The Effect of Reservoir Cultivation on Conventional Maize in Sandy-Loam Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
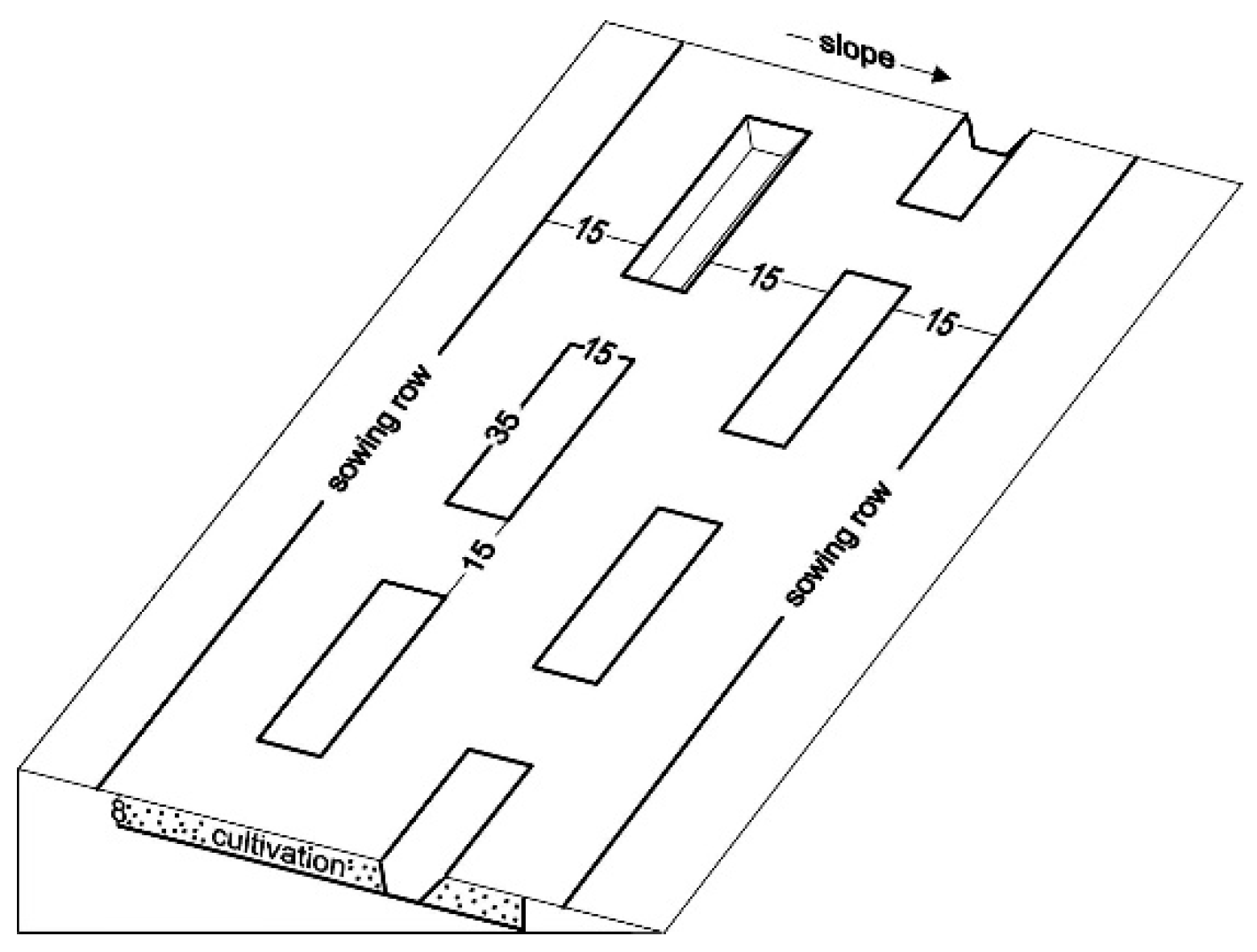
2.1. Design of Field Trials
2.2. Trial Sites
2.3. Weather Monitoring
2.4. Rain Simulation
2.5. Physical Properties of Soil
2.6. Soil Hydraulic Conductivity Measurement
2.7. Soil Surface Roughness
2.8. Maize Yield
2.9. Data Curation and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weather
3.2. Rain Simulation
3.3. Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity
3.4. Yield of Maize
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brant, V.; Kroulík, M.; Pivec, J.; Zábranský, P.; Hakl, J.; Holec, J.; Kvíz, Z.; Procházka, L. Splash Erosion in Maize Crops under Conservation Management in Combination with Shallow Strip-Tillage before Sowing. Soil Water Res. 2017, 12, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamelová, B.; Malaťák, J.; Velebil, J.; Gendek, A.; Aniszewska, M. Impact of Torrefaction on Fuel Properties of Aspiration Cleaning Residues. Materials 2022, 15, 6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavinia, M.; Saleh, F.N.; Asadi, H. Effects of Rainfall Patterns on Runoff and Rainfall-Induced Erosion. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 34, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assouline, S.; Ben-Hur, M. Effects of Rainfall Intensity and Slope Gradient on the Dynamics of Interrill Erosion during Soil Surface Sealing. Catena 2006, 66, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, X.; Sample, D.J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Runoff and Nutrient Losses in Alfalfa (Medicago Sativa L.) Production with Tied-Ridge-Furrow Rainwater Harvesting on Sloping Land. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2022, 10, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menšík, L.; Kincl, D.; Nerušil, P.; Srbek, J.; Hlisnikovský, L.; Smutný, V. Water Erosion Reduction Using Different Soil Tillage Approaches for Maize (Zea Mays L.) in the Czech Republic. Land 2020, 9, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhart, M.; Dumbrovský, M.; Šarapatka, B.; Drbal, K.; Bednář, M.; Kapička, J.; Pavlík, F.; Kottová, B.; Zástěra, V.; Muchová, Z. Evaluation of Monitored Erosion Events in the Context of Characteristics of Source Areas in Czech Conditions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogliatto, S.; Milan, M.; De Palo, F.; Ferrero, A.; Vidotto, F. Effectiveness of Mechanical Weed Control on Italian Flint Varieties of Maize. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2019, 34, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkrábek, J.; Urban, J.; Dvořák, P.; Bečková, L. Effect of Soil Loosening during Vegetation on Soil Erosion and Sugar Beet Production. Listy Cukrov. Reparske 2019, 135, 188–195. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.S.; Maruthi, V.; Pankaj, P.K.; Kumar, M.; Pushpanjali; Prabhakar, M.; Reddy, A.G.K.; Reddy, K.S.; Singh, V.K.; Koradia, A.K. Water Footprint Assessment of Rainfed Crops with Critical Irrigation under Different Climate Change Scenarios in SAT Regions. Water 2022, 14, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaad, F.J.P.M.; Van der Zijp, M.; Van Dijk, P.M. Soil Conservation and Maize Cropping Systems on Sloping Loess Soils in the Netherlands. Soil Tillage Res. 1998, 46, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, E.C.; Shelton, D.P.; Jasa, P.J.; Peterson, T.; Peterson, T.R.; Asae, M. Soil Erosion from Tillage Systems Used in Soybean and Corn Soil Erosion from Tillage Systems Used in Soybean and Corn Residues Residues Soil Erosion from Tillage Systems Used in Soybean and Corn Residues. Biol. Syst. Eng. 1985, 28, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar]
