Spatiotemporal Evolution and Spatial Convergence Analysis of Total Factor Productivity of Citrus in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Measurement of TFP
2.2.2. Spatial Correlation Index
2.2.3. Convergence Model
3. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Citrus TFP
3.1. Time Series Evolution of Citrus TFP
3.2. Regional Differences in TFP for Citrus
3.3. Spatial Correlation Analysis of Citrus TFP
4. Convergence Analysis of TFP of Citrus
4.1. σ Convergence Test Result Analysis
4.2. Absolute β Convergence Test Result Analysis
4.3. Conditional β Convergence Test Result Analysis
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, X.X. The development trend of citrus industry and the adjustment of citrus variety structure in Guilin. South. Hortic. 2020, 31, 1–4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.J.; Gu, Y.M.; Zeng, Y. Progress of citrus industry economy in China. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2021, 40, 58–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Li, Z.P.; Fang, G.Z.; Qi, C.J. Study on spatial correlation effect of citrus price in main producing areas—Based on VAR model and SNA model. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2023, 44, 173–184. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, G.Z.; Qi, C.J.; Lei, Q.Y. Calculation of total factor productivity of citrus in China and the difference of region—Based on the DEA-Malmquist index method. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2019, 40, 29–34. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z. How to understand and calculate the growth of “total factor productivity”—Econometric analysis of evaluating a specific technical and economic problem. J. Quant. Technol. Econ. 1988, 4, 68–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.C.; Yu, M.M.; Chang, C.C.; Hsu, S.H. Total factor productivity growth in China’s agricultural sector. China Econ. Rev. 2008, 19, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Feng, C.; Qin, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Measuring China’s agricultural green total factor productivity and its drivers during 1998–2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, M.; Kangarshahi, A.A.; Amiri, N.A. Input-output energy analysis of citrus production in Mazandaran province of Iran. