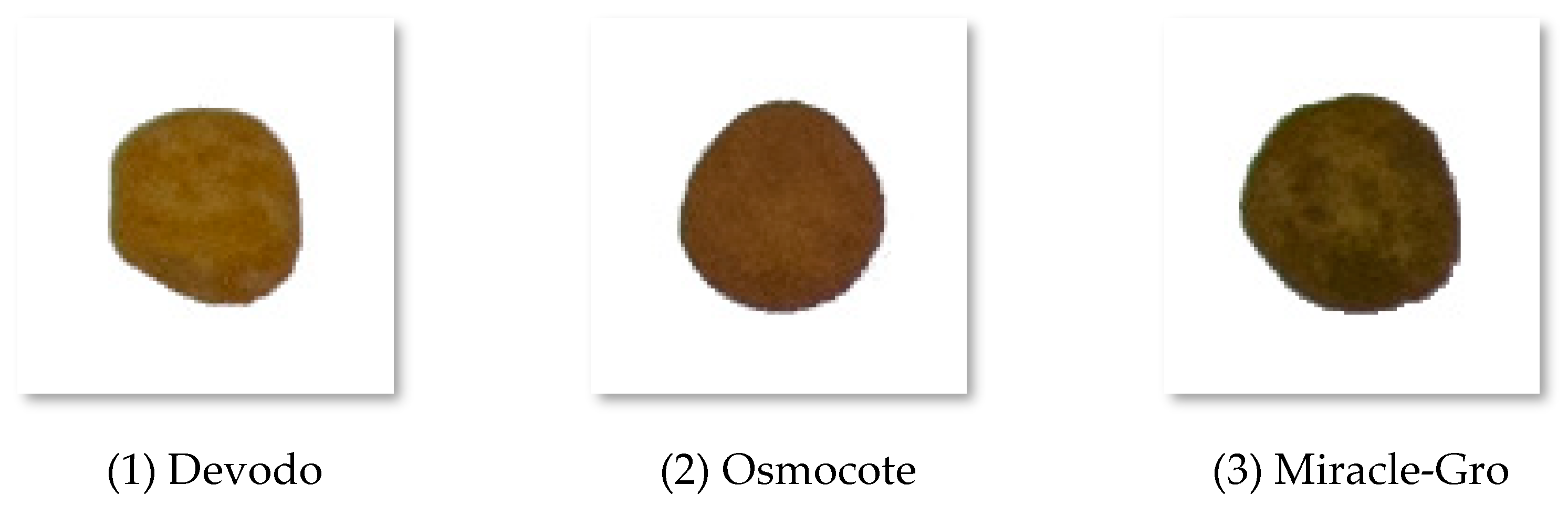
2.1. Collection of Morphological Characteristics and Crushing Force of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Granules
2.1.1. Phenotypic Characteristics
2.1.2. Triaxial Features
2.1.3. Sphericity
2.1.4. Granularity
2.1.5. Texture Features
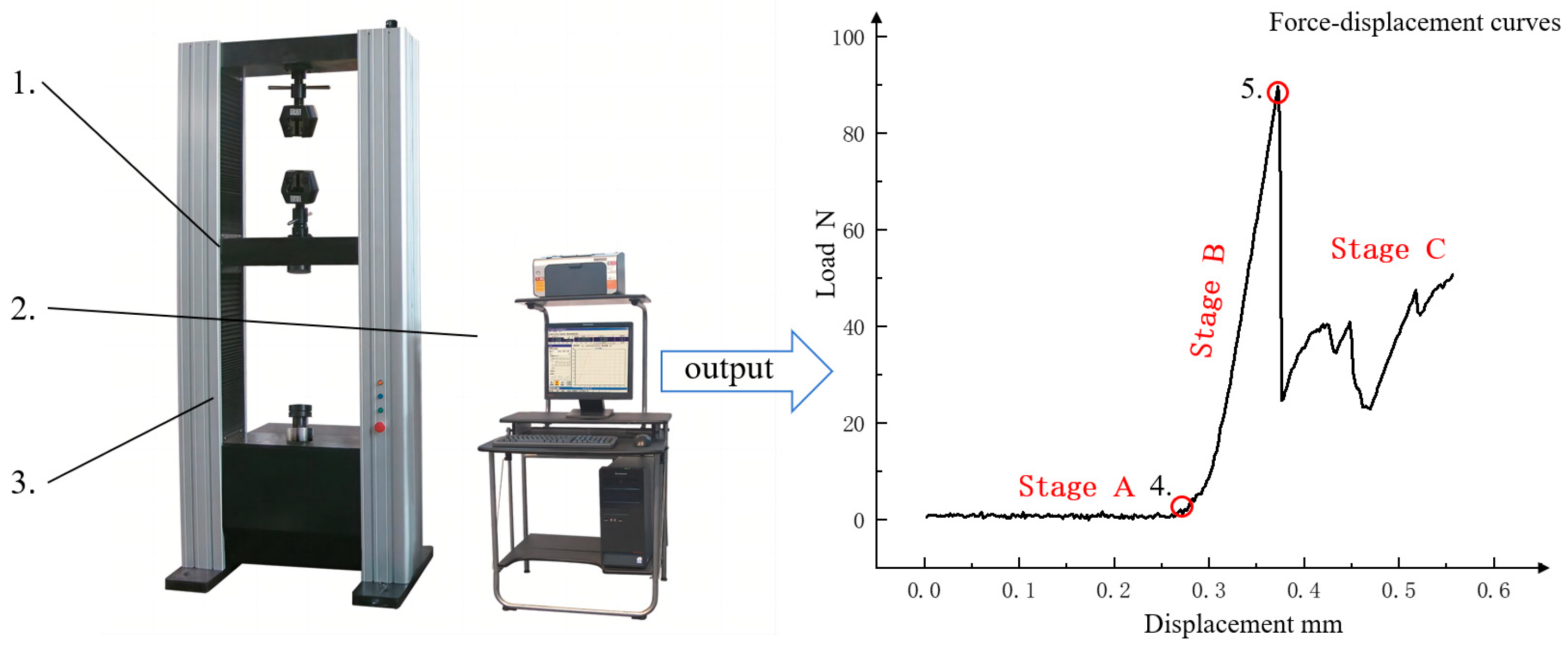
2.2. Crushing Force
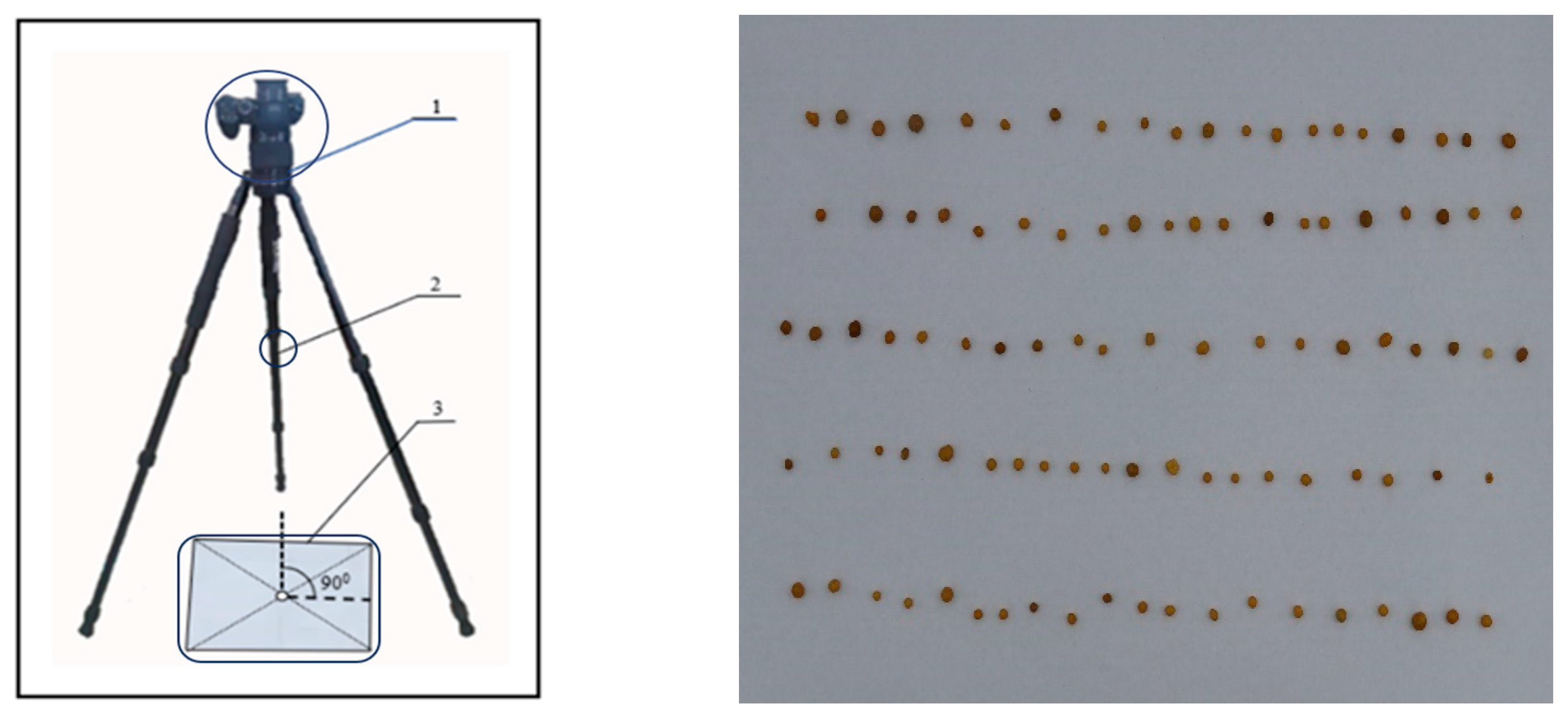
2.2.1. Image Acquisition and Pre-Processing
2.2.2. Acquisition of Triaxial Features
2.2.3. Acquisition of Texture Features
2.2.4. Acquisition of Crushing Force
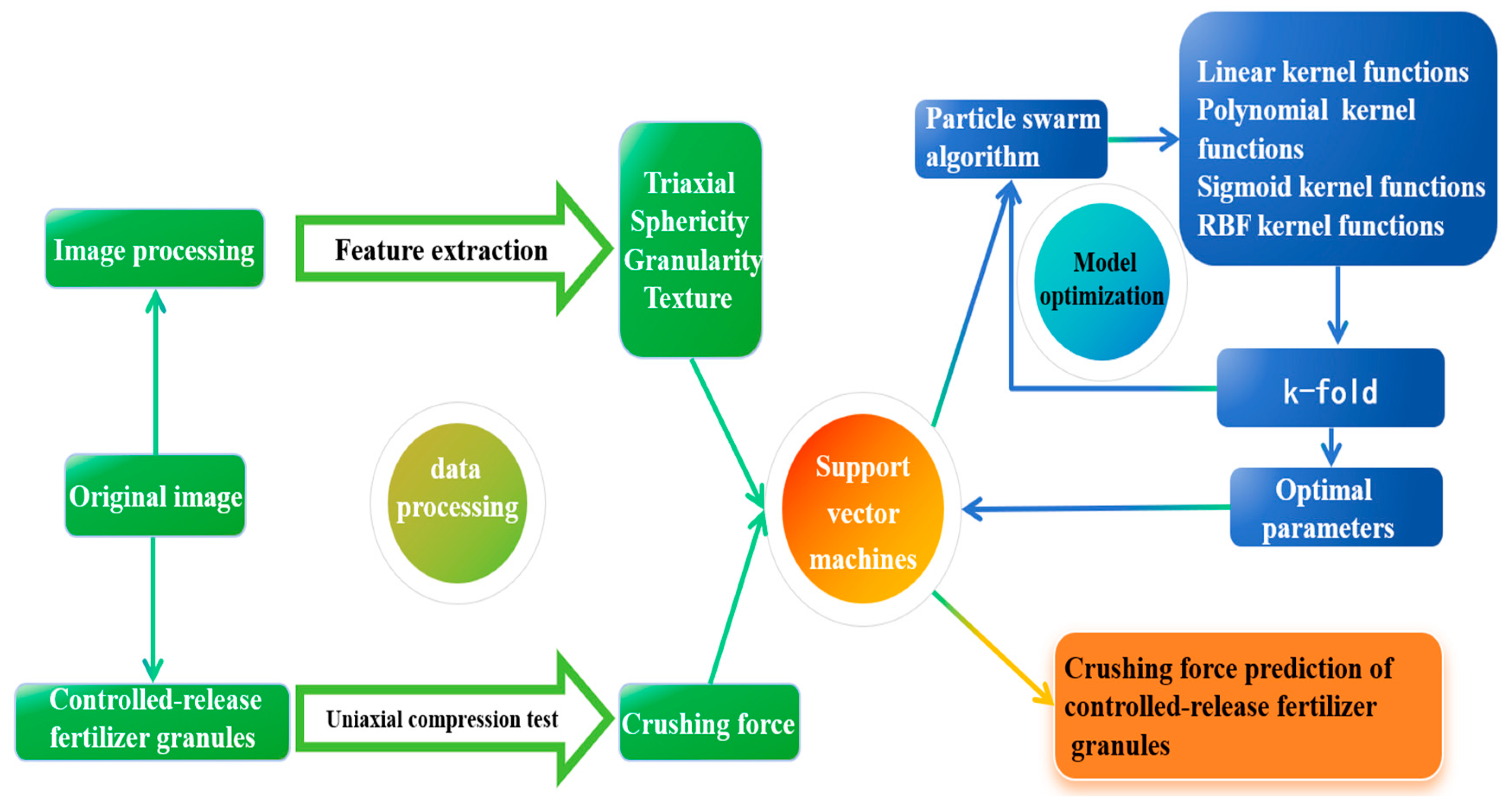
2.3. Construction of Crushing Force Prediction Model of Controlled-Release Fertilizer
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Prediction Model Based on Support Vector Machine Regression
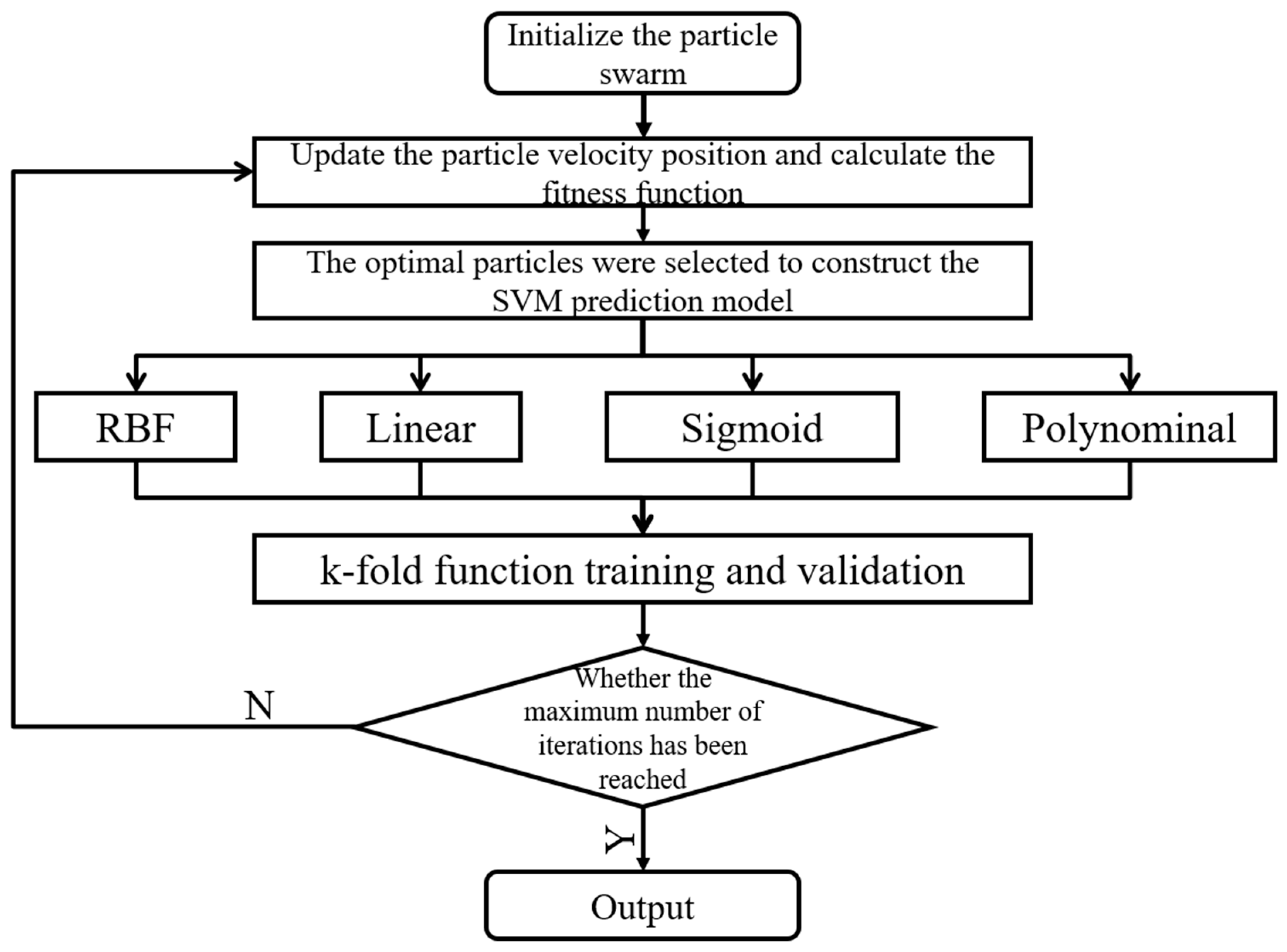
2.6. Predictive Model Optimization
2.6.1. Particle Swarm Algorithm
2.6.2. SVM Parameter Optimization Method Based on Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm and K-Fold Function
2.6.3. Predict Performance Evaluation Indicators
3. Results
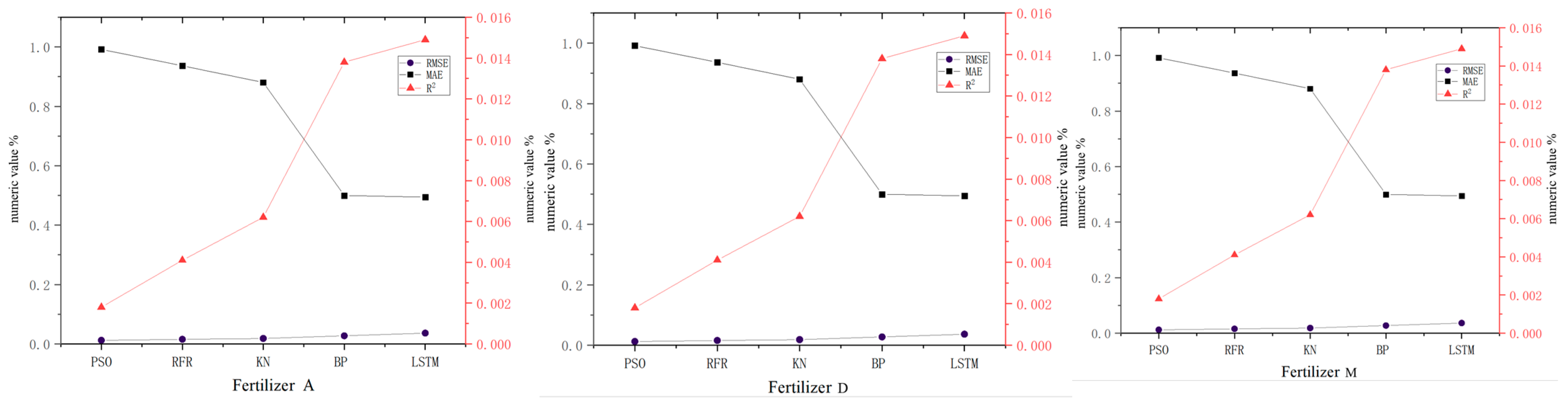
3.1. Comparative Analysis of Predictive Models
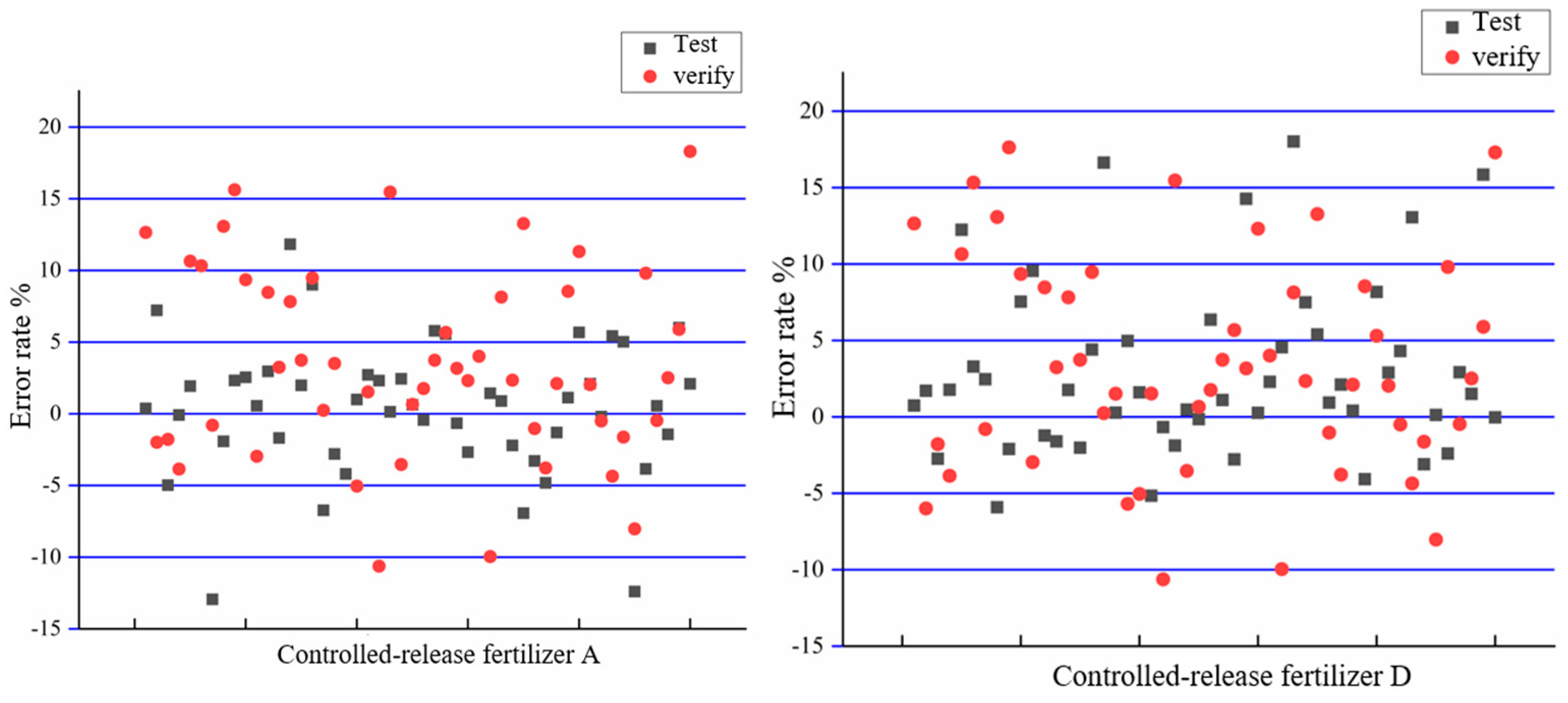
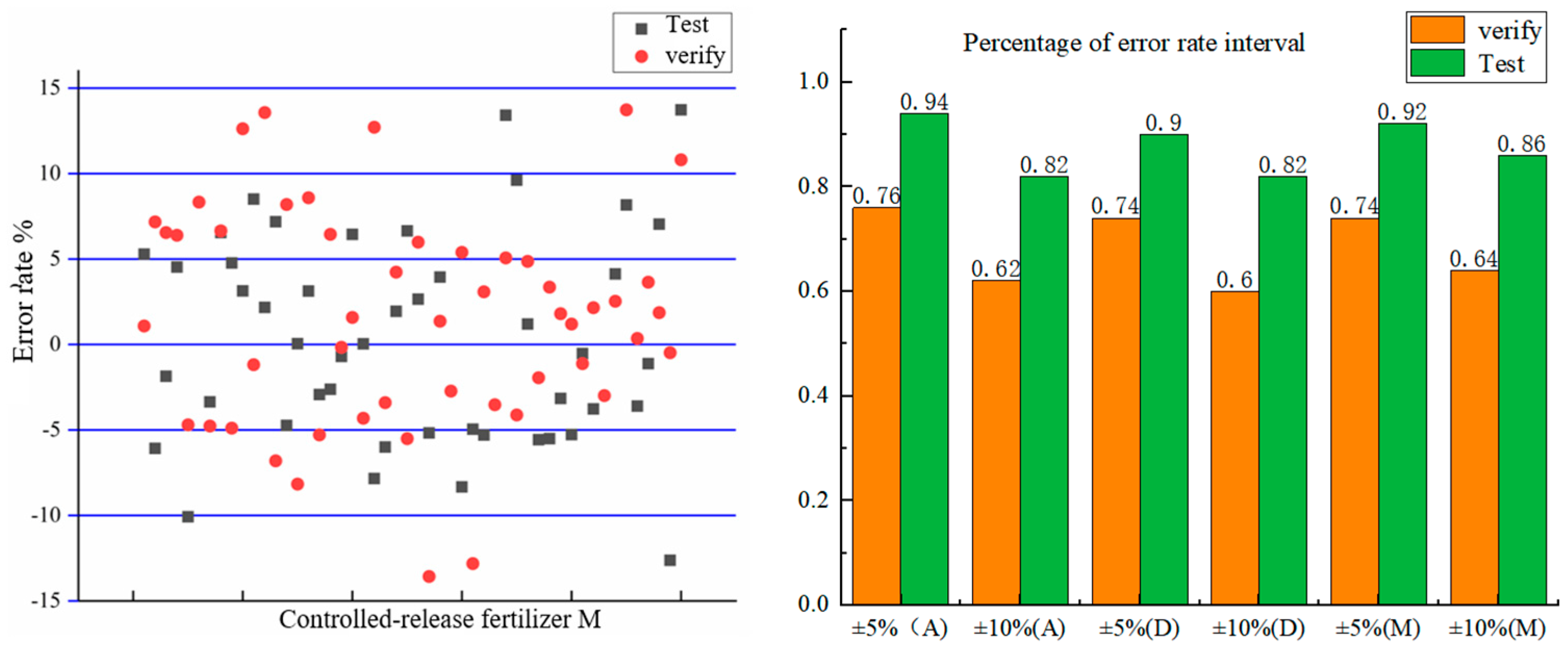
3.2. Validation Analysis of the PSO-SVM Prediction Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.H.; Zheng, W.T.; Zhang, J.T.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Zhao, Y.X.; Ma, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.H. Reserch progress and application of slow/controlled-release fertilizers. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2023, 42, 1–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.P.; Sun, J.R.; Pu, L.J. Comparative study on fertilization intensity and integrated efficiency in China and Euro-American major countries. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 9–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.B. Land consolidation and fertilizer reduction: Quasi-natural experimental evidence from China’s well-facilitated capital farmland construction. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2021, 4, 123–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.L. The situation and prospect of research on efficient fertilization. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 2116–2125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Jin, J.Y. Fer-tilizer use and food security in China. Plant Nutr. Fer-Tilizer Sci. 2013, 19, 259–273. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.H.; Sun, Y.X.; Xue, G.F.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, R.D.; Jian, C.F. Study on releasing mechanics of resin-coated controlled-release fertilizer in soil based on SUGIHARA model. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 42, 637–641. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fertahi, S.; Ilsouk, M.; Zeroual, Y.; Oukarroum, A.; Barakat, A. Recent trends in organic coating based on biopolymers and biomass for controlled and slow release fertilizers. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Wu, X.B.; Tan, D.S.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.H. Application and environmental effects of one-off fertilization technique in major cereal crops in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 3827–3839. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.M.; Song, H.H.; Li, L.X.; Cao, B.; Li, H.Y.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, J.Z. Preparation and application of polyester/polyether type polyurethane swap films. Eng. Plast. Appl. 2016, 44, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C. Key Technology on Variable Rate Application System. Ph.D. Thesis, Academy of Agricultural Mechanization Sciences, Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shan, J.; Xu, L.M.; Hu, D. In situ evaluation method of sphericity error based on spherical grinding texture. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. 2016, 50, 654–659. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Maroof, M.A.; Mahboubi, A.; Noorzad, A.; Safi, Y. A new approach to particle shape classification of granular materials. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 22, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.F.; Su, J.L.; Tang, C. Anti-caking measure for compound fertilizer by acid ammoniation process and its application. Phosphate Compd. Fertil. 2016, 31, 31–32. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hofstee, J.W.; Huisman, W. Handling and spreading of fertilizers part1: Physical properties of fertilizer in relation to particle motion. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1990, 47, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmeister, G.; Watkins, S.C.; Silverberg, J. Fertilizer Consistency, Bulk Blending of Fertilizer Material: Effect of Size, Shape, and Density on Segregation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1964, 12, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.; Lehr, J.R.; Hoffmeister, G., Jr. Fertilizer caking, microscopic study of the mechanism of caking and its prevention in some granular fertilizers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1958, 6, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, M.; Pang, L.; Sun, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, X. Exploring temperature-resilient recycled aggregate concrete with waste rubber: An experimental and multi-objective optimization analysis. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2023, 62, 20230347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, R.; Azeman, N.H.; Mokhtar, M.H.H.; Mobarak, N.N.; Bakar, M.H.; Bakar, A.A. Hybrid ensemble-based machine learning model for predicting phosphorus concentrations in hydroponic solution. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 304, 123327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zadeh, A.; Broach, C.; Nosoudi, N.; Weaver, B.; Conrad, J.; Duffy, K. Building analytical models for predicting de novo malignancy in pancreas transplant patients: A machine learning approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Shi, X.; Hu, J. Prediction model of oxygen supply by aerobic compost based on CGA-BP neural network. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 211–217. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Kuang, L.; Yuan, Y.M.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, G.H. Dissolved oxygen prediction method in water body based on an improved limit learning machine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 225–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, L.L.; Liu, P.Z.; Zhao, Y.P.; Li, T.H.; Li, H. Research on the environmental prediction model of solar greenhouse based on SSA-LSTM. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 351–358. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, J. Prediction Model of Dry Fertilizer Crushing Force Based on P-DE-SVM. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3612–3624. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.L.; Miller, J.D. 3D characterization and analysis of particle shape using X-ray microtomography (XMT). Powder Technol. 2005, 154, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, C.F.; Kwan, A.K.H. Sphericity, shape factor, and convexity measurement of coarse aggregate for concrete using digital image processing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotonirina, A.D.; Delenne, J.Y.; Radjai, F.; Wachs, A. Grains3D, a flexible DEM approach for particles of arbitrary convex shape-Part III: Extension to non-convex particles modelled as glued convex particles. Comput. Part. Mech. 2019, 6, 55–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masad, E.; Olcott, D.; White, T.; Tashman, L. Correlation of fine aggregate imaging shape indices with asphalt