- Stašek, J.; Krása, J.; Mistr, M.; Dostál, T.; Devátý, J.; Středa, T.; Mikulka, J. Using a Rainfall Simulator to Define the Effect of Soil Conservation Techniques on Soil Loss and Water Retention. Land 2023, 12, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adee, E.; Hansel, F.D.; Ruiz Diaz, D.A.; Janssen, K. Corn Response as Affected by Planting Distance from the Center of Strip-till Fertilized Rows. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak-Mensah, E.; Sam, F.E.; Safnat Kaito, I.O.I.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Q. Influence of Tied-Ridge with Biochar Amendment on Runoff, Sediment Losses, and Alfalfa Yield in Northwestern China. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovaříček, P.; Marešová, K.; Hůla, J.; Kroulík, M. Use of Ridge Tillage for Growing of Wide Row Crops. Listy Cukrov. Řepařské 2010, 126, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Vejchar, D.; Vacek, J.; Hájek, D.; Bradna, J.; Kasal, P.; Svobodová, A. Reduction of Surface Runoff on Sloped Agricultural Land in Potato Cultivation in De-Stoned Soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuti, R.C.; Lamb, M.C.; Sorensen, R.B.; Truman, C.C. Agronomic and Economic Response to Furrow Diking Tillage in Irrigated and Non-Irrigated Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.). Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlene, M.; Adviento-Borbe, A.; Barnes, B.D.; Iseyemi, O.; Mann, A.M.; Reba, M.L.; Robertson, W.J.; Massey, J.H.; Teague, T.G.; Gan, J. Water Quality of Surface Runoff and Lint Yield in Cotton under Furrow Irrigation in Northeast Arkansas. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemann, T.; Sprafke, T.; Bachmann, F.; Prasuhn, V.; Schwilch, G. The Effect of the Dyker on Infiltration, Soil Erosion, and Waterlogging on Conventionally Farmed Potato Fields in the Swiss Plateau. Catena 2019, 174, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nenciu, F.; Oprescu, M.R.; Biris, S.S. Improve the Constructive Design of a Furrow Diking Rotor Aimed at Increasing Water Consumption Efficiency in Sunflower Farming Systems. Agriculture 2022, 12, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agassi, M.; Levy, G.J. Effect of the Dyked Furrow Technique on Potato Yield. Potato Res. 1993, 36, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brhane, G.; Wortmann, C.S.; Mamo, M.; Gebrekidan, H.; Belay, A. Micro-Basin Tillage for Grain Sorghum Production in Semiarid Areas of Northern Ethiopia. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mupangwa, W.; Love, D.; Twomlow, S. Soil–Water Conservation and Rainwater Harvesting Strategies in the Semi-Arid Mzingwane Catchment, Limpopo Basin, Zimbabwe. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2006, 31, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, C.S.; Dang, Y.P. Strategic Tillage for the Improvement of No-Till Farming Systems. In No-Till Farming Systems for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Haruna, S.I.; Anderson, S.H. No-Till Farming Systems for Enhancing Soil Water Storage. In BT-No-Till Farming Systems for Sustainable Agriculture: Challenges and Opportunities; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 213–231. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, T. Energy Efficiency and Soil Conservation in Conventional, Minimum Tillage and No-Tillage. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2014, 2, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moitzi, G.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Kaul, H.P.; Wagentristl, H. Comparison of Energy Inputs and Energy Efficiency for Maize in a Long-Term Tillage Experiment under Pannonian Climate Conditions. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novák, P.; Kovaříček, P.; Hůla, J.; Buřič, M. Surface Water Runoff of Different Tillage Technologies for Maize. Agron. Res. 2019, 17, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarello, V.; Iovino, M.; Elrick, D. A Simplified Falling-Head Technique for Rapid Determination of Field-Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarello, V.; Elrick, D.E.; Iovino, M.; Sgroi, A. A Laboratory Analysis of Falling Head Infiltration Procedures for Estimating the Hydraulic Conductivity of Soils. Geoderma 2006, 135, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, W.D.; Elrick, D.E. Ponded Infiltration From a Single Ring: I. Analysis of Steady Flow. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1990, 54, 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamphorst, E.C.; Jetten, V.; Guérif, J.; Pitkänen, J.; Iversen, B.V.; Douglas, J.T.; Paz, A. Predicting Depressional Storage from Soil Surface Roughness. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herodowicz-Mleczak, K.; Piekarczyk, J.; Kaźmierowski, C.; Nowosad, J.; Mleczak, M. Estimating Soil Surface Roughness With Models Based on the Information About Tillage Practises and Soil Parameters. J. Adv. Model Earth Syst. 2022, 14, e2021MS002578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jester, W.; Klik, A.; Hauer, G.; Hebel, B.; Truman, C.C.; Jester, W.; Klik, A.; Professor, A.; Hauer, G. Rainfall and Surface Roughness Effects on Soil Loss and Surface Runoff. In Proceedings of the Soil Erosion Research for the 21st Century Symposium, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–5 January 2001; pp. 463–466. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.C.; He, S.Q.; Wu, F.Q. Changes of Soil Surface Roughness under Water Erosion Process. Hydrol. Process 2014, 28, 3919–3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittig, S.; Sur, R.; Baets, D. Runoff Mitigation via Micro-Dams and Conservation Tillage—Numerical Modeling of Runoff and Erosion from Maize Field Trials. Integr. Environ. Assess Manag. 2022, 18, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Y.; Ou, Y.; Yan, B.; Xu, X.; Rousseau, A.N.; Zhang, Y. Assessment of Micro-Basin Tillage as a Soil and Water Conservation Practice in the Black Soil Region of Northeast China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0152313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovář, P.; Vaššová, D.; Janeček, M. Surface Runoff Simulation to Mitigate the Impact of Soil Erosion, Case Study of Třebsín (Czech Republic). Soil Water Res. 2012, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, X.; Rubinato, M.