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 2558–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Yang, J.X. Change analysis of citrus total factor productivity in China. Acta Agric. Zhejiangensis 2018, 30, 470–478. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Chen, W. Evaluation of Sustainable Development Policy of Sichuan Citrus Industry in China Based on DEA–Malmquist Index and DID Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.H.; Guo, J.Y.; Zhu, S.B. On all-factor productivity, technological advances and efficiency in China’s orange industry. J. Jiangxi Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2010, 9, 43–47. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, W.; Qi, C.J. DEA analysis on citrus production efficiency in Hubei province. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. Soc. Sci. Ed. 2012, 5, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.R. The Research on Input and Output Efficiency of Citrus in China. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barro, R.J.; Sala-i-Martin, X. Convergence. J. Political Econ. 1992, 100, 223–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumol, W.J. Productivity growth, convergence, and welfare: What the long-run data show. Am. Econ. Rev. 1986, 76, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Mcerlean, S.; Wu, Z. Regional agricultural labour productivity convergence in China. Food Policy 2003, 28, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B. Agricultural productivity convergence in China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 60, 101423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.N.; Paudel, K.P.; Zilberman, D. Agricultural productivity convergence: Myth or reality? J. Agric. Appl. Econ. 2011, 43, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezitis, A.N. Agricultural productivity and convergence: Europe and the United States. Appl. Econ. 2010, 42, 1029–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhariyanto, K.; Thirtle, C. Asian agricultural productivity and convergence. J. Agric. Econ. 2001, 52, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmquist, S. Index numbers and indifference surfaces. Trab. De Estadística 1953, 4, 209–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caves, D.W.; Christensen, L.R.; Diewert, W.E. The economic theory of index numbers and the measurement of input, output, and productivity. Econ. J. Econ. Soc. 1982, 50, 1393–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Norris, M.; Zhang, Z. Productivity growth, technical progress, and efficiency change in industrialized countries. Am. Econ. Rev. 1994, 84, 66–83. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, P.F.; Li, G.J.; Luo, Q.Y.; Liu, S.; Chen, Y. Study on the Regional Difference and Spatial Structure of Agricultural Science and Technology Resources in China. J. Agrotech. Econ. 2021, 5, 108–120. [Google Scholar]
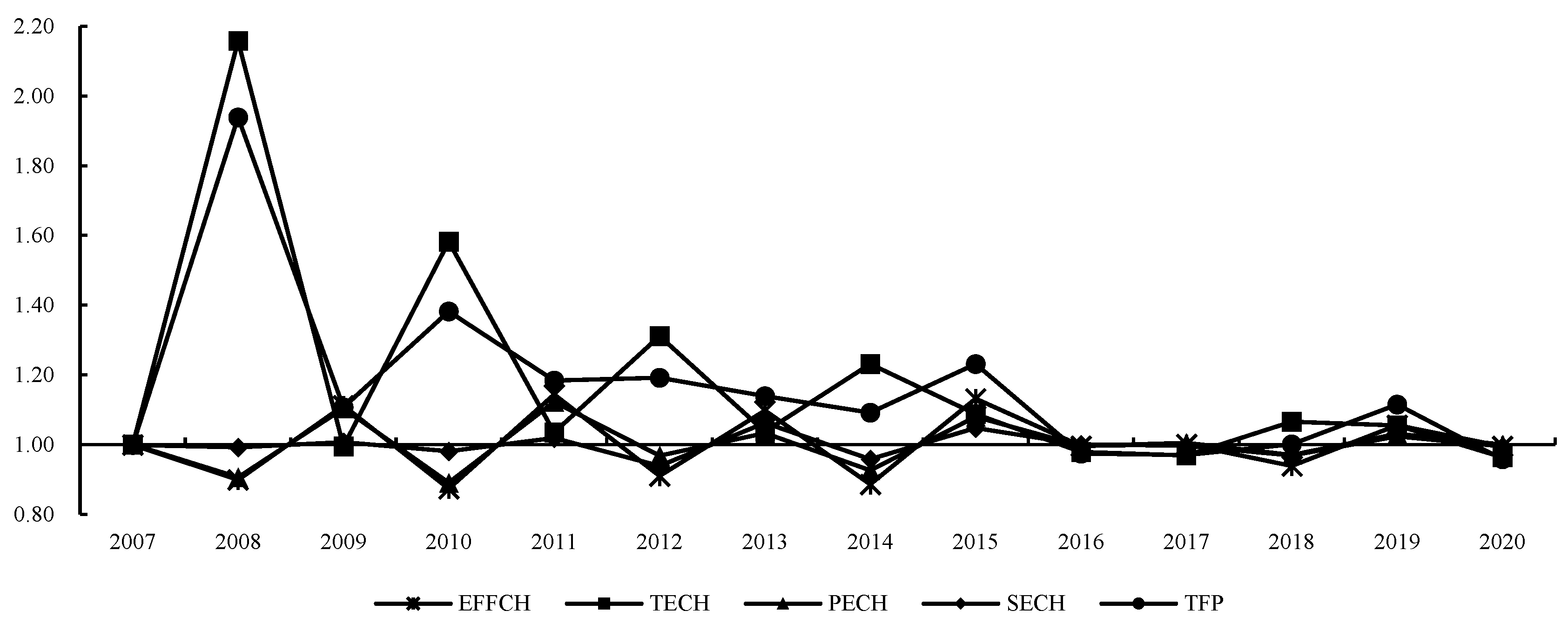
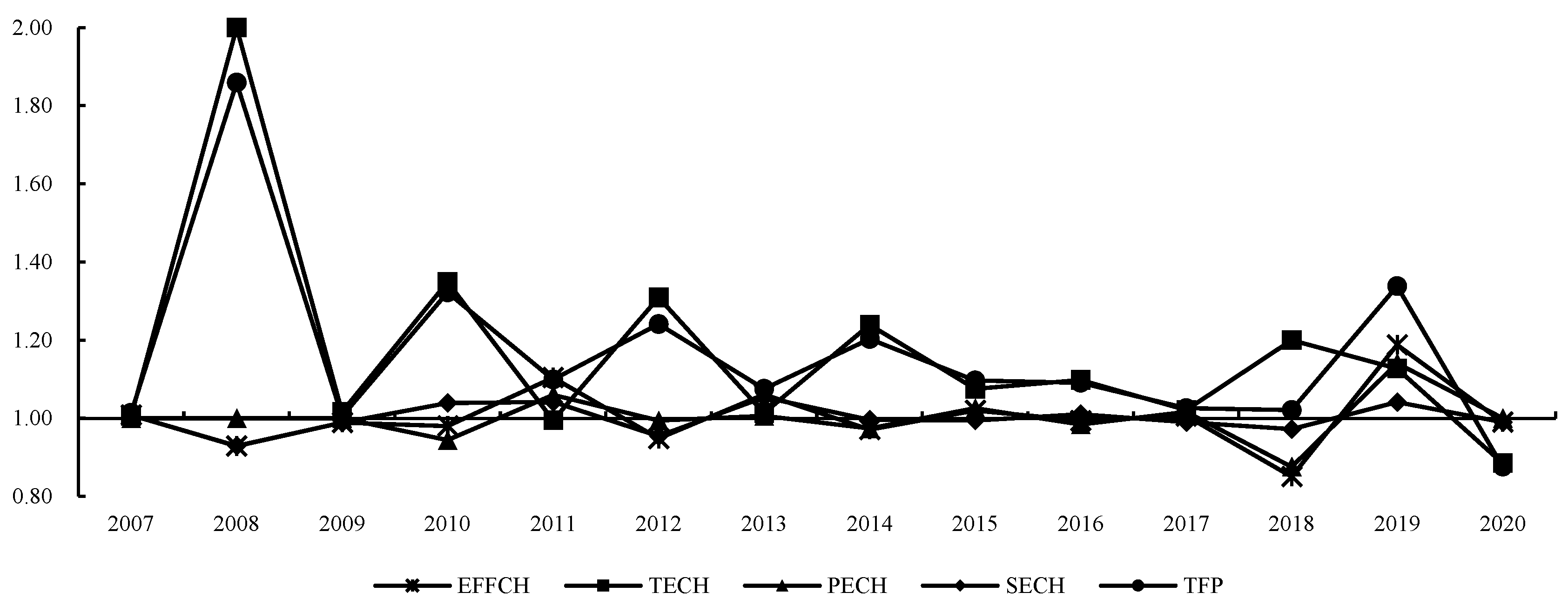
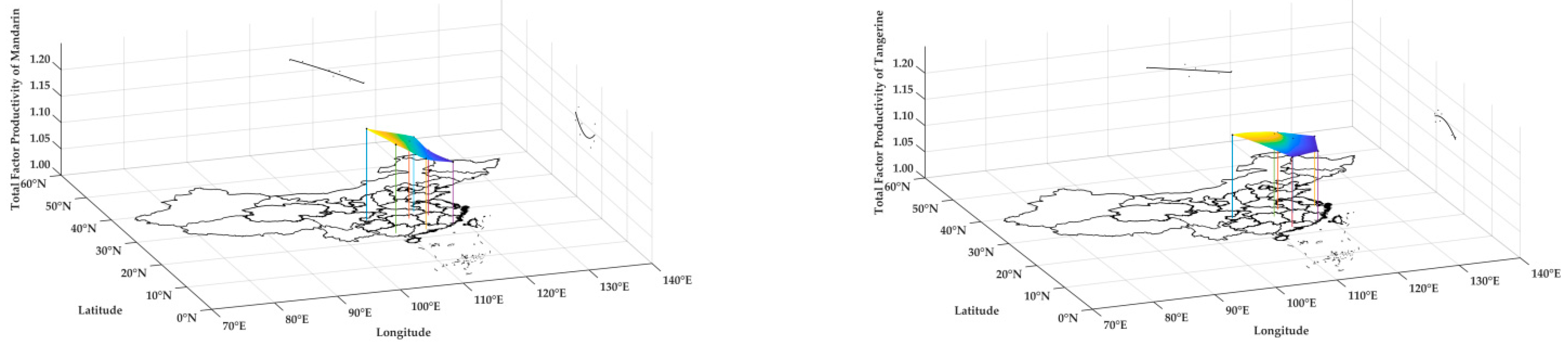
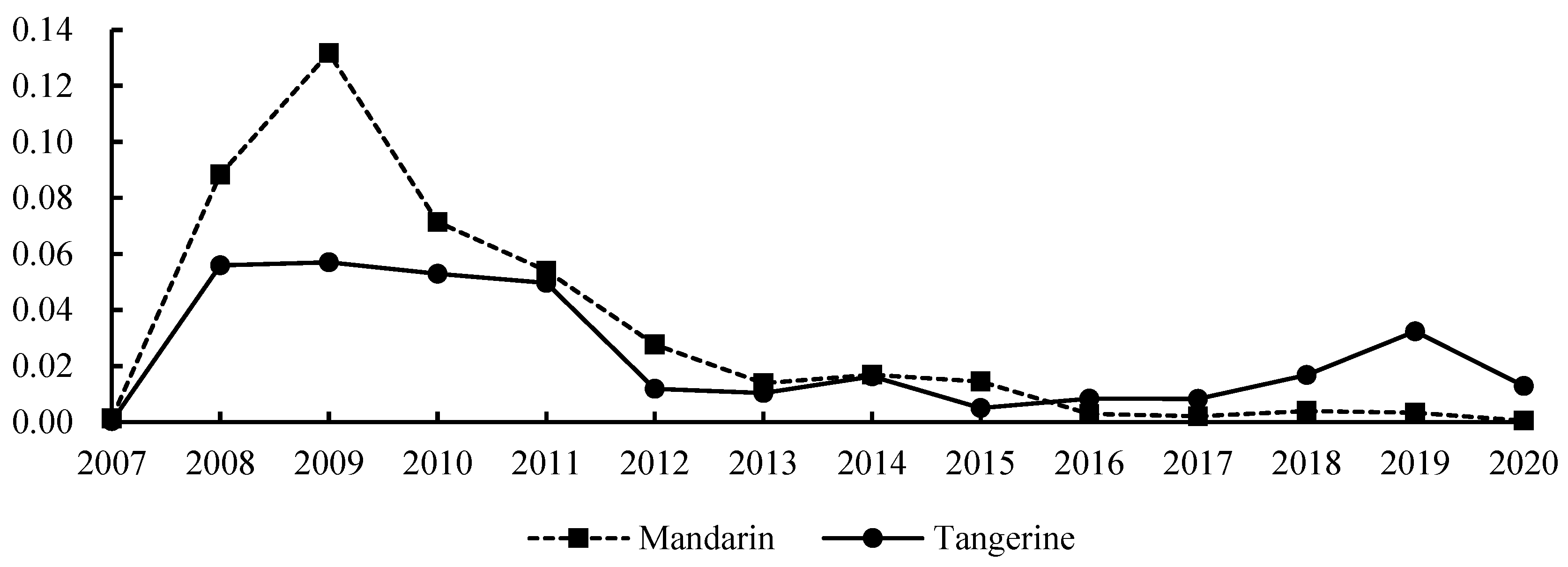
| Classification | Provinces | EFFCH | TECH | PECH | SECH | TFP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mandarin | Chongqing | 0.998 | 1.176 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 1.173 |
| Guangxi | 0.999 | 1.169 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.168 | |
| Hunan | 0.999 | 1.147 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.146 | |
| Hubei | 0.998 | 1.145 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 1.142 | |
| Guangdong | 0.999 | 1.135 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.134 | |
| Jiangxi | 1.000 | 1.123 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.123 | |
| Fujian | 1.000 | 1.116 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.116 | |