mixture performance. Transp. Res. Rec. 2001, 1757, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Lin, J.; Guo, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Extracting the flame image color feature after PCA transformation based on clustering analysis. J. Hunan Univ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 29, 64–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.D.; Guo, X.N.; Luo, X.Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Z. Improved modal parameter identification method based on particle swarm optimization. J. Vib. Shock. 2022, 41, 255–264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Du, W.; Ye, W.L.; Liu, W.; Wei, Z. Contact loss identification of CA mortar in prefabricated slab track based on PSO-SVM. J. Cent. South Univ. 2021, 52, 4021–4031. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Lan, H.; Li, M.Z.; Meng, C. Predicting bulk density and porosity of soil using image processing and support vector regression. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 144–151. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


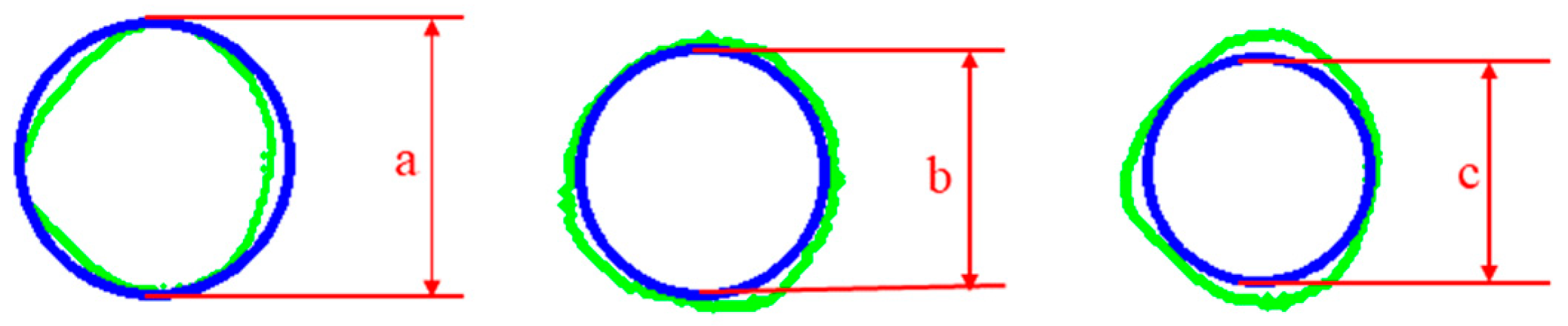
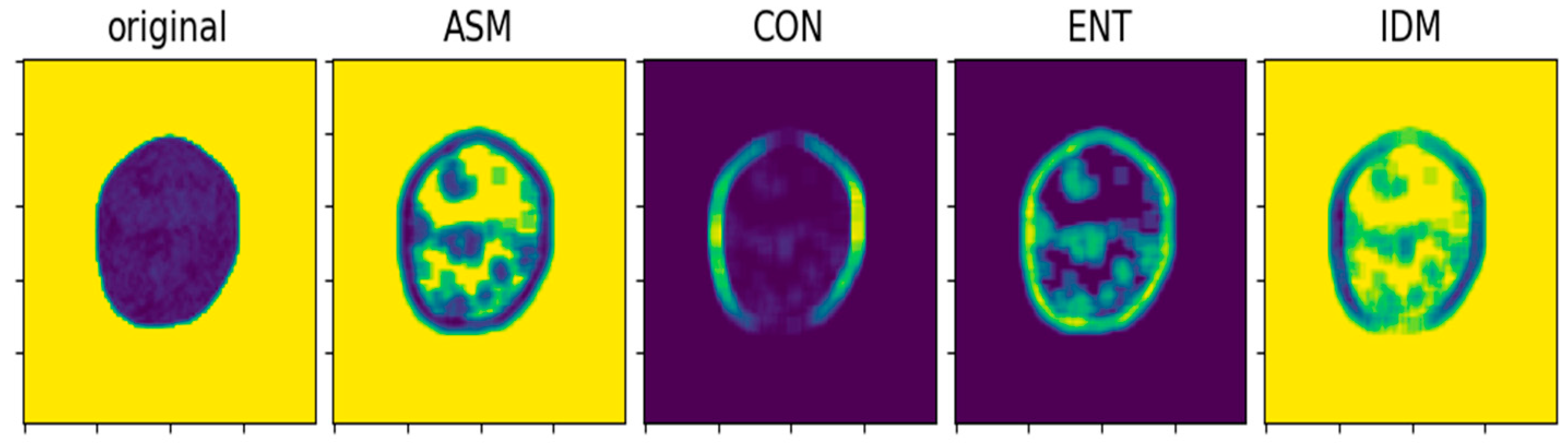

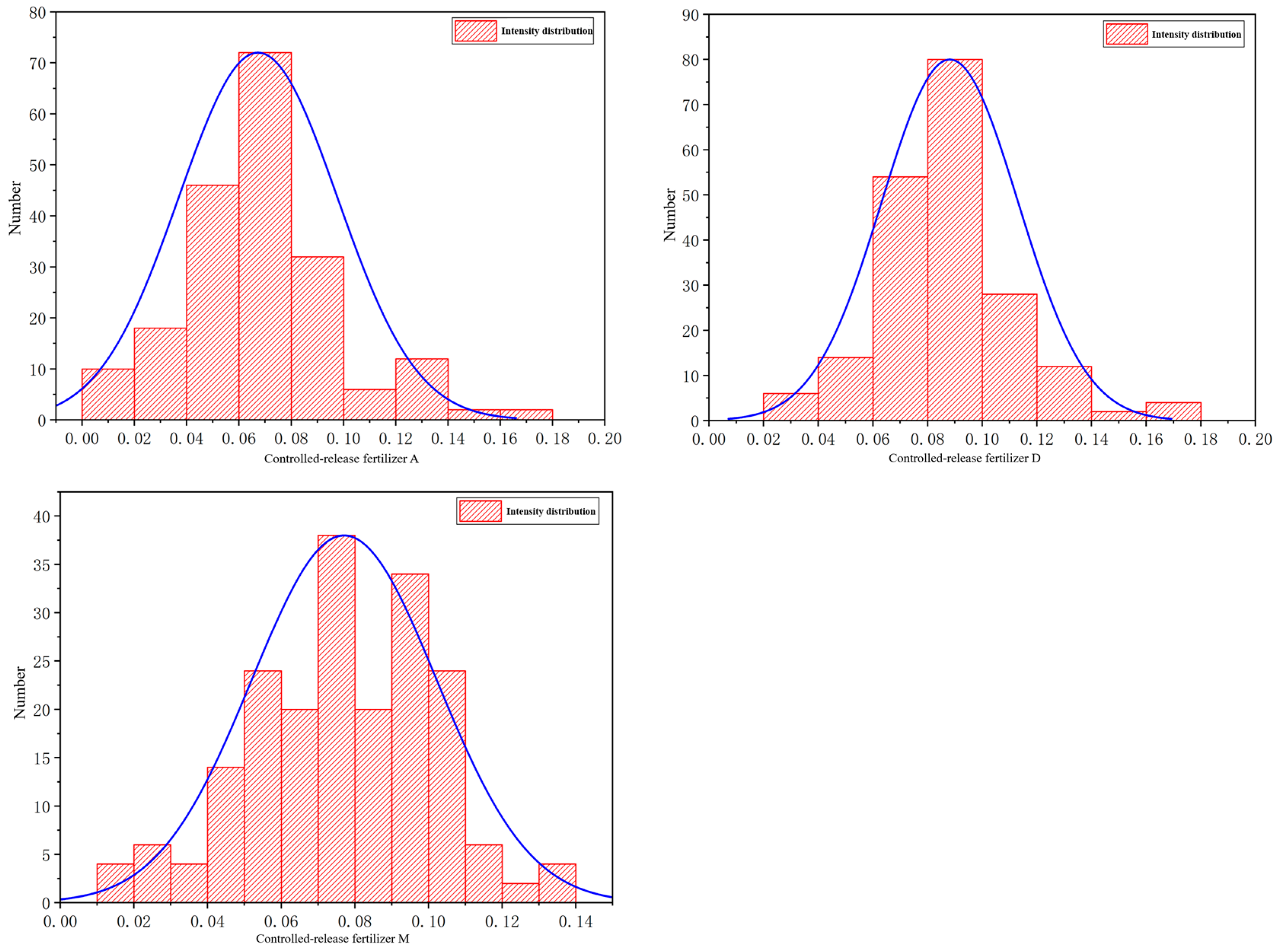
| Project | a/m | b/m | c/m | Granularity d | ASM | CON | ENT | Crushing Forces/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizer A | average value | 0.00941 | 0.00379 | 0.00317 | 3.521 | 0.707 | 0.523 | 0.740 | 62.0 |
| range | 0.00310 | 0.00309 | 0.003010 | 2.239 | 0.378 | 0.590 | 0.816 | 16.6 | |