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, J. Impact of Multiple Vegetation Covers on Surface Runoff and Sediment Yield in the Small Basin of Nverzhai, Hunan Province, China. Forests 2020, 11, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brant, V.; Zábranský, P.; Škeříková, M.; Pivec, J.; Kroulík, M.; Procházka, L. Effect of Row Width on Splash Erosion and Throughfall in Silage Maize Crops. Soil Water Res. 2017, 12, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, E.N.; Box, J.E. Stemflow, Rain Throughfall, and Erosion under Canopies of Corn and Sorghum. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.F.d.; Eduardo, E.N.; De Almeida, W.S.; Santos, L.A.F.; Alves Sobrinho, T. Water Erosion and Soil Water Infiltration in Different Stages of Corn Development and Tillage Systems. Rev. Bras. Eng. Agrícola Ambient. 2015, 19, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrick, D.E.; Reynolds, W.D.; Geering, H.R.; Tan, K.-A. Estimating Steady Infiltration Rate Times for Infiltrometers and Permeameters. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lado, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Soil Mineralogy Effects on Seal Formation, Runoff and Soil Loss. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 24, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Krasilnikov, P.; Taboada, M.A.; Xuan, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, B.; et al. Effects of Organic Amendments on Soil Pore Structure under Waterlogging Stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, H.; Moussavi, A.; Ghadiri, H.; Rose, C.W. Flow-Driven Soil Erosion Processes and the Size Selectivity of Sediment. J. Hydrol. 2011, 406, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doren, D.M. Van Influence of Plowing, Disking; Cultivation, Previous Crop and Surface Residues on Corn Yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1965, 29, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doren, D.M.; Triplett, G.B. Mulch and Tillage Relationships in Corn Culture. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1973, 37, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, H.M.G.; Klooster, J.J.; Van der Schans, D.A.; Boone, F.R.; Veen, B.W. The Effect of Inter-Row Cultivation on Yield of Weed-Free Maize. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 1991, 166, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Depth (cm) | Soil Type | Clay (% wt.) | Silt (% wt.) | Sand (% wt.) | Dry Bulk Density (g/cm3) | Porosity(%) | Slope for Rain Simulations (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 0–25 | sandy loam–loam | 11.8 | 29.3 | 58.9 | 1.36 | 48.5 | 4.7–5.9 |
| 2021 | 0–25 | sandy loam–loam | 14.3 | 29.1 | 56.6 | 1.52 | 41.2 | 3.8–5.8 |
| 2022 | 0–25 | sandy loam–loam | 22.5 | 49.3 | 28.2 | 1.55 | 41.9 | 4.2–5.8 |
| Year | May | June | July | August | September |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Long-term average (1991–2020) 1 | 75 | 92 | 94 | 85 | 56 |
| 2020 | 64 | 130 | 33 | 99 | 44 |
| 2021 | 89 | 71 | 98 | 114 | 18 |
| 2022 | 70 | 240 | 34 | 92 | 66 |
| Year | Variant 1 | Soil Roughness (mm) | Runoff Start (min) | Rainfall Retention until Start of Runoff (mm) | Rainfall Retention Compared to Control (mm) | Runoff Stabilization Time (min) | Stabilized Runoff (% of Rainfall Intensity) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | C | 24.6 ± 2.8 | 4.3 ± 1.1 | 10.2 ± 2.6 | - | 17.7 ± 0.1 | 43 ± 12 |