| Tangerine | Chongqing | 0.999 | 1.161 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.159 |
| Hunan | 1.000 | 1.157 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.157 | |
| Hubei | 0.998 | 1.148 | 1.000 | 0.998 | 1.147 | |
| Jiangxi | 1.000 | 1.141 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 1.141 | |
| Zhejiang | 1.001 | 1.131 | 1.000 | 1.001 | 1.133 | |
| Guangdong | 0.999 | 1.134 | 1.000 | 0.999 | 1.133 | |
| Fujian | 1.003 | 1.130 | 1.000 | 1.003 | 1.132 |
| Year | Mandarin | Tangerine | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | z | p | Moran’s I | z | p | |
| 2007 | −0.069 | 0.565 | 0.286 | −0.299 | −0.836 | 0.202 |
| 2008 | −0.026 | 1.078 | 0.140 | −0.192 | −0.188 | 0.425 |
| 2009 | −0.041 | 1.051 | 0.147 | −0.053 | 1.049 | 0.147 |
| 2010 | 0.169 ** | 1.762 | 0.039 | 0.199 ** | 1.850 | 0.032 |
| 2011 | 0.109 * | 1.462 | 0.072 | 0.136 * | 1.595 | 0.055 |
| 2012 | 0.215 ** | 1.906 | 0.028 | 0.280 ** | 2.171 | 0.015 |
| 2013 | 0.208 ** | 1.880 | 0.030 | 0.075 | 1.187 | 0.118 |
| 2014 | 0.074 | 1.211 | 0.113 | 0.384 *** | 2.615 | 0.004 |
| 2015 | 0.046 | 1.049 | 0.147 | 0.237 ** | 2.238 | 0.013 |
| 2016 | −0.041 | 0.696 | 0.243 | 0.184 ** | 1.766 | 0.039 |
| 2017 | −0.184 | −0.088 | 0.465 | −0.084 | 0.420 | 0.337 |
| 2018 | −0.274 | −0.733 | 0.232 | 0.118 ** | 2.303 | 0.011 |
| 2019 | −0.356 | −0.991 | 0.161 | −0.185 | −0.103 | 0.459 |
| 2020 | −0.139 | 0.160 | 0.436 | 0.053 * | 1.310 | 0.095 |
| Coefficient | Mandarin | Tangerine | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | SAR | SEM | SDM | OLS | SAR | SEM | SDM | |
| β | −1.699 *** (0.0848) | −1.094 *** (0.105) | −1.540 *** (0.0885) | −1.571 *** (0.0899) | −1.697 *** (0.0900) | −1.301 *** (0.102) | −1.576 *** (0.0904) | −1.568 *** (0.0939) |
| ρ or λ | — | 0.343 *** (0.0727) | 0.705 *** (0.0544) | 0.687 *** (0.0565) | — | 0.296 *** (0.0594) | 0.614 *** (0.0654) | 0.613 *** (0.0655) |
| γ | — | — | — | 1.191 *** (0.126) | — | — | — | 0.939 *** (0.149) |
| V | 0.026 | 0.169 | 0.044 | 0.040 | 0.026 | 0.086 | 0.039 | 0.040 |