| standard deviation | 0.00670 | 0.00060 | 0.00057 | 0.518 | 0.082 | 0.123 | 0.177 | 28.0 | |
| Fertilizer D | average value | 0.00399 | 0.00372 | 0.00359 | 3.744 | 0.616 | 0.521 | 0.971 | 69.0 |
| range | 0.00318 | 0.00259 | 0.00234 | 2.127 | 0.335 | 0.608 | 0.827 | 51.0 | |
| standard deviation | 0.00057 | 0.00047 | 0.00044 | 0.420 | 0.067 | 0.123 | 0.156 | 15.0 | |
| Fertilizer M | average value | 0.00370 | 0.00360 | 0.00305 | 3.335 | 0.700 | 0.522 | 0.759 | 57.0 |
| range | 0.00368 | 0.00314 | 0.00252 | 2.060 | 0.332 | 0.617 | 0.739 | 63.0 | |
| standard deviation | 0.00073 | 0.00056 | 0.00049 | 0.487 | 0.062 | 0.104 | 0.137 | 16 | |
| Class | a/m | b/m | c/m | Granularity d | ASM | CON | ENT | Crushing Force/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizer A | 0.00286 | 0.00319 | 0.00262 | 2.857 | 1.603 | 3.178 | 3.046 | 2.270 |
| Fertilizer D | 0.00303 | 0.00276 | 0.00310 | 2.791 | 2.894 | 2.985 | 2.455 | 2.947 |
| Fertilizer M | 0.00296 | 0.00302 | 0.00310 | 2.509 | 1.883 | 3.199 | 2.687 | 2.388 |
| Predictive Models | Class | RMSE | MAE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO-SVM | Fertilizer A | 0.0022 | 0.0018 | 0.9918 |
| Fertilizer D | 0.0016 | 0.0011 | 0.9948 | |
| Fertilizer M | 0.0009 | 0.0008 | 0.9988 | |
| Random forest regression | Fertilizer A | 0.0055 | 0.0041 | 0.9364 |
| Fertilizer D | 0.0028 | 0.0023 | 0.9405 | |
| Fertilizer M | 0.0017 | 0.0015 | 0.9650 | |
| K-nearest neighbor | Fertilizer A | 0.0085 | 0.0062 | 0.8804 |
| Fertilizer D | 0.0074 | 0.0070 | 0.8867 | |
| Fertilizer M | 0.0065 | 0.0046 | 0.8930 | |
| BP neural network | Fertilizer A | 0.0174 | 0.0138 | 0.4998 |