| CU | 18.8 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 5.0 ± 0.1 | −5.2 | 15.2 ± 0.2 | 70 ± 14 | |
| RC | 31.3 ± 2.3 | 6.3 ± 0.5 | 14.8 ± 1.2 | 4.7 | 20.7 ± 1.3 | 58 ± 13 | |
| 2021 | C | 22.3 ± 2.6 | 5.5 ± 2.8 | 12.8 ± 6.5 | - | 15.9 ± 1.5 | 74 ± 5 |
| CU | 21.5 ± 0.8 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | 13.5 ± 0.9 | 0.7 | 12.9 ± 2.4 | 45 ± 14 | |
| RC | 30.4 ± 1.4 | 8.2 ± 2.9 | 19.2 ± 6.9 | 6.5 | 23.4 ± 6.0 | 54 ± 10 | |
| 2022 | C | 23.5 ± 1.4 | 4.2 ± 1.1 | 9.9 ± 2.6 | - | 15.2 ± 1.1 | 77 ± 9 |
| CU | 21.4 ± 0.9 | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 12.4 ± 1.9 | 2.6 | 13.4 ± 1.1 | 72 ± 11 | |
| RC | 27.3 ± 1.6 | 8.4 ± 1.7 | 19.7 ± 4.0 | 9.9 | 17.2 ± 1.9 | 68 ± 9 |
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant 1 | C | CU | RC | C | CU | RC | C | CU | RC |
| Average 2 | 70.5 ab | 82.3 a | 17.8 b | 33.1 a | 56.9 a | 6.8 b | 30.8 a | 40.6 a | 13.7 b |
| S.D. | 49.8 | 56.0 | 13.0 | 27.1 | 48.6 | 3.1 | 19.6 | 16.5 | 8.9 |
| C.V. (%) | 70.6 | 68.1 | 72.7 | 81.9 | 85.4 | 46.1 | 63.7 | 40.7 | 65.3 |
| Max. | 142.9 | 167.8 | 33.0 | 98.7 | 154.1 | 11.1 | 72.7 | 68.5 | 33.8 |
| Min. | 12.6 | 8.0 | 3.5 | 10.0 | 16.6 | 3.3 | 12.6 | 18.2 | 5.7 |
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant 1 | C | CU | RC | C | CU | RC | C | CU | RC |
| Average | 100.0 | 106.9 | 108.7 | 100.0 | 95.8 | 94.3 | 100.0 | 103.8 | 109.7 |
| S.D. | 10.4 | 11.3 | 19.2 | 3.4 | 7.4 | 2.5 | 8.2 | 12.2 | 7.4 |
| C.V. (%) | 10.4 | 10.6 | 17.7 | 3.4 | 7.8 | 2.7 | 8.2 | 11.8 | 6.8 |
| Max. | 111.4 | 125.4 | 135.9 | 102.6 | 104.3 | 96.6 | 110.2 | 117.3 | 120.1 |
| Min. | 91.0 | 94.1 | 88.3 | 96.2 | 90.2 | 91.6 | 91.7 | 84.8 | 95.2 |
| ANOVA | p = 0.72 | p = 0.40 | p = 0.15 | ||||||
| 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variant 1 | C | CU | RC | C | CU | RC | C | CU | RC |
| Average | 100.0 | 109.2 | 106.1 | 100.0 | 94.4 | 94.9 | 100.0 | 106.7 | 105.5 |
| S.D. | 11.6 | 10.5 | 21.2 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 6.0 | 9.6 | 12.1 | 8.0 |
| C.V. (%) | 11.6 | 9.6 | 20.0 | 5.4 | 9.5 | 6.4 | 9.6 | 11.3 | 7.6 |
| Max. | 111.6 | 126.2 | 139.1 | 105.8 | 104.7 | 101.8 | 110.0 | 122.0 | 114.9 |
| Min. | 88.4 | 97.5 | 87.4 | 95.2 | 88.0 | 91.3 | 87.9 | 88.3 | 92.3 |
| ANOVA | p = 0.72 | p = 0.58 | p = 0.43 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vejchar, D.; Velebil, J.; Kubín, K.; Bradna, J.; Malaťák, J. The Effect of Reservoir Cultivation on Conventional Maize in Sandy-Loam Soil. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13061201
Vejchar D, Velebil J, Kubín K, Bradna J, Malaťák J. The Effect of Reservoir Cultivation on Conventional Maize in Sandy-Loam Soil. Agriculture. 2023; 13(6):1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13061201
Chicago/Turabian StyleVejchar, Daniel, Jan Velebil, Karel Kubín, Jiří Bradna, and Jan Malaťák. 2023. "The Effect of Reservoir Cultivation on Conventional Maize in Sandy-Loam Soil" Agriculture 13, no. 6: 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13061201
APA StyleVejchar, D., Velebil, J., Kubín, K., Bradna, J., & Malaťák, J. (2023). The Effect of Reservoir Cultivation on Conventional Maize in Sandy-Loam Soil. Agriculture, 13(6), 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture13061201