| Time effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.919 | 0.605 | 0.675 | 0.697 | 0.928 | 0.760 | 0.781 | 0.781 |
| Coefficient | Mandarin | Tangerine | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OLS | SAR | SEM | SDM | OLS | SAR | SEM | SDM | |
| β | −1.716 *** (0.0861) | −1.574 *** (0.0872) | −1.646 *** (0.0752) | −1.638 *** (0.0807) | −1.701 *** (0.0935) | −1.557 *** (0.0883) | −1.674 *** (0.0797) | −1.598 *** (0.0877) |
| ρ or λ | — | 0.0997 * (0.0604) | 0.309 *** (0.117) | 0.198 * (0.122) | — | 0.151 *** (0.0534) | 0.349 *** (0.106) | 0.260 ** (0.107) |
| γ | — | — | — | 0.342 * (0.212) | — | — | — | 0.308 (0.207) |
| V | 0.024 | 0.040 | 0.031 | 0.032 | 0.025 | 0.042 | 0.028 | 0.037 |
| Control variables | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Time effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Individual effect | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| R2 | 0.925 | 0.725 | 0.663 | 0.535 | 0.930 | 0.869 | 0.841 | 0.541 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Y.; Qi, C.; Liu, F.; Lei, Q.; Ding, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Spatial Convergence Analysis of Total Factor Productivity of Citrus in China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13061258
Gu Y, Qi C, Liu F, Lei Q, Ding Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Spatial Convergence Analysis of Total Factor Productivity of Citrus in China. Agriculture. 2023; 13(6):1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13061258
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Yumeng, Chunjie Qi, Fuxing Liu, Quanyong Lei, and Yuchao Ding. 2023. "Spatiotemporal Evolution and Spatial Convergence Analysis of Total Factor Productivity of Citrus in China" Agriculture 13, no. 6: 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13061258
APA StyleGu, Y., Qi, C., Liu, F., Lei, Q., & Ding, Y. (2023). Spatiotemporal Evolution and Spatial Convergence Analysis of Total Factor Productivity of Citrus in China. Agriculture, 13(6), 1258. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13061258