| Fertilizer D | 0.0148 | 0.0137 | 0.5106 | |
| Fertilizer M | 0.0118 | 0.0104 | 0.5227 | |
| LSTM neural network | Fertilizer A | 0.0165 | 0.0149 | 0.4943 |
| Fertilizer D | 0.0156 | 0.0141 | 0.4035 | |
| Fertilizer M | 0.0151 | 0.0136 | 0.5150 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Jing, L.; Wang, J.; Cao, X.; Fu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H. Crushing Force Prediction Method of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Based on Particle Phenotype. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122235
Sun L, Chen X, Chen Z, Jing L, Wang J, Cao X, Fu S, Jiang Y, Zhang H. Crushing Force Prediction Method of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Based on Particle Phenotype. Agriculture. 2024; 14(12):2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122235
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Linlin, Xiubo Chen, Zixu Chen, Linlong Jing, Jinxing Wang, Xinpeng Cao, Shenghui Fu, Yuanmao Jiang, and Hongjian Zhang. 2024. "Crushing Force Prediction Method of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Based on Particle Phenotype" Agriculture 14, no. 12: 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122235
APA StyleSun, L., Chen, X., Chen, Z., Jing, L., Wang, J., Cao, X., Fu, S., Jiang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2024). Crushing Force Prediction Method of Controlled-Release Fertilizer Based on Particle Phenotype. Agriculture, 14(12), 2235. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture14122235





